1. Introduction
Considered among the most common respiratory conditions in veterinary practice worldwide, canine infectious respiratory disease complex (CIRDC) is a multifactorial syndrome characterized by an acute onset of respiratory symptoms, including nasal, and ocular discharge, coughing, sneezing, and fever (Buonavoglia and Martella 2007). These clinical signs are mostly self-limiting and affected dogs may recover within days or weeks. However, there is a possibility that some cases may evolve into a severe form of disease with pulmonary tissue involvement such as pneumonia but rarely result in death (Buonavoglia and Martella 2007; Kawakami et al. 2010). Several viral and bacterial agents are involved in causing CIRDC in the respiratory tract and these pathogens can sequentially or synergistically act to result in a particular clinical picture. Pet or shelter dogs of all ages could be infected by these respiratory pathogens, but puppies have been previously shown to be the most affected (Radhakrishnan et al. 2007; Maboni et al. 2019). Coinfection is frequent and previous studies have shown that it may result in a complicated form of the disease including pneumonia (Maboni et al. 2019; Decaro et al. 2016).
The principal CIRDC causative organisms are Bordetella bronchiseptica (Bemis, Greisen, and Appel 1977), canine adenovirus type 2 (CAV-2) (Ditchfield, Macpherson, and Zbitnew 1962), canine parainfluenza virus (CPIV) (Appel and Percy 1970), canine herpes virus (CHV) (Karpas et al. 1968) and canine distemper virus (CDV) (Erles et al. 2004). Over time, additional agents has been found to be implicated in the disease complex, which includes relatively novel pathogens such as canine influenza virus (CIV) (Crawford et al. 2005), Mycoplasma sp.(Chalker et al. 2004), Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus (Chalker, Brooks, and Brownlie 2003), canine coronavirus (CCoV) (Erles and Brownlie 2008) and canine pneumovirus (CPnV) (Mitchell et al. 2013). Canine reovirus (Binn et al. 1977), canine bocavirus (Kapoor et al. 2012) and canine hepacivirus (El-Attar et al. 2015) have been recently identified in CIRDC, not as big players as some of the other agents, but their causal role and contribution to the complex have yet been elucidated.
The CIRDC pathogens are often highly infectious and transmitted mostly by aerosol route, particularly when many dogs are housed in high-density environments such as boarding kennels, rehoming centers, and shelters (Pesavento and Murphy 2014; Erles et al. 2004). Dog parks, daycare facilities, and even veterinary clinics may present the same opportunities for crowded spaces due to the large number of dogs and can also potentially facilitate CIRDC transmission. Precedent reports have described an outbreak associated with canine parainfluenza virus and canine herpes virus among dogs in a veterinary hospitals (Weese and Stull 2013; Kawakami et al. 2010). Because clinical signs are not sufficient to distinguish amongst the various causes of CIRDC, laboratory diagnostic tests (ELISA, Bacterial culture, virus isolation, RT-PCR) are crucial and are routinely performed for determining the etiologic agent. There is no specific treatment for the syndrome. However, it is recommended that antibiotics should be administered for primary and secondary bacterial infections. Several monovalent and multivalent vaccines generally formulated for intranasal administration are available for some pathogens but not for all, which may explain the occasional lack of protection. Another possible cause of that lack of protection could be justified by the presence of antigenic variants. Despite the availability of vaccines and antibiotic regimens adopted, outbreaks are still reported worldwide, and there is very little information on the prevalence of CIRDC in the
United States. The purpose of this study was to retrospectively conduct a data analysis to determine the prevalence of CIRDC pathogens over 5 years and provide new insights into the epidemiology of its etiologic agents.
2. Materials and Methods
A total of 459 respiratory specimens (nasal, oropharyngeal, nasopharyngeal swabs, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. etc.) were obtained from veterinary practices across the southeastern United States that were submitted by veterinarians to the Athens Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory (AVDL, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA) for CIRDC testing, using a real-time RT-PCR for a time period from 2018 to 2023. The signalments accession number, received date, specimen types, age, and sex were recorded from the sample submission forms.
Nucleic acids from the respiratory specimens were extracted by either IndiSpin Pathogen Kit (Cat# SP54106, Indical Bioscience, Orlando, FL) or IndiMag Pathogen Kit-formerly MagAttract 96 cador Pathogen Kit (Indical BioSciences Cat# SP947257) according to manufacturer’s instruction using with Qiacube automated nucleic acid extraction system (Qiagen, Redwood City, CA) or KingFisher Flex/Apex purification system (Thermo Fisher).
All polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays were performed with an exogenous internal control which both ensures the quality of the extraction process and detects the presence of naturally occurring inhibitory compounds in the submitted specimens. The internal control is added into each sample during the extraction procedure to monitor the quality of both purification and amplification. The primers and probes used in the PCR assays are provided in table 1. All PCR assays were performed and analyzed using standard procedures (please see references listed in table 1) and following guidelines as per the Minimums Information for publication of Quantitative real-time PCR Experiments (MIQE) (Bustin et al. 2010; Bustin et al. 2009).
We performed a retrospective analysis (2018-2022) by querying the database using the Laboratory Information Management System called VetView (Athens, GA) to retrieve all submitted cases that requested a CIRDC PCR panel over the 5 years (2018-2022). During that period, the test panel targeted ten CIRDC pathogens and we analyzed the variables such as age, sex, and seasonality according to the pathogen detection rate. Information about previous exposure, vaccination status, and treatment regimens was not assessed. We split the seasonality into the cold (October 15th to April 15th) and warm seasons (April 16th to October 14th) to analyze the impact of seasons on the prevalence of CIRDC pathogens. To determine the rate of pathogen detection by age, we also divided the dog population into four categories: puppies (< 1 year old), adolescents (1-4 years old) adults (4-10 years old), and seniors (> 10 years old) dogs.
Data in this study were recorded in Excel spreadsheets and imported into JMP software for statistical analysis. Associations between pathogen occurrence, sex, and seasonality variables were examined using Chi-square and Fisher’s test. Multivariable logistic regression was used to examine pathogen occurrence depending on the age variable. A p-value of < 0.05 was considered significant.
No animal experiments were conducted as part of this study. Specimens collected and submitted by veterinarians from their canine patients were used for laboratory diagnostic testing and reporting of results back to the submitting veterinarian. All confidential animal and owner identification information were removed before compiling the data.
Table 1.
Primers and/or probes used in the polymerase chain reaction assays for the detection of canine infectious respiratory disease pathogens in respiratory specimens in dogs.
Table 1.
Primers and/or probes used in the polymerase chain reaction assays for the detection of canine infectious respiratory disease pathogens in respiratory specimens in dogs.
| Pathogen |
Primers/Probes |
Reference |
| Canine adenovirus (CAV-2) |
CAV-F CGC GCT GAA CAT TAC TAC CTT GTC
CAV-R CCT AGA GCA CTT CGT GTC CGC TT |
(Chaturvedi et al. 2008) |
| Canine Distemper virus (CDV) |
CDV-F ACT ATT GAG AGA CCT CCA GCT GAA A
CDV-R TGC GGT ATC CTT CGG TTT GT
CDV-P CCG ATT GCC GAG CTA GAC TCT TTG TCA/56-FAM/3BHQ-1 |
(Saito et al. 2006) |
| Influenza A virus (IAV) |
M+25 Foward AGA TGA GTC TTC TAA CCG AGG TCG
M-124-2002 Reverse TGC AAA AAC ATC TTC AAG TCT CTG
M-124-2009 Reverse TGC AAA GAC ACT TTC CAG TCT CTG
M+ 64 Probe TCA GGC CCC CTC AAA GCC GA/56FAM/ZEN/3IABkFQ
Primary PCR |
(Spackman et al. 2003) |
| Canine Parainfluenza virus (CPIV) |
PNP1- AGT TTG GGC AAT TTT TCG TCC
PNP2- TGC AGG AGA TAT CTC GGG TTG
DNA standard Secondary PCR
PNP3- CGT GGA GAG ATC AAT GCC TAT GC
PNP4- GCA GTC ATG CAC TTG CAA GTC ACT A |
(Erles et al. 2004)
|
| Canine Respiratory Coronavirus (CCoV) |
CRCoV-F ACG TGG TGT TCC TGT TGT TAT AGG
CRCoV-R AAC ATC TTT AAT AAG GCG ACG TAA CAT
CRCoV-P CCA CTA AAT TTT ATG GCG GCT GGG ATG/56-FAM/ZEN/3IABkFQ |
(Spiss et al. 2012) |
| Canine herpes Virus-1 (CHV-1) |
CHV-F ACA GAG TTG ATT GAT AGA AGA GGT ATG
CHV-R CTG GTG TAT TAA ACT TTG AAG GCT TTA
CHV-P TCT CTG GGG TCT TCA TCC TTA TCA AAT GCG/56-FAM/ /3BHQ-1 |
(Decaro et al. 2010) |
| Bordetella bronchiseptica |
bfr-Qf CGGAGTGAGATCGTGCATCA
bfr-Qr CCACCAAACGCAATGACCTG
bfr-P TCGGGAAGGTGCAGCATGTCCTGGAAATA
5’6FAM/Zen/3’ABKFQ |
(Hozbor, Fouque, and Guiso 1999)
|
| Streptococcus zooepidemicus |
SodA-F AGA GCA ATT CAC AGC AGC A
SodA-R ACC AGC CTT ATT CAC AAC CA SodA-Bd-R ACC GGC TTG GTT AAC CAC TA
SodA-P CAG GCC CAA CCT GAG CCA AA
/56-FAM/36-TAMSp |
(Baverud, Johansson, and Aspan 2007) |
| Mycoplasma canis |
F CAC CGC CCG TCA CAC CA
R CTGTCGGGGTTATCTCGAC
P TTATCAATTATTATTTTAAATGTCA
5/56FAM/3MGBEc |
(Chalker et al. 2004) |
| Mycoplasma cynos |
F CAC CGC CCG TCA CAC CA
R GATACATAAACACAACATTATAATATTG
P CGGAGTACAAGTTACAATTCATTTTAG
5/JOE/3 NHS/ZEN/3’IBFQ |
(Chalker et al. 2004) |
3. Results
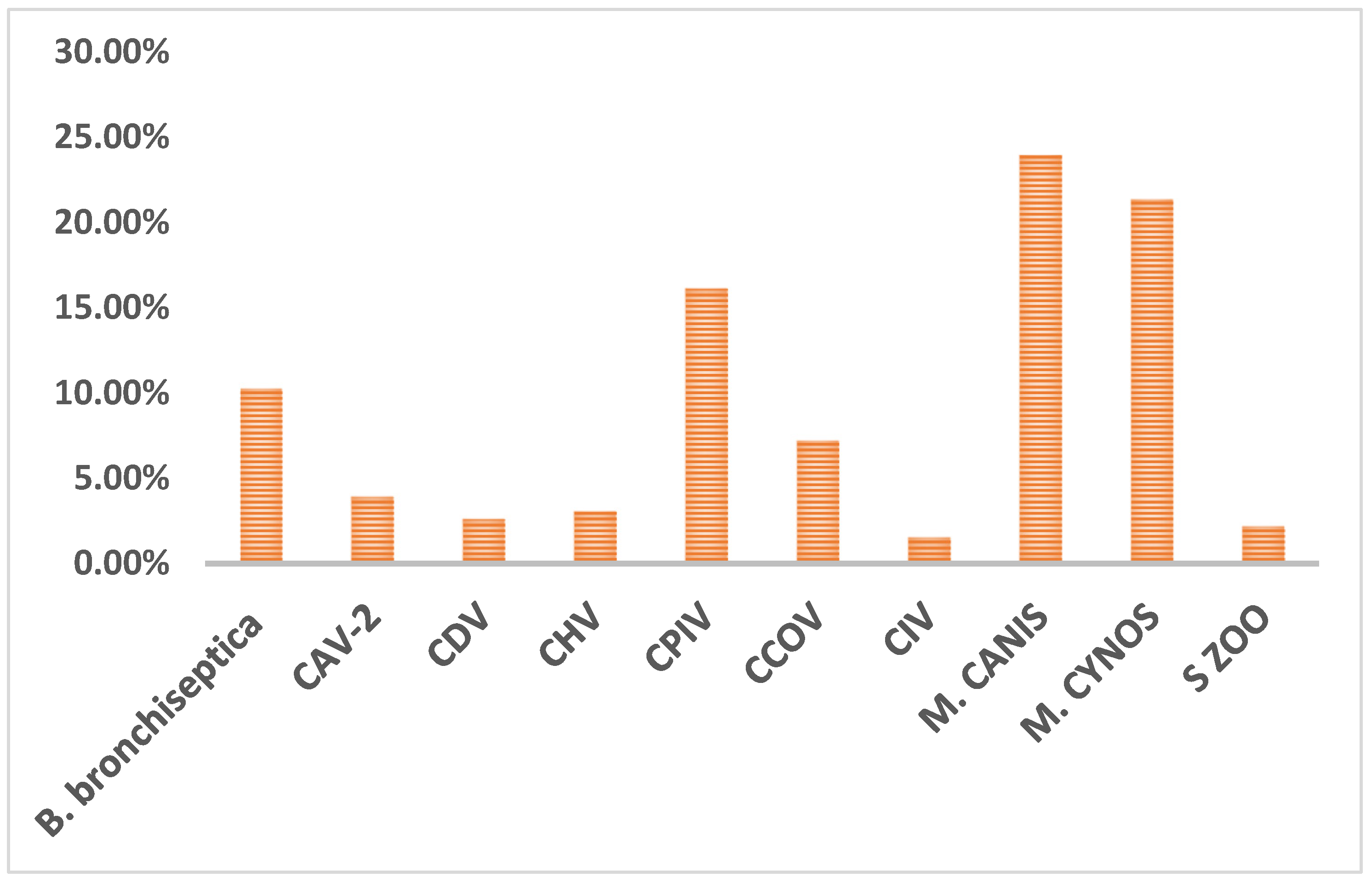
The data were first summarized based on the results of bacterial and viral infections. Viral pathogens were detected in 34% (n=158 out of 459 tested) of cases while bacterial infections were detected in 58% (n=265) of the cases. As illustrated in
Figure 1,
M. canis (24%,110/459),
M. cynos (21%,98/459), and CPIV (16%,74/459) were the most common detected pathogens, followed by
B. bronchiseptica (10%,47/459), CCOV (7%,33/459), CAV-2 (4%,18/459), CDV (3%,12/459), CHV (3%,14/459), CIV (2%,7/459) and
S. zooepidemicus (2%,10/459).
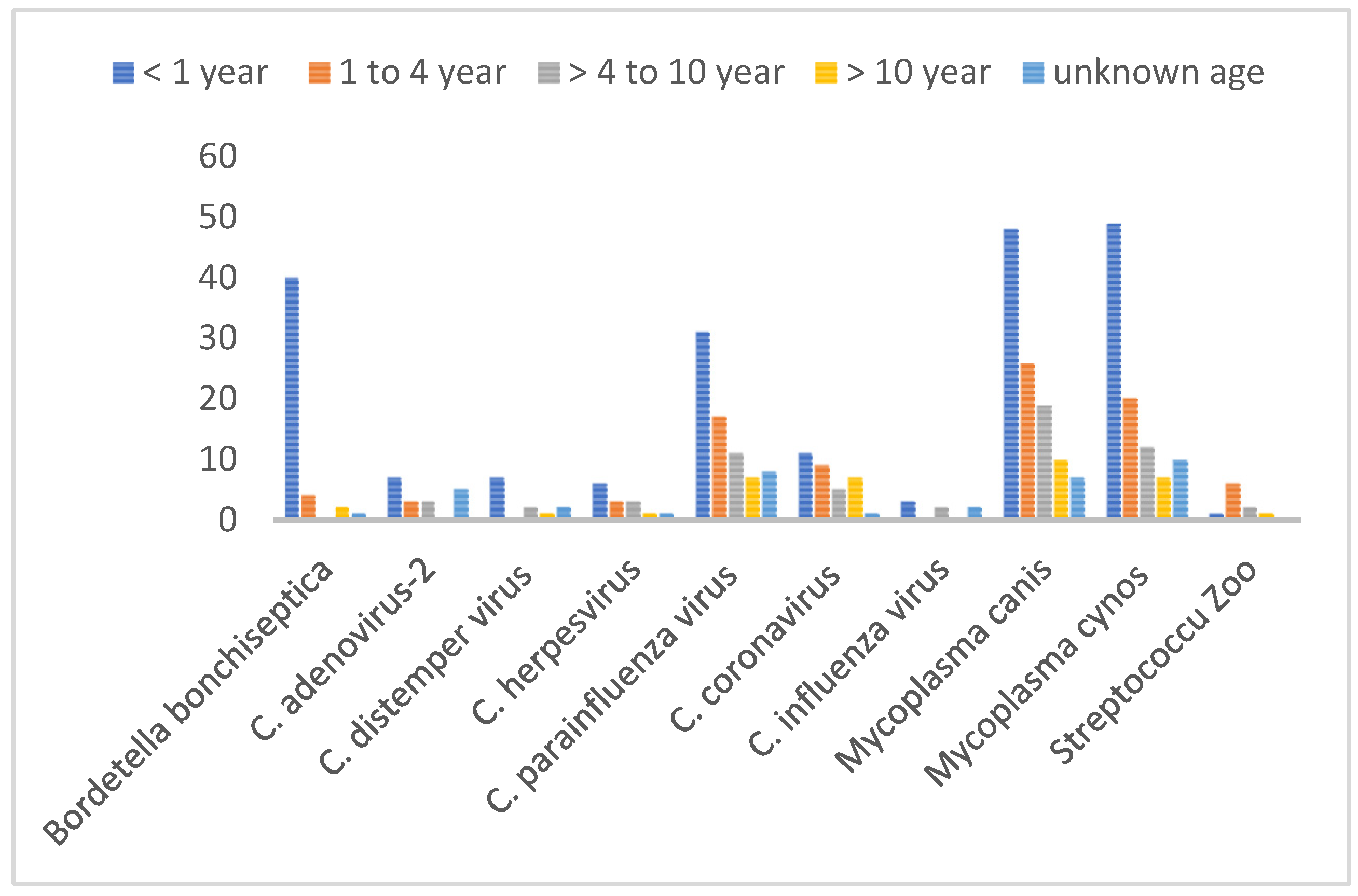
Regarding age susceptibility to infections, some of the CIRDC pathogens were not detected in all age categories, namely
B. bronchiseptica was absent in adult dogs, CAV and CIV were not detected in senior dogs. We also noticed the absence of CDV and CIV in adolescent dogs. Still, puppies were significantly more affected than other age groups with
B. bronchiseptica, M. canis and
M. cynos. (p<0.0001, P<0.04 and p<0.0001 respectively). Adolescents were the second most affected age group and with the same pathogens as in puppies (
Figure 2).
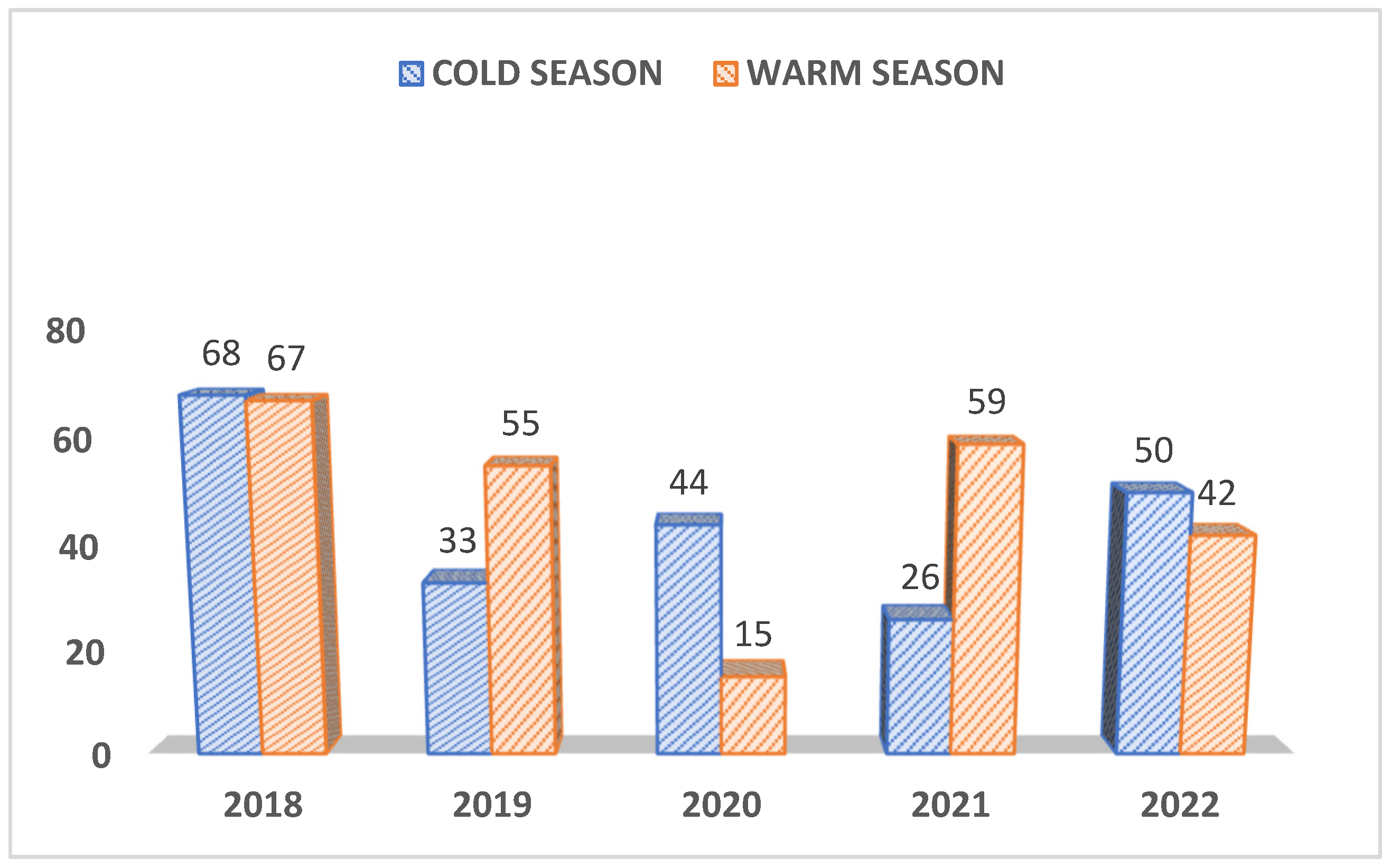
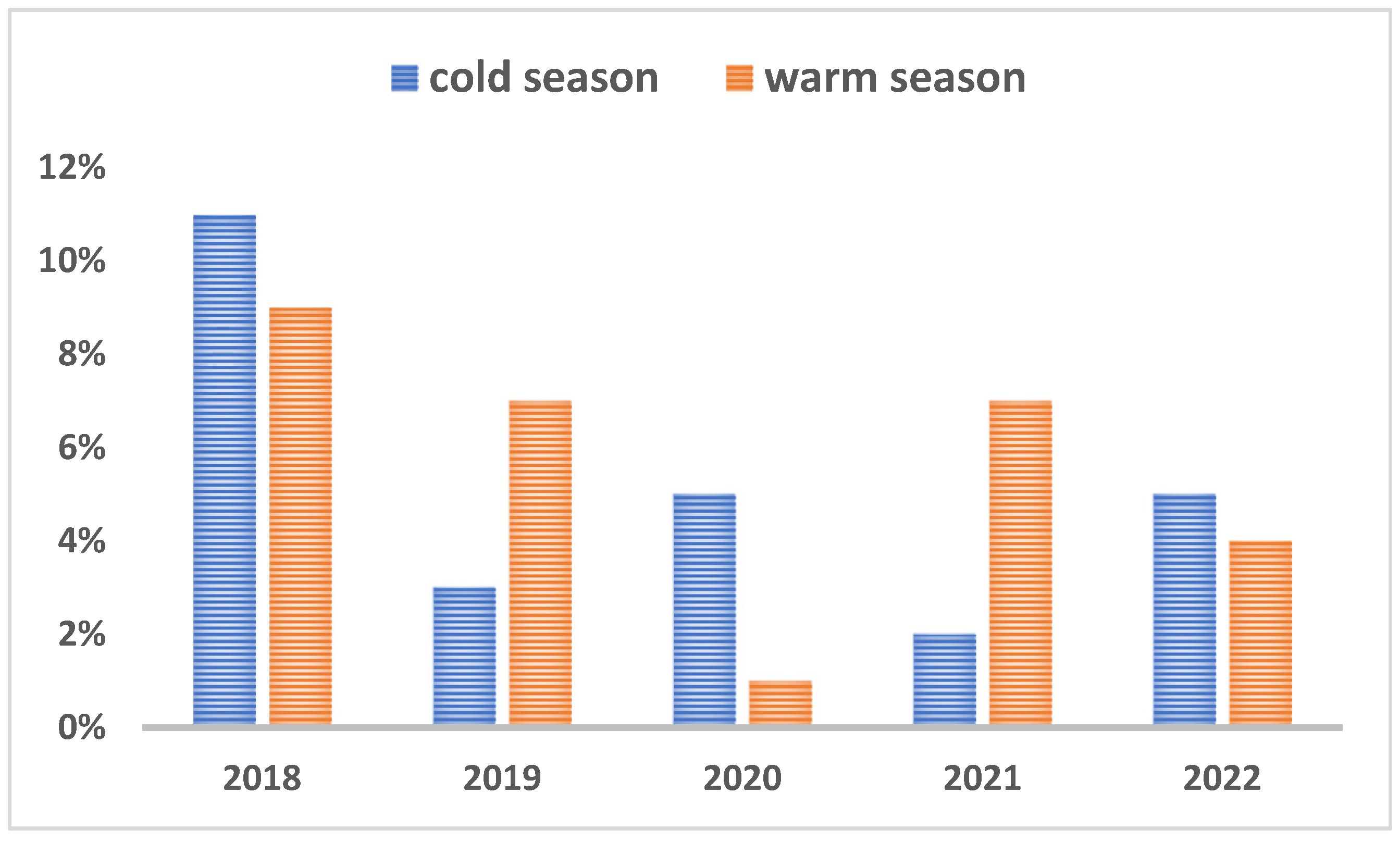
There was no significant relation between the pathogen occurrence and the sex except for CDV which was detected more often in males than in females (P<0.0475) and CIV was detected more frequently in females than in males (P<0.0054). As depicted in Figure 3A, regarding the seasonality of infections, more samples were received during the warm weather (n=238) than the cold season (n=221), but these case submissions fluctuated year by year as shown in figure 3A. Subsequently, the prevalence of positives cases also differed from year to year and did not show any particular trend (Figure 3 B).
Figure 1.
Overall prevalence of CIRDC pathogens.
Figure 1.
Overall prevalence of CIRDC pathogens.
Figure 2.
Age-wise distribution of CIRDC pathogens (2018-2022).
Figure 2.
Age-wise distribution of CIRDC pathogens (2018-2022).
Figure 3A.
Number of cases received during cold and warm seasons.
Figure 3A.
Number of cases received during cold and warm seasons.
Figure 3B.
Prevalence of positives cases during cold and warm seasons.
Figure 3B.
Prevalence of positives cases during cold and warm seasons.
4. Discussion
The study aimed to determine the prevalence of etiologic agents associated with CIRDC by doing a retrospective analysis of the cases submitted to the Athens Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory, University of Georgia, Athens, GA. We explored many aspects of the CIRDC in the present study including the prevalence of pathogens by age, sex, and seasonality. Our findings showed that puppies are the most affected by the CIRDC and that pathogens such as CPIV, M. cynos, and M. canis and B. bronchiseptica are predominantly associated with the disease condition. A previous study found that younger dogs were also commonly infected but with CCOV instead, and they tend to develop more severe clinical signs (Mitchell et al. 2017).
Kennel cough has always been seen as a regular common respiratory disease with truly little clinical significance that could be prevented through vaccination. In the past few years, the resurgence or emergence of new pathogens has progressively boosted the interest in this condition and is mostly seen as a complex now caused by multiple pathogens (Priestnall et al. 2014). Some of those emerging pathogens such as S. zooepidemicus, a commensal organism in horses, are often associated with opportunistic infections. S. zooepidemicus has been recently described as being involved in fatal hemorrhagic pneumonia in dogs (Byun et al. 2009; Chalker, Brooks, and Brownlie 2003) and M. cynos, was also isolated from several cases of lethal bronchopneumonia in puppies (Zeugswetter et al. 2007). Additionally, CCOV was shown to be prevalent and related to CIRDC complications in a European study (Mitchell et al. 2017). Given these points, we could infer there might be a possibility that emerging pathogens are associated with the increasing severity of disease which highlights the urge to implement good management and control measures. While S. zooepidemicus was not detected in another study (Maboni et al. 2019), we identified some positive cases of S. zooepidemicus in the present study.
The present study also demonstrated an exceptionally low occurrence of traditional CIRDC pathogens such as CDV, CAV-2 and B. bronchiseptica while surprisingly noticing other pathogens such as M. canis, M. cynos being commonly identified. These results might be suggesting that the widespread use of vaccines in the United States is successful. Paradoxically, this could convey the need to implement new vaccine regimens that include emerging pathogens. The kennel cough multivalent vaccines have been developed conferring protection against CDV, CAV type 1 and 2 and CPIV, also available in combination with B. bronchiseptica but not with emerging pathogens such as M. cynos.and M. canis Vaccination plays a significant role in CIRDC management by reducing the spread of pathogens and limiting the risk of developing a severe form of disease. Therefore, having more inclusive vaccines could be crucial to prevent the pathology.
It is noteworthy that CIRDC is a constantly evolving syndrome with pathogens continuing to emerge, and new agents are being identified at an increasingly rapid rate especially with the advance in sophisticated diagnostic techniques. Continued monitoring of CIRDC pathogens through rapid and accurate diagnostic testing and finetuning of vaccine strategies are critical in the prevention and control of CIRDC in dogs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.V. and H.N.; methodology, A.Y., A.K., and B.V. ; validation, B.V., and H.N.; formal analysis, A.Y., and A.K.; investigation, A.Y., and A.K.; resources, B.V., and H.N.; data curation, A.Y., and A.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.Y.; writing—review and editing, B.V.; visualization, B.V.; supervision, B.V., and H.N.; project administration, B.V.; funding acquisition, B.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Please add: This research was funded by the Athens Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory, College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Georgia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No additional data is available due to privacy or client confidentiality policy of the Athens Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the faculty and staff of Athens and Tifton veterinary diagnostic laboratories. We thankfully acknowledge the contribution of Dr. Keys for the support and guidance with the statistical analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Appel, M. J., and D. H. Percy. 1970. "SV-5-like parainfluenza virus in dogs." J Am Vet Med Assoc 156 (12):1778-81.
- Baverud, V., S. K. Johansson, and A. Aspan. 2007. "Real-time PCR for detection and differentiation of Streptococcus equi subsp. equi and Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus." Vet Microbiol 124 (3-4):219-29. [CrossRef]
- Bemis, D. A., H. A. Greisen, and M. J. Appel. 1977. "Pathogenesis of canine bordetellosis." J Infect Dis 135 (5):753-62. [CrossRef]
- Binn, L. N., R. H. Marchwicki, K. P. Keenan, A. J. Strano, and W. F. Engler. 1977. "Recovery of reovirus type 2 from an immature dog with respiratory tract disease." Am J Vet Res 38 (7):927-9.
- Buonavoglia, C., and V. Martella. 2007. "Canine respiratory viruses." Vet Res 38 (2):355-73. [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S. A., J. F. Beaulieu, J. Huggett, R. Jaggi, F. S. Kibenge, P. A. Olsvik, L. C. Penning, and S. Toegel. 2010. "MIQE precis: Practical implementation of minimum standard guidelines for fluorescence-based quantitative real-time PCR experiments." BMC Mol Biol 11:74. [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S. A., V. Benes, J. A. Garson, J. Hellemans, J. Huggett, M. Kubista, R. Mueller, T. Nolan, M. W. Pfaffl, G. L. Shipley, J. Vandesompele, and C. T. Wittwer. 2009. "The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments." Clin Chem 55 (4):611-22. [CrossRef]
- Byun, J. W., S. S. Yoon, G. H. Woo, B. Y. Jung, and Y. S. Joo. 2009. "An outbreak of fatal hemorrhagic pneumonia caused by Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus in shelter dogs." J Vet Sci 10 (3):269-71. [CrossRef]
- Chalker, V. J., H. W. Brooks, and J. Brownlie. 2003. "The association of Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus with canine infectious respiratory disease." Vet Microbiol 95 (1-2):149-56. [CrossRef]
- Chalker, V. J., W. M. Owen, C. Paterson, E. Barker, H. Brooks, A. N. Rycroft, and J. Brownlie. 2004. "Mycoplasmas associated with canine infectious respiratory disease." Microbiology (Reading) 150 (Pt 10):3491-7. [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, U., A. K. Tiwari, B. Ratta, P. V. Ravindra, Y. S. Rajawat, S. K. Palia, and A. Rai. 2008. "Detection of canine adenoviral infections in urine and faeces by the polymerase chain reaction." J Virol Methods 149 (2):260-3. [CrossRef]
- Crawford, P. C., E. J. Dubovi, W. L. Castleman, I. Stephenson, E. P. Gibbs, L. Chen, C. Smith, R. C. Hill, P. Ferro, J. Pompey, R. A. Bright, M. J. Medina, C. M. Johnson, C. W. Olsen, N. J. Cox, A. I. Klimov, J. M. Katz, and R. O. Donis. 2005. "Transmission of equine influenza virus to dogs." Science 310 (5747):482-5. [CrossRef]
- Decaro, N., F. Amorisco, C. Desario, E. Lorusso, M. Camero, A. L. Bellacicco, R. Sciarretta, M. S. Lucente, V. Martella, and C. Buonavoglia. 2010. "Development and validation of a real-time PCR assay for specific and sensitive detection of canid herpesvirus 1." J Virol Methods 169 (1):176-80. [CrossRef]
- Decaro, N., V. Mari, V. Larocca, M. Losurdo, G. Lanave, M. S. Lucente, M. Corrente, C. Catella, S. Bo, G. Elia, G. Torre, E. Grandolfo, V. Martella, and C. Buonavoglia. 2016. "Molecular surveillance of traditional and emerging pathogens associated with canine infectious respiratory disease." Vet Microbiol 192:21-25. [CrossRef]
- Ditchfield, J., L. W. Macpherson, and A. Zbitnew. 1962. "Association of Canine Adenovirus (Toronto A 26/61) with an Outbreak of Laryngotracheitis ("Kennel Cough"): A Preliminary Report." Can Vet J 3 (8):238-47.
- El-Attar, L. M. R., J. A. Mitchell, H. Brooks Brownlie, S. L. Priestnall, and J. Brownlie. 2015. "Detection of non-primate hepaciviruses in UK dogs." Virology 484:93-102. [CrossRef]
- Erles, K., and J. Brownlie. 2008. "Canine respiratory coronavirus: An emerging pathogen in the canine infectious respiratory disease complex." Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract 38 (4):815-25, viii. [CrossRef]
- Erles, K., E. J. Dubovi, H. W. Brooks, and J. Brownlie. 2004. "Longitudinal study of viruses associated with canine infectious respiratory disease." J Clin Microbiol 42 (10):4524-9. [CrossRef]
- Hozbor, D., F. Fouque, and N. Guiso. 1999. "Detection of Bordetella bronchiseptica by the polymerase chain reaction." Res Microbiol 150 (5):333-41. [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A., N. Mehta, E. J. Dubovi, P. Simmonds, L. Govindasamy, J. L. Medina, C. Street, S. Shields, and W. I. Lipkin. 2012. "Characterization of novel canine bocaviruses and their association with respiratory disease." J Gen Virol 93 (Pt 2):341-346. [CrossRef]
- Karpas, A., N. W. King, F. G. Garcia, F. Calvo, and R. E. Cross. 1968. "Canine tracheobronchitis: Isolation and characterization of the agent with experimental reproduction of the disease." Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 127 (1):45-52. [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, K., H. Ogawa, K. Maeda, A. Imai, E. Ohashi, S. Matsunaga, Y. Tohya, T. Ohshima, and M. Mochizuki. 2010. "Nosocomial outbreak of serious canine infectious tracheobronchitis (kennel cough) caused by canine herpesvirus infection." J Clin Microbiol 48 (4):1176-81. [CrossRef]
- Maboni, G., M. Seguel, A. Lorton, R. Berghaus, and S. Sanchez. 2019. "Canine infectious respiratory disease: New insights into the etiology and epidemiology of associated pathogens." PLoS ONE 14 (4):e0215817. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J. A., J. M. Cardwell, H. Leach, C. A. Walker, S. Le Poder, N. Decaro, M. Rusvai, H. Egberink, P. Rottier, M. Fernandez, E. Fragkiadaki, S. Shields, and J. Brownlie. 2017. "European surveillance of emerging pathogens associated with canine infectious respiratory disease." Vet Microbiol 212:31-38. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J. A., J. M. Cardwell, R. W. Renshaw, E. J. Dubovi, and J. Brownlie. 2013. "Detection of canine pneumovirus in dogs with canine infectious respiratory disease." J Clin Microbiol 51 (12):4112-9. [CrossRef]
- Pesavento, P. A., and B. G. Murphy. 2014. "Common and emerging infectious diseases in the animal shelter." Vet Pathol 51 (2):478-91. [CrossRef]
- Priestnall, S. L., J. A. Mitchell, C. A. Walker, K. Erles, and J. Brownlie. 2014. "New and emerging pathogens in canine infectious respiratory disease." Vet Pathol 51 (2):492-504. [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, Anant, Kenneth J. Drobatz, William T. N. Culp, and Lesley G. King. 2007. "Community-acquired infectious pneumonia in puppies: 65 cases (1993–2002)." Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association 230 (10):1493-1497. [CrossRef]
- Saito, T. B., A. A. Alfieri, S. R. Wosiacki, F. J. Negrao, H. S. Morais, and A. F. Alfieri. 2006. "Detection of canine distemper virus by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction in the urine of dogs with clinical signs of distemper encephalitis." Res Vet Sci 80 (1):116-9. [CrossRef]
- Spackman, E., D. A. Senne, L. L. Bulaga, T. J. Myers, M. L. Perdue, L. P. Garber, K. Lohman, L. T. Daum, and D. L. Suarez. 2003. "Development of real-time RT-PCR for the detection of avian influenza virus." Avian Dis 47 (3 Suppl):1079-82. [CrossRef]
- Spiss, S., V. Benetka, F. Künzel, I. Sommerfeld-Stur, K. Walk, M. Latif, and K. Möstl. 2012. "Enteric and respiratory coronavirus infections in Austrian dogs: Serological and virological investigations of prevalence and clinical importance in respiratory and enteric disease." Wiener Tierarztliche Monatsschrift 99 (3-4):67-81.
- Weese, J. S., and J. Stull. 2013. "Respiratory disease outbreak in a veterinary hospital associated with canine parainfluenza virus infection." Can Vet J 54 (1):79-82.
- Zeugswetter, F., H. Weissenböck, S. Shibly, J. Hassan, and J. Spergser. 2007. "Lethal bronchopneumonia caused by Mycoplasma cynos in a litter of golden retriever puppies." Vet Rec 161 (18):626-7. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).