Submitted:
24 October 2023
Posted:
25 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodological approach
2.1. Background
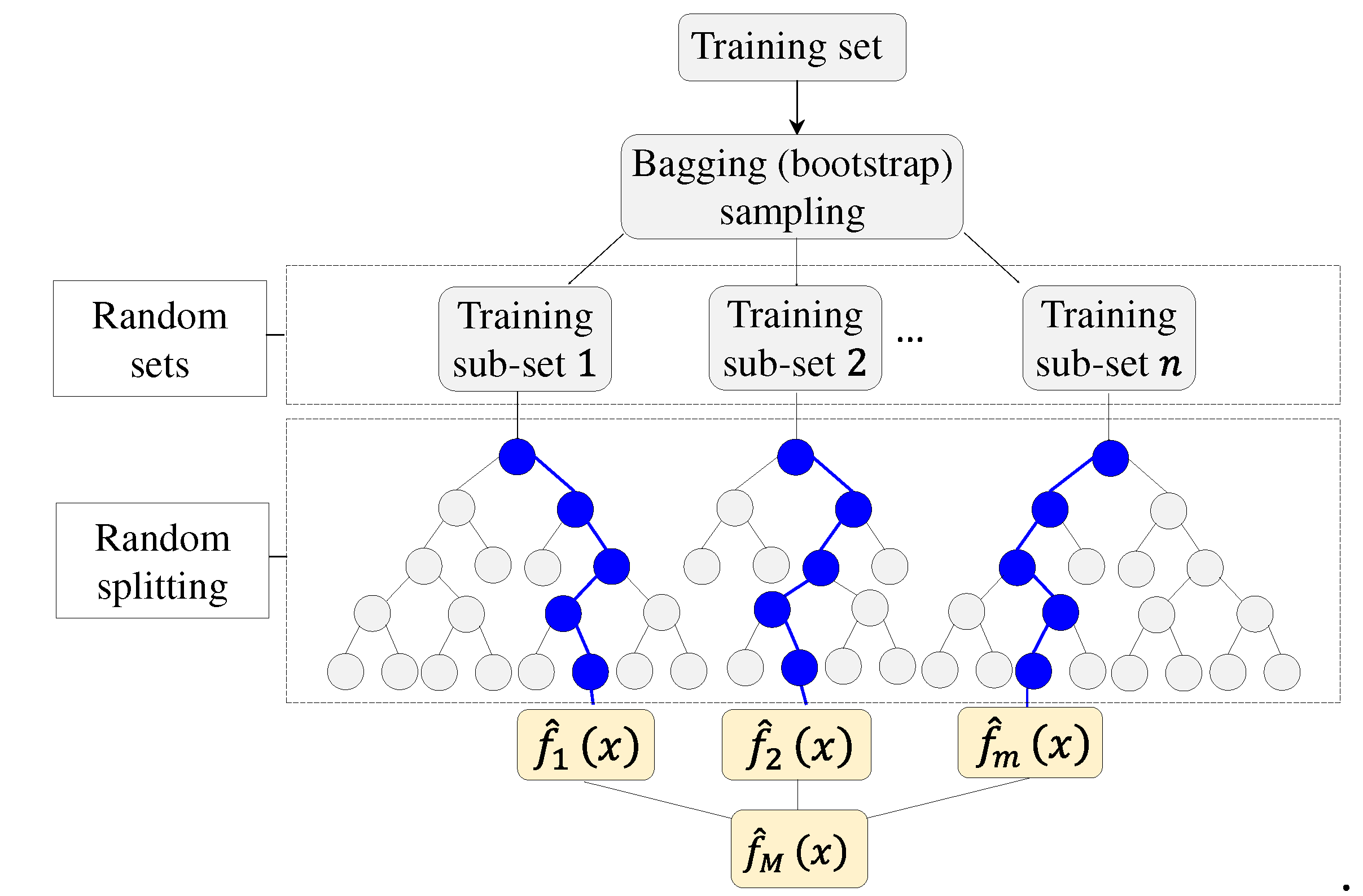
2.2. XG boost algorithm development
2.3. Indicators of prediction performance
3. Data collection, characteristics, and handling
3.1. Data compilation
3.2. Data wrangling and statistical analysis
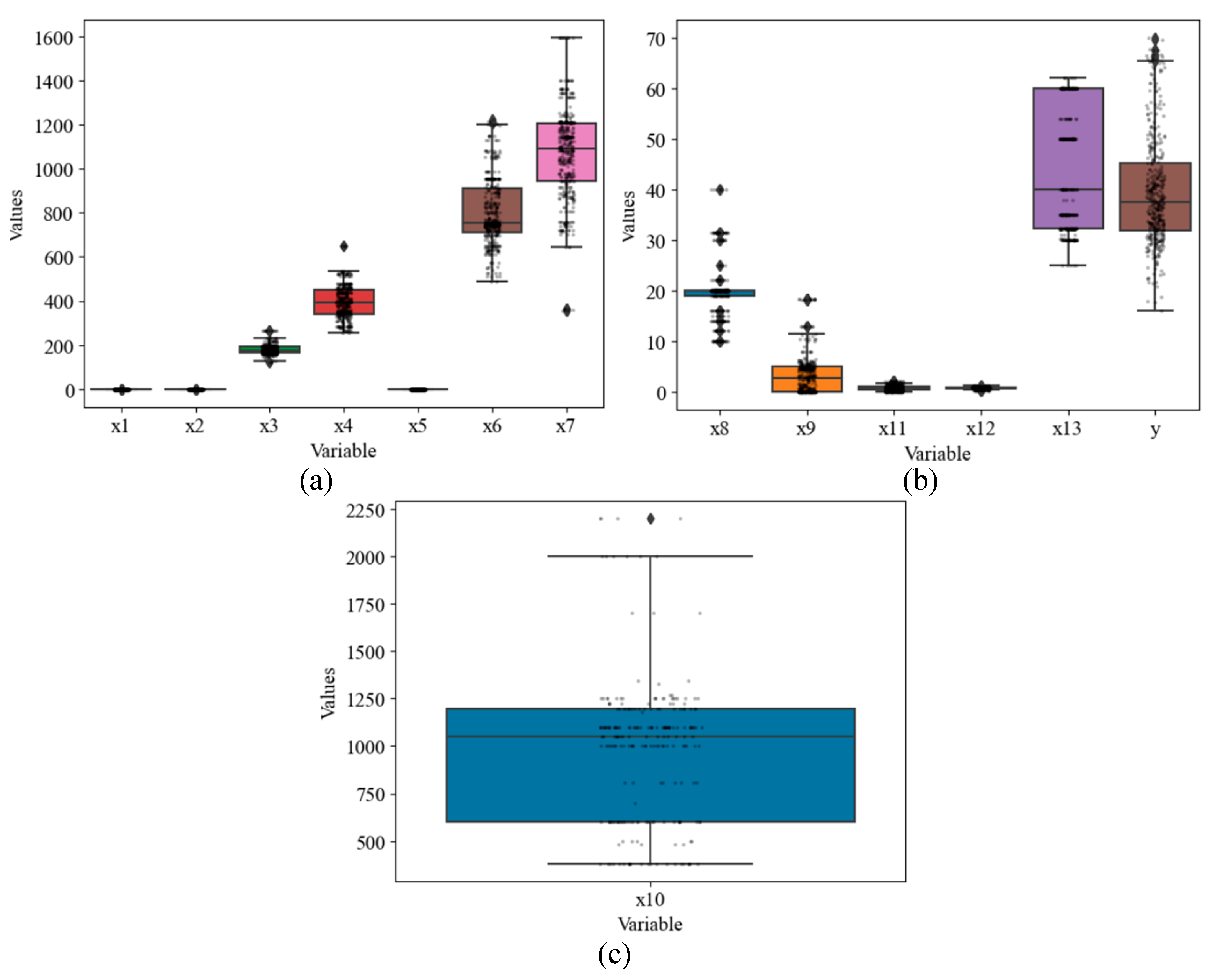
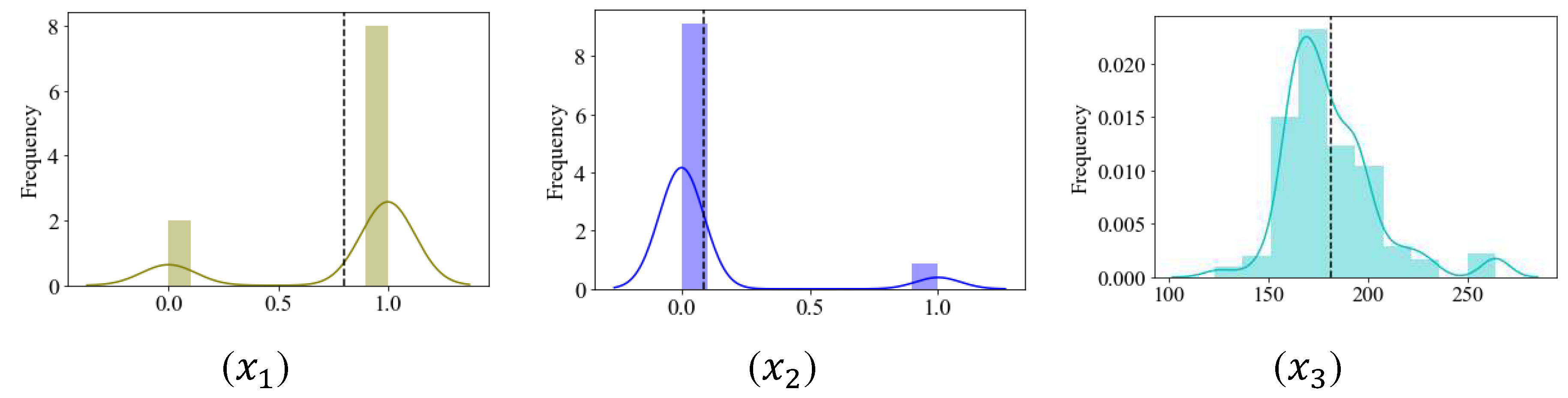
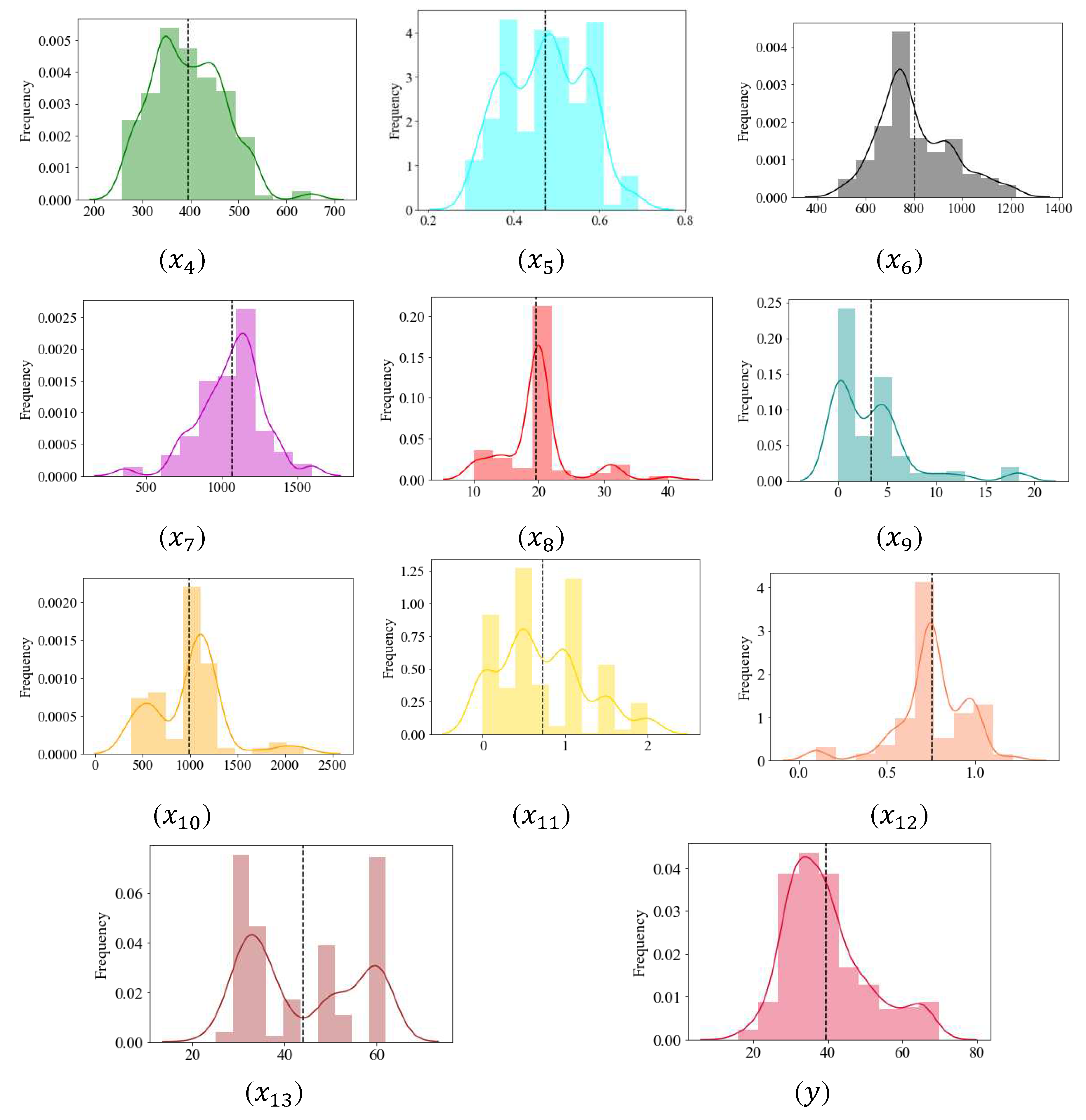
3.2.1. Treatment of outliers
3.2.2. Data descriptive statistics and visualization
4. Results and discussion
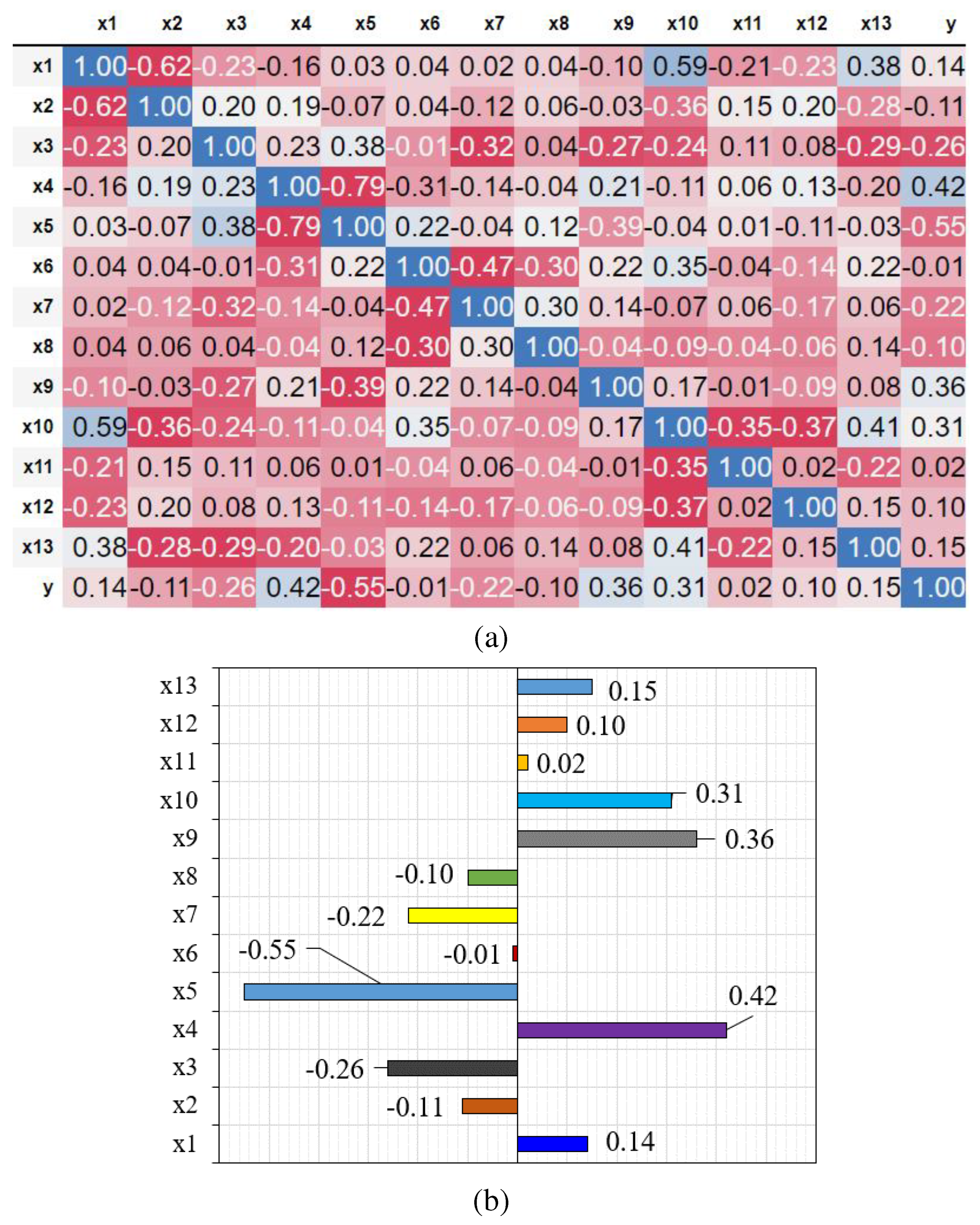
4.1. Features and label relations
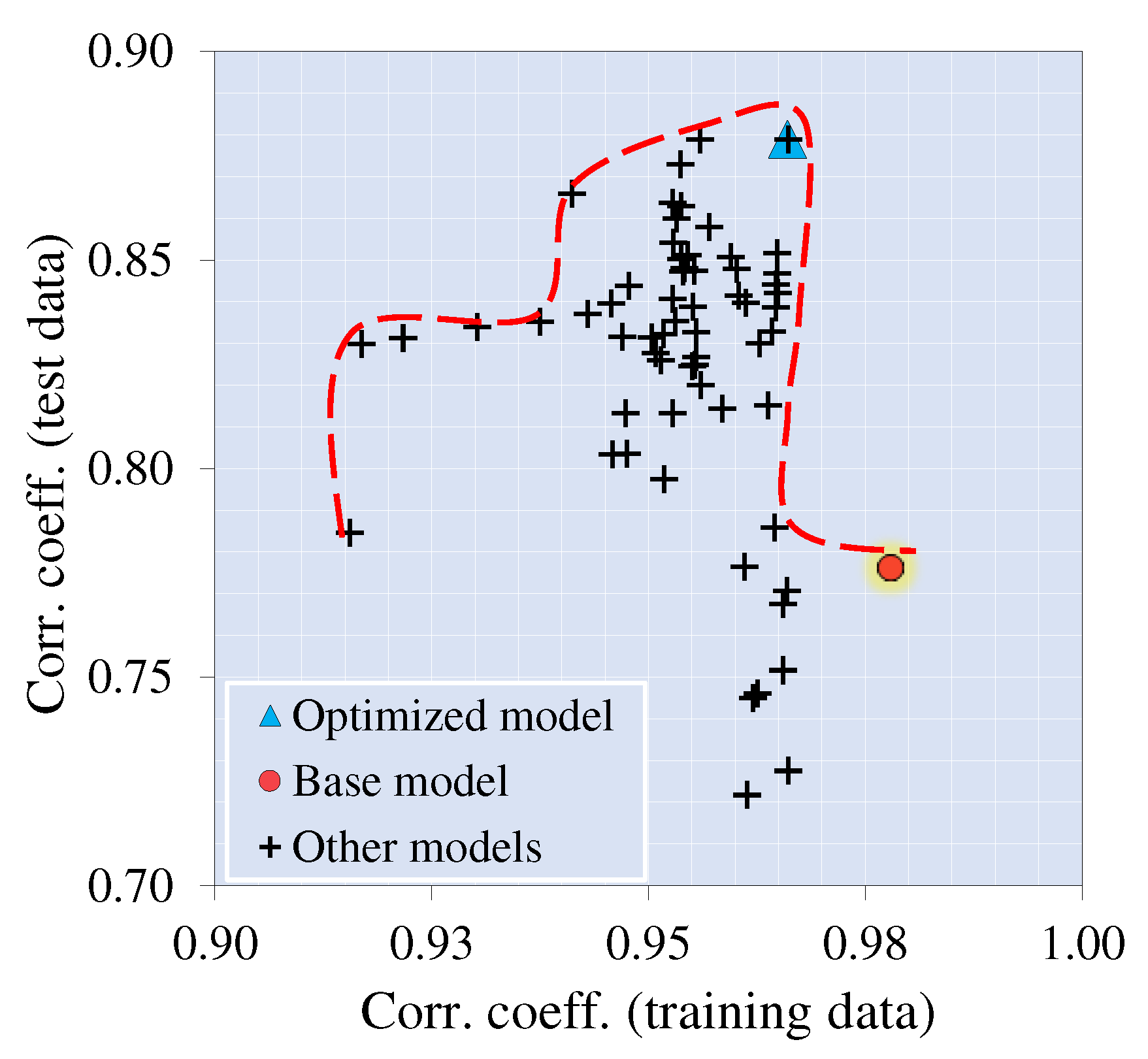
4.2. Development and performance of the initial model
4.3. Fine-tuned model
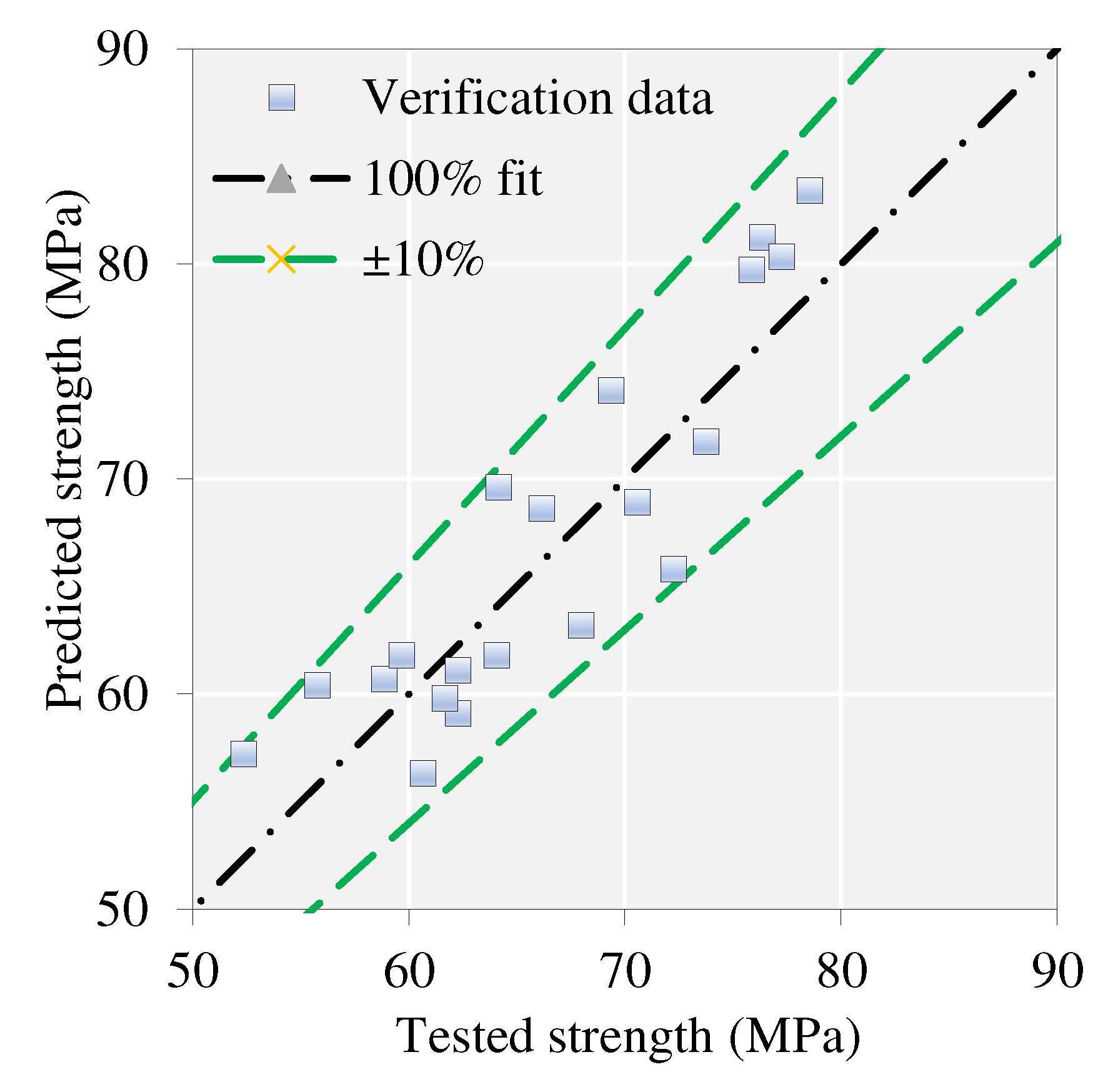
4.4. Experimental verification
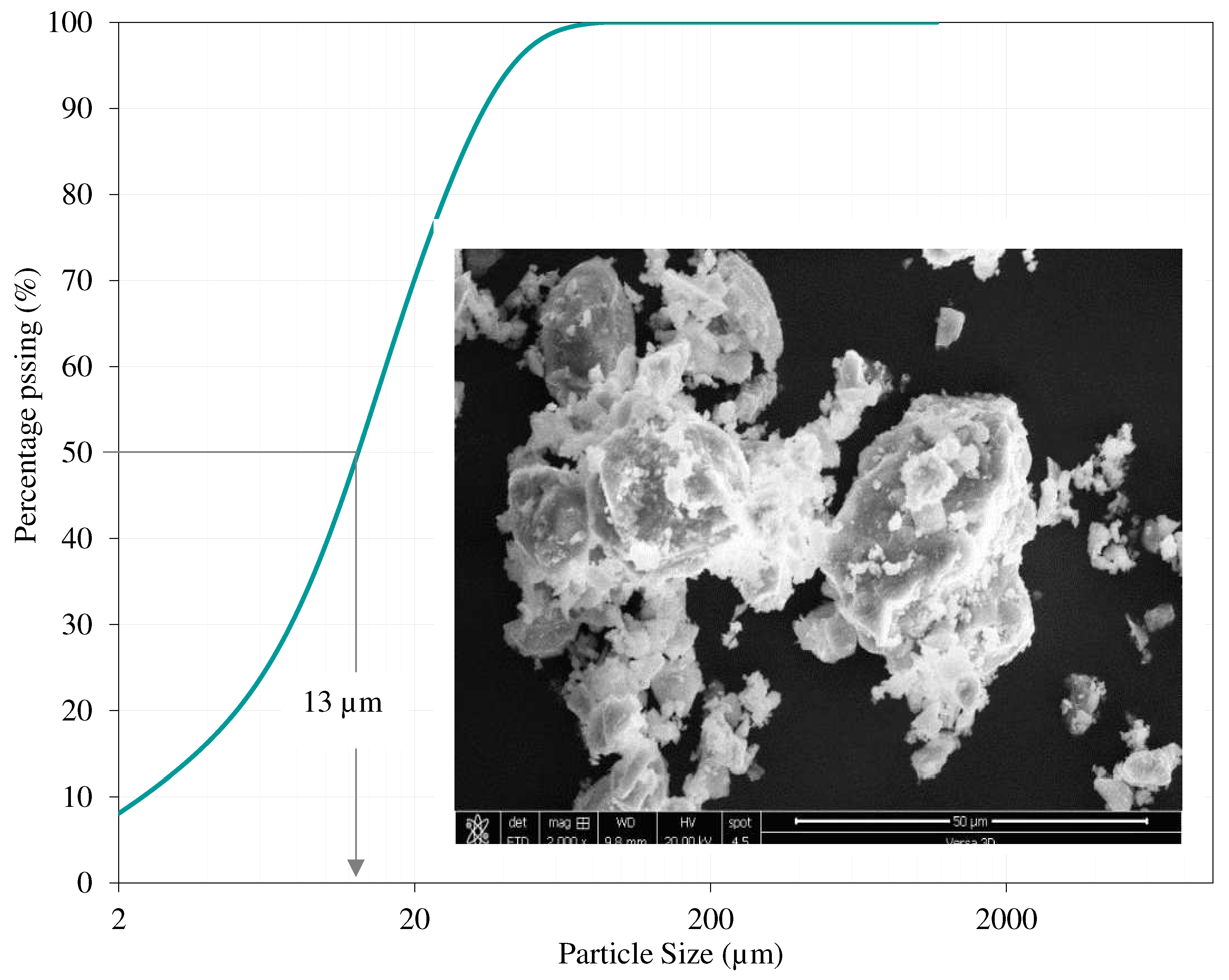
4.4.1. Materials
4.4.2. Methods
4.4.2.1. Preparation of the test specimens
4.4.2.2. Detail of testing
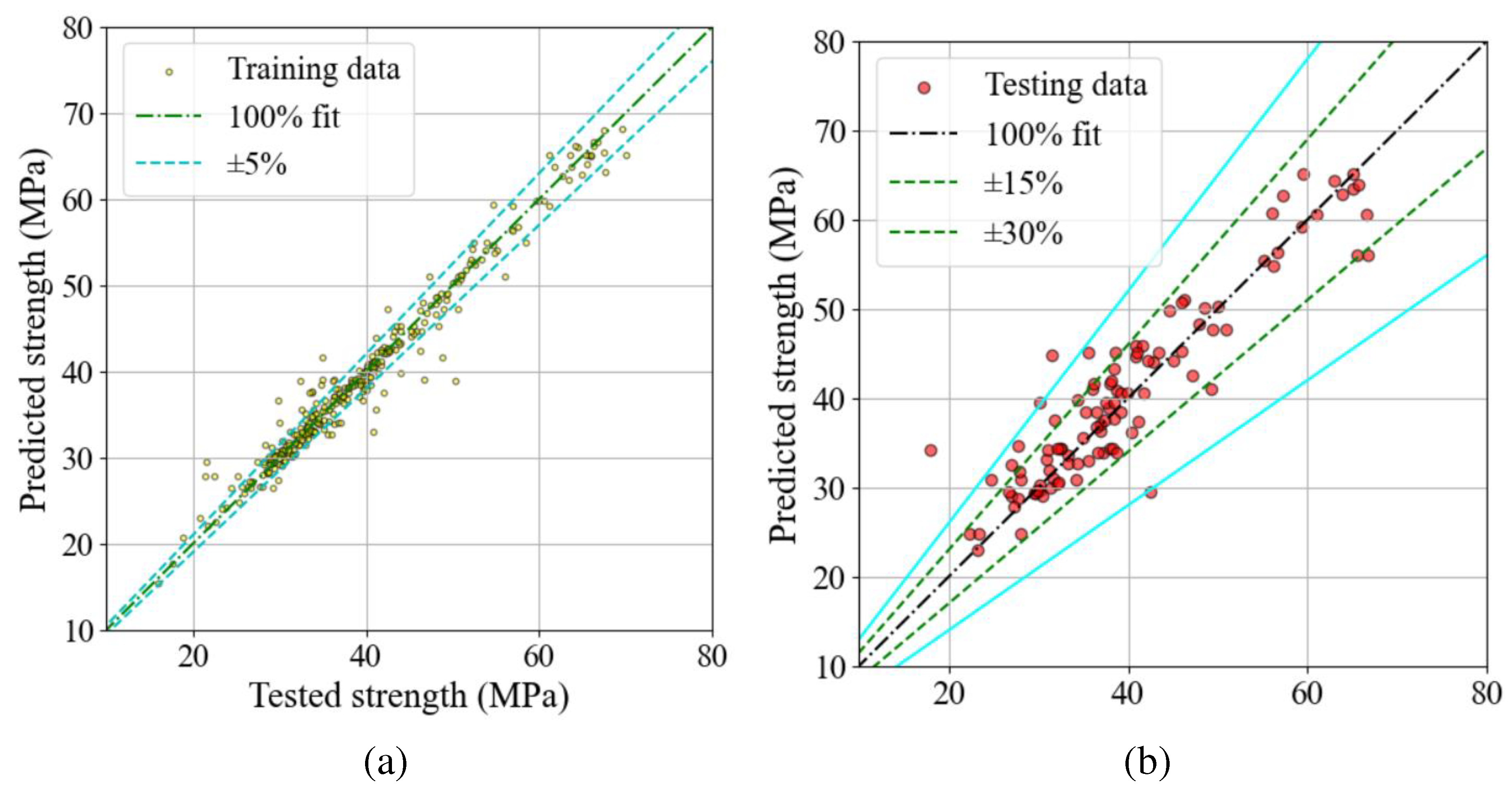
4.4.3. Test and model results
5. Model implementation
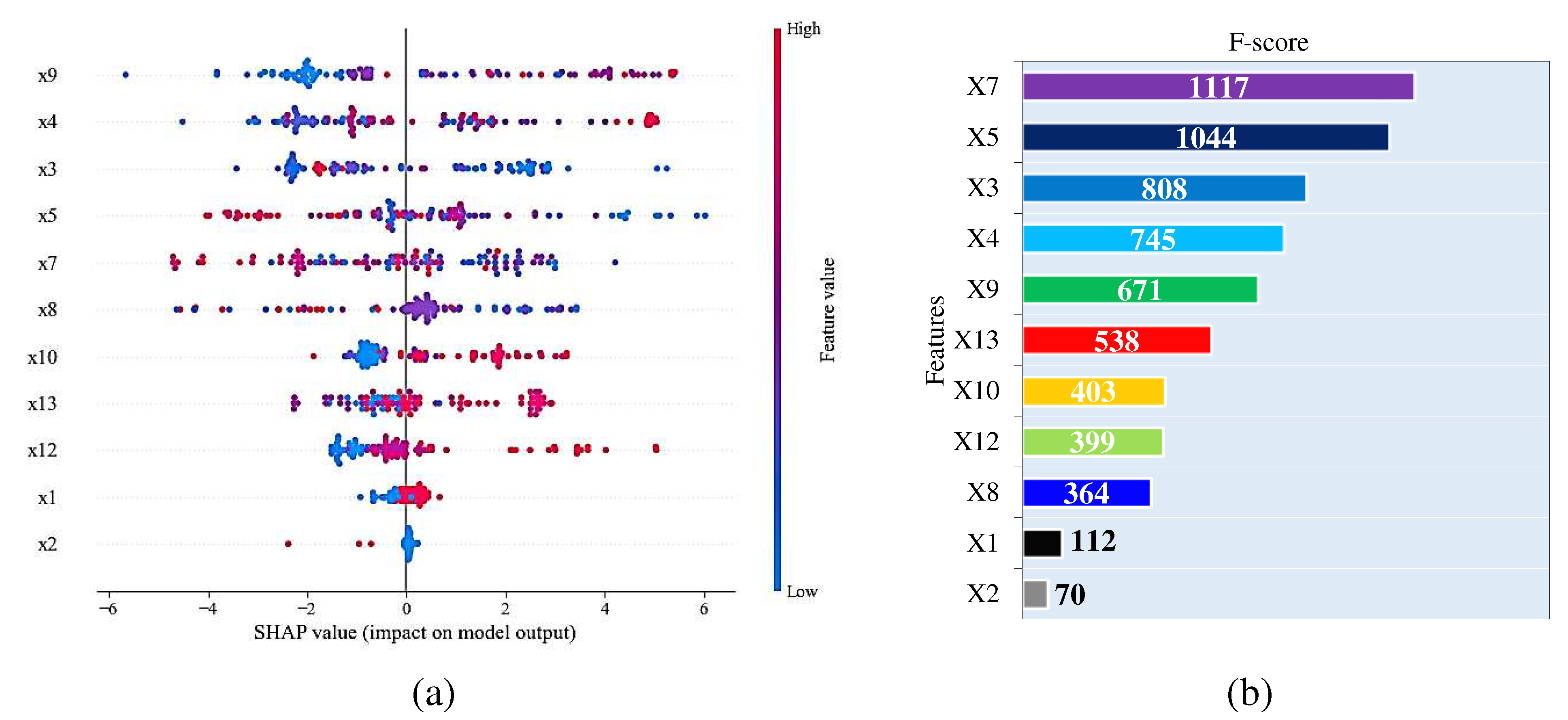
5.1. Feature ranking
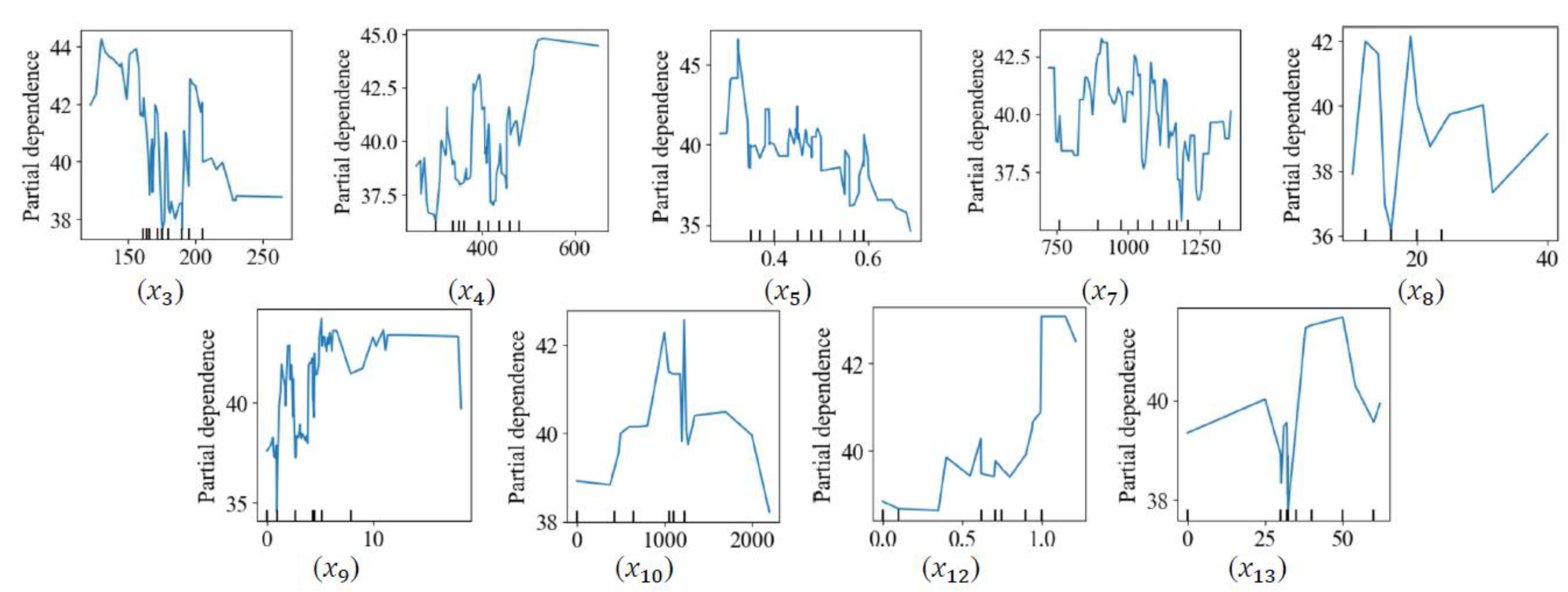
5.2. Partial dependence plots
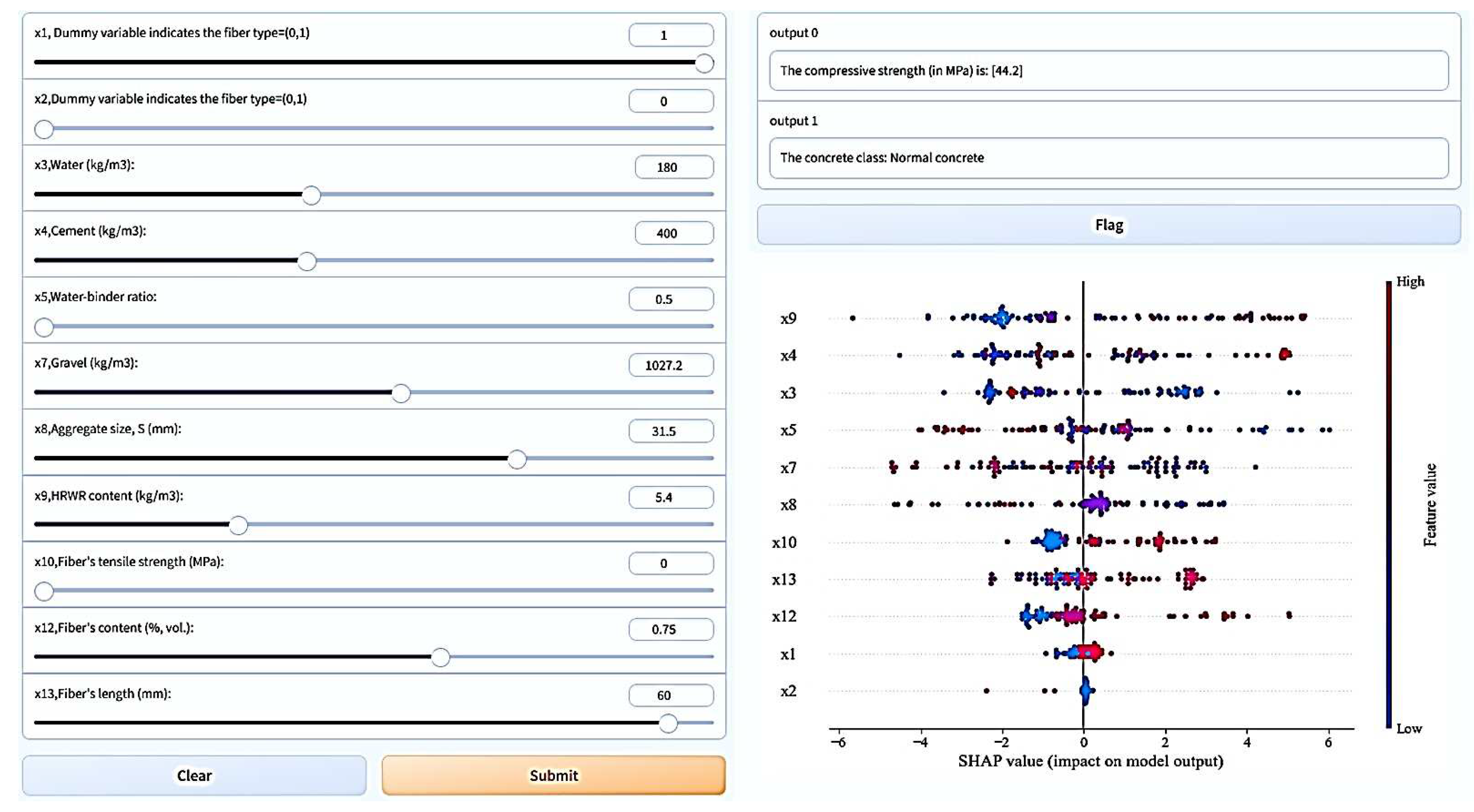
5.3. Graphical user interface development
6. Conclusions, implications, and future research
Acknowledgments
References
- Bennett, B.; Visintin, P.; Xie, T. Global Warming Potential of Recycled Aggregate Concrete with Supplementary Cementitious Materials. Journal of Building Engineering 2022, 52, 104394. [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, B.D.G.; Visintin, P.; Oehlers, D.J. Fatigue Bond-Slip Properties of Steel Reinforcing Bars Embedded in UHPFRC: Extraction and Development of an Accumulated Damage Law. Case Studies in Construction Materials 2022, 17, e01370. [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Y.M.; Fares, G.; Iqbal Khan, M. Depth-Dependent Flexural Behavior of Plain and Bar-Reinforced Ultra-High-Performance Hybrid Fiber-Reinforced Concrete –Analytical, Numerical, and Uncertainty Modeling. Structures 2023, 52, 723–741. [CrossRef]
- Abellan-Garcia, J.; Fernández, J.; Khan, M.I.; Abbas, Y.M.; Carrillo, J. Uniaxial Tensile Ductility Behavior of Ultrahigh-Performance Concrete Based on the Mixture Design – Partial Dependence Approach. Cem Concr Compos 2023, 140, 105060. [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Y.M.; Iqbal Khan, M. Fiber–Matrix Interactions in Fiber-Reinforced Concrete: A Review. Arab J Sci Eng 2016, 41, 1183–1198. [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Su, J.; Cao, J.; Liu, R. Investigation of Orientation Coefficient on Meso-Damage Evolution of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Cement Composites. Eng Fract Mech 2023, 284, 109210. [CrossRef]
- Pakzad, S.S.; Roshan, N.; Ghalehnovi, M. Comparison of Various Machine Learning Algorithms Used for Compressive Strength Prediction of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 3646. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, H.; Demartino, C.; Chen, W.; Yu, Y. Mechanical Properties of SFRC: Database Construction and Model Prediction. Case Studies in Construction Materials 2022, 17, e01484. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Abbas, Y.M. Intelligent Data-Driven Compressive Strength Prediction and Optimization of Reactive Powder Concrete Using Multiple Ensemble-Based Machine Learning Approach. Constr Build Mater 2023, 404, 133148. [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Y.M.; Fares, G.; Khan, M.I. Impact of Hot Weather Conditions on the Performance of Supplementary Cementitious Materials Concrete. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8393. [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Y.M.; Hussain, L.A.; Khan, M.I. Constitutive Compressive Stress–Strain Behavior of Hybrid Steel-PVA High-Performance Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 2022, 34. [CrossRef]
- Guerini, V.; Conforti, A.; Plizzari, G.; Kawashima, S. Influence of Steel and Macro-Synthetic Fibers on Concrete Properties. Fibers 2018, 6, 47. [CrossRef]
- Ortiz Navas, F.; Navarro-Gregori, J.; Leiva Herdocia, G.; Serna, P.; Cuenca, E. An Experimental Study on the Shear Behaviour of Reinforced Concrete Beams with Macro-Synthetic Fibres. Constr Build Mater 2018, 169, 888–899. [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, A.; Wetzel, B.; Klingler, A.; Friedrich, K. Mechanical Properties and Fracture Behavior of High-performance Epoxy Nanocomposites Modified with Block Polymer and Core–Shell Rubber Particles. J Appl Polym Sci 2020, 137. [CrossRef]
- Mujalli, M.A.; Dirar, S.; Mushtaha, E.; Hussien, A.; Maksoud, A. Evaluation of the Tensile Characteristics and Bond Behaviour of Steel Fibre-Reinforced Concrete: An Overview. Fibers 2022, 10, 104. [CrossRef]
- Mpalaskas, A.C.; Matikas, T.E.; Aggelis, D.G.; Alver, N. Acoustic Emission for Evaluating the Reinforcement Effectiveness in Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 3850. [CrossRef]
- Hollý, I.; Bilčík, J. Effect of Chloride-Induced Steel Corrosion on Working Life of Concrete Structures. Solid State Phenomena 2018, 272, 226–231. [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Y.M.; Tuken, A.; Siddiqui, N.A. Improving the Structural Behavior of Shear-Deficient RC Deep Beams Using Steel Fibers: Experimental, Numerical and Probabilistic Approach. Journal of Building Engineering 2022, 46, 103711. [CrossRef]
- Cucchiara, C.; La Mendola, L.; Papia, M. Effectiveness of Stirrups and Steel Fibres as Shear Reinforcement. Cem Concr Compos 2004. [CrossRef]
- Tarawneh, A.; Almasabha, G.; Alawadi, R.; Tarawneh, M. Innovative and Reliable Model for Shear Strength of Steel Fibers Reinforced Concrete Beams. Structures 2021, 32, 1015–1025. [CrossRef]
- Lantsoght, E.O.L. How Do Steel Fibers Improve the Shear Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Beams without Stirrups? Compos B Eng 2019, 175, 107079. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Jacobsen, S.; He, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Lee, S.F.; Lein, H.L. Application of Nanoindentation Testing to Study of the Interfacial Transition Zone in Steel Fiber Reinforced Mortar. Cem Concr Res 2009, 39, 701–715. [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Wan, X.; Gao, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, P. Study on the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Subjected to Sulfate Erosion. Arab J Sci Eng 2022, 47, 13639–13653. [CrossRef]
- Guojie; W. Chuanlin; J. ZHANG; L. Zeping; T. ZHANG; Y. ZHANG Influence of Steel Fiber Shape on the Performance of High-Performance Concrete. 复合材料学报, 2021; 38, 4313–4324.
- Wu, X.; Ding, F.; Xiang, P.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, C. Multiaxial Damage Ratio Strength Criteria for Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. J Eng Mech 2022, 148. [CrossRef]
- Frazão, C.; Camões, A.; Barros, J.; Gonçalves, D. Durability of Steel Fiber Reinforced Self-Compacting Concrete. Constr Build Mater 2015, 80, 155–166. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hunag, X.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Deng, X.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, B. Studies on Mechanical Properties and Durability of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete Incorporating Graphene Oxide. Cem Concr Compos 2022, 130, 104508. [CrossRef]
- Parvez, A.; Foster, S.J. Fatigue of Steel-Fibre-Reinforced Concrete Prestressed Railway Sleepers. Eng Struct 2017, 141, 241–250. [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, R.; Dou, G.; Du, X. Fire Resistance of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete Beams after Low-Velocity Impact Loading. Fire Saf J 2018, 98, 24–37. [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wu, C. Investigation on Thermal Conductivity of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete Using Mesoscale Modeling. Int J Thermophys 2018, 39, 142. [CrossRef]
- Qing, L.; Zhang, H.; Niu, C.; Mu, R.; Li, M. Preparation and Fracture Behavior of Annularly Aligned Steel Fiber Reinforced Cementitious Composite: Experiment and Simulation. Journal of Building Engineering 2023, 67, 106019. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, Z.; Yu, H.; Fang, Q. Fracture Properties of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete: Size Effect Study via Mesoscale Modelling Approach. Eng Fract Mech 2022, 260, 108193. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Xu, J.-J.; Wang, S.-C.; Xie, T.-Y. Evaluation of Shear Capacity of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete Beams without Stirrups Using Artificial Intelligence Models. Materials 2022, 15, 2407. [CrossRef]
- Abbass, W.; Khan, M.I.; Mourad, S. Evaluation of Mechanical Properties of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete with Different Strengths of Concrete. Constr Build Mater 2018, 168, 556–569. [CrossRef]
- Bai M; Niu DT; Jiang L; Miao Y. Research on Improving the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Concrete with Steel Fiber. Chinese.] Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 32, 2084–2089.
- H. Chang; P. Shen; F. Gu Analysis of the Influence Law of Steel Fiber on Concrete Thermal Conductivity and Pressure Strength. Concrete 2021, 4, 67–69.
- Y. Wang Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete Durability in the Atmospheric Environmental Based on Multi-Factor Effects. Doctoral dissertation, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, 2011.
- Açikgenç, M.; Ulaş, M.; Alyamaç, K.E. Using an Artificial Neural Network to Predict Mix Compositions of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. Arab J Sci Eng 2015, 40, 407–419. [CrossRef]
- Thai, H.-T. Machine Learning for Structural Engineering: A State-of-the-Art Review. Structures 2022, 38, 448–491. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wei, T.; Jiang, D.; Wang, M. Wind Turbine Blades Surface Crack-Detection Algorithm Based on Improved YOLO-v5 Model. J Electron Imaging 2023, 32. [CrossRef]
- Cardellicchio, A.; Ruggieri, S.; Nettis, A.; Renò, V.; Uva, G. Physical Interpretation of Machine Learning-Based Recognition of Defects for the Risk Management of Existing Bridge Heritage. Eng Fail Anal 2023, 149, 107237. [CrossRef]
- Awolusi, T.F.; Oke, O.L.; Akinkurolere, O.O.; Sojobi, A.O.; Aluko, O.G. Performance Comparison of Neural Network Training Algorithms in the Modeling Properties of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01115. [CrossRef]
- Karahan, O.; Tanyildizi, H.; Atis, C.D. An Artificial Neural Network Approach for Prediction of Long-Term Strength Properties of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete Containing Fly Ash. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A 2008, 9, 1514–1523. [CrossRef]
- Rathakrishnan, V.; Bt. Beddu, S.; Ahmed, A.N. Predicting Compressive Strength of High-Performance Concrete with High Volume Ground Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag Replacement Using Boosting Machine Learning Algorithms. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 9539. [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Additive Logistic Regression: A Statistical View of Boosting (With Discussion and a Rejoinder by the Authors). The Annals of Statistics 2000, 28. [CrossRef]
- T. Chen; C. Guestrin Xgboost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 22nd acm sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining; 2016; pp. 785–794.
- Wikipedia contributors XGBoost Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XGBoost (accessed on 29 August 2022).
- Wikiedia contributors Outlier Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Outlier (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Kivrak, M.; Guldogan, E.; Colak, C. Prediction of Death Status on the Course of Treatment in SARS-COV-2 Patients with Deep Learning and Machine Learning Methods. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2021, 201, 105951. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Yuan, C.; Zhai, Q.; Tian, X.; Wu, L.; Mi, Y. Identifying Diseases That Cause Psychological Trauma and Social Avoidance by GCN-Xgboost. BMC Bioinformatics 2020, 21, 504. [CrossRef]
- Carmona, P.; Dwekat, A.; Mardawi, Z. No More Black Boxes! Explaining the Predictions of a Machine Learning XGBoost Classifier Algorithm in Business Failure. Res Int Bus Finance 2022, 61, 101649. [CrossRef]
- G.V. Rossum; J.F. Drake Python Reference Manual; Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informatica : Amsterdam, 1995;
- M. Yalcin Optimization and Performance Based Design of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concretes, Istanb. Tech. Univ., 1994.
- Nili, M.; Afroughsabet, V. Combined Effect of Silica Fume and Steel Fibers on the Impact Resistance and Mechanical Properties of Concrete. Int J Impact Eng 2010, 37, 879–886. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Minh, L.; Rovňák, M.; Tran-Quoc, T.; Nguyenkim, K. Punching Shear Resistance of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete Flat Slabs. Procedia Eng 2011, 14, 1830–1837. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.S.; Che Bakar, M.B. Effects on Mechanical Properties of Industrialised Steel Fibres Addition to Normal Weight Concrete. Procedia Eng 2011, 14, 2616–2626. [CrossRef]
- Eren, Ö.; Marar, K. Effects of Limestone Crusher Dust and Steel Fibers on Concrete. Constr Build Mater 2009, 23, 981–988. [CrossRef]
- Şahin, Y.; Köksal, F. The Influences of Matrix and Steel Fibre Tensile Strengths on the Fracture Energy of High-Strength Concrete. Constr Build Mater 2011, 25, 1801–1806. [CrossRef]
- Buratti, N.; Mazzotti, C.; Savoia, M. Post-Cracking Behaviour of Steel and Macro-Synthetic Fibre-Reinforced Concretes. Constr Build Mater 2011, 25, 2713–2722. [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.; Anson, M. Effect of High Temperatures on High Performance Steel Fibre Reinforced Concrete. Cem Concr Res 2006, 36, 1698–1707. [CrossRef]
- Shakya, K.; Watanabe, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Niwa, J. Application of Steel Fibers in Beam–Column Joints of Rigid-Framed Railway Bridges to Reduce Longitudinal and Shear Rebars. Constr Build Mater 2012, 27, 482–489. [CrossRef]
- Soulioti, D. V.; Barkoula, N.M.; Paipetis, A.; Matikas, T.E. Effects of Fibre Geometry and Volume Fraction on the Flexural Behaviour of Steel-Fibre Reinforced Concrete. Strain 2011, 47. [CrossRef]
- Ünal, O.; Demir, F.; Uygunoğlu, T. Fuzzy Logic Approach to Predict Stress–Strain Curves of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concretes in Compression. Build Environ 2007, 42, 3589–3595. [CrossRef]
- Carmona, S.; Aguado, A.; Molins, C. Characterization of the Properties of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete by Means of the Generalized Barcelona Test. Constr Build Mater 2013, 48, 592–600. [CrossRef]
- Cantin, R.; Pigeon, M. Deicer Salt Scaling Resistance of Steel-Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. Cem Concr Res 1996, 26, 1639–1648. [CrossRef]
- Pigeon, M.; Cantin, R. Flexural Properties of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concretes at Low Temperatures. Cem Concr Compos 1998, 20, 365–375. [CrossRef]
- Z.X. C Experimental Study on Constitutive Relation of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete under Uniaxial Compresion, Zhengzhou University, 2017.
- J.Y. Chen The Study of the Effect of Aggregate Size and the Steel Fiber’s Length on the Fracture Property of SFRC, Zhengzhou University, 2016.
- C.C. Li Study on Mechanical Properties and Relationship of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete Cubic and Cylindrical Specimen, Zhengzhou University, 2016.
- J. Yue; Y. Xia; H. Fang Experimental Study on Fracture Mechanism and Tension Damage Constitutive Relationship of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete. China Civ. Eng. J 2021, 54, 93–106.
- Y. Yang Effect of Fiber Dosage and Bond Length on Pullout Mechanical Property Study, Guangzhou University, 2015.
- Zhang L J. Mixture Design and Performance Calculation Method of Steel Fiber Recycled Concrete, Zhengzhou University, 2016.
- L. Liao Study on the Optimisation of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete, Taiyuan Technology University, 2011.
- C.Y. Fan Study on Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete, Zhengzhou University, 2017.
- W.W. Yang Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties and Durability of Fiber Reinforced Concrete, Shandong University, 2012.
- B. Raja Rajeshwari; M. Sivakumar Influence of Coarse Aggregate Properties on Specific Fracture Energy of Steel Fiber Reinforced Self Compacting Concrete. Advances in concrete construction 2020, 9, 173–181.
- C. Gao Experimental Research on Mechanical Properties of Concrete and Reinfroced Oncrete after High Temperature, Yangzhou University, 2013.
- H.Q. Cheng Experimental Research on Adherence Property of Fresh Fiber Reinforced Concrete to Old Concrete, Zhengzhou University, 2007.
- J. Liu Study on the Relationship between Pressure and Tensile Properties of Steel Fiber Reinforced Recycled Concrete, Zhengzhou University, 2016.
- Z.Y. Ma An Experimental Study on the Properties of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete at Early Ages, Beijing Technology University, 2003.
- Q. Li; Y. Fang; C. Y L Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties of Concrete with Adding Steel Fiber at Early Age. Concrete 2020, 6, 102–105.
- T.Y. Zhu The Mechanical Properties of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete at Low Fiber Content, Zhengzhou University, 2011.
- L.L. Niu; S.P. Zhang; Y.X. Wei Effect of Fiber Dosage on the Mechanical Property of SFRC. China Concrete and Cement Products 2019, 3.
- H.X. Peng Experimental Research of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete on Speed-Repairing the Airport Pavement, Beijing Technology University, 2002.
- M. Gul; A. Bashir; J.A. Naqash Study of Modulus of Elasticity of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol 2014, 3, 304–309.
- F. Minelli; A. Conforti; E. Cuenca; G. Plizzari Are Steel Fibres Able to Mitigate or Eliminate Size Effect in Shear? Materials and structures 2014, 459–473.
- Conforti, A.; Minelli, F.; Plizzari, G.A. Wide-Shallow Beams with and without Steel Fibres: A Peculiar Behaviour in Shear and Flexure. Compos B Eng 2013, 51, 282–290. [CrossRef]
- Cuenca, E. On Shear Behavior of Structural Elements Made of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-13685-1.
- Characterization and Modelling of SFRC Elements, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, 2013.
- Facconi, L.; Minelli, F. Behavior of Lightly Reinforced Fiber Reinforced Concrete Panels under Pure Shear Loading. Eng Struct 2020, 202, 109879. [CrossRef]
- Conforti, A.; Zerbino, R.; Plizzari, G.A. Influence of Steel, Glass and Polymer Fibers on the Cracking Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Beams under Flexure. Structural Concrete 2019, 20, 133–143. [CrossRef]
- Tiberti, G.; Minelli, F.; Plizzari, G. Cracking Behavior in Reinforced Concrete Members with Steel Fibers: A Comprehensive Experimental Study. Cem Concr Res 2015, 68, 24–34. [CrossRef]
- Committee, A. 318 Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete (ACI 318-19) and Commentary.; American Concrete Institute, 2022.
- Wu, B.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, X. Shape Effect on Compressive Mechanical Properties of Compound Concrete Containing Demolished Concrete Lumps. Constr Build Mater 2018, 187, 50–64. [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, C.C. An Introduction to Outlier Analysis. In Outlier Analysis; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2017; pp. 1–34.
- Atkinson, A.; Riani, M. Robust Diagnostic Regression Analysis; Springer New York: New York, NY, 2000; ISBN 978-1-4612-7027-0.
- Pimentel, M.A.F.; Clifton, D.A.; Clifton, L.; Tarassenko, L. A Review of Novelty Detection. Signal Processing 2014, 99, 215–249. [CrossRef]
- Zimek, A.; Schubert, E.; Kriegel, H. A Survey on Unsupervised Outlier Detection in High-dimensional Numerical Data. Statistical Analysis and Data Mining: The ASA Data Science Journal 2012, 5, 363–387. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Abbas, Y.M. Robust Extreme Gradient Boosting Regression Model for Compressive Strength Prediction of Blast Furnace Slag and Fly Ash Concrete. Mater Today Commun 2023, 35, 105793. [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia contributors Pearson Correlation Coefficient Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pearson_correlation_coefficient (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Ayan, E.; Saatçioğlu, Ö.; Turanli, L. Parameter Optimization on Compressive Strength of Steel Fiber Reinforced High Strength Concrete. Constr Build Mater 2011, 25, 2837–2844. [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Chen, W.; He, J. Experimental and Multi-Scale Numerical Investigation of Ultra-High Performance Fiber Reinforced Concrete (UHPFRC) with Different Coarse Aggregate Content and Fiber Volume Fraction. Constr Build Mater 2020, 260, 120444. [CrossRef]
- V. Pareto Cours d’économie Politique; Librairie Droz, 1964;
- Hastie, T.; Friedman, J.; Tibshirani, R. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer New York: New York, NY, 2001; ISBN 978-1-4899-0519-2.
- Gong, J.; Chu, S.; Mehta, R.K.; McGaughey, A.J.H. XGBoost Model for Electrocaloric Temperature Change Prediction in Ceramics. NPJ Comput Mater 2022, 8, 140. [CrossRef]
- A. Abid; A. Abdalla; A. Abid; D. Khan; A. Alfozan; J. Zou Gradio: Hassle-Free Sharing and Testing of Ml Models in the Wild. arXiv preprint arXiv 2019.
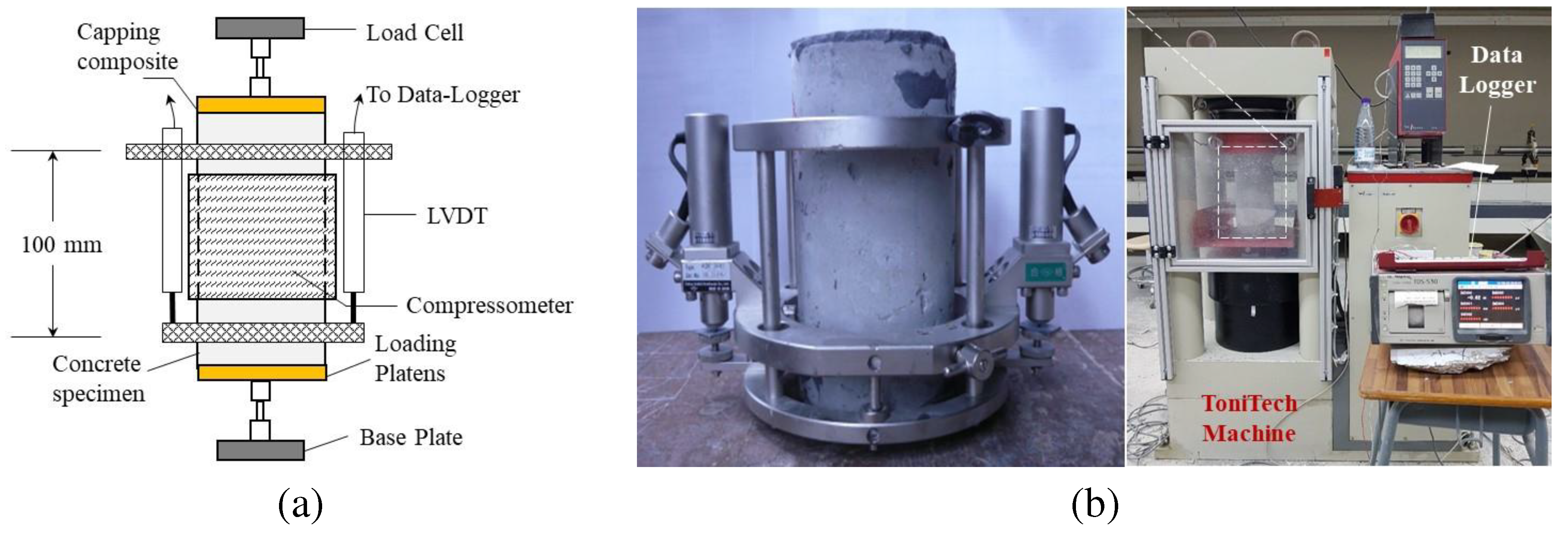


| Fiber type | Hooked | Mil-cut | Crimped |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| variable | Unit | Description | variable | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kg/m3 | Water content | kg/m3 | HRWR content | ||
| Cement content | MPa | Tensile strength of the fiber | |||
| –– | water-binder ratio | mm | Diameter of the fiber | ||
| kg/m3 | Fine aggregate content | %, vol. | Dosage of the fiber | ||
| Coarse aggregate content | mm | Length of the fiber | |||
| mm | Maximum aggregate size | MPa | 28d CS of the SFRC |
| Ref. | Data-sets | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [53] | 17 | 1 | 0 | 180–192.5 | 280–400 | 0.5|0.6|0.7 | 713.8–762.6 | 1027.2–1097.4 | 31.5 | 3.4–6.6 | –– | 0.19–0.64 | 0.55–0.9 | 30–60 | 29.7–46.7 |
| [54] | 12 | 1 | 0 | 162–177 | 354–450 | 0.4|0.5 | 893–920 | 858–887 | 19 | 2.3–6.5 | 1050 | 0–1 | 0.75 | 60 | 31.5–53.3 |
| [55] | 4 | 1 | 0 | 181.2 | 453 | 0.4 | 624 | 1242 | 22 | 1 | 1100 | 0–0.8 | 0.75 | 60 | 21.7–25.3 |
| [56] | 5 | 1 | 0 | 230.2 | 338 | 0.7 | 1049.2 | 760 | 10 | 0.7 | –– | 0–1.25 | 0.75 | 60 | 25.6–28.1 |
| [57] | 40 | 1 | 0 | 175 | 350 | 0.5 | 952.2 | 1321.2–1398.8 | 20 | 4.5 | 1100–1250 | 0–1.5 | 0–1.5 | 50–60 | 17.9–40.8 |
| [58] | 14 | 1 | 0 | 178–179 | 325–396 | 0.4|0.6 | 842–891 | 913–965 | 19 | 0.9–1.4 | 1050–2000 | 0–1 | 0.71–0.75 | 60 | 47.2–61.1 |
| [59] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 175.6 | 351 | 0.5 | 914.8 | 994.7 | 22 | 2.7 | –– | 0.26–0.45 | 1 | 50 | 33.3–33.4 |
| [60] | 5 | 1 | 0 | 205–398 | 311–458 | 0.6|0.7 | 408–665 | 1156–1407 | 20 | 3.1–7.3 | 1700 | 0–1 | 0.4 | 25 | 31.2–88.0 |
| [61] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 169.8–177.6 | 283–296 | 0.6 | 705–838 | 968–1071 | 10 | 2.8–3.3 | –– | 1–1.5 | 0.62 | 30 | 23.3–30.0 |
| [62] | 7 | 1 | 0 | 220 | 440 | 0.5 | 1193–1225 | 356–366 | 10 | 3–4 | –– | 0–1.5 | 0.75 | 25–31 | 35.1–43.8 |
| [63] | 8 | 1 | 0 | 191.2–191.6 | 324 | 0.6 | 1052.8–1064.2 | 750.0–758.3 | 22 | 3.2 | 1200 | 0.19–0.76 | 0.5–0.75 | 30–60 | 34.0–48.0 |
| [64] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 185 | 410 | 0.5 | 915 | 866 | 20 | 2–4 | 1100 | 0.5–1.0 | 1 | 50 | 50.0–52.0 |
| [65] | 10 | 0|1 | 0 | 150–168 | 341–429 | 0.3|0.4|0.5 | 800 | 975 | 14 | 2.8–11 | –– | 0.51 | 1 | 54–60 | 40.9–67.6 |
| [66] | 18 | 1 | 0 | 123–167 | 325–439 | 0.6 | 741–885 | 846–998 | 14 | 0.5–11.4 | –– | 0.48–0.75 | 1 | 54–60 | 38.2–69.6 |
| [36] | 6 | 1 | 0 | 195 | 342 | 0.3|0.5|0.6 | 701 | 1143 | 20 | 10.3 | –– | 0–1.5 | 0.75 | 30 | 24.6–30.6 |
| [67] | 23 | 1 | 0 | 164–185 | 308.3–529.1 | 0.3|0.6 | 639.3–763.9 | 928.6–1232.7 | 20 | 0–5.8 | 600–1000 | 0-2 | 0.55–0.75 | 35 | 26.7–65.4 |
| [68] | 32 | 1 | 0 | 172–195 | 336–521 | 0.6 | 652–750 | 1080–1145 | 10–40 | 0–5.2 | 1100 | 0-1 | 0.75 | 30–60 | 25.8–67.4 |
| [69] | 21 | 0|1 | 0 | 166 | 286 | 0.4 | 739 | 1170–1259 | 20 | 0–0.6 | 600 | 0–2 | 0.75 | 30–40 | 28.0–33.0 |
| [35] | 5 | 0 | 0 | 165 | 367 | 0.3|0.4|0.5 | 702–765 | 1053–1146 | 16 | 2.2 | 380 | 0–2 | 0.5 | 30 | 26.8–31.0 |
| [70] | 12 | 1 | 0 | 195–200 | 415–651 | 0.4|0.7 | 527–610 | 1022–1182 | 20 | 0 | 1000 | 0–1.5 | 0.75 | 32 | 30.9–58.5 |
| [71] | 6 | 1 | 0 | 185 | 268–524 | 0.4|0.5|0.6 | 488–725 | 1056–1185 | 31.5 | 0 | 1000 | 0–0.63 | 1 | 50 | 16.0–34.4 |
| [72] | 22 | 0|1 | 0|1 | 172–196 | 321–475 | 0.4|0.5 | 622.8–886.0 | 960–1171 | 20 | 0–4.5 | –– | 0–2 | 0.75–0.94 | 32.3–62 | 26.6–43.6 |
| [73] | 6 | 1 | 0 | 156–165 | 312–381 | 0.6 | 817–1200 | 700–1214 | 20 | 2.2–5.3 | 1000 | 0.38–0.77 | 1 | 50 | 63.9–67.5 |
| [74] | 13 | 0|1 | 0 | 264 | 480 | 0.4 | 716.5–769.1 | 895.1–989.5 | 20 | 0 | 380–500 | 0–2 | 0.9–1.2 | 30.2–32.3 | 27.7–34.3 |
| [75] | 4 | 1 | 0 | 175 | 461 | 0.4 | 512 | 1252 | 10 | 0 | 600 | 0–1.5 | 1.0 | 35 | 28.5–31.4 |
| [76] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 160 | 400 | 0.4|0.6 | 750 | 1140 | 20 | 8 | 1700 | 0–0.5 | 0.5 | 30 | 42.7–45.1 |
| [77] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 230 | 535 | 0.5 | 556 | 1079 | 16 | 0 | 1345 | 0–1.0 | 0.6 | 30 | 36.5–41.1 |
| [37] | 2 | 0 | 0 | 165 | 300–471 | 0.4 | 690–760 | 1038–1140 | 20 | 1.8–2.8 | 380 | 1 | 0.5 | 30 | 23.8–39.0 |
| [78] | 18 | 0 | 1 | 195–228 | 361–475 | 0.4 | 630–875 | 715–1180 | 20 | 0 | 380 | 0–2 | 0.94 | 32.2 | 28.1–34.1 |
| [79] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 166 | 415 | 0.4 | 838.6 | 1024.9 | 20 | 0 | 1345 | 0–1 | 0.55 | 35 | 40.8–42.6 |
| [80] | 5 | 0 | 1 | 161 | 460 | 0.4 | 1150 | 1048.8 | 20 | 18.4 | 808.6 | 0–1 | 0.8 | 32 | 30.0–40.6 |
| [81] | 4 | 0 | 1 | 215.5 | 480 | 0.4 | 825 | 880 | 25 | 8 | –– | 0–0.51 | 0.5 | 38 | 40.6–49.3 |
| [82] | 16 | 0|1 | 0|1 | 160–200 | 258–513 | 0.4|0.5|0.6 | 540–868 | 1012–1283 | 20 | 0 | 500–1325 | 0–0.7 | 0.55–1.15 | 32–50 | 27.0–47.0 |
| [83] | 5 | 1 | 0 | 172 | 400 | 0.4 | 730 | 1046–1100 | 15 | 0 | –– | 0 | 0.8 | 32 | 27.7–37.0 |
| [84] | 10 | 0 | 0 | 161.0–167.7 | 453.3–460.0 | 0.4 | 699.2 | 1594.2 | 20 | 18.1–18.4 | 808.6 | 0–1.6 | 0.8 | 32–40 | 43.5–56.0 |
| [85] | 28 | 1 | 0 | 161.7 | 437 | 0.4 | 756 | 1210 | 20 | 1.3–6.1 | –– | 0–1.5 | 0.7 | 35–50 | 31.8–50.3 |
| [86] | 3 | 1 | 0 | 168.1 | 410 | 0.4 | 1073 | 645 | 16 | 4.1–5.7 | 1100 | 0–1 | 0.8 | 50 | 32.1–38.7 |
| [87] | 3 | 1 | 0 | 167.7 | 390 | 0.4 | 1075 | 758 | 16 | 2.3–3.1 | 1100 | 0–1.45 | 0.8 | 50 | 36.9–40.5 |
| [88] | 9 | 1 | 0 | 198–205 | 440–460 | 0.4|0.5 | 924–985 | 721–846 | 12 | 11.1–12.8 | 1225 | 0.76 | 0.62 | 40 | 52.4–70.0 |
| [89] | 5 | 1 | 0 | 165 | 300 | 0.6 | 1128.8 | 806.3 | 16 | 2.5 | 1050–1100 | 0–0.5 | 0.55–0.75 | 35–60 | 17.6–29.2 |
| [90] | 6 | 1 | 0 | 190 | 380 | 0.6 | 1082.0 | 742.0 | 12 | 0.0–2.4 | 2200 | 0–0.63 | 0.35 | 30 | 21.6–43.92 |
| [91] | 3 | 1 | 0 | 169.1 | 412.4 | 0.4 | 927.8 | 890.7 | 12 | 0.0 | 1100 | 0–0.63 | 1 | 50 | 40.1–41.6 |
| [92] | 3 | 1 | 0 | 188.0 | 400.0 | 0.5 | 610.0 | 1132.0 | 10 | 3.3 | 1270 | 0–1 | 0.62 | 30 | 36.4–40.5 |
| Tot. | 422 | 0|1 | 0|1 | 123–398 | 258–651 | 0.3–0.7 | 408–1225 | 356.0–1594.2 | 10–40 | 0.0–18.4 | 380–2200 | 0–2 | 0.1–1.2 | 25–62 | 16–88 |
| Specimen type | Conversion factor | Source | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cubic | 0.80 | ACI 318 [93] | Below 60 MPa strength |
| Cubic | 0.90 | ACI 318 [93] | Above 60 MPa strength |
| Prismatic | 0.96 | Wu et al. [94] | –– |
| Variable | Mean | StDev | Minimum | Q1 | Median | Q3 | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8012 | 0.3997 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.0865 | 0.2814 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 181.19 | 23.62 | 123.00 | 165.00 | 175.00 | 192.50 | 264.00 | |
| 394.97 | 74.01 | 258.00 | 342.00 | 392.00 | 450.00 | 651.00 | |
| 0.472 | 9.23 | 0.285 | 0.390 | 0.4800 | 0.550 | 0.690 | |
| 804.05 | 152.58 | 488.00 | 713.00 | 756.00 | 911.00 | 1225.00 | |
| 1067.6 | 210.6 | 356.0 | 945.0 | 1088.6 | 1206.3 | 1594.2 | |
| 19.542 | 5.218 | 10.000 | 19.000 | 20.000 | 20.000 | 40.000 | |
| 3.451 | 4.131 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 2.750 | 4.963 | 18.400 | |
| 989.4 | 378.5 | 380.0 | 600.0 | 1050.0 | 1200.0 | 2200.0 | |
| 0.7246 | 0.5377 | 0.0000 | 0.3840 | 0.5780 | 1.0000 | 2.0000 | |
| 0.7553 | 0.1970 | 0.1000 | 0.7000 | 0.7500 | 0.9000 | 1.2150 | |
| 44.015 | 12.178 | 25.000 | 32.300 | 40.000 | 60.000 | 62.000 | |
| 39.677 | 11.034 | 16.000 | 31.800 | 37.418 | 45.358 | 70.000 |
| Hyperparameter | Role | Range | Default value (Model-0) | Optimized value (Model-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| max_depth | Tree Maximum Depth: Modifying this parameter to higher values results in a more intricate model, increasing the risk of overfitting. | 6 | 52 | |
| n_estimators | This hyperparameter dictates the quantity of boosting iterations or trees incorporated within the ensemble. | 100 | 325 | |
| learning_rate | step size shrinkage employed during updates is intended to mitigate overfitting | 0–1 | 0 | 0.2 |
| colsample_bytree | The subsample ratio of columns determines the proportion of features used when constructing each tree. | 0–1 | 1 | 0.1 |
| subsample | Subsample ratio of training instance (e.g., 0.5 indicates 50% of data used prior to growing trees). | >0–1 | 1 | 0.5 |
| reg_alpha | L1 regularization (increasing its value makes the model more conservative). | –– | 0 | 0.01 |
| reg_lambda | L2 regularization (increasing its value makes the model more conservative). | –– | 1 | 10 |
| gamma | Regularization parameter for tree pruning that specifies the minimum loss reduction required to make a split. | 0 | 0.1 |
| Performance indicator | Model-0 | Model-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | Testing set | Training set | Testing set | |
| 0.742 | 3.541 | 1.239 | 2.797 | |
| 2.576 | 28.413 | 4.008 | 16.997 | |
| 1.605 | 5.330 | 2.002 | 3.933 | |
| 0.978 | 0.776 | 0.966 | 0.879 | |
| Oxide composition (%) | L.O.I. (%) | Specific gravity | Fineness (m2/kg) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | Na2Oeq | SO3 | |||
| 20.20 | 5.49 | 4.12 | 65.43 | 0.71 | 0.26 | 2.61 | 1.38 | 3.14 | 373 |
| Fiber | Length (mm) |
Diameter (mm) |
Aspect ratio | Young’s Modulus (GPa) |
Tensile strength (MPa) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| shape | ID | |||||
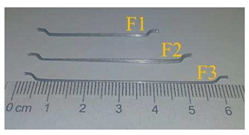 |
F1 | 40 | 0.62 | 65 | 210 | 1250 |
| F2 | 50 | 0.62 | 80 | |||
| F3 | 60 | 0.75 | 80 | |||
| Model’s input variables | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | ID | ||||||||||||||||
| 1 | H-F1-0.5 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 450 | 0.35 | 716 | 1053 | 10 | 0.68 | 1250 | 0.62 | 0.5 | 65 | 69.4 | 74.1 | 0.937 |
| 2 | N-F1-0.5 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 350 | 0.45 | 798 | 1078 | 10 | 0.42 | 1250 | 0.62 | 0.5 | 65 | 60.7 | 56.3 | 1.078 |
| 3 | H-F1-1.0 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 450 | 0.35 | 716 | 1053 | 10 | 0.68 | 1250 | 0.62 | 1.0 | 65 | 72.3 | 65.8 | 1.099 |
| 4 | N-F1-1.0 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 350 | 0.45 | 798 | 1078 | 10 | 0.42 | 1250 | 0.62 | 1.0 | 65 | 64.1 | 61.8 | 1.037 |
| 5 | H-F1-1.5 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 450 | 0.35 | 716 | 1053 | 10 | 0.68 | 1250 | 0.62 | 1.5 | 65 | 75.9 | 79.7 | 0.952 |
| 6 | N-F1-1.5 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 350 | 0.45 | 798 | 1078 | 10 | 0.42 | 1250 | 0.62 | 1.5 | 65 | 62.3 | 59.1 | 1.054 |
| 7 | H-F2-0.5 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 450 | 0.35 | 716 | 1053 | 10 | 0.68 | 1250 | 0.62 | 0.5 | 80 | 73.8 | 71.7 | 1.029 |
| 8 | N-F2-0.5 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 350 | 0.45 | 798 | 1078 | 10 | 0.42 | 1250 | 0.62 | 0.5 | 80 | 55.8 | 60.4 | 0.924 |
| 9 | H-F2-1.0 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 450 | 0.35 | 716 | 1053 | 10 | 0.68 | 1250 | 0.62 | 1.0 | 80 | 76.4 | 81.2 | 0.941 |
| 10 | N-F2-1.0 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 350 | 0.45 | 798 | 1078 | 10 | 0.42 | 1250 | 0.62 | 1.0 | 80 | 62.3 | 61.1 | 1.020 |
| 11 | H-F2-1.5 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 450 | 0.35 | 716 | 1053 | 10 | 0.68 | 1250 | 0.62 | 1.5 | 80 | 77.3 | 80.3 | 0.963 |
| 12 | N-F2-1.5 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 350 | 0.45 | 798 | 1078 | 10 | 0.42 | 1250 | 0.62 | 1.5 | 80 | 64.2 | 69.6 | 0.922 |
| 13 | H-F3-0.5 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 450 | 0.35 | 716 | 1053 | 10 | 0.68 | 1250 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 80 | 68.0 | 63.2 | 1.076 |
| 14 | N-F3-0.5 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 350 | 0.45 | 798 | 1078 | 10 | 0.42 | 1250 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 80 | 58.9 | 60.7 | 0.970 |
| 15 | H-F3-1.0 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 450 | 0.35 | 716 | 1053 | 10 | 0.68 | 1250 | 0.75 | 1.0 | 80 | 70.6 | 68.9 | 1.025 |
| 16 | N-F3-1.0 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 350 | 0.45 | 798 | 1078 | 10 | 0.42 | 1250 | 0.75 | 1.0 | 80 | 59.7 | 61.8 | 0.966 |
| 17 | H-F3-1.5 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 450 | 0.35 | 716 | 1053 | 10 | 0.68 | 1250 | 0.75 | 1.5 | 80 | 78.6 | 83.4 | 0.942 |
| 18 | N-F3-1.5 | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 350 | 0.45 | 798 | 1078 | 10 | 0.42 | 1250 | 0.75 | 1.5 | 80 | 66.2 | 68.6 | 0.965 |
| 19 | H-CTRL | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 450 | 0.35 | 716 | 1053 | 10 | 0.68 | –– | –– | –– | –– | 61.7 | 59.8 | 1.032 |
| 20 | N-CTRL | 1 | 0 | 157.5 | 350 | 0.45 | 798 | 1078 | 10 | 0.42 | –– | –– | –– | –– | 52.4 | 57.2 | 0.916 |
| 0.992 | |||||||||||||||||
| 0.058 | |||||||||||||||||
| CV | 0.059 | ||||||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





