Submitted:
24 October 2023
Posted:
25 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. The Translocator protein (TSPO)
1.1. Introduction
1.2. First generation of TSPO radiotracer
[11. C](R)PK11195
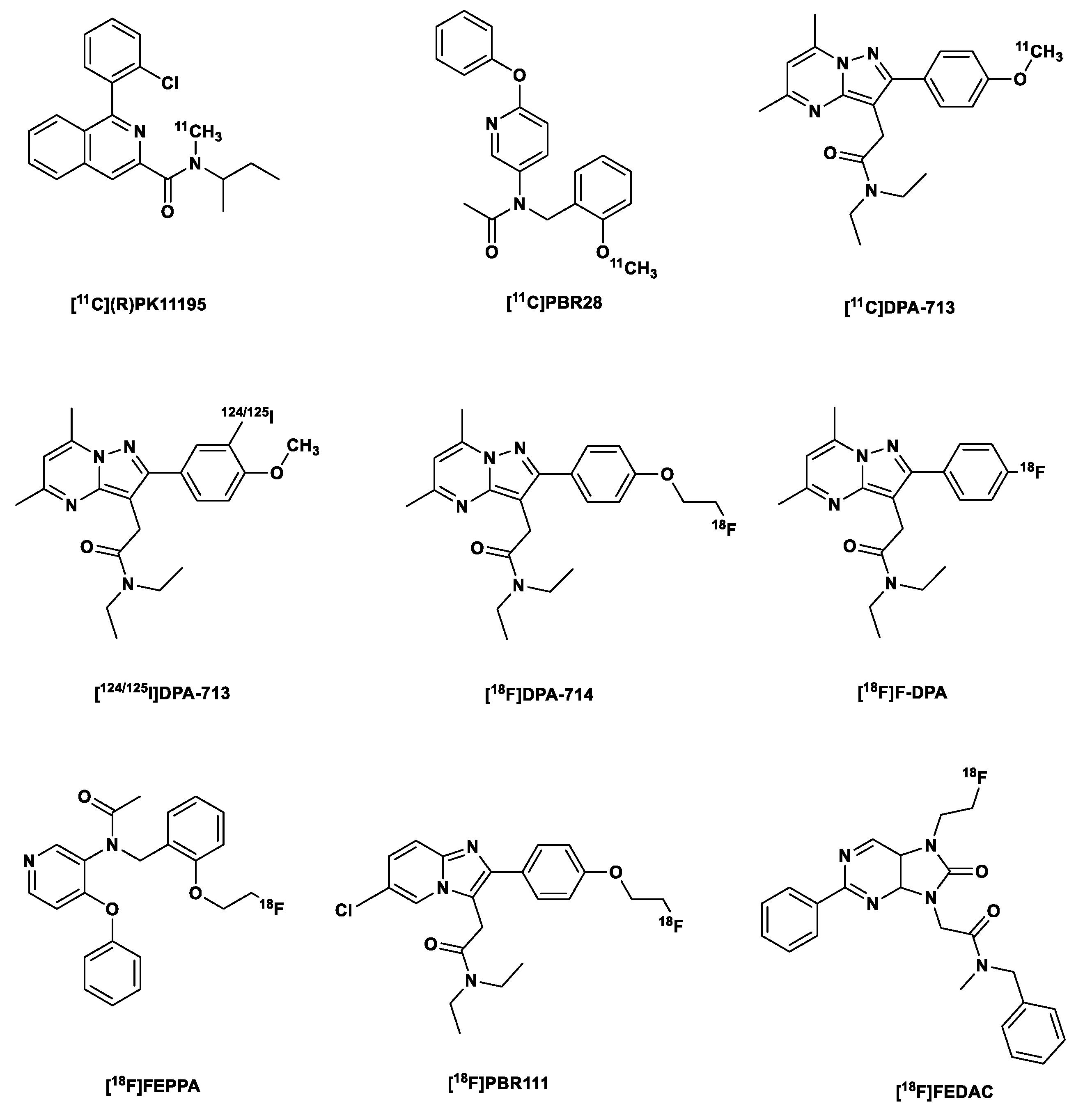
1.3. Second generation TSPO tracers
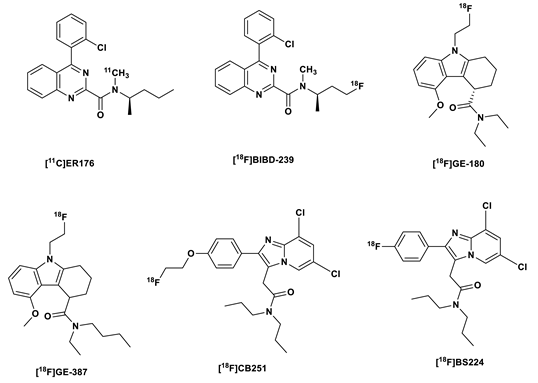
1.4. Third generation TSPO tracers
2. The Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) enzyme
2.1. Introduction
2.1. PET COX-2 radiotracers
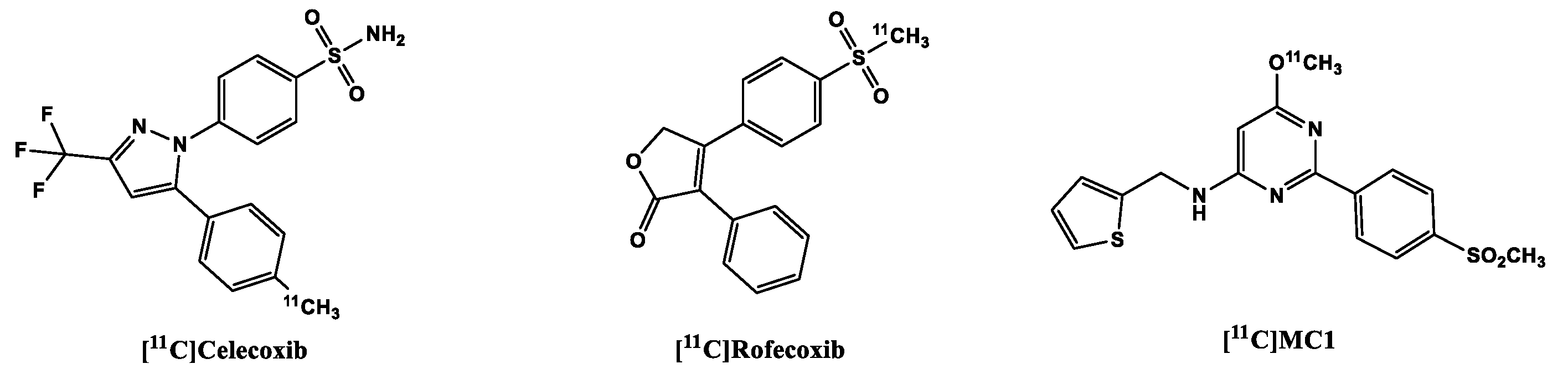
2.1.1. [11C]Carbon labeled COX-2 tracers
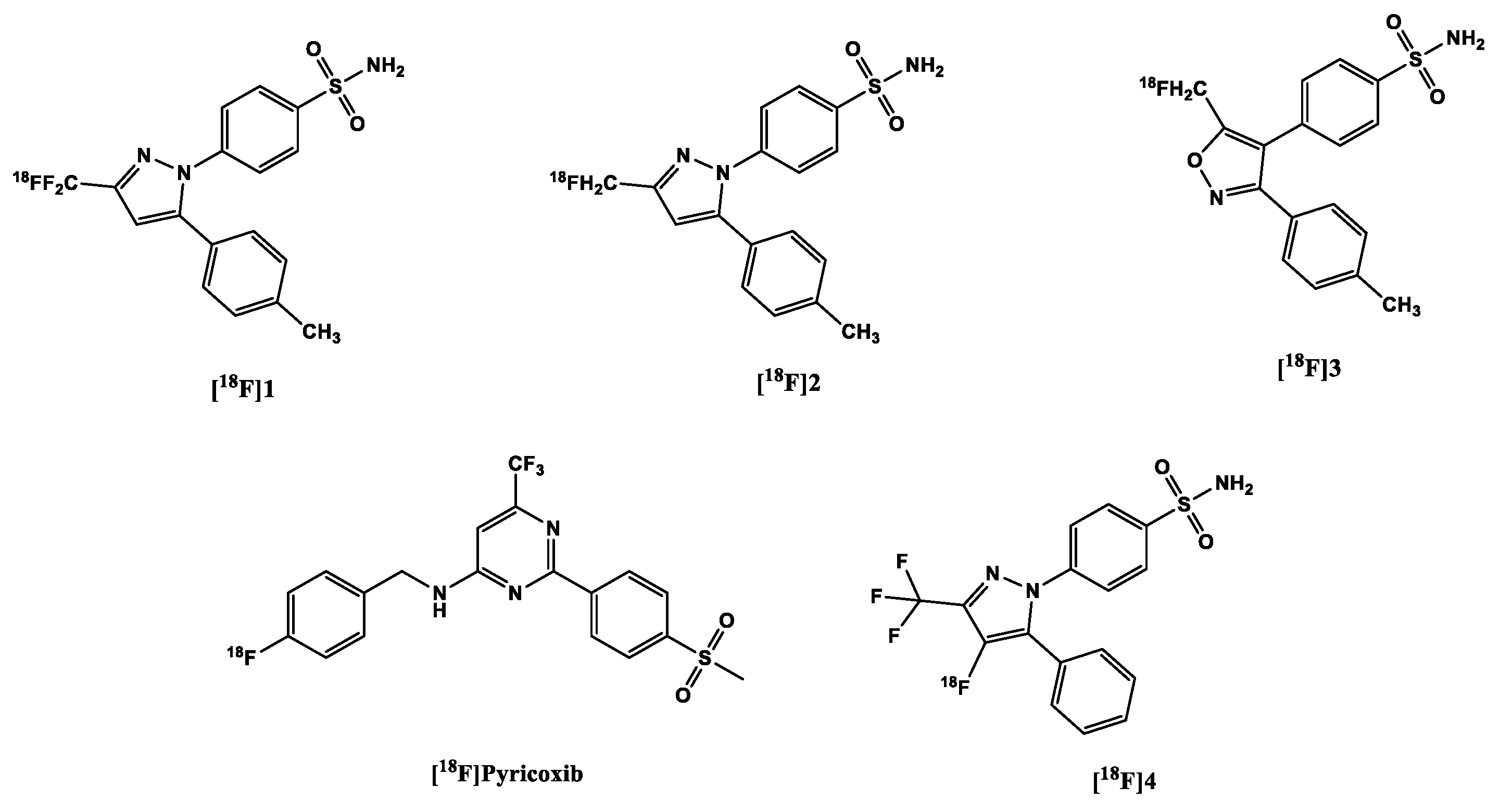
2.1.2. [18F]Fluorine-labeled COX-2 tracers
- i)
- a PET study comparing the uptake of the tracer in both inflamed (carrageenan-treated rat paws) and non-inflamed tissues (non-treated). It showed 1.53-fold increase in the former over the non-treated paws [98];
- ii)
- pre-dosing with celecoxib (10mg/kg), which significantly decreased tracer uptake in the inflamed rat paw (there was just only 1.7x times decrease in uptake [98];
- iii)
- experiments in COX-2 null mice further confirmed the specificity of the tracer; there was no increased tracer uptake in the inflamed carrageenan-treated paws of these mice compared to controls, i.e. non-inflamed carrageenan-treated paws of the same COX-2 knock-out mice with a ratio of 1.08. This contrasts significantly with the uptake in the inflamed paws of wild-type mice versus the control paws (1.48) [98];
- iv)
- results obtained using nude mice with both COX-2 positive 1483 HNSCC tumor and COX-2 negative HCT116 tumor suggest that the difference in the uptake in both tumors correlates to the difference in their expression of COX-2 (3-fold higher in the COX-2 positive tumor). The blocking of COX-2 active site in the former prevents the binding of the tracer (with tumor to muscle uptake ratio 1.01-fold), in comparison to control (2.94-fold) [98].
2.2. SPECT COX-2 radiotracers
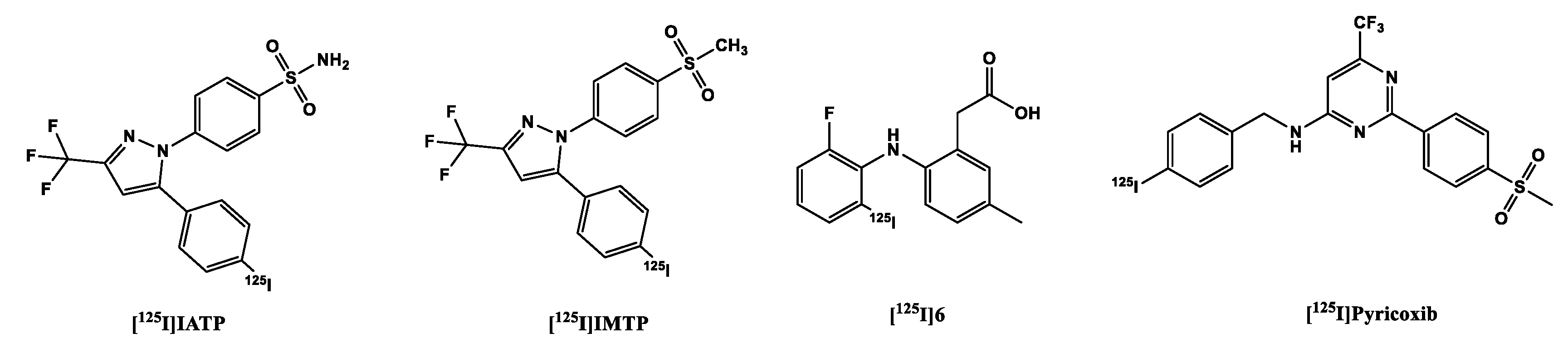
2.2.1. [123,125. I]Iodine-labeled COX-2 tracers
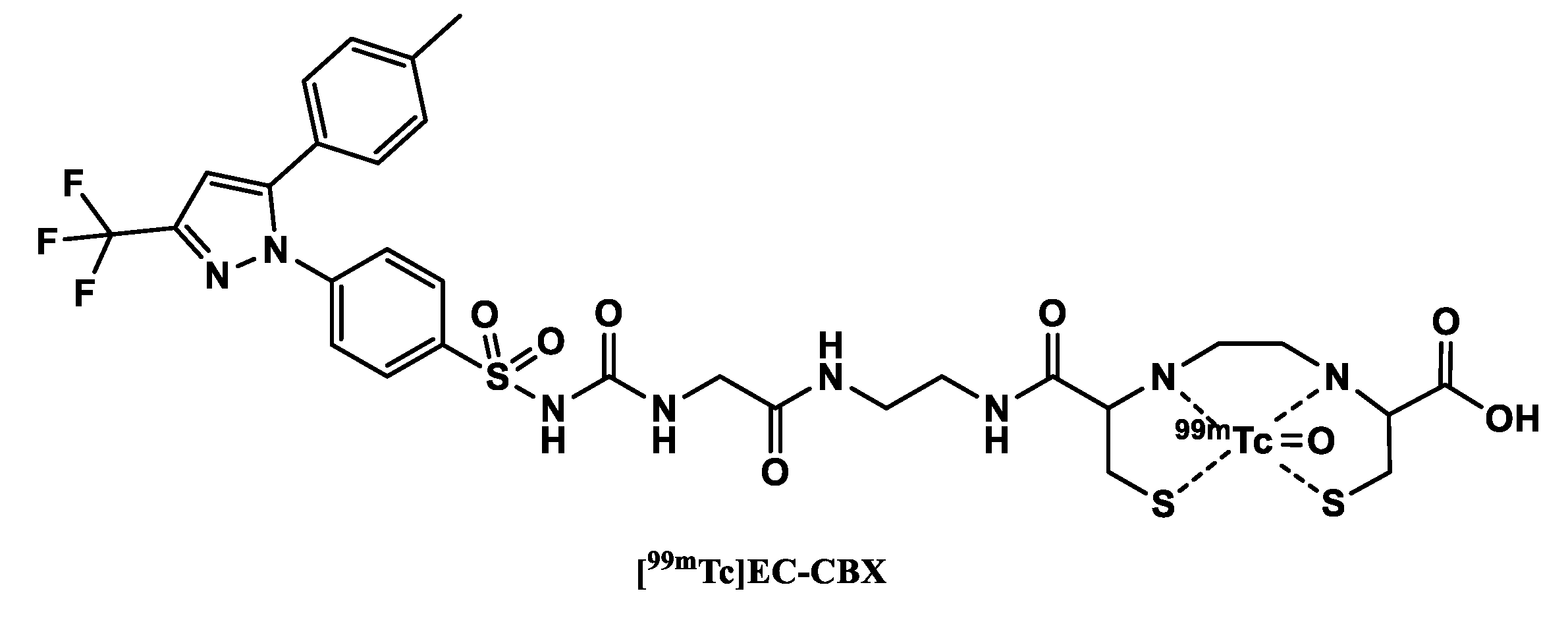
2.3.2. 99. mTc-labeled COX-2 tracers
3. PET and SPECT imaging of TSPO and COX-2 in diseases
3.1. Introduction
3.2. Pulmonary inflammation
3.3. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
3.4. Cardiac pathology
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papadopoulos, V.; Baraldi, M.; Guilarte, T.R.; Knudsen, T.B.; Lacapère, J.-J.; Lindemann, P.; Norenberg, M.D.; Nutt, D.; Weizman, A.; Zhang, M.-R.; et al. Translocator protein (18kDa): new nomenclature for the peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor based on its structure and molecular function. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.; Fisher, E.; McMurray, L.; Milicevic Sephton, S.; Hird, M.; Kuzhuppilly-Ramakrishnan, N.; Williamson, D.J.; Zhou, X.; Werry, E.; Kassiou, M.; et al. Radiosynthesis of (R,S)-18 FGE387: A Potential PET Radiotracer for Imaging Translocator Protein 18 kDa (TSPO) with Low Binding Sensitivity to the Human Gene Polymorphism rs6971. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damont, A.; Hinnen, F.; Kuhnast, B.; Schöllhorn-Peyronneau, M.-A.; James, M.; Luus, C.; Tavitian, B.; Kassiou, M.; Dollé, F. Radiosynthesis of [ 18 F]DPA-714, a selective radioligand for imaging the translocator protein (18 kDa) with PET. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2008, 51, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largeau, B.; Dupont, A.-C.; Guilloteau, D.; Santiago-Ribeiro, M.-J.; Arlicot, N. TSPO PET Imaging: From Microglial Activation to Peripheral Sterile Inflammatory Diseases? Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2017, 2017, 6592139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanotti-Fregonara, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jenko, K.J.; Gladding, R.L.; Zoghbi, S.S.; Fujita, M.; Sbardella, G.; Castellano, S.; Taliani, S.; Martini, C.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of translocator 18 kDa protein (TSPO) positron emission tomography (PET) radioligands with low binding sensitivity to human single nucleotide polymorphism rs6971. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, A.; Valkimadi, P.-E.; Pagano, G.; Cousins, O.; Dervenoulas, G.; Politis, M. Applications of amyloid, tau, and neuroinflammation PET imaging to Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 5424–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werry, E.L.; Bright, F.M.; Piguet, O.; Ittner, L.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Hodges, J.R.; Kiernan, M.C.; Loy, C.T.; Kril, J.J.; Kassiou, M. Recent Developments in TSPO PET Imaging as A Biomarker of Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, B.; Vugts, D.J.; Windhorst, A.D.; Mach, R.H. PET Imaging of Microglial Activation-Beyond Targeting TSPO. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreisl, W.C.; Henter, I.D.; Innis, R.B. Imaging Translocator Protein as a Biomarker of Neuroinflammation in Dementia. Adv. Pharmacol. 2018, 82, 163–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhard, A. TSPO imaging in parkinsonian disorders. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2016, 4, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloli, S.; Morari, M.; Murtaj, V.; Valtorta, S.; Moresco, R.M.; Gilardi, M.C. Translation Imaging in Parkinson’s Disease: Focus on Neuroinflammation. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doorduin, J.; Klein, H.C.; Dierckx, R.A.; James, M.; Kassiou, M.; Vries, E.F.J. de. 11C-DPA-713 and 18F-DPA-714 as new PET tracers for TSPO: a comparison with 11C-(R)-PK11195 in a rat model of herpes encephalitis. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2009, 11, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, M.L.; Fulton, R.R.; Henderson, D.J.; Eberl, S.; Meikle, S.R.; Thomson, S.; Allan, R.D.; Dolle, F.; Fulham, M.J.; Kassiou, M. Synthesis and in vivo evaluation of a novel peripheral benzodiazepine receptor PET radioligand. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 6188–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Ikawa, M.; Gunn, R.N.; Rabiner, E.A.; Owen, D.R.; Zoghbi, S.S.; Haskali, M.B.; Telu, S.; Pike, V.W.; et al. Comparison of four 11C-labeled PET ligands to quantify translocator protein 18 kDa (TSPO) in human brain: (R)-PK11195, PBR28, DPA-713, and ER176-based on recent publications that measured specific-to-non-displaceable ratios. EJNMMI Res. 2017, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, D.R.; Yeo, A.J.; Gunn, R.N.; Song, K.; Wadsworth, G.; Lewis, A.; Rhodes, C.; Pulford, D.J.; Bennacef, I.; Parker, C.A.; et al. An 18-kDa translocator protein (TSPO) polymorphism explains differences in binding affinity of the PET radioligand PBR28. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilarte, T.R.; Rodichkin, A.N.; McGlothan, J.L.; La Acanda De Rocha, A.M.; Azzam, D.J. Imaging neuroinflammation with TSPO: A new perspective on the cellular sources and subcellular localization. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 234, 108048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notter, T.; Schalbetter, S.M.; Clifton, N.E.; Mattei, D.; Richetto, J.; Thomas, K.; Meyer, U.; Hall, J. Neuronal activity increases translocator protein (TSPO) levels. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 2025–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camsonne, R.; Crouzel, C.; Comar, D.; Mazière, M.; Prenant, C.; Sastre, J.; Moulin, M.; Syrota, A. Synthesis of N-(11C) methyl, N-(methyl-1 propyl), (chloro-2 phenyl)-1 isoquinoleine carboxamide-3 (PK 11195): A new ligand for peripheral benzodiazepine receptors. J. Label Compd. Radiopharm. 1984, 21, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yao, J.-Q.; Fang, X.-X.; Dai, W.; Wang, Y.-H.; Zhang, L.-M.; Li, Y.-F. Involvement of regulation of the excitation:inhibition functional balance in the mPFC in the antidepressant-anxiolytic effect of YL-IPA08, a novel TSPO ligand. Metab. Brain Dis. 2022, 37, 2305–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jučaite, A.; Cselényi, Z.; Arvidsson, A.; Ahlberg, G.; Julin, P.; Varnäs, K.; Stenkrona, P.; Andersson, J.; Halldin, C.; Farde, L. Kinetic analysis and test-retest variability of the radioligand 11C(R)-PK11195 binding to TSPO in the human brain - a PET study in control subjects. EJNMMI Res. 2012, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreisl, W.C.; Fujita, M.; Fujimura, Y.; Kimura, N.; Jenko, K.J.; Kannan, P.; Hong, J.; Morse, C.L.; Zoghbi, S.S.; Gladding, R.L.; et al. Comparison of (11)C-(R)-PK 11195 and (11)CPBR28, two radioligands for translocator protein (18 kDa) in human and monkey: Implications for positron emission tomographic imaging of this inflammation biomarker. NeuroImage 2010, 49, 2924–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Jiang, T.; Telu, S.; Zoghbi, S.S.; Gunn, R.N.; Rabiner, E.A.; Owen, D.R.; Guo, Q.; Pike, V.W.; Innis, R.B.; et al. 11C-DPA-713 has much greater specific binding to translocator protein 18 kDa (TSPO) in human brain than 11C-(R)-PK11195. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, A.S.C.; Kuhnast, B.; Damont, A.; Roeda, D.; Tavitian, B.; Dollé, F. Current paradigm of the 18-kDa translocator protein (TSPO) as a molecular target for PET imaging in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Insights Into Imaging 2012, 3, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnin, A.; Brooks, D.J.; Kennedy, A.M.; Gunn, R.N.; Myers, R.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Jones, T.; Banati, R.B. In-vivo measurement of activated microglia in dementia. The Lancet, 358(9280), 461-467. Lancet 2001, 358, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcia, P.; Tauber, C.; Vercoullie, J.; Arlicot, N.; Prunier, C.; Praline, J.; Nicolas, G.; Venel, Y.; Hommet, C.; Baulieu, J.-L.; et al. Molecular imaging of microglial activation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PloS One 2012, 7, e52941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhard, A.; Pavese, N.; Hotton, G.; Turkheimer, F.; Es, M.; Hammers, A.; Eggert, K.; Oertel, W.; Banati, R.B.; Brooks, D.J. In vivo imaging of microglial activation with 11C(R)-PK11195 PET in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 21, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulyás, B.; Tóth, M.; Schain, M.; Airaksinen, A.; Vas, A.; Kostulas, K.; Lindström, P.; Hillert, J.; Halldin, C. Evolution of microglial activation in ischaemic core and peri-infarct regions after stroke: a PET study with the TSPO molecular imaging biomarker ((11))Cvinpocetine. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 320, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, Y.; Yoshikawa, E.; Sekine, Y.; Futatsubashi, M.; Kanno, T.; Ogusu, T.; Torizuka, T. Microglial activation and dopamine terminal loss in early Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 57, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavese, N.; Gerhard, A.; Tai, Y.F.; Ho, A.K.; Turkheimer, F.; Barker, R.A.; Brooks, D.J.; Piccini, P. Microglial activation correlates with severity in Huntington disease: a clinical and PET study. Neurology 2006, 66, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politis, M.; Lahiri, N.; Niccolini, F.; Su, P.; Wu, K.; Giannetti, P.; Scahill, R.I.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Tabrizi, S.J.; Piccini, P. Increased central microglial activation associated with peripheral cytokine levels in premanifest Huntington’s disease gene carriers. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 83, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuno, F.; Kosaka, J.; Ota, M.; Higuchi, M.; Ito, H.; Fujimura, Y.; Nozaki, S.; Takahashi, S.; Mizukami, K.; Asada, T.; et al. Increased binding of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor in mild cognitive impairment-dementia converters measured by positron emission tomography with ¹¹CDAA1106. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 203, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannaccone, S.; Cerami, C.; Alessio, M.; Garibotto, V.; Panzacchi, A.; Olivieri, S.; Gelsomino, G.; Moresco, R.M.; Perani, D. In vivo microglia activation in very early dementia with Lewy bodies, comparison with Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2013, 19, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollé, F.; Luus, C.; Reynolds, A.; Kassiou, M. Radiolabelled molecules for imaging the translocator protein (18 kDa) using positron emission tomography. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2899–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.R.J.; Gunn, R.N.; Rabiner, E.A.; Bennacef, I.; Fujita, M.; Kreisl, W.C.; Innis, R.B.; Pike, V.W.; Reynolds, R.; Matthews, P.M.; et al. Mixed-Affinity Binding in Humans with 18-kDa Translocator Protein Ligands. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 52(1), 24-32. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.R.; Howell, O.W.; Tang, S.-P.; Wells, L.A.; Bennacef Idriss; Bergstrom, M.; Gunn, R.N.; Rabiner, E.A.; Wilkins, M.R.; Reynolds, R.; et al. Two Binding Sites for [3H]PBR28 in Human Brain: Implications for TSPO PET Imaging of Neuroinflammation. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1038/jcbfm.2010.63?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%20%200pubmed (accessed on 14 October 2020).
- Chauveau, F.; van Camp, N.; Dollé, F.; Kuhnast, B.; Hinnen, F.; Damont, A.; Boutin, H.; James, M.; Kassiou, M.; Tavitian, B. Comparative evaluation of the translocator protein radioligands 11C-DPA-713, 18F-DPA-714, and 11C-PK11195 in a rat model of acute neuroinflammation. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, T.; Yokokura, M.; Yoshikawa, E.; Futatsubashi, M.; Kono, S.; Konishi, T.; Miyajima, H.; Hashizume, T.; Ouchi, Y. Extrastriatal spreading of microglial activation in Parkinson’s disease: a positron emission tomography study. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2016, 30, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, T.; Krzyczmonik, A.; Forsback, S.; Picón, F.R.L.; Kirjavainen, A.K.; Takkinen, J.; Rajander, J.; Cacheux, F.; Damont, A.; Dollé, F.; et al. Radiosynthesis and Preclinical Evaluation of 18FF-DPA, A Novel Pyrazolo1,5apyrimidine Acetamide TSPO Radioligand, in Healthy Sprague Dawley Rats. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2017, 19, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, R.; Fujinaga, M.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hatori, A.; Kumata, K.; Yang, J.; Vasdev, N.; Du, Y.; et al. A Facile Radiolabeling of 18FFDPA via Spirocyclic Iodonium Ylides: Preliminary PET Imaging Studies in Preclinical Models of Neuroinflammation. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 5222–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yao, S.; Tang, R.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, L.; Gong, J.; Chen, Q.; Collier, T.L.; Xu, H.; Liang, S.H. A concisely automated synthesis of TSPO radiotracer 18 FFDPA based on spirocyclic iodonium ylide method and validation for human use. J. Label. Comp. Radiopharm. 2020, 63, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, T.; López-Picón, F.R.; Krzyczmonik, A.; Forsback, S.; Takkinen, J.S.; Rajander, J.; Teperi, S.; Dollé, F.; Rinne, J.O.; Haaparanta-Solin, M.; et al. Comparison of high and low molar activity TSPO tracer 18FF-DPA in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2020, 40, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Picón, F.R.; Keller, T.; Bocancea, D.; Helin, J.S.; Krzyczmonik, A.; Helin, S.; Damont, A.; Dollé, F.; Rinne, J.O.; Haaparanta-Solin, M.; et al. Direct Comparison of 18FF-DPA with 18FDPA-714 and 11CPBR28 for Neuroinflammation Imaging in the same Alzheimer’s Disease Model Mice and Healthy Controls. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2022, 24, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikawa, M.; Lohith, T.G.; Shrestha, S.; Telu, S.; Zoghbi, S.S.; Castellano, S.; Taliani, S.; Da Settimo, F.; Fujita, M.; Pike, V.W.; et al. 11C-ER176, a Radioligand for 18-kDa Translocator Protein, Has Adequate Sensitivity to Robustly Image All Three Affinity Genotypes in Human Brain. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Columbia University. Imaging Inflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease With 11C-ER176: NCT03744312, AAAR6570. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03744312 (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- Chen, H.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zheng, W.; Sun, Y.; Yu, Z.; Yang, T.; Zhang, L.; Yan, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. 18FBIBD-239: 18F-Labeled ER176, a Positron Emission Tomography Tracer Specific for the Translocator Protein. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 2351–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadsworth, H.; Jones, P.A.; Chau, W.-F.; Durrant, C.; Fouladi, N.; Passmore, J.; O’Shea, D.; Wynn, D.; Morisson-Iveson, V.; Ewan, A.; et al. ¹⁸FGE-180: a novel fluorine-18 labelled PET tracer for imaging Translocator protein 18 kDa (TSPO). Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, A.; Hanani, R.; Hibbs, D.; Damont, A.; Da Pozzo, E.; Selleri, S.; Dollé, F.; Martini, C.; Kassiou, M. Pyrazolo1,5-apyrimidine acetamides: 4-Phenyl alkyl ether derivatives as potent ligands for the 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO). Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 5799–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaney, A.; Cropper, H.C.; Johnson, E.M.; Lechtenberg, K.J.; Peterson, T.C.; Stevens, M.Y.; Buckwalter, M.S.; James, M.L. 11C-DPA-713 Versus 18F-GE-180: A Preclinical Comparison of Translocator Protein 18 kDa PET Tracers to Visualize Acute and Chronic Neuroinflammation in a Mouse Model of Ischemic Stroke. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeney, C.; Scott, G.; Raffel, J.; Roberts, S.; Coello, C.; Jolly, A.; Searle, G.; Goldstone, A.P.; Brooks, D.J.; Nicholas, R.S.; et al. Kinetic analysis of the translocator protein positron emission tomography ligand 18FGE-180 in the human brain. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 2201–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotti-Fregonara, P.; Pascual, B.; Rizzo, G.; Yu, M.; Pal, N.; Beers, D.; Carter, R.; Appel, S.H.; Atassi, N.; Masdeu, J.C. Head-to-Head Comparison of 11C-PBR28 and 18F-GE180 for Quantification of the Translocator Protein in the Human Brain. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreisl, W.C.; Jenko, K.J.; Hines, C.S.; Lyoo, C.H.; Corona, W.; Morse, C.L.; Zoghbi, S.S.; Hyde, T.; Kleinman, J.E.; Pike, V.W.; et al. A genetic polymorphism for translocator protein 18 kDa affects both in vitro and in vivo radioligand binding in human brain to this putative biomarker of neuroinflammation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanotti-Fregonara, P.; Veronese, M.; Pascual, B.; Rostomily, R.C.; Turkheimer, F.; Masdeu, J.C. The validity of 18F-GE180 as a TSPO imaging agent. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 1205–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, N.L.; Unterrainer, M.; Brendel, M.; Kaiser, L.; Zweckstetter, M.; Cumming, P.; Bartenstein, P. In response to: The validity of 18F-GE180 as a TSPO imaging agent. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 1208–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridharan, S.; Lepelletier, F.-X.; Trigg, W.; Banister, S.; Reekie, T.; Kassiou, M.; Gerhard, A.; Hinz, R.; Boutin, H. Comparative Evaluation of Three TSPO PET Radiotracers in a LPS-Induced Model of Mild Neuroinflammation in Rats. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2017, 19, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, R. López-Picón; Anniina Snellman; Olli Eskola; Semi Helin; Olof Solin; Merja Haaparanta-Solin; Juha O. Rinne. Neuroinflammation Appears Early on PET Imaging and Then Plateaus in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer Disease. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzgreve, A.; Pötter, D.; Brendel, M.; Orth, M.; Weidner, L.; Gold, L.; Kirchner, M.A.; Bartos, L.M.; Unterrainer, L.M.; Unterrainer, M.; et al. Longitudinal 18FGE-180 PET Imaging Facilitates In Vivo Monitoring of TSPO Expression in the GL261 Glioblastoma Mouse Model. Biomedicines 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, N.K.; Hird, M.; Thompson, S.; Williamson, D.J.; Qiao, L.; Owen, D.R.; Brooks, A.F.; Scott, P.J.H.; Bacallado, S.; O’Brien, J.T.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of (S)-18FGE387, a novel 18-kDa translocator protein (TSPO) PET radioligand with low binding sensitivity to human polymorphism rs6971. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 49, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, B.A.; Rowland, D.J.; Sisó, S.; Guignet, M.A.; Harmany, Z.T.; Bandara, S.B.; Saito, N.; Harvey, D.J.; Bruun, D.A.; Garbow, J.R.; et al. TSPO PET Using 18FPBR111 Reveals Persistent Neuroinflammation Following Acute Diisopropylfluorophosphate Intoxication in the Rat. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 170, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottoy, J.; Picker, L. de; Verhaeghe, J.; Deleye, S.; wyffels, L.; Kosten, L.; Sabbe, B.; Coppens, V.; Timmers, M.; van Nueten, L.; et al. 18F-PBR111 PET Imaging in Healthy Controls and Schizophrenia: Test–Retest Reproducibility and Quantification of Neuroinflammation. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Kim, H.; Bae, S.-H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H.; Na, J.; Lee, C.-H.; Lee, M.S.; Ko, G.B.; Kim, K.Y.; et al. 18FCB251 PET/MR imaging probe targeting translocator protein (TSPO) independent of its Polymorphism in a Neuroinflammation Model. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9315–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Denora, N.; Laquintana, V.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Lopedota, A.; Lopalco, A.; Cutrignelli, A.; Franco, M.; Delre, P.; Song, I.H.; et al. Radiosynthesis and characterization of [18F]BS224: a next-generation TSPO PET ligand insensitive to the rs6971 polymorphism. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 49, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Garavito, R.M.; Ferguson-Miller, S. Protein structure. Crystal structures of translocator protein (TSPO) and mutant mimic of a human polymorphism. Science 2015, 347, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaremko, M.; Jaremko, Ł.; Giller, K.; Becker, S.; Zweckstetter, M. Structural Integrity of the A147T Polymorph of Mammalian TSPO. Chembiochem 2015, 16, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaremko, M.; Jaremko, Ł.; Giller, K.; Becker, S.; Zweckstetter, M. Backbone and side-chain resonance assignment of the A147T polymorph of mouse TSPO in complex with a high-affinity radioligand. Biomol. NMR Assign. 2016, 10, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berroterán-Infante, N.; Tadić, M.; Hacker, M.; Wadsak, W.; Mitterhauser, M. Binding Affinity of Some Endogenous and Synthetic TSPO Ligands Regarding the rs6971 Polymorphism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midzak, A.S.; Akula, N.; Rone, M.B.; Papadopoulos, V. Computational modeling and biological validation of novel non-steroidal ligands for the cholesterol recognition/interaction amino acid consensus (CRAC) motif of the mitochondrial translocator protein (TSPO). Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, C.; Stathis, M.; Coughlin, J.M.; Pomper, M.; Slusher, B.S. The Low-Affinity Binding of Second Generation Radiotracers Targeting TSPO is Associated with a Unique Allosteric Binding Site. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ENZYME - 1.14.99.1 Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase. Available online: https://enzyme.expasy.org/EC/1.14.99.1 (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Yamagata, K.; Matsumura, K.; Inoue, W.; Shiraki, T.; Suzuki, K.; Yasuda, S.; Sugiura, H.; Cao, C.; Watanabe, Y.; Kobayashi, S. Coexpression of microsomal-type prostaglandin E synthase with cyclooxygenase-2 in brain endothelial cells of rats during endotoxin-induced fever. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 2669–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummel, C.; Sachot, C.; Poole, S.; Luheshi, G.N. Circulating interleukin-6 induces fever through a STAT3-linked activation of COX-2 in the brain. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2006, 291, R1316–R1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, A.A.; Hunter, J.C.; Phipps, S.M.; Nucci, T.B.; Oliveira, D.L.; Roberts, J.L.; Scheck, A.C.; Simmons, D.L.; Romanovsky, A.A. Cyclooxygenase-1 or -2--which one mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced hypothermia? Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 297, R485–R494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietz, O.; Wuest, M.; Marshall, A.; Glubrecht, D.; Hamann, I.; Wang, M.; Bergman, C.; Way, J.D.; Wuest, F. PET imaging of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in a pre-clinical colorectal cancer model. EJNMMI Res. 2016, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Fur, G.; Perrier, M.L.; Vaucher, N.; Imbault, F.; Flamier, A.; Benavides, J.; Uzan, A.; Renault, C.; Dubroeucq, M.C.; Guérémy, C. Peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites: Effect of PK 11195, 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-n-methyl-n-(1-methylpropyl)-3-isoquinolinecarboxamide. Life Sciences, 32(16), 1839-1847. Life Sci. 1983, 32, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Kim, M.-J.; Eldridge, M.; Lehmann, M.L.; Frankland, M.; Liow, J.-S.; Yu, Z.-X.; Cortes-Salva, M.; Telu, S.; Henter, I.D.; et al. PET measurement of cyclooxygenase-2 using a novel radioligand: upregulation in primate neuroinflammation and first-in-human study. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz Moro, M.; Vargas Sanchez, P.K.; Lupepsa, A.C.; Baller, E.M.; Nobre Franco, G.C. Biología de la ciclooxigenasa en la función renal – Revisión de la literatura. Rev. Colomb. Nefrol. 2017, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, K.; Zhang, Y.; Leahy, K.; Hauser, S.; Masferrer, J.; Perkins, W.; Lee, L.; Isakson, P. Pharmacological and biochemical demonstration of the role of cyclooxygenase 2 in inflammation and pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12013–12017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, K.; Bredehöft, J.; Mooren, F.C.; Rummel, C. Different effects of strength and endurance exercise training on COX-2 and mPGES expression in mouse brain are independent of peripheral inflammation. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2016, 121, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelle Cortes; Prachi Singh; Cheryl Morse; Saurav Shrestha; Kimberly Jenko; Aneta Kowalski; Sami Zoghbi; Masahiro Fujita; Robert Innis; Victor Pike. Synthesis of PET radioligands as potential probes for imaging COX-2 in neuroinflammation. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1092.
- Min-Jeong Kim; Stal Shrestha; Mark Eldridge; Michelle Cortes; Prachi Singh; Jeih-San Liow; Robert Gladding; Sami Zoghbi; Masahiro Fujita; Victor Pike; et al. Novel PET radioligands show that, in rhesus monkeys, COX-1 is constitutively expressed and COX-2 is induced by inflammation. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 203.
- Sejdiu, B.I.; Tieleman, D.P. COX-1 – lipid interactions: arachidonic acid, cholesterol, and phospholipid binding to the membrane binding domain of COX-1, 2020.
- Lebedev, A.; Jiao, J.; Lee, J.; Yang, F.; Allison, N.; Herschman, H.; Sadeghi, S. Radiochemistry on electrodes: Synthesis of an 18F-labelled and in vivo stable COX-2 inhibitor. PloS One 2017, 12, e0176606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Attur, M.G.; Dave, M.; Abramson, S.B.; Amin, A.R. Regulation of Cytosolic COX-2 and Prostaglandin E2 Production by Nitric Oxide in Activated Murine Macrophages. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 4191–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietz, O.; Marshall, A.; Wuest, M.; Wang, M.; Wuest, F. Radiotracers for molecular imaging of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) enzyme. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 4350–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietz, O.; Dzandzi, J.; Bhardwaj, A.; Valliant, J.F.; Wuest, F. Design and synthesis of (125)IPyricoxib: A novel (125)I-labeled cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 1516–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, A.; Boisgard, R.; Thézé, B.; van Camp, N.; Kuhnast, B.; Damont, A.; Kassiou, M.; Dollé, F.; Tavitian, B. Evaluation of the PBR/TSPO radioligand (18)FDPA-714 in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Matsumura, K.; Yamagata, K.; Watanabe, Y. Endothelial cells of the rat brain vasculature express cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA in response to systemic interleukin-1 beta: a possible site of prostaglandin synthesis responsible for fever. Brain Res. 1996, 733, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teismann, P.; Tieu, K.; Choi, D.-K.; Wu, D.-C.; Naini, A.; Hunot, S.; Vila, M.; Jackson-Lewis, V.; Przedborski, S. Cyclooxygenase-2 is instrumental in Parkinson’s disease neurodegeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5473–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Scientist. Up to 140,000 heart attacks linked to Vioxx. Available online: https://www.newscientist.com/article/dn6918-up-to-140000-heart-attacks-linked-to-vioxx/?ignored=irrelevant (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- fda/cder. label.
- Prabhakaran, J.; Underwood, M.D.; Parsey, R.V.; Arango, V.; Majo, V.J.; Simpson, N.R.; van Heertum, R.; Mann, J.J.; Kumar, J.S.D. Synthesis and in vivo evaluation of 18F-4-5-(4-methylphenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-ylbenzenesulfonamide as a PET imaging probe for COX-2 expression. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 1802–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashima-Hirano, M.; Takashima, T.; Katayama, Y.; Wada, Y.; Sugiyama, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Doi, H.; Suzuki, M. Efficient sequential synthesis of PET Probes of the COX-2 inhibitor 11Ccelecoxib and its major metabolite 11CSC-62807 and in vivo PET evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 2997–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, A.; Casini, A.; Heine, A.; Kuhn, D.; Supuran, C.T.; Scozzafava, A.; Klebe, G. Unexpected nanomolar inhibition of carbonic anhydrase by COX-2-selective celecoxib: new pharmacological opportunities due to related binding site recognition. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaki, Y.; Kawamura, K.; Wang, W.-F.; Ishiwata, K.; Yamamoto, F.; Kuwano, T.; Ono, M.; Maeda, M. Radiosynthesis and in vivo evaluation of 11C-labeled 1,5-diarylpyrazole derivatives for mapping cyclooxygenases. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2005, 19, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Wang, M.; Miller, K.D.; Hutchins, G.D.; Zheng, Q.-H. Synthesis of carbon-11 labeled celecoxib derivatives as new candidate PET radioligands for imaging of inflammation. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2009, 67, 2019–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vries, E.F.J. de; Doorduin, J.; Dierckx, R.A.; van Waarde, A. Evaluation of (11)Crofecoxib as PET tracer for cyclooxygenase 2 overexpression in rat models of inflammation. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2008, 35, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Search results for 11C-MC1 - Clinical Trials Registry - ICH GCP. Available online: https://ichgcp.net/clinical-trials-registry/research/list?intr=11C-MC1 (accessed on 8 January 2021).
- Barrio, J.R.; Satyamurthy, N.; Huang, S.C.; Keen, R.E.; Nissenson, C.H.; Hoffman, J.M.; Ackermann, R.F.; Bahn, M.M.; Mazziotta, J.C.; Phelps, M.E. 3-(2’-18Ffluoroethyl)spiperone: in vivo biochemical and kinetic characterization in rodents, nonhuman primates, and humans. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1989, 9, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.J.; Crews, B.C.; Ghebreselasie, K.; Huda, I.; Kingsley, P.J.; Ansari, M.S.; Tantawy, M.N.; Reese, J.; Marnett, L.J. Fluorinated COX-2 inhibitors as agents in PET imaging of inflammation and cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 2011, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemal, D.M. Perspective on fluorocarbon chemistry. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secrieru, A.; O’Neill, P.M.; Cristiano, M.L.S. Revisiting the Structure and Chemistry of 3(5)-Substituted Pyrazoles. Molecules 2019, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Kumadaki, I. Reactions of aromatic trifluoromethyl compounds with nucleophilic reagents. Acc. Chem. Res. 1978, 11, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyokuni, T.; Kumar, J.S.D.; Walsh, J.C.; Shapiro, A.; Talley, J.J.; Phelps, M.E.; Herschman, H.R.; Barrio, J.R.; Satyamurthy, N. Synthesis of 4-(5-18Ffluoromethyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide, a new 18Ffluorinated analogue of valdecoxib, as a potential radiotracer for imaging cyclooxygenase-2 with positron emission tomography. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 4699–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Qi, J.; Ren, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Xiao, H.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Meng, L.; Ma, N.; et al. Developing Isoxazole as a Native Photo-Cross-Linker for Photoaffinity Labeling and Chemoproteomics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed Engl. 2022, 61, e202209947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swarbrick, M.E.; Beswick, P.J.; Gleave, R.J.; Green, R.H.; Bingham, S.; Bountra, C.; Carter, M.C.; Chambers, L.J.; Chessell, I.P.; Clayton, N.M.; et al. Identification of 4-4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyrimidinyl amines and ethers as potent and selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4504–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietz, O.; Sharma, S.K.; Kaur, J.; Way, J.; Marshall, A.; Wuest, M.; Wuest, F. Synthesis of three 18F-labelled cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors based on a pyrimidine scaffold. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 8052–8064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuge, Y.; Katada, Y.; Shimonaka, S.; Temma, T.; Kimura, H.; Kiyono, Y.; Yokota, C.; Minematsu, K.; Seki, K.-i.; Tamaki, N.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of radioiodinated cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors as potential SPECT tracers for cyclooxygenase-2 expression. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2006, 33, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabalka, G.W.; Mereddy, A.R.; Schuller, H.M. Synthesis of an iodine-123-labeled celecoxib analogue: a potential spect agent. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2005, 48, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuller, H.M.; Kabalka, G.; Smith, G.; Mereddy, A.; Akula, M.; Cekanova, M. Detection of overexpressed COX-2 in precancerous lesions of hamster pancreas and lungs by molecular imaging: implications for early diagnosis and prevention. ChemMedChem 2006, 1, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.J.; Crews, B.C.; Ghebreselasie, K.; Tantawy, M.N.; Marnett, L.J. I-Celecoxib Analogues as SPECT Tracers of Cyclooxygenase-2 in Inflammation. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuge, Y.; Obokata, N.; Kimura, H.; Katada, Y.; Temma, T.; Sugimoto, Y.; Aita, K.; Seki, K.-i.; Tamaki, N.; Saji, H. Synthesis and evaluation of a radioiodinated lumiracoxib derivative for the imaging of cyclooxygenase-2 expression. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2009, 36, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.J.; Bryant, J.; Chang, J.Y.; Mendez, R.; Oh, C.-S.; Yu, D.-F.; Ito, M.; Azhdarinia, A.; Kohanim, S.; Edmund Kim, E.; et al. Assessment of cyclooxygense-2 expression with 99mTc-labeled celebrex. Anticancer. Drugs 2004, 15, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méric, J.-B.; Rottey, S.; Olaussen, K.; Soria, J.-C.; Khayat, D.; Rixe, O.; Spano, J.-P. Cyclooxygenase-2 as a target for anticancer drug development. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2006, 59, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, N.; El-Tawoosy, M.; Ayoub, S.; El-Bayoumy, A.S. Optimization of the reaction conditions for the preparation of 99mTc-celecoxib and its biological evaluation. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 2011, 290, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayta D Chadha, Pearl laird, Gowsia Jan and Anna Ara Khan. Radiosynthesis, Biodistribution and Scintigraphic Imaging of 99mtc-Celecoxib in Experimental Rat Model of Colon Carcinogenesis. Available online: https://austinpublishinggroup.com/nuclear-medicine-radiotherapy/fulltext/ajnmr-v2-id1010.php (accessed on 28 February 2021).
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-X.; Zhou, M.; Ma, H.-L.; Qiao, Y.-B.; Li, Q.-S. The Role of Chronic Inflammation in Various Diseases and Anti-inflammatory Therapies Containing Natural Products. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 1576–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, E.; Del Rey, A.; Krüger, K.; Rummel, C. 2nd European Psychoneuroimmunology Network Autumn School: The Skin-Brain Axis and the Breaking of Barriers. Neuroimmunomodulation 2023, 30 Suppl 1, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajinka, O.; Simbilyabo, L.; Tan, Y.; Jabang, J.; Saleem, S.A. Lung-brain axis. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 48, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, C.; Del, R.A.; Bähr, L.; Krüger, K.; Peters, E. 1st European Psychoneuroimmunology Network (EPN) Autumn School: Lung-Brain Axis in Health and Disease. Neuroimmunomodulation 2022, 29 Suppl 2. [CrossRef]
- Hosang, L.; Canals, R.C.; van der Flier, F.J.; Hollensteiner, J.; Daniel, R.; Flügel, A.; Odoardi, F. The lung microbiome regulates brain autoimmunity. Nature 2022, 603, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Chen, W.; Lin, F.; Li, W.; Wang, P.; Liao, G.; Zhang, L. Functional Two-Way Crosstalk Between Brain and Lung: The Brain-Lung Axis. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzghool, O.M.; van Dongen, G.; van de Giessen, E.; Schoonmade, L.; Beaino, W. α-Synuclein Radiotracer Development and In Vivo Imaging: Recent Advancements and New Perspectives. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, J.; Schäffer, J.; Herden, C.; Pflieger, F.J.; Reiche, S.; Körber, S.; Kitagawa, H.; Welter, J.; Michels, S.; Culmsee, C.; et al. n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Modulate LPS-Induced ARDS and the Lung-Brain Axis of Communication in Wild-Type versus Fat-1 Mice Genetically Modified for Leukotriene B4 Receptor 1 or Chemerin Receptor 23 Knockout. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goggi, J.L.; Claser, C.; Hartimath, S.V.; Hor, P.X.; Tan, P.W.; Ramasamy, B.; Abdul Rahman, H.; Cheng, P.; Chang, Z.W.; Nguee, S.Y.T.; et al. PET Imaging of Translocator Protein as a Marker of Malaria-Associated Lung Inflammation. Infect. Immun., 89. [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.L.; Agapov, E.; Wu, K.; Engle, J.T.; Solingapuram Sai, K.K.; Arentson, E.; Spayd, K.J.; Moreland, K.T.; Toth, K.; Byers, D.E.; et al. Selective Imaging of Lung Macrophages Using 11CPBR28-Based Positron Emission Tomography. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2021, 23, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, N.; Mandhair, H.; Smyth, E.; Dakin, S.G.; Kiriakidis, S.; Wells, L.; Owen, D.; Sabokbar, A.; Taylor, P. The macrophage marker translocator protein (TSPO) is down-regulated on pro-inflammatory ’M1’ human macrophages. PloS One 2017, 12, e0185767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatori, A.; Yui, J.; Yamasaki, T.; Xie, L.; Kumata, K.; Fujinaga, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Nengaki, N.; Kawamura, K.; et al. PET imaging of lung inflammation with 18FFEDAC, a radioligand for translocator protein (18 kDa). PloS One 2012, 7, e45065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.A.; Valind, S.O.; Clark, I.C.; Bolden, G.E.; Krausz, T.; Schofield, J.B.; Boobis, A.R.; Haslett, C. Kinetics of lung macrophages monitored in vivo following particulate challenge in rabbits. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2002, 183, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swati Shah; Sanhita Sinharay; Reema Patel; Jeffrey Solomon; Ji Hyun Lee; William Schreiber-Stainthorp; Falguni Basuli; Xiang Zhang; Katie R. Hagen; Rebecca Reeder; et al. PET imaging of TSPO expression in immune cells can assess organ-level pathophysiology in high-consequence viral infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2022, 119. [CrossRef]
- Ordonez, A.A.; Pokkali, S.; DeMarco, V.P.; Klunk, M.; Mease, R.C.; Foss, C.A.; Pomper, M.G.; Jain, S.K. Radioiodinated DPA-713 imaging correlates with bactericidal activity of tuberculosis treatments in mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Bedoya, C.A.; Mota, F.; Ordonez, A.A.; Foss, C.A.; Singh, A.K.; Praharaj, M.; Mahmud, F.J.; Ghayoor, A.; Flavahan, K.; Jesus, P. de; et al. 124I-Iodo-DPA-713 Positron Emission Tomography in a Hamster Model of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2022, 24, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Krogt, J.M.A.; van Binsbergen, W.H.; van der Laken, C.J.; Tas, S.W. Novel positron emission tomography tracers for imaging of rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstappen, M.; van Steenbergen, H.W.; Jong, P.H.P. de; van der Helm-van Mil, A.H.M. Unraveling heterogeneity within ACPA-negative rheumatoid arthritis: the subgroup of patients with a strong clinical and serological response to initiation of DMARD treatment favor disease resolution. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novella-Navarro, M.; Plasencia, C.; Tornero, C.; Navarro-Compán, V.; Cabrera-Alarcón, J.L.; Peiteado-López, D.; Nuño, L.; Monjo-Henry, I.; Franco-Gómez, K.; Villalba, A.; et al. Clinical predictors of multiple failure to biological therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Xie, D.; He, D.; Lu, A.; Liang, C. Toward Overcoming Treatment Failure in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 755844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruijnen, S.T.G.; Verweij, N.J.F.; Gent, Y.Y.J.; Huisman, M.C.; Windhorst, A.D.; Kassiou, M.; van de Ven, P.M.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Voskuyl, A.E.; et al. Imaging disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis by macrophage targeting using second generation translocator protein positron emission tomography tracers. PloS One 2019, 14, e0222844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, N.; Owen, D.R.; Mandhair, H.; Smyth, E.; Carlucci, F.; Saleem, A.; Gunn, R.N.; Rabiner, E.A.; Wells, L.; Dakin, S.G.; et al. Translocator Protein as an Imaging Marker of Macrophage and Stromal Activation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Pannus. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, Y.Y.J.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Kloet, R.W.; van Schaardenburg, D.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Dijkmans, B.A.C.; Lammertsma, A.A.; van der Laken, C.J. Macrophage positron emission tomography imaging as a biomarker for preclinical rheumatoid arthritis: findings of a prospective pilot study. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, Y.Y.; Ahmadi, N.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Hoetjes, N.; van, K.C.; Britsemmer, K.; Turkstra, F.; Boers, M.; Hoekstra, O.S.; van, d.L.C. Detection of subclinical synovitis with macrophage targeting and positron emission tomography in patients with rheumatoid arthritis without clinical arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gent, Y.Y.J.; Ter Wee, M.M.; Voskuyl, A.E.; den Uyl, D.; Ahmadi, N.; Dowling, C.; van Kuijk, C.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Boers, M.; Lems, W.F.; et al. Subclinical synovitis detected by macrophage PET, but not MRI, is related to short-term flare of clinical disease activity in early RA patients: an exploratory study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugliese, F.; Gaemperli, O.; Kinderlerer, A.R.; Lamare, F.; Shalhoub, J.; Davies, A.H.; Rimoldi, O.E.; Mason, J.C.; Camici, P.G. Imaging of vascular inflammation with 11C-PK11195 and positron emission tomography/computed tomography angiography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xiao, J.; Liang, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Yan, B.; et al. Inhibition of mitochondrial translocator protein prevents atrial fibrillation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 632, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellberg, S.; Silvola, J.M.U.; Kiugel, M.; Liljenbäck, H.; Savisto, N.; Li, X.-G.; Thiele, A.; Lehmann, L.; Heinrich, T.; Vollmer, S.; et al. 18-kDa translocator protein ligand 18F-FEMPA: Biodistribution and uptake into atherosclerotic plaques in mice. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2017, 24, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maulik, S.K.; Kumar, S. Oxidative stress and cardiac hypertrophy: a review. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2012, 22, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Liang, D.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.-H. 4’-Chlorodiazepam, a translocator protein (18 kDa) antagonist, improves cardiac functional recovery during postischemia reperfusion in rats. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2010, 235, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, T.; Tian, J.; Tian, Y.; Yun, M.; Li, J.; Dong, W.; Lu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Mi, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Automated synthesis and preliminary evaluation of 18FFDPA for cardiac inflammation imaging in rats after myocardial infarction. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thackeray, J.T.; Bengel, F.M. Molecular Imaging of Myocardial Inflammation With Positron Emission Tomography Post-Ischemia: A Determinant of Subsequent Remodeling or Recovery. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, 1340–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thackeray, J.T.; Hupe, H.C.; Wang, Y.; Bankstahl, J.P.; Berding, G.; Ross, T.L.; Bauersachs, J.; Wollert, K.C.; Bengel, F.M. Myocardial Inflammation Predicts Remodeling and Neuroinflammation After Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, A.; Visanji, N.P.; Momen, M.A.; Feng, R.; Francis, B.M.; Bolz, S.-S.; Hazrati, L.-N. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Underlies Loss of Cortical Dendritic Spine Density in a Mouse Model of Congestive Heart Failure. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




