Submitted:
01 October 2023
Posted:
02 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Organic versus Conventional Food
3. Impact on Human Health
4. Epidemiological Findings Related to Human Health
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsu, S.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, T.T. An Analysis of Purchase Intentions toward Organic Food on Health Consciousness and Food Safety with/under Structural Equation Modeling. Br. Food J. 2016, 118, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneret, L.; Mitchell, M.; Seufert, V.; Aviron, S.; Djoudi, E.A.; Pétillon, J.; Plantegenest, M.; Thiéry, D.; Rusch, A. Evidence That Organic Farming Promotes Pest Control. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, T.; Pimentel, D.; Paoletti, M.G. Environmental Impact of Different Agricultural Management Practices: Conventional vs. Organic Agriculture. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2011, 30, 95–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantsæter, A.L.; Ydersbond, T.A.; Hoppin, J.A.; Haugen, M.; Meltzer, H.M. Organic Food in the Diet: Exposure and Health Implications. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2017, 38, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
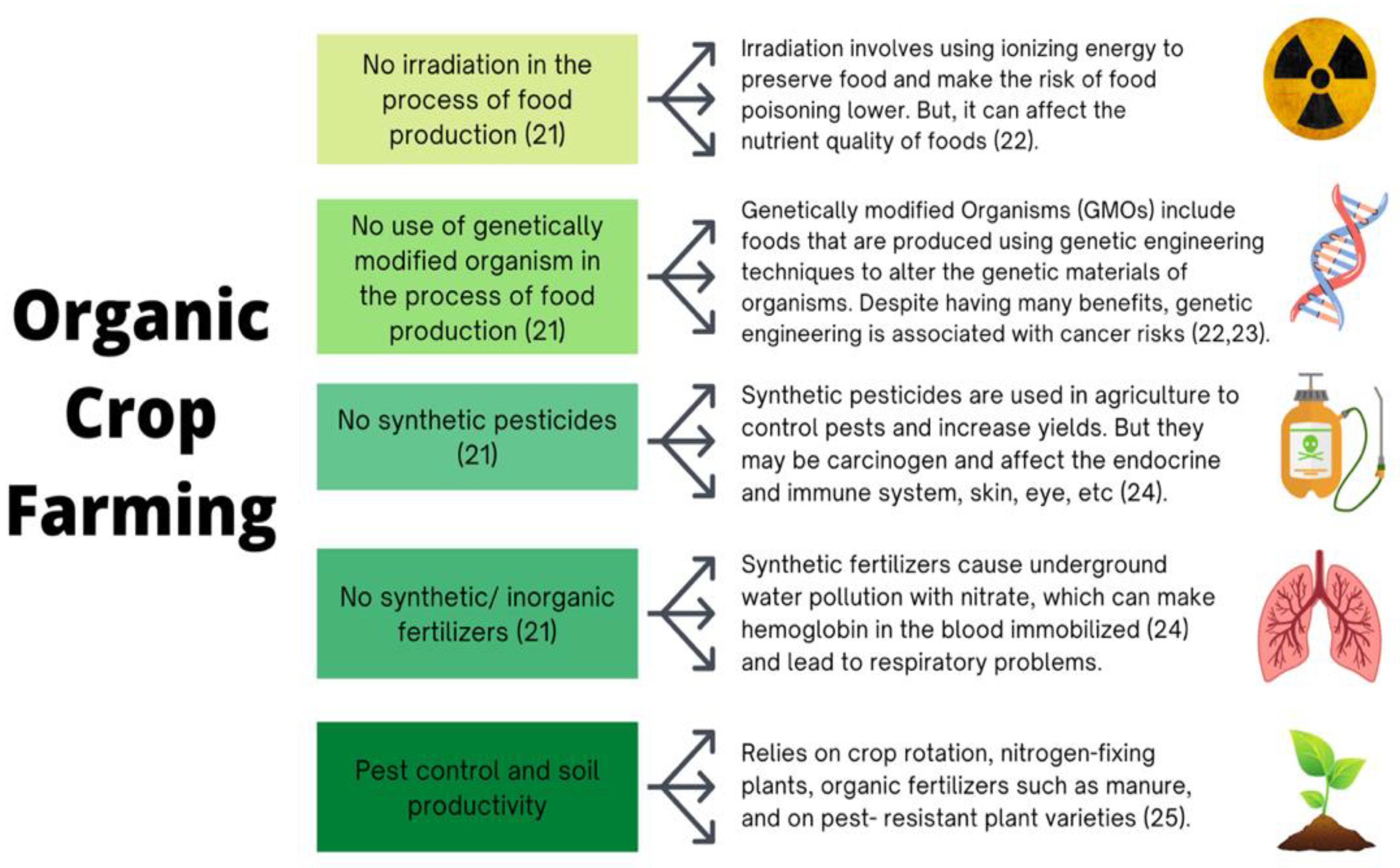
- Migliorini, P.; Wezel, A. Converging and Diverging Principles and Practices of Organic Agriculture Regulations and Agroecology. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado-Barroso, S.; Tresserra-Rimbau, A.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Organic Food and the Impact on Human Health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, K.; Mølgaard, J.P. Organic Agriculture: Does It Enhance or Reduce the Nutritional Value of Plant Foods? : Nutritional Value of Organic Plants. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woese, K.; Lange, D.; Boess, C.; Bögl, K.W. A Comparison of Organically and Conventionally Grown Foods— Results of a Review of the Relevant Literature. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1997, 74, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonaro, M.; Mattera, M.; Nicoli, S.; Bergamo, P.; Cappelloni, M. Modulation of Antioxidant Compounds in Organic vs Conventional Fruit (Peach, Prunus Persica L., and Pear, Pyrus Communis L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5458–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampieri, F.; Mazzoni, L.; Cianciosi, D.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Regolo, L.; Sánchez-González, C.; Capocasa, F.; Xiao, J.; Mezzetti, B.; Battino, M. Organic vs Conventional Plant-Based Foods: A Review. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzaoui Essoussi, L.; Zahaf, M. Exploring the Decision-making Process of Canadian Organic Food Consumers: Motivations and Trust Issues. Qual. Mark. Res. Int. J. 2009, 12, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boobalan, K.; Nachimuthu, G.S. Organic Consumerism: A Comparison between India and the USA. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2020, 53, 101988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Załęcka, A.; Bügel, S.; Paoletti, F.; Kahl, J.; Bonanno, A.; Dostalova, A.; Rahmann, G. The Influence of Organic Production on Food Quality - Research Findings, Gaps and Future Challenges: Influence of Organic Production on Food Quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 2600–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, A. Consumer Purchasing Process of Organic Food Product: An Empirical Analysis. J. Manag. Syst.-Qual. Access Success QAS 2020, 21, 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Suciu, N.A.; Ferrari, F.; Trevisan, M. Organic and Conventional Food: Comparison and Future Research. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 84, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriwy, P.; Mecking, R.-A. Health and Environmental Consciousness, Costs of Behaviour and the Purchase of Organic Food: Purchase of Organic Food. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2012, 36, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibowski, P. Organic Food and Health. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2020, 71, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tscharntke, T.; Grass, I.; Wanger, T.C.; Westphal, C.; Batáry, P. Beyond Organic Farming – Harnessing Biodiversity-Friendly Landscapes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2021, 36, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Foodomics: A New Tool to Differentiate between Organic and Conventional Foods: General. ELECTROPHORESIS 2016, 37, 1784–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, N.; Marquès, M.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J.L. Occurrence of Environmental Pollutants in Foodstuffs: A Review of Organic vs. Conventional Food. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith-Spangler, C.; Brandeau, M.L.; Hunter, G.E.; Bavinger, J.C.; Pearson, M.; Eschbach, P.J.; Sundaram, V.; Liu, H.; Schirmer, P.; Stave, C.; et al. Are Organic Foods Safer or Healthier Than Conventional Alternatives? : A Systematic Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 157, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hug, K. Genetically Modified Organisms: Do the Benefits Outweigh the Risks? Medicina (Mex.) 2008, 44, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrama, M.; de Haan, J.J.; Kroonen, M.; Verstegen, H.; Van der Putten, W.H. Crop Yield Gap and Stability in Organic and Conventional Farming Systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 256, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.M.; Teixeira, P. Organic versus Conventional Food: A Comparison Regarding Food Safety. Food Rev. Int. 2016, 33, 424–446, doiorg/101080/8755912920161196490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, G.; Koutros, S.; Hofmann, J.N.; Sandler, D.P.; Lubin, J.H.; Lynch, C.F.; Lerro, C.C.; De Roos, A.J.; Parks, C.G.; Alavanja, M.C.; et al. Glyphosate Use and Cancer Incidence in the Agricultural Health Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matich, E.K.; Laryea, J.A.; Seely, K.A.; Stahr, S.; Su, L.J.; Hsu, P.-C. Association between Pesticide Exposure and Colorectal Cancer Risk and Incidence: A Systematic Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 219, 112327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatcher, J.M.; Delea, K.C.; Richardson, J.R.; Pennell, K.D.; Miller, G.W. Disruption of Dopamine Transport by DDT and Its Metabolites. Neurotoxicology 2008, 29, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lairon, D. Nutritional Quality and Safety of Organic Food. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crinnion, W.J. Organic Foods Contain Higher Levels of Certain Nutrients, Lower Levels of Pesticides, and May Provide Health Benefits for the Consumer. Altern. Med. Rev. J. Clin. Ther. 2010, 15, 4–12. [Google Scholar]
- Rembiałkowska, E. Quality of Plant Products from Organic Agriculture. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 2757–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, V. Nutritional Quality of Organic versus Conventional Fruits, Vegetables, and Grains. J. Altern. Complement. Med. N. Y. N 2001, 7, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, K.; Leifert, C.; Sanderson, R.; Seal, C.J. Agroecosystem Management and Nutritional Quality of Plant Foods: The Case of Organic Fruits and Vegetables. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2011, 30, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafar, A. Nitrogen Fertilizers and the Amount of Vitamins in Plants: A Review. J. Plant Nutr. 1993, 16, 2479–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Guo, L.; Jiang, G.; Song, Y.; Muminov, M.A. Advances of Organic Products over Conventional Productions with Respect to Nutritional Quality and Food Security. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barański, M.; Rempelos, L.; Iversen, P.O.; Leifert, C. Effects of Organic Food Consumption on Human Health; the Jury Is Still Out! Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1287333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, G.J.; Graham, A.B.; Lawrence, J.R.; Wiles, D.; Paterson, J.R. Salicylic Acid in Soups Prepared from Organically and Non-Organically Grown Vegetables. Eur. J. Nutr. 2001, 40, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, J.R.; Lawrence, J.R. Salicylic Acid: A Link between Aspirin, Diet and the Prevention of Colorectal Cancer. QJM Mon. J. Assoc. Physicians 2001, 94, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mie, A.; Andersen, H.R.; Gunnarsson, S.; Kahl, J.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Rembiałkowska, E.; Quaglio, G.; Grandjean, P. Human Health Implications of Organic Food and Organic Agriculture: A Comprehensive Review. Environ. Health, 2017, 16, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Héroux, M.-È.; Adélaïde, L.; Allès, B.; Andrianasolo, R.M.; Andreeva, V.A.; Assmann, K.E.; Balti, E.V.; Baudry, J.; Bénard, C.; Bertin, M. Key Findings of the French Bionutrinet Project on Organic Food-based Diets: Description, Determinants, and Relationships to Health and the Environment. 2022; 13, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ouyang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, G.; Bao, W.; Hu, F.B. Fruit and Vegetable Consumption and Mortality from All Causes, Cardiovascular Disease, and Cancer: Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. BMJ 2014, 349, g4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesse-Guyot, E.; Péneau, S.; Méjean, C.; Edelenyi, F.S. de; Galan, P.; Hercberg, S.; Lairon, D. Profiles of Organic Food Consumers in a Large Sample of French Adults: Results from the Nutrinet-Santé Cohort Study. PLOS ONE, 2013, 8, e76998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abete, I.; Romaguera, D.; Vieira, A.R.; Munain, A.L. de; Norat, T. Association between Total, Processed, Red and White Meat Consumption and All-Cause, CVD and IHD Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Hou, L.; Chen, W.; Chen, P.; Lei, C.; Wei, Q.; Tan, W.; Zheng, S. Associations of Dietary Patterns with the Risk of All-Cause, CVD and Stroke Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, J.; Pointereau, P.; Seconda, L.; Vidal, R.; Taupier-Letage, B.; Langevin, B.; Allès, B.; Galan, P.; Hercberg, S.; Amiot, M.-J.; et al. Improvement of Diet Sustainability with Increased Level of Organic Food in the Diet: Findings from the BioNutriNet Cohort. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1173–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guéguen, L.; Pascal, G. Organic Foods. In Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier, 2022; p. B978012821848800158X. ISBN 978-0-08-100596-5.
- Vigar, V.; Myers, S.; Oliver, C.; Arellano, J.; Robinson, S.; Leifert, C. A Systematic Review of Organic Versus Conventional Food Consumption: Is There a Measurable Benefit on Human Health? Nutrients 2019, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisinger-Watzl, M.; Wittig, F.; Heuer, T.; Hoffmann, I. Customers Purchasing Organic Food - Do They Live Healthier? Eur. J. Nutr. Food Saf. 2015, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC Defining Adult Overweight and Obesity Available online:. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/adult/defining.html (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- Obesity and Overweight Available online:. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- Kesse-Guyot, E.; Baudry, J.; Assmann, K.E.; Galan, P.; Hercberg, S.; Lairon, D. Prospective Association between Consumption Frequency of Organic Food and Body Weight Change, Risk of Overweight or Obesity: Results from the NutriNet-Santé Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cueto, F.J.A.; Verbeke, W.; de Barcellos, M.D.; Kehagia, O.; Chryssochoidis, G.; Scholderer, J.; Grunert, K.G. Food-Related Lifestyles and Their Association to Obesity in Five European Countries. Appetite 2010, 54, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, C.J.; Goncalves, A.; Ehrminger, M.; Valliant, R. Association of Organic Food Consumption with Obesity in a Nationally Representative Sample. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-M. (“Mark”); O’Brien, K.; Sandler, D. Association Between Organic Food Consumption and Risk of Obesity in Women. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2020, 4, 1667–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.-W.; Li, J.; Pang, G.-F.; Ren, F.; Fang, B. Effects of Diethyl Phosphate, a Non-specific Metabolite of Organophosphorus Pesticides, on Serum Lipid, Hormones, Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota. 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Clemente, L.; Hernández-Álvarez, J.Á.; Rayo-Mares, D.; González-Avila, M.; García-García, E. Organic Food in the Diet: Exposure and Health Implications. 2017, 38, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Rembialkowska, E.; Średnicka-Tober, D.; Bügel, S.; Vijver, L. Organic food and impact on human health: Assessing the status quo and prospects of research. NJAS-Wagen. J. Life. Sc. 2011, 58, 3–4,103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, K.C.; Konstantinou, C.; Andrianou, X.D.; Charisiadis, P.; Kyriacou, A.; Gribble, M.O.; Costas, A.C. A cluster-randomized crossover trial of organic diet impact on biomarkers of exposure to pesticides and biomarkers of oxidative stress/inflammation in primary school children. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curl, C.L.; Porter, J.; Penwell, I.; Phinney, R; Ospina, M; Calafat, A.M. Effect of a 24-week randomized trial of an organic produce intervention on pyrethroid and organophosphate pesticide exposure among pregnant women. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 104957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões-Wüst, A.P.; Moltó-Puigmartí, C.; Jansen, E.H.; van Dongen, M.C.; Dagnelie, P.C.; Thijs, C. Organic Food Consumption during Pregnancy and Its Association with Health-Related Characteristics: The KOALA Birth Cohort Study. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 2145–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brants æter, A.L.; Torjusen, H.; Meltzer, H.M.; Papadopoulou, E.; Hoppin, J.A.; Alexander, J.; Lieblein, G.; Roos, G.; Holten, J.M.; Swartz, J.; et al. Organic Food Consumption during Pregnancy and Hypospadias and Cryptorchidism at Birth: The Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study (MoBa). Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y. H.; Williams, P. L.; Gillman, M. W.; Gaskins, A. J.; Mínguez-Alarcón, L.; Souter, I.; Toth, T. L.; Ford, J. B.; Hauser, R.; Chavarro, J. E.; et al. Association Between Pesticide Residue Intake From Consumption of Fruits and Vegetables and Pregnancy Outcomes Among Women Undergoing Infertility Treatment With Assisted Reproductive Technology. JAMA internal medicine, 2018, 178, 17–26, doiorg/101001/jamainternmed20175038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torjusen, H.; Brantsaeter, A.L.; Haugen, M.; Alexander, J.; Bakketeig, L.S.; Lieblein, G.; Stigum, H.; Naes, T.; Swartz, J.; Holmboe-Ottesen, G.; et al. Reduced Risk of Pre-Eclampsia with Organic Vegetable Consumption: Results from the Prospective Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e006143–e006143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.L.; Whitley, G.S.; Cartwright, J.E. Pre-Eclampsia: Fitting Together the Placental, Immune and Cardiovascular Pieces. J. Pathol. 2010, 221, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, K.E.; Balkwill, A.; Spencer, E.A.; Roddam, A.W.; Reeves, G.K.; Green, J.; Key, T.J.; Beral, V.; Pirie, K.; The Million Women Study Collaborators. Organic Food Consumption and the Incidence of Cancer in a Large Prospective Study of Women in the United Kingdom. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2321–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, J.; Assmann, K.E.; Touvier, M.; Allès, B.; Seconda, L.; Latino-Martel, P.; Ezzedine, K.; Galan, P.; Hercberg, S.; Lairon, D.; et al. Association of Frequency of Organic Food Consumption With Cancer Risk: Findings From the NutriNet-Santé Prospective Cohort Study. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrón, T.; Requena, M.; Hernández, A.F.; Alarcón, R. Environmental Exposure to Pesticides and Cancer Risk in Multiple Human Organ Systems. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 230, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dich, J.; Zahm, S.H.; Hanberg, A.; Adami, H.O. Pesticides and Cancer. Cancer Causes Control CCC 1997, 8, 420–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Component | Mean % difference | Range (%) | Number of studies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | +28.7 | −38 to +135.5 | 21 |
| Phenolic compounds | +119.3 | −56.6 to +734.2 | 15 |
| Iron | +21.1 | −73 to +240 | 16 |
| Magnesium | +29.3 | −35 to +1206 | 17 |
| Phosphorus | +13.6 | −44 to +240 | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).