1. Introduction
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) refer to abnormal connections between arteries and veins through a tangled low-resistance, high-flow vascular nidus, devoid of intervening capillaries. The rupture of brain AVMs (BAVMs) results in intracerebral hemorrhage, a life-threatening form of stroke. Traditionally, BAVMs have been regarded as congenital lesions present from birth. However, recent cases of
de novo BAVMs challenge the established notion that BAVMs originate congenitally [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8].
Approximately 95% of BAVMs are considered sporadic, lacking discernible inherited patterns. Somatic mosaic mutations in genes implicated in the rat sarcoma (RAS) signaling pathway have been identified within endothelial cells of sporadic BAVM lesions. Notably, mutations in the Kirsten RAS (
KRAS) gene are prevalent in over 50% of human sporadic BAVMs [
9,
10,
11].
In contrast, approximately 5% of BAVMs are familial and primarily associated with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT). HHT is an autosomal-dominant vascular disease, characterized by the occurrence of AVMs in the brain, lungs, and visceral organs. Mutations in the endoglin (
ENG), activin receptor-like kinase 1 (
ACVRL1 or
ALK1), or
SMAD4 genes have been identified as the underlying cause of this disorder [
12,
13,
14]. The proteins encoded by HHT-associated genes are crucial mediators in the signaling pathway of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) family of growth factors. Recent genetic studies have provided evidence that the development of AVMs is underpinned by a deficiency in the linear ENG-ALK1-SMAD4 pathway [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19]. In mouse models of HHT, the induction of AVMs requires homozygous deletion of the
Alk1,
Eng or
Smad4 gene [
16,
18,
19,
20,
21]. Furthermore, additional factors such as wounding or angiogenic stimulation, in addition to genetic deletion of HHT genes, are necessary for inducing AVMs in adult mice [
18,
22,
23,
24]. In mouse models of familial BAVMs, deletion of HHT-associated genes during embryonic and neonatal stages resulted in the concurrent development of BAVMs and visceral AVMs [
22,
24,
25,
26]. However, when the
Alk1 or
Eng gene was deleted during adulthood, it led to the formation of visceral AVMs but not BAVMs [
27]. Nevertheless, viral vector–mediated delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), the most potent angiogenic factor, along with genetic deletions of
Eng or
Alk1 resulted in BAVM-like cerebrovascular dysplasia in adult mice [
24,
28,
29,
30]. This suggests that HHT-associated gene deletion alone is insufficient to induce BAVMs in adult mice, emphasizing the need for additional angiogenic stimulation for BAVM development in adulthood. In contrast, a recent study with sporadic BAVM models revealed that endothelial cell–specific induction of mutant KRAS expression alone was sufficient for BAVM development in adult mice [
31,
32]. Collectively, these observations suggest the possibility of distinct underlying mechanisms between familial and sporadic cases in
de novo development of BAVMs.
In this study, we investigated the specific postnatal stages at which deletion of an HHT-associated gene triggers development of BAVMs. To identify these critical stages, we employed endothelial cell–specific, tamoxifen-inducible conditional Eng mutant mice. Our investigations revealed that BAVMs exclusively formed when Eng was deleted within the first 2 weeks of the postnatal period. This timeframe closely aligned with heightened VEGFR2 expression levels in the brain. These results suggest that a proangiogenic milieu during postnatal brain development may be critical for the development of BAVMs in this type I HHT mouse model. Furthermore, most Eng mutants displayed BAVMs in the forebrain and hindbrain, thus rendering this model a useful preclinical model for studying forebrain and cerebellar BAVMs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Transgenic mice and conditional gene deletion
All animal procedures were conducted in accordance with guidelines established by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Barrow Neurological Institute and St. Joseph Hospital Medical Center. The
Eng2f alleles were established in laboratory mice using techniques previously described [
16,
33]. The inducible endothelial cell–specific Cre transgenic mouse line,
SclCreER(+), [
34] was generously provided by Dr. Yunchao Su. While the conventional knockout of the
Eng gene results in early embryonic lethality [
17,
35,
36], the conditional knockout in
SclCreER(+) mice allows for the postnatal time- and tissue-specific deletion of the
Eng gene, particularly in the endothelium [
34]. To generate mutant mice (
SclCreER(+);
Eng2f/2f), we crossed
SclCreER(+) mice with floxed conditional
Eng deletion mice (
Eng2f/2f). These mice were on a mixed (129Sv/C57BL6) background. The
Eng gene was deleted at 4 different stages of postnatal life by administering tamoxifen (50 μg/day) intragastrically for 3 consecutive days at either postnatal days P1-3, P8-10, P15-17, or P22-24. An alternative high-dose tamoxifen strategy used a dosage of 250 μg/day was administered for 3 consecutive days at P22-24. Furthermore, we utilized
Flk1-LacZ knock-in reporter mice, kindly provided by Dr. J. Rossant, and in a mixed (129Sv/C57BL6) background, to analyze the promoter activity of
Flk1, which encodes vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2).
2.2. AVM visualization using latex dye perfusion
Mice were anesthetized using a ketamine (100 mg/kg body weight) and xylazine (10 mg/kg body weight) mixture. Following this, the thoracic cavity was opened to expose the heart. Blue latex dye (5 μL/g body weight; VWR, Radnor, PA) was injected through the left heart following sequential perfusion with vasodilating and fixative reagents, as previously described [
37]. After overnight fixation, the brains were isolated, dehydrated, and cleared using organic solvents, in accordance with established methods [
22]. The cleared brains were sectioned into 1-mm-thick coronal slices using a brain slicer matrix (Zivic Instruments, Pittsburgh, PA). The sectioned brains were imaged with a CCD camera (Leica, Allendale, NJ) to capture the latex dye–perfused cerebrovasculature and BAVMs. To assess the formation of skin AVMs, a wound was induced at 3 weeks of age through ear tagging. This was followed by perfusion of 0.5 mL latex dye through the left heart at 2 to 3 months of age. After overnight fixation, the ears were placed on Styrofoam and cleared using organic solvents, following the previously described protocol [
22].
2.3. Hemoglobin concentration
Hemoglobin levels in the blood were quantified using a hemoglobin photometer (Hemopoint H2, STANBIO Laboratory).
2.4. Western blotting
The right cerebrum brain tissues were lysed using RIPA lysis buffer (Thermo Scientific) containing 1X Halt™ Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (Pierce) and 1X Halt™ Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (Pierce). The protein concentration was determined using the DC™ Protein Assay kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories), and proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE. Subsequently, the samples were transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane (Bio-Rad Laboratories). The following primary antibodies were used: anti-VEGFR2 (2479, Cell Signaling, 1:1000), anti-CD31 (ab124432, Abcam, 1:1000), and anti-β-actin (A1978, Sigma, 1:5000). Secondary antibodies included HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (NA934, GE healthcare, 1:5000) and HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (NA931, GE healthcare, 1:5000). Detection was accomplished using the ECL western blotting substrate (Pierce), and the bands were quantified using ImageJ software, version 1.53t.
2.5. Magnetic resonance imaging
BAVMs in mice were examined using brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and 3D time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (MRA). Each mouse was induced and maintained under isoflurane anesthesia (3% induction, 1-2% maintenance) in medical air. Respiratory activity was continuously monitored using a pillow sensor positioned under the abdomen (SA Instruments, Stony Brook, NY), and normal body temperature (36–37 °C) was maintained using a circulating warm water blanket (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL).
MRI was performed using a 7T small-animal, 30-cm horizontal-bore magnet and BioSpec Avance III spectrometer (Bruker, Billerica, MA) with a 116-mm high-power gradient set (600 mT/m) and a 30-mm whole-body mouse quadrature coil. Fast spin-echo scout images were acquired in three orthogonal planes to cover the brain (repetition time [TR]=1000 ms, echo time [TE]=12.5 ms, effective echo time [TEeff]=50 ms, 128×128 matrix, 0.234×0.234×1.5-mm voxels, number of acquisitions [NEX]=1). These scout images were then used to determine the placement of T2-weighted MRI and MRA images. Coronal T2-weighted rapid acquisition with relaxation enhancement MRI images were acquired to span the volume of the brain and identify BAVM lesions (TR=5000 ms, TE=12 ms, TEeff=60 ms, Rare Factor=8, 180×180 matrix, 0.1×0.1×0.5-mm voxels, 30 slices, NEX=4). Three-dimensional time-of-flight MRA images were acquired using a flow-compensated gradient echo method (TR=30 ms, TE=3.5 ms, α= 30°, 180×180×200 matrix, 0.1×0.1×0.1 voxels, NEX=4). Magnetization transfer pulses were added to the MRA acquisition to provide additional background tissue suppression (offset frequency= 1500 Hz, r.f. amplitude= 0.5 μT).
2.6. X-gal staining and vascular density quantification
Anesthesia was induced in Flk1-LacZ mice through intraperitoneal injection of a mixture comprising ketamine (100 mg/kg body weight) and xylazine (10 mg/kg body weight). Mice were transcardially perfused using a GP1000 peristaltic pump (Fisher Scientific) with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) containing heparin (50 units/mL). Brains were extracted from the cranium and fixed in a PBS solution containing 1% formaldehyde, 2 mM MgCl2, 5 mM EGTA, and 0.02% NP-40 for 5 minutes. This was followed by an additional 10-minute fixation period after coronal slicing. After washing with PBS, the fixed brain sections were incubated with X-gal staining solution containing 5 mM K3Fe(CN)6, 5 mM K4Fe(CN)6, 2 mM MgCl2, 0.01% sodium deoxycholate, 0.02% NP-40, 0.5 mg/mL X-gal in dimethylformamide, PBS (1/10 vol), and 2.5 mM EGTA at 37˚C overnight. VEGFR2 (Flk1)-expressing blood vessels appeared blue and were imaged using the CCD camera (Leica, Allendale, NJ). Vascular density was quantified using ImageJ in conjunction with the vessel analysis plugin.
2.7. Statistical analysis
Categorical data are represented as numbers and percentages, and continuous data are represented as mean and standard deviation (SD). The variations in VEGFR2/CD31/β-actin levels, the mean vascular density, and the hemoglobin levels were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey multiple comparison tests. The threshold for statistical significance was established as p<0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Endothelial cell Eng gene deletion induces BAVM development
To induce the deletion of the
Eng gene within endothelial cells, we administered tamoxifen (25 μg/g body weight) to
SclCreER(+);
Eng2f/2f mice intragastrically for 3 consecutive days, starting on P1 (P1-3). Approximately 60% of
SclCreER(+);
Eng2f/2f mice treated with tamoxifen at P1-3 did not survive beyond 6 months, likely due to hemorrhages caused by AVMs in the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and brain (
Supplementary Figure S1) [
25,
26,
38].
The presence of BAVMs was assessed at 2 to 3 months of age using latex dye perfusion, a technique that enables the visualization of arteriovenous shunts because the latex dye passes through the nidus and directly enters enlarged venous channels (
Figure 1) [
38]. Approximately 90% of mutant mice treated with tamoxifen at P1-3 developed BAVMs, with a predominant localization in the forebrain (
Figure 1B), cerebellum (
Figure 1C), or both regions (
Figure 1D). Notably, cerebellar BAVMs constituted the most frequent subtype, accounting for 48% (N=10/21) of all BAVMs observed, followed by forebrain BAVMs (33%, N=7/21). The BAVM phenotype was characterized by a vascular nidus composed of enlarged, tortuous vessels derived from feeding arteries and draining veins. These characteristics were discernible in latex dye–perfused coronal brain sections (
Figure 1F-H).
3.2. Longitudinal monitoring of BAVMs using magnetic resonance angiography
In our previous study, we employed high-resolution MRA to study BAVM progression in
TaglnCre(+);
Alk12f/2f mutant mice, where Cre recombinase is expressed in smooth muscle cells and a subset of endothelial cells [
38]. In that model, BAVMs predominantly developed in the parietal lobe, establishing a reliable preclinical longitudinal model for studying brain BAVMs. Since
SclCreER(+);
Eng2f/2f mutant mice in this study displayed nidal BAVMs in the forebrain and cerebellum, we explored their potential as an alternative longitudinal mouse model, particularly for forebrain and cerebellar BAVMs.
As anticipated, the control mice displayed a normal arterial angioarchitecture of the anterior and posterior circulations, as well as the Circle of Willis. No vascular malformations were observed in control mice (n=3) throughout the 9-month study duration (
Figure 2A-C). In contrast,
Eng mutant mice (81%, 17/21) exhibited forebrain and cerebellar BAVMs characterized by a vascular nidus, feeding arteries, and draining veins (
Figure 2D-I). These BAVMs remained stable throughout the 9-month study period. Additionally, cerebellar BAVMs were characterized by a substantial nidus that occupied most of the cerebellum (
Figure 1C-D) and drained bilaterally through the transverse sinus (
Figure 2G-I).
3.3. The early postnatal period is critical for BAVM development
To address the prevailing belief that BAVMs are congenital in nature, we employed a time-dependent gene deletion strategy. Our objective was to investigate the possibility of inducing BAVMs at specific postnatal time points through targeted deletion of the
Eng gene. Tamoxifen was administered to
Eng mutant mice at various postnatal intervals, including at 1 week (P8-10), 2 weeks (P15-17), and 3 weeks (P22-24) of age, in addition to the previously studied P1-3 timeframe. Subsequently, we assessed the presence of BAVMs in these mice at the age of 2 to 3 months using latex dye perfusion (
Figure 3).
The P8-10 group exhibited a similar frequency of BAVM formation (86%, N=6/7) compared to the P1-3 group (88%, N=21/24). The P15-17 group displayed a slightly lower frequency of BAVM formation (55%, N=6/11) compared to the P1-3 and P8-10 groups (
Figure 3I). Additionally, both the P8-10 and P15-17 groups developed smaller BAVMs compared to the P1-3 group. Notably, the majority of BAVMs in the P8-10 and P15-17 groups were localized in the parietal lobe (83%, N=10/12), distinguishing them from the forebrain and cerebellar BAVMs observed in the P1-3 group (
Figure 3B-C, 3F-G). Interestingly, the P22-24 group did not exhibit any BAVM development, raising concerns about inadequate tamoxifen levels for initiating BAVM formation, considering their increased body weight. To eliminate the possibility of insufficient tamoxifen blood levels in the P22-24 group, we increased the tamoxifen dosage (250 μg/day, 25 μg/g body weight) to match that of the P1-3 group. Nonetheless, the high-dose treatment did not yield BAVMs in the P22-24 group (
Figure 3I). However, we observed skin AVMs in wounded ears (
Figure 4), confirming that tamoxifen levels were adequate in the P22-24 group. Collectively, these findings suggest that within the first 2 weeks of the postnatal period, physiologic stimuli play a pivotal role in shaping the microenvironment essential for the induction of BAVMs, in conjunction with a genetically induced
Eng deficiency.
3.4. VEGFR2 expression predominates in the early postnatal period
In our quest to understand the nature of these critical physiological stimuli within the microenvironment, we focused our investigations on the proangiogenic conditions present in the early postnatal brain. This direction was informed by previous studies demonstrating the need for angiogenic stimulation to induce BAVMs, in addition to genetic deletions of the
Alk1 or
Eng gene [
24,
39]. Moreover, studies have provided insights into the temporal dynamics of angiogenic activity in the rodent brain, with peak levels observed during the first postnatal week, followed by a gradual decline over the subsequent weeks [
40,
41,
42]. Among the proangiogenic pathways, the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling cascade, with VEGFR2 as the primary receptor, is one of the most extensively studied [
43]. Previous reports have shown that VEGFR2 expression is most pronounced during the initial 2 postnatal weeks, after which it significantly declines in the mouse brain vasculature [
44].
To substantiate these findings, we analyzed the protein expression of VEGFR2 and CD31 in the brains of control mice (Cre-negative,
Eng2f/2f mice) at various postnatal time points, including P8, P15, P22, and P29. Our analysis revealed that VEGFR2 expression in the brain was notably abundant during the initial 2-week postnatal period, gradually declining thereafter. Conversely, the expression of CD31, an endothelial cell marker, continued to increase throughout the postnatal period (
Figure 5).
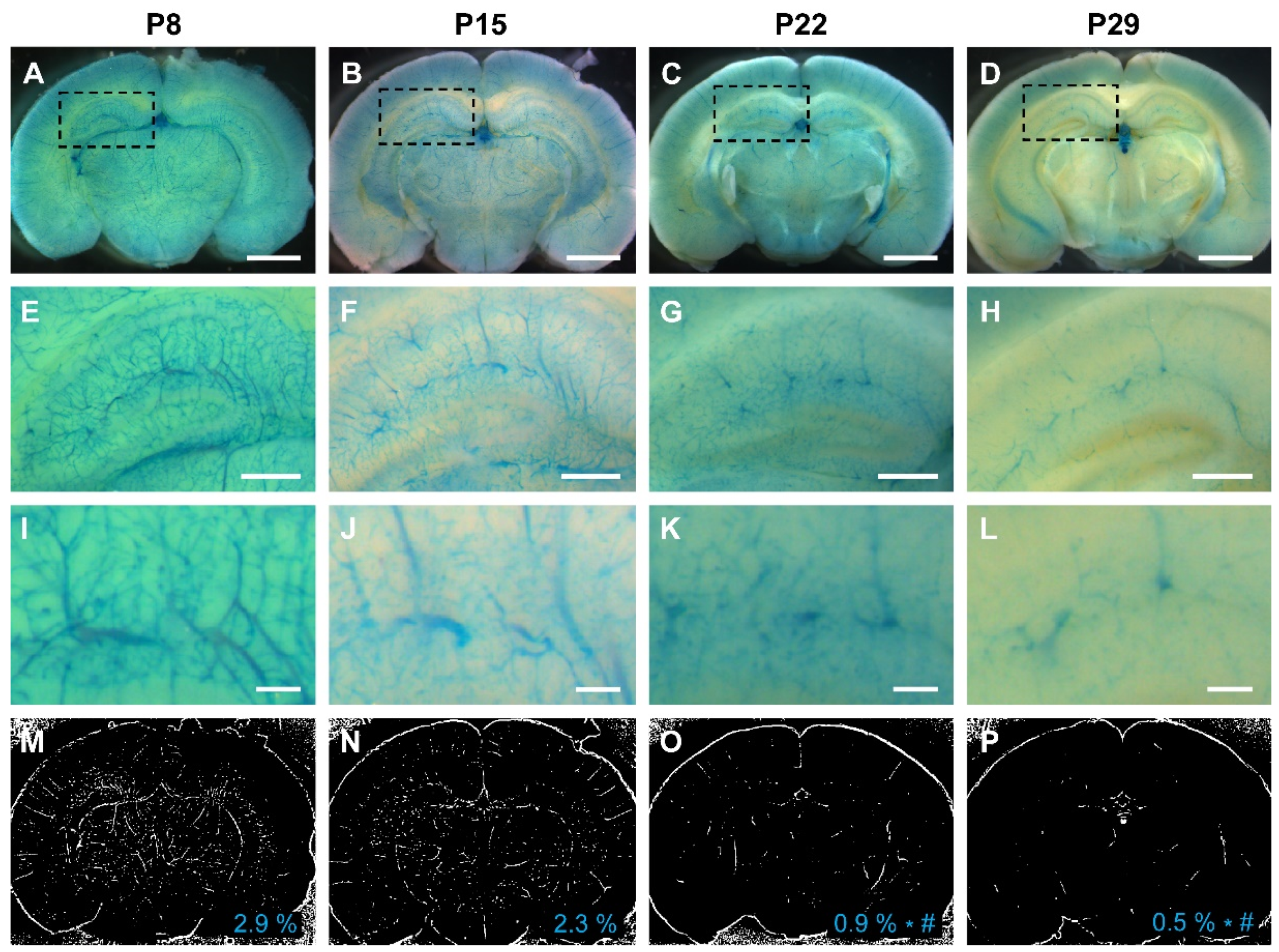
To further validate our results, we leveraged a
Vegfr2 (
Flk1)-LacZ reporter mouse line, wherein β-galactosidase expression is controlled by the
Vegfr2 promoter. Consistent with our biochemical observations, the activity of the
Vegfr2 promoter in the brain peaked during the first 2 postnatal weeks (2.9% in the first week and 2.3% in the second week), with a significant decline in the third and fourth weeks (0.9% in the third week and 0.5 % in the fourth week) (
Figure 6).
4. Discussion
4.1. Postnatal development of BAVMs in a type I HHT mouse model
In this study, we have introduced a novel longitudinal mouse model of familial BAVMs by employing tamoxifen-mediated, endothelial cell–deletion of the Eng gene during the neonatal stages. Our investigations have revealed that BAVMs effectively emerge when Eng is deleted within the initial 2 weeks after birth. This discovery informs the contribution of a crucial physiological microenvironment during the early postnatal period, which plays a pivotal role in driving BAVM development. The predominant expression of VEGFR2 in the developing mouse brain during this initial 2-week postnatal period strongly suggests the presence of a proangiogenic milieu functioning as an intrinsic co-factor in the development of BAVMs.
4.2. The congenital nature of BAVMs
The classification of BAVMs as a congenital disease remains a subject of ongoing debate. Previous studies involving HHT mouse models, including both
Alk1 and
Eng mice, have lent support to the hypothesis that BAVMs develop congenitally [
22,
24,
39]. Furthermore, when either the
Alk1 or
Eng gene was deleted in adult mice, neither BAVMs [
24,
39] nor skin AVMs [
22] developed. However, BAVMs did manifest when VEGF expression was induced in the
Alk1- or
Eng-deleted adult mouse brain [
24,
39]. Likewise, the infliction of a wound or the induction of VEGF in the back skin of
Alk1-deleted adult mice resulted in the development of skin AVMs at those sites [
22,
37]. Collectively, these findings suggest that HHT gene deletion alone is insufficient to induce BAVMs in the adult mouse brain. An additional factor, such as wounding, appears to be crucial for the definitive formation of BAVMs. Within the context of our study, we observed that deletion of the
Eng gene in endothelial cells during the first 2 postnatal weeks is a critical prerequisite for inducing BAVMs, providing further reinforcement of the prevailing theory that BAVMs are inherently congenital in nature.
4.3. Angiogenesis as an endogenous secondary hit
What plays such a critical role in the initial 2 weeks of the postnatal period that leads to the formation of BAVMs? If indeed an endogenous secondary event is effective during this period, what characterizes or defines the nature of this event? The concept of angiogenesis has emerged as a prominent factor in the “secondary hit” hypothesis regarding BAVM pathogenesis [
20,
45].
In the mouse brain, capillaries constitute the predominant vessel type, accounting for over 90% of the total cerebrovascular length [
46]. However, at birth, the capillary network is relatively sparse and incomplete compared to the dense capillary network found in the adult mouse brain. During the first few weeks of life, the cortical capillary network of rodents undergoes a dramatic expansion, primarily driven by VEGF-regulated angiogenesis. This expansion reaches its peak between postnatal days 15 to 25, after which the angiogenic capacity within the capillary network gradually subsides as the capillary density stabilizes [
46,
47,
48,
49]. During this phase of stabilization, both pericyte and endothelial cell proliferation rates decline [
47]. The findings of our study align with this temporal pattern of angiogenic activity. We observed that BAVMs develop when the
Eng gene is conditionally deleted at P1-3, P8-10, and P15-17 but not at P22-24. This suggests that mice produce ample endogenous angiogenic stimuli to facilitate BAVM formation up to P15-17, beyond which there is a gradual decline in angiogenic activity, rendering VEGF levels inadequate to serve as a secondary hit for BAVM formation.
In rodents, postnatal day 10 is approximately equivalent to the developmental stage of a 40-week gestational period in humans [
50]. This timing suggests that the events occurring during the first 2 weeks after birth in rodents are relevant to the prenatal and neonatal development of the cerebrovasculature in humans. This alignment may elucidate why BAVMs are predominantly regarded as congenital lesions and why the occurrence of
de novo BAVMs is relatively rare compared to congenital cases.
4.4. Pathogenesis of de novo BAVMs
The occurrence of
de novo BAVM formation in the adult human brain, particularly when angiogenesis is not actively occurring, is a rare and challenging phenomenon to understand. Given that angiogenesis alone is unlikely to serve as a direct catalyst for BAVM formation [
51], patients with
de novo BAVMs may have genetic predispositions for BAVM development, such as carrying HHT gene mutations [
12,
13] or exhibiting somatic mutations in the
KRAS gene [
9].
Over the course of a lifetime, the stabilized cerebrovascular network can be influenced by an array of events capable of modifying angiogenic activity, such as ischemia [
2], traumatic brain injury [
7], intracerebral hemorrhage [
6], seizures [
3], intracranial tumors [
5], and inflammatory processes caused by bacterial and viral infections [
1], among others. These inciting events, when combined with genetically predisposed or somatically mutated cerebrovascular cells, may collectively contribute to the development of
de novo BAVMs by increasing angiogenic activity beyond a certain threshold. Conversely, it has been reported that
Kras mutations alone have the capacity to induce
de novo BAVMs in adult mice without the need for an additional stimulus [
31,
32]. While this may not entirely align with the congenital theory of BAVMs, it is important to note that
Kras mutant mice have exhibited enhanced VEGF-associated angiogenesis [
31,
32]. Therefore, it remains plausible that angiogenic stimuli still play a role in the formation of
de novo BAVMs in cases associated with
KRAS mutations.
4.5. A novel mouse model for forebrain and hindbrain BAVMs
In HHT patients, the 2 most common locations of BAVMs were the frontal lobes (43.6%) and the cerebellum (15.4%) [
52] while in other BAVMs, BAVMs occurred more commonly in the frontal lobe (18-21%) and temporal lobe (18-19%) [
53,
54].
In our previous study, we used
TaglnCre(+);
Alk1 mutant mice to establish a longitudinal BAVM mouse model [
38]. In that model, the predominant site for BAVM development was the parietal lobe, with BAVMs frequently localized along the posterior cerebral artery or within its vascular territory. In contrast, our present study with
SclCreER(+);
Eng2f/2f mutant mice reveals a different pattern of BAVM localization. Here, mice primarily developed cerebellar BAVMs (48%) and forebrain BAVMs (33%). This model offers a valuable resource for studying both forebrain and hindbrain BAVMs in a longitudinal preclinical framework.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we have established a novel mouse model to investigate the pathogenesis of BAVMs, with a particular focus on forebrain and hindbrain BAVMs, utilizing SclCreER(+);Eng2f/2f mice. Through tamoxifen-dependent, endothelial cell–specific gene deletion, we demonstrated that deletion of the Eng gene within endothelial cells reliably results in the development of BAVMs during the initial 2-week postnatal period. This timeframe corresponds to elevated expression of the VEGFR2 receptor. The temporal correlation between early postnatal BAVM development and heightened angiogenic activity suggests that angiogenesis may contribute to a specific physiological microenvironment critical for initiating BAVM development. Consequently, our investigations support the prevailing belief that BAVMs derive congenitally, primarily governed by angiogenesis as an endogenous secondary hit during the early postnatal period.
In summary, our study presents a promising preclinical model for advancing the development of novel therapeutic strategies for BAVM treatment. In addition, it contributes to a deeper understanding of the complex mechanisms implicated in BAVM development.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1: Survival analysis and hemoglobin studies in the type I HHT mouse model.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.P.O. and M.T.L.; methodology, C.H., T.D.S.; investigation, C.H.; data curation, C.H. and C.N.; writing—original draft preparation, C.H. and S.P.O; writing—review and editing, L.S., H.M.A., M.T.L., S.P.O.; funding acquisition, S.P.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Barrow Neurological Foundation (BNF), the Leducq Foundation (ATTRACT), and the US Department of Defense (PR161205) awarded to S.P.O., and a BNF Postdoctoral Fellowship Grant awarded to C.H.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal procedures were conducted in accordance with guidelines established by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Barrow Neurological Institute and St. Joseph Hospital Medical Center (protocols #531 and #573).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Alberto E. Fuentes and Gregory H. Turner from the BNI-ASU Center for Preclinical Imaging for technical assistance with magnetic resonance imaging.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Florian, I.A.; Beni, L.; Moisoiu, V.; Timis, T.L.; Florian, I.S.; Balasa, A.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. 'De Novo' Brain AVMs-Hypotheses for Development and a Systematic Review of Reported Cases. Medicina (Kaunas) 2021, 57. [CrossRef]
- Pabaney, A.H.; Rammo, R.A.; Tahir, R.A.; Seyfried, D. Development of De Novo Arteriovenous Malformation Following Ischemic Stroke: Case Report and Review of Current Literature. World Neurosurg 2016, 96, 608 e605-608 e612. [CrossRef]
- Dogan, S.N.; Bagcilar, O.; Mammadov, T.; Kizilkilic, O.; Islak, C.; Kocer, N. De Novo Development of a Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation: Case Report and Review of the Literature. World Neurosurg 2019, 126, 257-260. [CrossRef]
- Torres-Quinones, C.; Koch, M.J.; Raymond, S.B.; Patel, A. Left Thalamus Arteriovenous Malformation Secondary to Radiation Therapy of Original Vermian Arteriovenous Malformation: Case Report. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2019, 28, e53-e59. [CrossRef]
- Lo Presti, A.; Rogers, J.M.; Assaad, N.N.A.; Rodriguez, M.L.; Stoodley, M.A.; Morgan, M.K. De novo brain arteriovenous malformation after tumor resection: Case report and literature review. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2018, 160, 2191-2197. [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues de Oliveira, L.F.; Castro-Afonso, L.H.; Freitas, R.K.; Colli, B.O.; Abud, D.G. De Novo Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformation-Case Report and Literature Review. World Neurosurg 2020, 138, 349-351. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, L.F.; Bristol, R.E.; Porter, R.W.; Spetzler, R.F. De novo presentation of an arteriovenous malformation. Case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg 2005, 102, 726-729. [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, Y.; Osanai, T.; Nakayama, N.; Ushikoshi, S.; Hokari, M.; Shichinohe, H.; Abumiya, T.; Kazumata, K.; Houkin, K. De novo arteriovenous malformation in a patient with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2016, 17, 330-335. [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, S.I.; Vetiska, S.; Bonilla, X.; Boudreau, E.; Jauhiainen, S.; Rezai Jahromi, B.; Khyzha, N.; DiStefano, P.V.; Suutarinen, S.; Kiehl, T.R.; et al. Somatic Activating KRAS Mutations in Arteriovenous Malformations of the Brain. N Engl J Med 2018, 378, 250-261. [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Radovanovic, I.; Ma, X.; Shao, Y.W.; Yu, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ling, F.; et al. High prevalence of KRAS/BRAF somatic mutations in brain and spinal cord arteriovenous malformations. Brain 2019, 142, 23-34. [CrossRef]
- Oka, M.; Kushamae, M.; Aoki, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kitazato, K.; Abekura, Y.; Kawamata, T.; Mizutani, T.; Miyamoto, S.; Takagi, Y. KRAS G12D or G12V Mutation in Human Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. World Neurosurg 2019, 126, e1365-e1373. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; Berg, J.N.; Baldwin, M.A.; Gallione, C.J.; Marondel, I.; Yoon, S.J.; Stenzel, T.T.; Speer, M.; Pericak-Vance, M.A.; Diamond, A.; et al. Mutations in the activin receptor-like kinase 1 gene in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2. Nat Genet 1996, 13, 189-195. [CrossRef]
- McAllister, K.A.; Grogg, K.M.; Johnson, D.W.; Gallione, C.J.; Baldwin, M.A.; Jackson, C.E.; Helmbold, E.A.; Markel, D.S.; McKinnon, W.C.; Murrell, J.; et al. Endoglin, a TGF-beta binding protein of endothelial cells, is the gene for hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia type 1. Nat Genet 1994, 8, 345-351. [CrossRef]
- Gallione, C.J.; Repetto, G.M.; Legius, E.; Rustgi, A.K.; Schelley, S.L.; Tejpar, S.; Mitchell, G.; Drouin, E.; Westermann, C.J.; Marchuk, D.A. A combined syndrome of juvenile polyposis and hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia associated with mutations in MADH4 (SMAD4). Lancet 2004, 363, 852-859. [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Hanes, M.A.; Dickens, T.; Porteous, M.E.; Oh, S.P.; Hale, L.P.; Marchuk, D.A. A mouse model for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) type 2. Hum Mol Genet 2003, 12, 473-482. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.O.; Lee, Y.J.; Seki, T.; Hong, K.H.; Fliess, N.; Jiang, Z.; Park, A.; Wu, X.; Kaartinen, V.; Roman, B.L.; et al. ALK5- and TGFBR2-independent role of ALK1 in the pathogenesis of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2. Blood 2008, 111, 633-642. [CrossRef]
- Bourdeau, A.; Dumont, D.J.; Letarte, M. A murine model of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. J Clin Invest 1999, 104, 1343-1351. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Choe, S.W.; Chae, M.Y.; Hong, S.; Oh, S.P. SMAD4 Deficiency Leads to Development of Arteriovenous Malformations in Neonatal and Adult Mice. J Am Heart Assoc 2018, 7, e009514. [CrossRef]
- Crist, A.M.; Lee, A.R.; Patel, N.R.; Westhoff, D.E.; Meadows, S.M. Vascular deficiency of Smad4 causes arteriovenous malformations: A mouse model of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. Angiogenesis 2018, 21, 363-380. [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.; Allinson, K.R.; Zhai, Z.; Oakenfull, R.; Ghandi, P.; Adams, R.H.; Fruttiger, M.; Arthur, H.M. Pathogenesis of arteriovenous malformations in the absence of endoglin. Circ Res 2010, 106, 1425-1433. [CrossRef]
- Tual-Chalot, S.; Mahmoud, M.; Allinson, K.R.; Redgrave, R.E.; Zhai, Z.; Oh, S.P.; Fruttiger, M.; Arthur, H.M. Endothelial depletion of Acvrl1 in mice leads to arteriovenous malformations associated with reduced endoglin expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98646. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.O.; Wankhede, M.; Lee, Y.J.; Choi, E.J.; Fliess, N.; Choe, S.W.; Oh, S.H.; Walter, G.; Raizada, M.K.; Sorg, B.S.; et al. Real-time imaging of de novo arteriovenous malformation in a mouse model of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. J Clin Invest 2009, 119, 3487-3496. [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Martin, E.M.; Nguyen, H.L.; Cunningham, T.A.; Choe, S.W.; Jiang, Z.; Arthur, H.M.; Lee, Y.J.; Oh, S.P. Common and distinctive pathogenetic features of arteriovenous malformations in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia 1 and hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia 2 animal models--brief report. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2014, 34, 2232-2236. [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.J.; Chen, W.; Jun, K.; Arthur, H.M.; Young, W.L.; Su, H. Novel brain arteriovenous malformation mouse models for type 1 hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88511. [CrossRef]
- Scherschinski, L.; Han, C.; Kim, Y.H.; Winkler, E.A.; Catapano, J.S.; Schriber, T.D.; Vajkoczy, P.; Lawton, M.T.; Oh, S.P. Localized conditional induction of brain arteriovenous malformations in a mouse model of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Angiogenesis 2023, 26, 493-503. [CrossRef]
- Milton, I.; Ouyang, D.; Allen, C.J.; Yanasak, N.E.; Gossage, J.R.; Alleyne, C.H., Jr.; Seki, T. Age-dependent lethality in novel transgenic mouse models of central nervous system arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 2012, 43, 1432-1435. [CrossRef]
- Tual-Chalot, S.; Garcia-Collado, M.; Redgrave, R.E.; Singh, E.; Davison, B.; Park, C.; Lin, H.; Luli, S.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Loss of Endothelial Endoglin Promotes High-Output Heart Failure Through Peripheral Arteriovenous Shunting Driven by VEGF Signaling. Circ Res 2020, 126, 243-257. [CrossRef]
- Walker, E.J.; Su, H.; Shen, F.; Degos, V.; Amend, G.; Jun, K.; Young, W.L. Bevacizumab attenuates VEGF-induced angiogenesis and vascular malformations in the adult mouse brain. Stroke 2012, 43, 1925-1930. [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.J.; Walker, E.J.; Shen, F.; Oh, S.P.; Arthur, H.M.; Young, W.L.; Su, H. Minimal homozygous endothelial deletion of Eng with VEGF stimulation is sufficient to cause cerebrovascular dysplasia in the adult mouse. Cerebrovasc Dis 2012, 33, 540-547. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Guo, Y.; Walker, E.J.; Shen, F.; Jun, K.; Oh, S.P.; Degos, V.; Lawton, M.T.; Tihan, T.; Davalos, D.; et al. Reduced mural cell coverage and impaired vessel integrity after angiogenic stimulation in the Alk1-deficient brain. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2013, 33, 305-310. [CrossRef]
- Park, E.S.; Kim, S.; Huang, S.; Yoo, J.Y.; Korbelin, J.; Lee, T.J.; Kaur, B.; Dash, P.K.; Chen, P.R.; Kim, E. Selective Endothelial Hyperactivation of Oncogenic KRAS Induces Brain Arteriovenous Malformations in Mice. Ann Neurol 2021, 89, 926-941. [CrossRef]
- Fish, J.E.; Flores Suarez, C.P.; Boudreau, E.; Herman, A.M.; Gutierrez, M.C.; Gustafson, D.; DiStefano, P.V.; Cui, M.; Chen, Z.; De Ruiz, K.B.; et al. Somatic Gain of KRAS Function in the Endothelium Is Sufficient to Cause Vascular Malformations That Require MEK but Not PI3K Signaling. Circ Res 2020, 127, 727-743. [CrossRef]
- Allinson, K.R.; Carvalho, R.L.; van den Brink, S.; Mummery, C.L.; Arthur, H.M. Generation of a floxed allele of the mouse Endoglin gene. Genesis 2007, 45, 391-395. [CrossRef]
- Gothert, J.R.; Gustin, S.E.; van Eekelen, J.A.; Schmidt, U.; Hall, M.A.; Jane, S.M.; Green, A.R.; Gottgens, B.; Izon, D.J.; Begley, C.G. Genetically tagging endothelial cells in vivo: Bone marrow-derived cells do not contribute to tumor endothelium. Blood 2004, 104, 1769-1777. [CrossRef]
- Arthur, H.M.; Ure, J.; Smith, A.J.; Renforth, G.; Wilson, D.I.; Torsney, E.; Charlton, R.; Parums, D.V.; Jowett, T.; Marchuk, D.A.; et al. Endoglin, an ancillary TGFbeta receptor, is required for extraembryonic angiogenesis and plays a key role in heart development. Dev Biol 2000, 217, 42-53. [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Y.; Sorensen, L.K.; Brooke, B.S.; Urness, L.D.; Davis, E.C.; Taylor, D.G.; Boak, B.B.; Wendel, D.P. Defective angiogenesis in mice lacking endoglin. Science 1999, 284, 1534-1537. [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Choe, S.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Acharya, A.P.; Keselowsky, B.G.; Sorg, B.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Oh, S.P. VEGF neutralization can prevent and normalize arteriovenous malformations in an animal model for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia 2. Angiogenesis 2014, 17, 823-830. [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Lang, M.J.; Nguyen, C.L.; Luna Melendez, E.; Mehta, S.; Turner, G.H.; Lawton, M.T.; Oh, S.P. Novel experimental model of brain arteriovenous malformations using conditional Alk1 gene deletion in transgenic mice. J Neurosurg 2021, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Sun, Z.; Han, Z.; Jun, K.; Camus, M.; Wankhede, M.; Mao, L.; Arnold, T.; Young, W.L.; Su, H. De novo cerebrovascular malformation in the adult mouse after endothelial Alk1 deletion and angiogenic stimulation. Stroke 2014, 45, 900-902. [CrossRef]
- Reemst, K.; Noctor, S.C.; Lucassen, P.J.; Hol, E.M. The Indispensable Roles of Microglia and Astrocytes during Brain Development. Front Hum Neurosci 2016, 10, 566. [CrossRef]
- Thion, M.S.; Garel, S. On place and time: Microglia in embryonic and perinatal brain development. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2017, 47, 121-130. [CrossRef]
- Robertson, P.L.; Du Bois, M.; Bowman, P.D.; Goldstein, G.W. Angiogenesis in developing rat brain: An in vivo and in vitro study. Brain Res 1985, 355, 219-223. [CrossRef]
- Hoeben, A.; Landuyt, B.; Highley, M.S.; Wildiers, H.; Van Oosterom, A.T.; De Bruijn, E.A. Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Rev 2004, 56, 549-580. [CrossRef]
- Kremer, C.; Breier, G.; Risau, W.; Plate, K.H. Up-regulation of flk-1/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 by its ligand in a cerebral slice culture system. Cancer Res 1997, 57, 3852-3859.
- Schimmel, K.; Ali, M.K.; Tan, S.Y.; Teng, J.; Do, H.M.; Steinberg, G.K.; Stevenson, D.A.; Spiekerkoetter, E. Arteriovenous Malformations-Current Understanding of the Pathogenesis with Implications for Treatment. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [CrossRef]
- Coelho-Santos, V.; Shih, A.Y. Postnatal development of cerebrovascular structure and the neurogliovascular unit. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol 2020, 9, e363. [CrossRef]
- Harb, R.; Whiteus, C.; Freitas, C.; Grutzendler, J. In vivo imaging of cerebral microvascular plasticity from birth to death. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2013, 33, 146-156. [CrossRef]
- Walchli, T.; Mateos, J.M.; Weinman, O.; Babic, D.; Regli, L.; Hoerstrup, S.P.; Gerhardt, H.; Schwab, M.E.; Vogel, J. Quantitative assessment of angiogenesis, perfused blood vessels and endothelial tip cells in the postnatal mouse brain. Nat Protoc 2015, 10, 53-74. [CrossRef]
- Zeller, K.; Vogel, J.; Kuschinsky, W. Postnatal distribution of Glut1 glucose transporter and relative capillary density in blood-brain barrier structures and circumventricular organs during development. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 1996, 91, 200-208. [CrossRef]
- Semple, B.D.; Blomgren, K.; Gimlin, K.; Ferriero, D.M.; Noble-Haeusslein, L.J. Brain development in rodents and humans: Identifying benchmarks of maturation and vulnerability to injury across species. Prog Neurobiol 2013, 106-107, 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Vates, G.E.; Hashimoto, T.; Young, W.L.; Lawton, M.T. Angiogenesis in the brain during development: The effects of vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin-2 in an animal model. J Neurosurg 2005, 103, 136-145. [CrossRef]
- Brinjikji, W.; Iyer, V.N.; Yamaki, V.; Lanzino, G.; Cloft, H.J.; Thielen, K.R.; Swanson, K.L.; Wood, C.P. Neurovascular Manifestations of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: A Consecutive Series of 376 Patients during 15 Years. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2016, 37, 1479-1486. [CrossRef]
- Lunsford, L.D.; Niranjan, A.; Kondziolka, D.; Sirin, S.; Flickinger, J.C. Arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery: A twenty year perspective. Clin Neurosurg 2008, 55, 108-119.
- Yang, W.Y.; Luo, C.B.; Tsuei, Y.S.; Guo, W.Y.; Wu, H.M.; Chung, W.Y. A single-institution study of predisposing factors of patients with BAVMs to flow-related aneurysm. J Formos Med Assoc 2019, 118, 707-712. [CrossRef]
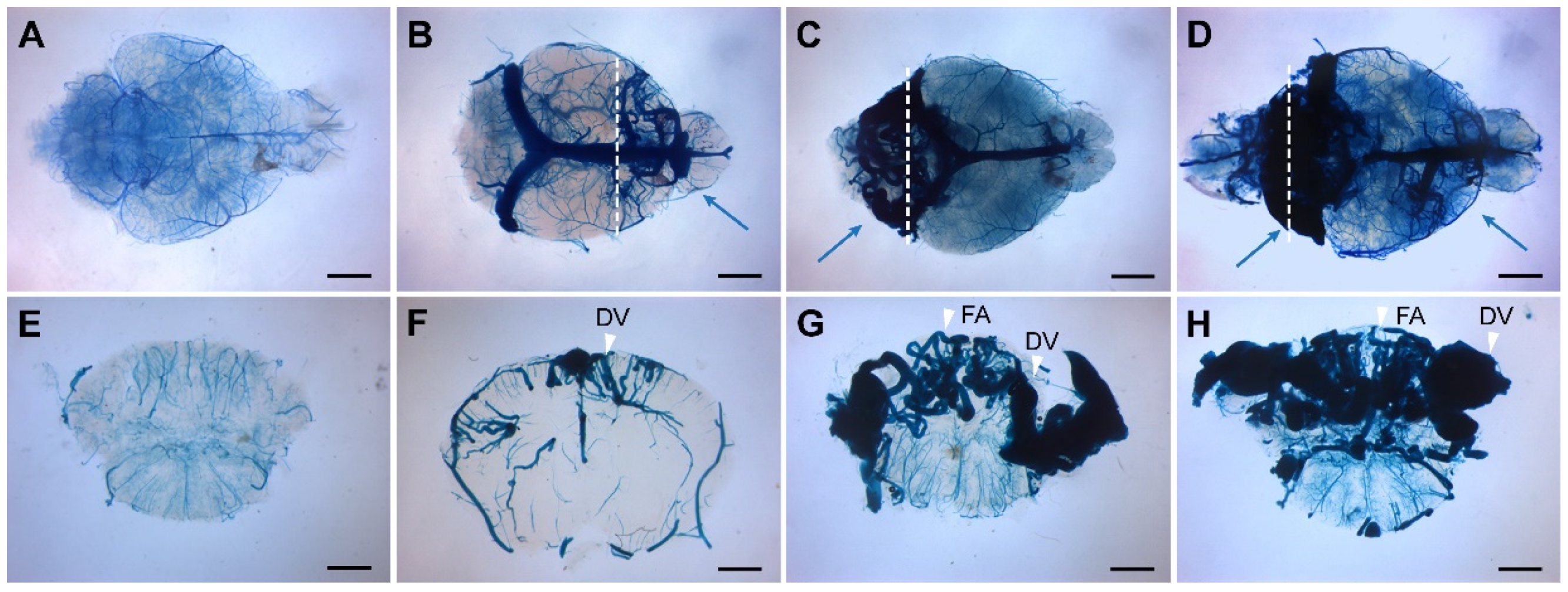
Figure 1.
Endothelial cell-deletion of the Eng gene at P1-3 induces BAVMs. The cerebrovasculature was visualized at age 2-3 months using latex dye perfusion and examined in whole brains (A-D) and their corresponding coronal brain sections (E-H). BAVMs were not detected in control brains (A, E), while mutant mice exhibited BAVMs in the forebrain (B, F), hindbrain (C, G), or both regions (D, H). Blue arrows indicate BAVM lesions, and white arrowheads indicate the feeding arteries (FA) and draining veins (DV). White dashed lines indicate the cutting planes. Scale bars: 2 mm.
Figure 1.
Endothelial cell-deletion of the Eng gene at P1-3 induces BAVMs. The cerebrovasculature was visualized at age 2-3 months using latex dye perfusion and examined in whole brains (A-D) and their corresponding coronal brain sections (E-H). BAVMs were not detected in control brains (A, E), while mutant mice exhibited BAVMs in the forebrain (B, F), hindbrain (C, G), or both regions (D, H). Blue arrows indicate BAVM lesions, and white arrowheads indicate the feeding arteries (FA) and draining veins (DV). White dashed lines indicate the cutting planes. Scale bars: 2 mm.
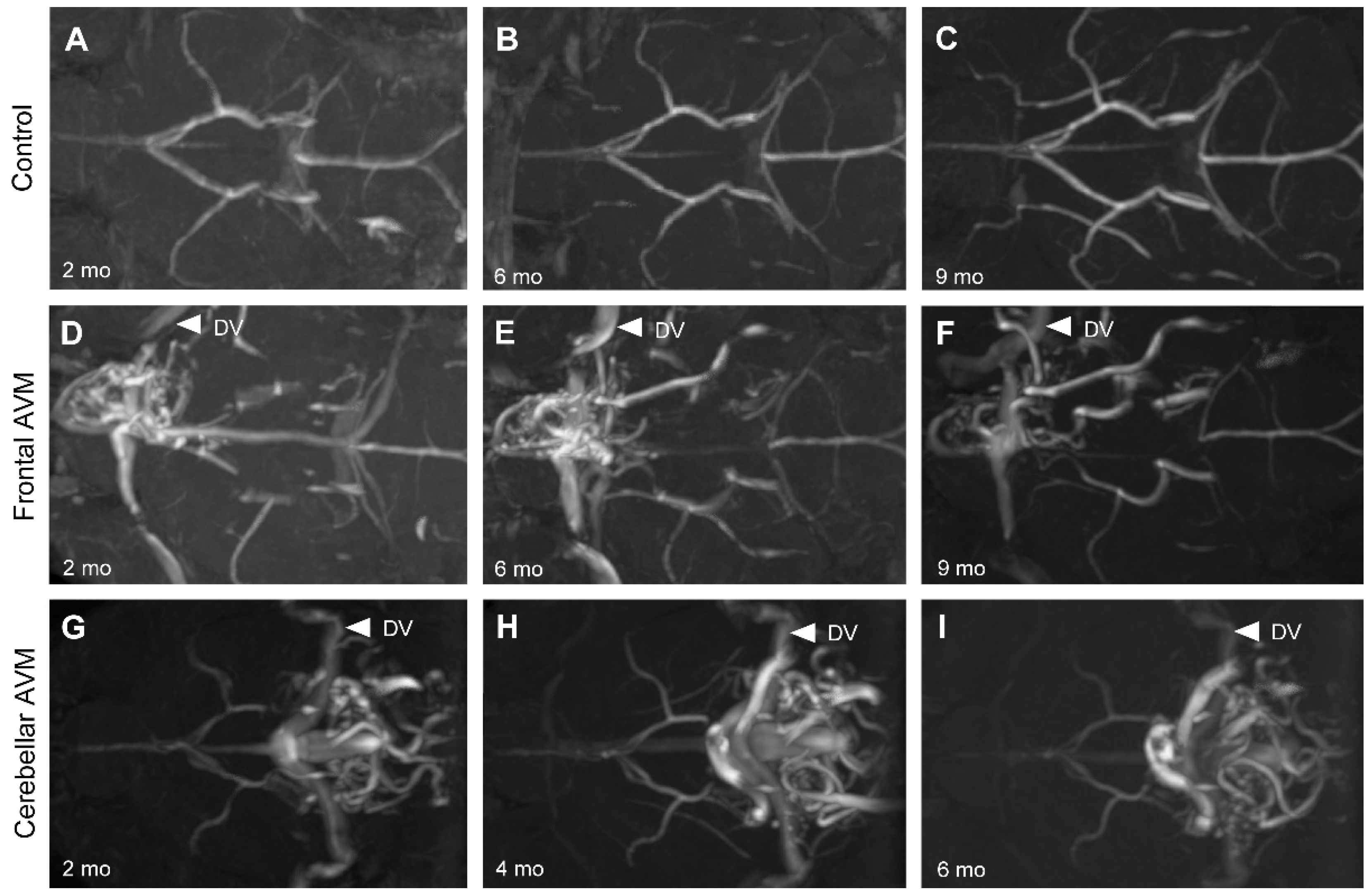
Figure 2.
Longitudinal magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) imaging of nidal BAVMs. Endothelial cell-deletion of the Eng gene at P1-3 induced BAVMs. BAVMs of Eng mutants were monthly monitored through MRA imaging. Representative MRA images show axial views of a control brain (A-C) displaying the major cerebral arteries without aberrant vasculature at 2, 6, and 9 months. Representative MRA images show axial views of a forebrain BAVM (D-F) and cerebellar BAVM (G-I) at 2, 6, and 9 months. White arrowheads indicate the draining veins (DV).
Figure 2.
Longitudinal magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) imaging of nidal BAVMs. Endothelial cell-deletion of the Eng gene at P1-3 induced BAVMs. BAVMs of Eng mutants were monthly monitored through MRA imaging. Representative MRA images show axial views of a control brain (A-C) displaying the major cerebral arteries without aberrant vasculature at 2, 6, and 9 months. Representative MRA images show axial views of a forebrain BAVM (D-F) and cerebellar BAVM (G-I) at 2, 6, and 9 months. White arrowheads indicate the draining veins (DV).
Figure 3.
Timing of Endoglin (Eng) gene deletion dictates BAVM development. Tamoxifen was administered at different time points during the postnatal stage (P8-10; P15-17; P22-24, high or low dose). The cerebrovasculature was visualized using latex dye perfusion at 2-3 months of age and examined in whole brains (A-D) and their corresponding coronal brain sections (E-H). BAVMs were not detected in control brains (A), while Eng mutant mice displayed parietal lobe BAVMs in the P8-10 group (B) and the P15-17 group (C) but not in the P22-24 group (D). Magnified views of coronal brain sections show a normal cerebrovasculature in the control brain (E) and dilated, fistula-like vessels in mutant brains (E-H). White arrowheads indicate BAVM lesions in whole-brain images and enlarged, tortuous blood vessels in coronal brain sections. (I) The bar graph shows the frequency of postnatal BAVM development in the type I HHT mouse model among treatment groups. P1-3 (88%, N=21/24), P8-10 (86%, N=6/7), P15-17 (55%, N=6/11), P22-24 (low dose, 0%, N=0/8), and P22-24 (high dose, 0%, N=0/6). Scale bars: 3 mm (A-D) and 1 mm (E-H). TM, tamoxifen.
Figure 3.
Timing of Endoglin (Eng) gene deletion dictates BAVM development. Tamoxifen was administered at different time points during the postnatal stage (P8-10; P15-17; P22-24, high or low dose). The cerebrovasculature was visualized using latex dye perfusion at 2-3 months of age and examined in whole brains (A-D) and their corresponding coronal brain sections (E-H). BAVMs were not detected in control brains (A), while Eng mutant mice displayed parietal lobe BAVMs in the P8-10 group (B) and the P15-17 group (C) but not in the P22-24 group (D). Magnified views of coronal brain sections show a normal cerebrovasculature in the control brain (E) and dilated, fistula-like vessels in mutant brains (E-H). White arrowheads indicate BAVM lesions in whole-brain images and enlarged, tortuous blood vessels in coronal brain sections. (I) The bar graph shows the frequency of postnatal BAVM development in the type I HHT mouse model among treatment groups. P1-3 (88%, N=21/24), P8-10 (86%, N=6/7), P15-17 (55%, N=6/11), P22-24 (low dose, 0%, N=0/8), and P22-24 (high dose, 0%, N=0/6). Scale bars: 3 mm (A-D) and 1 mm (E-H). TM, tamoxifen.
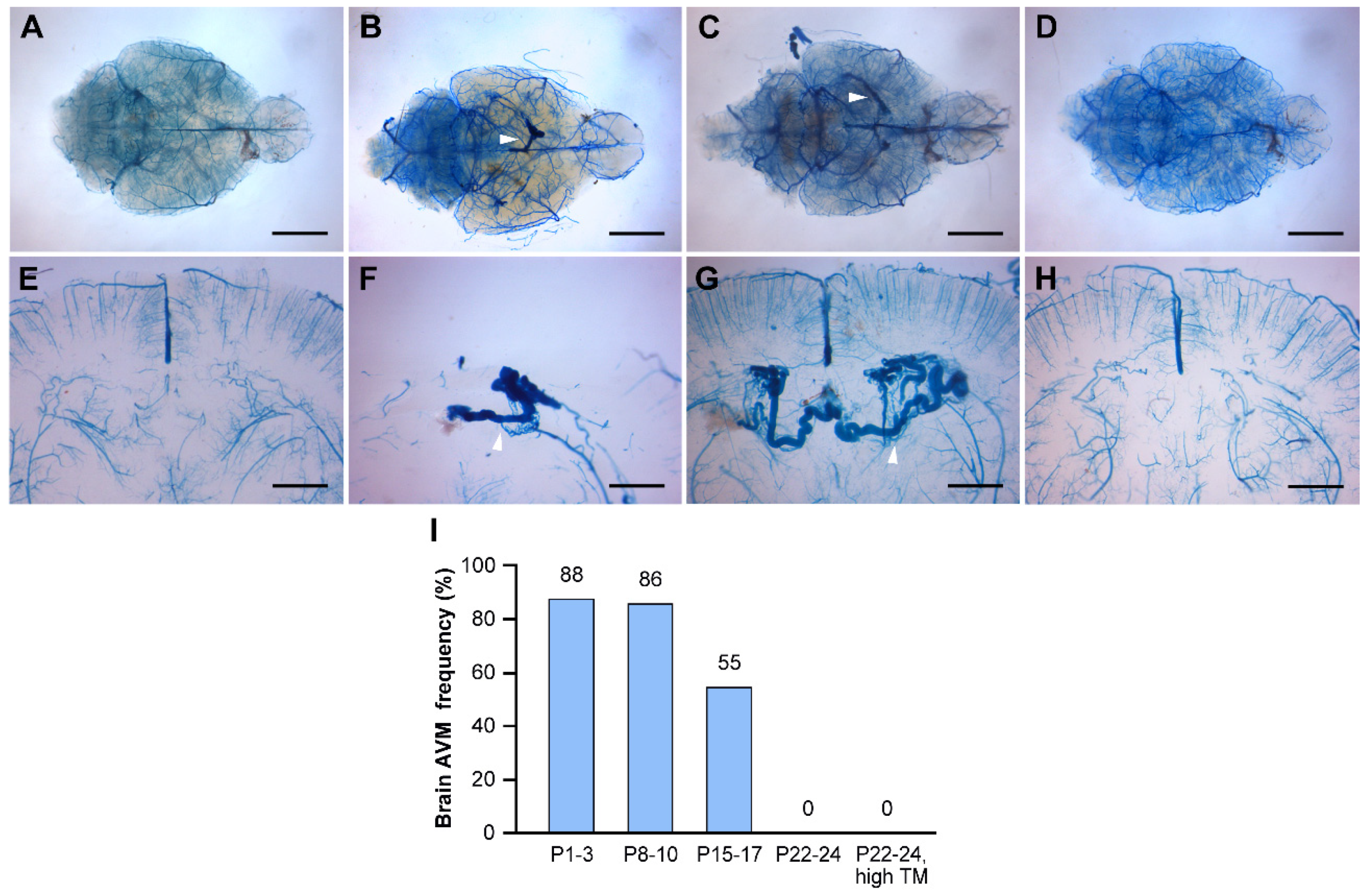
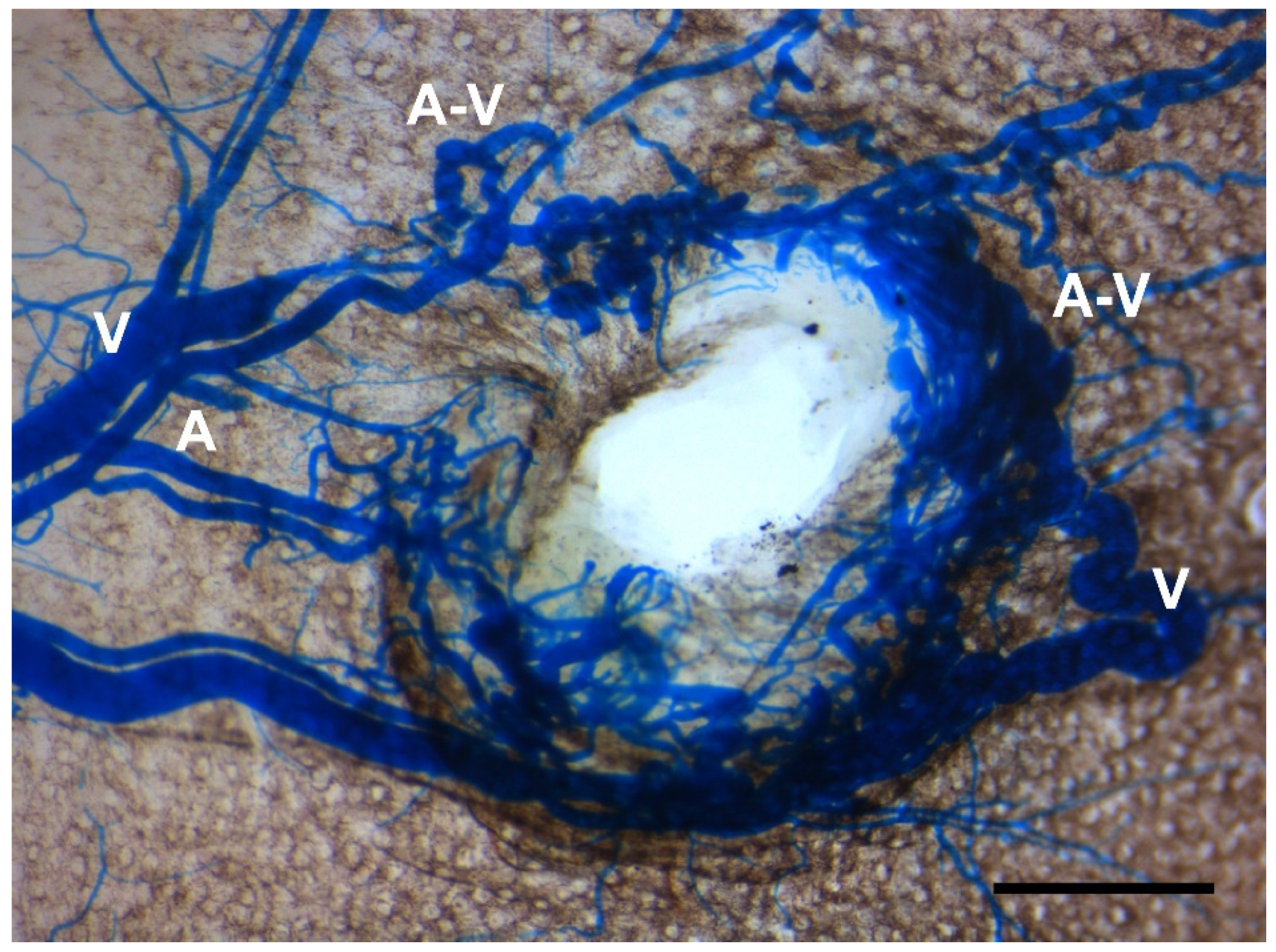
Figure 4.
Reduced angiogenic activity impedes development of BAVMs but not skin AVMs. When conditional Eng mutant mice were treated with high-dose tamoxifen at 3 weeks of age, they developed skin AVMs around wounded ears but did not develop BAVMs, suggesting a pivotal role of angiogenic stimulation in BAVM development. A: artery; V: vein; A-V: arteriovenous shunt. Scale bar: 1 mm.
Figure 4.
Reduced angiogenic activity impedes development of BAVMs but not skin AVMs. When conditional Eng mutant mice were treated with high-dose tamoxifen at 3 weeks of age, they developed skin AVMs around wounded ears but did not develop BAVMs, suggesting a pivotal role of angiogenic stimulation in BAVM development. A: artery; V: vein; A-V: arteriovenous shunt. Scale bar: 1 mm.
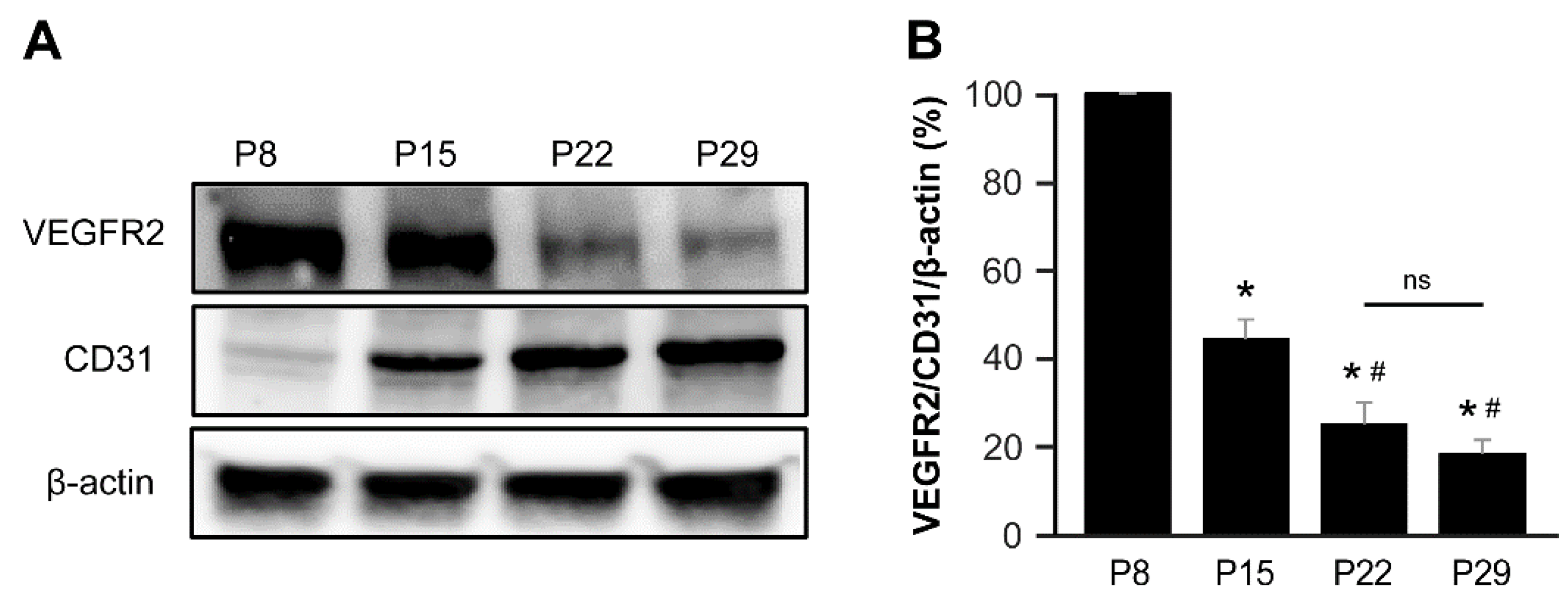
Figure 5.
VEGFR2 is predominantly expressed during the first 2 weeks of the postnatal period in the mouse brain. (A) Western blot analysis depicts the protein levels of VEGFR2, CD31, and β-actin in mouse brains at P8, P15, P22, and P29. (B) The bar graph represents the percentage expression of VEGFR2/CD31/β-actin at P8, P15, P22, and P29 normalized to the P8 levels. The P8 and P15 groups showed significantly higher expression of VEGFR2 compared to the P22 and P29 groups. *, P < 0.001 vs P8; #, P < 0.005 vs P15; N.S., not significant. N=5.
Figure 5.
VEGFR2 is predominantly expressed during the first 2 weeks of the postnatal period in the mouse brain. (A) Western blot analysis depicts the protein levels of VEGFR2, CD31, and β-actin in mouse brains at P8, P15, P22, and P29. (B) The bar graph represents the percentage expression of VEGFR2/CD31/β-actin at P8, P15, P22, and P29 normalized to the P8 levels. The P8 and P15 groups showed significantly higher expression of VEGFR2 compared to the P22 and P29 groups. *, P < 0.001 vs P8; #, P < 0.005 vs P15; N.S., not significant. N=5.
Figure 6.
The promoter activity of Vegfr2 (Flk1) in the mouse brain is most pronounced during the first 2 weeks of the postnatal period. (A-D) The promoter activity of Vegfr2 is indicated by blue staining within the cerebrovasculature of Flk1-LacZ reporter mice at P8, P15, P22, and P29. (E-L) Dashed rectangular areas in each group indicate the hippocampus. Images of both low-magnification (E-H) and high-magnification (I-L) show the promoter activity of Vegfr2 in the hippocampi at P8, P15, P22, and P29. (M-P) Representative images illustrate the quantification of Vegfr2 promoter activity, measured by density of Flk1-positive vessels, at P8 (2.9%), P15 (2.3%), P22 (0.9%), and P29 (0.5%). The mean density of each group is displayed in the lower-right corner. The P8 and P15 groups had significantly higher Vegfr2 promoter activity compared to the P22 and P29 groups. *: P < 0.001 vs P8, #: P < 0.05 vs P15, Scale bars: 2 mm (A-D), 500 μm (E-H), and 125 μm (I-L). N=5.
Figure 6.
The promoter activity of Vegfr2 (Flk1) in the mouse brain is most pronounced during the first 2 weeks of the postnatal period. (A-D) The promoter activity of Vegfr2 is indicated by blue staining within the cerebrovasculature of Flk1-LacZ reporter mice at P8, P15, P22, and P29. (E-L) Dashed rectangular areas in each group indicate the hippocampus. Images of both low-magnification (E-H) and high-magnification (I-L) show the promoter activity of Vegfr2 in the hippocampi at P8, P15, P22, and P29. (M-P) Representative images illustrate the quantification of Vegfr2 promoter activity, measured by density of Flk1-positive vessels, at P8 (2.9%), P15 (2.3%), P22 (0.9%), and P29 (0.5%). The mean density of each group is displayed in the lower-right corner. The P8 and P15 groups had significantly higher Vegfr2 promoter activity compared to the P22 and P29 groups. *: P < 0.001 vs P8, #: P < 0.05 vs P15, Scale bars: 2 mm (A-D), 500 μm (E-H), and 125 μm (I-L). N=5.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).