Submitted:
18 October 2023
Posted:
20 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. AGD Evaluating Indicator Framework
2.2. AGD Evaluating Methods
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Area and Data
3.2. AGD Evaluating Method-Projection Pursuit Method
3.3. Obstacle Degree Calculating Model
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. AGD Evaluating Indicator Framework for Beijing ECDA
4.2. Weight of Integrated Evaluating Indicators
4.3. Green Agricultural Production
4.4. Green Agricultural Revenue
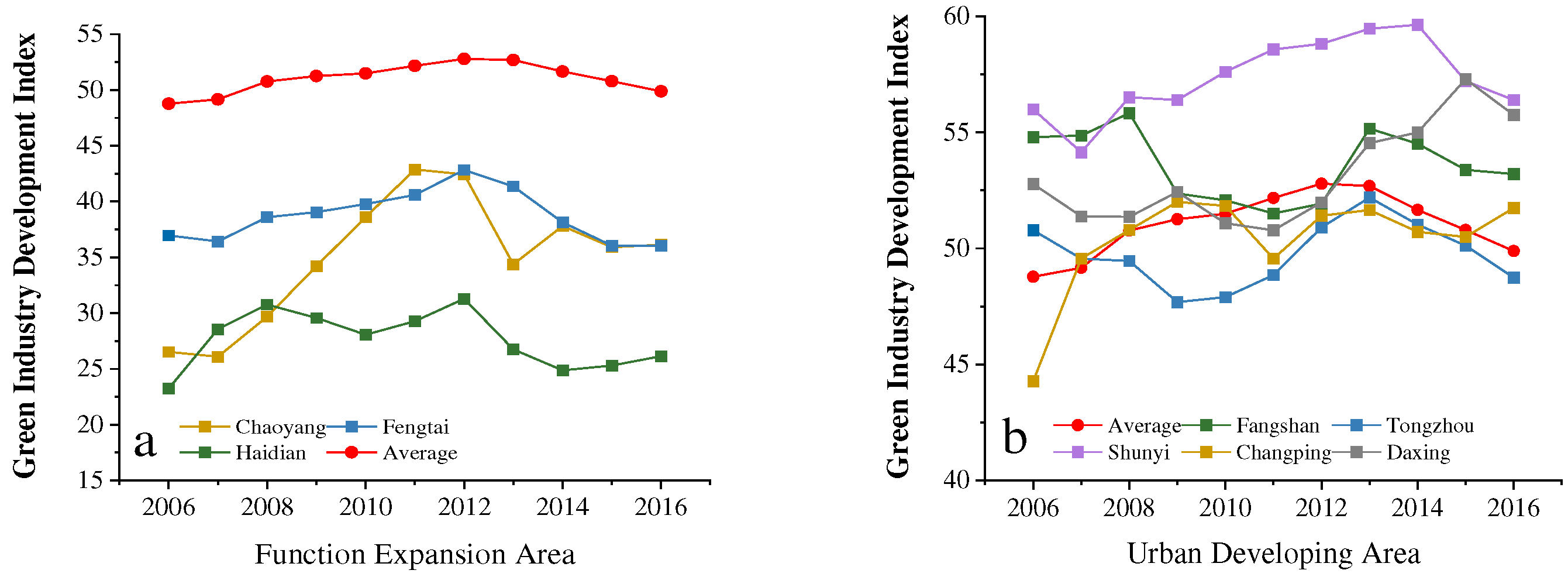
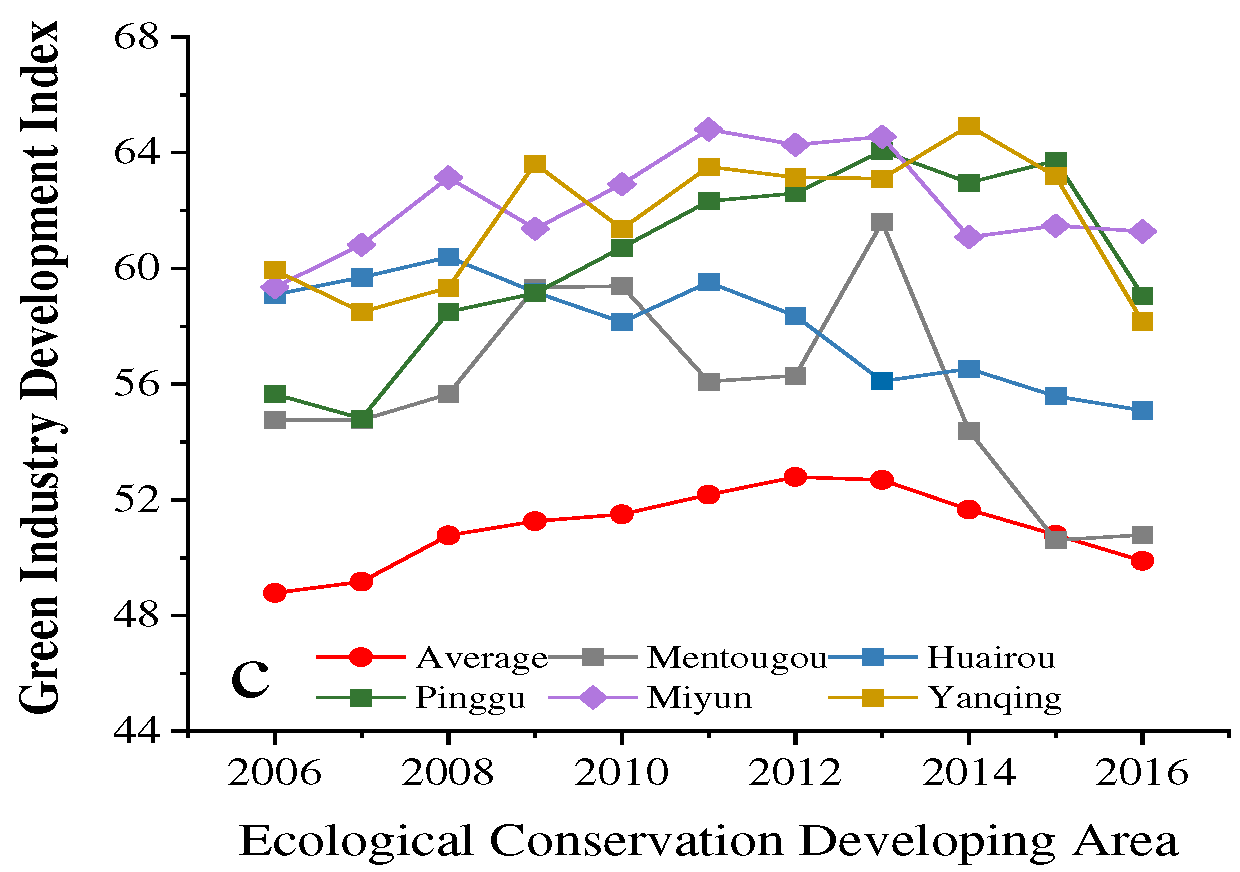
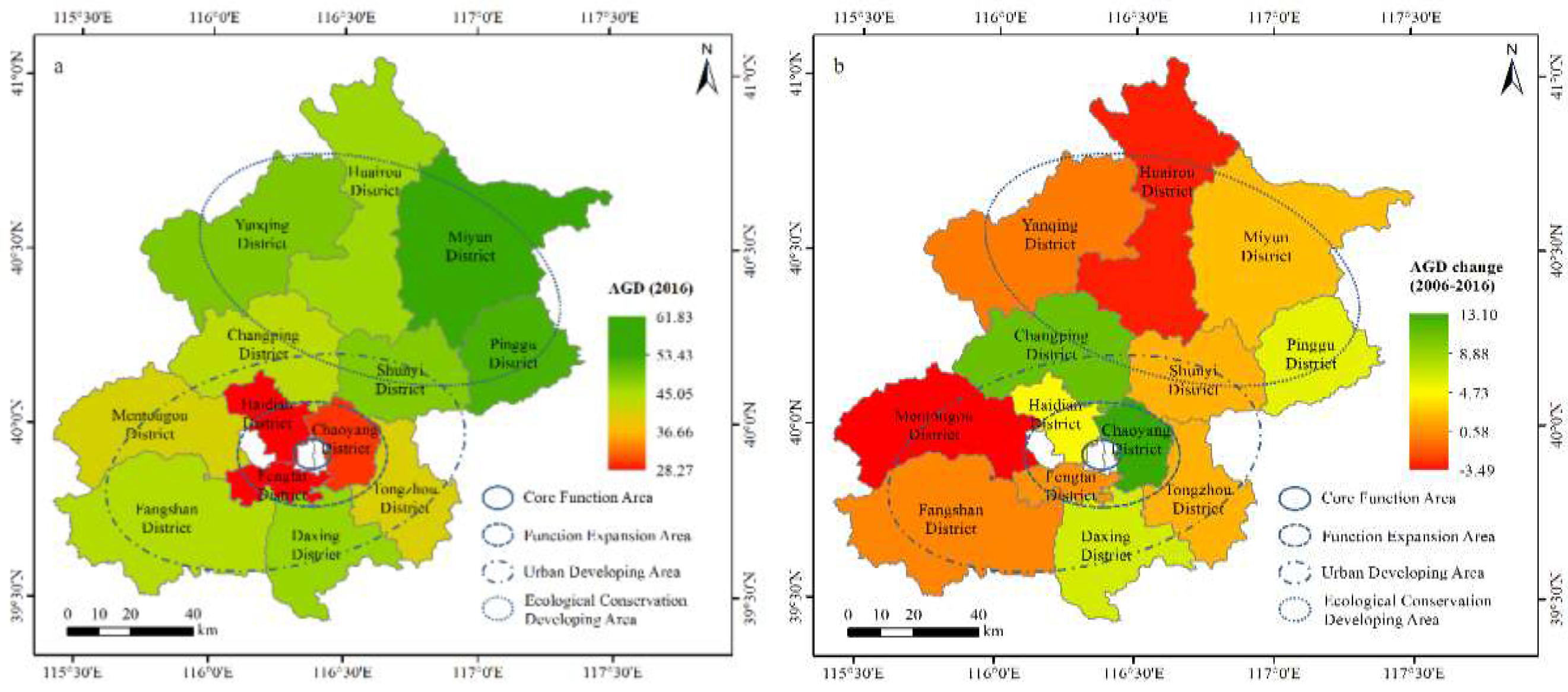
4.5. Temporal and Spatial Variations of AGD in Beijing ECDA
5. Discussion
5.1. Poor Infrastructure Hindering Development of Green Agricultural Industries
5.2. Slow Improvement of Agritourism Quality Affecting AGD in ECDA
5.3. Low Labor Productivity Hampering AGD in ECDA
5.4. Low Resource Utilization Efficiency Restricted AGD in ECDA
6. Conclusion and Corresponding Policy Recommendations
6.1. Effectiveness of the Selected AGD Indicators and Evaluation Method in Beijing
6.2. AGD Level Presented Obvious Heterogeneous Characteristics of Spatial and Temporal Characteristics on District Level for Beijing
6.3. Corresponding Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gibbs, D.; Longhurst, J. Sustainable development and environmental technology: A comparison of policy in Japan and the European Union. Environmentalist 1995, 15, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, X.; Liao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Ye, Y.; Wang, Y. Modeling the optimal ecological security pattern for guiding the urban constructed land expansions. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 19, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Yao, G.; Liu, G. Spatial evaluation of the ecological importance based on GIS for environmental management: A case study in Xingguo county of China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 51, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lu, Z.; Li, F.; Crittenden, J.C. Analyzing spatio-temporal changes and trade-offs to support the supply of multiple ecosystem services in Beijing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, E.; Linnerud, K.; Banister, D. The imperatives of sustainable development. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 25, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Program (UNEP). Guidelines for AEO Cities Integrated Environmental Assessment and Report. United Nations Environment Program (UNEP, 2005; pp. 52–143. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Program (UNEP). Green Economy: Cities Investing in Energy and Resource Efficiency. 2011. Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/handle/20.500.11822/7979.
- Bolcárová, P.; Kološta, S. Assessment of sustainable development in EU 27 using aggregated SD index. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cracolici, M.F.; Cuffaro, M.; Lacagnina, V. Assessment of sustainable well-being in the Italian Regions: An Activity Analysis Model. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 143, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Hu, Z.; Yao, Q. Comprehensive evaluation and proposals about the development of green industry in Fujian Province. Log. Eng. Manage. 2014, 36, 136–139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, X. Metro construction risk assessment based on PPC-D-S evidence theory. Mod. Tunn. Technol. 2021, 58, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Bai, Z.; Ma, W.; Guo, M.; Jiang, R.; Liu, J.; Oenema, O.; Velthof, G.L.; Whitmore, A.P.; Crawford, J.; et al. Exploring future food provision scenarios for China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Ministry of AgricultuFre and Rural Affairs (MARA). 2021. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-09/07/5635867/files/737ff96c0cc74f788394eb6194cc44c6.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Nandy, S.; Singh, C.; Das, K.K.; Kingma, N.C.; Kushwaha, S.P.S. Environmental vulnerability assessment of eco-development zone of Great Himalayan National Park, Himachal Pradesh, India. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S. Spatial correlation and influencing factors of agricultural green development in China. Commercial Sci. Res. 2018, 6, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Li, X. Analysis of spatial heterogeneity of green agricultural production level: Based on empirical data of Shandong province from 2010 to 2019. Rev. Econ. Manage. 2021, 37, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lv, J. The comprehensive evaluation of agricultural green development level and analysis of its obstacle factors in Gansu Province. Terri. Nat. Resour. Stud. 2022, 22, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J. Evaluation of agricultural green development level in Henan Province based on close value method. Shanxi Agric. Econ. 2022, 14, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Duan, L. Identification of driving factors and performance evaluation of Zhejiang agricultural green development. Chinese, J. Agric. Resour. Region. Plan. 2022, 43, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, A.; Yue, Y.; Cao, S. Comprehensive evaluation of green agricultural development level in Guangxi. J. Guangxi Agric. 2022, 37, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y. Evaluation and regional difference analysis of agricultural green development level in Bohai Rim Region. J. Agric. Resour. Region. Plan. 2022. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3513.S.20220318.1604.028.html.
- Zha, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y. Evaluation of agricultural green development level in the Yellow river. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Region. Plan. 2022, 1, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J. Evaluation, regional difference analysis and optimization path of agricultural green development in Yangtze River Economic Belt. Rural Econ. 2021, 12, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X. Study on measurement and enhancement path of the level of the agricultural green development: An empirical example from 11 Cities in the Pearl River-West River economic belt. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 38, 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.C.; Zhou, L.D.; Sun, D.F.; Li, H.; Yu, M. Proposal for developing carbon sequestration economy in ecological conservation area of Beijing. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 524, 3424–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Xiong, N.; Chen, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; An, L. Analysis of Ecological Blockage Pattern in Beijing Important Ecological Function Area, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jogo, W.; Hassan, R. Balancing the use of wetlands for economic well-being and ecological security: The case of the Limpopo wetland in southern Africa. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Evaluation and spatial difference of agricultural green development level in the Yellow River basin based on entropy weight-TOPSIS. Hubei Agr. Sci. 2022, 61, 230–236. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Q.; Ning, L. Ecological security evaluations of the tourism industry in ecological conservation development areas: A case study of Beijing's ECDA. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Chen, M.X.; Tang, Z.P.; Liu, W.; Lu, D.; Zhang, Y. The “valley economy” model of regional development: A case study of mountain areas in Beijing, Northern China. J. Mt. Sci. 2014, 11, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Ouyang, Z.; Kong, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; He, W.; Yang, S. Policy evolution of green agricultural development in the United States and its enlightenments to China. Agr. Outlook. 2022, 18, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xin, Z.; He, W.; Lin, Q.; Yang, X.; Kong, L.; Ouyang, Z. Status quo of agricultural green development policy in Netherlands and its enlightenments to China. Agr. Outlook. 2022, 18, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Yu, H.; Zhou, J. Sustainable agriculture development under the green perspective in Japan: Paths, results and policy inspirations. Chinese J. Eco-Agr. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Huang, Y. Construction and empirical analysis of evaluation indicator system of agricultural green development in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Agr. Outlook 2022, 18, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Yang, P.; Zheng, S. Evaluation of green development level of agriculture in Yangtze River Delta. J. Anhui Univ. Sci. Tech. 2022, 24, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, Y.; Zhao, G.; Jiang, Y. Comprehensive evaluation of the green development level of agriculture in Tianjin. J. Chinese Agr. Mech. 2021, 42, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cui, S.; Ma, L.; Ma, W.; Wei, J. Temporal and spatial characteristics of agricultural green development indicators in counties of Hebei Province. Chinese J. Eco-Agri. 2020, 28, 1168–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Ma, W.; Ma, L.; Ding, S.; Zhao, H. Spatial and temporal characteristics of agricultural green development indicators in Hainan Island. Chinese J. Eco-Agri. 2020, 28, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X. Promoting Agriculture Green Development to realize the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation. Front. Agr. Sci. Eng. 2020, 7, 112–113. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.; Li, F.; Wang, S.; Hao, A. The concept, connotation and principle of agricultural green development in China. Chinese J. Agri. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2021, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L. The influence of the Sci-Tech finance ecosystem on technological innovation from symbiotic perspective. Syst. Eng. 2021, 39, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Mu, L.; Zhao, Y. Research on evaluation and countermeasures of regional green industry development. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 33, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Gai, M.; Yang, Q.; He, Y. Spatiotemporal changes and influencing factors of agricultural green development level in main grain producing areas in Northeast China. Resour. Sci. 2022, 44, 927–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hu, X. Evaluation of agricultural green development in main grain producing counties of Sichuan Province. Agr. Outlook. 2022, 18, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Feng, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, Q. Time variation characteristics of county agricultural green development index in Jilin Province-take Lishu County as an example. Chinese J. Eco-Agr. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Wang, L. Study on agricultural green development efficiency and influencing factors based on unexpected output model-taking 11 cities in Hebei Province as an example. Innov. Sci. Tech. 2021, 21, 80–88. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J. Construction and empirical research on county agricultural green development index—Based on county cross-sectional data of Hubei Province in 2017. Jiangsu Agr. Sci. 2021, 49, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Yu, C.; Li, S.; Zhong, Z.; He, Y. A comprehensive assessment of agricultural green development at the county level on the Tibetan plateau-a case study in Bailang County. Chinese J. Agri. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, A. Evaluation of agricultural green development level and obstacle factor analysis in Gansu Province. Terr. Nat. Resour. Stud. 2023, 1, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Wang, W. Spatial heterogeneity of manufacturing development quality in China: Analysis based on projection pursuit model. East China Econ. Manag. 2020, 34, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petridis, K.; Drogalas GZografidou, E. Internal auditor selection using a TOPSIS/nonlinear programming model. Ann. Oper. Res. 2021, 296, 513–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neogi, D. Performance appraisal of select nations in mitigation of COVID-19 pandemic using entropy based TOPSIS method. Cien. Saude. Colet. 2021, 26, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z. Evaluation of agricultural extension service for sustainable agricultural development using a hybrid entropy and TOPSIS method. Sustain. 2021, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Qahmash, A. Implementing fuzzy AHP and FUCOM to evaluate critical success factors for sustained academic quality assurance and ABET accreditation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zizovic, M.; Pamučar, D. New model for determining criteria weights: Level based weight assessment (LBWA) model. Decis. Ma. Appl. Manage. Eng. 2019, 2, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Projection pursuit technology (PPT) and its progress of application. Nat. Mag. 1997, 19, 224–227. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Zhao, X. Principle and Application of Projection Pursuit Model; Science Press: Beijing, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.; Cook, D.; Klinke, S.; Lumley, T. Projection pursuit for exploratory supervised classification. J. Comput. Graph. Statist. 2005, 14, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochowski, M.; Duch, W. Projection Pursuit Constructive Neural Networks Based on Quality of Projected Clusters, in: International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin, 2008; pp. 754–762. [Google Scholar]
- Grear, T.; Avery, C.; Patterson, J.; Jacobs, D.J. Molecular function recognition by supervised projection pursuit machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Q. Evaluation of water and land resources system bearing capacity and path optimization for rural revitalization. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Liu, D.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Y.; Wu, C. Evaluation model of water resources carrying capacity based on projection pursuit weight optimization. Water Resour. Prot. 2021, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T. Agriculture Tourism and the Transformation of Rural Countryside. Tour. Geogr. 2018, 20, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unite States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Farm Security and Rural Investment Act of 2002. Available online: https://www.fns.usda.gov/pl-107-171 (accessed on 9 May 2023).
- He, W.; Ouyang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Lin, Q.; Kong, L.; Liu, X. Current situation and characteristics of green agricultural development in Japan and its enlightenments to China. Agr. Outlook. 2022, 6, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
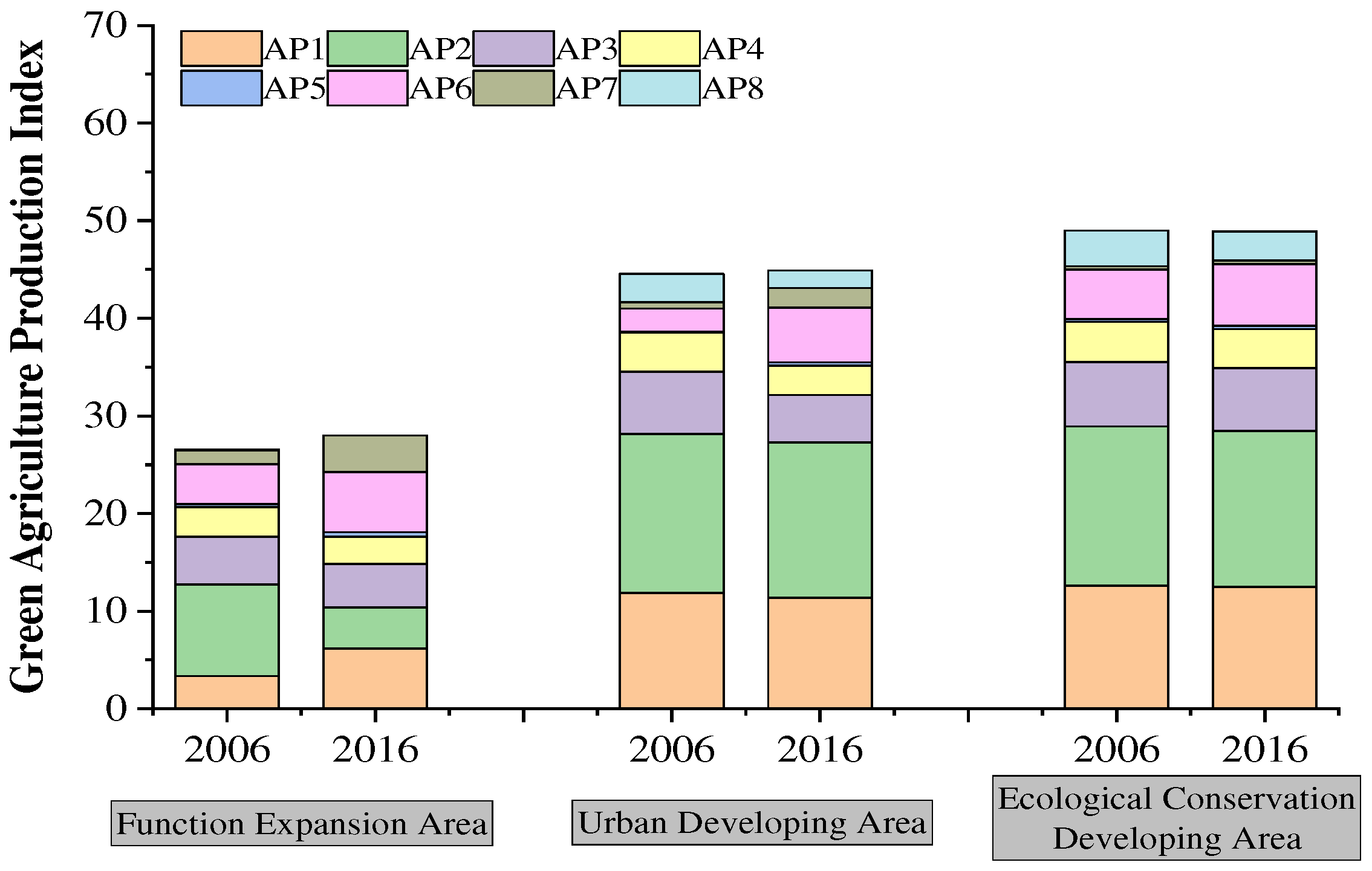
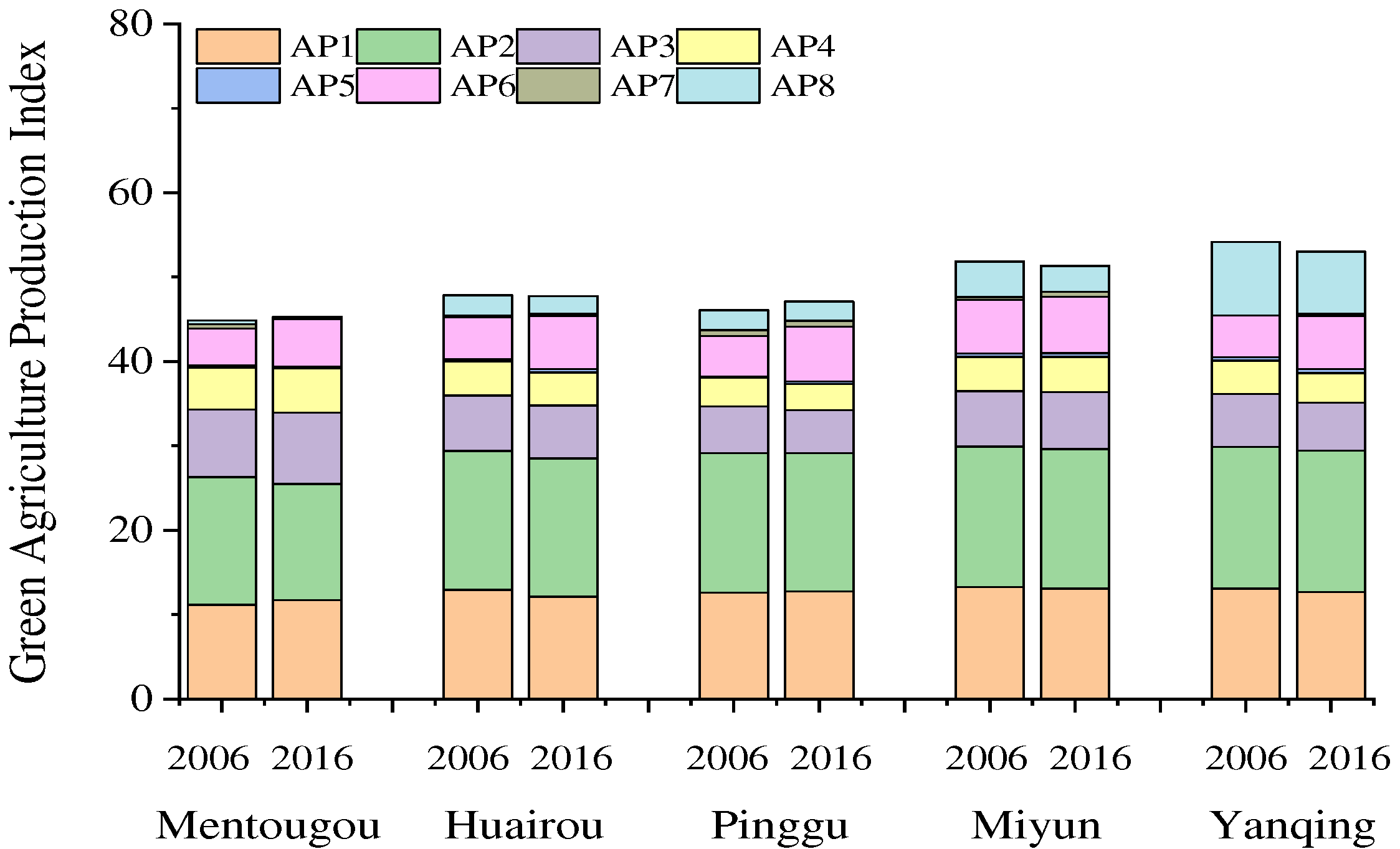
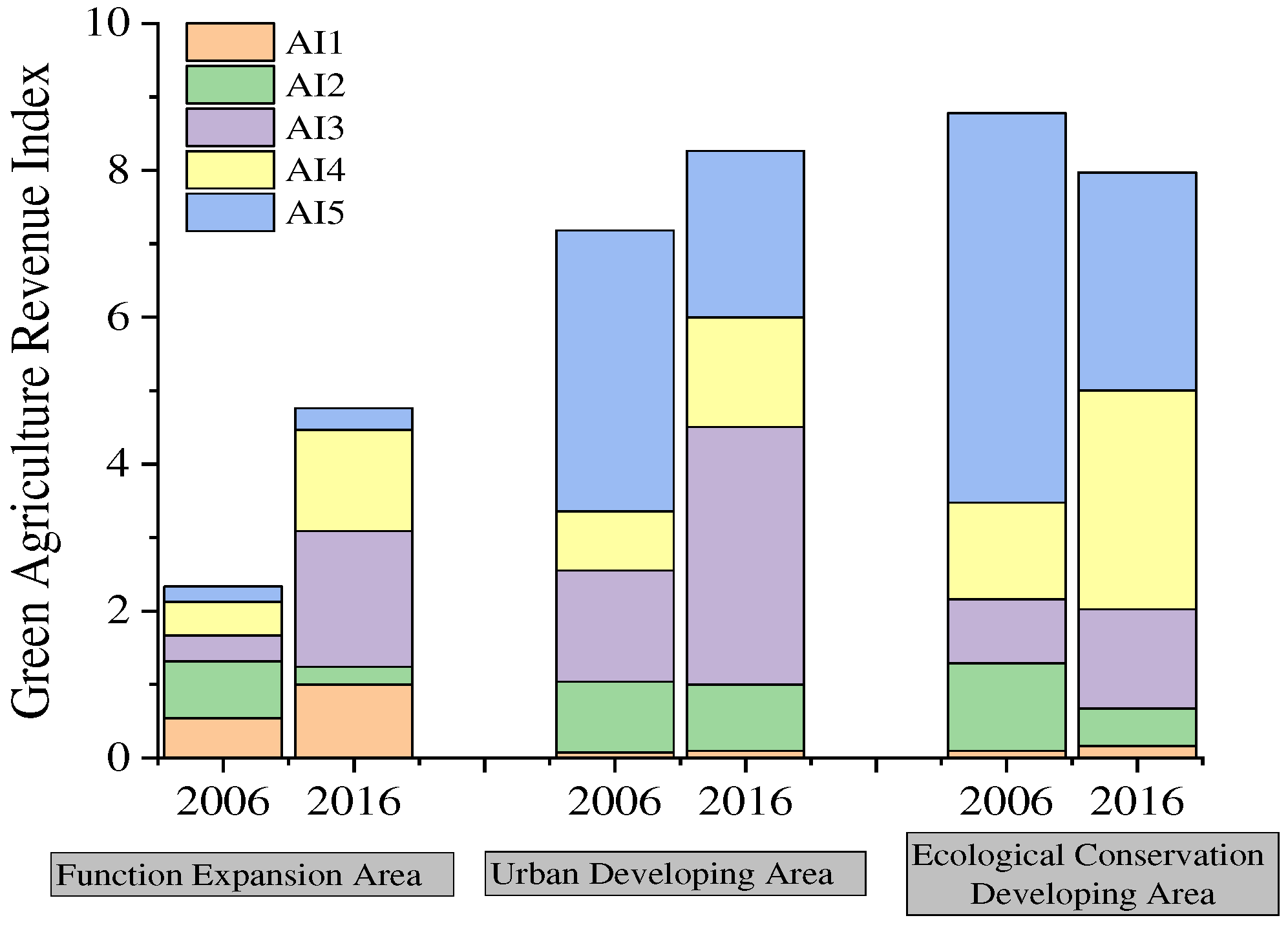
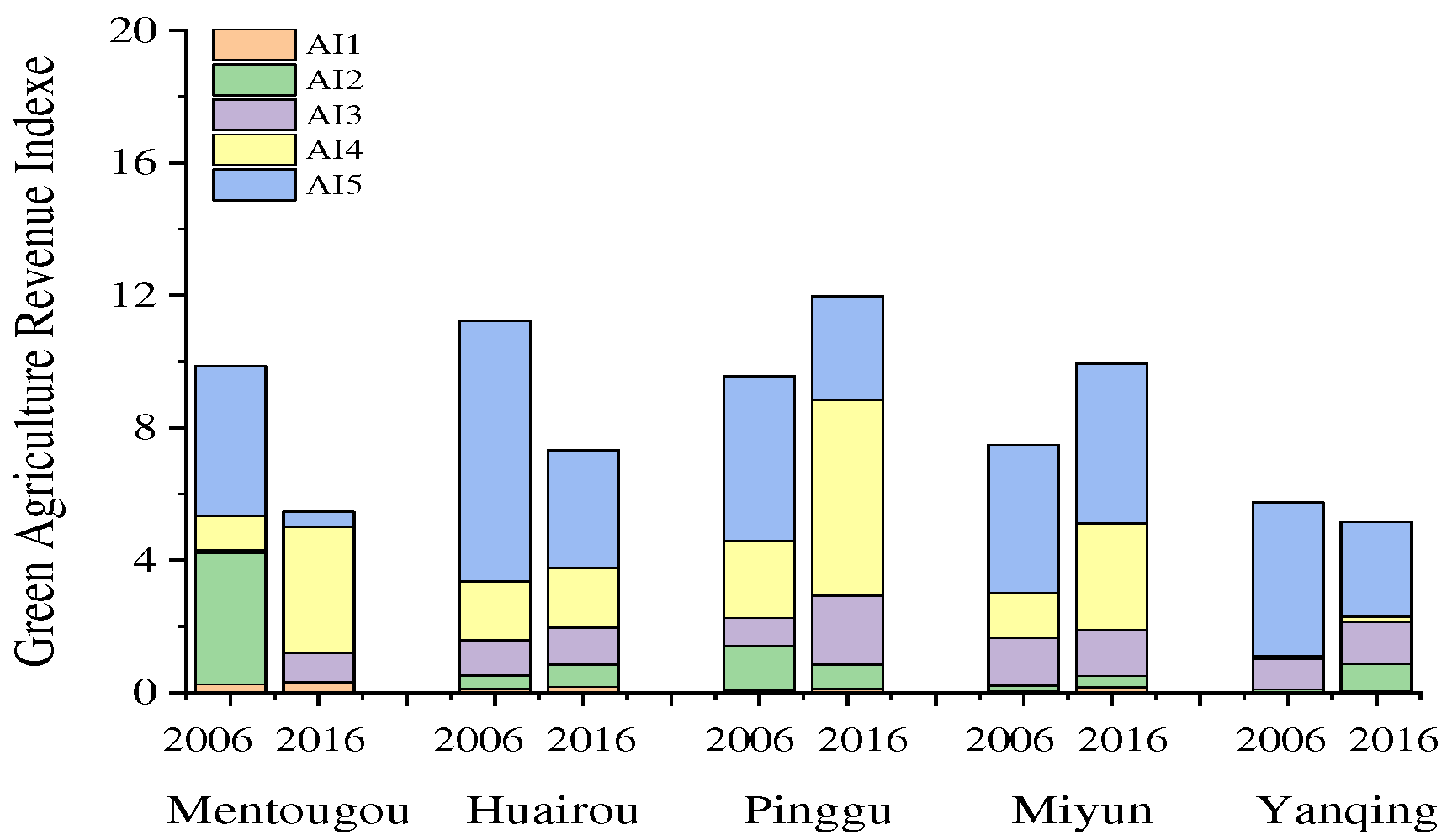
| Evaluation Layer | Index | Type | Unit | Weight Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green agricultural production 2.08 |
AP1: energy consumption per unit of gross agricultural output value | Negative | 1000 tons of standard coal/1000 yuan | 0.4220 |
| AP2: energy consumption per unit of arable land area | Negative | 1000 tons of standard coal/ha | 0.5329 | |
| AP3: fertilizer usage per unit of sown area | Negative | ton/ha | 0.2753 | |
| AP4: fertilizer usage per unit of gross agriculture output value | Negative | kg/1000 Yuan | 0.1711 | |
| AP5: water consumption per unit of arable land area | Negative | ton/ha | 0.0169 | |
| AP6: water consumption per unit of gross agricultural output value | Negative | m3/1000 Yuan | 0.2239 | |
| AP7: proportion of facility agriculture area in arable land area | Positive | % | 0.1530 | |
| AP8: arable land area per capita | Positive | Ha/capita | 0.2809 | |
| Green agricultural revenue 1.10 |
AI1: proportion of agritourism revenue in gross agricultural output value | Positive | % | 0.0695 |
| AI2: proportion of seed industry revenue in gross agricultural output value | Positive | % | 0.2040 | |
| AI3: agricultural labor productivity | Positive | 1000 yuan/capita | 0.2314 | |
| AI4: agricultural output value per unit of arable land area | Positive | 10 million yuan/ha | 0.3428 | |
| AI5: proportion of fixed asset investment in rural areas | Positive | % | 0.2503 |
| Ranking | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | AP7 (8.35) | AI1 (8.06) | AI3 (7.85) | AI2 (7.43) | AI4 (7.38) | AP3 (6.27) |
| 2007 | AP7 (8.50) | AI1 (8.05) | AI3 (7.82) | AI2 (7.58) | AI4 (7.38) | AP3 (6.87) |
| 2008 | AP7 (8.47) | AI1 (8.04) | AI3 (7.83) | AI2 (7.58) | AI4 (7.33) | AP3 (6.76) |
| 2009 | AI1 (8.13) | AP7 (8.07) | AI3 (7.84) | AI4 (7.25) | AI2 (7.16) | AP3 (6.76) |
| 2010 | AP7 (8.68) | AI1 (8.17) | AI3 (7.80) | AI2 (7.32) | AI4 (7.14) | AP3 (6.93) |
| 2011 | AP7 (9.02) | AI1 (8.36) | AI3 (7.80) | AI2 (7.75) | AI4 (6.96) | AP3 (6.49) |
| 2012 | AP7 (9.18) | AI1 (8.22) | AI3 (8.05) | AI2 (7.76) | AI4 (6.99) | AP5 (6.41) |
| 2013 | AP7 (9.57) | AI1 (8.21) | AI3 (8.10) | AI2 (7.71) | AP5 (7.67) | AP8 (6.46) |
| 2014 | AP7 (10.08) | AI3 (8.41) | AI1 (8.09) | AI2 (7.53) | AP5 (7.47) | AI4 (6.75) |
| 2015 | AP7 (10.74) | AP5 (8.43) | AI3 (8.32) | AI1 (8.31) | AI2 (7.62) | AP4 (7.10) |
| 2016 | AP7 (11.26) | AI3 (9.15) | AI1 (8.39) | AP5 (8.07) | AI2 (7.81) | AP4 (7.25) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




