Submitted:
27 October 2023
Posted:
01 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
Is there a growing interest in nudibranch studies over time? (2) Which species and locations are the most extensively studied? (3) Are there specific species or families that frequently exhibit identified biological activity? (4) Is there a prevailing focus on biological activity or chemical characterization in the studies? (5) Is there a particular class of metabolites that dominates the research on the most studied species? (6) Which chemical characterization methods are most employed? (7) What are the primary and/or secondary metabolites that are frequently discovered? (8) Which types of biological activities are most frequently investigated?
2. Systemic analysis of secondary metabolites and biological activity of the extracts and compounds from nudibranchs
3. Secondary metabolites isolated from Nudibranchs
3.1. Alkaloids
3.1.1. Bis-pyrrole
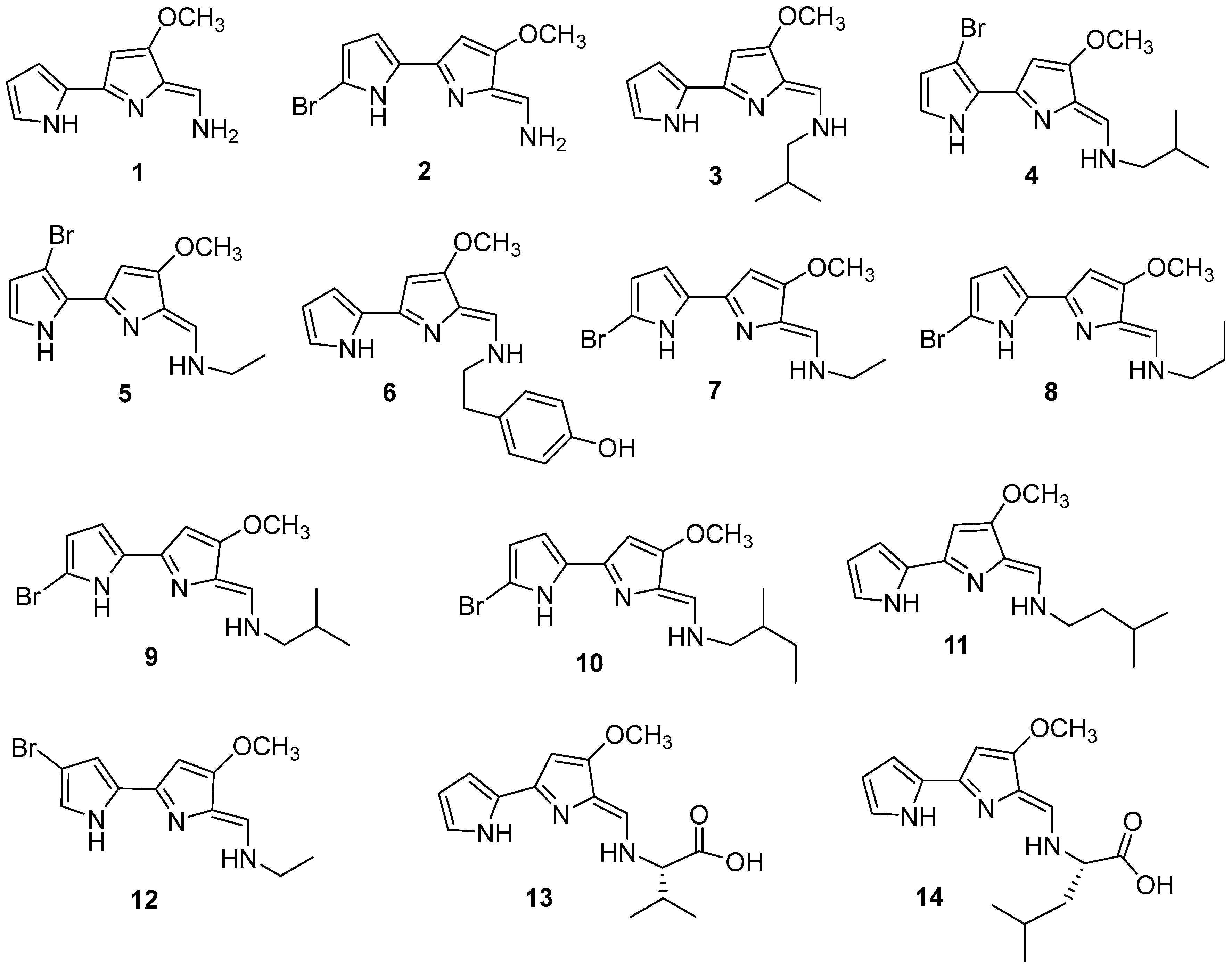
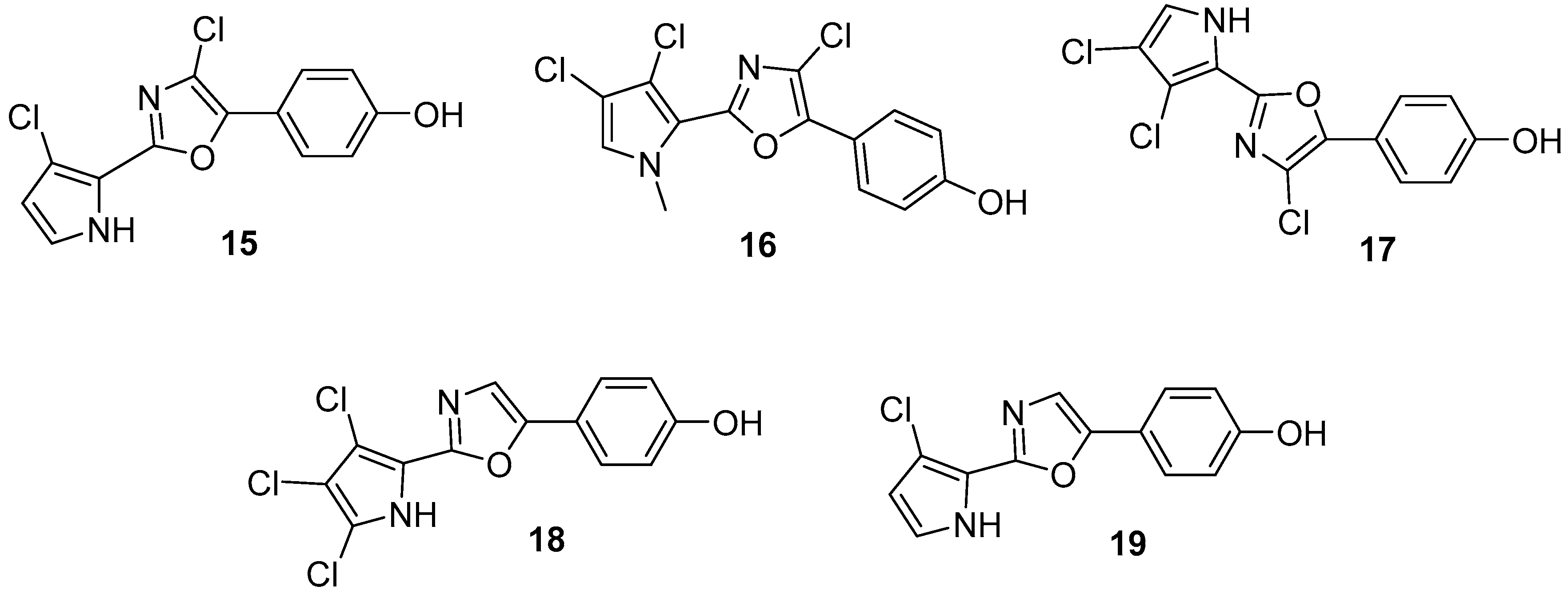
3.1.2. Isoquinoline
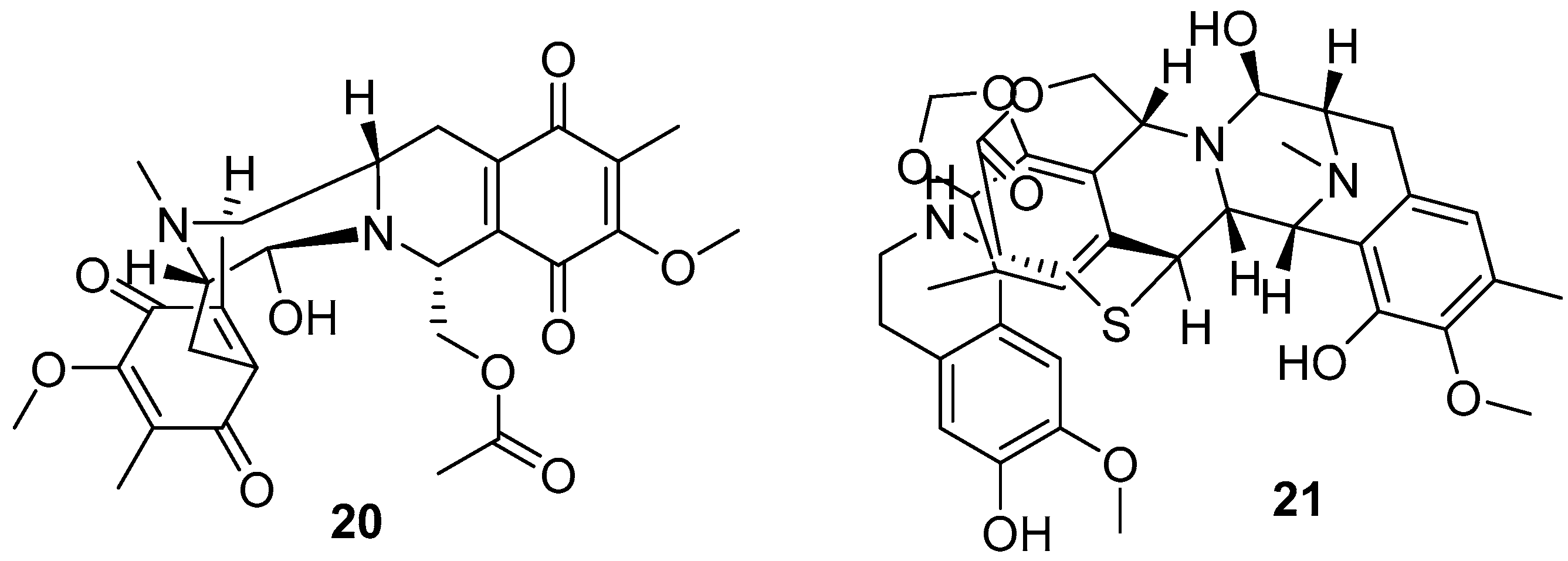
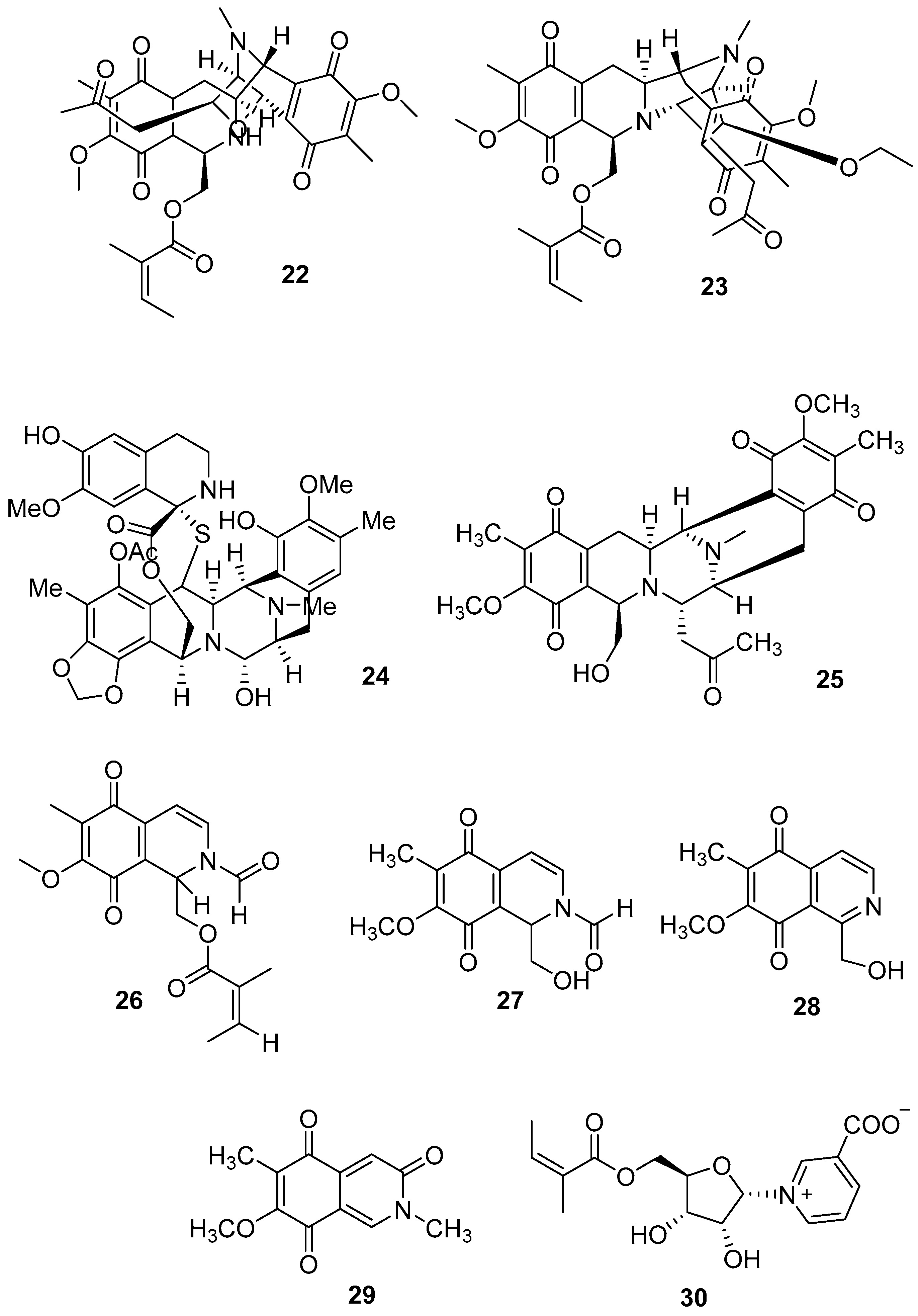
3.2. Terpenoids
3.2.1. Sesquiterpenes
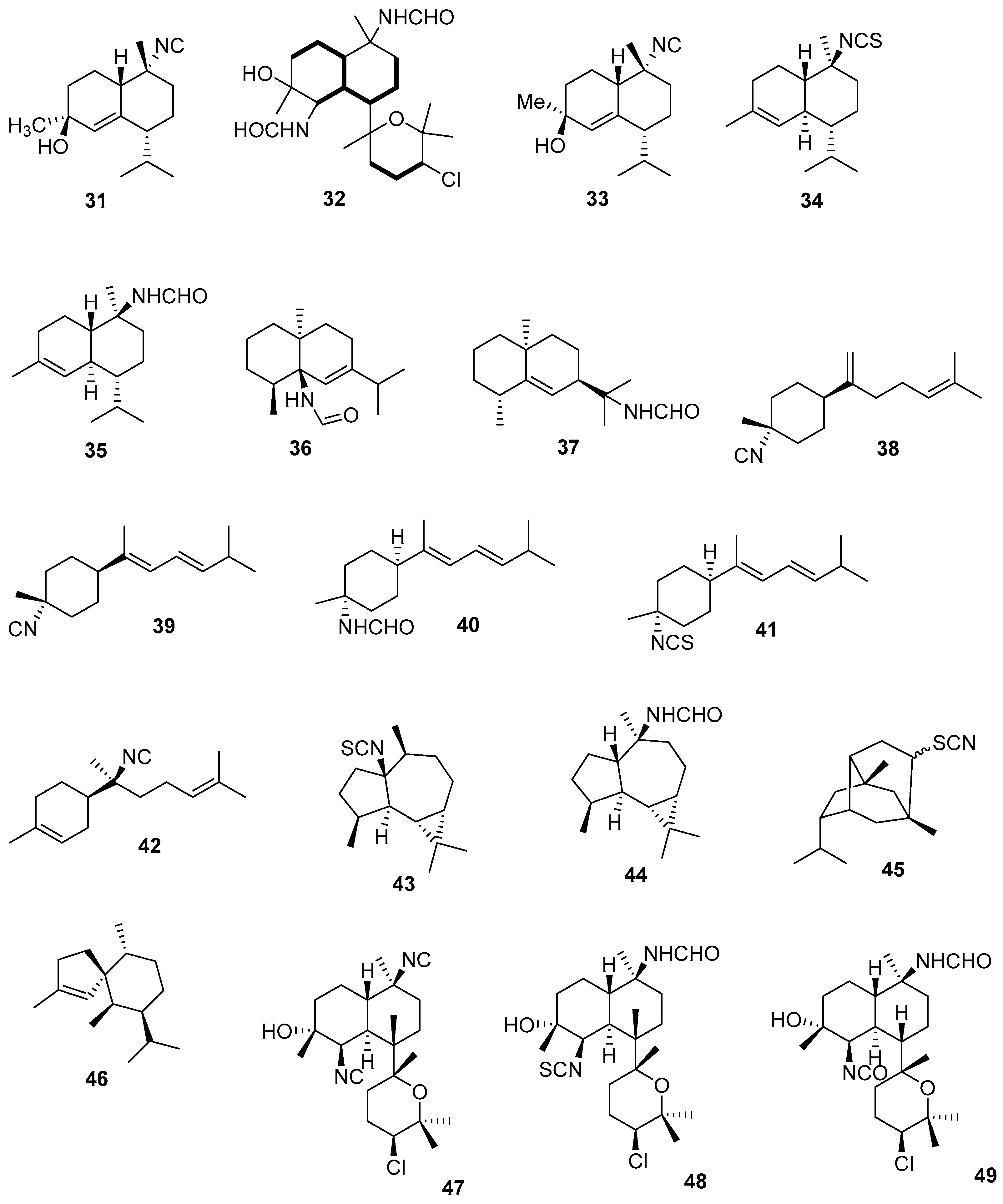
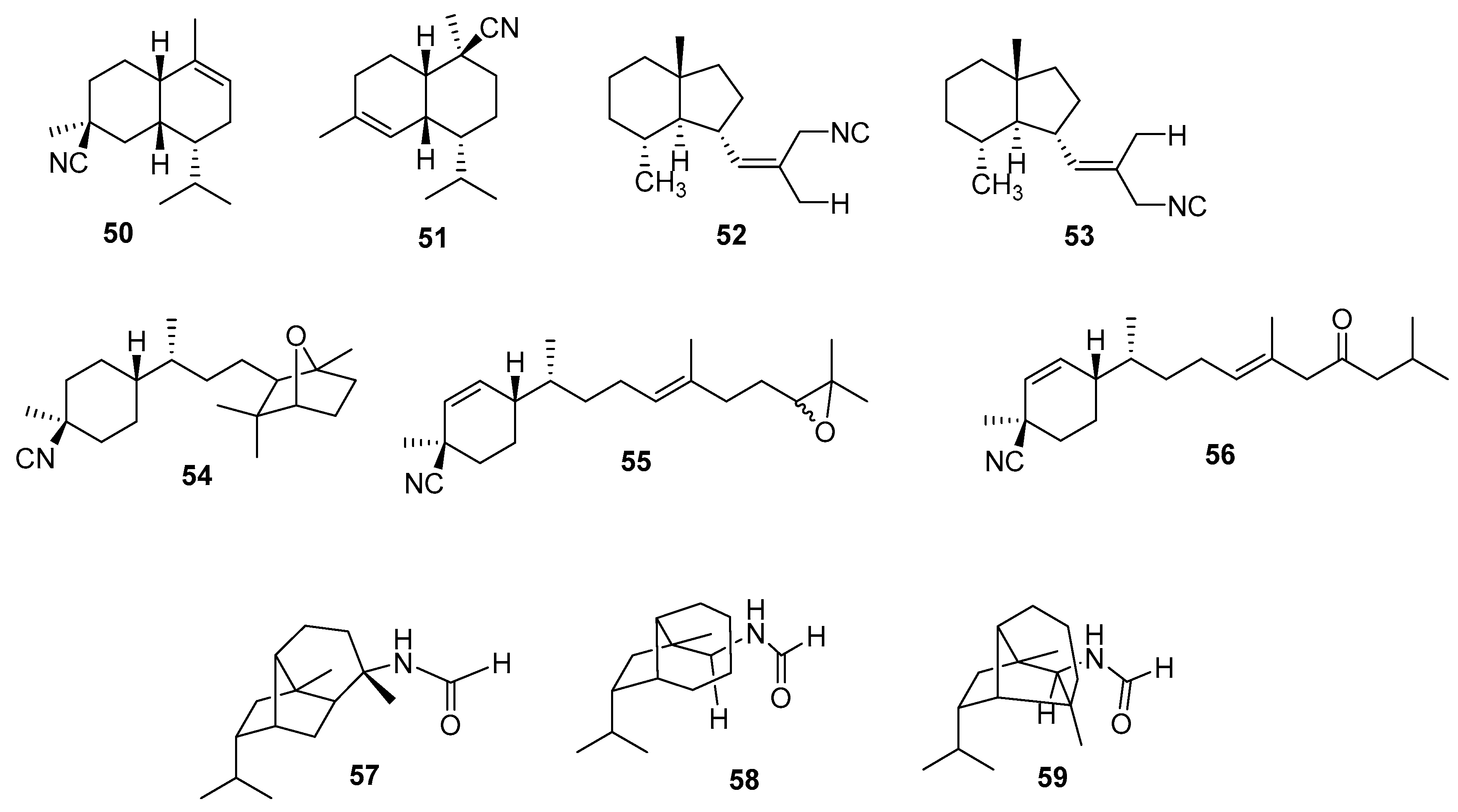
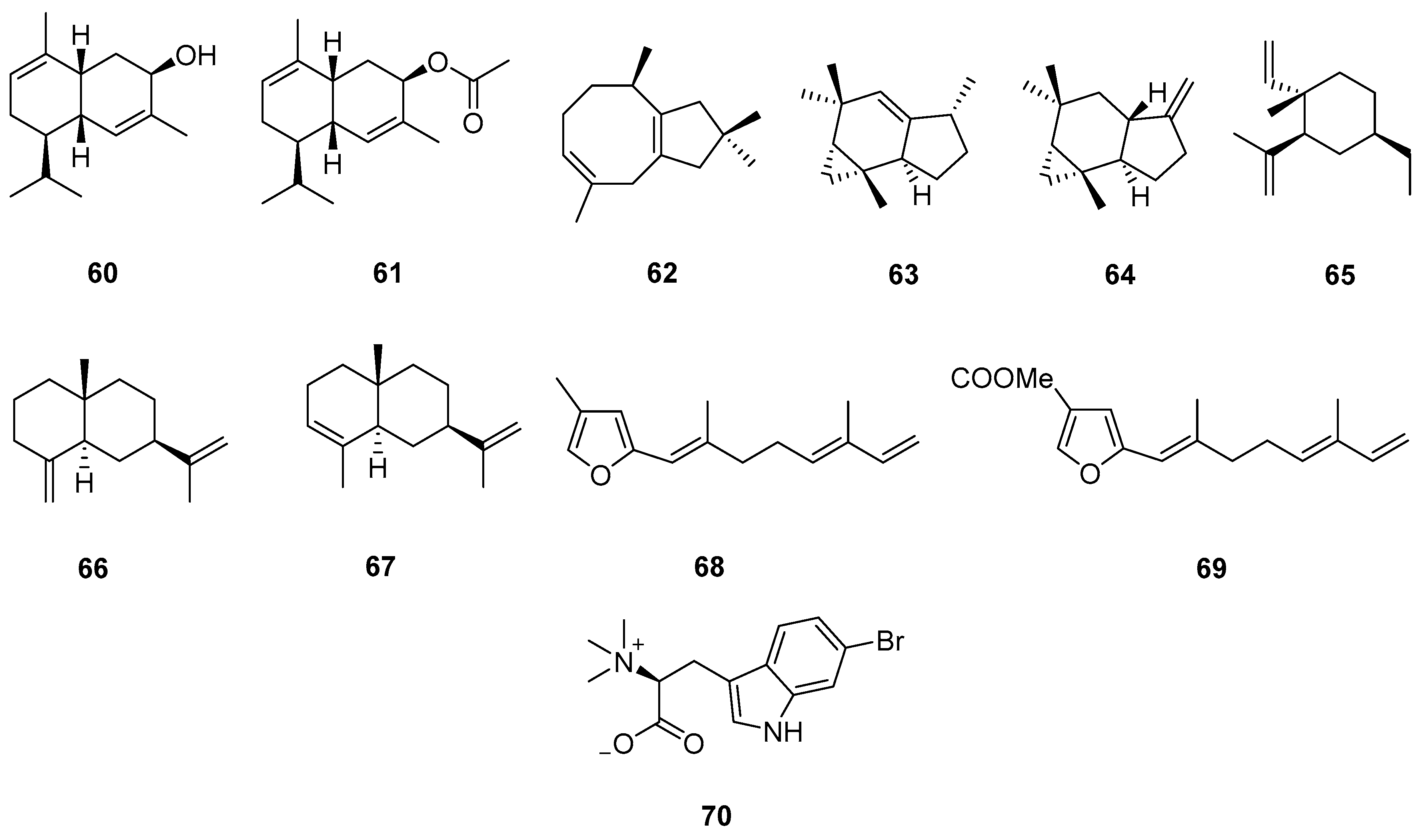
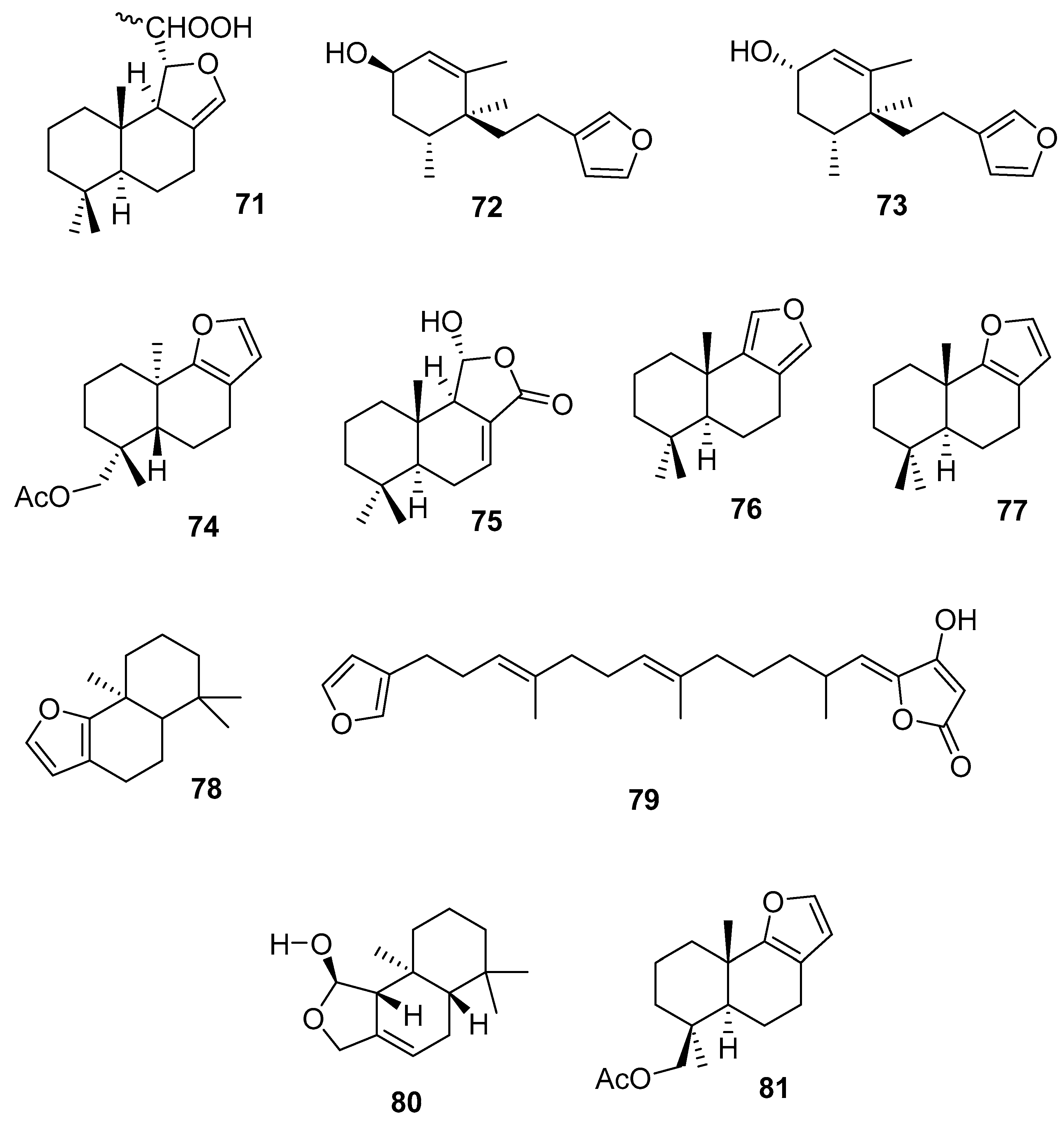
3.2.2. Diterpenes
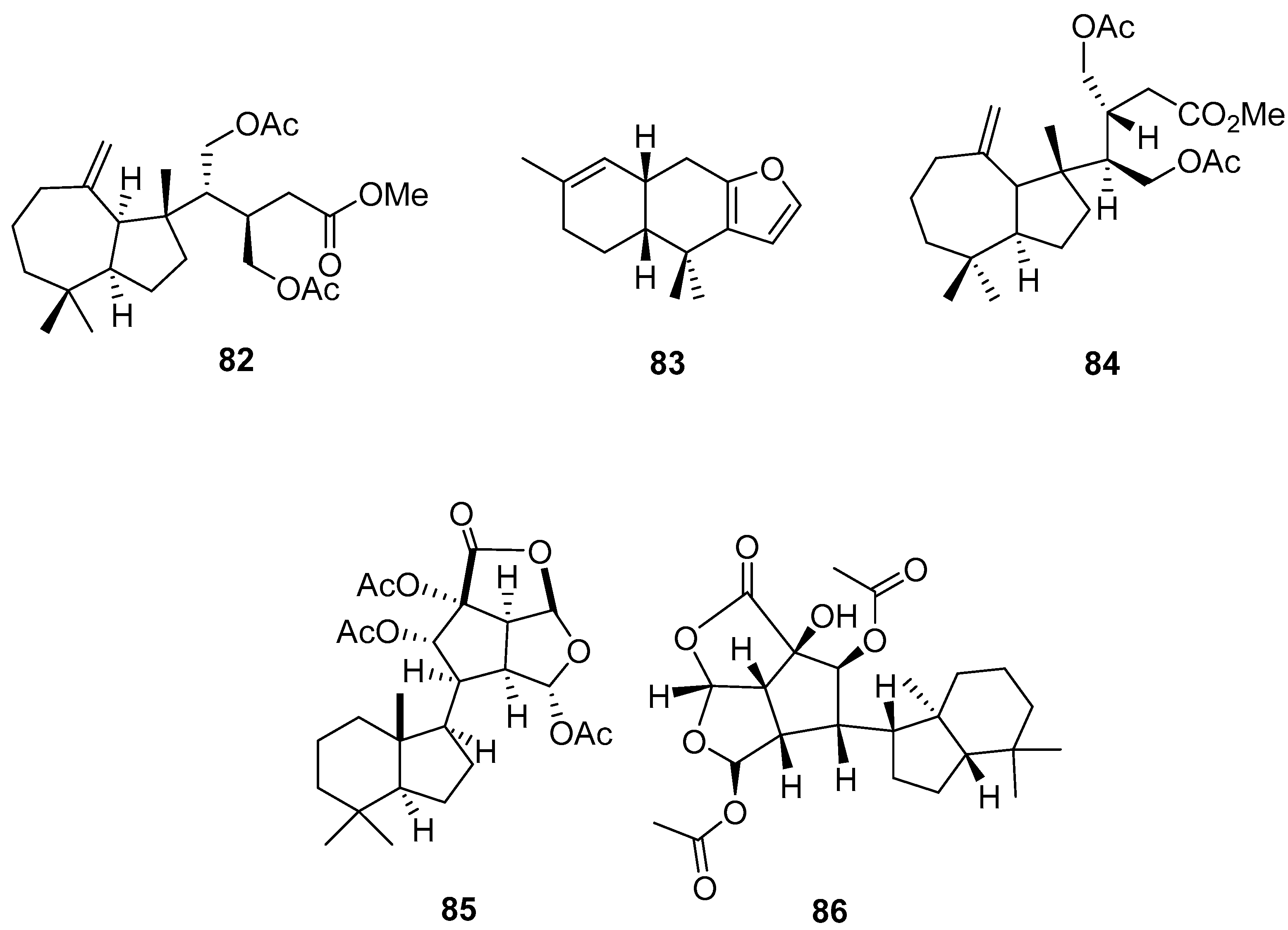
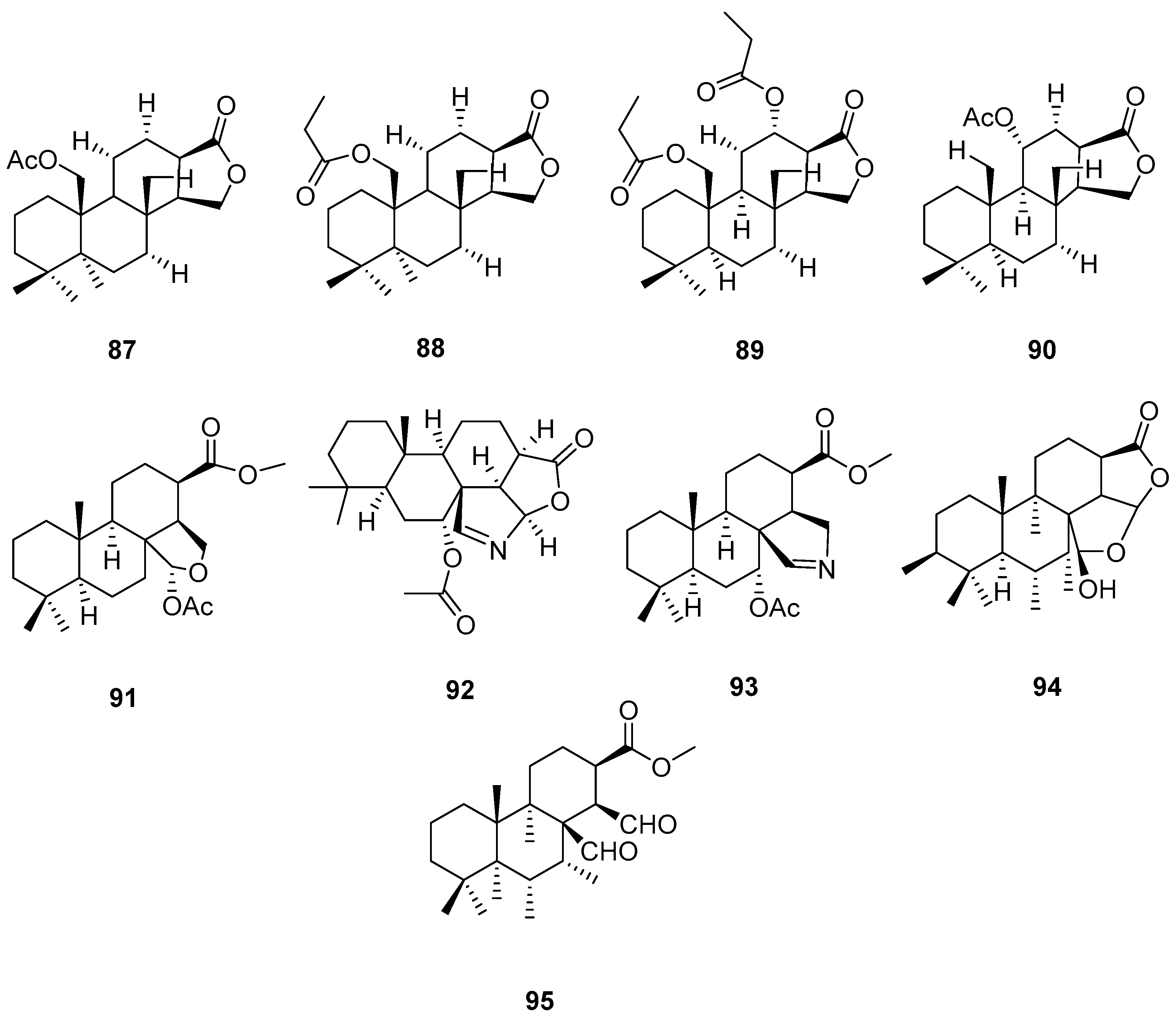
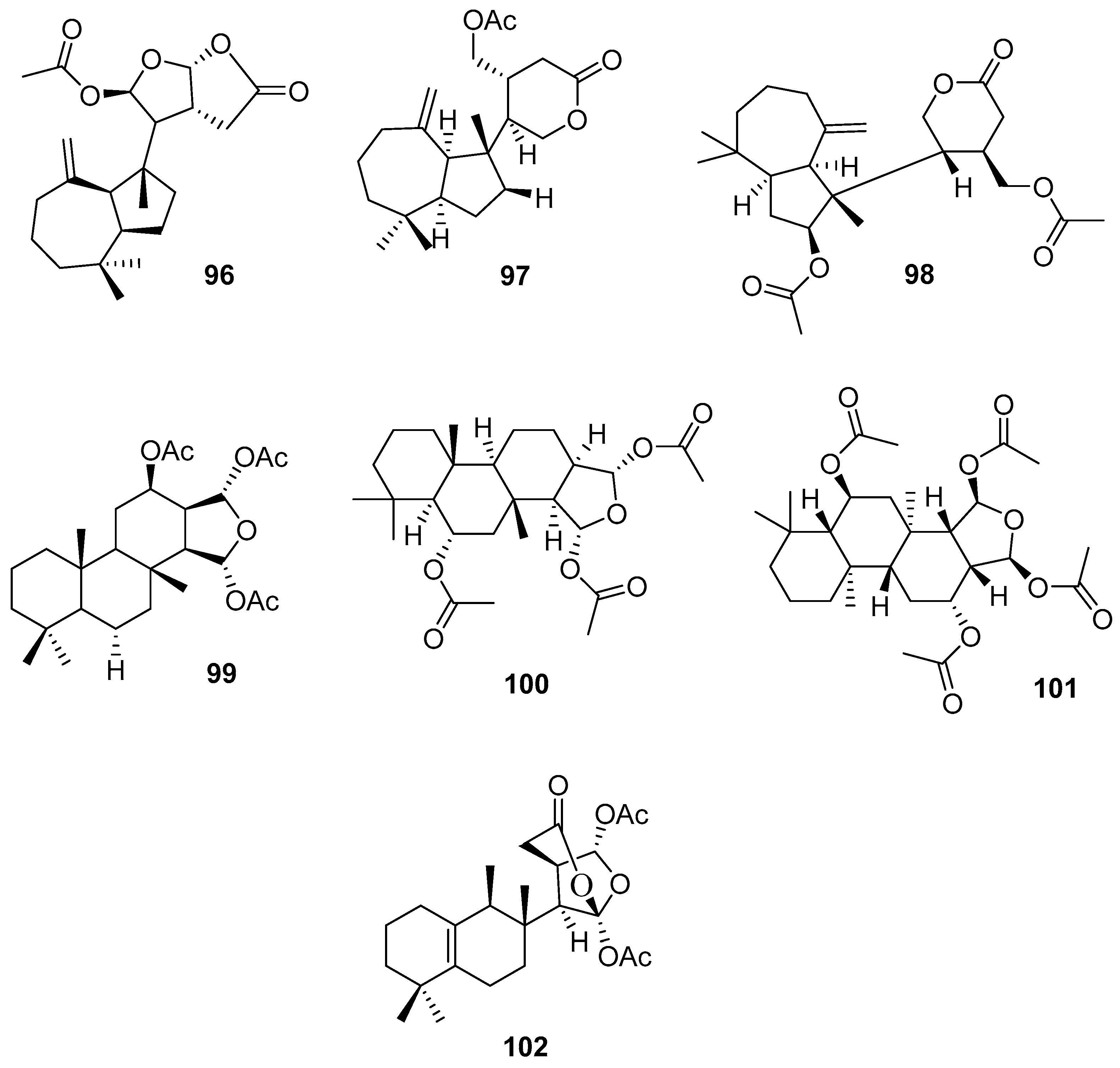
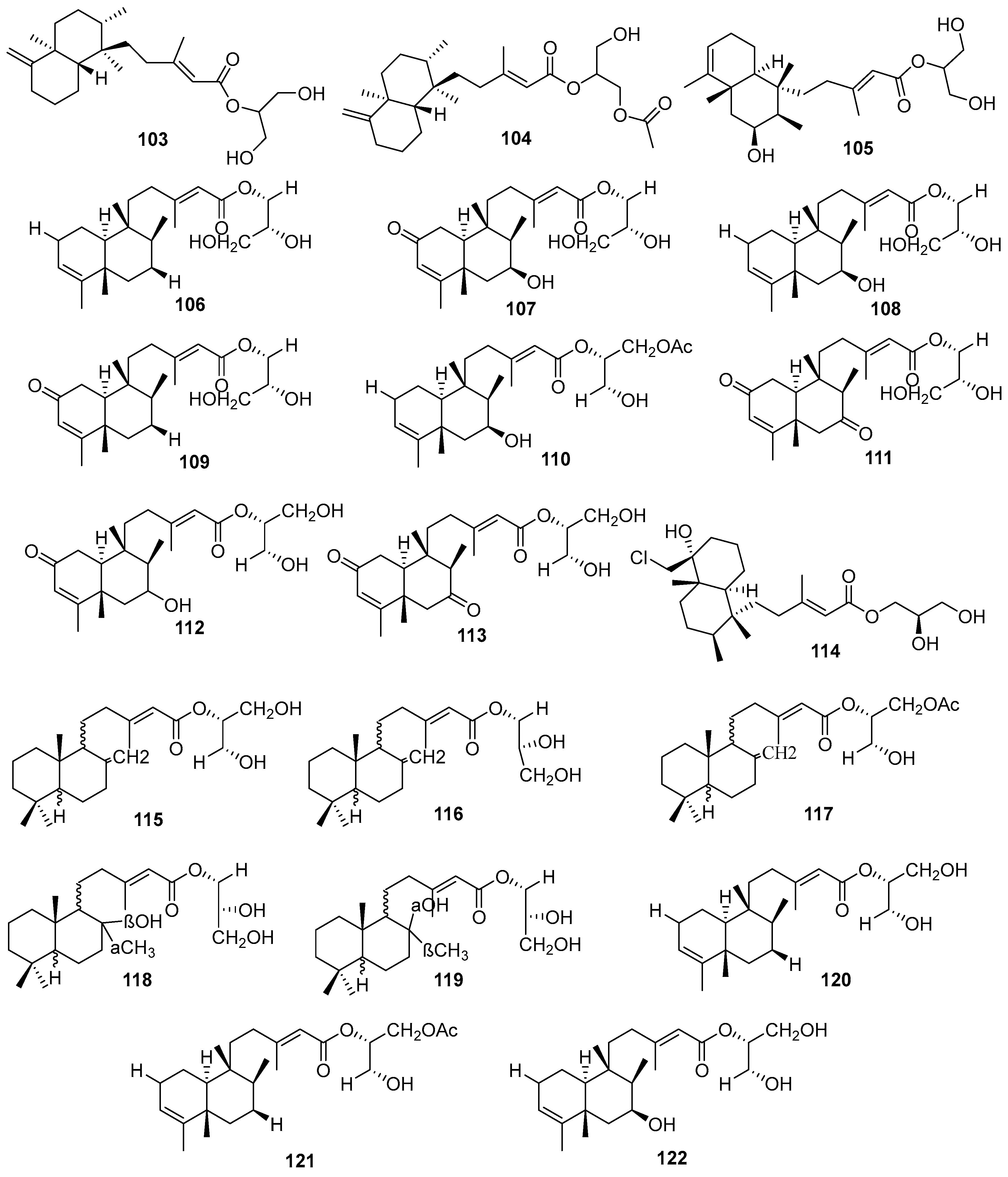
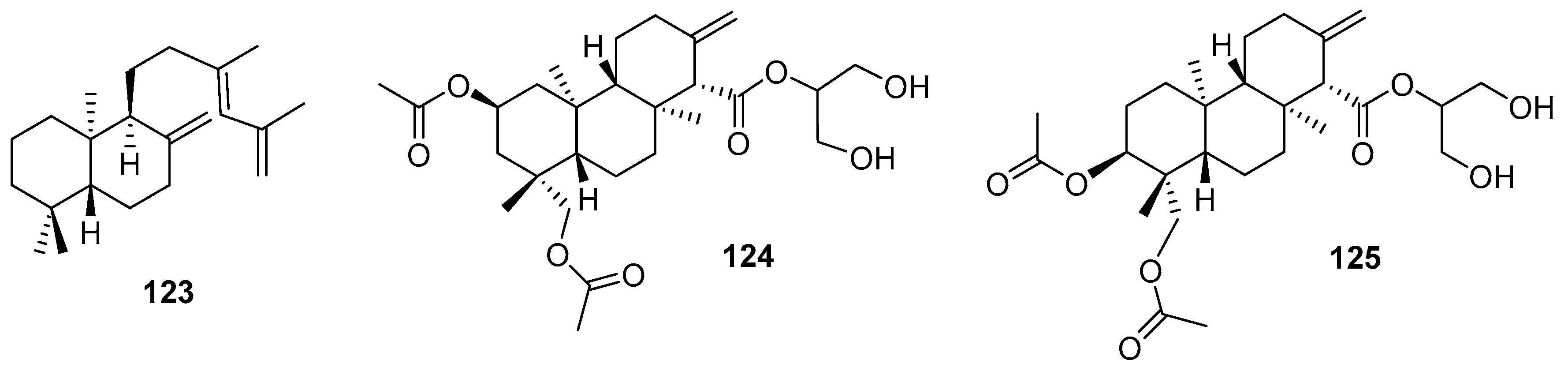
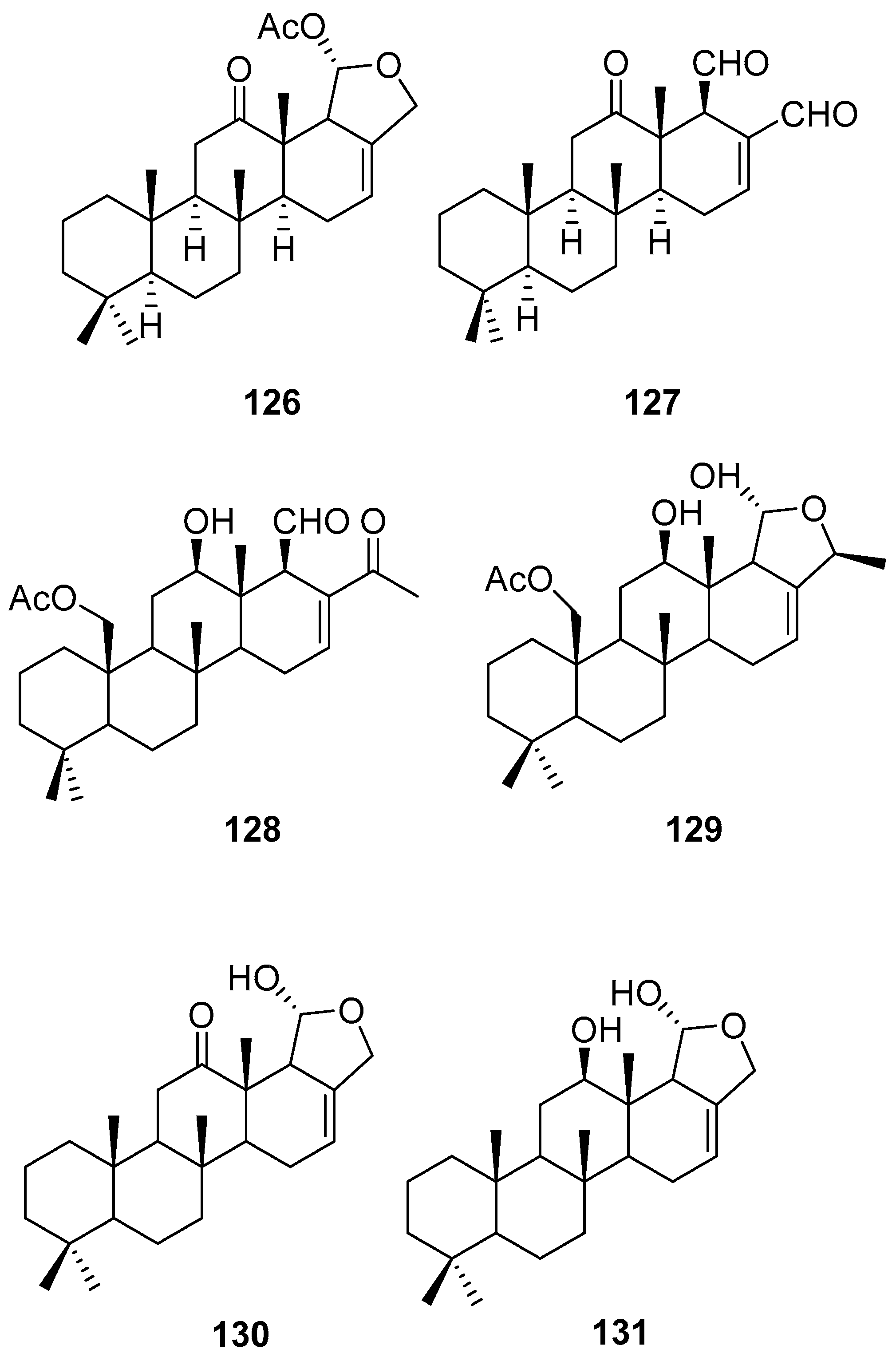
3.2.3. Sesterterpenes and other compounds
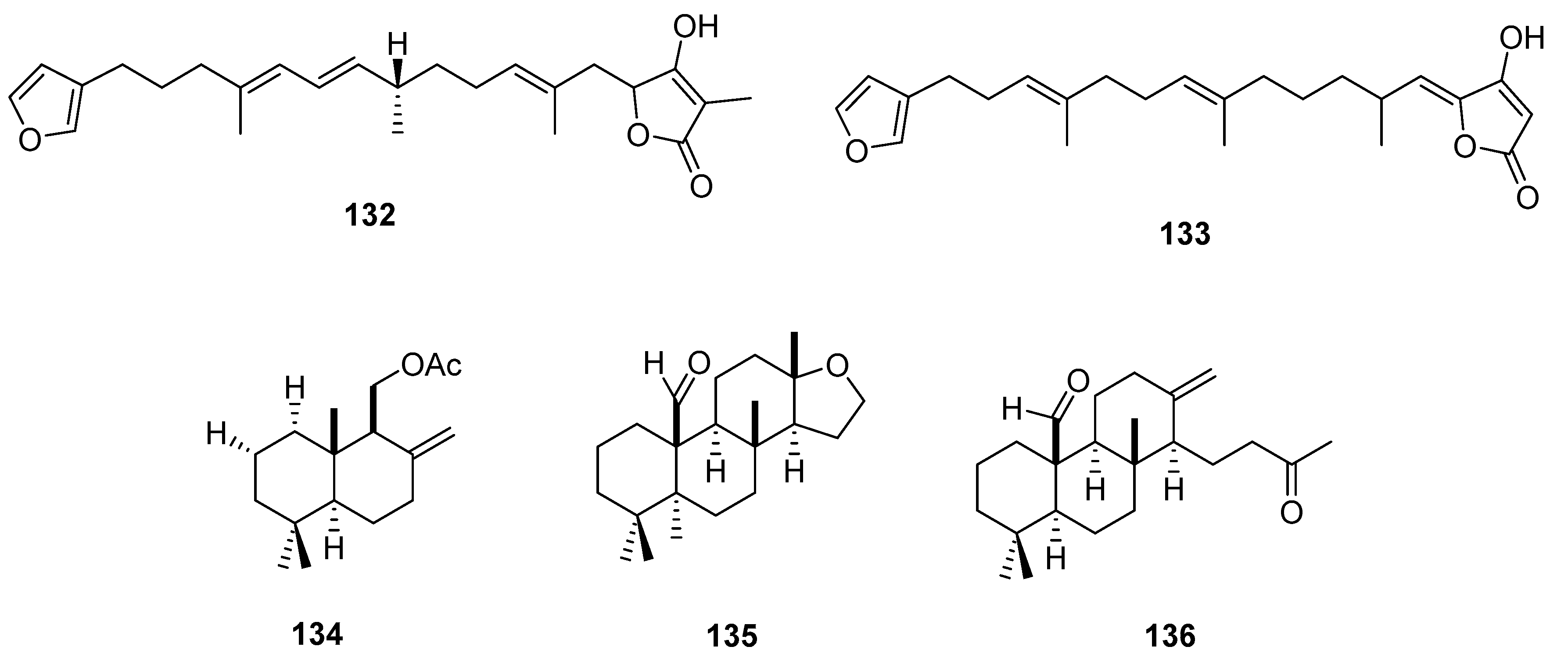
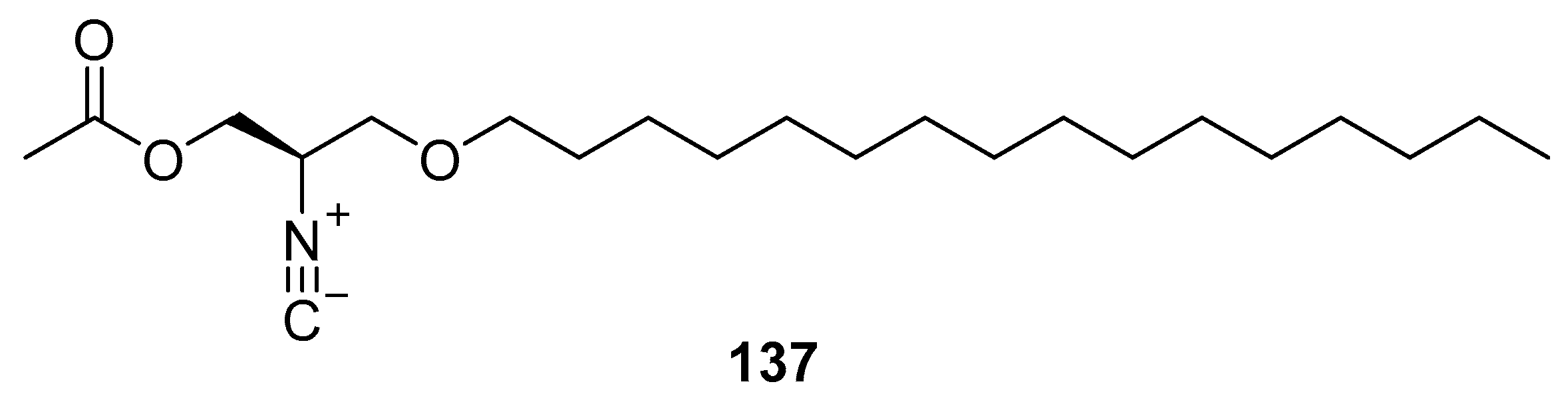
3.3. Lipid based on a 1,3-propanediol ether skeleton
3.4. Amino Acids
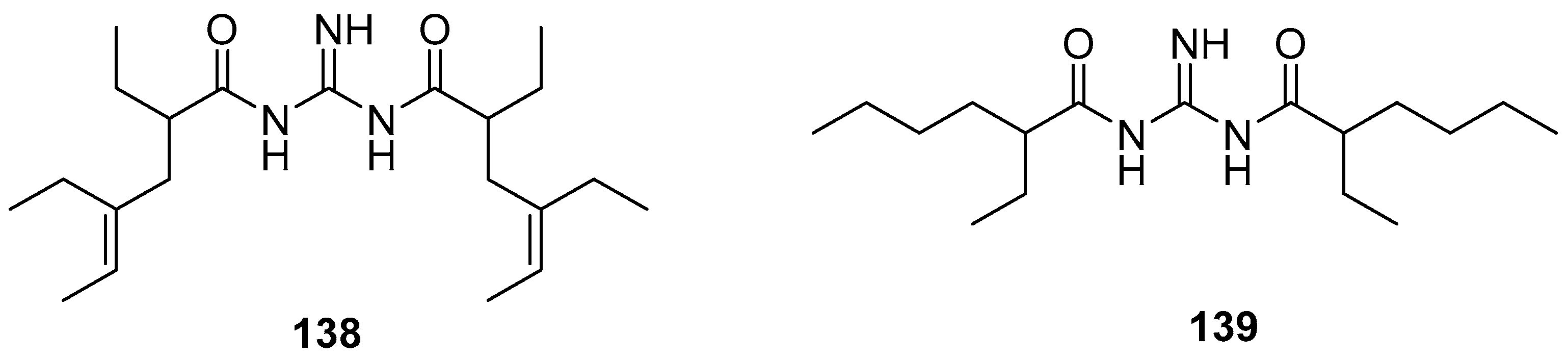
4. Biological /pharmacological activities of Secondary metabolites isolated from nudibranchs
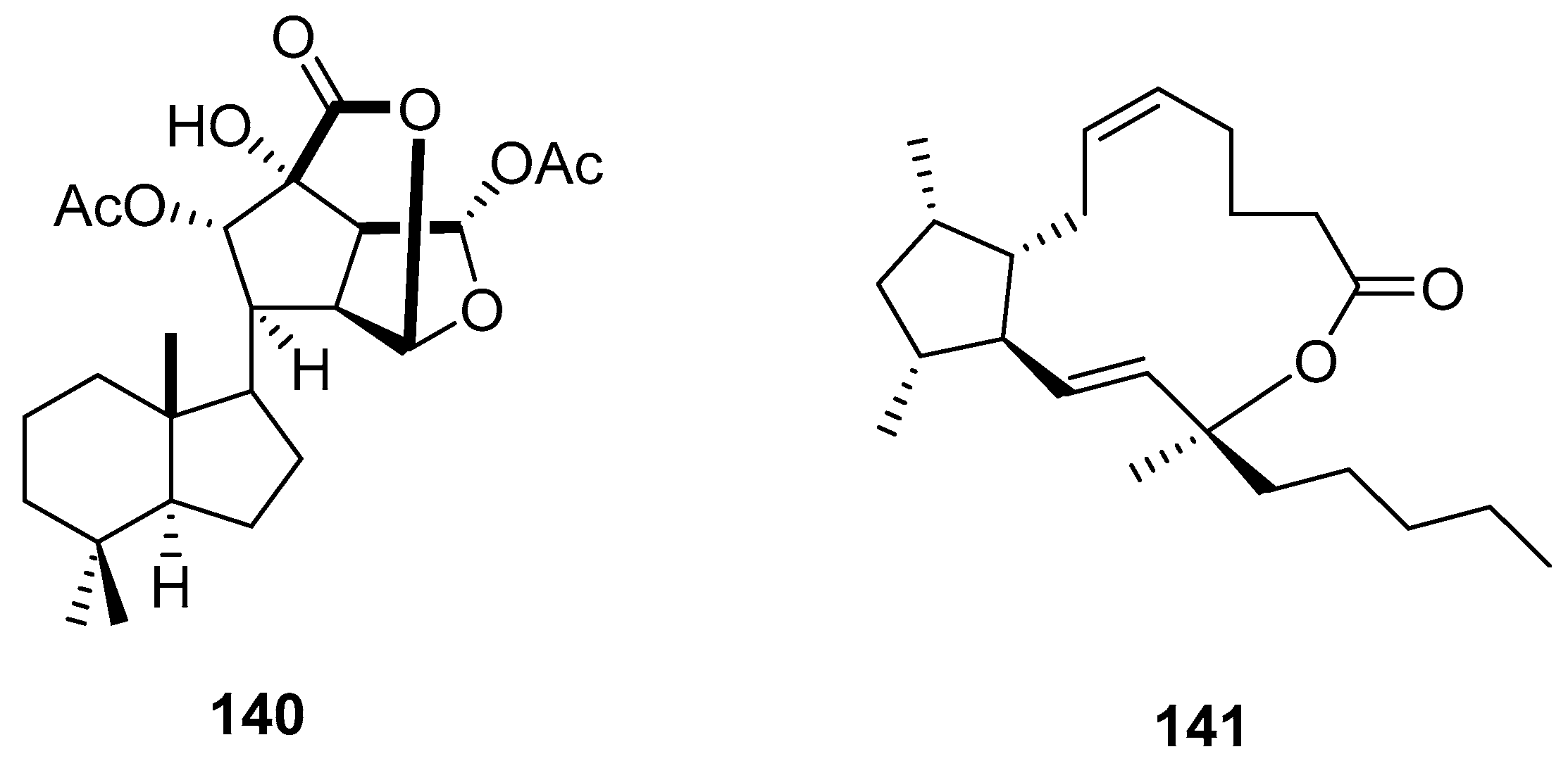
5. Conclusions and perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 175–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, C.W.O.N.; Kim, H.J.O.O.; Lee, S.H.U.N. Therapeutic application of diverse marine-derived natural products in cancer therapy. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 5261–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, T.B.; Cheung, R.C.F.; Wong, J.H.; Bekhit, A.A.; Bekhit, A.E.D. Antibacterial products of marine organisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 4145–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, P.C.; Wilke, D.V.; Branco, P.C.; Bauermeister, A.; Rezende-Teixeira, P.; Gaudêncio, S.P.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V. Enriching cancer pharmacology with drugs of marine origin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Bardón, M.; Pérez-Pertejo, Y.; Ordóñez, C.; Sepúlveda-Crespo, D.; Carballeira, N.M.; Tekwani, B.L.; Murugesan, S.; Martinez-Valladares, M.; García-Estrada, C.; Reguera, R.M.; Balaña-Fouce, R. Screening marine natural products for new drug leads against trypanosomatids and malaria. Mar. Drugs. 2020, 18, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nweze, J.A.; Mbaoji, F.N.; Huang, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Pan, L.; Yang, D. Antibiotics development and the potentials of marine-derived compounds to stem the tide of multidrug-resistant pathogenic bacteria, fungi, and protozoa. Mar. Drugs. 2020, 18, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, L.J.; Prinsep, M.R. The chemistry and chemical ecology of nudibranchs. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 1359–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Y.; Chen, W.T.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Li, X.W.; Guo, Y.W. Bioactive isoquinolinequinone alkaloids from the South China Sea nudibranch Jorunna funebris and its sponge-prey Xestospongia sp. Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, R.R.; Iorio, N.L.P.P.; Póvoa, H.C.C.; Chianca, G.C.; Kachlicki, P.; Ożarowski, M.; Silva, V.O.; Félix, H.P.; Lopes, I.C.; Chaves, D.S.A. Composição química e atividade anticariogênica do nudibrânquio Tambja stegosauriformis. Rev. Virtual de Química 2019, 11, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, D.C.M.; Wayan Mudianta, I.; White, A.M.; Martiningsih, N.W.; Loh, J.J.M.; Cheney, K.L.; Garson, M.J. New sesquiterpenoid isonitriles from three species of phyllidid nudibranchs. Fitoterapia 2018, 126, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.M.; Pierens, G.K.; Forster, L.C.; Winters, A.E.; Cheney, K.; Garson, M.J. Rearranged diterpenes and norditerpenes from three Australian Goniobranchus molluscs. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, L.C.; Winters, A.E.; Cheney, K.L.; Dewapriya, P.; Capon, R.J.; Garson, M.J. Spongian-16-one diterpenes and their anatomical distribution in the Australian nudibranch Goniobranchus collingwoodi. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winters, A.E.; White, A.M.; Dewi, A.S.; Mudianta, I.W.; Wilson, N.G.; Forster, L.C.; Garson, M.J.; Cheney, K.L. Distribution of defensive metabolites in nudibranch molluscs. J. Chem. Ecol. 2018, 44, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyšek, P.; Richardson, D.M.; Pergl, J.; Jarošík, V.; Sixtová, Z.; Weber, E. Geographical and taxonomic biases in invasion ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramya, M.S.; Sivasubramanian, K.; Ravichandran, S.; Anbuchezhian, R. Screening of antimicrobial compound from the sea slug Armina babai. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erngren, I.; Smit, E.; Pettersson, C.; Cárdenas, P.; Hedeland, M. The Effects of sampling and storage conditions on the metabolite profile of the marine sponge Geodia barretti. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flórez-Fernández, N.; Balboa, E.M.; Domínguez, H. Extraction and purification of fucoidan from marine sources. Encyclopedia of Mar. Biotechnol. 2020, 1093–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, S.M.; Dosoky, N.S.; Hanora, A.M.; Lopanik, N.B. Metabolomic Profiling and Molecular Networking of Nudibranch-Associated Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 001680. Molecules. 2022, 27, 4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerwick, W.H.; Moore, B.S. Lessons from the past and charting the future of marine natural products drug discovery and chemical biology. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genoveffa, N.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Kiss, R.; Mathieu, V.; Leclercqz, H.; Manzo, E.; Villani, G.; Mollo, E.; Lefranc, F.; D'Souza, L.; Gavagnin, M.; Cimino, G. Chemistry of the nudibranch Aldisa andersoni: structure and biological activity of phorbazole metabolites. Mar. Drugs. 2012, 10, 1799–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittakoop, P.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, S. Alkaloids as Important Scaffolds in Therapeutic Drugs for the Treatments of Cancer, Tuberculosis, and Smoking Cessation. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. 2013, 14, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagi, S.; Avula, B.; Wang, Y.H.; Khan, I.A. Quantification and characterization of alkaloids from roots of Rauwolfia serpentine using ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-photo diode array-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.; Verpoorte, R. Catharanthus terpenoid indole alkaloids: biosynthesis and regulation. Phytochem. Rev. 2007, 6, 277–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanowska-Karamyan, A.J.; Hamann, M.T. Marine indole alkaloids: potential new drug leads for the control of depression and anxiety. Chem Rev. 2010, 110, 4489–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempone, A.G.; Pieper, P.; Borborema, S.E.T.; Thevenard, F.; Lago, J.H.G.; Croft, S.L.; Anderson, E.A. Marine alkaloids as bioactive agents against protozoal neglected tropical diseases and malaria. Natural Product Reports. 2021, 38, 2214–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yang, S.; Wang, K.; Bao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Liu, H.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, T.; Yu, H. Alkaloids from Traditional Chinese Medicine against hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019, 120, 109543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcanti, B.C.; Júnior, H.V.N.; Seleghim, M.H.R.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; Cunha, G.M.A.; Moraes, M.O.; Pessoa, C. Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of tambjamine D, an alkaloid isolated from the nudibranch Tambja eliora, on Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2008, 174, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, C.; Angulo-Preckler, C. Bioactive Compounds from Marine Heterobranchs. Marine Drugs 2020, 18, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaki, M.; Freire, V.F.; Nicacio, K.J.; Bertonha, A.F.; Nagashima, N.; Sarpong, R.; Berlinck, R.G.S. Metabolomics Reveals Minor Tambjamines in a Marine Invertebrate Food Chain. Journal of Natural Products 2020, 84, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, A.; Li, C. New Tambjamine Alkaloids From the Marine Bryozoan Bugula dentata. Australian Journal of Chemistry 1994, 47, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, A.C.; Oliveira, J.H.H.L.; Seleghim, M.H.R.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; Macedo, M.L.; Ferreira, A.G.; Cavalcanti, B.C. Produtos naturais da ascídia Botrylloides giganteum, das esponjas Verongula gigantea, Ircinia felix, Cliona delitrix e do nudibrânquio Tambja eliora, da costa do Brasil. Quím. Nova, 2005, 28, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, M.; Irace, C.; Costagliola, F.; Castelluccio, F.; Villani, G.; Calado, G.; Gavagnin, M. A new cytotoxic tambjamine alkaloid from the Azorean nudibranch Tambja ceutae. Bioorganic. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2668–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuzzo, G.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Kiss, R.; Mathieu, V.; Leclercqz, H.; Manzo, E.; Cimino, G. Chemistry of the nudibranch Aldisa andersoni: structure and biological activity of phorbazole metabolites. Mar. Drugs. 2012, 10, 1799–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.Y.; Suresh Kumar, G. Natural isoquinoline alkaloids: binding aspects to functional proteins, serum albumins, hemoglobin, and lysozyme. Biophysical Reviews, 2015, 7, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, A.; Cavaliere, P.; Wahidulla, S.; Naik, C.G.; Cimino, G.A. New antitumor isoquinoline alkaloid from the marine nudibranch Jorunna funebris. Tetrahedron, 2000, 56, 7305–7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisch, K.; Hertzer, C.; Böhringer, N.; Wuisan, Z.; Schillo, D.; Bara, R.; Schäberle, T. The potential of Indonesian heterobranchs found around Bunaken Island for the production of bioactive compounds. Mar. Drugs. 2017, 15, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-Y.; Chen, W.-T.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.-W. Bioactive isoquinolinequinone alkaloids from the South China Sea nudibranch Jorunna funebris and its sponge-prey Xestospongia sp. Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Li, S.-W.; de Voogd, N.J.; Wang, H.; Yao, L.-G.; Guo, Y.-W.; Li, X.-W. Marine alkaloids as the chemical marker for the prey–predator relationship of the sponge Xestospongia sp. and the nudibranch Jorunna funebris. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, C. Terpenoids in Marine Heterobranch Molluscs. Marine Drugs, 2020, 18, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, H.; König, G.M. Terpenoids from Marine Organisms: Unique Structures and their Pharmacological Potential. Phytochemistry Reviews, 2006, 5, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianora, A.; Boersma, M.; Casotti, R.; Fontana, A.; Harder, J.; Hoffmann, F.; Pavia, H.; Potin, P.; Poulet, S.A.; Toth, G. The Htodum synthesis essay: New trends in marine chemical ecology. Estuar. Coast. 2006, 29, 531–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-L.; Wang, B.-W.; Sun, Z.-C.; Yang, J.-S.; Xu, X.-D.; Ma, G.-X. Natural Nitrogenous Sesquiterpenoids and Their Bioactivity: A Review. Molecules, 2020, 25, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, W.-T.; Li, S.-W.; Ye, J.-Y.; Huan, X.-J.; Gavagnin, M.; Guo, Y.-W. Cytotoxic nitrogenous terpenoids from two South China sea nudibranchs Phyllidiella pustulosa, Phyllidia coelestis, and their sponge-prey Acanthella cavernosa. Mar. Drugs. 2019, 17, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, A.M.; Dao, K.; Vrubliauskas, D.; Könst, Z.A.; Pierens, G.K.; Mándi, A.; Vanderwal, C.D. Catalyst-controlled stereoselective synthesis secures the structure of the antimalarial isocyanoterpene pustulosaisonitrile-1. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 13313–13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaisamut, S.; Prabpai, S.; Tancharoen, C.; Yuenyongsawad, S.; Hannongbua, S.; Kongsaeree, P.; Plubrukarn, A. Bridged tricyclic sesquiterpenes from the tubercle nudibranch Phyllidia coelestis Bergh. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 2158–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyakhova, E.G.; Kolesnikova, S.A.; Kalinovskii, A.I.; Stonik, V.A. Secondary metabolites of the Vietnamese nudibranch mollusk Phyllidiella pustulosa. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2010, 46, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affeld, S.; Kehraus, S.; Wägele, H.; König, G.M. Dietary derived sesquiterpenes from Phyllodesmium lizardensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.-C.; Gavagnin, M.; Mollo, E.; Guo, Y.-W. A new rare asteriscane sesquiterpene and other related derivatives from the Hainan aeolid nudibranch Phyllodesmium magnum. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2011, 39, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, A.; Kehraus, S.; Bleidissel, S.; Preisfeld, G.; Schillo, D.; Piel, J.; König, G.M. Defense in the Aeolidoidean Genus Phyllodesmium (Gastropoda). J. Chem. Ecol. 2014, 40, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheverov, I.; Shelukhina, I.; Kudryavtsev, D.; Makarieva, T.; Spirova, E.; Guzii, A.; Tsetlin, V. 6-Bromohypaphorine from marine nudibranch mollusk Hermissenda crassicornis is an agonist of human α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Mar. Drugs. 2015, 13, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raverty, W.; Thomson, R.; King, T. Metabolites from the sponge Pachymatisma johnstoni; L-6-bromohypaphorine, a new amino-acid (and its crystal structure). J. Chem. Soc. 1977, 10, 1204–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, A.; Borrelli, F.; Capasso, R. Conicamin, a novel histamine antagonist from the mediterranean tunicate Aplidium conicum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 4481–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, K.; Nishi, J. Two new tryptophan-derived alkaloids from the Okinawan marine sponge Aplysina sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, H.; Gavagnin, M.; Calado, G.; Castelluccio, F.; Mollo, E.; Cimino, G. Pelseneeriol-1 and -2: new furanosesquiterpene alcohols from porostome nudibranch Doriopsilla pelseneeri. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 11032–11037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavagnin, M.; Mollo, E.; Calado, G.; Fahey, S.; Ghiselin, M.; Ortea, J.; Cimino, G. Chemical studies of porostome nudibranchs: comparative and ecological aspects. Chemoecology 2001, 11, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, Y.; Torres-Mendoza, D.; Jones, G.E.; Fernandez, P.L. Marine Diterpenoids as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Agents. Mediators of Inflammation 2015, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.H.; Hossain, M.K.; Nigar, M.; Roy, M.C.; Tanaka, J. New cytotoxic spongian-class rearranged diterpenes from a marine sponge. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2012, 48, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, L.C.; Pierens, G.K.; Garson, M.J. Elucidation of relative and absolute configurations of highly rearranged diterpenoids and evidence for a putative biosynthetic intermediate from the Australian nudibranch Goniobranchus geometricus. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudianta, I.W.; Martiningsih, N.W.; Prasetia, I.N.D.; Nursid, M. Bioactive terpenoid from the balinese nudibranch Hypselodoris infucata. Indones. J. Pharm. 2016, 27, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katavic, P.L.; Jumaryatno, P.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Blanchfield, J.T.; Garson, M.J. Oxygenated terpenoids from the Australian sponges Coscinoderma matthewsi and Dysidea sp. , and the nudibranch Chromodoris albopunctata. Aust. J. Chem. 2012, 65, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suciati, S.; Lambert, L.K.; Garson, M.J. Structures and anatomical distribution of oxygenated diterpenes in the Australian nudibranch Chromodoris reticulata. Aust. J. Chem. 2011, 64, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, E.D.; Morris, S.A.; Miao, S.; Dumdei, E.; Andersen, R.J. Terpenoid metabolites from skin extracts of four Sri Lankan nudibranchs in the genus Chromodoris. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diyabalanage, T.; Iken, K.B.; McClintock, J.B.; Amsler, C.D.; Baker, B.J. Palmadorins A−C, diterpene glycerides from the Antarctic nudibranch Austrodoris kerguelenensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maschek, J.A.; Mevers, E.; Diyabalanage, T.; Chen, L.; Ren, Y.; McClintock, J.B.; Baker, B.J. Palmadorin chemodiversity from the Antarctic nudibranch Austrodoris kerguelenensis and inhibition of Jak2/STAT5-dependent HEL leukemia cells. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 9095–9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutignano, A.; Zhang, W.; Avila, C.; Cimino, G.; Fontana, A. Intrapopulation variability in the terpene metabolism of the Antarctic opisthobranch mollusk Austrodoris kerguelenensis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 27, 5383–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavagnin, M.; De Napoli, A.; Castelluccio, F.; Cimino, G. Austrodorin-A and -B: first tricyclic diterpenoid 2′-monoglyceryl esters from an Antarctic nudibranch. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 8471–8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, C.; Paul, V.J. Chemical ecology of the nudibranch Glossodoris pallida: is the location of diet-derived metabolites important for defense? Marine Ecology Progress Series 1997, 150, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavagnin, M.; Mollo, E.; Docimo, T.; Guo, Y.-W.; Cimino, G. Scalarane metabolites of the nudibranch Glossodoris rufomarginata and its dietary sponge from the South China sea. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 2104–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, A.; Mollo, E.; Ortea, J.; Gavagnin, M.; Cimino, G. Scalarane and homoscalarane compounds from the nudibranchs Glossodoris sedna and Glossodoris dalli: Chemical and Biological Properties. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, A.; Cavaliere, P.; Ungur, N.; D’Souza, L.; Parameswaram, P.S.; Cimino, G. New scalaranes from the nudibranch Glossodoris atromarginata and its sponge prey. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, A.; Belluga, M.D.L.; Scognamiglio, G.; Cimino, G. Morphological and chemical camouflage of the mediterranean nudibranch Dioscodoris indecora on the sponger Ircinia variabilis and Ircinia fasciculata. J. Molluscan Stud. 1997, 63, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubanek, J.; Graziani, E.I.; Andersen, R.J. Investigations of terpenoid biosynthesis by the dorid nudibranch Cadlina luteomarginata. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 7239–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzo, E.; Carbone, M.; Mollo, E.; Irace, C.; Di Pascale, A.; Li, Y.; Gavagnin, M. Structure and synthesis of a unique isonitrile lipid isolated from the marine mollusk Actinocyclus papillatus. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 1897–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Herrero-Barrencua, A.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Castro, J.J.; Cervera, J.L.; Gavagnin, M. Occurrence of symmetrical diacylguanidines triophamine and limaciamine in three polyceridae species from Canary Islands: are they chemical markers of these nudibranchs? Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2019, 83, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Džunková, M.; La Clair, J.J.; Tyml, T.; Doud, D.; Schulz, F.; Piquer-Esteban, S.; Porcel Sanchis, D.; Osborn, A.; Robinson, D.; Louie, K.B.; Bowen, B.P.; Bowers, R.M.; Lee, J.; Arnau, V.; Díaz-Villanueva, W.; Stepanauskas, R.; Gosliner, T.; Date, S.V.; Northen, T.R.; Cheng, J.F.; Burkart, M.D.; Woyke, T. Synthase-selected sorting approach identifies a beta-lactone synthase in a nudibranch symbiotic bacterium. Microbiome 2023, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzati, F.; Warsito, M.F.; Bayu, A.; Prasetyoputri, A.; Atikana, A.; Sukmarini, L.; Putra, M.Y. Chemical Diversity and Biological Activity of Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Indonesian Marine Invertebrates. Molecules 2021, 26, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudianta, I.W.; White, A.M.; Suciati Katavic, P.L.; Krishnaraj, R.R.; Winters, A.E.; Garson, M.J. Chemoecological studies on marine natural products: terpene chemistry from marine mollusks. Pure and Applied Chemistry 2014, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiana, R.; Ayuningrum, D.; Yohanna, M.; Dirgantara, D.; Hanafi, M.; Radjasa, O.K.; Sabdono, A. Characterization and identification of antibacterial compound from Pseudoalteromonas piscicida associated with Chromodoris lochi. AIP Conference Proceedings 2120 2019, 080008, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, C. Natural products of opisthobranch molluscs: a biological review. Oceanography and Marine Biology: an Annual Review, 1995, 33, 487–559. [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama, Y.; Katavic, P.L.; White, A.M.; Pierens, G.K.; Lambert, L.K.; Winters, A.E.; Garson, M.J. New Cytotoxic Norditerpenes from the Australian Nudibranchs Goniobranchus Splendidus and Goniobranchus Daphne. Australian Journal of Chemistry 2016, 69, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okino, T.; Yoshimura, E.; Hirota, H.; Fusetani, N. New antifouling sesquiterpenes from four nudibranchs of the family Phyllidiidae. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 9447–9454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papu, A.; Bogdanov, A.; Bara, R.; Kehraus, S.; König, G.M.; Yonow, N.; Wägele, H. Phyllidiidae (Nudibranchia, Heterobranchia, Gastropoda): an integrative taxonomic approach including chemical analyses. Org. Divers. Evol. 2022, 22, 585–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, K.T.; Walduck, A.; Kelso, M.J.; Fairlie, D.P.; Saul, A.; Parsons, P.G. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 761−768. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.M.; Li, S.W.; Su, M.Z.; Yao, L.G.; Appendino, G.; Guo, Y.W. Structurally Diverse Diterpenoids from the Sanya Bay Nudibranch Hexabranchus sanguineus and Its Sponge-Prey Chelonaplysilla sp. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202203858, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollo, E.; Gavagnin, M.; Carbone, M.; Castelluccio, F.; Pozone, F.; Roussis, V.; Cimino, G. Factors promoting marine invasions: A chemoecological approach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2008, 105, 4582–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
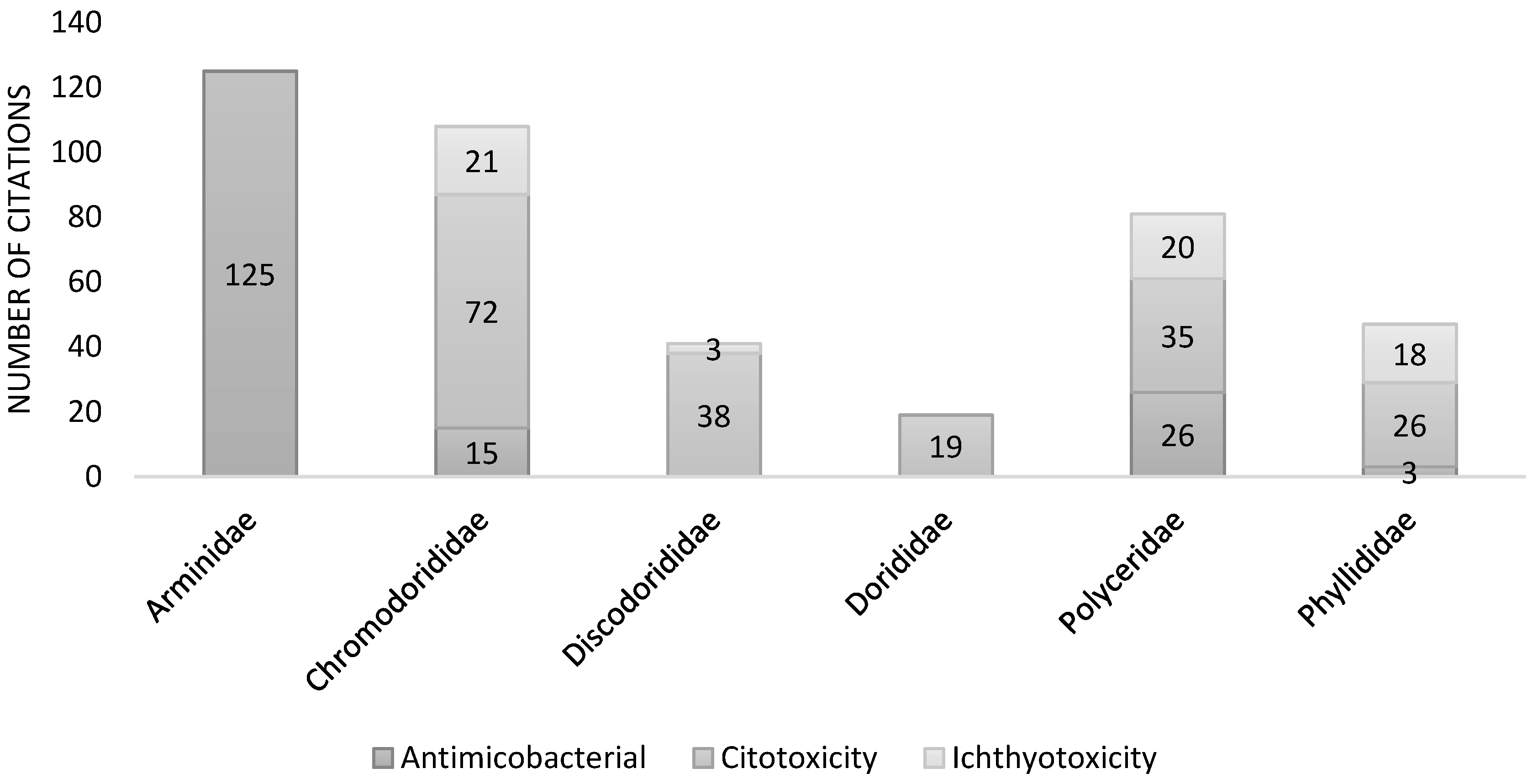
| Journal | Number of journal |
Chemical characterization* |
Biological Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biochemical Systematics and Ecology | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Journal Of Natural Products | 22 | 22 | 8 |
| Journal Of Molluscan Studies | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Marine Drugs | 5 | 5 | 3 |
| Biological Sciences | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Fitoterapia | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Journal of Chemical Ecology | 7 | 7 | 2 |
| Journal of Organic Chemistry | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| Chemistry & Biodiversity | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| Plos One | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Indonesian Journal of Pharmacy | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Future Medicinal Chemistry | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Natural Product Communications | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Bangladesh Journal of Pharmacology | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Tetrahedron | 11 | 11 | 4 |
| Chemistry of Natural Compounds | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Quimica Nova | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| Australian Journal of Chemistry | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| European Journal of Organic Chemistry | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Organic Letters | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Biological Bulletin | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Chemico-Biological Interactions | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Arkivoc | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Chemoecology | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| Tetrahedron Letters | 8 | 8 | 1 |
| Marine Biology | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Molecules | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Journal Of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Italian Journal of Zoology | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Journal of Molluscan Studies | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Canadian Journal of Chemistry-Revue | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Experientia | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Revista Virtual De Quimica | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Biomolecules | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Integrative and Comparative Biology | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Peerj | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Journal of Asian Natural Products Research | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Chinese Journal of Chemistry | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Organisms Diversity & Evolution | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Diversity-Basel | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Chemistry-A European Journal | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Marine Genomics | 1 | 0 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




