Submitted:
05 October 2023
Posted:
06 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
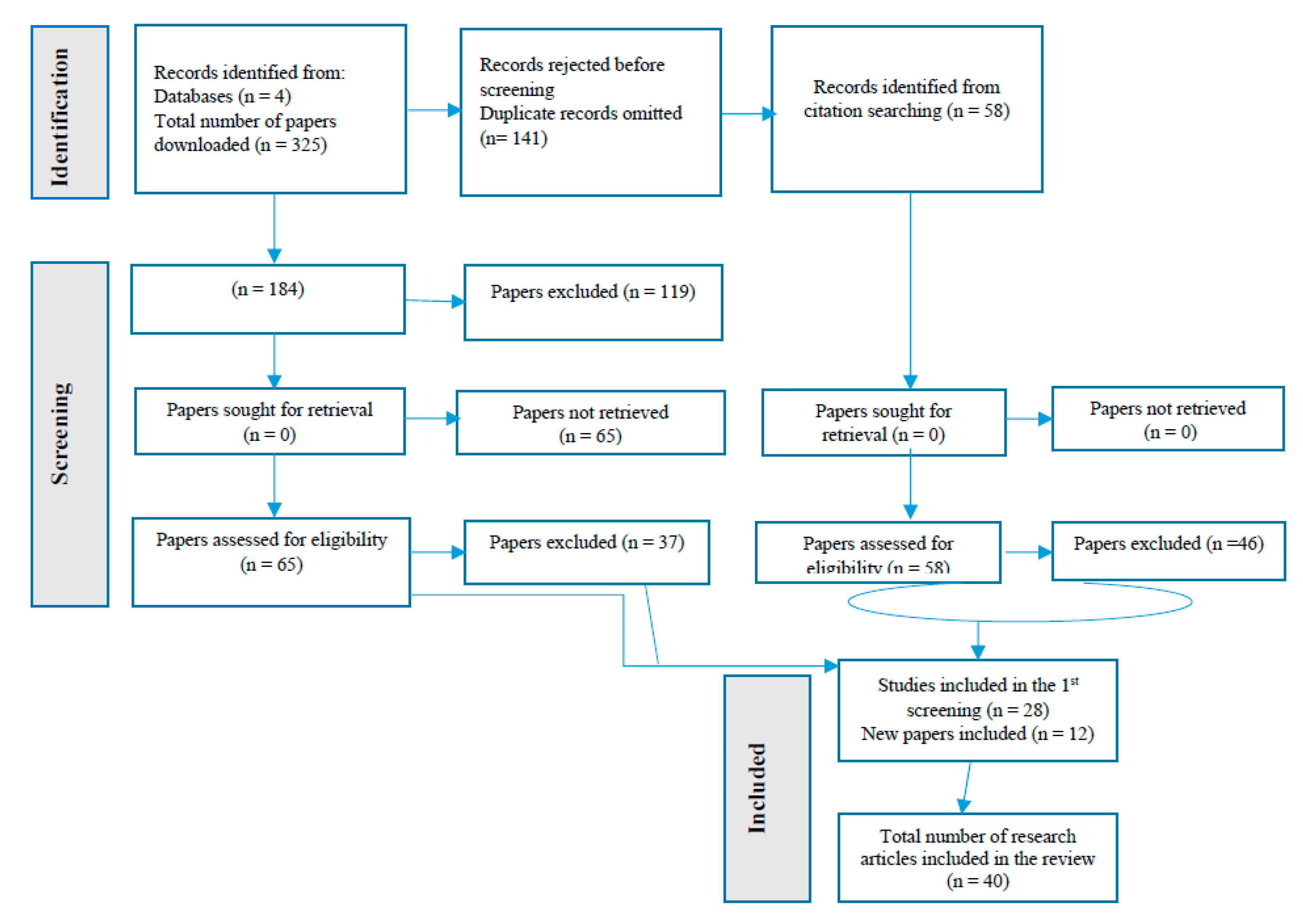
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
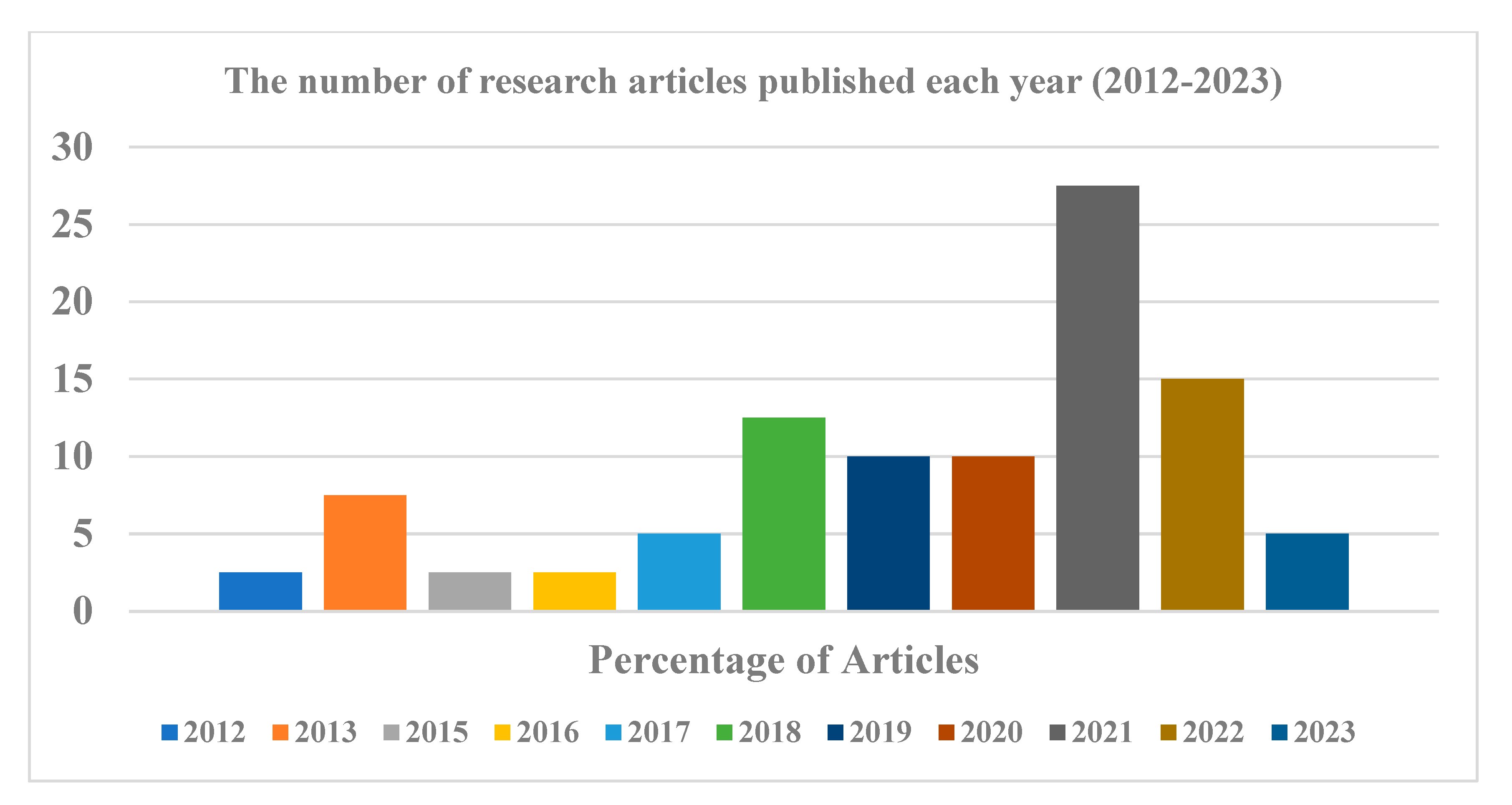
3.1. Overview of literatures
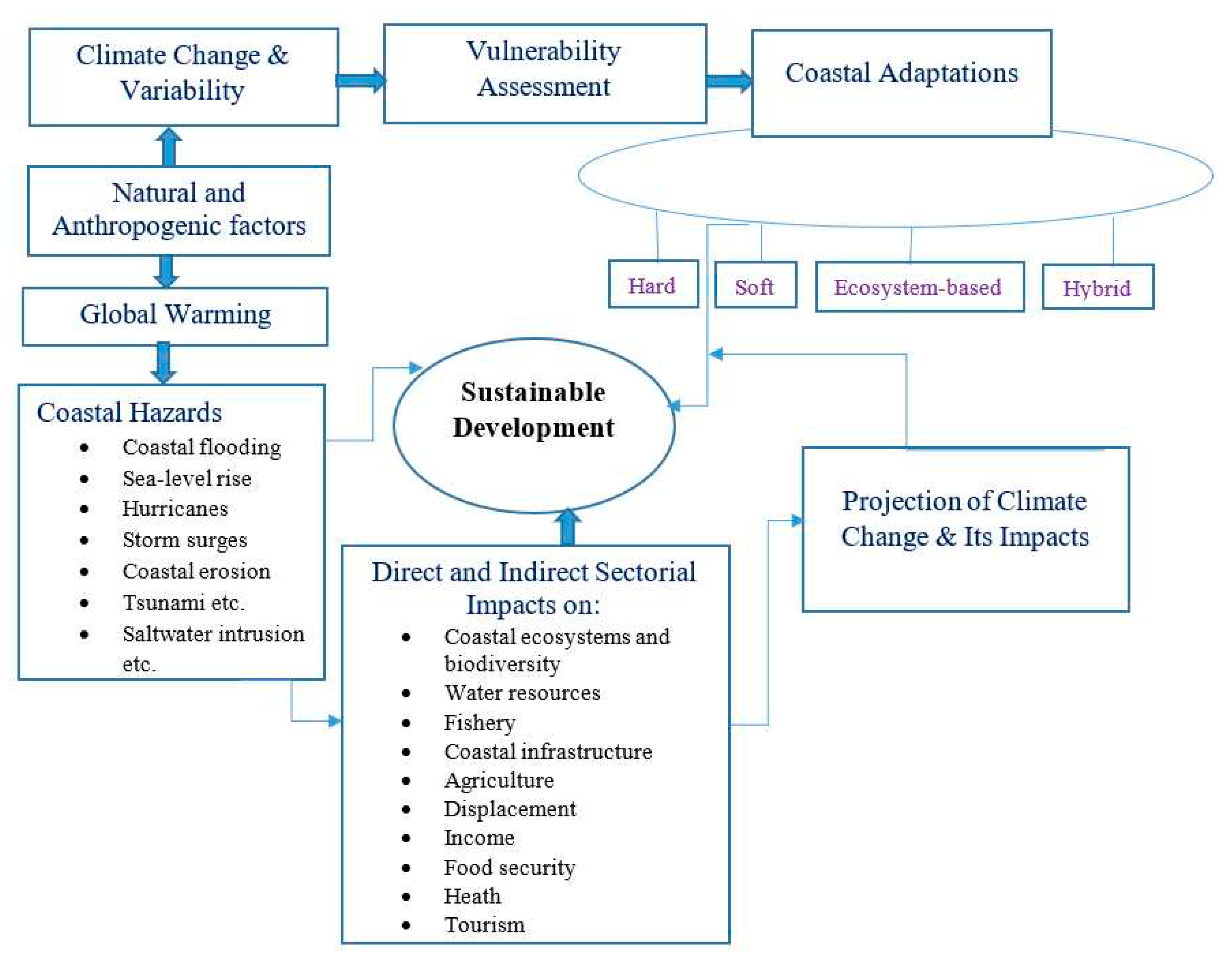
3.2. Climate-Induced Coastal Hazards and Sectoral impacts
3.2.1. Coastal hazards
3.2.2. Impacts of coastal hazards on different sectors
3.3. Vulnerability to climate-induced hazards and projections of climate change
3.4. Coastal Adaptations
- Hard adaptations
- Soft Adaptations
- Ecosystem-based Adaptations
- Hybrid Adaptations
4. Conclusions and policy implications
Author contribution statement
Funding statement
Data availability statement
Declaration of competing
Additional information
Acknowledgements
Appendix A. Proportion of journals that have been used in the literature review
| Journal | Number of Articles |
| Journal of Hydrology | 2 (5%) |
| Springer | 2 (5%) |
| Water | 2 (5%) |
| Scientific Reports | 2 (5%) |
| Advances in Climate Change Research | 1 (2.5%) |
| African Journal of Hospitality | 1 (2.5%) |
| American Journal of Environmental Sciences | 1 (2.5%) |
| Applied sciences | 1 (2.5%) |
| Applied Water Science | 1 (2.5%) |
| Climate Change | 1 (2.5%) |
| Coastal Management | 1 (2.5%) |
| Earth and Environmental Science | 1 (2.5%) |
| Earth Systems and Environment | 1 (2.5%) |
| Economic and Environmental Studies | 1 (2.5%) |
| Environmental Economics | 1 (2.5%) |
| Environmental Science and Policy | 1 (2.5%) |
| Fishes | 1 (2.5%) |
| Frontiers in Environmental Science | 1 (2.5%) |
| Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems | 1 (2.5%) |
| Geoenvironmental Disasters | 1 (2.5%) |
| Heliyon | 1 (2.5%) |
| Indian Journal of Geo-marine Sciences | 1 (2.5%) |
| International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research | 1 (2.5%) |
| Journal of marine Science and Engineering | 1 (2.5%) |
| Journal of Materials and Environmental Science | 1 (2.5%) |
| Marine Policy | 1 (2.5%) |
| Marine Science and Engineering | 1 (2.5%) |
| Middle East Journal of Scientific Research | 1 (2.5%) |
| Modeling Earth Systems and Environment | 1 (2.5%) |
| Natural Hazards and earth System Sciences | 1 (2.5%) |
| Regional Studies in Marine Science | 1 (2.5%) |
| Royal Society of Chemistry Advances | 1 (2.5%) |
| Science of the Total Environment | 1 (2.5%) |
| Scientific Journal for Damietta Faculity of Science | 1 (2.5%) |
| SN Applied Sciences | 1 (2.5%) |
| Social Change | 1 (2.5%) |
| Total | 40 (100%) |
References
- Pecl, G.T.; Araújo, M.B.; Bell, J.D.; Blanchard, J.; Bonebrake, T.C.; Chen, I.-C.; Clark, T.D.; Colwell, R.K.; Danielsen, F.; Evengård, B.; et al. Biodiversity redistribution under climate change: Impacts on ecosystems and human well-being. Science 2017, 355, eaai9214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- B. Berlie, “Global Warming : A Review of the Debates on the Causes, Consequences and Politics of Global Response,” Ghana J. Geogr., vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 144–164, 2018.
- Islam, M.M.; Islam, N.; Habib, A.; Mozumder, M.M.H. Climate Change Impacts on a Tropical Fishery Ecosystem: Implications and Societal Responses. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Butt, A.R.; Uzma, F.; Ahmed, R.; Irshad, S.; Rehman, A.; Yousaf, B. A comprehensive review of climate change impacts, adaptation, and mitigation on environmental and natural calamities in Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 192, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- W. J. Mok, M. A. Ghaffar, M. Iqbal, M. Noor, and F. Lananan, “Understanding Climate Change and Heavy Metals in Coastal,” pp. 1–18, 2023.
- Neumann, B.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Zimmermann, J.; Nicholls, R.J. Future coastal population growth and exposure to sea-level rise and coastal flooding-a global assessment. PloS ONE 2015, 10, e0118571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morim, J.; Trenham, C.; Hemer, M.; Wang, X.L.; Mori, N.; Casas-Prat, M.; Semedo, A.; Shimura, T.; Timmermans, B.; Camus, P.; et al. A global ensemble of ocean wave climate projections from CMIP5-driven models. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- J. Morim, L. E., Sean Vitousek, Mark Hemer, Borja Reguero, M. Casas-Prat, T. S. Xiaolan LWang, Alvaro Semedo, Nobuhito Mori, L. Mentaschi, and and Ben Timmermans, “Global-scale changes to extreme ocean wave events due to anthropogenic warming OPEN ACCESS Global-scale changes to extreme ocean wave events due to anthropogenic warming,” Environ. Res. Lett., vol. 16, p. 074056, 2021.
- Doust, K.; Wejs, A.; Zhang, T.-T.; Swan, A.; Sultana, N.; Braneon, C.; Luetz, J.; Casset, L.; Fatorić, S. Adaptation to climate change in coastal towns of between 10,000 and 50,000 inhabitants. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 212, 105790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez, P.; Losada, I.J.; Torres-Ortega, S.; Narayan, S.; Beck, M.W. The Global Flood Protection Benefits of Mangroves. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griggs, G.; Reguero, B.G. Coastal Adaptation to Climate Change and Sea-Level Rise. Water 2021, 13, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R. Planning for the Impacts of Sea Level Rise. Oceanography 2011, 24, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkens, J.-L.; Reimann, L.; Hinkel, J.; Vafeidis, A.T. Gridded population projections for the coastal zone under the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 145, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.; Icely, J.; Cristina, S.; Perillo, G.M.E.; Turner, R.E.; Ashan, D.; Cragg, S.; Luo, Y.; Tu, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Anthropogenic, Direct Pressures on Coastal Wetlands. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P. on C. (IPCC) Change, “Climate Change 2022 Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability,” 2022.
- Rahman, M.; Hossain, A.; Ali, R.; Ahmed, Z.; Islam, A.H.M.H. Assessing vulnerability and adaptation strategy of the cyclone affected coastal area of Bangladesh. Geoenvironmental Disasters 2022, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Aguilar, I.C.; Sánchez-Dávila, G.; Wildermann, N.E.; Clark, D.; Floerl, L.; Villamizar, E.; Matteucci, S.D.; Sevilla, N.P.M.; Nagy, G.J. Methodological approaches to assess climate vulnerability and cumulative impacts on coastal landscapes. Front. Clim. 2022, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, K.; Kituyi, E.; Harvey, B.; Leone, M.; Murali, K.S.; Ford, J.D. Vulnerability to climate change in three hot spots in Africa and Asia: key issues for policy-relevant adaptation and resilience-building research. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2015, 15, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, C. Better use and management of levees: reducing flood risk in a changing climate. Environ. Rev. 2015, 23, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. Lawyer, L. An, and E. Goharian, “A Review of Climate Adaptation Impacts and Strategies in Coastal Communities : From Agent-Based Modeling towards a,” Water, vol. 15, p. 2635, 2023.
- Riera-Spiegelhalder, M.; Campos-Rodrigues, L.; Enseñado, E.M.; Dekker-Arlain, J.D.; Papadopoulou, O.; Arampatzis, S.; Vervoort, K. Socio-Economic Assessment of Ecosystem-Based and Other Adaptation Strategies in Coastal Areas : A Systematic Review Socio-Economic Assessment of Ecosystem-Based and Other Adaptation Strategies in Coastal Areas : A Systematic Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; et al. he PRISMA 2020 statement : an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M. N. Hossain, M. R. Hassan, M. D. Alam, S. I. Mim, N. Akter, and F. Khanum, “Livelihood vulnerability and adaptation strategies of coastal areas in the face of climate change in Bangladesh : A literature review,” J. Mater. Environ. Sci., vol. 12, no. 12, pp. 1601–1613, 2021.
- Nagy, G.J.; Gutiérrez, O.; Brugnoli, E.; Verocai, J.E.; Gómez-Erache, M.; Villamizar, A.; Olivares, I.; Azeiteiro, U.M.; Filho, W.L.; Amaro, N. Climate vulnerability, impacts and adaptation in Central and South America coastal areas. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 29, 100683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Lathrop, R.G.; Obropta, C.C. Climate change vulnerability assessment and adaptation strategies through best management practices. J. Hydrol. 2019, 580, 124311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, T.; Brown, S.; Haigh, I.D.; Nilsen, J.E. . Coastal Sea Levels, Impacts, and Adaptation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Nagarajan, A.M.; Vinod, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Sivagami, K.; Theodore, T.; Sathyanarayanan, S.S.; Tamizhdurai, P.; Mangesh, V.L. Long-term impacts of climate change on coastal and transitional eco-systems in India: an overview of its current status, future projections, solutions, and policies. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 12204–12228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. H. Minar, M. B. Hossain, and N. Science, “Climate Change and Coastal Zone of Bangladesh : Vulnerability, Resilience and Adaptability Climate Change and Coastal Zone of Bangladesh : Vulnerability, Resilience and Adaptability,” Middle-East J. Sci. Res., no. January, 2013. [CrossRef]
- H. Ahmad and S. I. Jhara, “Present status of impacts of climate change and adaptations in Bangladesh coastal areas,” Soc. Change, vol. 9, no. January, 2021.
- L. James G. Lyimo James O. Ngana Emma and M. Faustin, “Climate change, impacts and adaptations in the coastal communities in Bagamoyo District, Tanzania,” Environ. Econ., vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 63–71, 2013.
- Njoroge, “Climate change- perceived impacts, risks, vulnerability, and response strategies : A case study of Mombasa coastal tourism, Kenya,” African J. Hosp. Tour. Leis., no. January, 2015.
- M. Touitou and A.-A. Abul Quasem, “Climate change and water resources in Algeria : Vulnerability, impact and adaptation strategy Climate change and water resources in Algeria : vulnerability, impact and adaptation strategy,” Econ. Environ. Stud., vol. 18, pp. 411–429, 2018.
- Schernewski, G.; Konrad, A.; Roskothen, J.; von Thenen, M. Coastal Adaptation to Climate Change and Sea Level Rise: Ecosystem Service Assessments in Spatial and Sectoral Planning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torresan, S.; Critto, A.; Rizzi, J.; Marcomini, A. Assessment of coastal vulnerability to climate change hazards at the regional scale: the case study of the North Adriatic Sea. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 2347–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.-J. The Socioeconomic Impact of Coastal Environment Changes on Fishing Communities and Adaptation Strategies. Fishes 2022, 7, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T. Pham, T. A. Nguyen, and R. Kandpal, “Extreme Weather Events and Coastal fishery : Impacts, vulnerability, and adaptation strategies in Viet Nam,” Springer Nat., 2022.
- Mycoo, M.; Robinson, S.-A.; Nguyen, C.; Nisbet, C.; Tonkel, R. Human Adaptation to Coastal Hazards in Greater Bridgetown, Barbados. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkauer, K.A.; Bowling, L.C.; Byun, K.; Chaubey, I.; Chin, N.; Ficklin, D.L.; Hamlet, A.F.; Kines, S.J.; Lee, C.I.; Neupane, R.; et al. Climate change impacts and strategies for adaptation for water resource management in Indiana. Clim. Chang. 2021, 165, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Shen, Z.; Leng, G.; Xie, H.; Hou, X.; Wei, G. Impacts of climate change on watershed systems and potential adaptation through BMPs in a drinking water source area. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abutaleb, K.A.A.; Mohammed, A.H.E.-S.; Ahmed, M.H.M. Climate Change Impacts, Vulnerabilities and Adaption Measures for Egypt’s Nile Delta. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 2, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulu, S.; Hasimuna, O.J.; Haambiya, L.H.; Monde, C.; Musuka, C.G.; Makorwa, T.H.; Munganga, B.P.; Phiri, K.J.; Nsekanabo, J.D. Climate Change Effects on Aquaculture Production: Sustainability Implications, Mitigation, and Adaptations. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakariya; Islam, N. Evaluation of climate change induced vulnerability and adaptation strategies at Haor areas in Bangladesh by integrating GIS and DIVA model. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2017, 3, 1303–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnny, B.; Dolor, E. Impacts and Adaptation Strategies on Climate Variability and Change of Coastal Communities along Banate Bay Impacts and Adaptation Strategies on Climate Variability and Change of Coastal Communities along Banate Bay. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 755, 012087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, R.; VishnuRadhan, R.; Eldho, T.I.; Inamdar, A. Flood risk and adaptation in Indian coastal cities: recent scenarios. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, K.A.; Sabuj, K.M.C.; Sudhir, R.; Devdyuti, B. Chennai City and Coastal Hazards: Addressing Community-Based Adaptation Through the Lens of Climate Change and Sea-Level Rise (CBACCS). Springer 2020, 777–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payus, C.M.; Herman, F.; Sentian, J. Combined climate impacts and vulnerability index on coastal ecosystems in prediction of future scenarios: extended sustainable indicator tool for adaptive strategy. SN Appl. Sci. 2022, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. D. Gonzales and M. E. Bernabe, “Coastal Hazards, Impacts And Interventions,” Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res., vol. 6, no. 10, 2017.
- Islam, M.; Rahman, A.; Khan, M.S.; Mondal, G.; Khan, M.I. Transformational Adaptations to Climatic Hazards : Insights from Mangroves- Based Coastal Fisheries Dependent Communities of Bangladesh Transformational adaptations to climatic hazards : Insights from mangroves- based coastal fisheries dependent communiti. Mar. Policy 2021, 128, 104475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, E. Climate Impacts and Adaptation Strategies of the Bangladeshi Coastal Communities. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 14, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Hasan, K.; Hasan, R.; Younos, T.B. Climate change impacts and adaptations on health of Internally Displaced People (IDP): An exploratory study on coastal areas of Bangladesh. Heliyon 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeeb, A.R.; Elemam, D.A. Climate Change in the Coastal Areas : Consequences, Adaptations, and Projections for the Northern Coastal Area, Egypt. Sci. J. Damietta Faculity Sci. 2023, 12, 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- Azhoni and M. Kumar, “Diagnosing climate change impacts and identifying adaptation strategies by involving key stakeholder organisations and farmers in Sikkim , India : Challenges and opportunities,” Sci. Total Environ., vol. 626, pp. 468–477, 2018.
- Taherkhani, M.; Vitousek, S.; Barnard, P.L.; Frazer, N.; Anderson, T.R.; Fletcher, C.H. Sea-level rise exponentially increases coastal flood frequency. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, R.W.; Seidel, V.; Henderson, C.; De Freese, D. Adaptation Actions to Reduce Impairment of Indian River Lagoon Water Quality Caused by Lagoon Water Quality Caused by Climate Change. Coast. Manag. 2021, 49, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogianni, A.; Tourkolias, C.; Damigos, D.; Skourtos, M. Assessing sea level rise costs and adaptation benefits under uncertainty in Greece. Environ. Sci. Policy 2014, 37, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. Mills, P. Ruggiero, J. P. Bolte, K. A. Serafin, and E. Lipiec, “Quantifying Uncertainty in Exposure to Coastal Hazards Associated with both Climate Change and Adaptation Strategies : A U. S. Pacific Northwest Alternative Coastal Futures Analysis,” Water, vol. 13, p. 545, 2021.
- Magnan, A.K.; Oppenheimer, M.; Garschagen, M.; Buchanan, M.K.; Duvat, V.K.E.; Forbes, D.L.; Ford, J.D.; Lambert, E.; Petzold, J.; Renaud, F.G.; et al. Sea level rise risks and societal adaptation benefits in low-lying coastal areas. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- S. Khan, A. Ramachandran, K. Palanivelu, and V. Selvam, “Climate change induced sea-level rise projections for the Pichavaram mangrove region of the Tamil Nadu coast, India : A way forward for framing time-based adaptation strategies,” Indian J. Geo-marine Sci., vol. 45, no. February, pp. 296–303, 2016.
- Bastidas-Arteaga, E.; Creach, A. Climate change for coastal areas: Risks, adaptation and acceptability. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2020, 11, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Country | Number of articles |
|---|---|
| Bangladesh | 8 |
| USA | 6 |
| Global | 5 |
| India | 5 |
| Egypt | 2 |
| Greek | 2 |
| Philippines | 2 |
| Tanzania | 1 |
| Kenya | 1 |
| Algeria | 1 |
| Germany | 1 |
| Italy | 1 |
| Malaysia | 1 |
| Taiwan | 1 |
| Vet Nam | 1 |
| China | 1 |
| Barbados | 1 |
| Total | 40 |
| Coastal Hazards | Number of articles | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Sea-level rise | 22 | 55% |
| Coastal flooding | 21 | 52.50% |
| Climate change and variability (Rainfall & temperature) | 21 | 52.50% |
| Cyclones | 13 | 32.50% |
| Storm surges | 11 | 27.50% |
| Coastal erosion | 11 | 27.50% |
| Salt water intrusion | 7 | 17.50% |
| Hurricane | 5 | 12.50% |
| Typhoons | 3 | 7.50% |
| Coastal Hazards | Impacts | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Increasing cyclones, flooding, sea-level rise, storm surge, tsunami, hurricanes, El Niño, riverbank erosion, inundation, rising water tables and salinity intrusion | Adverse effects on population, coastal ecosystems, biodiversity, transportation, people's income, employment, food security, the inundation of major cities, loss of coastal infrastructure, increased saltwater intrusion, damage to coastal aquifers and endemic species | [11,16,23,27,29,44,48,50,51,52] |
| Rising temperatures and precipitation, decrease in rainfall amounts and variability | Poses serious threats to the quantity and quality of water, results in rise in surface runoff, streamflow, sediment and total phosphorous load, the fluctuations of water flows in the rivers and inundation of the coastal areas | [25,36,37,38,43,44] |
| Natural disasters, water scarcity, drought, coral reef bleaching, changes in beach structure | They had direct and indirect impacts on the fishery-based communities by affecting aquaculture production sustainability, agricultural livelihood, tourism, health and migration. | [31,36,41,42,47,49,53] |
| Assessment | Number of studies addressed only one of the assessments | Percentage | Number of studies addressed both assessments | Percentage | Total Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vulnerability to climate-induced hazards | 12 | 30% | 2 | 5% | 35% |
| Projected climate-induced hazards | 11 | 27.50% | 2 | 5% | 32.50% |
| Climate-induced Hazards/Impacts | Adaptation Responses | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Water scarcity, coral reef bleaching, changes in precipitation, flooding, and changes in beach structure | Construction of a mega dam and coast zone management through mangrove forest and coral restoration | [31] |
| Variability in rainfall patterns and amount, increased incidences of drought, saltwater intrusion | Growing of drought tolerant crops, increased frequency of fishing, cultivation of wetlands and keeping small stocks | [30] |
| Sea- level rise | Non-structural adaptation measures such as community-based adaptation and ecosystem-based adaptation | [24,45] |
| Cyclones, flooding, sea-level rise, storm surge, salinity intrusion and riverbank and land erosion | System-wide, restructuring, path-shifting and innovative transformational adaptations. Constructions of embankments and mangrove plantation. | [29,48] |
| Impacts on watershed systems | Integration of non-structural and structural best management practices | [39] |
| Sea-level rise, nuisance flooding, hurricanes, cyclones and typhoons, wave action | Do nothing Beach nourishment or adding sand to beaches Preventive actions through soft or hard solutions Managed or unmanaged retreat or realignment• Regulatory and restriction options on new development |
[11] |
| Flood risks | Raising the plinth height in the built environment; building of mobile beach bars and warnings using the help of information technology | [37,44] |
| Impacts on coastal fishery | Passive adaptations such as harvesting early and reinforcing ponds and equipment. Proactive adaptations, including monitoring the weather daily, changing to aquatic species with better tolerance and investing in modern technology | [36] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).