Submitted:
07 October 2023
Posted:
07 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
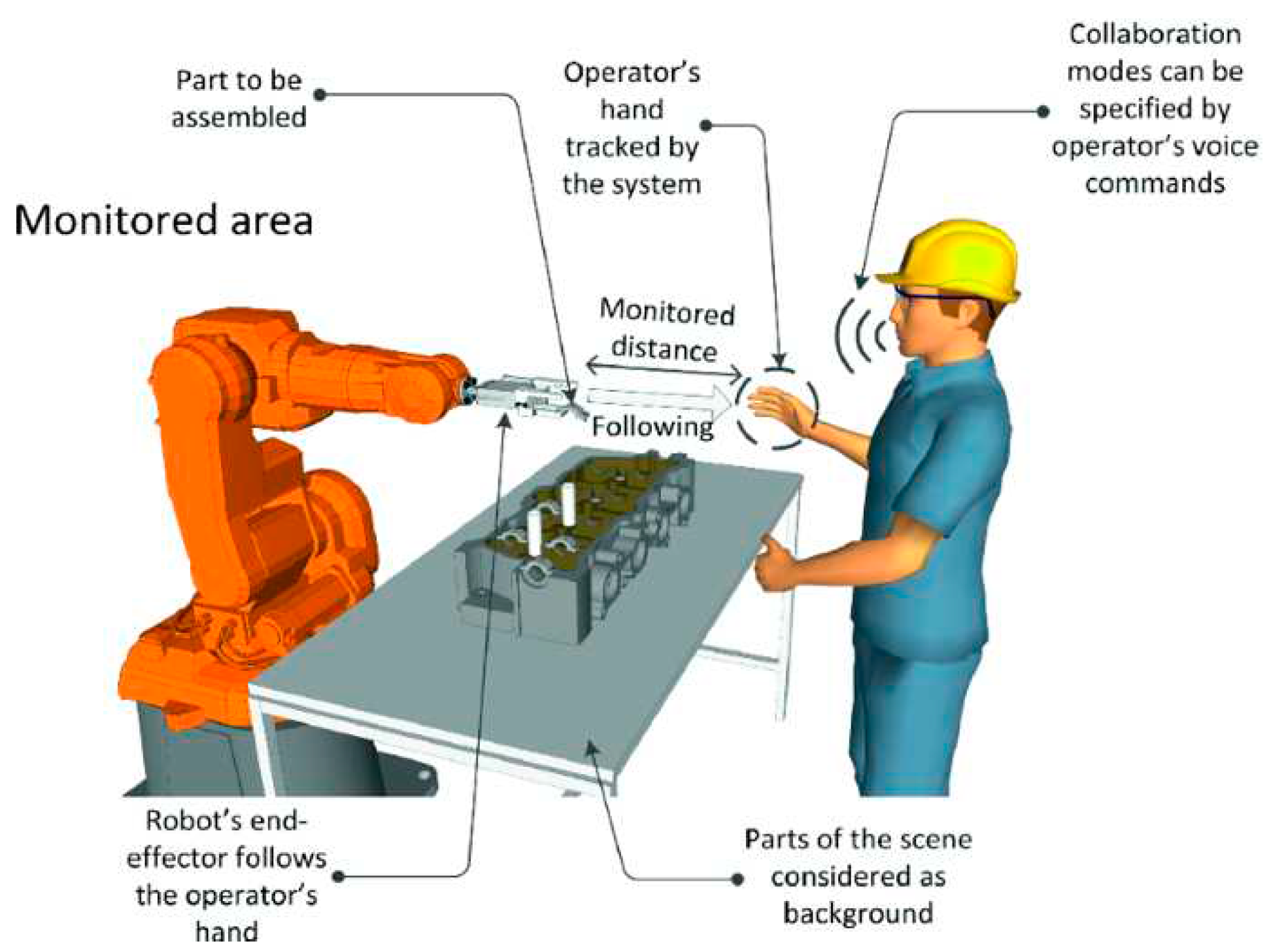
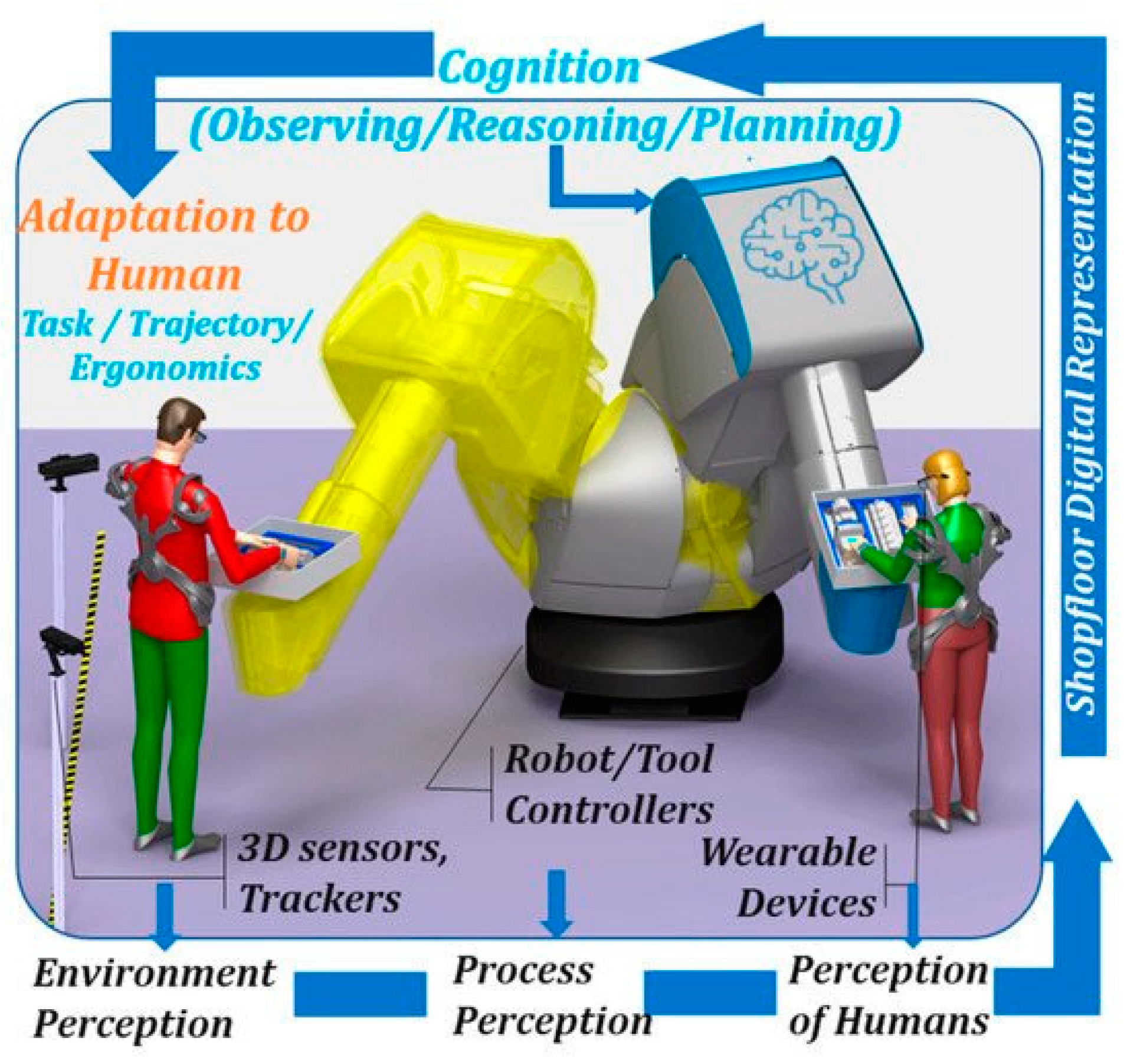
2. Review
2.1. Methodologies
2.1.1. Human-Robot Collaborative Method
2.1.2. Task Allocation
2.1.3. Reinforcement Learning
2.1.4. CPS-based Robotic Assembly Sequence Planning Approach
2.1.5. HRC Assembly using Artificial Intelligence and Wearable Devices
2.1.6. Programming-Free Approaches for HRC Assembly Tasks
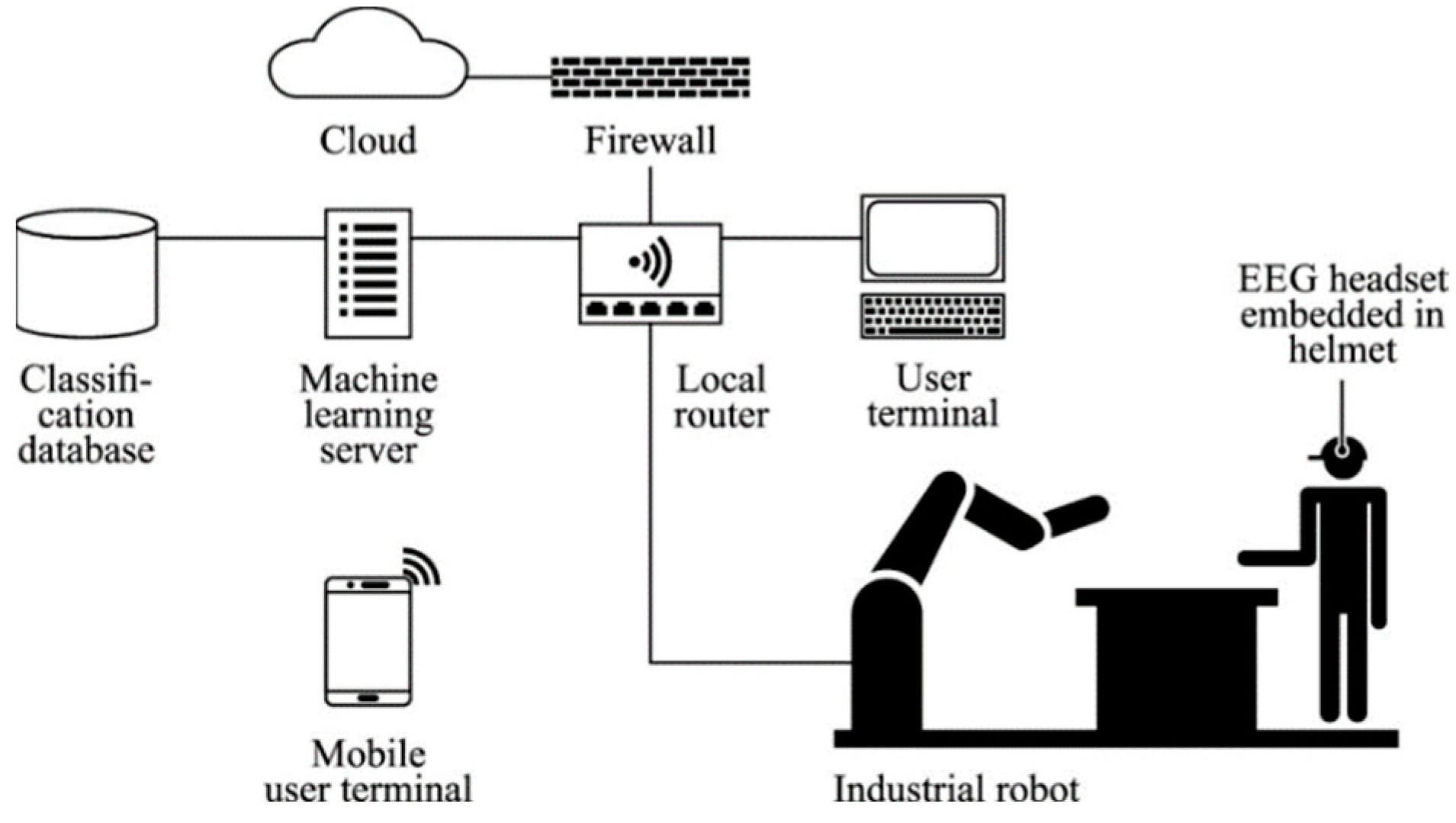
2.1.7. Intelligent Assembly enabled by Brain EEG
2.1.8. Human-Robot Collaboration for Disassembly (HRCD)
2.1.9. Human Activity Pattern Prediction for HRC Assembly Tasks
2.1.10. Intuitive and Robust Multimodal Robot Control
2.2. Experiments
3. Future Trends
4. Conclusion
References
- Xu, W., et al., Disassembly sequence planning using discrete Bees algorithm for human-robot collaboration in remanufacturing. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2020. 62: p. 101860. [CrossRef]
- Mateus, J.E.C., et al., Method for transition from manual assembly to human-robot collaborative assembly. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2018. 51(11): p. 405-410. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R., et al., A reinforcement learning method for human-robot collaboration in assembly tasks. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2022. 73: p. 102227. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., et al. Overview of human-robot collaboration in manufacturing. in Proceedings of 5th international conference on the industry 4.0 model for advanced manufacturing. 2020. Springer.
- Thiruvady, D., A. Nazari, and A. Elmi. An Ant Colony Optimisation Based Heuristic for Mixed-model Assembly Line Balancing with Setups. in 2020 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). 2020. IEEE.
- Gualtieri, L., et al., Safety, ergonomics and efficiency in human-robot collaborative assembly: design guidelines and requirements. Procedia CIRP, 2020. 91: p. 367-372. [CrossRef]
- Li, K., et al., Sequence planning considering human fatigue for human-robot collaboration in disassembly. Procedia CIRP, 2019. 83: p. 95-104. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.V., et al., Human–robot collaborative assembly in cyber-physical production: Classification framework and implementation. CIRP annals, 2017. 66(1): p. 5-8. [CrossRef]
- Yu, T., J. Huang, and Q. Chang, Mastering the working sequence in human-robot collaborative assembly based on reinforcement learning. IEEE Access, 2020. 8: p. 163868-163877. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.M. and Y. Wang, Mutual trust-based subtask allocation for human–robot collaboration in flexible lightweight assembly in manufacturing. Mechatronics, 2018. 54: p. 94-109. [CrossRef]
- Zanchettin, A.M., et al., Prediction of human activity patterns for human–robot collaborative assembly tasks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018. 15(7): p. 3934-3942. [CrossRef]
- Yan, L., et al. Human-Robot Collaboration by Intention Recognition using Deep LSTM Neural Network. in 2019 IEEE 8th International Conference on Fluid Power and Mechatronics (FPM). 2019. IEEE.
- Chowdhury, H. and M.T. Islam. Multiple Charger with Adjustable Voltage Using Solar Panel. in International Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Renewable Energy 2015 (ICMERE2015). 2015. Chittagong University of Engineering and Technology.
- Nian, R., J. Liu, and B. Huang, A review on reinforcement learning: Introduction and applications in industrial process control. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2020. 139: p. 106886. [CrossRef]
- Papakostas, N., C. Constantinescu, and D. Mourtzis, Novel Industry 4.0 Technologies and Applications. 2020, Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute.
- Matheson, E., et al., Human–robot collaboration in manufacturing applications: a review. Robotics, 2019. 8(4): p. 100. [CrossRef]
- Dimitropoulos, N., G. Michalos, and S. Makris, An outlook on future hybrid assembly systems-the Sherlock approach. Procedia Cirp, 2021. 97: p. 441-446. [CrossRef]
- Dimitropoulos, N., et al., Seamless Human–Robot Collaborative Assembly Using Artificial Intelligence and Wearable Devices. Applied Sciences, 2021. 11(12): p. 5699. [CrossRef]
- Richardson, B.S., et al., The design of an additive manufactured dual arm manipulator system. Additive Manufacturing, 2018. 24: p. 467-478. [CrossRef]
- Omer, L., et al. Induction Initiated Curing of Additively Manufactured Thermoset Composites. in Solid Freeform Fabrication 2022: Proceedings of the 33rd Annual International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium – An Additive Manufacturing Conference. 2022.
- Whitney, D., et al., Comparing robot grasping teleoperation across desktop and virtual reality with ROS reality, in Robotics Research. 2020, Springer. p. 335-350.
- Michniewicz, J. and G. Reinhart, Cyber-Physical-Robotics–Modelling of modular robot cells for automated planning and execution of assembly tasks. Mechatronics, 2016. 34: p. 170-180. [CrossRef]
- Repta, D., et al. A cyber-physical systems approach to develop a generic enterprise architecture. in 2014 International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation (ICE). 2014. IEEE.
- Napoleone, A., M. Macchi, and A. Pozzetti, A review on the characteristics of cyber-physical systems for the future smart factories. Journal of manufacturing systems, 2020. 54: p. 305-335. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. and X. Xu, Resource virtualization: a core technology for developing cyber-physical production systems. Journal of manufacturing systems, 2018. 47: p. 128-140. [CrossRef]
- Michniewicz, J. and G. Reinhart, Cyber-physical robotics–automated analysis, programming and configuration of robot cells based on Cyber-Physical-Systems. Procedia Technology, 2014. 15: p. 566-575. [CrossRef]
- Ying, K.-C., et al., Cyber-physical assembly system-based optimization for robotic assembly sequence planning. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2021. 58: p. 452-466. [CrossRef]
- Gjeldum, N., et al., Collaborative robot task allocation on an assembly line using the decision support system. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2021: p. 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Akkaladevi, S.C., et al., Programming-free approaches for human–robot collaboration in assembly tasks, in Advanced Human-Robot Collaboration in Manufacturing. 2021, Springer. p. 283-317.
- Mohammed, A. and L. Wang, Intelligent human–robot assembly enabled by brain EEG, in Advanced Human-Robot Collaboration in Manufacturing. 2021, Springer. p. 351-371.
- Gualtieri, L., et al., An evaluation methodology for the conversion of manual assembly systems into human-robot collaborative workcells. Procedia Manufacturing, 2019. 38: p. 358-366. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. and L. Wang, Gesture recognition for human-robot collaboration: A review. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2018. 68: p. 355-367. [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, P., et al., Human-robot collaboration demonstrator combining speech recognition and haptic control. Procedia CIRP, 2017. 63: p. 396-401. [CrossRef]
- Mei, K., et al., Training more discriminative multi-class classifiers for hand detection. Pattern Recognition, 2015. 48(3): p. 785-797. [CrossRef]
- Xin, X., et al., Semi-supervised person re-identification using multi-view clustering. Pattern Recognition, 2019. 88: p. 285-297. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H., et al., Towards robust human-robot collaborative manufacturing: Multimodal fusion. IEEE Access, 2018. 6: p. 74762-74771. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. and L. Wang, An AR-based worker support system for human-robot collaboration. Procedia Manufacturing, 2017. 11: p. 22-30. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. and L. Wang, Human motion prediction for human-robot collaboration. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2017. 44: p. 287-294. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P., et al., Deep learning-based human motion recognition for predictive context-aware human-robot collaboration. CIRP annals, 2018. 67(1): p. 17-20. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J., et al., Recurrent neural network for motion trajectory prediction in human-robot collaborative assembly. CIRP annals, 2020. 69(1): p. 9-12. [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A. and L. Wang, Brainwaves driven human-robot collaborative assembly. CIRP annals, 2018. 67(1): p. 13-16. [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A. and L. Wang, Advanced Human-Robot Collaborative Assembly Using Electroencephalogram Signals of Human Brains. Procedia CIRP, 2020. 93: p. 1200-1205. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S., et al., Brain–machine interfacing-based teleoperation of multiple coordinated mobile robots. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016. 64(6): p. 5161-5170. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. and L. Wang, Collision-free human-robot collaboration based on context awareness. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2021. 67: p. 101997. [CrossRef]
- de Giorgio, A., M. Lundgren, and L. Wang, Procedural knowledge and function blocks for smart process planning. Procedia Manufacturing, 2020. 48: p. 1079-1087. [CrossRef]
- Nan, Z., et al., Learning to infer human attention in daily activities. Pattern Recognition, 2020. 103: p. 107314. [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, H., Semiconductor Manufacturing Process Improvement Using Data-Driven Methodologies, in Preprints. 2023, Preprints.
- Bilberg, A. and A.A. Malik, Digital twin driven human–robot collaborative assembly. CIRP Annals, 2019. 68(1): p. 499-502. [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.A. and A. Brem, Digital twins for collaborative robots: A case study in human-robot interaction. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2021. 68: p. 102092. [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.A. and A. Bilberg, Collaborative robots in assembly: A practical approach for tasks distribution. Procedia Cirp, 2019. 81: p. 665-670. [CrossRef]
- Chen, F., et al., An assembly strategy scheduling method for human and robot coordinated cell manufacturing. International Journal of Intelligent Computing and Cybernetics, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Tsarouchi, P., et al., On a human-robot collaboration in an assembly cell. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2017. 30(6): p. 580-589.
- Bänziger, T., A. Kunz, and K. Wegener, Optimizing human–robot task allocation using a simulation tool based on standardized work descriptions. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2020. 31(7): p. 1635-1648. [CrossRef]
- Dalle Mura, M. and G. Dini, Designing assembly lines with humans and collaborative robots: A genetic approach. CIRP Annals, 2019. 68(1): p. 1-4. [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S., et al., Dynamic multi-robot task allocation under uncertainty and temporal constraints. Autonomous Robots, 2021: p. 1-17.
- Arana-Arexolaleiba, N., et al., Transferring Human Manipulation Knowledge to Industrial Robots Using Reinforcement Learning. Procedia Manufacturing, 2019. 38: p. 1508-1515. [CrossRef]
- Akkaladevi, S.C., et al., Towards reinforcement based learning of an assembly process for human robot collaboration. Procedia Manufacturing, 2019. 38: p. 1491-1498. [CrossRef]
- Fan, L., et al. Surreal: Open-source reinforcement learning framework and robot manipulation benchmark. in Conference on Robot Learning. 2018. PMLR.
- Tung, A., et al. Learning multi-arm manipulation through collaborative teleoperation. in 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). 2021. IEEE.
- Oliff, H., et al., Reinforcement learning for facilitating human-robot-interaction in manufacturing. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2020. 56: p. 326-340. [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, H. and B. Asiabanpour, A Smart Circular Economy for Integrated Organic Hydroponic-Aquaponic Farming. 2023, Texas State University.
- Chowdhury, H., Circular Economy Integration in Additive Manufacturing, in Preprints. 2023, Preprints.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




