Submitted:
17 October 2023
Posted:
17 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Targets Recognition for Plant Protection
2.1. Plant Diseases
2.2. Plant Insects
2.3. Rats and Rabbits
2.4. Harmful Plants
2.5. Indirect Targets
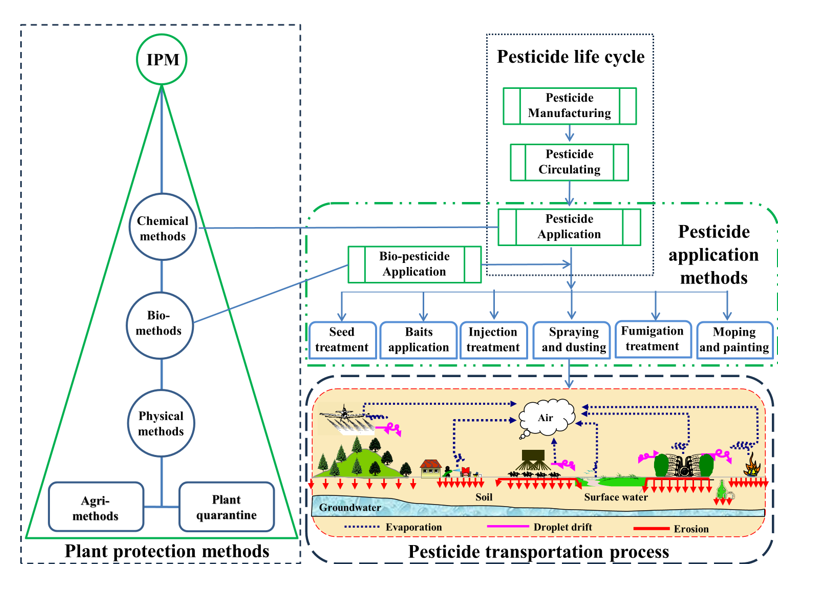
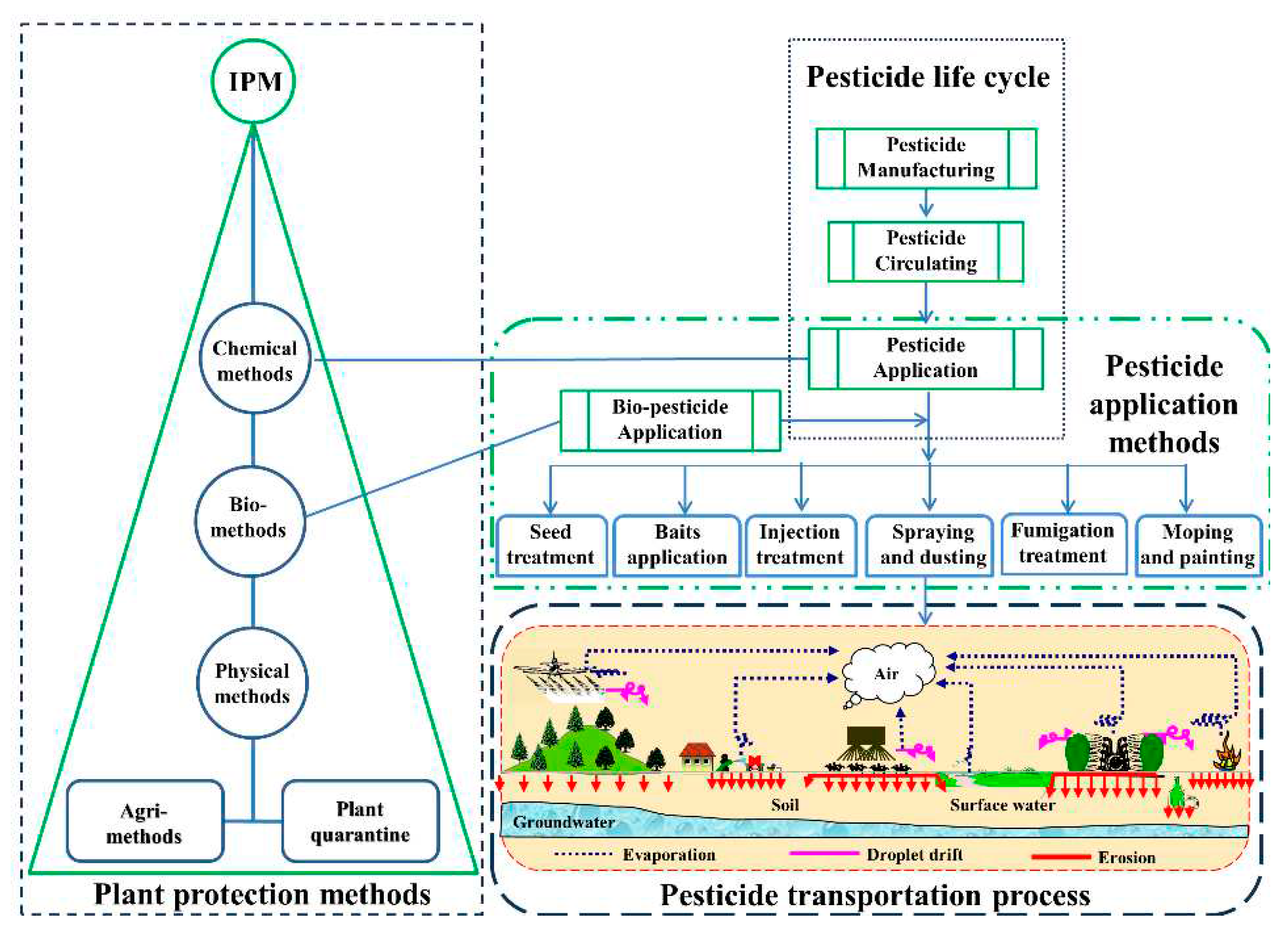
3. Development of Plant Protection Methods
3.1. Agricultural Practice Methods
3.1.1. Row Intercropping to Defeat the Pests
3.1.2. Crops Rotation
3.1.3. Managing Soil Moisture and Fertility
3.1.4. Trimming and Bridge-Grafting
3.1.5. Seed and Seedling Treatments
3.1.6. Field ecological construction
3.2. Physical Methods
3.2.1. Mechanical Measures to Control Pests
3.2.2. Trapping/Killing Insects via Insect Behaviors
3.2.3. Barrier Isolation of Pests
3.2.4. Electromagnetic Control of Pests
3.2.5. Intense Heat Treatment of Pests
3.2.6. Radiation Suppression and Killing of Pests
3.3. Bio-Methods
3.3.1. Natural Enemy Predating
3.3.2. Natural Enemy Parasitizing
3.3.3. Bio-Pesticides Application
3.3.4. Plant Immunization
3.3.5. Pheromone Interference
3.3.6. Gene-Driven Operation
3.4. Chemical Methods
3.4.1. Pesticide Spraying
3.4.2. Pesticide Fumigation
3.4.3. Pesticide Injection
3.4.4. Pesticide Mopping and Painting
3.4.5. Baits Application
3.4.6. Seed and Seedling Treatments
3.5. Plant Quarantine
3.5.1. Interruption in Pests Proliferation
3.5.2. Quarantine Inspection in Original Planting Area
3.5.3. Epidemic Source Investigation and Inspection
3.5.4. Epidemic Area Control
3.5.5. Virus-Free Plant Breeding
3.5.6. Disinfestation of Plant Quarantine Objects
3.6. Integrated Pest Management
3.6.1. Timely Pests Control
3.6.2. Managing Plant Population
3.6.3. Food Chain Regulation on Plants-Pests-Natural Enemies
3.6.4. Customized Cultivation of Resistant Plants
3.6.5. Continuous Comprehensive Pests Treatments
3.6.6. Plant-Centered Prevention and Control Philosophy
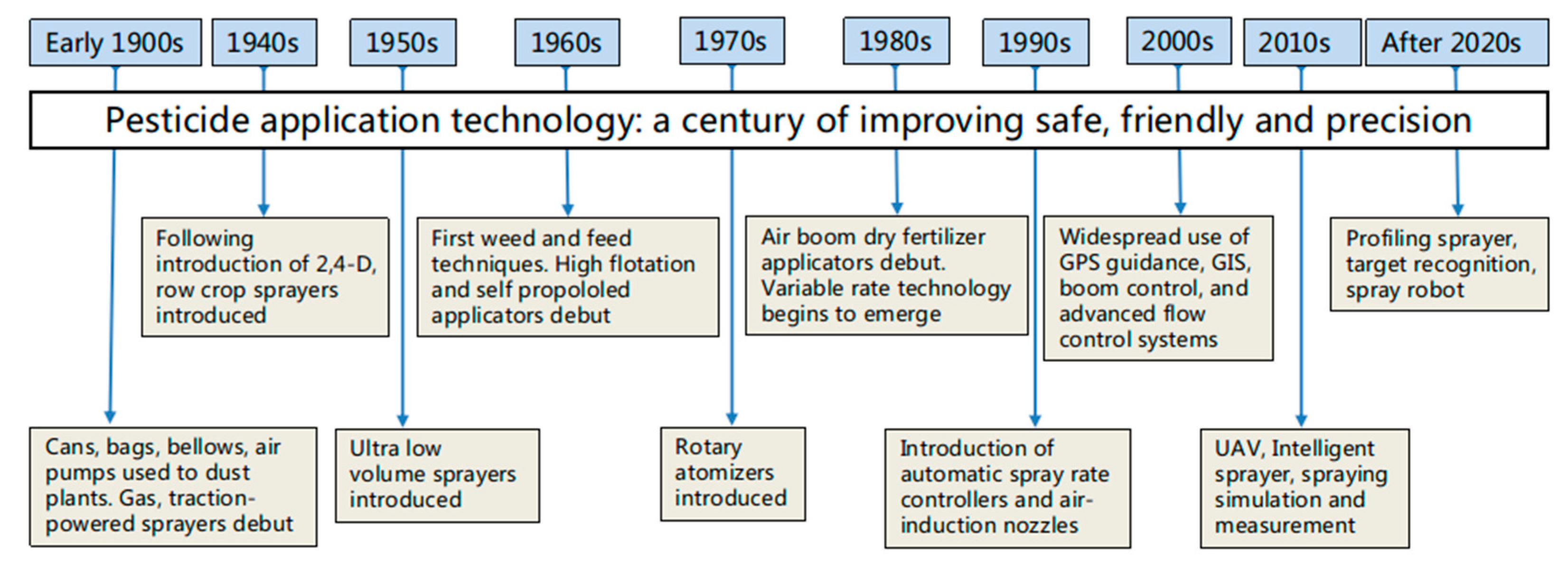
4. Advances in Pesticide Application Technology
4.1. Pesticide Spraying Machinery
4.2. Pesticide Fumigation Technique
4.3. Pesticide Injection Application Measures
4.4. Pesticide Mopping and Painting Measures
4.5. Baits Application Technique
4.6. Seed and Seedling Enhancement Technology
5. Key Technologies for Pesticide Spraying System
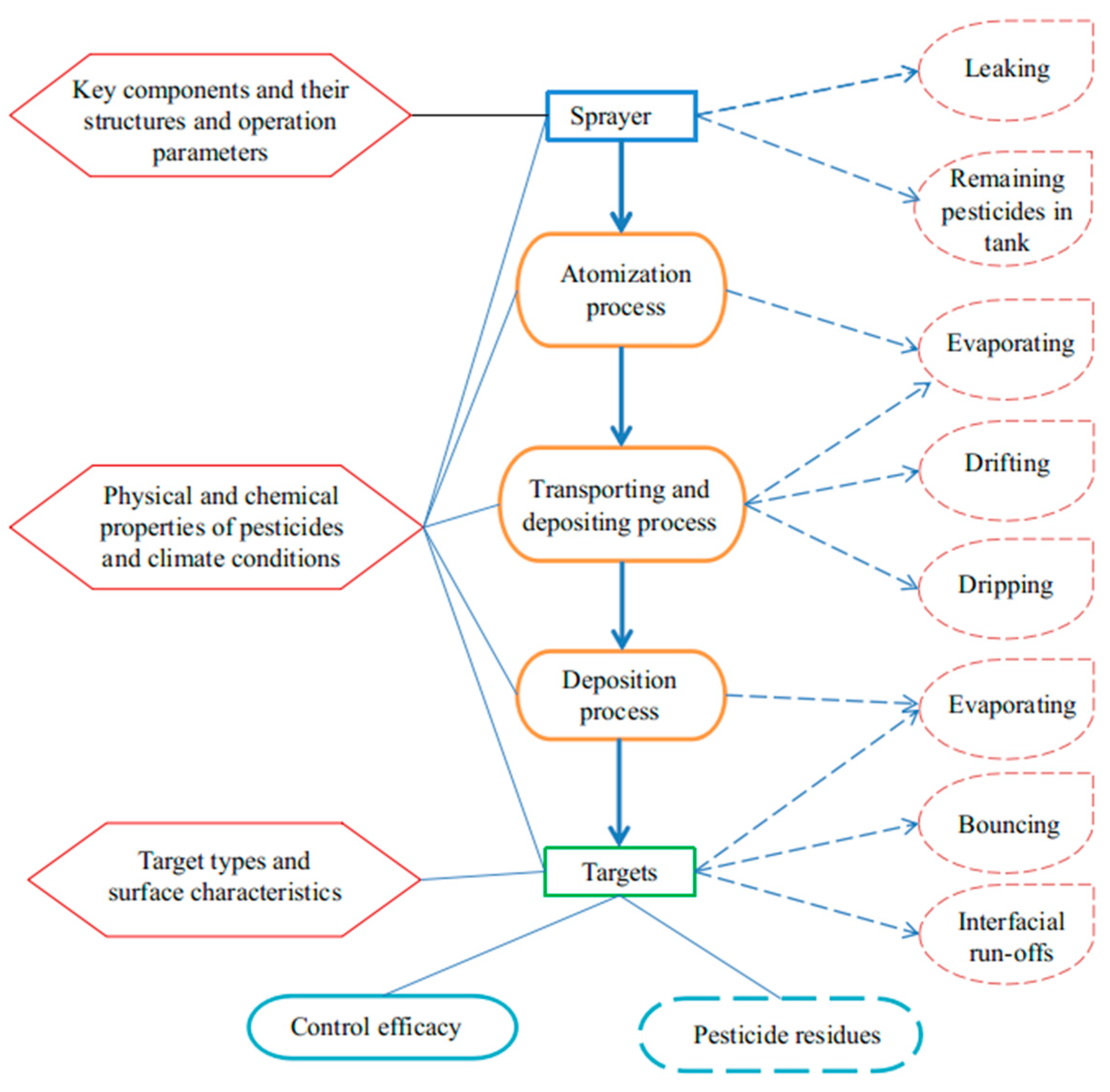
5.1. Pesticide Spraying Process and 3R/3E/3M Analysis
5.2. Key Components of Pesticide Sprayers
5.2.1. Atomizing Nozzles and Nozzle Wear
5.2.2. Variable Rate Control System
5.2.3. Direct Injection System and Inline Mixing
5.2.4. Droplet Drift Control
5.2.5. Spray Boom and Boom Balance
5.2.6. Profiling Spraying Mechanism
5.2.7. Flexible Sprayer Chassis
5.3. Performance Measurement of Pesticide Spraying Process
5.3.1. Measurements in Atomization Process
5.3.2. Measurements in Droplet Transporting and Depositing Process
5.3.3. Measurements in Deposition Process
5.4. Simulation and Modeling of Pesticide Spraying
5.4.1. Simulation and Modeling of Pesticide Atomization Process
5.4.2. Simulation and Modeling of Pesticide Transporting and Depositing Process
5.4.3. Simulation and Modeling of Pesticide Deposition Process
5.5. Measurements and Analysis of Pesticide Spraying Efficacy
6. Summary and Future Research Suggestions
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, J.; Zhou, H.; Xu, Y. Precision Pesticide Application Technique; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, Q. Advances and Prospects of Target Recognition Techniques for Forest Pest Control at Home and Abroad. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 2023, 59, 152–166. [Google Scholar]
- Venkataraman, S.; Badar, U.; Shoeb, E. An inside look into biological miniatures: molecular mechanisms of viroids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhen, Z. Research progress in the spread of Phytoplasma and PCR detection in forest trees. Forestry and Ecological Sciences 2021, 36, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yin, Y.; Wu, Y. Regular LAMP and fast LAMP for the detection of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri. Plant Protection 2013, 39, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, R.; Fei, X.; Li, M. Development of CRISPR/Cas-based detection method and its application in plant pathogens. Plant Quarantine 2021, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kim. S.; Lee, W.; Lim, C. et al. Hyperspectral analysis of pine wilt disease to determine an optimal detection index. Forests 2018, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.; Scherm, H.; Serman, N. Ground penetrating radar to detect and quantify residual root fragments following peach orchard clearing. HortTechnology 2005, 15, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susaeta, A.; Soto, J.; Adams, D. , et al. Expected timber-based economic impacts of a wood-boring beetle (Acanthotomicus Sp.) that kills American Sweetgum. J Econ Entomol 2017, 110, 1942–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineza, A.; Fischbeina, D; Villacidea, J. et al. 2019.Trapping success and flight behavior of two parasitoid species of the woodwasp sirex noctilio. Biological Control 2019, 134, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Luo, Y. , et al. Small object detection for infected trees based on the deep learning method. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 2021, 57, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Cui, J. Early recognition of feeding sound of trunk borers based on artificial intelligence. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 2021, 57, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wilschut, L.; Heesterbeek, J.; Begon, M. Detecting plague-host abundance from space: Using a spectral vegetation index to identify occupancy of great gerbil burrows. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2018, 64, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Qu, Y. Comparative test on different prevention and control measures of rabbit harm in region of western Liaoning Province. Protection Forest Science and Technology 2020, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; Cheng, X.; Dong, Y. Analysis of the activity rhythms of the great gerbil (Rhombomys opimus) and its predators and their correlations based on infrared camera technology. Global ecology and conservation 2020, 24, e01337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, Q. Development of plant protection machinery at home and abroad and prospects of intelligent integrated pest management system. China Plant Protection 2022, 42, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmudul Hasan, A.; Ferdous, S.; Dean, D. A survey of deep learning techniques for weed detection from images. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2021, 184, 106067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, B. Real-time mosaicing system and distance detection based on dynamic tree image sequence. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 2014, 50, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, C.; Mohammed, C. Application of remote sensing technologies for assessing planted forests damaged by insect pests and fungal pathogens: a review. Current Forestry Reports 2017, 3, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, H. , et al. Online measurement of tree crown volume using vehicle-borne 2-D Laser scanning. Trans. of the CSAM 2016, 47, 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- Xavier, T.; Souto, R.; Statella, T.; Galbieri, R.; Santos, E.; Suli, G.; Zeilhofer, P. Identification of Ramularia Leaf Blight Cotton Disease Infection Levels by Multispectral, Multiscale UAV Imagery. Drones 2019, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, R. Silent Spring; Holybird Publishing, 1962.
- Bargués-Ribera1, M.; Gokhale, C. . Eco-evolutionary agriculture: a study in crop rotations. bioRxiv, Aug. 2018, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wyk, A.; Van Staden, E.; Nel, W.; Prinsloo, G. The feasibility of bridge-grafting to restore the flow of sucrose in girdled Ocotea bullata and Curtisia dentata medicinal trees. South African Journal of Botany 2019, 123, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaim, N.; Tan, H.; Rahman, S.; et al. Recent Advances in Seed Coating Treatment Using Nanoparticles and Nanofibers for Enhanced Seed Germination and Protection. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, S. Technical development on mechanized control of locust. Trans. CSAM 2005, 36, 171–173. [Google Scholar]
- Bhusal, S.; Khanal, K.; Goel, S.; et al. Bird deterrence in a vineyard using an unmanned aerial system (UAS). Trans. of the ASABE 2019, 62, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X. The effect of ultrasound-stress on physiology and biochemistry and feeding behavior of Monochemus alternatus. Hope. Thesis, for Master, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kshetri, S.; Jiken, J.; Steward, B.; et al. Investigating the effects of interaction of single-tine and rotating -tine mechanisms with soil on weeding performance using simulated weeds. Trans. of the ASABE 2019, 62, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, D.; Lu, X.; Wang, X. Optimization of leg structure parameter of quadruped laser weeding robot. Trans. of the CSAE 2020, 36, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda, M.; Honda, K. Insect reactions to light and its applications to pest management. Applied Entomology and Zoology 2013, 48, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Lin, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Control effects of fly nets to the pests of vegetables in greenhouses. Plant Protection 2013, 39, 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Feat, A.; Federle, W.; Kamperman, M.; van der Gucht, J. Coatings preventing insect adhesion-An overview. Progress in Organic Coatings 2019, 134, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xue, S.; Chen, J.; et al. Parameter optimization on killing aphid by using high-voltage electrostatic discharge. Trans. of the CSAE 2013, 29 (Supp.1), 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, F.; Wayland, J.; Merkle, M. Ultrahigh frequency electromagnetic fields for weed control: phytotoxicity and selectivity. Science 1971, 173, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Ehsani, R.; Zheng, J.; Xu, L.; Zhou, H.; Ding, R. Heating characteristics and field control effect of rapid citrus huanglongbing steam heat treatment. Trans. of the CSAE 2017, 33, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, G.; Chen, H.; Wen, S.; Yin, X.; Deng, X. Experiment on Temperature Field Distribution Characteristics of Citrus HLB Far Infrared Heat Treatment. Trans. of the CSAM 2019, 50, 175–188. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Tang, J. Radio frequency and microwave alternative treatments for insect control in nuts: a review. Agricultural Engineering Journal 2001, 10, 105–120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, S.; Wang, G. Research on Microwave Control of Stem Borer Pests. Chinese Landscape Architecture 1988, 4, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Rahi, G.; Rich, J. Potential of microwaves to control plant-parasitic nematodes in soil. Journal of Microwave Power & Electromagnetic Energy 2008, 42, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gaetani, R.; Lacotte, V.; Dufour, V.; et al. Sustainable laser based technology for insect pest control. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 11068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, P. Inactivation of Tilletia controversa Kuhn by Cobalt 60- γ radiation. Plant Quarantine 1993, 7, 267–268. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Z.; Zuo, C. Report of Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle to Release Trichogramma. Chinese Journal of Biological Control 2013, 29, 455–458. [Google Scholar]
- Bzowska-Bakalarz, M.; Bulak, P.; Bere, P.; et al. Using gyroplane for application of Trichogramma spp. Against the European corn borer in maize. Pest Management Science 2020, 76, 2243–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, P.; Khelifi, M.; Dionne, A.; et al. Technical feasibility of spraying Trichogramma ostriniae Pupae to control the European corn borer in sweet corn crops. Applied Engineering in Agriculture 2019, 35, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, L.; Ownley, B. Can we use entomopathogenic fungi as endophytes for dual biological control of insect pests and plant pathogens? Biological Control 2018, 116, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fife, J.; Derksen, R.; Ozkan, H. E.; et al. Evaluation of a contraction flow field on hydrodynamic damage to entomopathogenic nematodes-a biological pest control agent. Biotechnology & Bioengineering 2010, 86, 96–107. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, E.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, H.; Ru, Y.; Li, J. Effects of flat-fan nozzle wear on application of microbial pesticides. Journal of Forestry Engineering 2018, 3, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Yang, S.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y. Plant immunity inducers: from discovery to agricultural application. Stress Biology 2022, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abid, I.; Laghfiri, M.; Bouamri, R.; et al. Integrated pest management (IPM) for Ectomyelois ceratoniae on date palm. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health 2021, 19, 100219. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Shen, Z.; Fang, M.; et al. Application effect of sex pheromone disorientation on prevention and control of Grapholitha molesta Busck in yellow peach orchard. China Plant Protection 2020, 40, 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Nong, W.; Wang, F. Broad-spectrum pheromone appear in the insect repellent world. China Science Daily 2019-02-12.
- Yu, M.; Tang, H.; Ye, X. Progresses on Wheat Improvement by Using Transgenic and Genome Editing Technologies. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources 2023, 24, 102–116. [Google Scholar]
- Stejskal, V.; Vendl, T.; Aulicky, R.; Athanassiou, C. Synthetic and Natural Insecticides: Gas, Liquid, Gel and Solid Formulations for Stored-Product and Food-Industry Pest Control. Insects 2021, 12, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; An, Y.; Qian, L.; Yang, X.; Xu, M.; Wu, C.; Wei, C.; Niu, L.; Gan, Y. Development and application of quarantine insect DNA barcoding technology. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology 2015, 52, 382–389. [Google Scholar]
- National Forestry and Grassland Administration. Technical rules for producing site quarantine of forestry plants. LY/T 1829-2020, The People's Republic of China.
- Van Maanen, A.; Xu, X. Modelling plant disease epidemics. European Journal of Plant Pathology 2003, 109, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture. Regulations on Plant Quarantine. The People's Republic of China,1992.
- Panattoni, A.; Luvisi, A.; Triolo, E. Review. Elimination of viruses in plants: twenty years of progress. Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research 2013, 11, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Overbeek, L.; Runia,W. ; Kastelein, P.; Molendijk, L. Anaerobic disinfestation of tare soils contaminated with Ralstonia solanacearum biovar 2 and Globodera pallida. Eur J Plant Pathol 2014, 138, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguine, J.; Aubertot, J.; Flor, R.; Lescourret, F.; Wyckhuys, K.; Ratnadass, A. Integrated pest management: good intentions, hard realities. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development 2021, 41, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ouyang, F.; Ge, F. Quantitative evaluation and case analysis of the economic and ecological benefits of integrated pest control. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology 2020, 57, 206–213. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.; Lumactud, R.; Li, N.; Bell, T.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Lee, Y. Harnessing Chemical Ecology for Environment-Friendly Crop Protection. Phytopathology 2021, 111, 1697–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matteo, D.; Gudrun, S.; Jochen, K.; Ingolf, S. Complementarity among natural enemies enhances pest suppression. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaba, S.; Lescourret, F.; Boudsocq, S.; Enjalbert, J.; Hinsinger, P.; Journet, E.; Navas, M.; Wery, J.; Louarn, G.; Malézieux, E.; Pelzer, E.; Prudent, M.; Ozier-Lafontaine, H. Multiple cropping systems as drivers for providing multiple ecosystem services from concepts to design. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.R.; Pickett, J.A.; Van den Berg, J.; Wadhams, L.J.; Woodcock, C.M. Exploiting chemical ecology and species diversity: stemborer and striga control for maize and sorghum in Africa. Pest Management Science 2000, 56, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pink, D.; Hand, P. Plant resistance and strategies for breeding resistant varieties. Plant Protection Science 2002, 38 (Suppl. 1), 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; de Kraker, J.; Bianchi, F.; Xiao, H.; Huang, J.; Deng, X.; van der Werf, W. Do diverse landscapes provide for effective natural pest control in subtropical rice? Journal of Applied Ecology 2020, 57, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguine, J.P.; Aubertot, J.N.; Flor, R.J. Integrated pest management: good intentions, hard realities. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev 2021, 41, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, L.E.; Bretthauer, S. Agricultural chemical application technology: a remarkable past and an amazing future. Trans. of the ASABE 2008, 51, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xu, Y. Development and prospect in environment-friendly pesticide sprayers. Trans. of the CSAM 2021, 52, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, H. Development and prospect on performance analysis and measurement techniques of pesticide spraying process. Journal of Forestry Engineering 2022, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, G.; Bateman, R.; Miller, P. Pesticide Application Methods, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Zhang, W. Design and experiment of multi-mode hydraulic steering system of high clearance self-propelled sprayer. Trans. of the CSAM 2020, 51, 366–373. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Zheng, J.; He, X.; et al. Pesticide Application Technique; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Chen, Q.; Xu, L.; Zhou, H.; Hou, X. Analysis on Atomization Effect of Thermal Atomization Pesticide for Pulsed Smoker/Fogger. Trans. of the CSAM 2020, 51, 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, S.; Nyamagoud, R.; Naik, H.; Futane, M. Fabrication of Portable Foot Operated Agricultural Fertilizers and Pesticides Spraying Pump. International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT), ISSN: 2278- 0181, 2015, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, L.; Li, G.; Qin, W. Development Status of Plant Protection Machinery in China. Agricultural Engineering 2021, 11, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, Y.; Chauhan, Jay. ; Tandan, J.; Patel, K.; Kaushik, S. Development of Multipurpose Battery Operated Wheel Sprayer. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, ISSN: 2319- 7706, 2019, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Rincón, V.; Sánchez-Hermosilla, J.; Páez, F.; et al. Assessment of the influence of working pressure and application rate on pesticide spray application with a hand-held spray gun on greenhouse pepper crops. Crop Protection 2017, 96, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alheidary, M.H.R. Performance of knapsack sprayer: effect of technological parameters on nanoparticles spray distribution. International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) 2017, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Raut, L.P.; Jaiswal, S.B.; Mohite, N.Y. Design, development and fabrication of agricultural pesticides sprayer with weeder. International Journal of Applied Research and Studies 2013, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Padhee, D.; Sonwani, S.; Sahu, T. Design, Fabrication and Evaluation of Wheel Operated Sprayer. Int.J. Curr. Microbiol. App.Sci. 2020, 9, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, S.B.; Punith, G.; Rakesh, C.N.; Prakash, M.H.; Lakshminarasimha, N. Design and Development of Trolley type Agrochemical Sprayer. Proceedings of the 5th National Conference on Topical Transcend in Mechanical Technology, SJBIT, Bangalore, India, 2017.
- John Deere. Sprayers & Applicators. Available online: https://www.deere.com/en/sprayers/# (Accessed on 2023).
- Wang, X.; Wei, L.; Li, M.; Dong, X.; Huang, W.; Yan, X. Dedsign and Experimental Analysis on the Sugarcane Hanging Type Spray Insecticide Machine of 3WXP - 800 with Tractor. Modern Agricultural Equipment 2016, 55–58, 63. [Google Scholar]
- CropCare. Trailer sprayer. Available online: https://cropcareequipment.com/trailer-sprayers/ (Accessed on 2023).
- Lan, Y.; Chen, S.; Fritz, B.K.; et al. Current status and future trends of precision agricultural aviation technologies. Int. J. Agric. & Biol. Eng. 2017, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Shi, Y.; Feng, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Shi, J.; Dong, N.; Huang, Q. Effect of flight parameters of B-7451 helicopter on distribution pattern of droplet deposition in jujube canopy. Journal of Fruit Science 2019, 36, 338–346. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z. Research on aerial spray testing system and spraying flow field for small unmanned aerial vehicle. Thesis for PhD, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2018.
- Liu, Y.; Ru, Y.; Chen, Q.; et al. Design and test of real-time monitoring system for UAV variable spray. Trans. of the CSAM 2020, 51, 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, Z.; Idris, N.; Rahim, M.Z. Preliminary Design of Aerial Spraying System for Microlight Aircraft. Journal of Physics: Conf. Series 2017, 914, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, H.; et al. Electric field distribution produced by circular electrode of induce charging nozzle. Trans. of the CSAE 2008, 24, 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Y.; Zheng, X.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Effect of ring electrode structure on spray morphology and droplet charging. Trans. of the CSAM 2019, 50, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Yamane, S.; Miyazaki, M. Study on Electrostatic Pesticide Spraying System for Low-Concentration, High-Volume Applications. Japan Agricultural Research Quarterly: JARQ 2017, 51, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y. Research on intelligent variable profiling sprayer and mechanism adaptive control based on canopy density detection. Thesis for PhD, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2020.
- Zheng, J.; Zhou, H.; Xu, Y.; et al. Toward-target precision pesticide application and its system design. Trans. of the CSAE 2005, 21, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Hočevar, M.; Širok, B.; Jejčič, V.; et al. Design and testing of an automated system for targeted spraying in orchards. Journal of Plant Diseases and Protection 2010, 117, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, X.; Song, J.; et al. Design and experiment of automatic profiling orchard sprayer based on variable air volume and flow rate. Trans. of the CSAE 2017, 33, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, D.L.; Hogmire, H.W. Evaluation of tunnel sprayer systems for dwarf fruit trees. Applied Engineering in Agriculture 1995, 11, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Fang, H.; Qiao, L.; Jian, S.; Zhu, Z.; Peng, Q. Design and experiment of high clearance type recycling tunnel sprayer. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization 2019, 40, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, X.; Yan, H.; et al. Anti-drift technology of super-high clearance boom sprayer with air-assisted system. Trans. of the CSAM 2012, 43, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Tsay, J.; Fox, R.D.; Ozkan, H.E.; et al. Evaluation of a pneumatic-shield spraying system by CFD simulation. Trans. of the ASAE 2002, 45, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, S.P.; Wise, J.; Grieshop, M.J. Season long pest management efficacy and spray characteristics of a solid set canopy delivery system in high density apples. Insects 2019, 193, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Imperatore, G.; Ghirardelli, A.; Strinna, L.; Baldoin, C.; Pozzebon, A.; Zanin, G.; Otto, S. Evaluation of a Fixed Spraying System for Phytosanitary Treatments in Heroic Viticulture in North-Eastern Italy. Agriculture 2021, 11, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, J.; et al. Research progress of intelligent spray machinery based on the phenotype of agricultural and forestry plants. World Forestry Research 2020, 33, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bahlol, H.Y.; Chandel, A.K.; Hoheisel, G.A.; et al. Smart spray analytical system for orchard sprayer calibration: a-proof-of-concept and preliminary results. Trans. of the ASABE 2020, 63, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Tian, L.F.; Zheng, J. Development of weeding robot based on direct herbicide application method. Trans. of the CSAM 2005, 36, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán, J.L.; Rodríguez, F.; Sánchez-Hermosilla, J.; et al. Robust pressure control in a mobile robot for spraying tasks. Trans. of the ASABE 2008, 51, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Z.; et al. Cucumber disease toward-target agrochemical application robot in greenhouse. Trans. of the CSAM 2011, 42, 177–180. [Google Scholar]
- Meshram, A.T.; Vanalkar, A.V.; Kalambe, K.B.; Badar, A.M. Pesticide spraying robot for precision agriculture: A categorical literature review and future trends. Journal of Field Robotics 2022. [CrossRef]
- Nasir, F.E.; Tufail, M.; Haris, M.; Iqbal, J.; Khan, S.; Khan, M.T. Precision agricultural robotic sprayer with real-time Tobacco recognition and spraying system based on deep learning. PLoS ONE 2023 18, e0283801. [CrossRef]
- Cantelli, L.; Bonaccorso, F.; Longo, D.; Melita, C.D.; Schillaci, G.; Muscato, G. A Small Versatile Electrical Robot for Autonomous Spraying in Agriculture. AgriEngineering 2019, 1, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, F.P.; Nascimento, G. H. do; Duarte, G. A.; Drews-Jr, P.L.J. Autonomous Agricultural Sprayer using Machine Vision and Nozzle Control. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems. [CrossRef]
- Chaitanya, P.; Kotte, D.; Srinath, A.; Kalyan, K.B. Development of Smart Pesticide Spraying Robot. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering (IJRTE) 2020, 8, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douda, O.; Manasova, M.; Zouhar, M.; Hnatek, J.; Stejskal, V. Field Validation of the Effect of Soil Fumigation of Ethanedinitrile (EDN) on the Mortality of Meloidogyne hapla and Carrot Yield Parameters. Agronomy 2021, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Ito, K. Establishing targeted control of creeping perennial weeds with soil-active chemical injections: Assessment of subterranean bud responses in contact. Weed Biology and Management 2021, 21, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishel, F.M.; Dale, A.G.; Klein, R.W. Pesticide injection and drenching. EDIS 2018. [CrossRef]
- Santra, L.; Furiosi, W.J.; Kundu, A.; Rajaraman, S. A minimally-invasive 3D-printed microneedle array applicator system (μNAAS) for delivery of therapeutics to citrus leaf tissue. Journal of Young Investigators 2021, 39, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Jorge, M.G. Sustainable forest management in poplar plantations: Forest Health and Biodiversity. Criteria. Thesis, for PhD, University of Valladolid, Spain, 2012; pp. 163–172.
- Pscheidt J., W. Tree Wound Paints. Available online: https://pnwhandbooks.org/plantdisease/pesticide-articles/tree-wound-paints (accessed on 2023).
- Zheng, J.; Wang, X. Development of tree trunk sprayer. China Forestry Science and Technology 1995, 21–22. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. Research on Autonomous Robot for Weed Control and Smart Spray System based on Variable Rate. Technology. Thesis, for PhD, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, S.; Fan, C.; et al. Design and experimental study of control system for spraying bait on bait spraying machine for deratization. Trans. of the CSAE 2014, 30, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Stejskal, V.; Vendl, T.; Aulicky, R.; Athanassiou, C. Synthetic and Natural Insecticides: Gas, Liquid, Gel and Solid Formulations for Stored-Product and Food-Industry Pest Control. Insects 2021, 12, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, G.P. Advances in Fluid Drilling. HortTechnology 1991, 1, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; An, J.; Dang, Z.; et al. Systemic control efficacy of neonicotinoids seeds dressing on English grain aphid (Hemiptera:Aphididae). Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology 2018, 21, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, V.S.; Erickson, T.E.; Merritt, D.J.; Madsen, M.D.; Hobbs, R.J.; Ritchie, A.L. A global review of seed enhancement technology use to inform improved applications in restoration. Science of the Total Environment 2021, 798, 149096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, T.P.; Ritchie, A.L.; Erickson, T.E.; Nimmo, D.G.; Price, J.N. Activated carbon seed technologies provide some protection to seedlings from the effects of post-emergent herbicides. Restor Ecol 2023, 31, e13875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Qi, S.; Yang, D. Studies on Cloudy-dusting in Plastic Tunnel. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica 2000, 27, 364–368. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L. Some Problems Relating to Atomization Theory in Plant Protection Machinery. Trans. of the CSAM 1980, 21, 78–88. [Google Scholar]
- Giles, D.K.; Ben-Salem, E. Spray droplet velocity and energy in intermittent flow from hydraulic nozzles. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research 1992, 51, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Jia, W.; Ou, M.; Zhong, W.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X. Effect of Physical Properties of an Emulsion Pesticide on the Atomisation Process and the Spatial Distribution of Droplet Size. Agriculture 2022, 12, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derksen, R C. ; Bode, L.E. Droplet size comparisons from rotary atomizers. Trans. of the ASAE 1986, 29, 1204–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xian, F. Research on wind-driven rotary-cage electrostatic spraying technique. Trans. of the CSAM 1990, 21, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Panneton, B. Geometry and performance of a rotary cup atomizer. Applied Engineering in Agriculture 2002, 18, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Lü, X.; et al. Numerical simulation and experimental study on the wind performance of the disc atomizer. Trans. of the CSAM 2012, 43, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhiar. I.A.; Gao, J.; Xu, X.; et al. Effects of various aeroponic atomizers (droplet sizes) on growth, polyphenol content, and antioxidant activity of leaf lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Trans. of the ASABE 2019, 62, 1475–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, H.; et al. Design and experiment of double-nozzle of aerial electrostatic sprayer. Trans. of the CSAM 2007, 38, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, E.; Zheng, J.; Ru, Y.; et al. Atomization mechanism and numerical simulation of external mixing two-fluid fan nozzle. EKOLOJI 2019, 28, 4277–4288. [Google Scholar]
- Himel, C.M. The optimum size for insecticide spray droplets. J. Econ. Entomol. 1969, 62, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.P. Drift of droplets from air-induction nozzles. Trans. of the ASABE 2019, 62, 1683–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Womac, A.R.; Bui, Q.D. Design and tests of a variable-flow fan nozzle. Trans. of the ASAE 2002, 45, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, L.E.; Langley, T.E.; Butler, B.J. Performance characteristics of bypass spray nozzles. Trans. of the ASAE 1979, 22, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.K.; Comino, J.A. Droplet size and spray pattern characteristics of an electronic flow controller for spray nozzles. J. Agric. Eng. Research 1990, 47, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Ahmad, H.; Moon, J.W.; Jung, S.Y. Nozzle with a Feedback Channel for Agricultural Drones. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, E.; Zheng, J.; Gan, Y. Set-up of Wear Measurement for Hydraulic Nozzles. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization 2013, 34, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Rockwell, A.D.; Agers, P.D. Variable rate sprayer development and evaluation. Applied Engineering in Agriculture 1994, 10, 307–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.F.; Zheng, J. Dynamic deposition pattern simulation of modulated spraying. Trans. of the ASAE 2000, 43, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, H.; et al. R&D of variable rate technology in precision agriculture management system. Trans. of the CSAM 2003, 34, 156–159. [Google Scholar]
- Llorens, J.; Gil, E.; Llop, J.; et al. Variable rate dosing in precision viticulture: Use of electronic devices to improve application efficiency. Crop Protection 2010, 29, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhu, H.; Sun, Li.; et al. Investigation of an experimental laser sensor-guided spray control system for greenhouse variable-rate applications. Trans. of the ASABE 2019, 62, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Chen, C.; Zhao, R.; Ren, L. Accurate Variable Control System for Boom Sprayer Based on Auxiliary Antidrift System. Journal of Sensors 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, J.; Kim, J.; Son, H. Field evaluations of a deep learning-based intelligent spraying robot with flow control for pear orchards. Precision Agriculture 2022, 23, 712–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womac, A.; Valcore, D.; Maynard, R. Variable-concentration direct injection from fixed-ratio diluent-driven pumps. Trans. of the ASAE 2002, 45, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vondricka, J.; Lammers, P.S. Real-time controlled direct injection system for precision farming. Precision Agriculture 2009, 10, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, J.; et al. Structural analysis and mixing uniformity experiments of swirling jet mixer for applying fat-soluble pesticides. Trans. of the CSAE 2016, 32, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Hu, C. Hardware and software design for premixing in-line injection system attached to variable-rate orchard sprayer. Trans. of the ASABE 2020, 63, 823–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peteinatos, G.G.; Kollenda, B.; Wang, P.; Gerhards, R. A new logarithmic sprayer for dose-response studies in the field. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, ; 2019, 157, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, P. .Experimental study on double-stage on-line jet mixing apparatus. International Journal of Modeling, Simulation, and Scientific Computing 2022, 13, 2142001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, J. Research advances of the technologies for spray drift control of pesticide application. Trans. of the CSAE 2005, 21, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- Nuyttens, D.; Schampheleire, M.D.; Baetens. K.; et al. Drift from field crop sprayers using an integrated approach: Results of a 5 year study. Trans. of the ASABE 2011, 54, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, J.A.L.; Cunha, J.P.A.R.da; Antuniassi, U.R. . Spectrum and velocity of droplets of spray nozzles with and without air induction. Engenharia Agrícola, Jaboticabal 2018, 38, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.F.; Xue, X.Y.; Ding, S.M.; Le, F.X. Development of a DSP-based electronic control system for the active spray boom suspension. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 166, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Qiu, B.; Yang, Y.; et al. Deformation analysis and control of elastic deformation for spray boom based on finite element model. Trans. of the CSAE 2014, 30, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, T.F.; Yang, X.J.; Dong, X.; Zhang, T.; Yan, H.R.; Sun, X. Research status and development trend of large self-propelled sprayer booms. Trans. of the CSAM 2018, 49, 189–198. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, J.; et al. Ecodesign method of intelligent boom sprayer based on preferable Brownfield process. Journal of Cleaner Production 2020, 268, 122206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xu, Y. Review and prospect of sensing technologies and wireless sensor networks for precision forestry. Journal of Forestry Engineering 2016, 1, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, Y. Research on intelligent variable profiling sprayer and mechanism adaptive control based on canopy density detection. Thesis for PhD, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2020.
- Duga, A.T.; Ruysen, K.; Dekeyse, R.D.; et al. Spray deposition profiles in pome fruit trees: effects of sprayer design, training system and tree canopy characteristics. Crop Protection 2015, 67, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gaadi, K.A.; Paul, D.A. Integrating GIS and GPS into a spatially variable rate herbicide application system. Applied Engineering in Agriculture 1999, 15, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, J.; Xu, Y. Study of auto disturbance rejection synchronous control for bilateral hydraulic motor of concept sprayer chassis. Journal of China Agricultural University 2017, 22, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Z.; et al. Inter-rows navigation method for corn crop protection vehicles under high occlusion environment. Trans. of the CSAM 2020, 51, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, L.P.; Rory, L.R. A review of the effects of droplet size and flow rate on the chargeability of spray droplets in electrostatic agricultural sprays. Trans. of the ASABE 2018, 61, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.; He, X.; Song, J.; et al. Comparative research of two kinds of flat fan nozzle atomization process. Trans. of the CSAE 2013, 29, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Dodge, L.G. Comparison of performance of drop-sizing instruments. Applied Optics 1987, 26, 1328–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Nie, W.; Lin, W.; et al. Research progress of optical measurement of particle size in spray. Laser Technology 2019, 43, 702–707. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J. Computer-aided laser imaging droplet sizing system. Computer Automated Measurement & Control 2000, 8, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Luck, J.D.; Shearer, S.A.; Sama, M.P. Development and preliminary evaluation of an integrated individual nozzle direct injection and carrier flow rate control system for pesticide applications. Trans. of the ASABE 2019, 62, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Evaluation of mixing uniformity for inline mixers by image processing. Trans. of the ASABE 2020, 63, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Jia, W.; Ou, M.; Zhong, W.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X. Effect of Physical Properties of an Emulsion Pesticide on the Atomisation Process and the Spatial Distribution of Droplet Size. Agriculture 2022, 12, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, R.R. A low-cost spot laser and camera system for fluorescent dye detection of agricultural aircraft pattern collection strings. Applied Engineering in Agriculture 2018, 34, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Mao, H.; Guan, X. Numerical simulation and experimental verification of the deposition concentration of an unmanned aerial vehicle. Applied Engineering in Agriculture 2019, 35, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xian, F.; Gao, L. Review on Measurement of Electrostatic Spraying Charge-to-Mass Ratio. Journal of Jiangsu Institute of Technology 1992, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Xian, F.; Gao, L.; et al. Charge attenuation pattern of charged droplets. Trans. of the CSAM 1993, 24, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.; Zhang, J.; Jia, W.; Ou, M.; Zhou, H.; Dong, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S. Experimental Study on the Droplet Size and Charge-to-Mass Ratio of an Air-Assisted Electrostatic Nozzle. Agriculture 2022, 12, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, E.; Balsari, P.; Gallart, M.; et al. Determination of drift potential of different flat fan nozzles on a boom sprayer using a test bench. Crop Protection 2014, 56, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, B.; Rolando, C.A.; Kimberley, M.O. Quantifying spray deposition from a UAV configured for spot spray applications to individual plants. Trans. of the ASABE 2020, 63, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, M.W.; Hanna, H.M.; Darr, M.J.; et al. Measuring sub-second wind velocity changes for agricultural drift one meter above the ground. Applied Engineering in Agriculture 2019, 35, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomantas, T.; Lekavičienė, K.; Steponavičius, D.; Andriušis, A.; Zaleckas, E.; Zinkevičius, R.; Popescu, C.V.; Salceanu, C.; Ignatavičius, J.; Kemzūraitė, A. The Influence of Newly Developed Spray Drift Reduction Agents on Drift Mitigation by Means of Wind Tunnel and Field Evaluation Methods. Agriculture 2023, 13, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasner, E.J.; Fenske, R.A.; Hoheisel, G.A.; Galvin, K.; Blanco, M.N.; Seto, E.Y.W.; Yost, M.G. Spray Drift from a Conventional Axial Fan Airblast Sprayer in a Modern Orchard Work Environment. Annals of Work Exposures and Health 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Song, W.; Lan, Y.; Wang, H.; Yue, X.; Yin, X.; Tang, Y. A Smart Droplet Detection Approach With Vision Sensing Technique for Agricultural Aviation Application. IEEE Sensors Journal 2021, 21, 17508–17516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massinon, M.; De Cock, N.; Forster, W.A.; et al. Spray droplet impaction outcomes for different plant species and spray formulations. Crop Protection 2017, 99, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, J.; et al. Oblique impact behavior of spray droplets on tea tree leaves surface. Trans. of the CSAM 2019, 50, 96–103. [Google Scholar]
- Dorr, G.J.; Wang, S.S.; Mayo, L.C.; et al. Impaction of spray droplets on leaves: influence of formulation and leaf character on shatter, bounce and adhesion. Experiments in Fluids 2015, 56, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nairn, J.J.; Forster, W.A.; Van Leeuwen, R.M. Quantification of physical (roughness) and chemical (dielectric constant) leaf surface properties relevant to wettability and adhesion. Pest Management Science 2011, 67, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpe, S.M.; Boyd, N.S.; Dittmar, P.J.; et al. Spray penetration into a strawberry canopy as affected by canopy structure, nozzle type, and application volume. Weed Technology 2018, 32, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhalfa, H.H.; Massinon, M.; Belhamra, M.; et al. Contribution of spray droplet pinning fragmentation to canopy retention. Crop Protection 2014, 56, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teske, M.E.; Thistle, H.W.; Riley, C.M.; et al. Laboratory measurements of evaporation rate of droplets at low relative wind speed. Trans. of the ASABE 2018, 61, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sama, M.P.; Weiss, A.M.; Benedict, E.K. Validating spray coverage rate using liquid mass on a spray card. Trans. of the ASABE 2018, 61, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.P.; Hewitt, A.J. Flat-fan spray atomization model. Trans. of the ASABE 2018, 61, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Luca, M.D.; Vallet, A. Pesticide atomization modelling for hollow cone nozzle. Agricultural Engineering International: the CIGR Ejournal, ALNARP08012, X, 2008.
- Lafferty, C.L.; Tian, L.F. Using computation fluid dynamics to determine the effect of internal nozzle flow on droplet size. ASAE International Annual Meeting, Sacramento, CA, USA, 29-08-2001.
- Liu, C.; Zheng, J.; Wang, K. Prediction model for atomization performance of electrostatic spraying nozzle. Trans. of the CSAM 2009, 40, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Chai, S.; Chen, L.; et al. Establishment and experiment of quadratic residual compensation atomization model of electricity atomizer. Trans. of the CSAM 2020, 51, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, J. Control system for precision pesticide application based on variable rate technology. Trans. of the CSAE 2005, 21, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, C.; Wang, X.; Mi, Y.; et al. Nozzle flow model of PWM variable-rate spraying. Trans. of the CSAM 2012, 43, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, J.; et al. . Simulation optimization analysis of shrinking tube pitch and splitter position of rotating jet mixer. J. Agric. Sci. Tech. 2019, 21, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Sidahmed, M.M.; Brown, R.B. Simulation of spray dispersal and deposition from a forestry airblast sprayer-part II: Droplet trajectory model. Trans. of the ASAE 2001, 44, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeau, F. Modelling the dynamic distribution of spray deposits. Biosys. Eng. 2004, 89, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delele, M.A.; Moor, A.De.; Sonck, B.; et al. . Modeling and validation of the air flow generated by a cross flow air-sprayer as affected by travel speed and fan speed. Biosys. Eng. 2005, 92, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Wang, J.; Qi, L.; et al. . CFD simulation and experimental verification of air-velocity distribution of air-assisted orchard sprayer. Trans. of the CSAE 2009, 25, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Wang, X.; Ding, W.; et al. . Simulation analysis on characteristics of droplet deposition base on CFD discrete phase model. Trans. CSAE 2012, 28, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, J.; et al. . Spray nozzle atomization performance and droplet deposition visual model. J. Forestry Engineering 2016, 1, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ru, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, H.; et al. Research on moving trajectory simulation of charged droplets. Chin. Agric. Mechan. 2011, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. . Modeling and compensation for characteristic of droplet drift on air-assisted boom spraying accounting for wind speeds. Trans. of the CSAE 2013, 29, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Baetens, K.; Nuyttens, D.; Verboven, P.; et al. . Predicting drift from field spraying by means of 3D computational fluid dynamics model. Computers Electron. Agric. 2007, 56, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-w.; Park, J.; Jeong,H. ; Lee, S.; Choi, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, H. Fluid Dynamic Approaches for Prediction of Spray Drift from Ground Pesticide Applications: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Models for pesticide risk assessment. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pesticide-science-and-assessing-pesticide-risks/models-pesticide-risk-assessment (accessed on 27-12-2020).
- Teske, M.E.; Thistle, H.W.; Fritz, B.K. Modeling aerially applied sprays: an update to AGDISP model development. Trans. of the ASABE 2019, 62, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, G.N.; Sweatman, W.L.; Forster, W.A. A model for spray droplet adhesion, bounce or shatter at a crop leaf surface. Mathematics in Industry 2010, 15, 945–951. [Google Scholar]
- Dorr, G.J.; Kempthorne, D.M.; Mayo, L.C.; et al. Towards a model of spray–canopy interactions: Interception, shatter, bounce and retention of droplets on horizontal leaves. Ecological Modelling 2014, 290(C), 94-101.
- Mayo, L.C. Mathematical modelling of the impaction and spreading of spray droplets on leaves. Thesis for PhD, Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, Australia, 2015.
- Ru, Y.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Fang, S. Droplet Penetration Model Based on Canopy Porosity for Spraying Applications. Agriculture 2023, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima Junior, I. dos S.; Degrande, P.E.; de Souza, C.M.A. Droplet distribution as a function of cotton interrow spacing and angles of sprayer displacement. Engenharia Agrícola, Jaboticabal 2018, 38, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, F.G.; Portes, M.F.; Silva, M.V.; Teixeira, M.M.; Furtado Júnior, M.R. Impact of sprayer drone flight height on droplet spectrum in mountainous coffee plantation. Brazilian Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Engineering 2022, 26, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagkaris, A.S.; Pulkrabova, J.; Hajslova, J. Optical screening methods for pesticide residue detection in food matrices: advances and emerging analytical trends. Foods 2021, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirghafouri, M.R.; Abbasi-Moayed, S.; Ghasemi, F.; et al. Nanoplasmonic sensor array for the detection and discrimination of pesticide residues in Citrus fruits. Analytical Methods 2020, 12, 5877–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, J.; Llop, J.; Gallart, M.; García-Ruiz, F.; Gras, A.; Salcedo, R.; Gil, E. Development of canopy vigour maps using UAV for site-specific management during vineyard spraying process. Precision Agriculture 2019. [CrossRef]
| Book name | Author(s) | Written Dynasty | Cited with keywords | |
| 1 | Zhou Rites | Duke of Zhou | Zhou Dynasty ( 1046-256 BCE) | Fumigating the pests |
| 2 | The Book of Songs•Xiaoya•Datian | Anonymity | Classification of pests Getting rid of the pests |
|
| 3 | Master Lü’s Spring and Autumn Annals•Buqu | Zuo Qiuming, Lü Buwei |
Warring States Period (c. 481-221 BCE) | Killing the locusts |
| 4 | Master Lü’s Spring and Autumn Annals•Rendi | Avoiding weeds or insects through deep cultivation etc |
||
| 5 | Master Huainan•Main Skilling, Garden of Eloquence•Xiuwen |
Liu An, Liu Xiang |
Han Dynasty (202BCE-220AD) | Timely prevention, survival rights of insects |
| 6 | Works of Fan Shengzhi | Fan Shengzhi | Seed treatment | |
| 7 | Discourses Weighed in the Balance•About Insects | Wang Chong | Soil moisture management for killing insects |
|
| 8 | Annotation for the Zhou Rites | Zheng Xuan | Using illicium anisatum to kill insects with fumigating |
|
| 9 | Book of Southern Vegetation | Ji Han | Jin Dynasty (266-420) | Natural enemy to kill insects |
| 10 | Important Arts for the Peoples Welfare | Jia Sixie | Northern Wei Dynasty(386-534) | Using burning sun to control pests |
| 11 | Biographies in the Southern Dynasties | Li Yanshou | Tang Dynasty (618-907) | Natural enemy of pests |
| 12 | The Imperial Decree for Catching Locusts | Zhao Xu, Song Emperor |
Song Dynasty (960-1279) | Law on locust control |
| 13 | Book on Agriculture by Wang Zhen | Wang Zhen | Yuan Dynasty (1271-1368) | Eliminating weeds |
| 14 | Complete Treatise on Agriculture | Xu Guangqi | Ming Dynasty (1368―1644) | Using lime and Tung oil to kill pests |
| 15 | On Agriculture | Ma Yilong | Soil and water management | |
| 16 | Shen's Treatise on Agriculture•Land Administration Rules | Shen, name unknown |
Examining and scraping off pests | |
| 17 | Outlines of Agriculture•Principles of Cultivating Crops | Yang Shen, Zheng Shiduo | Qing Dynasty (1616-1912) | Suitable soil and water management |
| Classification basis | Name | Explanations of measures and references |
| By spraying medium | Sprayer | Pesticide sprayer is the most important plant protection machinery at present which disperse the pesticides into droplets to deposit the targets[1,70,73,74]. |
| Duster | Pesticide duster generates an airflow or uses electrostatic charging to carry the low concentration or diluted pesticide powders on the targets[1,75]. | |
| Fogger | There are two types of pesticide foggers, normal-temperature fogger (like aerosol sprayer) and thermal fogger, which generally produce very fine fogging droplets for improving the pest control efficiency [1,76]. | |
| Bio-pesticide sprayer | Bio-pesticide sprayer is applied to spray the fragile biological pest control agents for ensuring the high viability[1,47]. | |
| By driven power source | Manual-operated | The manual-operated means include hand-pressure, pedal-operated, rocker-armed etc.[77]. |
| Animal-powered | The animal-powered means include livestock-driven or horse-drawn[78]. | |
| Electric-driven | The electric-driven means is generally battery-powered, which will have more potential applications in plant protection [79]. | |
| Engine-driven | The engine-driven means apply combustion engine which are mostly applied currently in plant protection[16,74]. | |
| Others | The helium or hydrogen balloon to spray pesticides was reported from China Global Television Network (CGTN) . | |
| By carrier platform | Portable | Portable platforms include hand-held [80], backpack or knapsack[81,82], hand-push wheel-operated[83], trolley type[84] and other manual platforms. |
| Ground vehicle | Ground mounted platforms include tractor mounted [85], 3pt.mounted with tractor [86], trailer [87], and high clearance self-propelled[74] etc.. | |
| Airborne platform (aerial application) | Aviation platforms include fixed-wing aircraft[88], helicopter [89], and plant protection UAVs [90,91], and micro aircraft[92]etc.. | |
| By function | Toward-target | Toward-target sprayers include electrostatic sprayer[93,94,95], profiling sprayer[96,97,98,99], tunnel sprayer[100,101]. |
| Anti-drift | Anti-drift sprayers include air-assisted sprayer[102], shielded sprayer[103], recycling tunnel sprayer [101], and fixed spraying system [104,105]etc.. | |
| Intelligent | With the development of sensors, AI and other technologies, intelligent sprayers [106,107], plant protection robots and spraying robots[108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115] are widely developed. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





