1. Introduction
Over the past few decades, there have been two shifts in the understanding of host-microbe interactions. The first occurred in the 1990s with the first discovery of the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) gene Toll in the innate immune system, which expresses proteins that sense microbes through conserved molecular structures [
1]. The second shift occurred after the concept of Holobiont was introduced, when researchers discovered that microorganisms retained traits favorable for survival during co-evolution with their hosts and formed a symbiotic whole with them, and that the genome of the Holobiont (the host and all the microorganisms associated with the host) was also known as the hologenome [2, 3]. Holobiont can function as a whole in anatomical, metabolic, immunological, developmental and evolutionary processes. It is believed that the microbiota is integrated into the physiology of the whole organism and regulates all aspects of balance in the organism through its influence on the host’s natural immune system. This system processes the information gathered at different physiological levels to dynamically adjust the activities of the host to the state of the surrounding microbial ecosystem. Normally, the presence of this balance serves to maintain health.
The intestine and liver communicate extensively through the bile ducts, portal vein, and body circulation; this bidirectional communication is known as the intestine-liver axis [4, 5]. The liver is not only a digestive gland, but also an immune tissue that receives a double infusion from the hepatic artery and the hepatic portal vein. 80% of the blood supply from the intestines through the hepatic portal system, which is rich in bacterial products, environmental toxins, and food antigens, and the liver is rich in innate immune cells, which carry out the immune response process by detecting pathogens entering the organism from the intestines [6-8]. Under normal conditions, the balance between immunity and tolerance in the liver is critical to liver function. Disruption of homeostasis in the gut leads to altered immune status and liver disease. Under normal conditions, the balance between immunity and tolerance in the liver is critical to liver function. Disruption of homeostasis in the gut leads to altered immune status and liver disease.
The microbiota plays an important role in the induction of the host immune system, shaping the functional diversity of various immune cells. The liver is considered a natural immune organ because it is responsible for the production of most of the immune molecules in the blood circulation, which contains a large number of natural immune cells [
9]. Macrophages are a key component of the innate immune system, and in the liver they consist of different cell subpopulations located in the hepatic reticuloendothelial system that serve as the main line of defense against microbial invasion, macrophages regulate intra-immune homeostasis in the liver either through phagocytosis or by acting as antigen-presenting cells [
10]. Traditionally, hepatic macrophage-expressed TLR sensing enteric-derived endotoxin (e.g., LPS) is one of the major factors in macrophage activation. Potential to prevent inflammatory macrophage activation and attenuate liver disease by targeting the LPS-TLR axis [11-13]. In addition to LPS, several bacterial metabolites modulate the immune status of hepatic macrophages. Tryptophan metabolites, including tryptamine and indole-3-acetic acid (I3-A), reduce proinflammatory cytokines in macrophages by activating the aryl hydrocarbon receptor or upregulating PFKFB 3 [14, 15].
The liver contains the largest population of natural killer cells. 30-50% of all lymphocytes in the liver can be defined as natural killer cells [16, 17]. Tumorigenesis or infection with multiple pathogens leads to downregulation of antigen-presenting molecules (e.g., MHC-I) in an attempt to evade the immune system. Natural killer cells utilize this self-deficiency to clear target cells and promote cell activation and cytokine production (e.g., IFNγ) [
16]. Although natural killer cells are innate lymphocytes, in recent years a growing body of research has shown that they are capable of producing memory. Although not as specific as classical lymphocytes, the memory of natural killer cells provides a faster and stronger response to secondary infection with a given viral pathogen [18, 19]. This innate memory has greatly expanded our understanding of the role of natural killer cells in immune surveillance and identified their importance in tissues such as the liver.
Studies on the interactions between the gut microbiota and the liver have tended to focus on aspects of liver disease, such as alcohol-related liver disease, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and cancer, and the immune role of the liver in the process of intestinal adaptation to microbes, especially beneficial microbes, has been little studied.
Interactions between the natural immune system and microorganisms that harmonize the physiology of the whole organism[
20]. The natural immune system senses information about the metabolic state of the microbiota and transmits signals to the host to adapt physiology at the tissue level and potentially adjust the composition and function of the microbiota [
21]. Genetic evidence from humans and mice suggests that the innate immune system plays an important role in regulating changes in microbiota composition over time and between individuals [
22]. The innate immune system may function to promote the growth of beneficial members of the microbiota and contribute to the maintenance of a stable microbial community. This is best demonstrated by the induction of epithelial fucoidan glycosylation by ILC 3 and IL-22. During starvation associated with intestinal infections, fucoidan glycosylated proteins are shed into the intestinal lumen and serve as an energy source for commensal bacteria [
23]. Thus, innate immune system resources can be mobilized to support the microbiota in the event of a disturbance of the intestinal ecosystem. Similarly, TLR1 signaling is required to maintain microbiota composition after Yersinia pestis infection in the small intestine colonization [
24].
Although changes in microbial communities and functions and how natural immunity genes dynamically regulate and adapt to microbial communities through time are still poorly understood, researchers have already begun to conduct studies starting with how microbiota control the development of the natural immune system. Mapping the network of interactions between gut microbes and natural immunity will be a focus of future research.
The mammalian gut is recognized as an important microbial ecosystem. In a given mammalian lineage, there is a dependency between the host and its associated microbes. Numerous human and mouse studies have reported the importance of early gut microbes for host health. However little research has been done on whether there are specific mechanisms for the host to recognize and adapt to beneficial microbes to better perform their life activities. Wenli Li et al. attempted to artificially manipulate rumen microbes to directly investigate the role of early gut (rumen) microbial colonization on GIT development or host health in neonatal ruminants [
25]. The team inoculated young heifers with exogenous rumen fluid obtained from adult donor cows every other week from birth to six weeks of age, and eight male Holstein calves were divided into two groups of four: the first group was inoculated with fresh rumen contents extracted from adult females, and the second group was inoculated with sterilized rumen contents, and whole-transcriptome RNA sequencing was used to study transcriptional changes in the host liver, which is a major metabolic organ and It is also an important immune organ and is critical for calf growth performance. Using the liver transcriptome differential gene data from this study, a joint comparative genome constructed bovine natural immunity gene set was used to explore microbial interactions with innate immunity in calves.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Comparative genomic analysis
2.1.1. Genome Data Query
Based on a published set of human innate immune genes[
26],a comparative genomic analysis of human innate immunity genes was performed with the species bovine(B.taurus). In this study, cds sequences, protein sequences and annotation files of 2 species were downloaded from the website of Ensembl (for the above species, for genes with variable splicing, only one longest transcript of one gene was retained in these analyses, in addition, the total number of mRNA: total number of genes: total cds sequences: total protein sequences = 1:1:1:1).
2.1.2. Innate Immunity Gene Family Analysis
OrthoFinder can find orthologous groups and infer rooted gene trees of all orthologous Groups[
27]. Extract people after the longest innate immune gene protein sequences for 1377, with bovine through OrthoFinder and DIAMOND software inference orthologous genes. Based on the results of gene family analysis, a common gene family was selected and the protein sequence of the innate immune gene of the species bovine was determined.The equations should be inserted in editable format from the equation editor.
2.1.3. Identification of Collinearity of Innate Immune Genes
Collinear segments refer to the homology of large segments within the same species or between two species, resulting from genome replication, chromosome replication, large segment replication and species differentiation. Conserved sequencing of genes within homologous fragments means that they may also be functionally conserved. In this study, JCVI (MCScan python) software was used to identify the collinear gene pairs of innate immune genes. Then, functional enrichment analysis was performed on all the above collinear blocks, and the interaction of innate immune gene networks in bovine collinear blocks was obtained by using the software Metascape (
http://metascape.org/gp/index.html#/main/step1).
2.2. Regulation of the Expression of Innate Immune Genes in Calf Liver
2.2.1. Data download
Download data from Wenli Li et al: Liver Transcriptome DEGs Dataset[
25].
2.2.2. Screening of Differentially Expressed Genes(DEGs) for Innate Immunity
Differentially expressed innate immunity genes were identified using a bovine 1473 innate immunity gene set overlapped with 338 DEGs, resulting in POLR3C, HSPA1A, NAMPT, TNK1, FGFR3, IRF1, FGB, HDAC1, SPON2, FYN, JAK2, HNRNPL, CASP6, FGFR1, LGALS1, and DUSP6.
2.2.3. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis(IPA)
Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software is a cloud-based graphical interface bioinformatics software that analyzes, integrates and understands genomics data from a biological pathway perspective for transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, etc.(Causal analysis approaches in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis).To understand the potential mechanisms by which microorganisms influence early innate immunity genes, network and pathway enrichment analyses of 338 DEGs and 16 innate immunity DEGs were performed using IPA and upstream analyses of 16 innate immunity DEGs.
3. Results
3.1. Innate Immune Gene Family
In this study, 1377 human innate immune gene protein sequences were used to perform all-vs-all sequence alignment of input sequences through OrthoFinder, so as to determine the innate immune gene protein sequences of other species. The protein sequences of 1473 innate immune genes were obtained by analysis. A total of 2850 protein-coding genes of the two species were used for the analysis of innate immunity gene families. 2834 genes were identified in 1177 orthogroups, including 984 single-copy gene families. 1164 orthogroups were species common and 13 orthogroups were species specific(
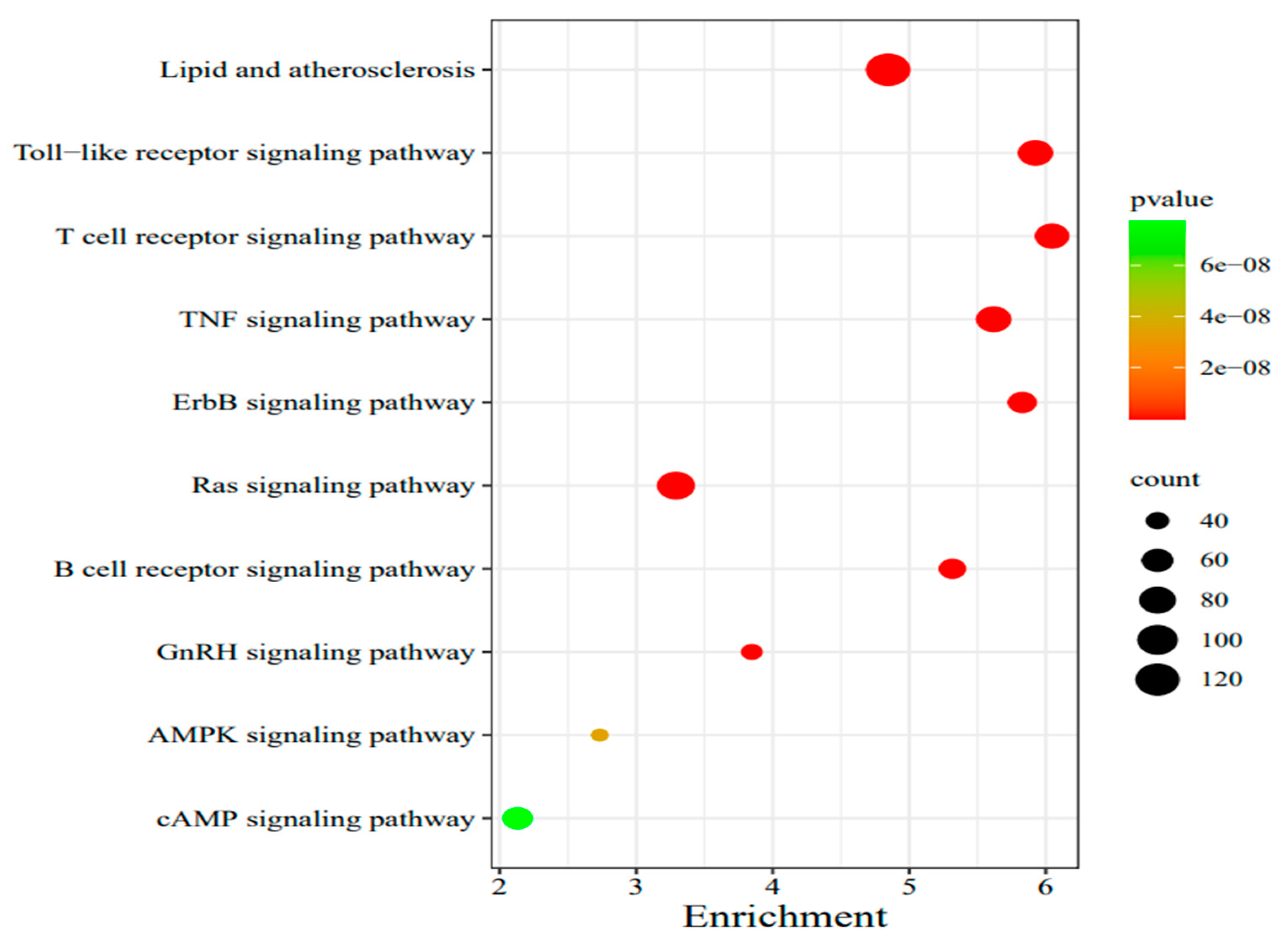
Table 1).In the common gene family, lipid and atherosclerosis, toll-like receptor signaling pathway and T cell receptor signaling pathway were significantly expressed, etc.(
Figure 1).
3.2. Collinearity and Enrichment Analysis of Innate Immune Genes
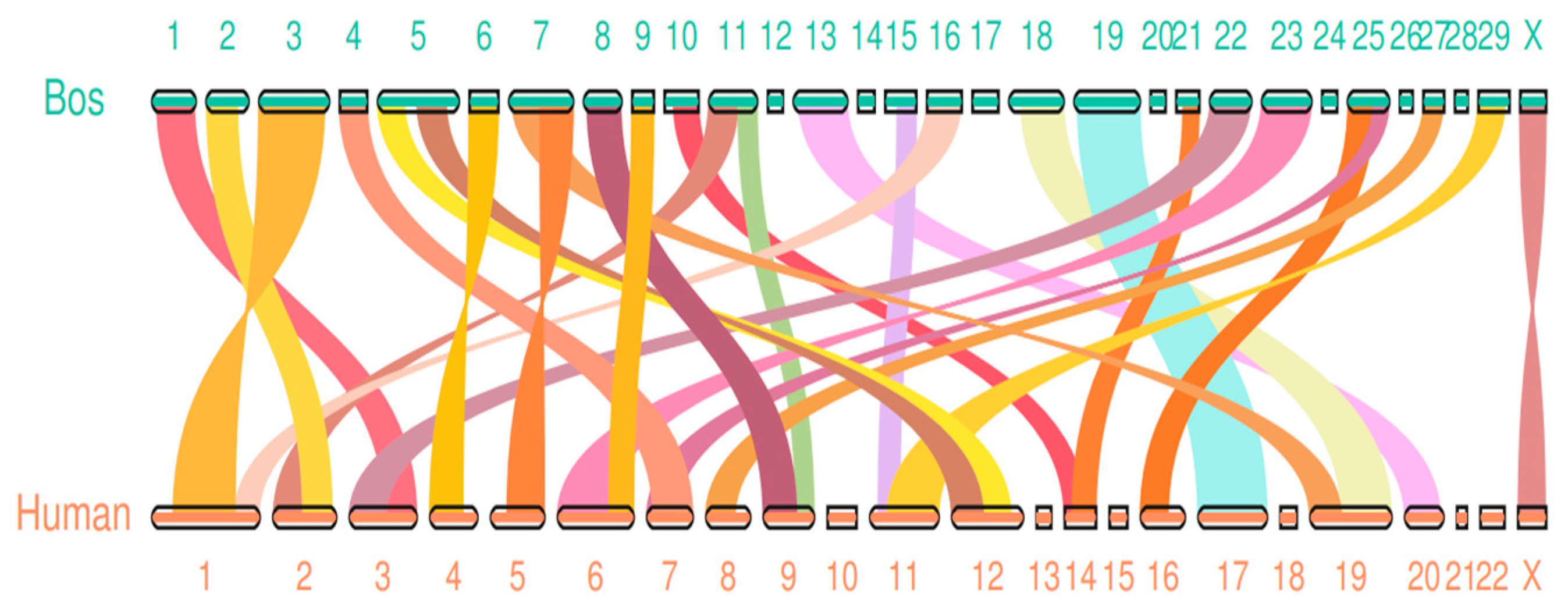
Since genomic collinearity can often predict homologous sequences, and homologous sequences may have similar functions, genome-wide collinearity analysis is valuable for functional prediction. The innate immune intergenomic collinearity was compared between bovine and human by JCVI software. It was found that there were 27 groups of collinear regions of innate immune genes between bovine and human, including 926 collinear gene pairs(
Figure 2)
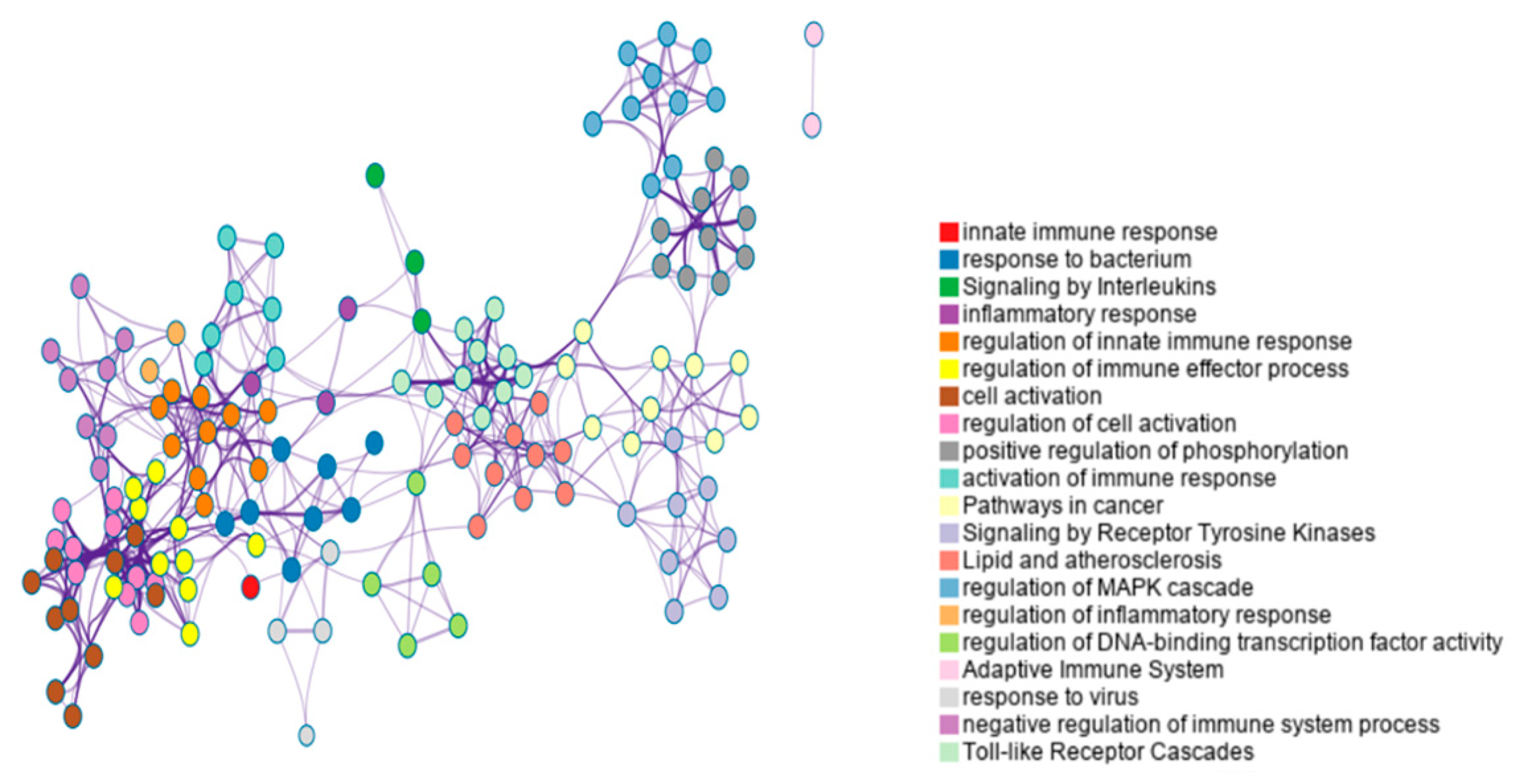
According to Metascape enrichment results, there is significant enrichment in the cytokine signaling in immune system, positive regulation of cytokine production, regulation of kinase activity、regulation of MAPK cascade、adaptive immune system、response to virus、Toll-like receptor cascades, immune response-regulating signaling pathway(
Figure 3).
3.3. Classical Pathway Analysis and Upstream Regulation Analysis
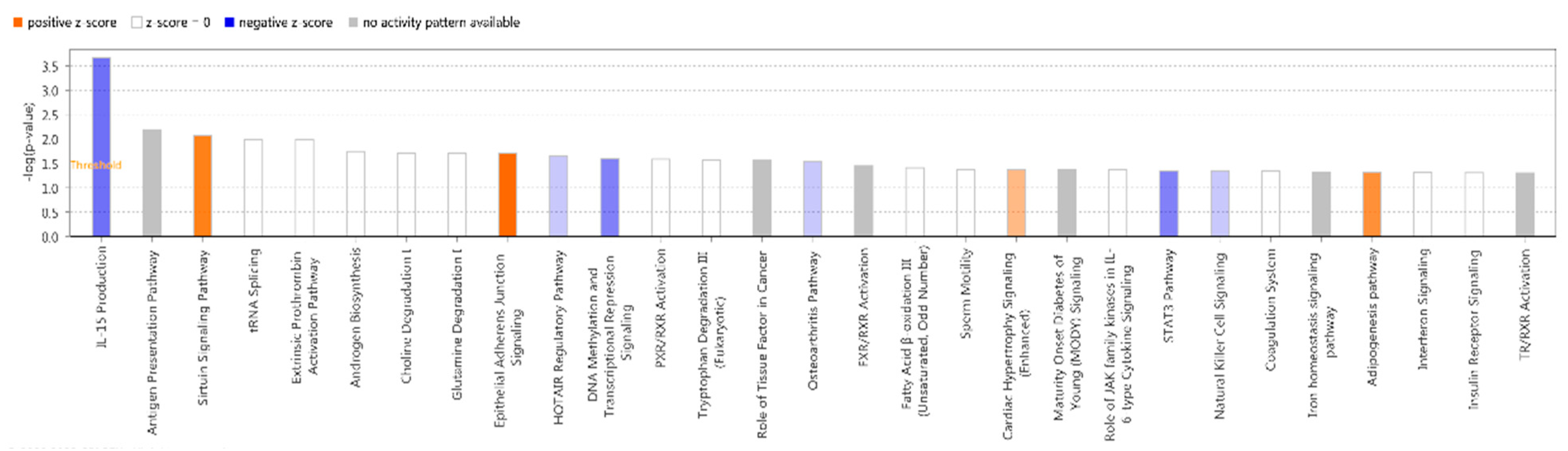
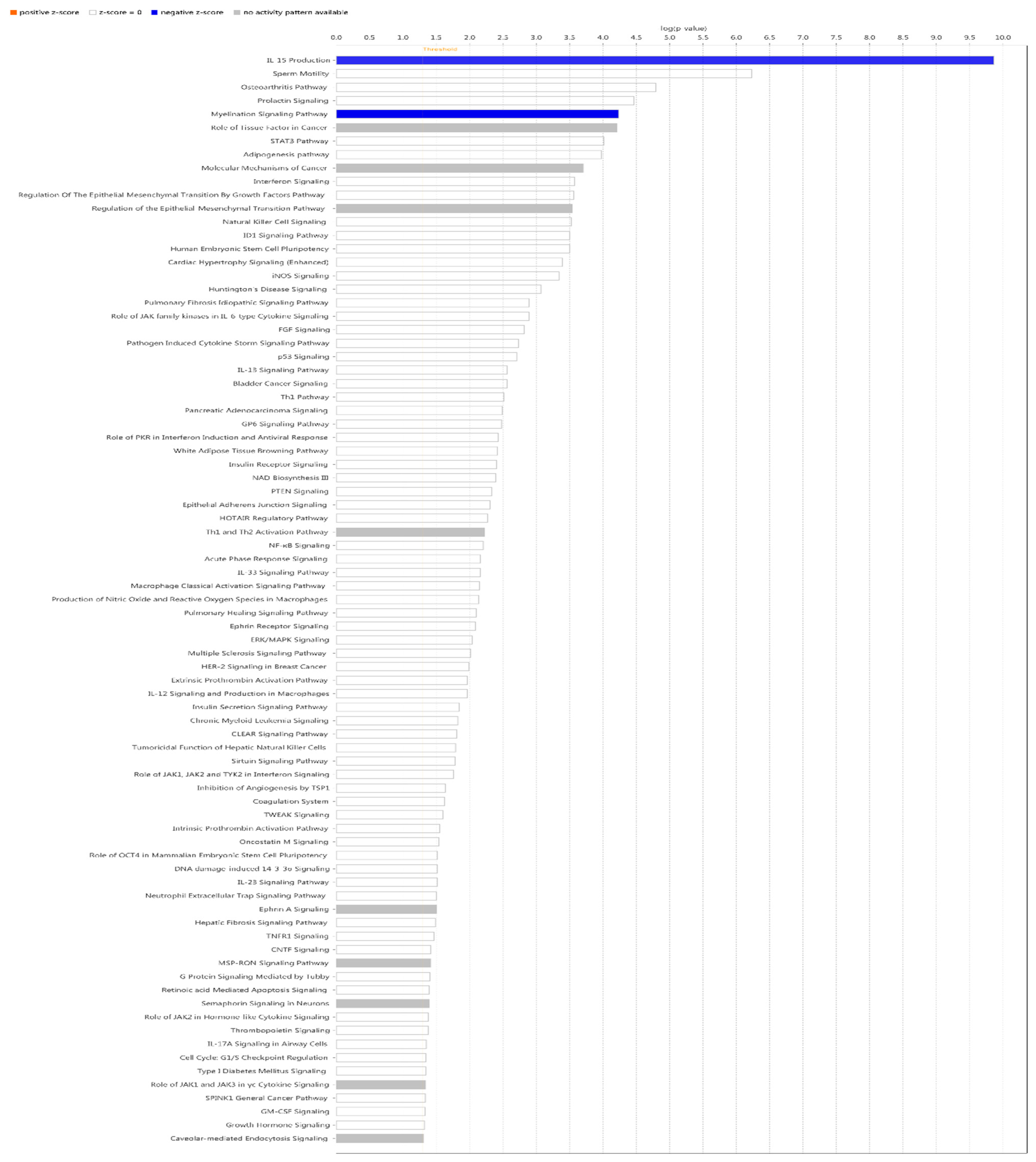
IPA did classical pathway enrichment analysis statistics on 338 DEGs, in which IL-15 production was significantly inhibited (
Figure 4). In addition, the IPA classical pathway enrichment results of 16 innate immunized DEGs showed that IL-15 production was also significantly inhibited (Figure A1). According to the results of the gene interaction network diagram (
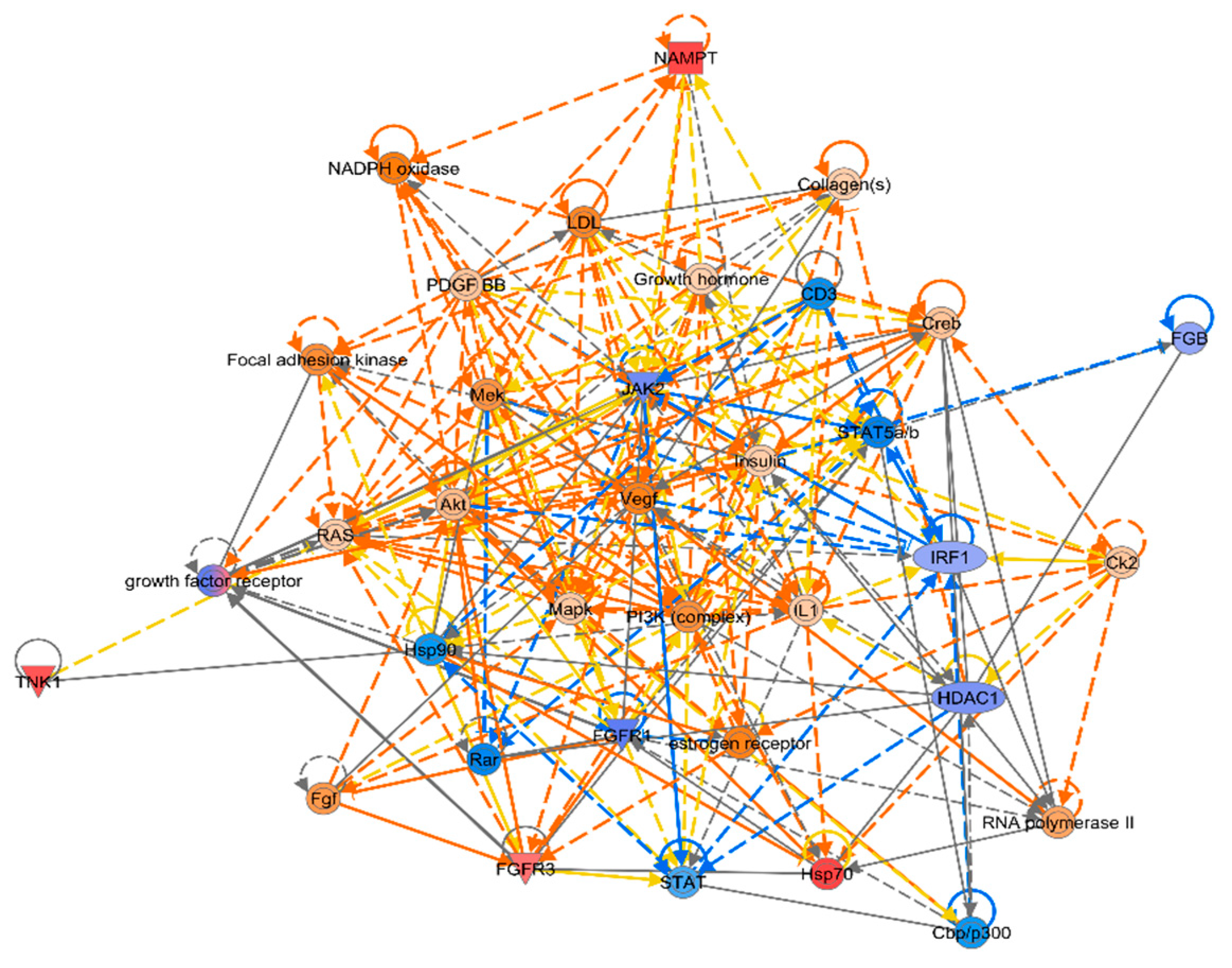
Figure 5), PI3K (complex), Akt, RAS, and Mapk were activated; STAT5a/b, etc. were inhibited; NAMPT, etc. were expressed at higher levels, and JAK2 and IRF1, etc. were expressed at lower levels.
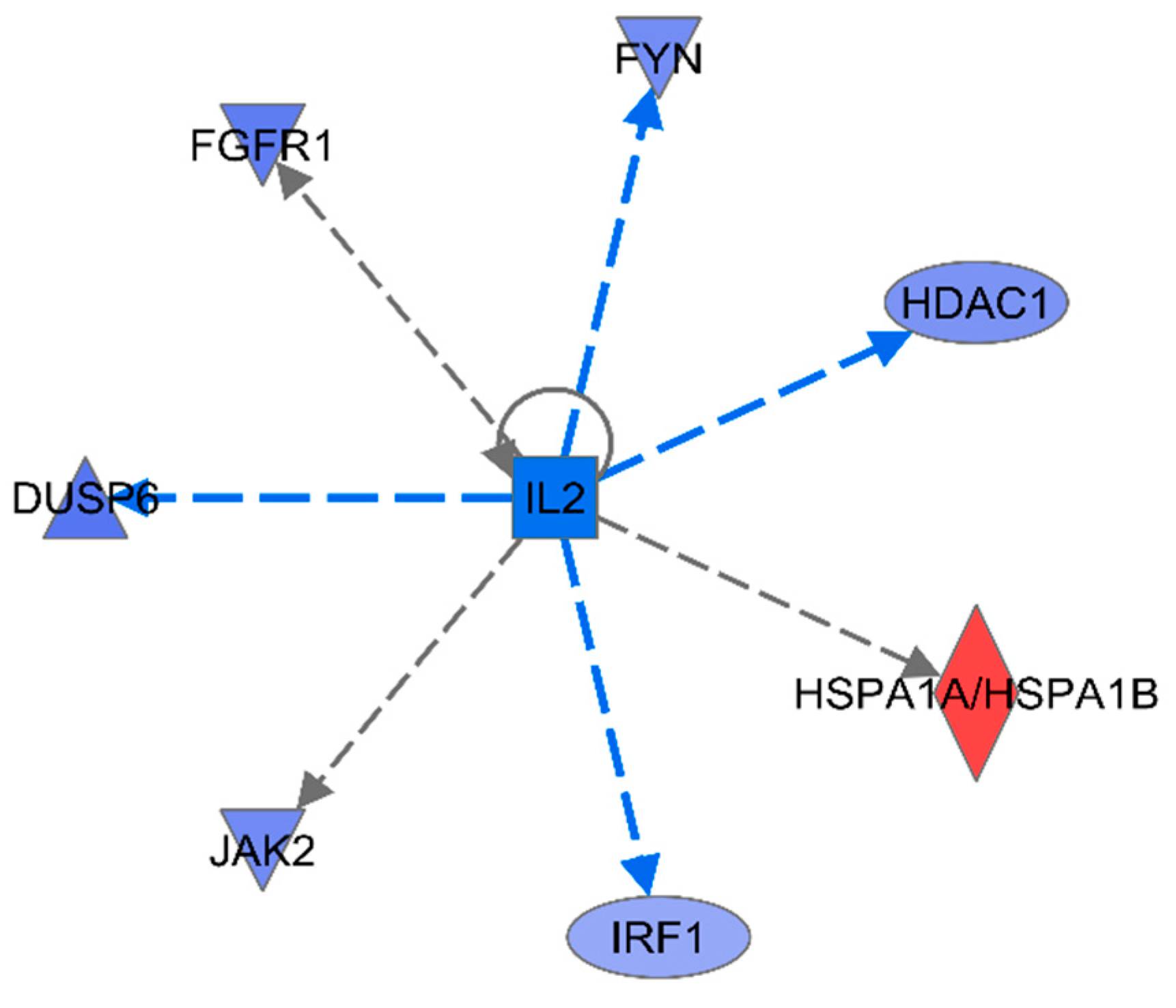
To obtain further information about the delivery of gene interaction network maps, upstream regulation was predicted using IPA. For the 16 innate immune DEGs, among the top 15 predicted upstream regulators, the most significant was IL-2 with very high significance (p<3E-07) and high negative activation Z-score (
Table 2) (
Figure 6). IL-2 is known to be a pleiotropic cytokine with an important role in the regulation of both innate and adaptive immune responses[
28], and is necessary to prevent chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract[
29], So IL-2 is very important regulatory candidate.
4. Discussion
Our team relies on published data to study the active adaptation of living organisms to beneficial microorganisms through the enterohepatic axis. Wenli Li et al. analyzed the microbial community composition of rumen inoculum by 16S rRNA genome sequencing, which showed that Anabaena phylum was the most abundant phylum (53.31 ± 1.85% SEM), followed by Thick-walled phylum (34.32 ± 1.82% SEM)[
25].Under the predominant influence of Anaplasma phylum and Thick-walled phylum, the researchers did not observe clinical signs associated with pathologic infections or with intestinal infections, suggesting that there may not have been a disruption of intestinal and organismal homeostasis.
In this thesis, the bovine innate immunity gene set was constructed from the comparative genome, using published human innate immunity genes as a reference to further identify innate immunity covariate gene pairs. Subsequent joint analysis with the calf Liver Transcriptome DEGs Dataset identified IL-2 as an important upstream regulator within the liver innate immunity gene cluster.
In the 1970s, IL-2 was initially identified as the first T-cell growth factor, and with decades of intensive research, the pleiotropic nature of IL-2’s action was revealed, suggesting a link between adaptive and innate immunity and a central place in all immune responses and homeostasis in the body[30-32].IL-2 is an O-glycosylated, four-a-helix bundle cytokine produced primarily by activated T cells, dendritic cells and B cells[
33].The spatial structure of IL-2 consists of four antiparallel a-helix cores and small β-fragments, which perform a variety of biological functions upon specific binding to IL-2R on the cell membrane[
31]. There are three receptor chains for IL-2: the a-chain (IL-2Ra, also known as CD25), the β-chain (IL-2Rβ, i.e., CD122, which is also expressed by IL-15 receptors), and the γ-chain (IL-2Rγ, i.e., CD132, which is co-expressed in IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, and IL-15 receptors), which bind to IL-2 with different affinities. IL-2Ra is expressed on activated lymphocytes and binds IL-2 with low affinity; IL-2Rβ and IL-2Rγ form a medium-affinity complex that binds IL-2 and is mainly expressed on NK cells and memory T fine, In addition, the heterodimerization of IL-2Rβ and IL-2Rγ is necessary for the activation of the JAK1 and JAK3 kinases by IL-2, because JAK1 and JAK3 transduces signals by binding to the intracellular structural domains of IL-2Rβ and IL-2Rγ[
34]; when the three receptor chains are co-expressed on activated T cells and Treg cells, IL-2 binds to all 3 with high affinity to form a tetrameric complex. Analysis of the three-dimensional structure with the tetrameric complex revealed that IL-2 initially binds IL-2Ra, then recruits IL-2Rβ, and finally binds IL-2Rγ[
35]. IL-2 specifically binds to IL-2R to activate intracellular signaling pathways and thus exert biological effects.IL-2 produces biological effects in different cells through its complex signaling mechanisms.Binding of IL-2 to IL-2R causes the activation of at least three major signaling pathways: the PI3K/AKt/mTOR, the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, and the JAK/STAT5 pathway[
35].Functionally, IL-2 normally induces IL-2 and IL-2Ra expression on activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and stimulates their proliferation. In contrast, IL-2 promotes the ability of regulatory T cells to differentiate and survive by initiating Fas-mediated cell death induced by CD4+ T cell activation following antigenic stimulation, and also plays an important role in maintaining peripheral self-tolerance[
33]. In addition to its important role in immunity, IL-2 has been shown to be necessary in the prevention of chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract[29, 36].
Gut immunomodulation of microbial changes to maintain homeostasis in the body was previously thought to be localized; with subsequent studies, researchers have found that the gut-liver axis plays an important role in this process. The liver has a dual blood supply, receiving infusions from both the hepatic artery and the hepatic portal vein, and receives 80% of its blood supply from the intestinal tract through the portal system, which is rich in bacterial products, environmental toxins, and dietary antigens, which enter the liver via the bloodstream and are picked up by a series of antigen-presenting cells and lymphocytes, triggering a complex immune response process[6-8].The liver contains a large number of immune cells involved in the immune response and immune reaction, which are divided into two main categories: hepatic resident cells and circulating recruited cells. Settled cells mainly include: Kupffer cells (KCs), liver, sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSEC), dendritic cells (DC), hepatic stellate cells (HSC); circulating recruited cells include: natural killer cells (NK cells), natural killer T-cells (NKT cells), neutrophils, T-cells, and so on[
37]. Lei Zhou et al. demonstrated for the first time that microbiota and IL-1β-dependent axis promote IL-2 production by ILC3 to coordinate immune regulation in the gut.IL-2 enters the liver via blood circulation.T cells, NK cells, DC cells, etc., which are the target cells of IL-2 action in the liver, bind to IL-2 and activate PI3K/AKt/mTOR, mitogen-activated protein kinase ( MAPK) pathway and JAK/STAT5 pathway, and thus immunomodulation. According to IPA analysis of liver innate immunity gene transcriptome data, inhibition of the upstream factor IL-2 under microbial influence leads to the activation of PI3K (complex), Akt, RAS, and Mapk, etc., in the liver; and STAT5a/b, etc., which are members of the PI3K/AKt/mTOR, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways and important factors in the JAK/STAT5 pathway, which in turn led to a decrease in IL-15 production. This provides new insights into the possible involvement of the liver in gut microbial immune regulation. In addition, we have observed that ipa analysis has great potential for cross-organ regulation of life processes, which may be useful for drug screening in the future, and that ipa analysis and new analytical protocols based on it will be important in the future for a better understanding of the occurrence of diseases and organ-organ interactions, as well as for the maintenance of the healthy functioning of living individuals.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we used Orthofinder sequence comparison analysis to obtain 1,473 bovine innate immunity genes, and initially constructed a bovine innate immunity gene set, followed by covariance analysis to predict the homologous sequences, and enrichment analysis to obtain bovine inate immunity-related pathways and interactions networks. The calf liver innate immunity differential genes under the main influence of Unimicron phylum and Thick-walled phylum were screened and matched to obtain 16 differentially expressed innate immunity genes, and the results of IPA analysis showed that the upstream factor IL-2 initiated the PI3K/AKt/mTOR, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, and the JAK/STAT5 pathway, which led to the involvement of liver in the intestinal microbial Immunomodulation.
Author Contributions
X.W. simulated, analyzed, and wrote the manuscript. The experiments were designed and supervised by W.Z. The study was carried out with the assistance of L.G. and C.C. The manuscript was discussed and improved by L.D. and B.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was supported by the National key research and development program [2021YFD1200905], Inner Mongolia Natural Science Foundation project [2021ZD0009], Inner Mongolia science and technology plan project [2021GG0008].
Data Availability Statement
We encourage all authors of articles published in MDPI journals to share their research data. In this section, please provide details regarding where data supporting reported results can be found, including links to publicly archived datasets analyzed or generated during the study. Where no new data were created, or where data is unavailable due to privacy or ethical restrictions, a statement is still required. Suggested Data Availability Statements are available in section “MDPI Research Data Policies” at
https://www.mdpi.com/ethics.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A
References
- HOIJMAN E, HäKKINEN H M, TOLOSA-RAMON Q, et al. Cooperative epithelial phagocytosis enables error correction in the early embryo [J]. Nature 2021, 590, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ROSENBERG E, KOREN O, RESHEF L, et al. The role of microorganisms in coral health, disease and evolution [J]. Nat Rev Microbiol 2007, 5, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ZILBER-ROSENBERG I, ROSENBERG E. Role of microorganisms in the evolution of animals and plants: the hologenome theory of evolution [J]. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2008, 32, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TRIPATHI A, DEBELIUS J, BRENNER D A, et al. The gut-liver axis and the intersection with the microbiome [J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018, 15, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CHOPYK D M, GRAKOUI A. Contribution of the Intestinal Microbiome and Gut Barrier to Hepatic Disorders [J]. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BERG R D. Bacterial translocation from the gastrointestinal tract [J]. Adv Exp Med Biol 1999, 473, 11–30. [Google Scholar]
- LUMSDEN A B, HENDERSON J M, KUTNER M H. Endotoxin levels measured by a chromogenic assay in portal, hepatic and peripheral venous blood in patients with cirrhosis [J]. Hepatology 1988, 8, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ODA M, YOKOMORI H, HAN J Y. Regulatory mechanisms of hepatic microcirculation [J]. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 2003, 29, 167–182. [Google Scholar]
- RACANELLI V, REHERMANN B. The liver as an immunological organ [J]. Hepatology 2006, 43 (2 Suppl 1), S54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KRENKEL O, TACKE F. Liver macrophages in tissue homeostasis and disease [J]. Nat Rev Immunol 2017, 17, 306–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SODERBORG T K, CLARK S E, MULLIGAN C E, et al. The gut microbiota in infants of obese mothers increases inflammation and susceptibility to NAFLD [J]. Nature Communications 2018, 9, 4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DAPITO D H, MENCIN A, GWAK G Y, et al. Promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma by the intestinal microbiota and TLR4 [J]. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAZAGOVA M, WANG L, ANFORA A T, et al. Commensal microbiota is hepatoprotective and prevents liver fibrosis in mice [J]. Faseb j 2015, 29, 1043–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KRISHNAN S, DING Y, SAEDI N, et al. Gut Microbiota-Derived Tryptophan Metabolites Modulate Inflammatory Response in Hepatocytes and Macrophages [J]. Cell Rep 2018, 23, 1099–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MA L, LI H, HU J, et al. Indole Alleviates Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis and Inflammation in a Manner Involving Myeloid Cell 6-Phosphofructo-2-Kinase/Fructose-2,6-Biphosphatase 3 [J]. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CRISPE I N. The liver as a lymphoid organ [J]. Annu Rev Immunol 2009, 27, 147–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DOHERTY D G, O’FARRELLY C. Innate and adaptive lymphoid cells in the human liver [J]. Immunol Rev 2000, 174, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’SULLIVAN T E, SUN J C, LANIER L L. Natural Killer Cell Memory [J]. Immunity 2015, 43, 634–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SUN J C, MADERA S, BEZMAN N A, et al. Proinflammatory cytokine signaling required for the generation of natural killer cell memory [J]. J Exp Med 2012, 209, 947–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- THAISS C A, LEVY M, SUEZ J, et al. The interplay between the innate immune system and the microbiota [J]. Curr Opin Immunol 2014, 26, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- THAISS C A, ZMORA N, LEVY M, et al. The microbiome and innate immunity [J]. Nature 2016, 535, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LEVY M, THAISS C A, ELINAV E. Metagenomic cross-talk: the regulatory interplay between immunogenomics and the microbiome [J]. Genome Med 2015, 7, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PICKARD J M, MAURICE C F, KINNEBREW M A, et al. Rapid fucosylation of intestinal epithelium sustains host-commensal symbiosis in sickness [J]. Nature 2014, 514, 638–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KAMDAR K, KHAKPOUR S, CHEN J, et al. Genetic and Metabolic Signals during Acute Enteric Bacterial Infection Alter the Microbiota and Drive Progression to Chronic Inflammatory Disease [J]. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LI W, EDWARDS A, RIEHLE C, et al. Transcriptomics analysis of host liver and meta-transcriptome analysis of rumen epimural microbial community in young calves treated with artificial dosing of rumen content from adult donor cow [J]. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DESCHAMPS M, LAVAL G, FAGNY M, et al. Genomic Signatures of Selective Pressures and Introgression from Archaic Hominins at Human Innate Immunity Genes [J]. Am J Hum Genet 2016, 98, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMMS D M, KELLY S. OrthoFinder: solving fundamental biases in whole genome comparisons dramatically improves orthogroup inference accuracy [J]. Genome Biol 2015, 16, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BENDICKOVA K, FRIC J. Roles of IL-2 in bridging adaptive and innate immunity, and as a tool for cellular immunotherapy [J]. J Leukoc Biol 2020, 108, 427–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BOYMAN O, SPRENT J. The role of interleukin-2 during homeostasis and activation of the immune system [J]. Nat Rev Immunol 2012, 12, 180–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MORGAN D A, RUSCETTI F W, GALLO R. Selective in vitro growth of T lymphocytes from normal human bone marrows [J]. Science 1976, 193, 1007–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MALEK T R, CASTRO I. Interleukin-2 receptor signaling: at the interface between tolerance and immunity [J]. Immunity 2010, 33, 153–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KLATZMANN D, ABBAS A K. The promise of low-dose interleukin-2 therapy for autoimmune and inflammatory diseases [J]. Nat Rev Immunol 2015, 15, 283–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LI L, HUANG B, SONG S, et al. A20 functions as mediator in TNFα-induced injury of human umbilical vein endothelial cells through TAK1-dependent MAPK/eNOS pathway [J]. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 65230–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WANG X, LUPARDUS P, LAPORTE S L, et al. Structural biology of shared cytokine receptors [J]. Annu Rev Immunol 2009, 27, 29–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LIAO W, LIN J X, LEONARD W J. IL-2 family cytokines: new insights into the complex roles of IL-2 as a broad regulator of T helper cell differentiation [J]. Curr Opin Immunol 2011, 23, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JOSEFOWICZ S Z, LU L F, RUDENSKY A Y. Regulatory T cells: mechanisms of differentiation and function [J]. Annu Rev Immunol 2012, 30, 531–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KUBES P, JENNE C. Immune Responses in the Liver [J]. Annu Rev Immunol 2018, 36, 247–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).