Submitted:
07 October 2023
Posted:
10 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and apparatus
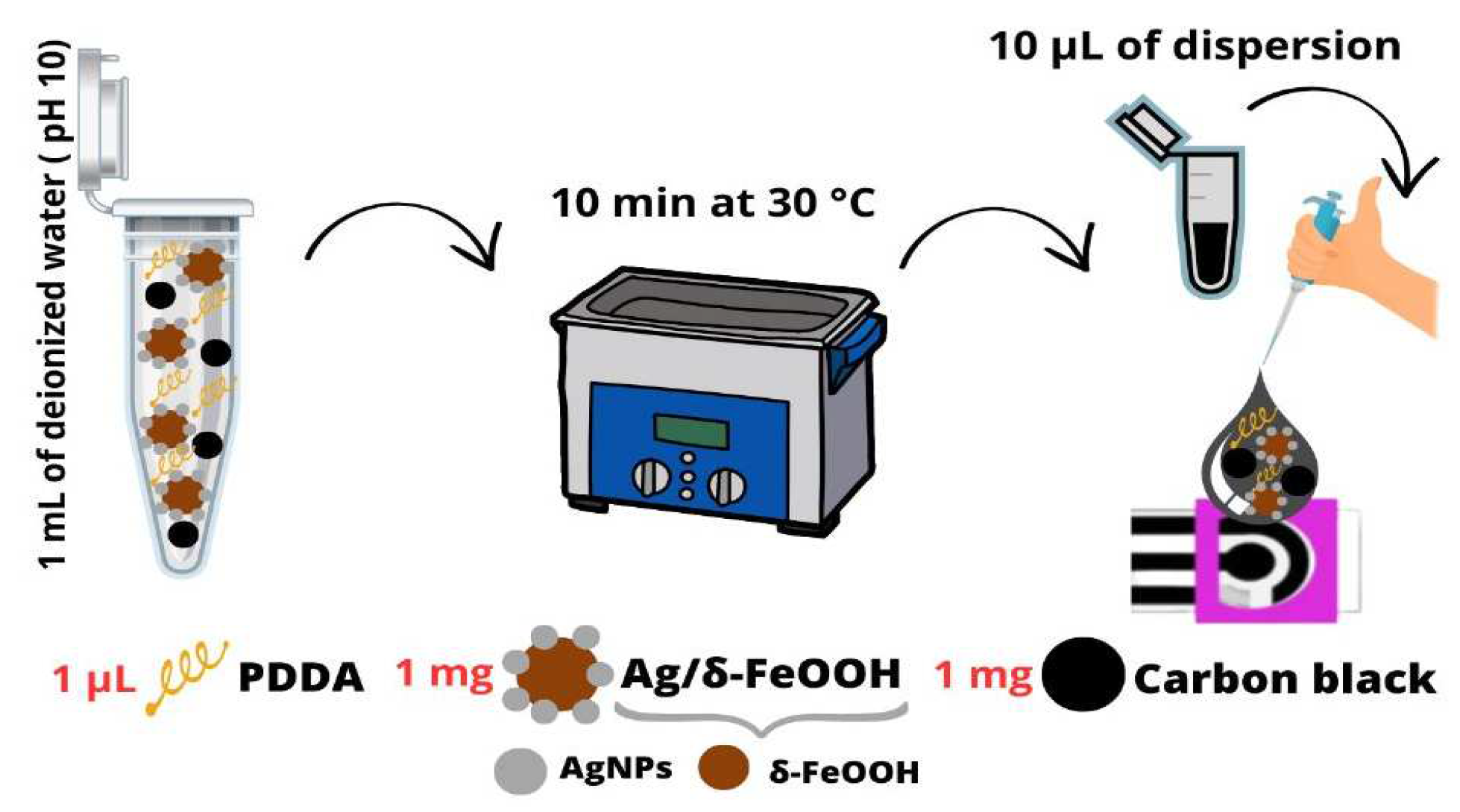
2.2. Synthesis of Ag/δ-FeOOH
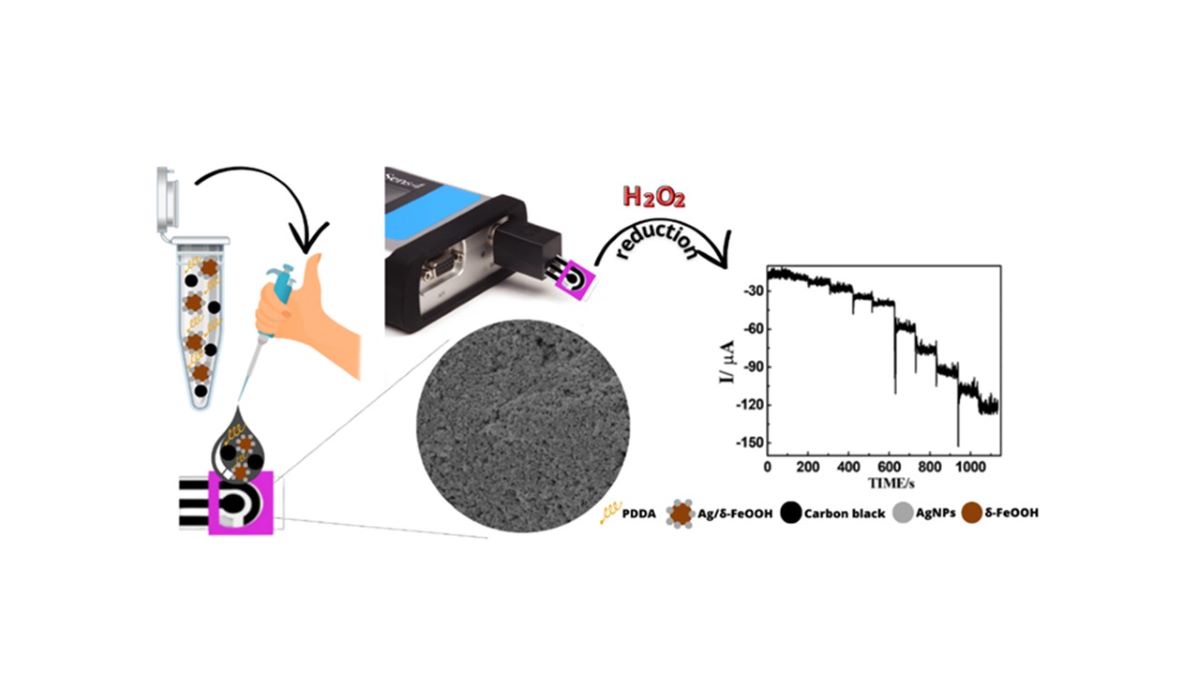
2.3. Preparation of DCell-CB//Ag/δ-FeOOH
2.4. Electrochemical characterization
3. Results and discussion
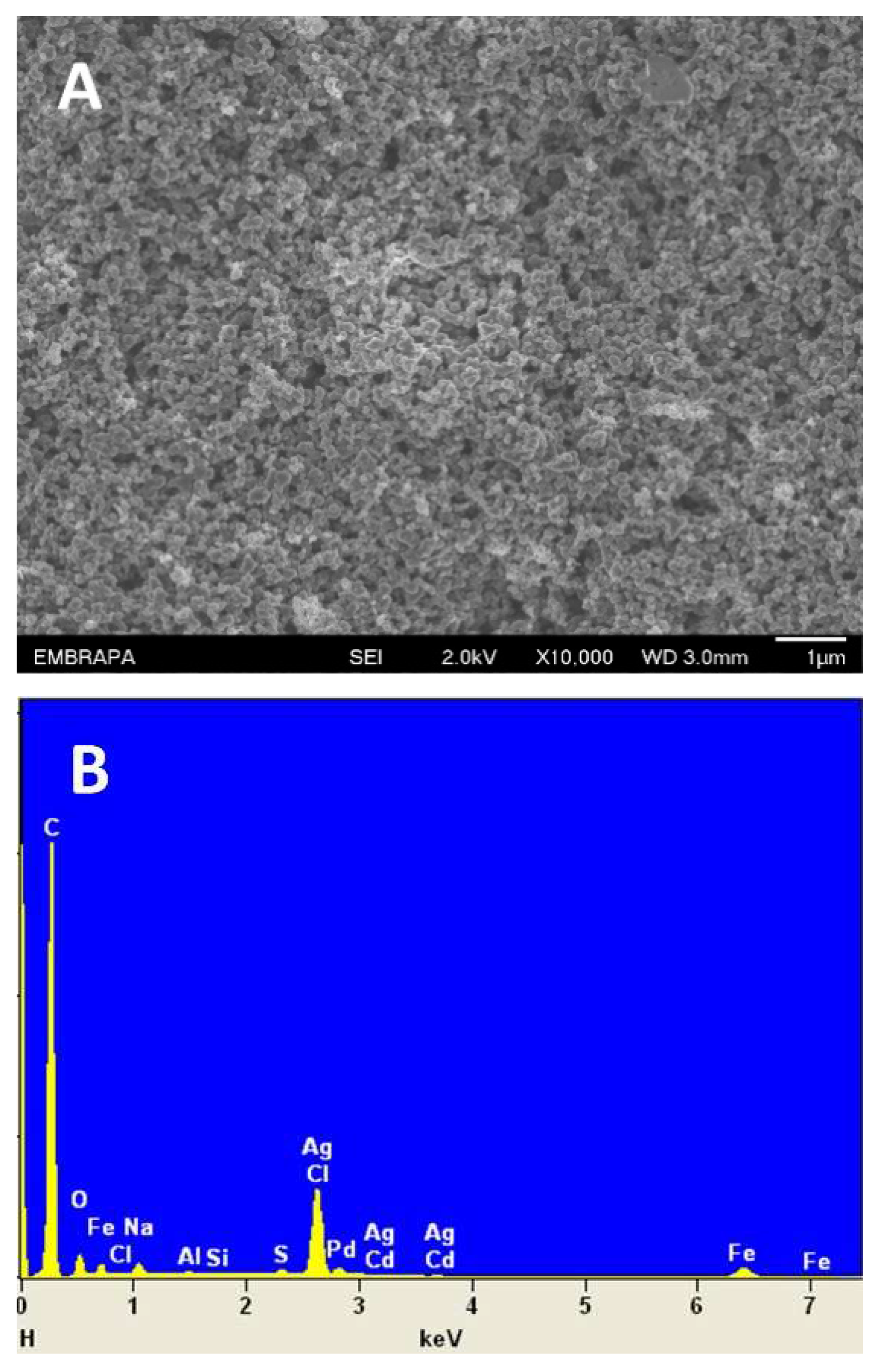
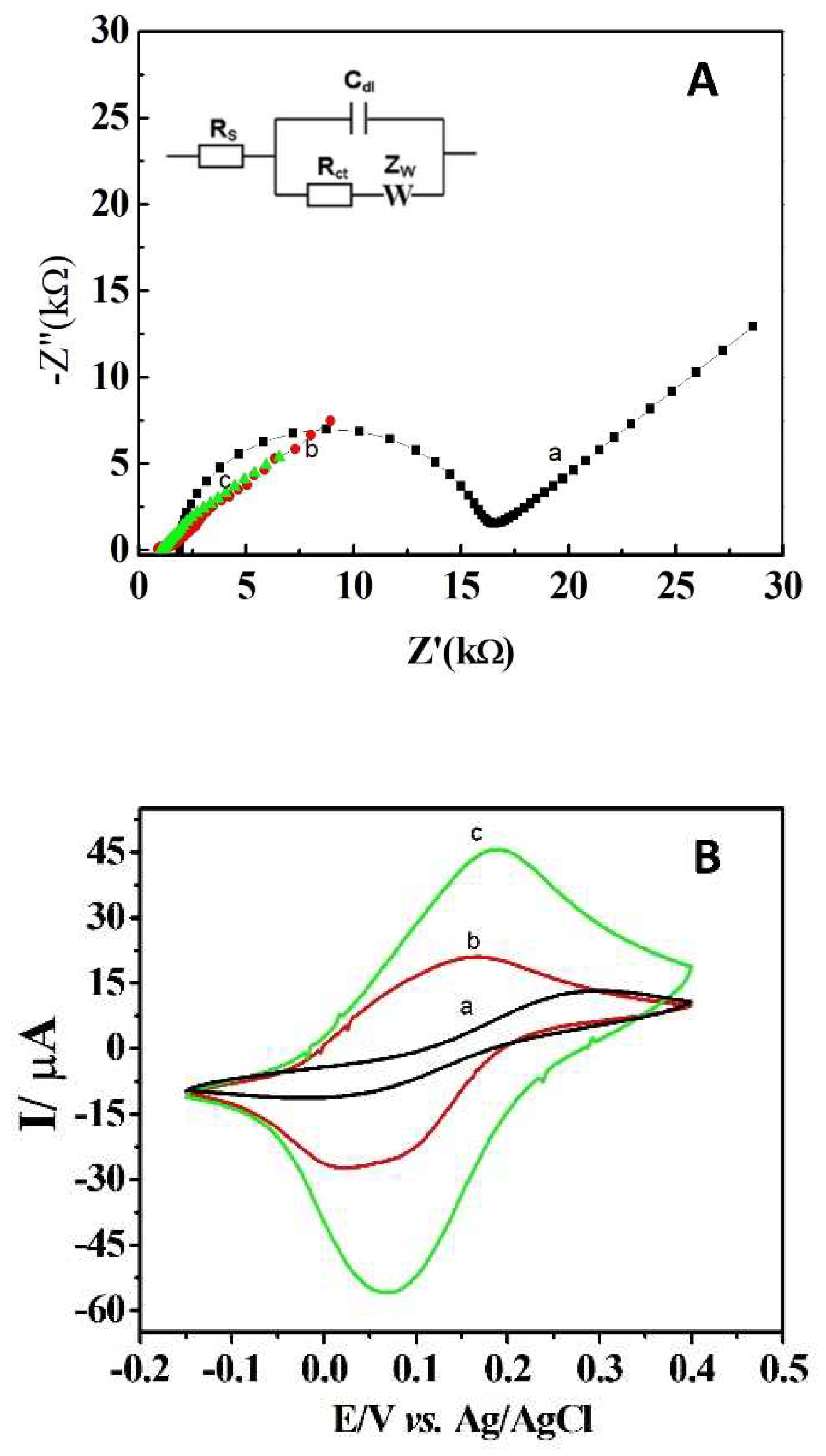
3.1. Morphological and electrochemical characterization of DCell-CB//Ag/δ-FeOOH
3.2. Electrochemical behavior of H2O2 in DCell-CB//Ag/δ-FeOOH
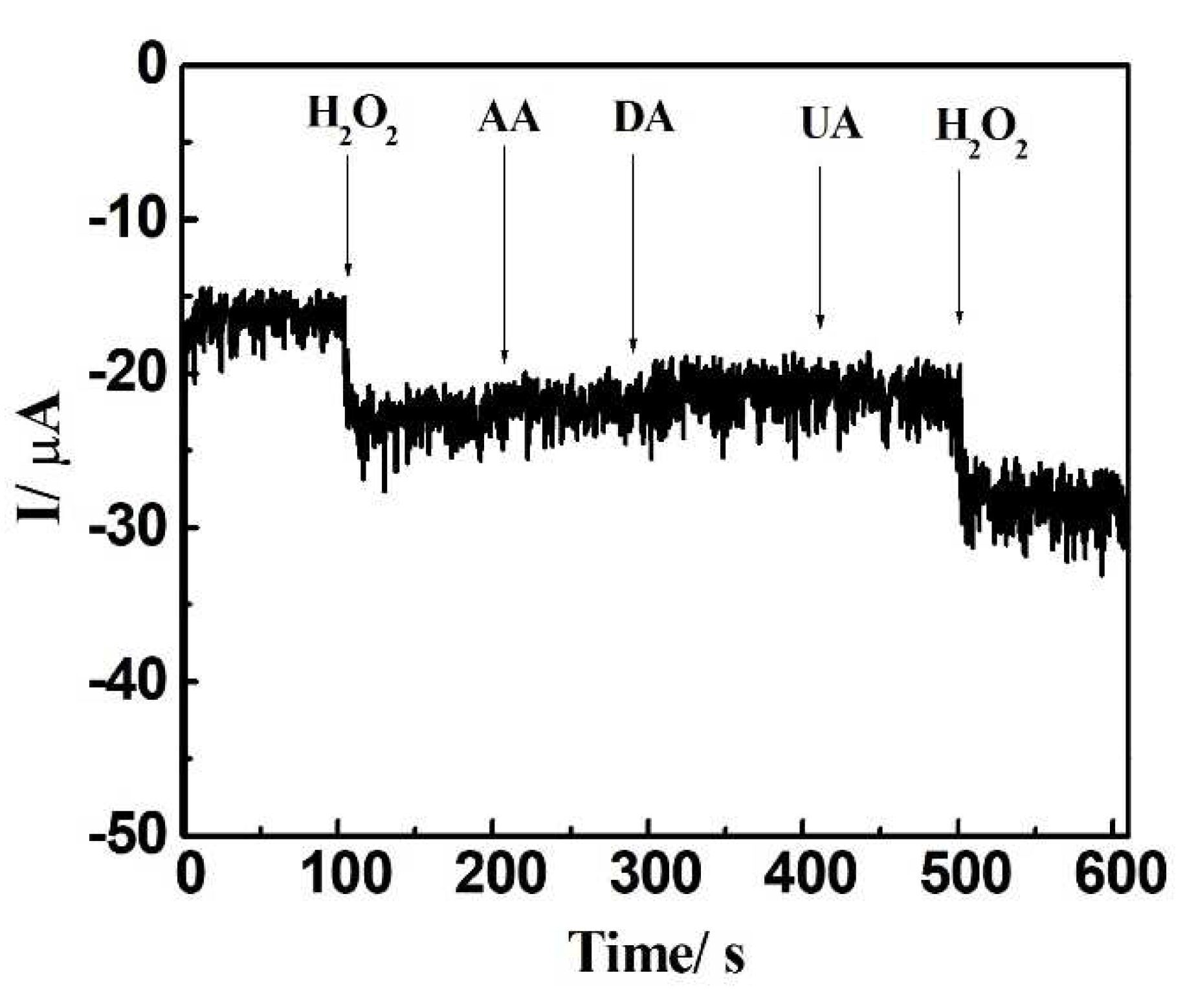
3.4. Repeatability, Interference Studies, and Biological Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berg, D. Biomarkers for the early detection of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurodegener. Dis. 2008, 5, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepe, M.S.; Etzioni, R.; Feng, Z.D.; Potter, J.D.; Thompson, M.L.; Thornquist, M.; Winget, M.; Yasui, Y. Phases of biomarker development for early detection of cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, A.S.; Muraoka, W.; Andreescu, S. Electrochemical sensors for oxidative stress monitoring. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 29, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraskevich, A.V.; Solomonenko, A.N.; Dorozhko, E.V.; Korotkova, E.I.; Barek, J. Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species in Biological Systems: A Critical Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.M.; Wu, G.H.; Cai, Z.X.; Oyama, M.; Chen, X. Advances in enzyme-free electrochemical sensors for hydrogen peroxide, glucose, and uric acid. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatikayala, D.; Ponnamma, D.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Cabibihan, J.J.; Al-Ali, A.K.; Malik, R.A.; Min, B. Progress of Advanced Nanomaterials in the Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Sensing of Glucose and H2O2. Biosensors-Basel 2020, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Meira, F.H.A.; Resende, S.F.; Monteiro, D.S.; Pereira, M.C.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Faria, R.C.; Afonso, A.S. A Non-enzymatic Ag/delta-FeOOH Sensor for Hydrogen Peroxide Determination using Disposable Carbon-based Electrochemical Cells. ELECTROANALYSIS 2020, 32, 2231–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.X.; Han, F.S.; Li, M.T.; Zhou, Z.H.; Guan, X.J.; Guo, L.J. Which phase of iron oxyhydroxides (FeOOH) is more competent in overall water splitting as a photocatalyst, goethite, akaganeite or lepidocrocite? A DFT-based investigation. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2019, 169, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Sheng, Q.L.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Dong, S.Y.; Zheng, J.B. Synthesis of FeOOH@PDA-Ag nanocomposites and their application for electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 781, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, J.B. An enzyme-free hydrogen peroxide sensor based on Ag/FeOOH nanocomposites. Analytical Methods 2015, 7, 1788–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.L.; Zhang, H.F.; Zheng, J.B. Synthesis of silver decorated sea urchin-like FeOOH nanocomposites and its application for electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 14369–14376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.L.; Liang, G.Z.; Lin, T.R.; Hou, L.; Ye, F.G.; Zhao, S.L. Magnetic Cu/Fe3O4@FeOOH with intrinsic HRP-like activity at nearly neutral pH for one-step biosensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 3801–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arduini, F.; Cinti, S.; Mazzaracchio, V.; Scognamiglio, V.; Amine, A.; Moscone, D. Carbon black as an outstanding and affordable nanomaterial for electrochemical (bio)sensor design. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 156, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti, S.; Arduini, F. Graphene-based screen-printed electrochemical (bio)sensors and their applications: Efforts and criticisms. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, K.; Kim, H. Fabrication of Nitrogen-Doped Reduced Graphene Oxide Modified Screen Printed Carbon Electrode (N-rGO/SPCE) as Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.W.; Jiang, J.Q.; Wu, D.; You, Y.L.; Yang, X.; Wu, F.; Hu, Y.J. A Novel Nonenzymatic Hydrogen Peroxide Electrochemical Sensor Based on Facile Synthesis of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Dopping into Graphene Sheets@Cerium Oxide Nanocomposites Sensitized Screen Printed Electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 8486–8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Hojamberdiev, M.; Geng, D.S. Recent advances in enzyme-free electrochemical hydrogen peroxide sensors based on carbon hybrid nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 6970–6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ouyang, Y.J.; Wu, F.; Hu, Y.J.; Zhang, H.F.; Wu, Z.Y. In situ & controlled preparation of platinum nanoparticles dopping into graphene sheets@cerium oxide nanocomposites sensitized screen printed electrode for nonenzymatic electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 777, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, A.S.; Uliana, C.V.; Martucci, D.H.; Faria, R.C. Simple and rapid fabrication of disposable carbon-based electrochemical cells using an electronic craft cutter for sensor and biosensor applications. Talanta 2016, 146, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.C.; Garcia, E.M.; da Silva, A.C.; Lorencon, E.; Ardisson, J.D.; Murad, E.; Fabris, J.D.; Matencio, T.; Ramalho, T.D.; Rocha, M.V.J. Nanostructured delta-FeOOH: a novel photocatalyst for water splitting. Journal of Materials Chemistry 2011, 21, 10280–10282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduini, F.; Di Nardo, F.; Amine, A.; Micheli, L.; Palleschi, G.; Moscone, D. Carbon Black-Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes as Electroanalytical Tools. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, R.S. THEORY AND APPLICATION OF CYCLIC VOLTAMMETRY FOR MEASUREMENT OF ELECTRODE REACTION KINETICS. Anal. Chem. 1965, 37, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.E.; Flavel, B.S.; Ellis, A.V.; Shapter, J.G. Comparison of double-walled with single-walled carbon nanotube electrodes by electrochemistry. Carbon 2011, 49, 2639–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, H.; Tahiri, I.A.; Muhammad, M.; Masood, Z.; Versiani, M.A.; Khaliq, O.; Latif, M.; Hanif, M. A comprehensive heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant evaluation of dissolved oxygen in DMSO at glassy carbon electrode measured by different electrochemical methods. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 775, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixao, T. Measuring Electrochemical Surface Area of Nanomaterials versus the Randles-Sevcik Equation. Chemelectrochem 2020, 7, 3414–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plowman, B.J.; Sidhureddy, B.; Sokolov, S.V.; Young, N.P.; Chen, A.C.; Compton, R.G. Electrochemical Behavior of Gold-Silver Alloy Nanoparticles. Chemelectrochem 2016, 3, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, M.; Alam, M.M.; Asiri, A.M.; Alsaiari, M.; Alruwais, R.S.; Jalalah, M.; Madkhali, O.; Rahman, M.M.; Harraz, F.A. Detection of hydrogen peroxide with low-dimensional silver nanoparticle-decorated PPy-C/TiO2 nanocomposites by electrochemical approach. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2023, 928, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Li, H.M.; Gong, S.P.; Chen, Y.N.; Xie, R.R.; Wu, Q.Q.; Tao, J.; Meng, F.L.; Zhao, P. A novel non-enzymatic electrochemical biosensor based on the nanohybrid of bimetallic PdCu nanoparticles/carbon black for highly sensitive detection of H2O2 released from living cells. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2019, 290, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, H.J.; Bernardo, A.; Davies, K.J.A. What is the concentration of hydrogen peroxide in blood and plasma? Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 603, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hong, Y.L.; Li, J.B.; Liu, J.L.; Jiang, H.; Sun, L.N. Upconversion luminescent sensor for endogenous H2O2 detection in cells based on the inner filter effect of coated silver layer. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2023, 376, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Dhar, S.; Debnath, K.; Majumder, T.; Mondal, S.P. Non-enzymatic and non-invasive glucose detection using Au nanoparticle decorated CuO nanorods. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2019, 283, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldiya, M.; Bhagat, D.; Narasimman, R.; Singh, S.; Kumar, A.; Ray, A.; Mukhopadhyay, I. Development of highly sensitive H2O2 redox sensor from electrodeposited tellurium nanoparticles using ionic liquid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 132, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.X.; Liu, S.W.; Su, B.Y.; Wang, D.J.; Huang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.G. Luminescent europium(III)-organic framework for visual and on-site detection of hydrogen peroxide via a tablet computer. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Valk, J. Fetal bovine serum-a cell culture dilemma. Science 2022, 375, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
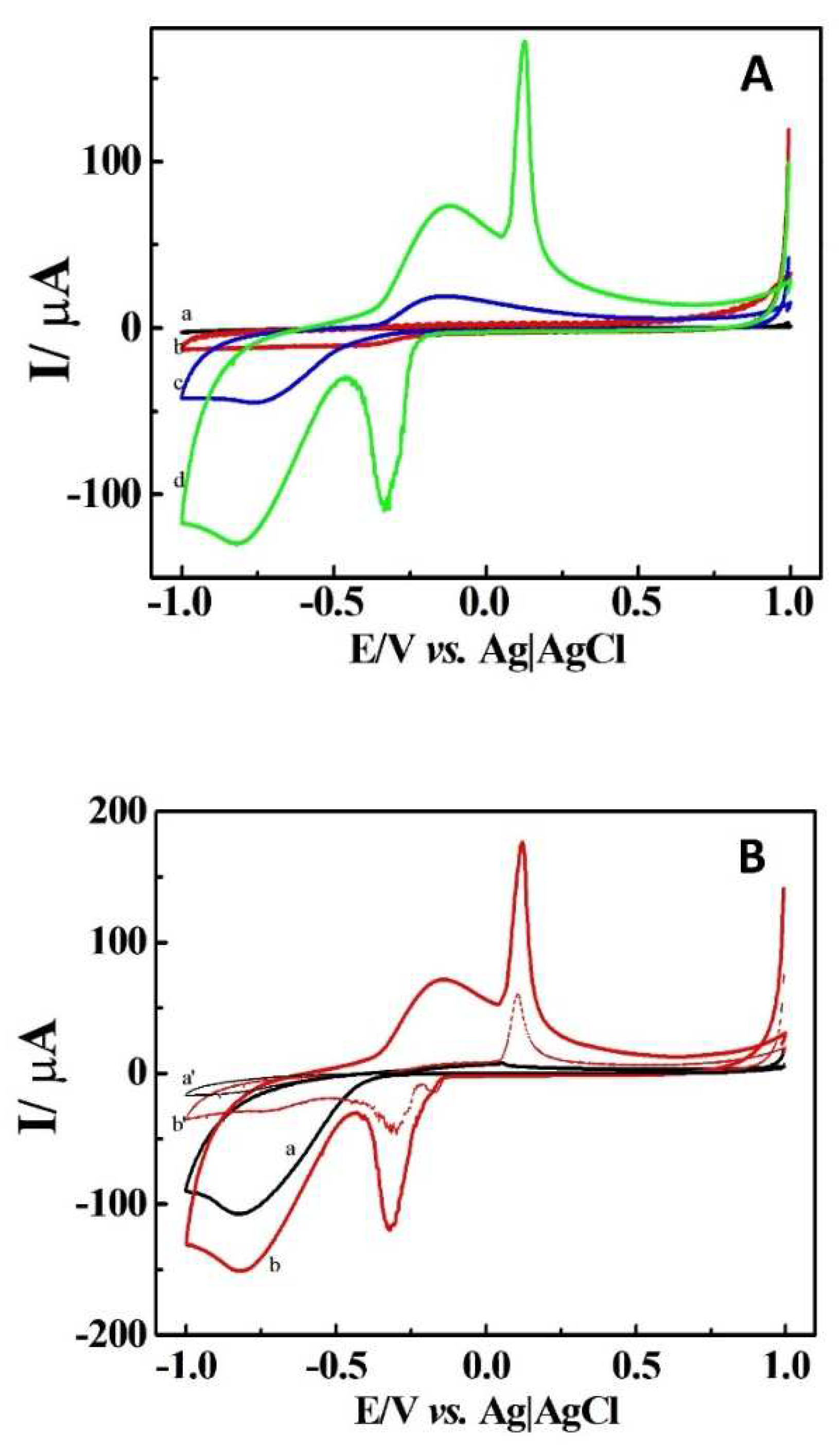
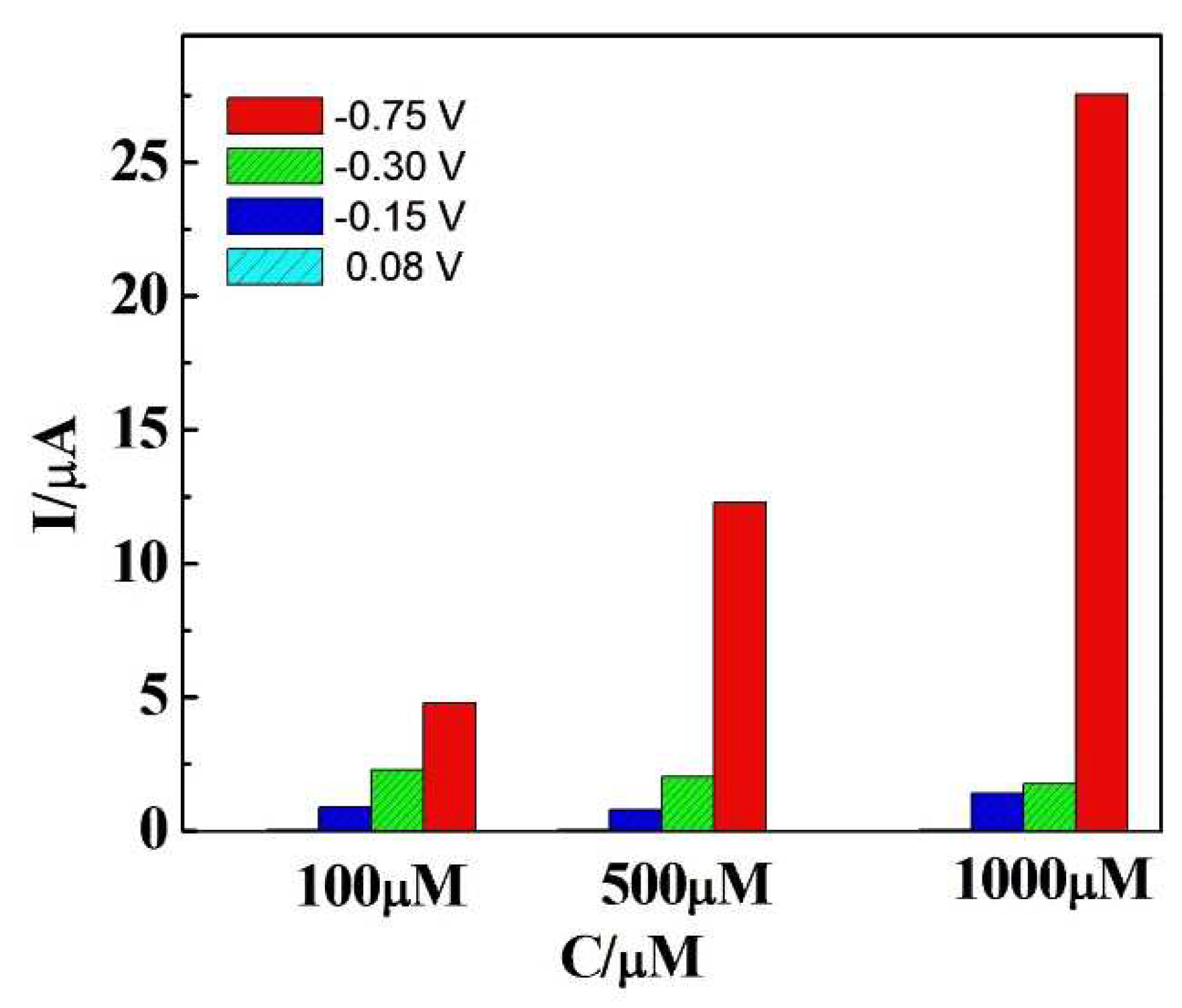
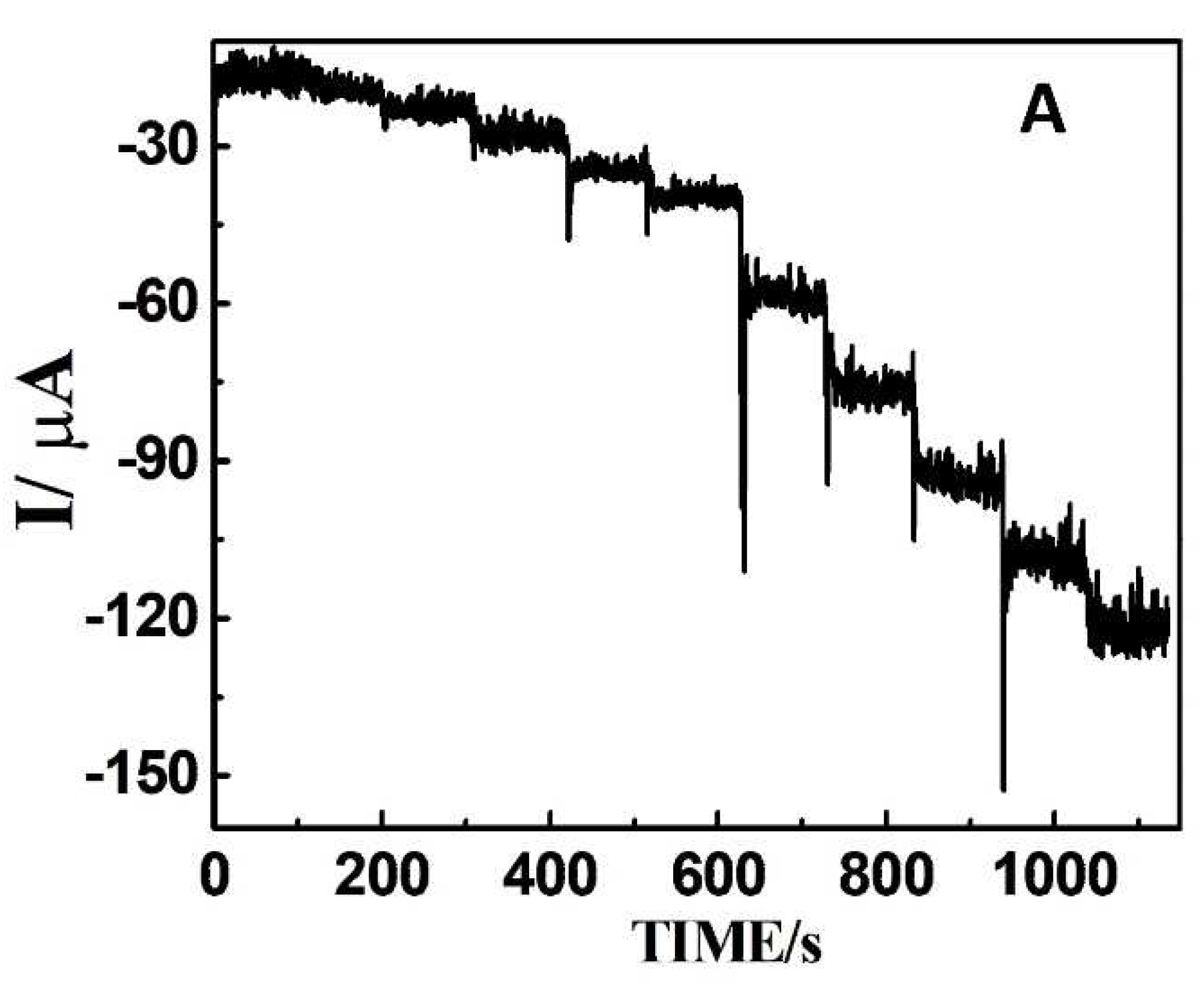
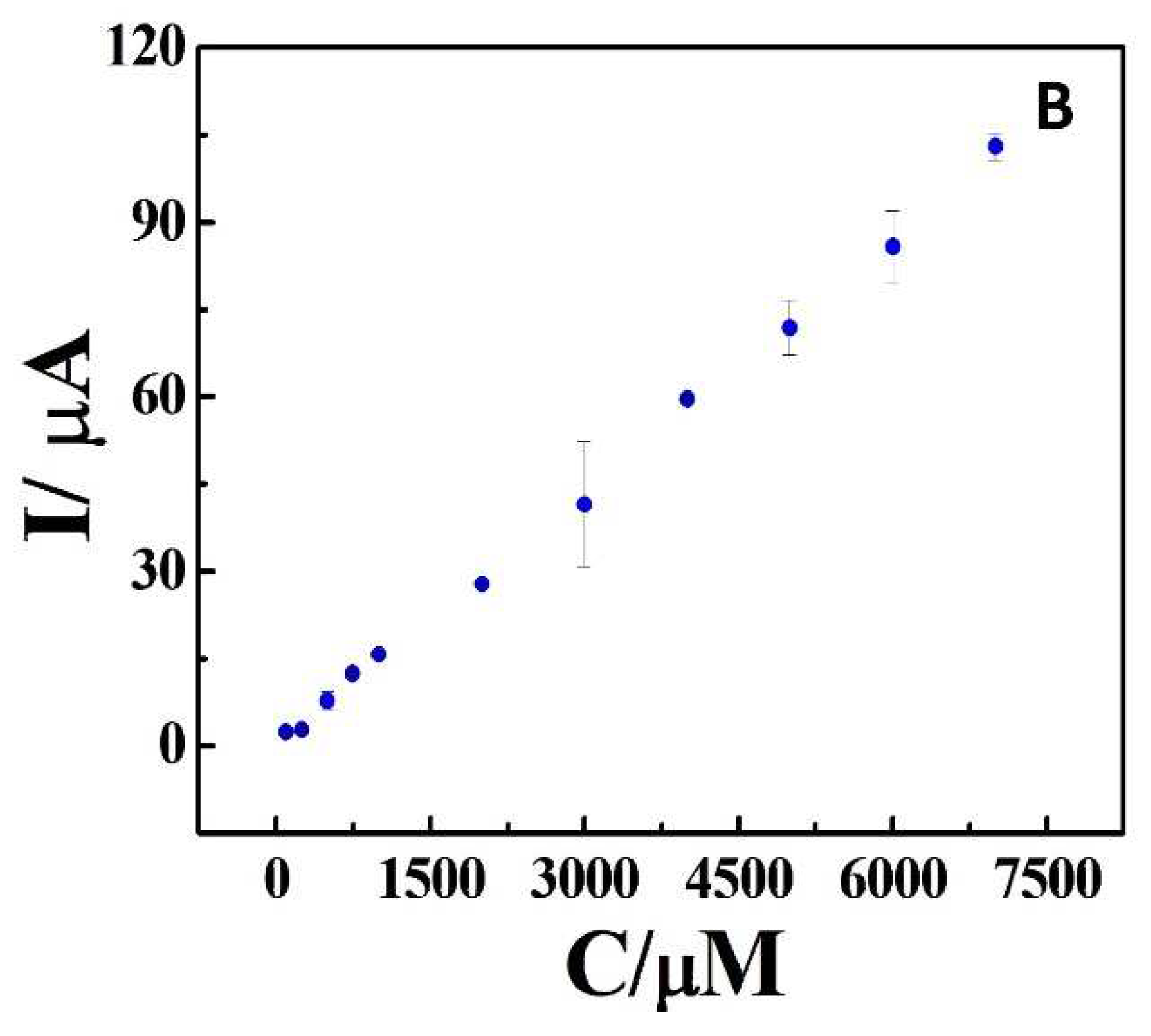
| Sample | Added (μM) | Found (μM) | Recovery (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 500 | 515.6 | 103% |
| 2 | 2000 | 1834.5 | 92% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





