Submitted:
06 October 2023
Posted:
09 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
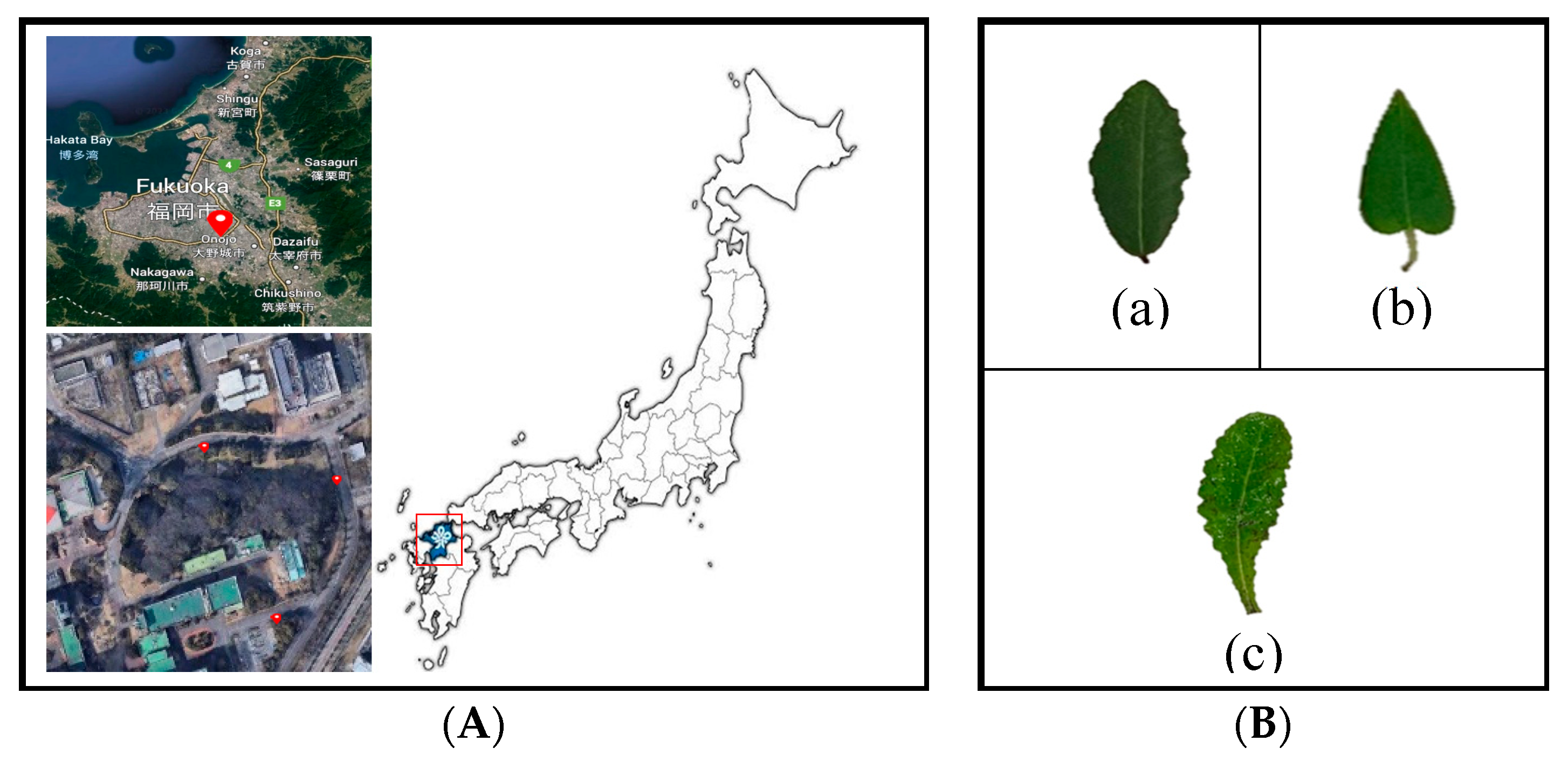
2.1. Leaves samples and experimental sites
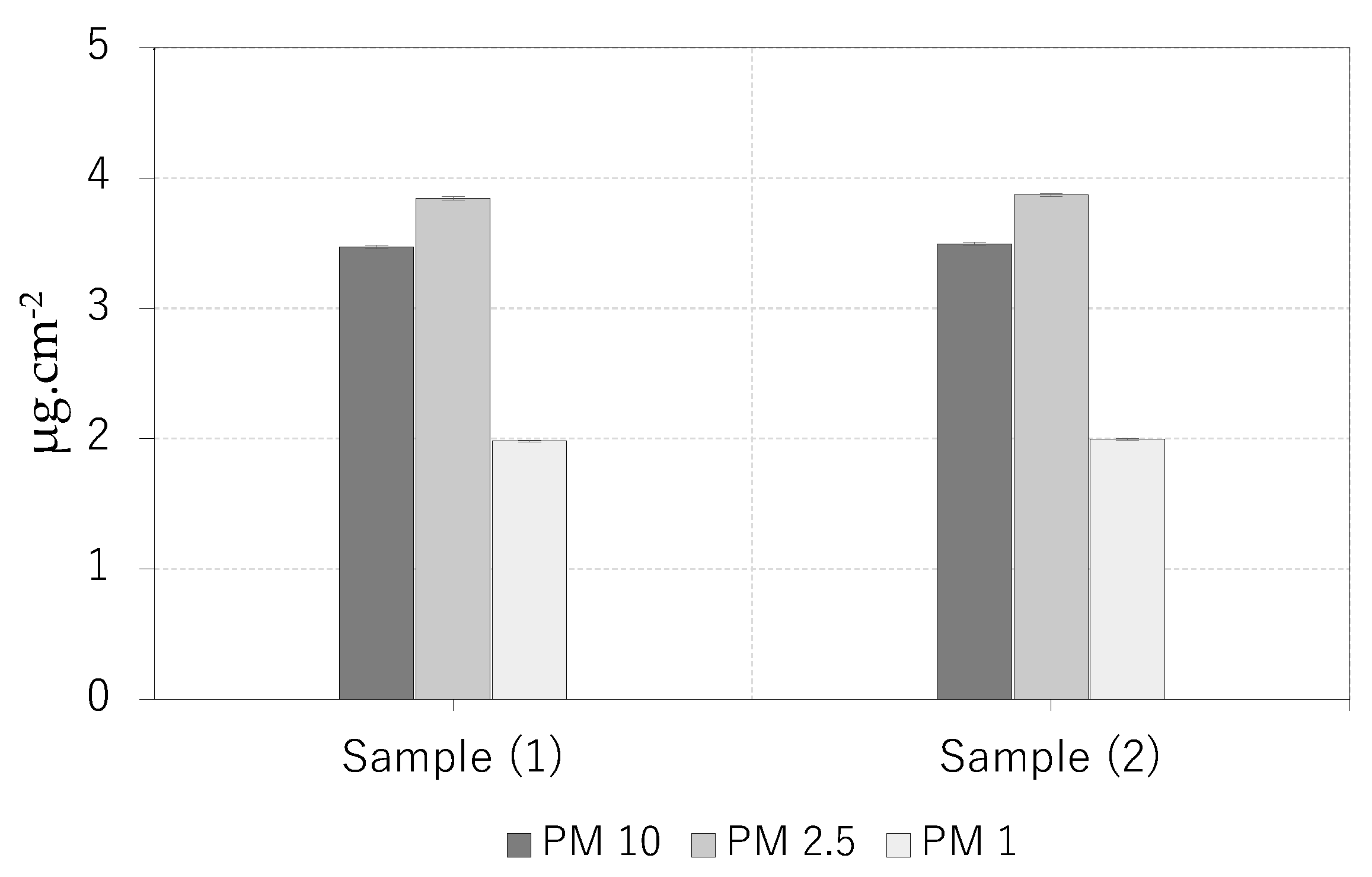
2.2. Quantitative Gravimetric analysis of PM
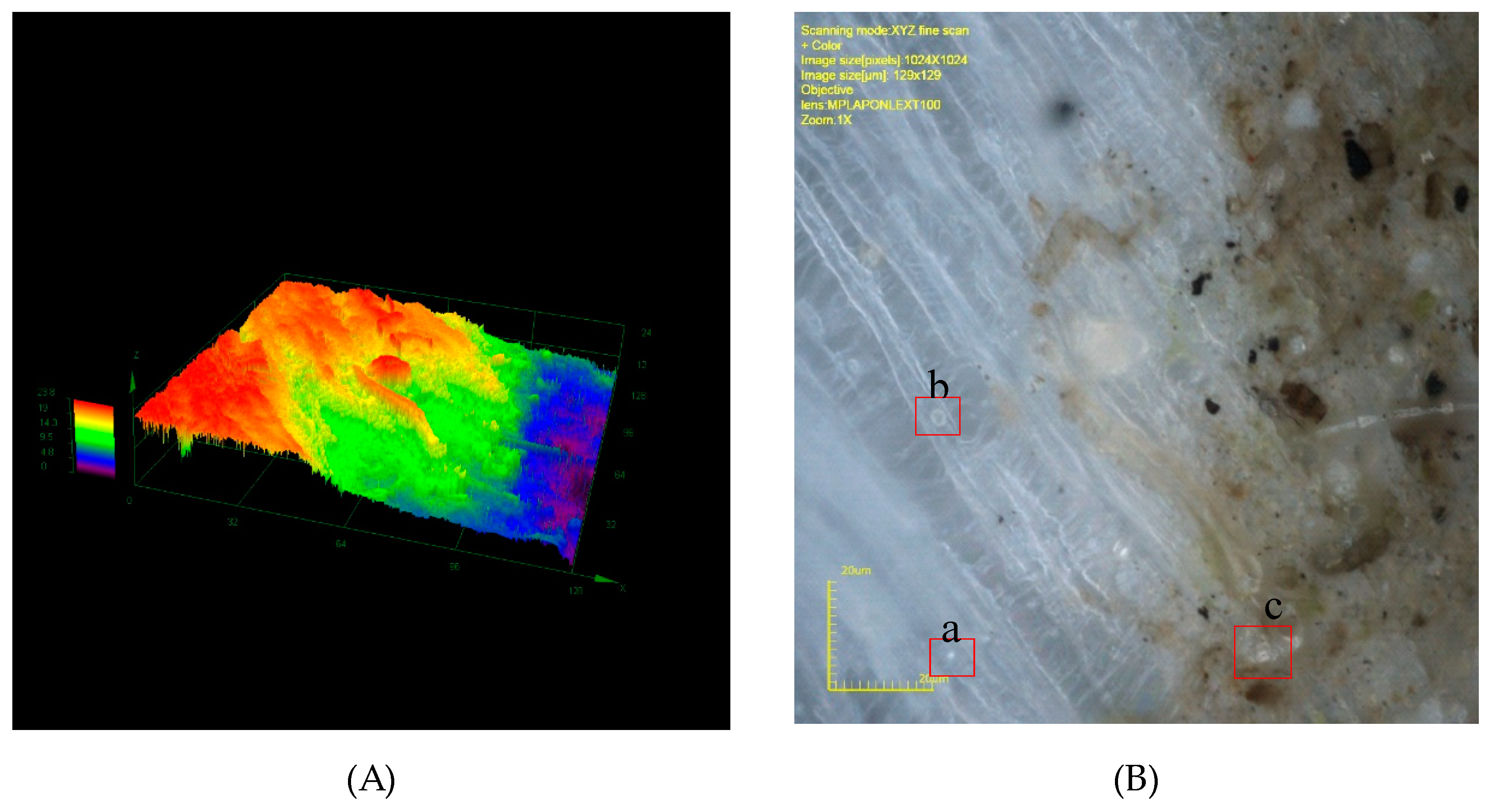
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
References
- Farmer, A. Effects of particulates. In: Bell JNB, Treshow M, editors. Air pollution and plant life. Hoboken (NJ): John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2002, p. 187–99.
- University of Idaho. Emissions and Smoke Portal. Available online: https://www.frames.gov/smoke/tutorial/module-1/particulate-matter (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- Laden, F.; Schwartz, J.; Speizer, F.E.; Dockery, D.W. Reduction in fine particulate air pollution and mortality: extended follow-up of the Harvard Six Cities study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodruff, T.J.; Parker, J.D.; Schoendorf, K.C. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) air pollution and selected causes of post-neonatal infant mortality in california. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A.; Brook, R.D.; Burnett, R.T.; Dockery, D.W. How is cardiovascular disease mortality risk affected by duration and intensity of fine particulate matter exposure? An integration of the epidemiologic evidence. Air Qual. Atmosphere Heal. 2010, 4, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, J.A. Particulate air pollution, systemic oxidative stress, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Air Qual. Atmos. Health. 2011, 4, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, H.R.; Favarato, G.; Atkinson, R.W. Erratum to: Long-term exposure to air pollution and the incidence of asthma: meta-analysis of cohort studies. Air Qual. Atmosphere Heal. 2012, 6, 541–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilli, F.; Fares, S.; Ghirardo, A.; de Visser, P.; Calatayud, V.; Muñoz, A.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Sebastiani, F.; Alivernini, A.; Varriale, V.; et al. Plants for Sustainable Improvement of Indoor Air Quality. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, R.W.; Anderson, H.R.; Sunyer, J.; Ayres, J.; Baccini, M.; Vonk, J.M.; Boumghar, A.; Forastiere, F.; Forsberg, B.; Touloumi, G.; et al. Acute Effects of Particulate Air Pollution on Respiratory Admissions. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1860–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Silva, R.; West, J.J.; Zhang, Y.; Anenberg, S.C.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Shindell, D.T.; Collins, W.J.; Dalsoren, S.; Faluvegi, G.; Folberth, G.; et al. Global premature mortality due to anthropogenic outdoor air pollution and the contribution of past climate change. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 034005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, T.; Ueda, K.; Seposo, X. T.; Nakashima, A.; Kinoshita, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Nitta, H. Health effects of PM2. 5 sources on children’s allergic and respiratory symptoms in Fukuoka, Japan. Science of The Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Michikawa, T.; Morokuma, S.; Yamazaki, S.; Nakahara, K.; Yoshino, A.; Sugata, S.; Takami, A.; Saito, S.; Hoshi, J.; et al. Trimester-Specific Association of Maternal Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter and its Components With Birth and Placental Weight in Japan. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2021, 63, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO), JOINT, et al. Health risks of particulate matter from long-range transboundary air pollution. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe 2006.
- Hirabayashi, S.; Kroll, C.N.; Nowak, D.J. I-Tree Eco Dry Deposition Model Descriptions (accessed on 2023.08.28).
- Fowler, D.; Coyle, M.; ApSimon, H.M.; Ashmore, M.R.; Bareham, S.A.; Battarbee, R.W.; Derwent, R.G.; Erisman, J.-W.; Goodwin, J.; Grennfelt, P.; Hornung, M.; Irwin, J.; Jenkins, A.; Metcalfe, S.E.; Ormerod, S.J.; Reynolds, B.; Woodin, S.; Hall, J.; Tipping, E.; Sutton, M.; Dragosits, U.; Evans, C.; Foot, J.; Harriman, R.; Monteith, D.; Broadmeadow, M.; Langan, S.; Helliwell, R.; Whyatt, D.; Lee, D.S.; Curtis, C. National Expert Group on Transboundary Air Pollution, 2001. Transboundary air pollution: acidification, eutrophication and ground-level ozone in the UK. NEGTAP 2001.
- Escobedo, F.J.; Kroeger, T.; Wagner, J.E. Urban forests and pollution mitigation: Analyzing ecosystem services and disservices. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2078–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, D.J.; Crane, D.E.; Stevens, J.C. Air pollution removal by urban trees and shrubs in the United States. Urban For. Urban Green. 2006, 4, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brack, C. Pollution mitigation and carbon sequestration by an urban forest. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 116, S195–S200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgrigna, G.; Sæbø, A.; Gawronski, S.; Popek, R.; Calfapietra, C. Particulate Matter deposition on Quercus ilex leaves in an industrial city of central Italy. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 197, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera, S.; Viecco, M.; Jorquera, H. Effects of biodiversity in green roofs and walls on the capture of fine particulate matter. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 63, 127229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierżanowski, K.; Popek, R.; Gawrońska, H.; Sæbø, A.; Gawroński, S.W. Deposition of Particulate Matter of Different Size Fractions on Leaf Surfaces and in Waxes of Urban Forest Species. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2011, 13, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, M.; Beswick, K.; Duyzer, J.; Westrate, H.; Choularton, T.; Hummelshøj, P. Measurements of aerosol fluxes to speulder forest using a micrometeorological technique. Atmospheric Environ. 1997, 31, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sæbø, A.; Popek, R.; Nawrot, B.; Hanslin, H.M.; Gawronska, H.; Gawroński, S.W. Plant species differences in particulate matter accumulation on leaf surfaces. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427–428, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, D.; Aguilar, B.; Fuentealba, R.; Préndez, M. Environmental studies in two communes of Santiago de Chile by the analysis of magnetic properties of particulate matter deposited on leaves of roadside trees. Atmospheric Environ. 2017, 152, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, S.; MacKenzie, A.; Bunce, R.; Stewart, H.; Donovan, R.; Stark, G.; Hewitt, C. Urban land classification and its uncertainties using principal component and cluster analyses: A case study for the UK West Midlands. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 78, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freer-Smith, P. H.; Beckett, K. P.; and Taylor, G. Deposition velocities to Sorbus aria, Acer campestre, Populus deltoides× trichocarpa ‘Beaupré’, Pinus nigra and× Cupressocy_paris leylandii for coarse, fine and ultra-fine particles in the urban environment. Environ. pollut. 2005, 133.1, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, E.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Bae, E.J.; Jeong, B.R.; Yong, S.H.; Choi, M.S. Particulate Matter Removal Ability of Ten Evergreen Trees Planted in Korea Urban Greening. Forest 2021, 12, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North Carolina Extension Gardener Plant Toolbox. Available online: https://plants.ces.ncsu.edu (accessed on 24 April 2023).
- Japan Meteorological Agency. Available online: https://www.jma.go.jp/bosai/#pattern=fore_cast&area_type=class20s&area_code=4021900 (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- Castelli, F.; Librando, V.; Sarpietro, M.G. Calorimetric Approach of the Interaction and Absorption of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons with Model Membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2717–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ImageJ (Rasband, W.S., ImageJ, U. S. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA. Available online: http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- Osunkoya, O.O.; Bayliss, D.; Panetta, F.D.; Vivian-Smith, G. Variation in ecophysiology and carbon economy of invasive and native woody vines of riparian zones in south-eastern Queensland. Austral Ecol. 2010, 35, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popek, R.; Gawrońska, H.; Wrochna, M.; Gawroński, S.W.; Sæbø, A. Particulate Matter on Foliage of 13 Woody Species: Deposition on Surfaces and Phytostabilisation in Waxes – a 3-Year Study. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2013, 15, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottelé, M.; van Bohemen, H.D.; Fraaij, A.L. Quantifying the deposition of particulate matter on climber vegetation on living walls. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, E.; Ruiz-Rudolph, P. The potential for indoor ultrafine particle reduction using vegetation under laboratory conditions. Indoor Built Environ. 2016, 27, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.-T.; Odsuren, U.; Kim, S.-Y.; Park, B.-J. Seasonal Variations in the Particulate Matter Accumulation and Leaf Traits of 24 Plant Species in Urban Green Space. Land 2022, 11, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.; Newton, J. Building Green A Guide to Using Plants on Roofs, Walls and Pavements. Greater London Authoritypp. 2004, 121. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandri, E.; Jones, P. Developing a one-dimensional heat and mass transfer algorithm for describing the effect of green roofs on the built environment: Comparison with experimental results. J. Affect. Disord. 2007, 42, 2835–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiquet, C.; Dover, J.W.; Mitchell, P. Birds and the urban environment: the value of green walls. Urban Ecosyst. 2012, 16, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dover, J.W. Green Infrastructure: Incorporating Plants and Enhancing Biodiversity in Buildings and Urban Environments. Routledge, Stoke-on-Trent. 2015, 120–282.
- Jepson, P. A rewilding agenda for Europe: creating a network of experimental reserves. Ecography 2015, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Kowarik, I.; Säumel, I. Herbaceous plants as filters: Immobilization of particulates along urban street corridors. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 186, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretzel, F.; Vannucchi, F.; Romano, D.; Malorgio, F.; Benvenuti, S.; Pezzarossa, B. Wildflowers: From conserving biodiversity to urban greening—A review. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 20, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybysz, A.; Popek, R.; Stankiewicz-Kosyl, M.; Zhu, C.; Małecka-Przybysz, M.; Maulidyawati, T.; Mikowska, K.; Deluga, D.; Griżuk, K.; Sokalski-Wieczorek, J.; et al. Where trees cannot grow – Particulate matter accumulation by urban meadows. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 785, 147310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaupp, H.; Blumenstock, M.; McLachlan, M.S. Retention and mobility of atmospheric particle-associated organic pollutant PCDD/Fs and PAHs in maize leaves. New Phyto. 2000, 148, 473–480. [Google Scholar]
- Brantley, H.L.; Hagler, G.S.; Deshmukh, P.J.; Baldauf, R.W. Field assessment of the effects of roadside vegetation on near-road black carbon and particulate matter. Sci. Total. Environ. 2013, 468-469, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, R.J.; McArthur, C.; Hochuli, D.F. Particulate matter deposition on roadside plants and the importance of leaf trait combinations. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 20, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyens, N.; Thijs, S.; Popek, R.; Witters, N.; Przybysz, A.; Espenshade, J.; Gawronska, H.; Vangronsveld, J.; Gawronski, S.W. The Role of Plant–Microbe Interactions and Their Exploitation for Phytoremediation of Air Pollutants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 25576–25604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paull, N.J.; Krix, D.; Irga, P.J.; Torpy, F.R. Airborne particulate matter accumulation on common green wall plants. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2019, 22, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, V.; Sancho-Knapik, D.; Guzmán, P.; Peguero-Pina, J.; Gil, L.; Karabourniotis, G.; Khayet, M.; Fasseas, C.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.A.; Heredia, A.; Gil-Pelegrin, E. Wettability, polarity and water absorption of holm oakleaves: effect of leaf side and age. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nicola, F.; Maisto, G.; Prati, M.; Alfani, A. Leaf accumulation of trace elements and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Quercus ilex L. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 153, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckett, K.P.; Taylor, G.; Freer-Smith, P.H. Particulate pollution capture by urban trees: effect of species and windspeed. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2000, 6, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.; Maher, B. Evaluation and application of biomagnetic monitoring of traffic-derived particulate pollution. Atmospheric Environ. 2009, 43, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerakkody, U.; Dover, J.W.; Mitchell, P.; Reiling, K. Particulate matter pollution capture by leaves of seventeen living wall species with special reference to rail-traffic at a metropolitan station. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 27, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litschke, T.; Kuttler, W. On the reduction of urban particle concentration by vegetation a review. Meteorol. Z. 2008, 17, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, H.; Krüger, G.H.J.; Kilbourn, M. Dynamic responses of photosystem II in the Namib Desert shrub, Zygophyllum prismatocarpum, during and after foliar deposition of limestone dust. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 146, 34–45. [Google Scholar]
| Species | Botanical name | Habit | Leaf length | Leaf shape | Hair | Leaf margin | Leaf arrangement | Leaf surface |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thorny Olive | Elaeagnus pungens | Shrub | 3-6 inches | Ovate | - | Undulate | Alternate | Leathery |
| Japanese mountain Yam | Dioscorea japonica | Climber | 3-6 inches | Cordate, heart shape with 3 lobes | - | Lobed | Opposite | sub-pleated |
| Bull Thistle | Cirsium vulgare | Herb | 6 inches | Lanceolate | + | Lobed | rosulate | Hairy |
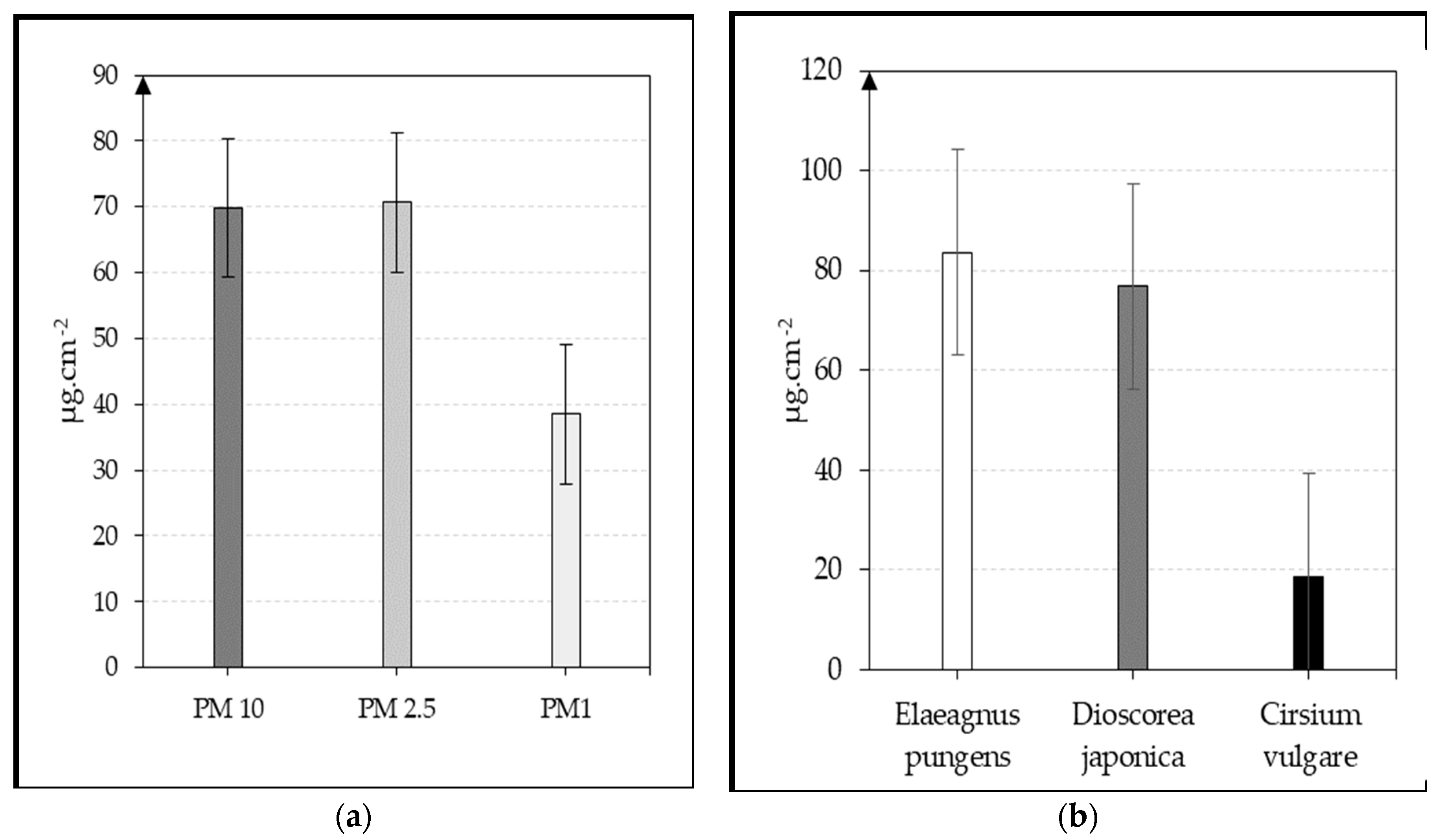
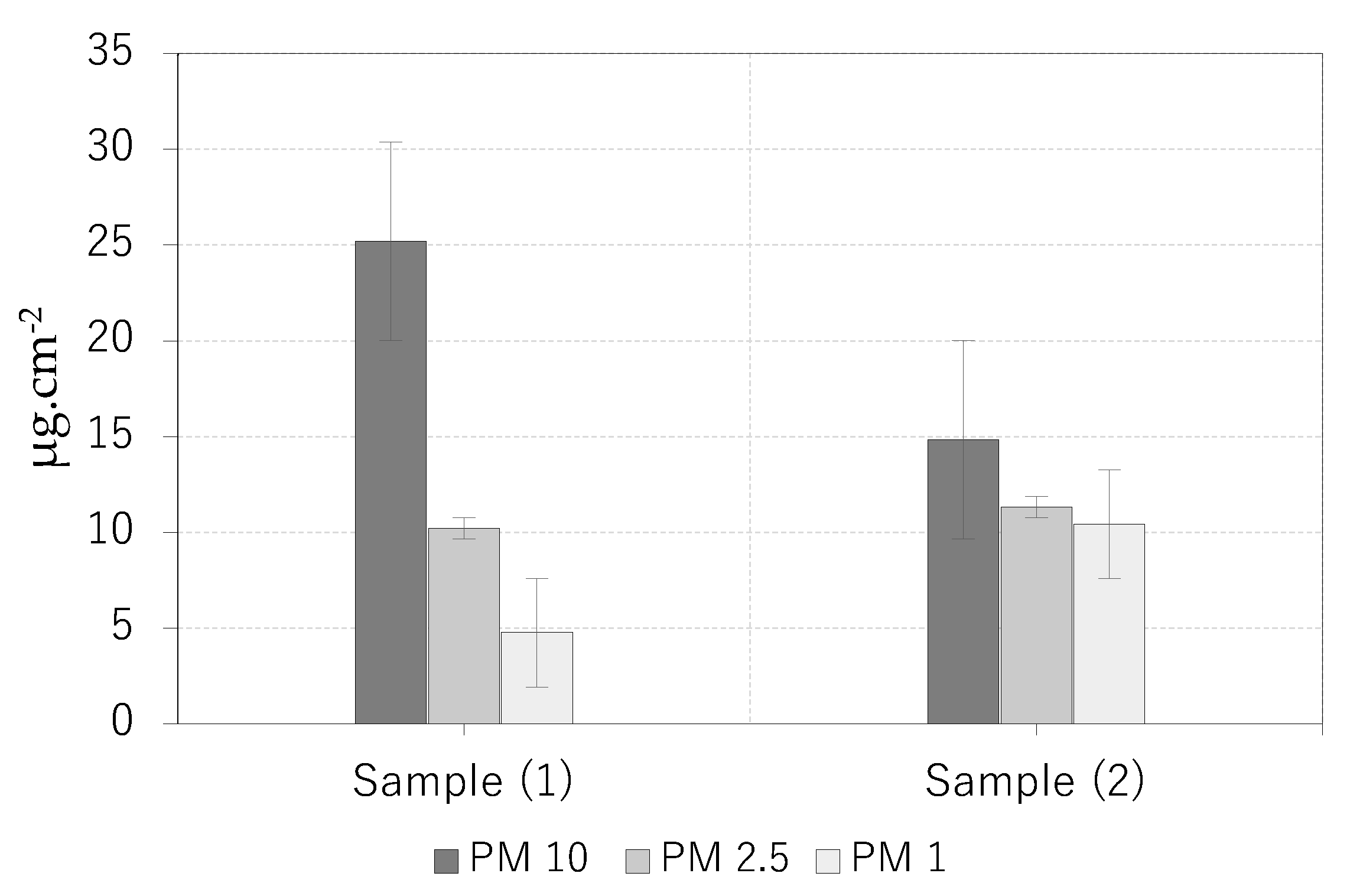
| Species | PM size fractions accumulation(μg.cm-2) | |||||
| Coarse (10-100μm) | (%) | Fine (2.5-10 μm) | (%) | Ultra-fine (0.2-2.5 μm) | (%) | |
| Elaeagnus pungens | 22.8 | 12.7 | 41.4 | 23.1 | 19.3 | 10.8 |
| Dioscorea japonica | 40.04 | 22.4 | 21.5 | 12.03 | 15.2 | 8.5 |
| Cirsium vulgare | 6.9 | 3.9 | 7.7 | 4.3 | 3.9 | 2.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





