Submitted:
30 October 2023
Posted:
31 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Background Works
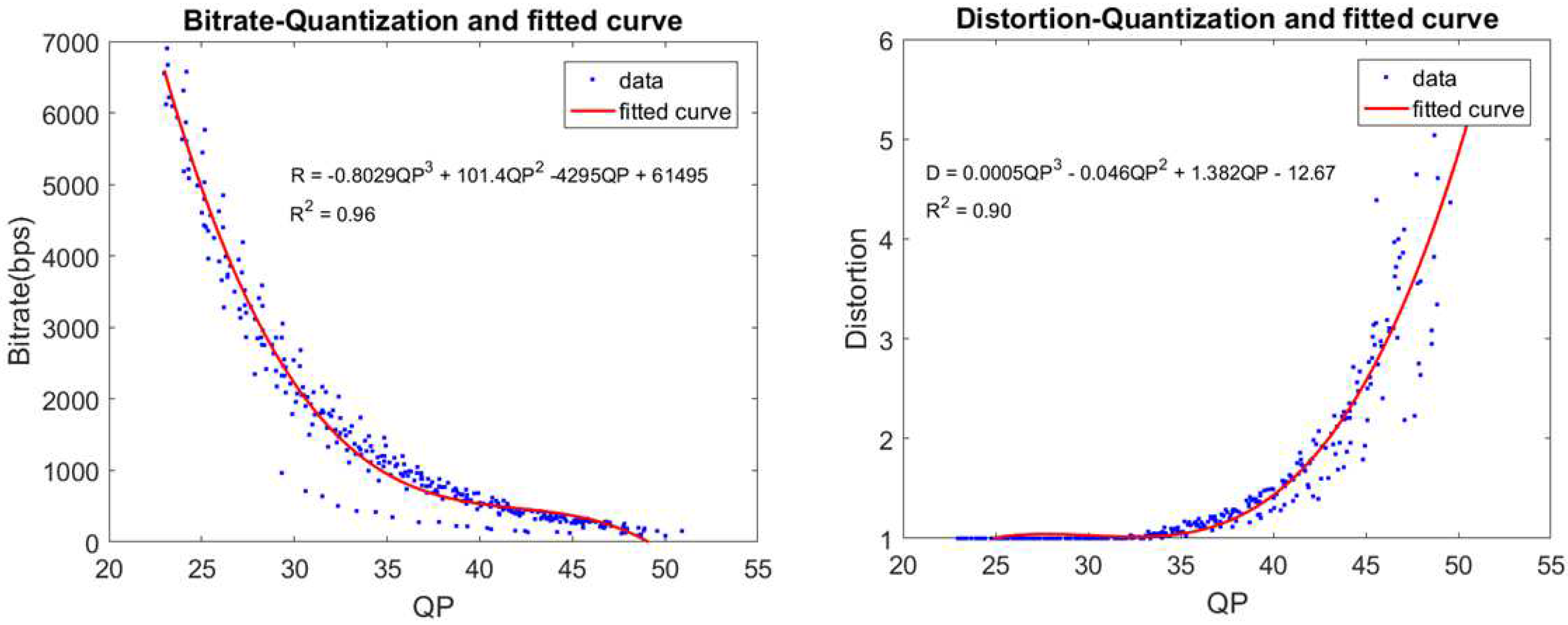
2.1. RDO Modeling
2.2. Perceptual RDO for Video Quality Consistency
3. Proposed Method
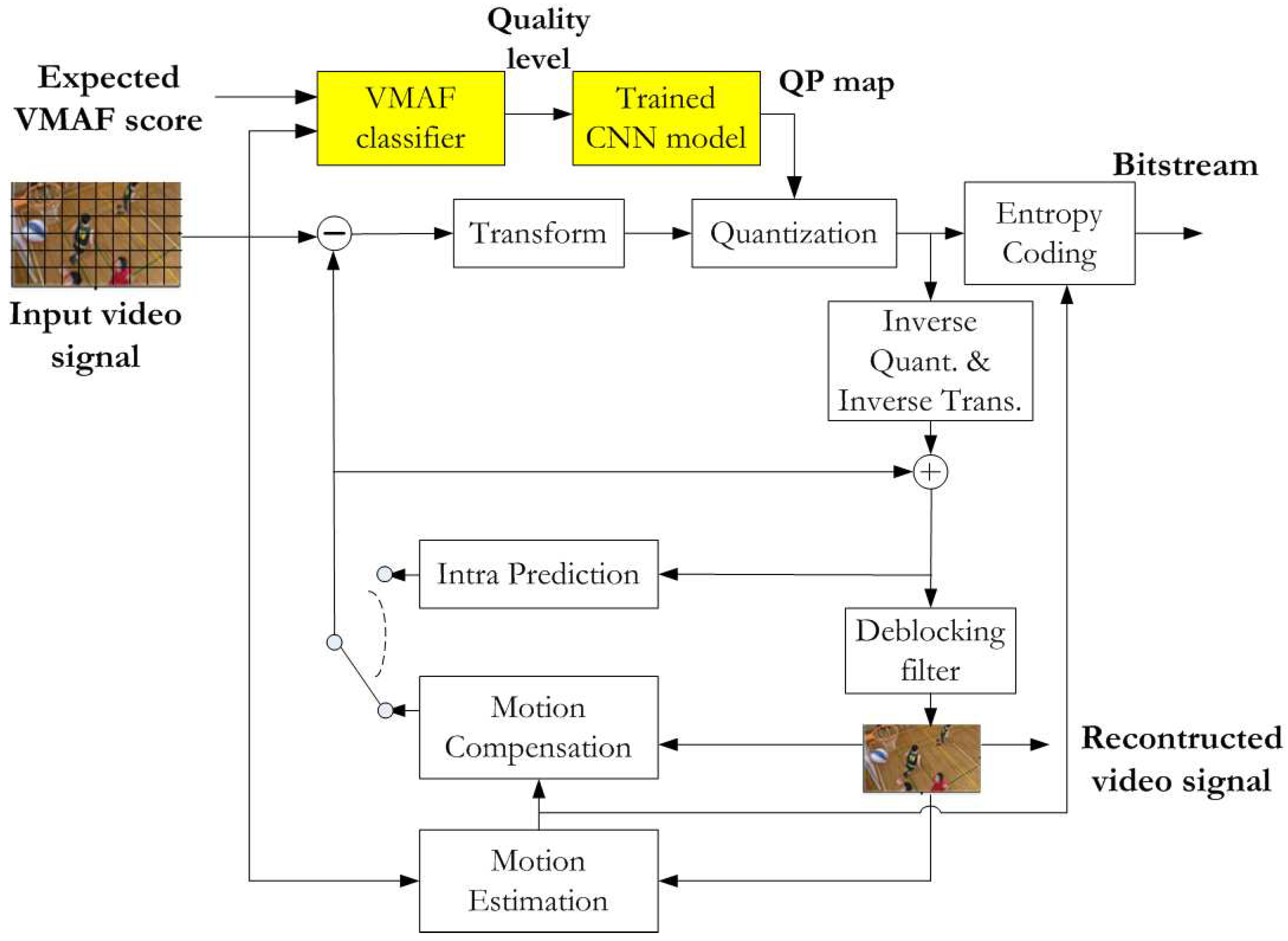
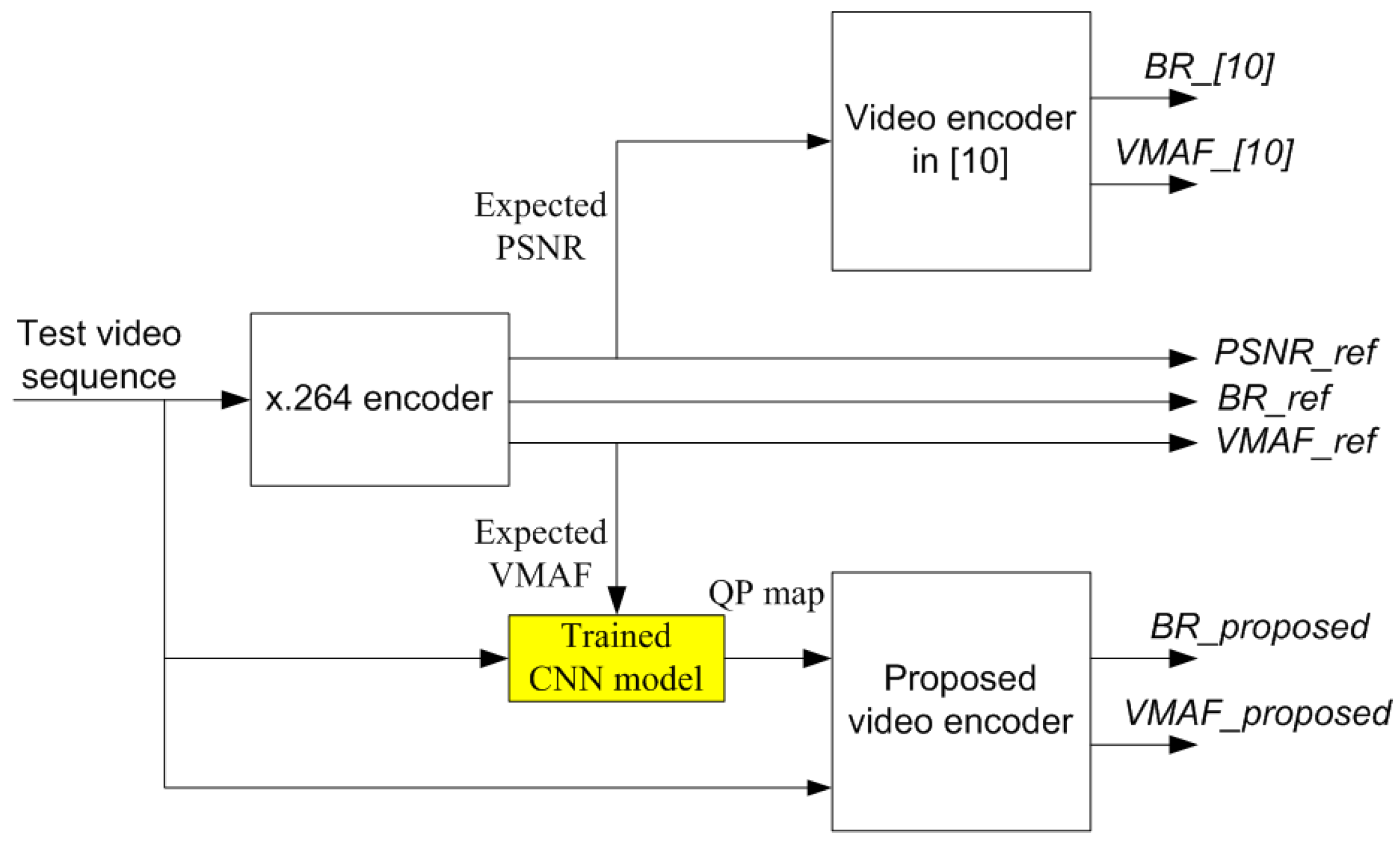
3.1. Overall Coding Framework
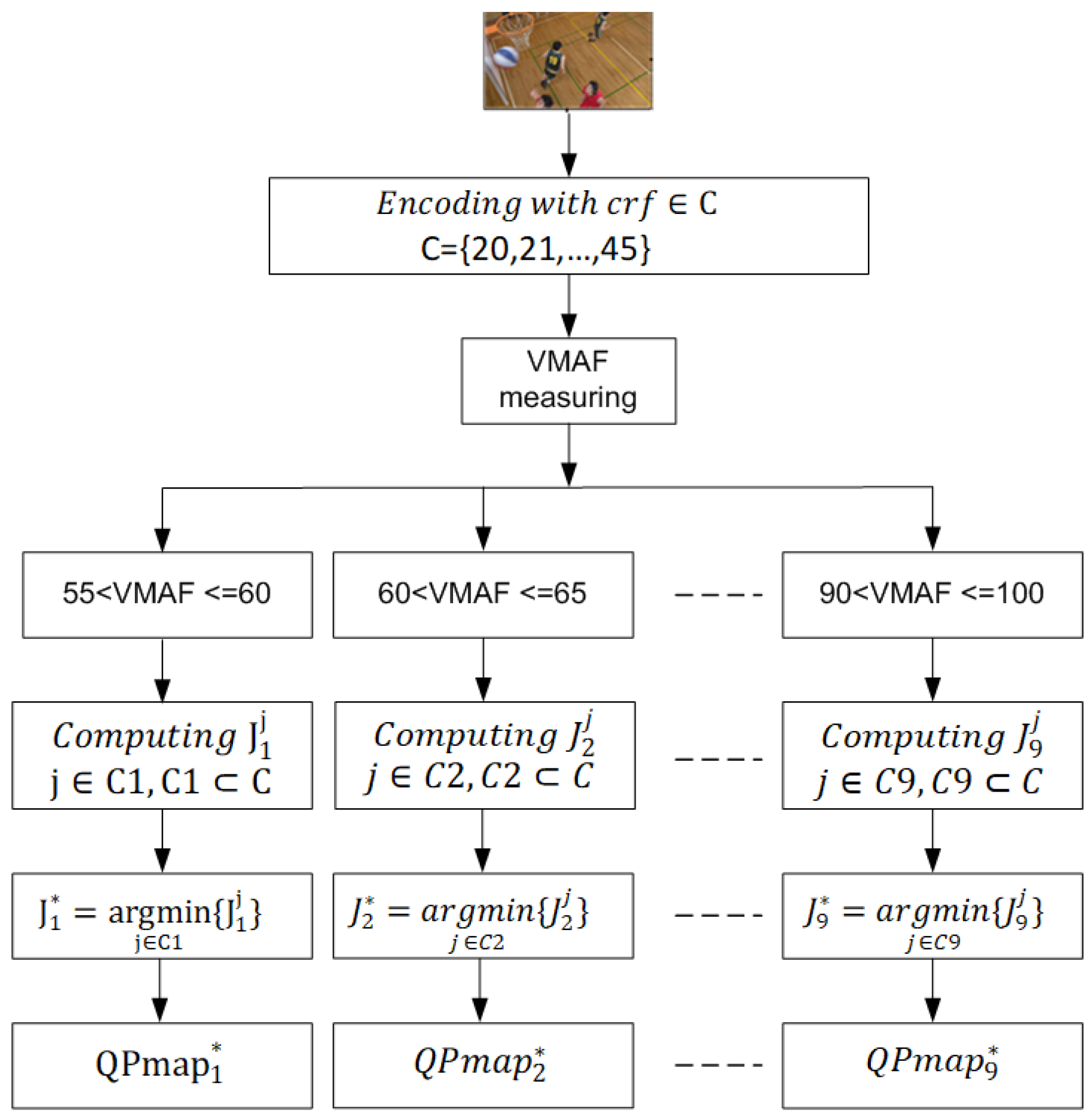
3.2. VMAF-based RDO Modelling
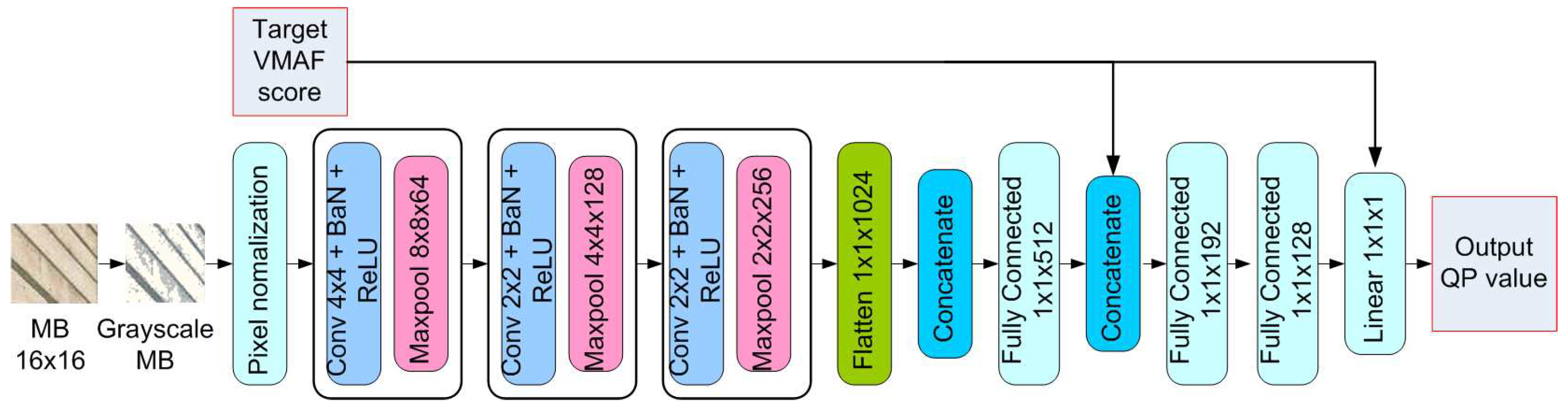
3.3. CNN Model for QP map Prediction
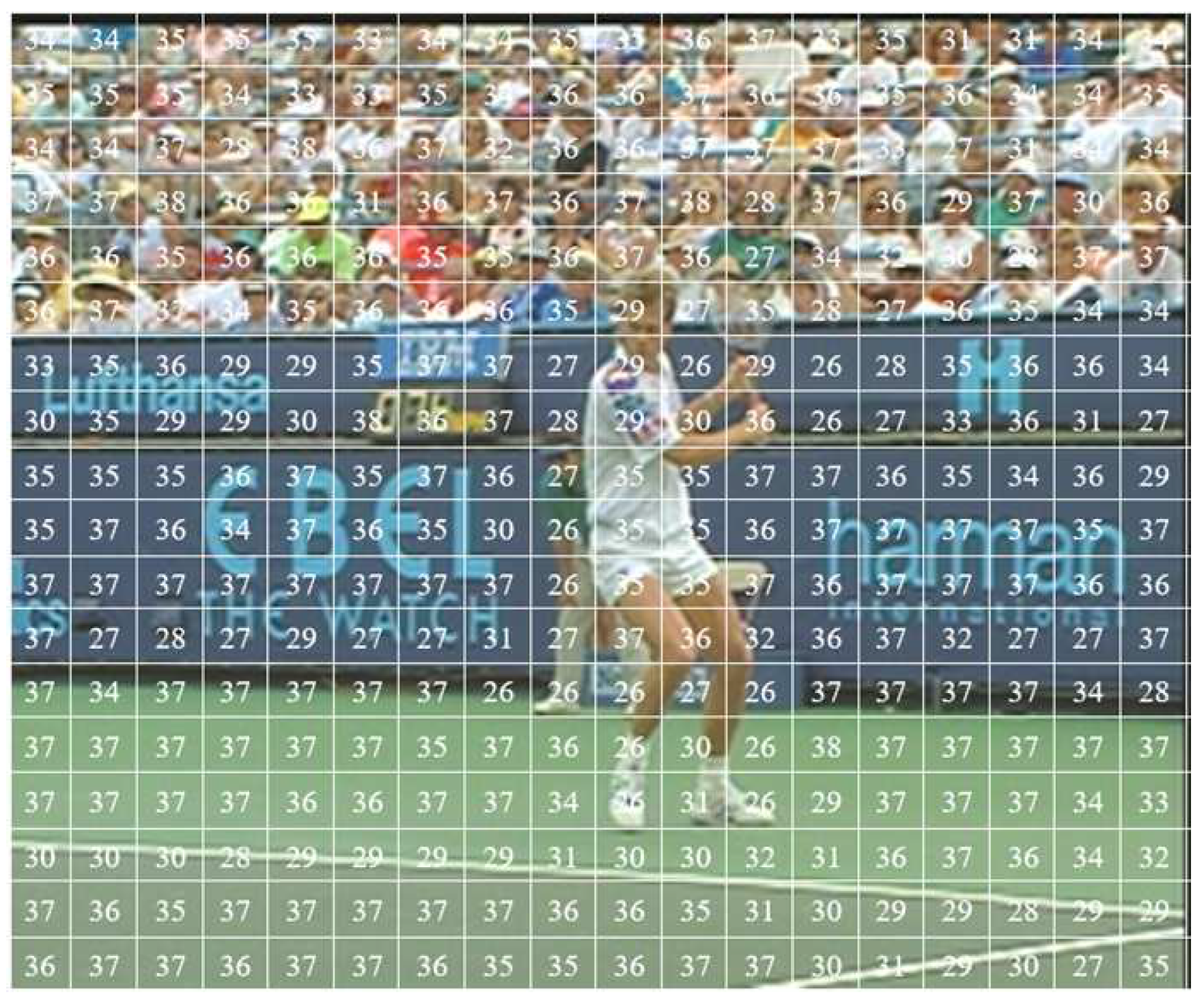
3.3.1. Dataset Collecting and Labelling
3.3.2. Training CNN model
- Preprocessing layers: The pixels of input MB 16 × 16 are preprocessed by converting into grayscale and then normalized to values between 0 and 1.
- Convolutional layers: The data through the preprocessing layers will be convolutionalized with 4 × 4 kernels at the first convolutional layer to extract the low-level features and 2 × 2 kernels for higher lever features. In addition, the batch normalization layer is used to normalize the feature map to stabilize the learning process and reduce the number of training epochs. After the convolutional layers, the pooling layer is added to reduce the size of each feature map. Besides, the dropout layer is used to drop features randomly with probabilities 20%.
- Fully connected layers: The feature maps from the convolutional layers are concatenated together and then flattened into a column vector. And then, the column vectors are passed through three fully connected layers which compile the features extracted by previous layers to form the final output as QP value. Because the target VMAF score is a requirement for output reconstructed video, a target VMAF score is supplemented as an external feature in the feature vectors for fully connected layers.
4. Performance Evaluation
4.1. Test Methodology
4.2. RD Performance Evaluation
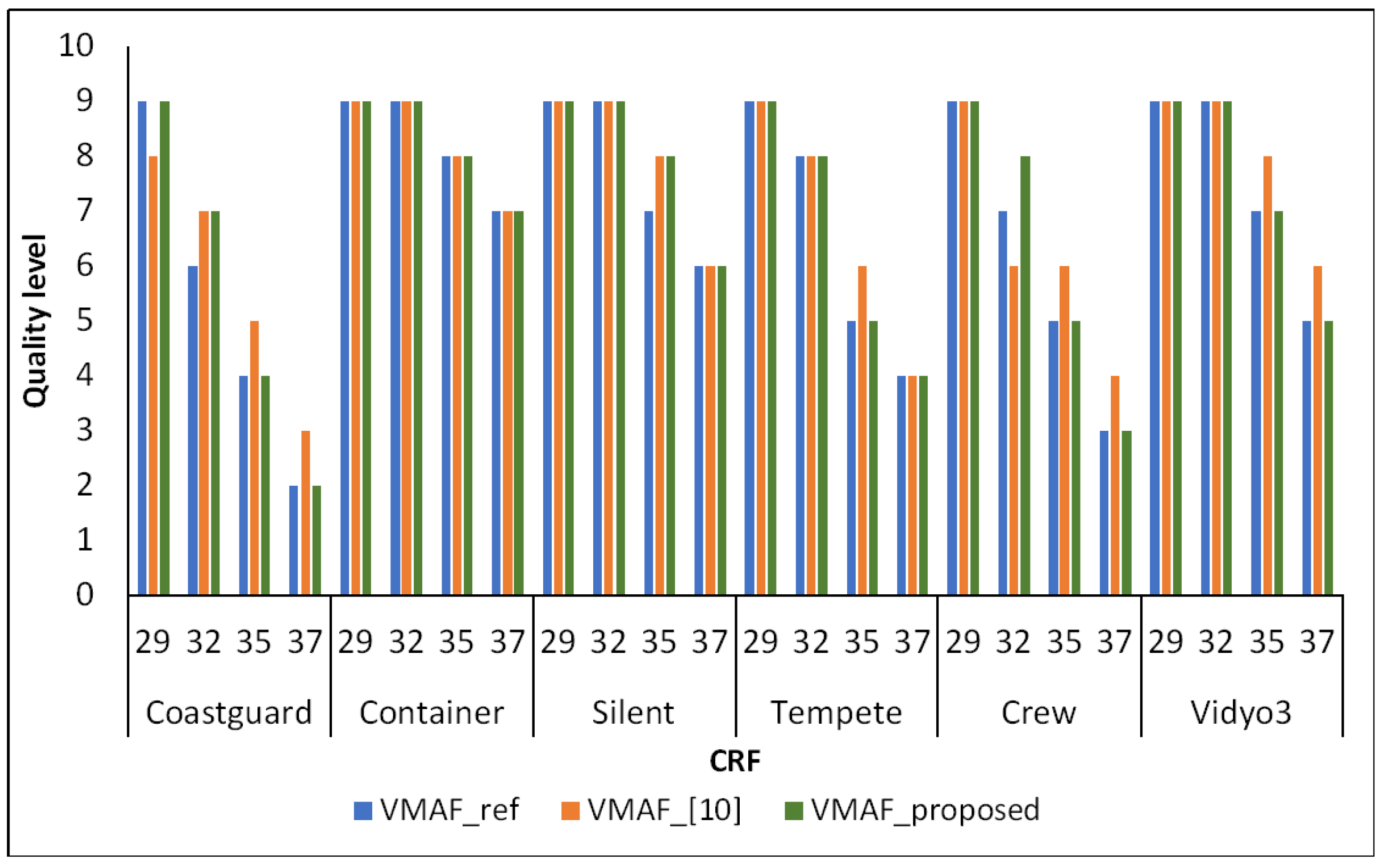
4.3. Expected Quality Level Assessment
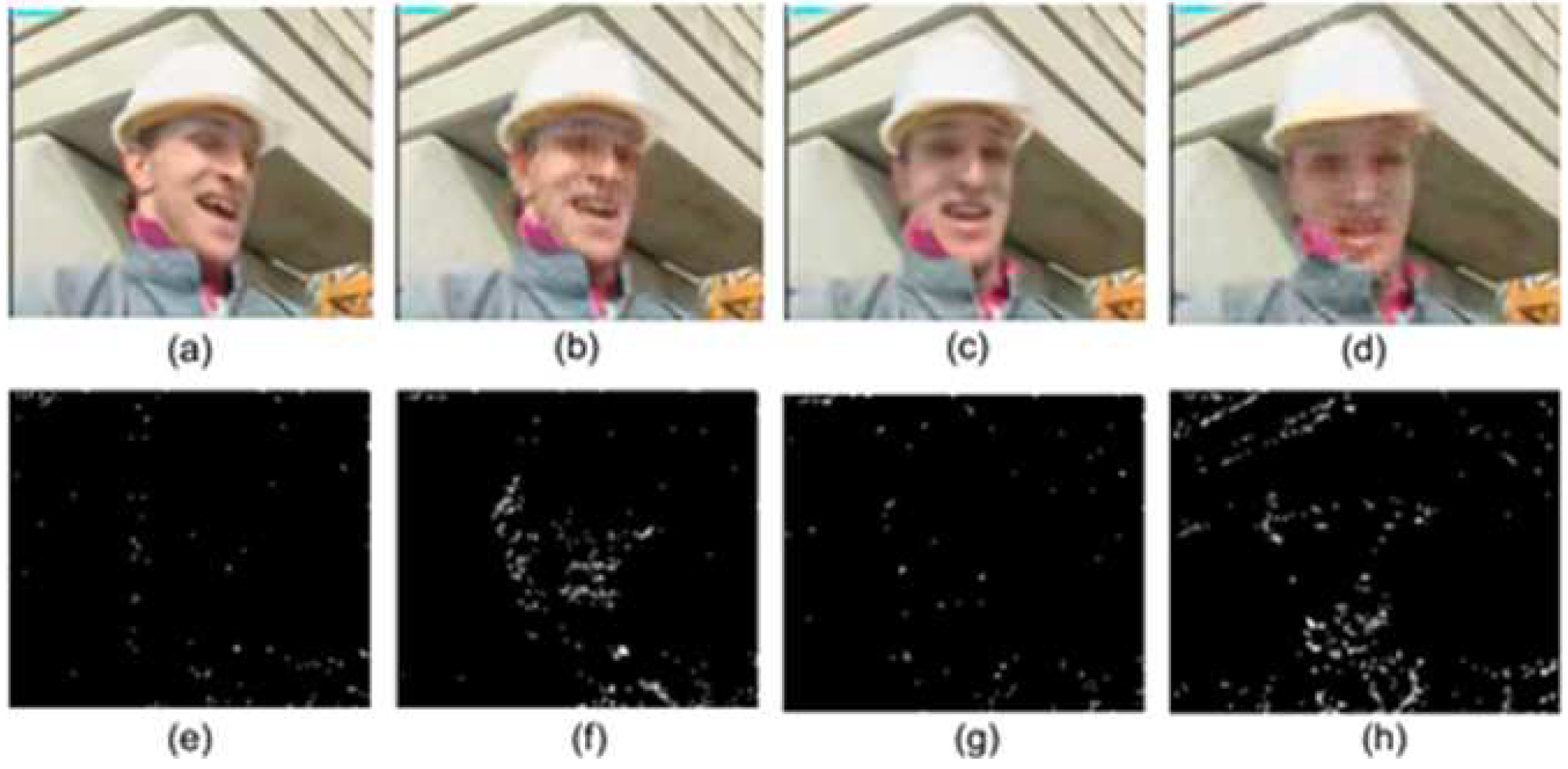
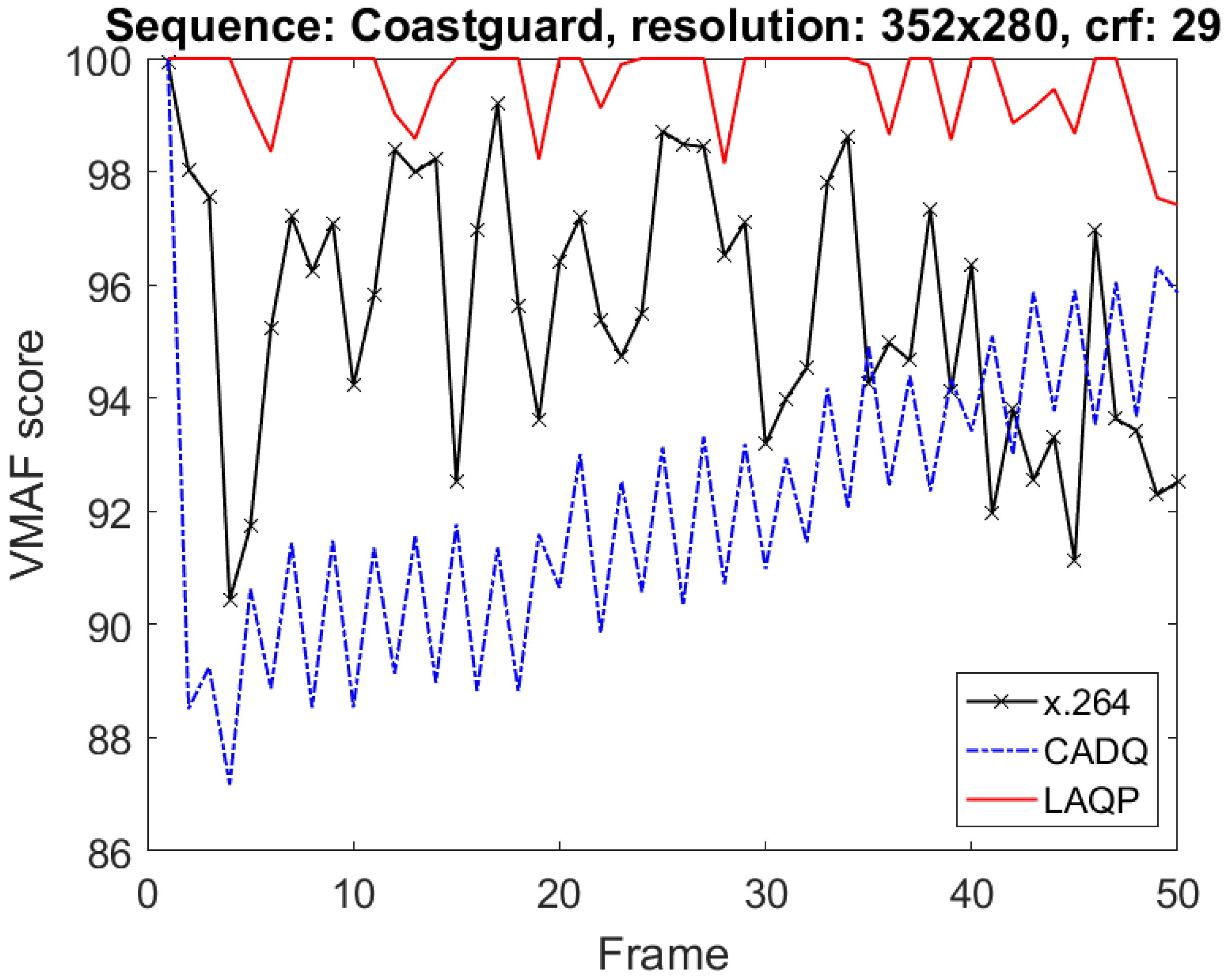
4.4. Quality Consistency Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kjell Brunnström, Sergio Ariel Beker, Katrien de Moor, Ann Dooms, Sebastian Egger, et al., “Qualinet white paper on definitions of quality of experience,“ 2013. hal-00977812.
- T. Hossfeld, M. Seufert, C. Sieber, and T. Zinner, “Assessing effect sizes of influence factors towards a QoE model for HTTP adaptive streaming,” 2014 6th Int. Work. Qual. Multimed. Exp. QoMEX 2014, pp. 111–116, 2014. [CrossRef]
- X. Chen, J. N. Hwang, D. Meng, K. H. Lee, R. L. De Queiroz, and F. M. Yeh, “A quality-of-content-based joint source and channel coding for human detections in a mobile surveillance cloud,” IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol., vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 19–31, 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Milani, R. Bernardini and R. Rinaldo, "A saliency-based rate control for people detection in video," 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2013, pp. 2016-2020. [CrossRef]
- Z. He, W. Zeng, and C. W. Chen, “Low-pass filtering of rate-distortion functions for quality smoothing in real-time video communication,” IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol., vol. 15, no. 8, pp. 973–981, 2005. [CrossRef]
- B. Xie and W. Zeng, “A sequence-based rate control framework for consistent quality real-time video,” IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol., vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 56–71, 2006. [CrossRef]
- L. Xu, S. Li, K. N. Ngan, and L. Ma, “Consistent visual quality control in video coding,” IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol., vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 975–989, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Q. Cai, Z. Chen, D. O. Wu, and B. Huang, “Real-time constant objective quality video coding strategy in high efficiency video coding,” IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol., vol. 30, no. 7, pp. 2215–2228, 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. W. Seo, J. H. Moon, and J. K. Han, “Rate control for consistent objective quality in high efficiency video coding,” IEEE Trans. Image Process., vol. 22, no. 6, pp. 2442–2454, 2013. [CrossRef]
- H. Avc, I. Applications, C.-Y. Wu, and P. Su, “A content-adaptive distortion – quantization model,” IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst., vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 113–126, 2014, [Online]. Available: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=6562767.
- F. De Vito and J. C. De Martin, “PSNR control for GOP-level constant quality in H.264 video coding,” Proc. Fifth IEEE Int. Symp. Signal Process. Inf. Technol., vol. 2005, pp. 612–617, 2005. [CrossRef]
- Z. Li, A. Aaron, A. Katsavounidis, Ioannis Moorthy, and M. Manohara, “Toward A Practical Perceptual Video Quality Metric,” Netflix Blog, 2016. http://techblog.netflix.com/2016/06/toward-practical-perceptual-video.html.
- H. R. Sheikh and A. C. Bovik, “Image information and visual quality,” IEEE Trans. Image Process., vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 430–444, 2006. [CrossRef]
- S. Li, F. Zhang, L. Ma, and K. N. Ngan, “Image quality assessment by separately evaluating detail losses and additive impairments,” IEEE Trans. Multimed., vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 935–949, 2011. [CrossRef]
- R. Rassool, “VMAF reproducibility: validating a perceptual practical video quality metric,” IEEE Int. Symp. Broadband Multimed. Syst. Broadcast. BMSB, 2017. [CrossRef]
- C. Lee, S. Woo, S. Baek, J. Han, J. Chae, and J. Rim, “Comparison of objective quality models for adaptive bit-streaming services,” 2017 8th Int. Conf. Information, Intell. Syst. Appl. IISA 2017, vol. 2018-Janua, pp. 1–4, 2018. [CrossRef]
- N. Barman, S. Schmidt, S. Zadtootaghaj, M. G. Martini, and S. Möller, “An evaluation of video ality assessment metrics for passive gaming video streaming,” Proc. 23th ACM Work. Pack. Video, PV 2018, pp. 7–12, 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. Deng, J. Han, and Y. Xu, “VMAF based rate-distortion optimization for video coding,” IEEE 22nd Int. Work. Multimed. Signal Process. MMSP 2020, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Z. Luo, C. Zhu, Y. Huang, R. Xie, L. Song, and C. C. J. Kuo, “VMAF oriented perceptual coding based on piecewise metric coupling,” IEEE Trans. Image Process., vol. 30, pp. 5109–5121, 2021. [CrossRef]
- I. Marzuki and D. Sim, “Perceptual adaptive quantization parameter selection using deep convolutional features for HEVC encoder,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 37052–37065, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. M. Alam, T. D. Nguyen, M. T. Hagan, and D. M. Chandler, “A perceptual quantization strategy for HEVC based on a convolutional neural network trained on natural images,” Appl. Digit. Image Process. XXXVIII, vol. 9599, p. 959918, 2015. [CrossRef]
- T. H. Vu, H. P. Cong, T. Sisouvong, X. HoangVan, S. NguyenQuang and M. DoNgoc, "VMAF based quantization parameter prediction model for low resolution video coding," 2022 International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Communications (ATC), Ha Noi, Vietnam, 2022, pp. 364-368. [CrossRef]
- T. Wiegand, G. Sullivan, and A. Luthra, “Draft ITU-T recommendation and final draft international standard of joint video specification (ITU-T Rec. H.264ISO/IEC 14 496-10 AVC),” vol. 2002, pp. 7–14, 2003.
- G. J. Sullivan and T. Wiegand, “Rate-distortion optimization for: Video compression,” IEEE Signal Process. Mag., vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 74–90, 1998. [CrossRef]
- C. L. Yang, R. K. Leung, L. M. Po, and Z. Y. Mai, “An SSIM-optimal H.264/AVC inter frame encoder,” Proc. - 2009 IEEE Int. Conf. Intell. Comput. Intell. Syst. ICIS 2009, vol. 4, pp. 291–295, 2009. [CrossRef]
- X. Wang, L. Su, Q. Huang and C. Liu, "Visual perception based Lagrangian rate distortion optimization for video coding," 2011 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 2011, pp. 1653-1656. [CrossRef]
- Z. Wang, A. C. Bovik, H. R. Sheikh, and E. P. Simoncelli, “Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity,” IEEE Trans. Image Process., vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 600–612, Apr. 2004. [CrossRef]
- X. Tong, C. Zhu, R. Xie, J. Xiong, and L. Song, “A VMAF directed perceptual rate distortion optimization for video coding,” IEEE Int. Symp. Broadband Multimed. Syst. Broadcast. BMSB, vol. 2020-Octob, pp. 3–7, 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. Zhu, Y. Huang, R. Xie, and L. Song, “HEVC VMAF-oriented perceptual rate distortion optimization using CNN,” 2021 Pict. Coding Symp. PCS 2021 - Proc., 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. Simonyan and A. Zisserman, “Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition,” 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556.
- G. Bjontegaard, “Calculation of average PSNR differences between RD-curves,” ITU-T VCEG-M33, 2011.
- https://x265.readthedocs.io/en/master/.
- Versatile Video Coding, Standard ISO/IEC 23090-3, ISO/IEC JTC 1, Jul. 2020.

| Video sequences | R-squared of | R-squared of |
|---|---|---|
| Hall | 0.95 | 0.93 |
| City | 0.96 | 0.90 |
| Foreman | 0.90 | 0.90 |
| Crew | 0.84 | 0.94 |
| Four-people | 0.92 | 0.94 |
| Ice | 0.94 | 0.91 |
| Kris | 0.89 | 0.91 |
| Mobile | 0.99 | 0.88 |
| Soccer | 0.91 | 0.97 |
| Waterfall | 0.98 | 0.83 |
| Average | 0.93 | 0.91 |
| Video sequence |
crf | x.264 codec | CADQ [10] | Our LAQP | LAQP vs. x.264 |
LAQP vs. CADQ |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
BR_ ref |
VMAF_ ref |
BR_ [10] |
VMAF_ [10] |
BR_ Proposed |
VMAF_ Proposed |
BD- Rate |
BD- VMAF |
BD- Rate |
BD- VMAF |
||
| Coastguard 352x288 |
29 | 339.26 | 96 | 469.73 | 92 | 524.46 | 100 | -2.15 | 0.53 | -16.21 | 3.55 |
| 32 | 241.02 | 84 | 280.23 | 85 | 275.41 | 90 | |||||
| 35 | 110.28 | 73 | 153.42 | 76 | 130.91 | 75 | |||||
| 37 | 75.22 | 65 | 102.87 | 69 | 80.09 | 64 | |||||
| Container 352x288 |
29 | 99.51 | 100 | 142.14 | 100 | 98.56 | 100 | 1.28 | 0.72 | -27.65 | 4.11 |
| 32 | 63.21 | 99 | 81.15 | 96 | 63.6 | 99 | |||||
| 35 | 43.56 | 93 | 50.5 | 92 | 44.85 | 95 | |||||
| 37 | 34.9 | 87 | 39.19 | 87 | 35.52 | 89 | |||||
| Silent 352x288 |
29 | 131.84 | 100 | 143.89 | 100 | 107.64 | 100 | -4.08 | 4.28 | -1.60 | 2.20 |
| 32 | 91.84 | 98 | 94.58 | 98 | 85.24 | 100 | |||||
| 35 | 63.91 | 88 | 60.5 | 91 | 61.45 | 93 | |||||
| 37 | 50.22 | 80 | 46.85 | 84 | 45.23 | 85 | |||||
| Tempete 352x288 |
29 | 283.87 | 98 | 382.01 | 98 | 306.59 | 100 | -4.74 | 0.89 | -7.88 | 1.57 |
| 32 | 187.94 | 91 | 217.23 | 92 | 217.2 | 95 | |||||
| 35 | 126.62 | 80 | 123.33 | 80 | 118.57 | 79 | |||||
| 37 | 98.92 | 72 | 88.69 | 72 | 83.34 | 71 | |||||
| Crew 1280x720 |
29 | 502.26 | 97 | 518.7 | 98 | 537.59 | 97 | -4.64 | 1.44 | -3.37 | 1.09 |
| 32 | 348.33 | 88 | 313.61 | 95 | 376.43 | 91 | |||||
| 35 | 245.98 | 77 | 254.21 | 81 | 249.18 | 80 | |||||
| 37 | 194.04 | 67 | 195.07 | 71 | 185.69 | 69 | |||||
| Vidyo3 1280x720 |
29 | 512.69 | 100 | 499.98 | 100 | 495.39 | 100 | -5.82 | 1.65 | -3.51 | 0.41 |
| 32 | 362.5 | 97 | 398.7 | 99 | 372.61 | 98 | |||||
| 35 | 255.7 | 88 | 253.45 | 90 | 241.93 | 90 | |||||
| 37 | 201.24 | 80 | 204.13 | 80 | 205.69 | 80 | |||||
| Average | -3.36 | 1.59 | -10.03 | 2.16 | |||||||
| Video sequence | crf | x.264 | CADQ | LAQP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coastguard | 29 | 5.57 | 6.68 | 0.59 |
| 32 | 4.98 | 6.18 | 4.83 | |
| 35 | 5.41 | 5.34 | 5.10 | |
| 37 | 4.24 | 5.81 | 4.51 | |
| Container | 29 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.11 |
| 32 | 2.83 | 0.47 | 1.11 | |
| 35 | 4.49 | 0.88 | 1.41 | |
| 37 | 5.05 | 0.99 | 0.89 | |
| Silent | 29 | 0.11 | 0.74 | 0.00 |
| 32 | 4.94 | 1.09 | 0.00 | |
| 35 | 12.94 | 1.59 | 1.34 | |
| 37 | 13.10 | 2.30 | 2.12 | |
| Tempete | 29 | 2.94 | 1.58 | 0.3 |
| 32 | 6.93 | 3.57 | 1.59 | |
| 35 | 5.84 | 4.71 | 3.67 | |
| 37 | 6.22 | 5.43 | 3.09 | |
| Crew | 29 | 10.15 | 15.67 | 10.60 |
| 32 | 20.53 | 18.73 | 12.04 | |
| 35 | 26.30 | 23.73 | 15.32 | |
| 37 | 37.39 | 26.90 | 18.89 | |
| Vidyo3 | 29 | 1.24 | 1.53 | 1.19 |
| 32 | 2.99 | 2.92 | 2.44 | |
| 35 | 7.23 | 5.21 | 2.49 | |
| 37 | 5.12 | 3.56 | 2.76 | |
| Average | 8.19 | 6.07 | 4.02 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





