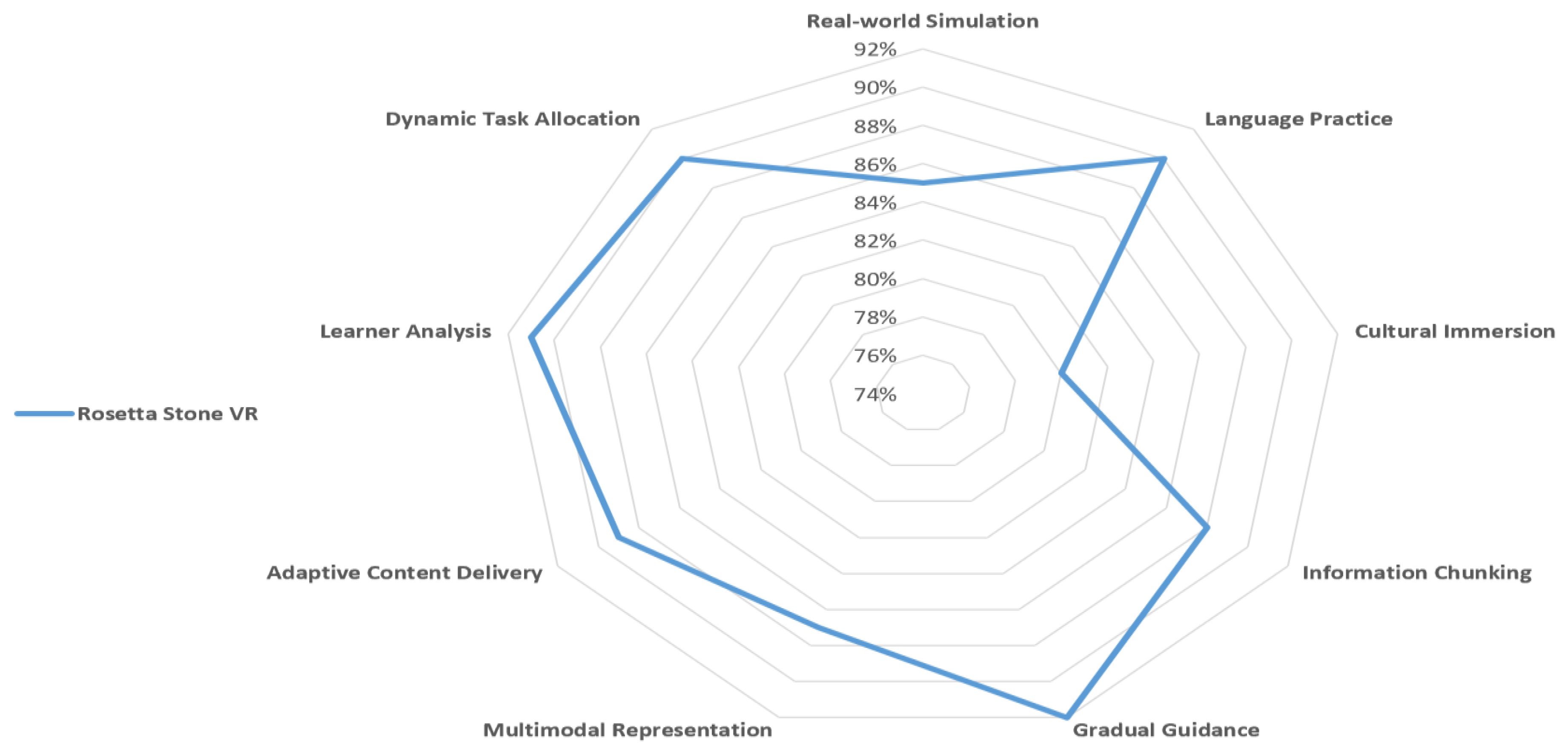
Incorporating Virtual Reality (VR) within the pedagogical tapestry, predominantly within the precincts of foreign language pedagogy, demands a meticulous methodology to unlock its latent prowess. Emerging from this exigency, the VR-CCL (Virtual Reality - Constructivism and Cognitive Load) paradigm offers an intricate tapestry, amalgamating the tenets of constructivist pedagogical axioms and the nuances of cognitive load theory cocooned within the VR milieu.
The architecture of this paradigm has been meticulously sculpted to navigate the labyrinthine intricacies and boundless vistas birthed by VR in the language acquisition odyssey. Harnessing the ethereal and symbiotic faculties of VR, the VR-CCL paradigm aspires to sculpt a harmonized learning sanctum, resonating with the cognitive oscillations of learners and fostering profound educational epiphanies.
Subsequent discourses shall pierce the veil of the VR-CCL paradigm’s nucleus, shedding luminescence on how each facet augments language mastery within the VR cosmos. As we embark on an erudite voyage through interactive resonance, cognitive burden orchestration, and tailoring tactics, a lucid compass shall manifest, guiding pedagogues and visionaries toward seizing the zenith of VR’s capabilities in foreign language enlightenment.
4.1. Interactive Engagement (Based on Constructivist Learning Theory)
Interactive resonance forms the bedrock of the VR-CCL paradigm, gleaning insights from the pillars of constructivist educational philosophy. Constructivism advocates for learners’ active chiseling of wisdom through their dynamic interplay with surrounding stimuli. Thus, VR’s inherently interactive milieu emerges as a sublime canvas for hands-on enlightenment. Such dynamisms amplify their essence, furnishing genuine backdrops where aspirants can immerse, practice, and assimilate novel linguistic patterns and lexicons. Succeeding segments shall plumb the depths of diverse dimensions of interactive resonance within VR, accentuating the quintessence of learner-content dialogues, peer-to-peer exchanges, objective-driven endeavors, and the paramountcy of reflexive mechanisms in orchestrating an enriching odyssey of learning.
4.1.1. Learner-content interaction in VR
Virtual Reality (VR) has revolutionized the pedagogical panorama, especially linguistics. With its tomes and spoken discourses, the conventional learning alcove has been eclipsed by VR’s enveloping, tridimensional realms. In these vistas, the nexus between scholar and material is not merely amplified; it undergoes metamorphosis.
Envision an instance where an apprentice, endeavoring to master French, is virtually conveyed to a charming alley in Paris. Meandering through this milieu, every placard, carte du jour, and periodical becomes a conduit to immerse in the dialect. They can virtually handle artifacts, peruse annotations, or even solicit refreshments at a bistro, honing articulation and phraseology in synchrony. Such engagements bestow upon the educational voyage a profound contextuality. Lexemes transform from nebulous concepts to memorized into instrumental conduits for exploration, discourse, and discernment in a virtual cosmos echoing the tangible.
This profundity of engagement is augmented by the pan-sensory resonance that VR dispenses. An aspirant does not merely visualize the term “pomme” at a virtual produce stand; they can ‘grasp’ the apple, ‘eavesdrop’ on its accurate enunciation, and even ‘per-ceive’ its tactile essence via haptic reverberations. These pan-sensory encounters ascertain that the acquisition process extends beyond the intellect into tangible experiences.
The VR milieu is malleable. Should a student grapple with the specific lexicon, the setting can orchestrate additional episodes accentuating those terminologies, fortifying assimilation and prowess. In contrast, the milieu can intensify for seasoned scholars, ushering in intricate lexicon and sophisticated syntactical paradigms.
VR rejuvenates the bond between scholar and content, rendering it vibrant, modifiable, and profoundly immersive, ensuring that linguistic mastery evolves from a scholastic chore into a palpable, evocative expedition.
4.1.2. Learner-learner interaction in VR
The domain of Virtual Reality (VR) not only magnifies the scholar’s communion with content but also recalibrates the intricacies of inter-peer dialogues. Conventional linguistic acquisition frequently encompasses dyadic or collective engagements, wherein students’ discourse, dramatize or amalgamate efforts on assignments. VR elevates these dialogues to an unparalleled plateau of veracity and engrossment.
Within a VR ambit, acolytes can assume personas, facilitating interactions in ambiances reflecting tangible life tableau. For illustration, scholars assimilating Spanish might be transported to a virtual bazaar in Barcelona, haggling with contemporaries, brokering terms, and effectuating acquisitions—such dialogues obligate acolytes to wield the dialect in pragmatic, instantaneous circumstances, bolstering eloquence and assurance.
VR proffers a cosmopolitan dais. An understudy in Tokyo can effortlessly commune with a counterpart in Buenos Aires, surmounting spatial and ethnocultural chasms. This planetary discourse acquaints scholars with many vernaculars, tonalities, and idiomatic expressions, augmenting their linguistic arsenal and ethnocultural discernment.
The alacrity of reciprocation in VR stands as another boon. Articulatory aberrations or syntactical lapses can be promptly rectified by contemporaries, engendering a synergistic learning milieu. Beyond this, the VR interface can assimilate instantaneous trans-literation utilities and articulation manuals, aiding scholars amidst exchanges.
VR metamorphoses scholarly interchanges from mere dialogic drills into profoundly engrossing, genuine, and international exchanges, rendering linguistic assimilation a communal and culturally opulent pursuit.
4.1.3. Task and goal-oriented interaction in VR
Virtual Reality (VR) furnishes a singular conduit for mission-centric and objective-driven engagements, especially within linguistic acquisition. Contrasting conventional techniques, wherein assignments might be circumscribed to textual endeavors or rudimentary exchanges, VR proffers an engulfing milieu wherein scholars can plunge into verisimilar tableaux, necessitating lingual dexterity to fulfill determinate ends.
Visualize, for a moment, an undertaking within VR that mandates steering through a nonnative metropolis employing solely the focal dialect. Disciples could pinpoint a dis-tinct locale, requisitioning sustenance or deciphering a conundrum, all while articulating solely in the vernacular under scrutiny. These tableaux not merely assay their lingual faculties but also their prowess in harnessing them in tangible, quotidien predicaments.
The engulfing essence of VR ascertains those disciples remain wholly enmeshed in the designated assignment. External diversions wane, and the palpable immersion within the virtual realm augments the gravitas of the mission, rendering efficacious discourse paramount. The intensified involvement and authenticity render VR endeavors more resonant and indelible, culminating in superior consolidation and employment of linguistic paradigms.
VR’s inherent malleability sanctions assignments to be modulated in alignment with individual adeptness tiers. Neophytes might be embroiled in more elementary liaisons, such as procuring commodities from a mercantile, while seasoned learners could broker commercial pacts or orate discourses.
In its quintessence, mission-centric and objective-driven liaisons within VR proffer a vivacious, captivating, and adaptable modality for linguistic acquisition, melding theoretical cognizance with pragmatic deployment.
4.1.4. Feedback and assessment mechanisms in interaction
Feedback, an integral pillar of efficacious learning, assumes an augmented stature within the purview of VR linguistic tutelage. Feedback metamorphoses within this enveloping VR expanse, becoming instantaneous, situationally apt, and markedly interactive. Distancing from archaic paradigms, where Feedback could be temporally staggered or unduly broad, VR proffers punctual rectifications and mentorship, ameliorating the trajectory of comprehension.
Envision, for a moment, a disciple engrossed in a virtual tableau. Herein, auditory discernment apparatuses could identify lapses in articulation, furnishing immediate redressals. Optical indicators, perhaps through chromatic delineations, might spotlight syntactic blemishes or lexemic deviations, empowering learners to amend transgressions posthaste. Such brisk interventions buttress apt lingual practices and elevate the learner’s self-assuredness.
VR architectures can seamlessly incorporate mutable evaluation instruments. The matrix can modulate the intricacy of assignments, safeguarding those conundrums consistently strike the optimal balance of profundity. This fluid evaluative approach assures incessant ascension without inundating or marginalizing the aspirant.
In augmentation, post-engagement dissections can furnish granular examinations into a scholar’s virtuosities and facets necessitating refinement. By gauging parameters such as lexemic expansiveness, syntactic intricacy, and engagement fruition coefficients, pedagogues and scholars can discern explicit domains ripe for concerted cultivation.
The evaluative and Feedback apparatuses inherent to VR linguistic pedagogy are avantgarde, bequeathing punctual, mutable, and nuanced perceptions that conventional methodologies scarcely rival.
4.2. Cognitive Load Management (Based on Cognitive Load Theory)
Cognitive Load Theory (CLT) articulates that potent learning transpires when cognitive requisites levied upon a learner are meticulously balanced. Within the sphere of VR linguistic education, supervising this cognitive demand emerges as a linchpin. While VR’s immersive essence proffers opulent pedagogical encounters, it could simultaneously weave intricacies potentially inundating a learner’s cognitive bandwidth. This segment ventures into tactics and tenets drawn from CLT, aspiring to galvanize VR’s capabilities while maintaining a cognitive equilibrium propitious for efficacious language mastery.
4.2.1. Simplifying extraneous elements to reduce extraneous load
Virtual Reality (VR) proffers a sumptuous, engulfing milieu for linguistic education, yet this opulence can occasionally bear ambivalent facets. The multifaceted-ness and profundity of VR journeys can usher in superfluous cognitive impositions upon scholars, termed the extrinsic burden. This imposition, albeit not intrinsically augmenting the educational trajectory, can detract from it by depleting cognitive assets primed for linguistic comprehension and integration.
Discerning and attenuating these extrinsic components is crucial for apex linguistic edification in VR. Contemplate potential diversions: elaborate visual renderings, non-germane animations, or even ambient sonorities misaligned with pedagogical aims. Albeit accentuating VR’s verisimilitude, they might misdirect a scholar’s focus from the principal linguistic corpus. Distilling or extirpating such constituents ensures that a scholar’s cognitive prowess is undeviatingly channeled towards linguistic mastery.
Furthermore, the architectural ethos of VR linguistic platforms ought to venerate lucidity and pertinence. Every facet within the VR ambit should embody a palpable educational intent. Through assiduous content and design curations, pedagogues and VR artisans can craft an educative sphere that accentuates immersion’s merits while eschewing the snares of unwarranted cognitive exertion. Striking this equilibrium is quintessential for leveraging VR’s entirety in linguistic pedagogy, certifying scholars remain engrossed and fixated on their cardinal pursuit: conquering a novel tongue.
4.2.2. Enhancing essential elements to increase germane load
In a VR language learning setting, reducing distractions is paramount. However, it is just as vital to spotlight elements that directly aid in mastering the language, thereby bolstering the relevant cognitive load. The relevant cognitive load pertains to the mental energy expended on assimilating and processing new data, which translates to linguistic material in this scenario.
In a VR framework, this can be realized by underscoring pivotal linguistic components, terms, and cultural subtleties. For instance, lucid visual indicators or recurring motifs can assist learners in recognizing and retaining fresh terms. Likewise, engaging simulations that echo everyday situations can be crafted to emphasize distinct grammatical facets, ensuring learners grasp and utilize them in a realistic context.
Sound-based tools, such as distinct pronunciation aids or diverse dialects, can be merged to facilitate auditory comprehension and accent mastery. By delivering on-the-spot Feedback within these simulations, learners can promptly rectify errors, solidifying the accurate linguistic patterns.
It is also advantageous to weave cultural aspects into the VR landscape. By submerging learners in settings that faithfully represent a culture, they attain a more pro-found grasp of the societal backdrop of the language, rendering their educational voyage more comprehensive and resonant. Fundamentally, a learner’s mental capacity is adeptly channeled by enhancing these crucial components, refining the educational trajectory within the immersive VR domain.
4.2.3. Gradual guidance and task decomposition
In the immersive world of VR language education, there is a real risk of learners becoming daunted by the vastness and intricacy of fresh linguistic content. Addressing this necessitates the implementation of careful scaffolding and task segmentation.
In this context, scaffolding means progressively introducing linguistic elements in a methodical and tiered fashion. Rather than immediately plunging learners into intricate dialogues or sentences, starting with basic vocabulary and fundamental grammatical constructs is beneficial. As they gain confidence and skill, the depth of the content can gradually intensify, ensuring that while they are consistently pushed, they never feel swamped.
Task segmentation, conversely, is about dissecting broader, intricate activities into more digestible, smaller undertakings. For example, instead of thrusting learners into an elaborate VR conversation, they might initially practice isolated phrases and then progress to brief exchanges, culminating in extended dialogues. This progressive method lets learners cement their grasp on individual segments, fostering confidence and solidifying their understanding before venturing into more involved tasks.
By weaving these approaches into VR language education, a more streamlined and organized learning path is carved, diminishing cognitive strain and amplifying the overall efficiency of the educational journey.
4.2.4. Feedback and self-assessment in managing cognitive load
Within the immersive realm of VR language education, Feedback and self-evaluation are crucial, especially in balancing cognitive demands. Well-structured feedback mechanisms can significantly slash unnecessary cognitive strain by offering learners clear insights into their performance, highlighting improvement areas, and solidifying correct practices.
Instant Feedback in VR, powered by up-to-the-minute analytics and AI-guided evaluations, provides learners with an immediate perspective on their linguistic proficiencies and areas needing attention. This promptness ensures that mistakes are nipped in the bud, averting the solidification of wrong practices. For example, suppose a student recurrently mispronounces a particular term or misapplies a grammar rule. In that case, on-the-spot Feedback can steer them correctly, ensuring these missteps do not evolve into persistent habits.
Conversely, self-evaluation gives learners the reins, prompting them to introspect on their accomplishments and bolstering metacognitive capabilities. By intermittently scrutinizing their progress, learners can chart achievable objectives, recalibrate their approaches, and take charge of their educational voyage. In the VR milieu, tools such as interactive tests, immersive simulations, and scenario-driven exercises can be harnessed to boost this self-reflection, offering students a chance to measure their grasp in an engaging, lifelike framework.
By embedding Feedback and self-assessment mechanisms in VR language education platforms, cognitive load can be deftly managed, ensuring students stay focused, enthused, and on a clear path to language proficiency.
4.3. Personalization and Adaptivity (Based on Input Hypothesis Theory)
The Input Hypothesis Theory, articulated by Stephen Krashen, accentuates the quintessence of intelligible linguistic stimuli in language assimilation. This doctrine highlights the paramountcy of bespoke curriculum and fluid adaptiveness within the confines of VR-infused linguistic pedagogy. Considering the kaleidoscope of scholastic antecedents and learning arches individuals’ traverse, it becomes quintessential to proffer meticulously curated content resonating with their linguistic prowess and pedagogic inclinations. Armed with its engrossing and malleable faculties, VR emerges as the consummate dais to execute such individualized and pliable methodologies. This discourse seeks to elucidate the amalgamation of Input Hypothesis Theory tenets into the VR-CCL paradigm, aiming to amplify linguistic pedagogic ramifications.
4.3.1. Dynamic content adaptation in VR
Virtual Reality (VR) emerges as a paradigm-shifting medium for content dissemination, boasting the capability to metamorphose dynamically in alignment with individual learner archetypes. Given the spectrum of learner proficiencies, educational modalities, and inclinations, this malleability becomes profoundly indispensable in linguistic pedagogy. Drawing cues from the Input Hypothesis Theory, it becomes imperative to furnish learners with linguistic stimuli marginally transcending their present proficiency, colloquially delineated as ‘i+1’, to ascertain pinnacle educational outcomes.
This dynamic content transmogrification manifests in multifarious avenues within the VR linguistic and educational sphere. Instantaneous evaluations can discern a learner’s linguistic stature, calibrating the intricacy of subsequent linguistic challenges. Neophytes may grapple with rudimentary lexicon and syntactical frameworks, while their seasoned counterparts delve into labyrinthine grammatical edifices and intricate lexemes.
VR can architect a lifelike tableau wherein learners liaise with ethereal entities. These virtual denizens can recalibrate their linguistic delivery in tempo, lexicon breadth, and intricacy, ensuring perpetually decipherable communication.
Feedback apparatus within VR can illuminate discrepancies, furnishing rectifications, thereby enriching the educational odyssey’s customization. As an exemplar, should a learner recurrently flounder with verbs of yesteryears, the VR mechanism can proliferate tableau accentuating that specific grammatical facet.
The dynamism of content transfiguration in VR, anchored in the tenets of the Input Hypothesis Theory, guarantees that learners perpetually find themselves on the precipice of challenge without tumbling into the abyss of bewilderment, laying the foundation for efficacious linguistic mastery.
4.3.2. Learner modeling and learning path recommendation
Deciphering the enigma of a learner stands paramount in any pedagogical arena, and VR linguistic instruction echoes this sentiment. Learner modeling delves into crafting a nuanced silhouette of a learner, extrapolating from their engagements, prowess, proclivities, and critiques within the VR tableau. This crafted archetype is the cornerstone, facilitating a bespoke educational journey attuned to the individual’s requisites, fortifying enthrallment and assimilation.
VR’s forte lies in its prowess to amass a kaleidoscope of data fragments during a learner’s symbiosis with the system. From the durations lavished on distinct undertakings, the momentary vacillations prior to responses, to the intricate tapestry of missteps woven, this amassed data is meticulously dissected to curate a holistic learner schematic. In its grandeur, this blueprint can prognosticate potential stumbling blocks, the learner’s favored pedagogical modality, and their intrinsic fervor.
The VR infrastructure can usher the learner down a tailored educational boulevard. An individual showcasing prowess in lexicon yet grappling with syntactical weaving might find themselves amidst scenarios accentuating grammatical nuances. In juxtaposition, an auditory aficionado might encounter an augmented array of listening endeavors within the VR milieu.
As the learner’s odyssey unfolds, this model undergoes perpetual refinement, ensuring perpetually apt recommendations. This fluid recalibration stands vital, particularly within linguistic pedagogy, where the path of ascension often eschews linearity, leading learners to grapple with unforeseen quandaries.
Learner modeling fused with bespoke educational pathway suggestions within VR proffers an individualized sojourn. This ensures that each learner’s unique characteristics and preferences are skillfully addressed, enhancing the chances of achieving successful language proficiency.
4.3.3. Personalized design of tasks and activities
At the heart of proficient language acquisition is the substance and the mode of its conveyance. Within the VR domain, the horizon for customization stretches immeasurably, allowing educators to craft endeavors that echo the learner’s ethos. This individualized touch profoundly amplifies the pedagogical voyage, infusing it with vibrancy and pertinence.
Visualize a duo of learners: one harbors a fervent passion for gastronomy, whereas the other is an insatiable wanderlust. Within a bespoke VR linguistic milieu, the gastronome might find themselves ensconced in a Parisian virtual culinary sanctum, acquiring French whilst orchestrating an iconic Gallic delicacy. On the other hand, the globe-trotter might traverse the labyrinthine byways of Tokyo, soliciting directions while imbibing nuances of Japanese.
Such tailored experiences spring from an amalgam of discerning learner profiles and avantgarde computational blueprints. By delving into a learner’s inclinations, avocations, and prior sojourns, VR paradigms can conjure milieus that transcend pedagogical bounds, resonating on a profoundly intimate plane. This stratagem ensures learners metamorphose from mere sponges of knowledge to zealous contributors in their educational odyssey.
The intricacy of these undertakings can seamlessly oscillate on the learner’s linguistic prowess. Neophytes might immerse in rudimentary endeavors like object delineation, while seasoned linguists could grapple with intricate dialogues or cerebral conundrums in the desired vernacular.
In its quintessence, the meticulous curation of endeavors within VR linguistic instruction guarantees that the substance resonates with the learner’s aptitude and their fervors and aspirations, nurturing an indomitable allegiance to the edifying voyage.
4.3.4. Personalized assessment and feedback
Evaluative processes are the linchpin of efficacious learning, granting pedagogues and pupils a lucid window into advancement and domains necessitating refinement. However, conventional evaluative methodologies frequently espouse a homogenized blueprint, potentially sidelining distinct pupils’ multifaceted requisites and prowess. Within the sphere of VR linguistic pedagogy lies a golden prospect to metamorphose this schema via individualized appraisals and responsive feedback channels.
Evaluation can be effortlessly interwoven into the educational tapestry within the VR ambit. Visualize post a simulated tête-à-tête with a vernacular conversationalist, the system promptly dissecting a pupil’s articulation, syntactical choices, and lexicon deployment. This expeditious critique, sculpted around the pupil’s execution, can elucidate commendable facets and spotlight zones beckoning deeper exploration.
VR’s fluidic canvas beckons malleable appraisals. Hinging on a pupil’s prowess in a delineated segment, ensuing examinations can modulate in intricacy, vouching that they perpetually encounter calibrated challenges. This fluidity does not merely sustain pupil immersion but also vouches those evaluations genuinely mirror their acumen.
Another boon tethered to VR-oriented bespoke critiques is its proclivity for immersive rectification. Rather than a mere quantitative grade or inscribed critique, pupils can be ushered into lifelike tableaux where errors can be addressed and amended. Envision a pupil grappling with orchestrating a meal order in Castilian nuances; they could find themselves ensconced in a virtual Iberian bistro, revisiting the dialogue till it is impeccably etched.
Bespoke evaluations and critiques within VR linguistic pedagogy unfurl a more granular, dynamic, and experiential avenue for gauging prowess. By resonating with individual requisites and proffering instantaneous, milieu-rich critiques, VR harbors the potential to elevate the evaluative journey, rendering it profoundly poignant and impactful for the linguistic voyager.