Submitted:
30 October 2023
Posted:
31 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and methods
Study design and patients
Technique
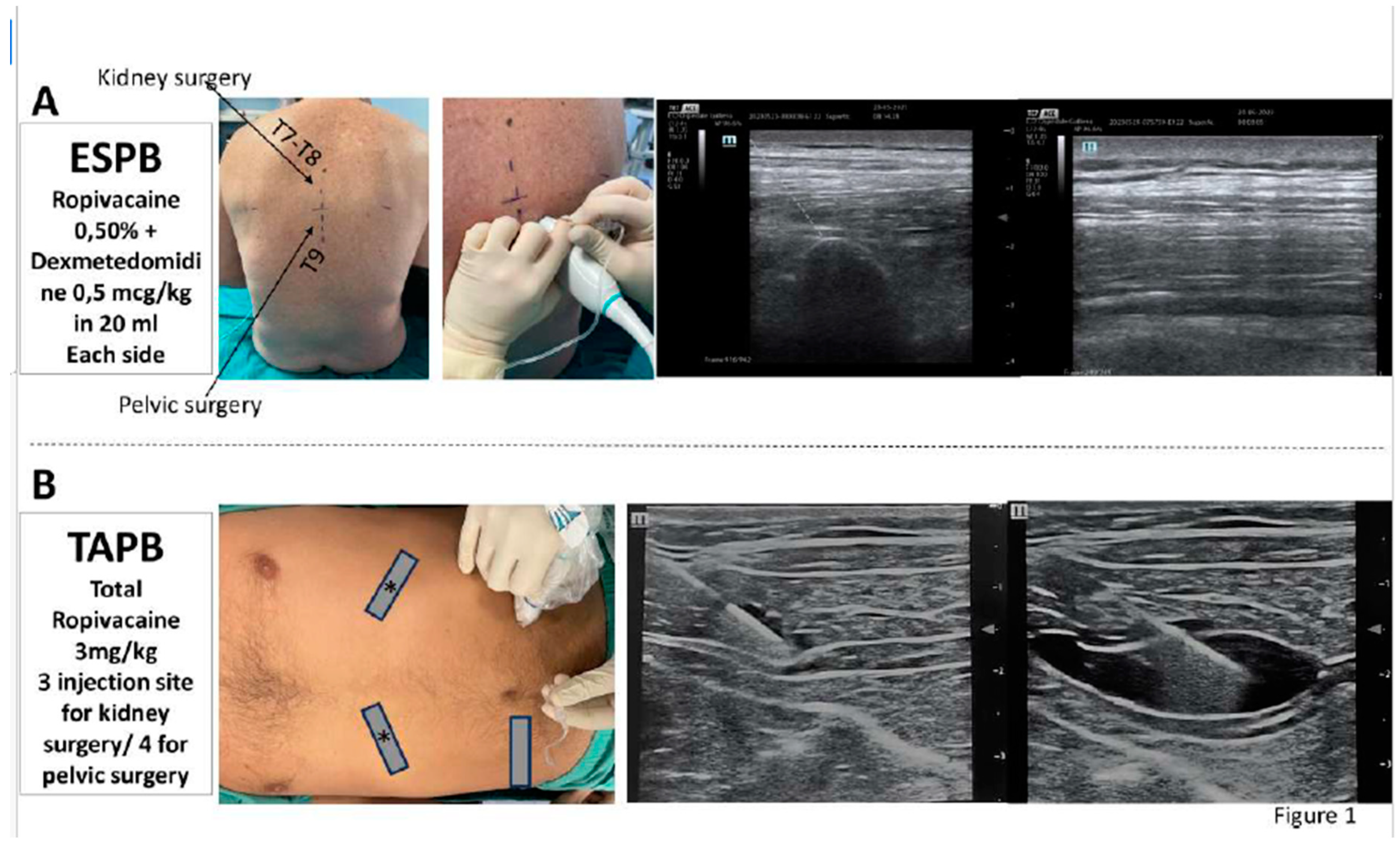
ESPB
TAPB
Anaesthesia management
Analgesia protocol and rescue analgesia
Outcomes
Statistical analyses
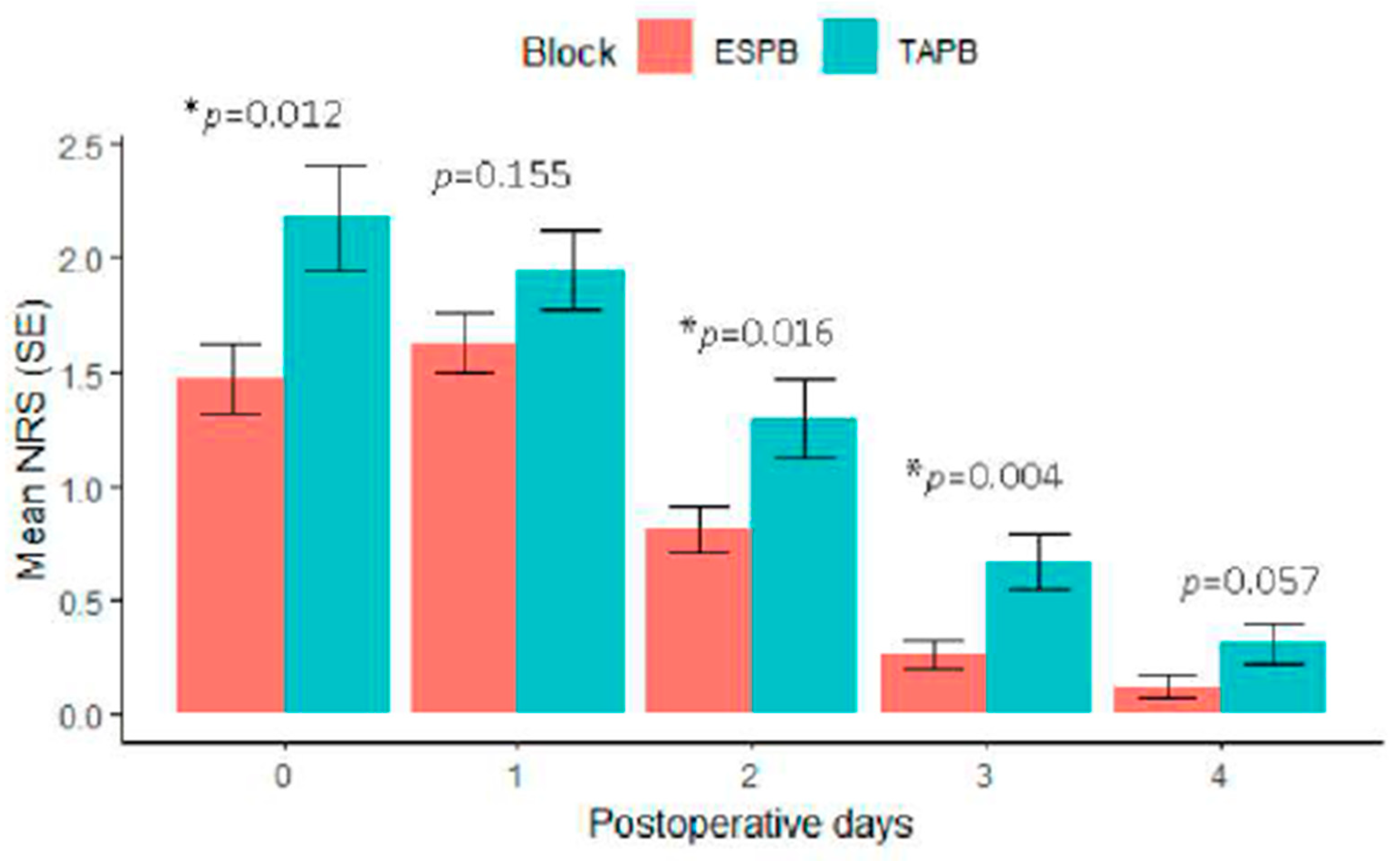
Results
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed consent statement
Data availability statement
References
- Ashrafi, A.N.; Yip, W.; Graham, J.N.; Yu, V.; Titus, M.; Widjaja, W.; Dickerson, S.; Berger, A.K.; Desai, M.M.; Gill, I.S.; et al. Implementation of a Multimodal Opioid-Sparing Enhanced Recovery Pathway for Robotic-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy. J Robot Surg 2022, 16, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Gu, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Gao, X.; Lu, X. Clinical Efficacy of an Enhanced Recovery after Surgery Protocol in Patients Undergoing Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy. J Int Med Res 2021, 49, 3000605211033173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavina, R.; Droghetti, M.; Bianchi, L.; Ercolino, A.; Chessa, F.; Casablanca, C.; Piazza, P.; Mottaran, A.; Recenti, D.; Salvador, M.; et al. The Robotic Approach Improves the Outcomes of ERAS Protocol after Radical Cystectomy: A Prospective Case-Control Analysis. Urol Oncol 2021, 39, 833.e1–833.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; Hong, H. Clinical Efficacy of Enhanced Recovery after Surgery (ERAS) Program in Patients Undergoing Radical Prostatectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World J Surg Oncol 2020, 18, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batley, S.E.; Prasad, V.; Vasdev, N.; Mohan-S, G. Post-Operative Pain Management in Patients Undergoing Robotic Urological Surgery. Curr Urol 2016, 9, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, N.; Comardelle, N.J.; Domingue, N.M.; Borroto, W.J.; Cornett, E.M.; Imani, F.; Rajabi, M.; Kaye, A.D. Current Strategies in Pain Regimens for Robotic Urologic Surgery: A Comprehensive Review. Anesth Pain Med 2022, 12, e127911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusasco, C.; Germinale, F.; Dotta, F.; Benelli, A.; Guano, G.; Campodonico, F.; Ennas, M.; Di Domenico, A.; Santori, G.; Introini, C.; et al. Low Intra-Abdominal Pressure with Complete Neuromuscular Blockage Reduces Post-Operative Complications in Major Laparoscopic Urologic Surgery: A before-after Study. J Clin Med 2022, 11, 7201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallan, D.; Sharan, S.; Saxena, S.; Singh, T.K. ; Faisal, null Anesthetic Techniques: Focus on Transversus Abdominis Plane (TAP) Blocks. Local Reg Anesth 2019, 12, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, M.; Lei, X.; Fu, Q. Analgesic Effect of Erector Spinae Plane Block in Adults Undergoing Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. BMC Anesthesiol 2023, 23, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltrini, R.; Cantoni, V.; Green, R.; Greco, P.A.; Calabria, M.; Bucci, L.; Corcione, F. Efficacy of Transversus Abdominis Plane (TAP) Block in Colorectal Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Tech Coloproctol 2020, 24, 787–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadawi, M.; Layera, S.; Aliste, J.; Bravo, D.; Leurcharusmee, P.; Tran, D.Q. Erector Spinae Plane Block: A Narrative Review with Systematic Analysis of the Evidence Pertaining to Clinical Indications and Alternative Truncal Blocks. J Clin Anesth 2021, 68, 110063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dost, B.; Kaya, C.; Ozdemir, E.; Ustun, Y.B.; Koksal, E.; Bilgin, S.; Bostancı, Y. Ultrasound-Guided Erector Spinae Plane Block for Postoperative Analgesia in Patients Undergoing Open Radical Prostatectomy: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J Clin Anesth 2021, 72, 110277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonvicini, D.; Boscolo-Berto, R.; De Cassai, A.; Negrello, M.; Macchi, V.; Tiberio, I.; Boscolo, A.; De Caro, R.; Porzionato, A. Anatomical Basis of Erector Spinae Plane Block: A Dissection and Histotopographic Pilot Study. J Anesth 2021, 35, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, A.A.F.; Amin, O.A.I.; Ibrahem, M.A.M. Bilateral Ultrasound-Guided Erector Spinae Plane Block Versus Transversus Abdominis Plane Block on Postoperative Analgesia after Total Abdominal Hysterectomy. Pain Physician 2020, 23, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.P.; Yadav, U.; Khan, M.M.A.; Singh, A.K.; Verma, S.; Nigam, S. Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Erector Spinae Plane Block in Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy. Cureus 2023, 15, e40186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unal, S.; Baskan, S.; Guven Aytac, B.; Aytac, I.; Balci, M. Should the Erector Spinae Plane Block Be Applied in the Pain Management of Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy? Cureus 2022, 14, e22554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonanno, P.; Logrieco, N.; Marra, A.; Spirito, L.; Califano, G.; Blasio, F.; Falco, N.D.; Aveta, A.; Spena, G.; Servillo, G. Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy: Comparison of Subarachnoid Analgesia, Erector Spine Plane Block, and Intravenous Analgesia for Postoperative Pain Management. Korean J Anesthesiol 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piliego, C.; Longo, F.; Agrò, F.E. Erector Spinae Plane Block Growing Potential: Pain Management in Laparoscopy Nephrectomy. Saudi J Anaesth 2020, 14, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şahin, A.; Baran, O. Effect of Ultrasound-Guided Erector Spinae Plane Block on Post-Surgical Pain in Patients Undergoing Nephrectomy: A Single-Center, Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial. J Int Med Res 2022, 50, 3000605221086737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taninishi, H.; Matsusaki, T.; Morimatsu, H. Transversus Abdominis Plane Block Reduced Early Postoperative Pain after Robot-Assisted Prostatectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-M.; Lee, J. Effect of Transversus Abdominis Plane Block on the Quality of Recovery in Laparoscopic Nephrectomy: A Prospective Double-Blinded Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Medicine (Baltimore) 2022, 101, e31168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdilek, A.; Beyoğlu, Ç.A.; Demirdağ, Ç.; Şen, Ö.; Erbabacan, Ş.E.; Ekici, B.; Altindaş, F.; Köksal, G.M. Perioperative Analgesic Effects of Preemptive Ultrasound-Guided Subcostal Transversus Abdominis Plane Block for Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: A Prospective, Randomized Trial. J Endourol 2020, 34, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, A.J.R.; Gitman, M.; Bornstein, K.J.; El-Boghdadly, K.; Weinberg, G. Updates in Our Understanding of Local Anaesthetic Systemic Toxicity: A Narrative Review. Anaesthesia 2021, 76 Suppl 1, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummett, C.M.; Hong, E.K.; Janda, A.M.; Amodeo, F.S.; Lydic, R. Perineural Dexmedetomidine Added to Ropivacaine for Sciatic Nerve Block in Rats Prolongs the Duration of Analgesia by Blocking the Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Current. Anesthesiology 2011, 115, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.-S.; Peng, H.; Wu, S.-N. Dexmedetomidine, an Alpha2-Adrenergic Agonist, Inhibits Neuronal Delayed-Rectifier Potassium Current and Sodium Current. Br J Anaesth 2009, 103, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshitomi, T.; Kohjitani, A.; Maeda, S.; Higuchi, H.; Shimada, M.; Miyawaki, T. Dexmedetomidine Enhances the Local Anesthetic Action of Lidocaine via an Alpha-2A Adrenoceptor. Anesth Analg 2008, 107, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi-Han, W.; Rong, T.; Jun, L.; Min, W.; Yan, Z.; Yi, L.; Jie-Ting, L.; Sheng-Hui, H. Dexmedetomidine Combined with Ropivacaine for Erector Spinae Plane Block after Posterior Lumbar Spine Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2022, 23, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carollo, D.S.; Nossaman, B.D.; Ramadhyani, U. Dexmedetomidine: A Review of Clinical Applications. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 2008, 21, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urits, I.; Virgen, C.G.; Alattar, H.; Jung, J.W.; Berger, A.A.; Kassem, H.; Shehata, I.M.; Elhassan, A.; Kaye, A.D.; Viswanath, O. A Comprehensive Review and Update of the Use of Dexmedetomidine for Regional Blocks. Psychopharmacol Bull 2020, 50, 121–141. [Google Scholar]
| Intra-operative analgesia strategies | TAPB + Morphine 5 mg + Paracetamol 1 gr + Ketorolac 30 mg/Ibuprofen 600 mg | |
| ESPB + Paracetamol 1 gr + Ketorolac 30 mg/Ibuprofen 600 mg | ||
| Post-operative analgesia strategy | POD 0-1 | Paracetamol 1 gr x 3/die Ketorolac 30 mg if NRS>4 (If NSAIDs forbidden, Morphine 3 mg s.c.) |
| POD 2 until discharge | Paracetamol 1 gr if NRS>4 Ketorolac 30 mg if paracetamol not effective (If NSAIDs forbidden, Morphine 3 mg s.c.) |
|
| TAPB-group (n. 93) | ESPB-group (n. 97) | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yr | 64 + 13 | 66 + 12 | 0.174 |
| Sex, m/f n | 77/16 | 87/10 | 0.207 |
| BMI, Kg/m2 | 26 + 4 | 25 + 4 | 0.646 |
| ASA class I II III |
14 68 11 |
5 81 11 |
|
| Type of surgery, n (%) Partial nephrectomy Radical nephrectomy Radical prostatectomy Adrenalectomy other |
17 (18) 13 (14) 57 (62) 2 (2) 4 (4) |
18 (19) 13 (13) 58 (60) 1 (1) 7 (7) |
|
| VLS/robotic surgery, n | 53/41 | 61/36 | 0.104 |
| Duration of surgery, min | 132 + 55 | 150 + 51 | 0.121 |
| Duration of anaesthesia, min | 173 + 53 | 177 + 50 | 0.592 |
| TAPB-group (n. 93) | ESPB-group (n. 97) | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total ropivacaine consumption, mg | 305 + 60 | 170 + 25 | <0.001 |
| Total patients requiring a rescue dose, n | 43 | 33 | 0.104 |
| Total rescue dose requested, n | 3 (2-5) | 1 (0-2) | <0.001 |
| Total NSAIDs consumption as rescue in POD1, n | 40 | 26 | 0.092 |
| Total morphine consumption as rescue in POD1, n | 2 | 0 | 0.502 |
| Total Paracetamol consumption as rescue in POD2 and over, n | 12 | 5 | 0.005 |
| Total NSAIDs consumption as rescue in POD2 and over, n | 29 | 6 | <0.001 |
| Total morphine consumption as rescue in POD2 and over, n | 6 | 0 | 0.033 |
| Time to first rescue analgesia, day | 1 (0-1) | 1 (0-1) | 0.195 |
| Intraoperative complications, n -bradycardia -hypotension |
0 0 |
0 0 |
0.999 0.999 |
| Postoperative complications, n -PONV -block related complications |
18 0 |
4 0 |
0.001 0.999 |
| Length of stay, n | 4 (3-6) | 4 (3-5) | 0.401 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





