Submitted:
27 September 2023
Posted:
28 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
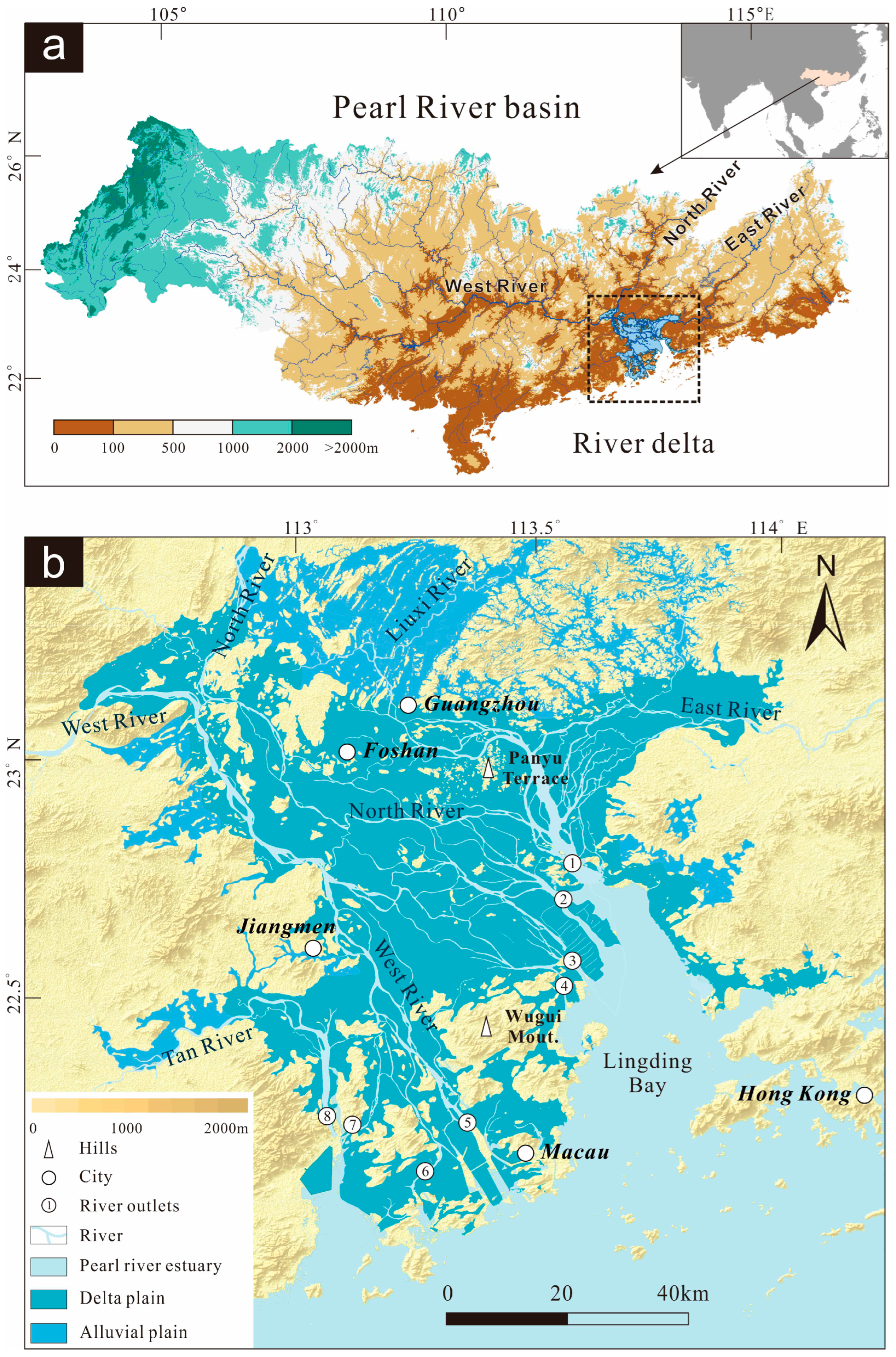
2. Regional setting
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Borehole data
3.2. Analysis of sediment cores and stratigraphic synthesis
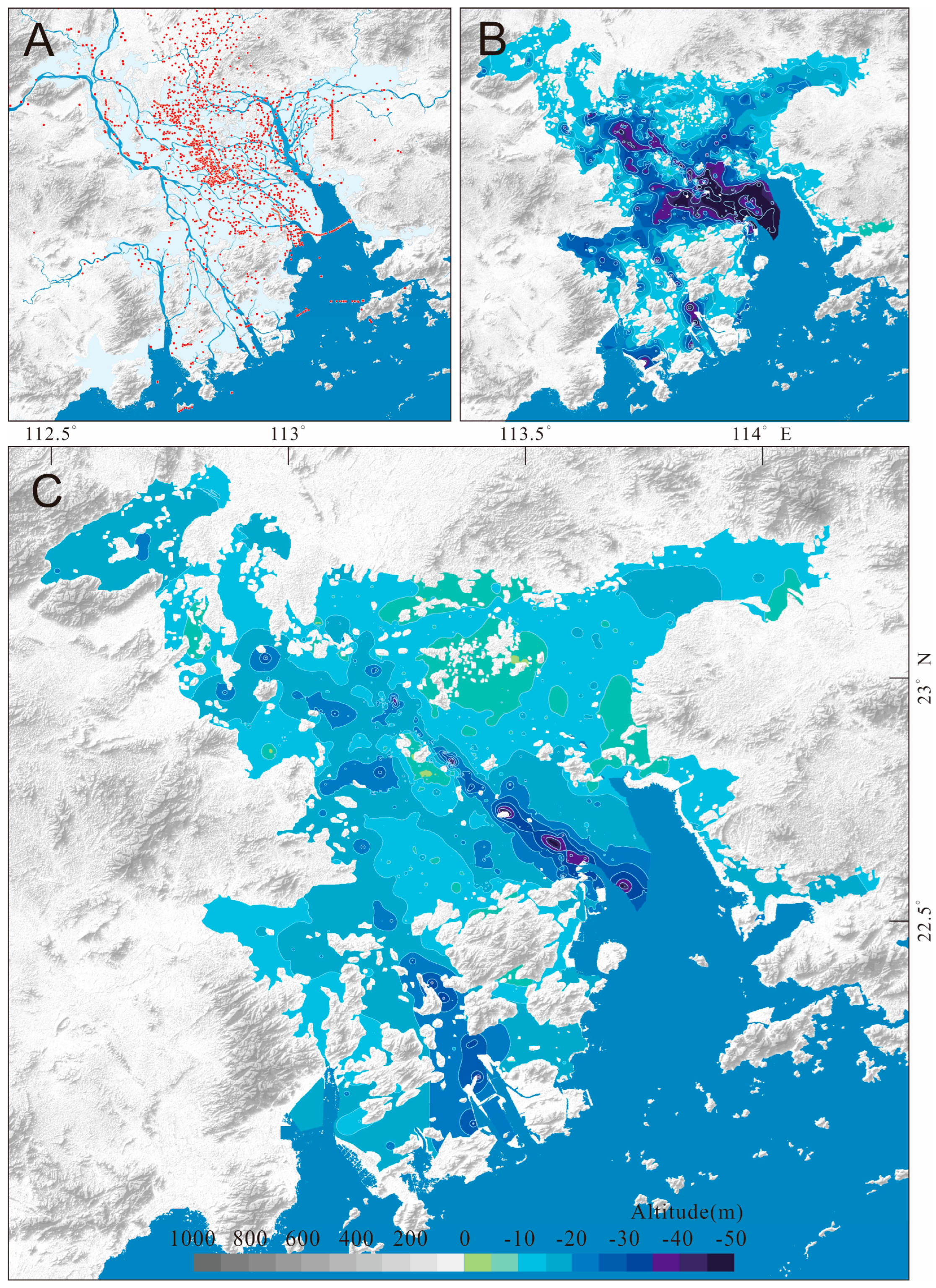
3.3. Method of isobath mapping
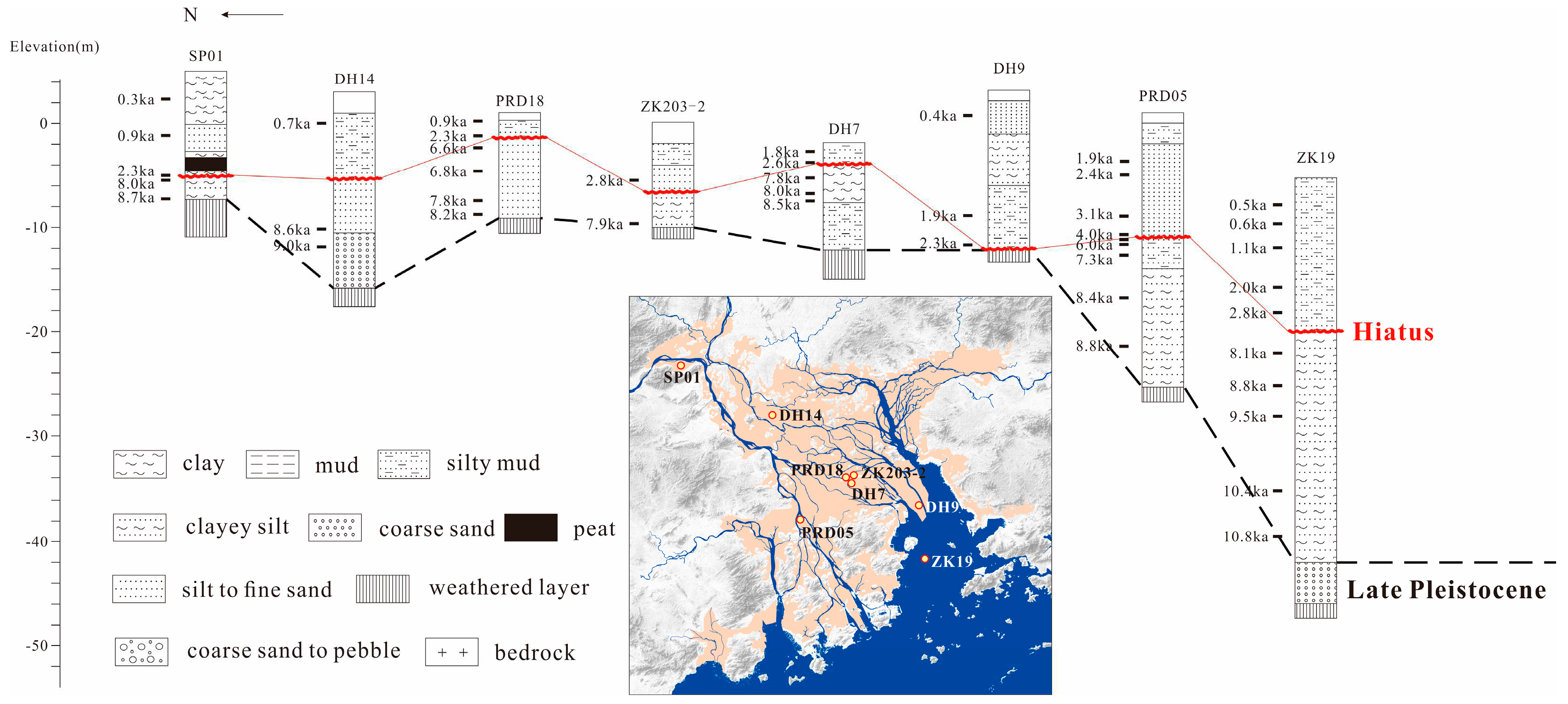
4. Results
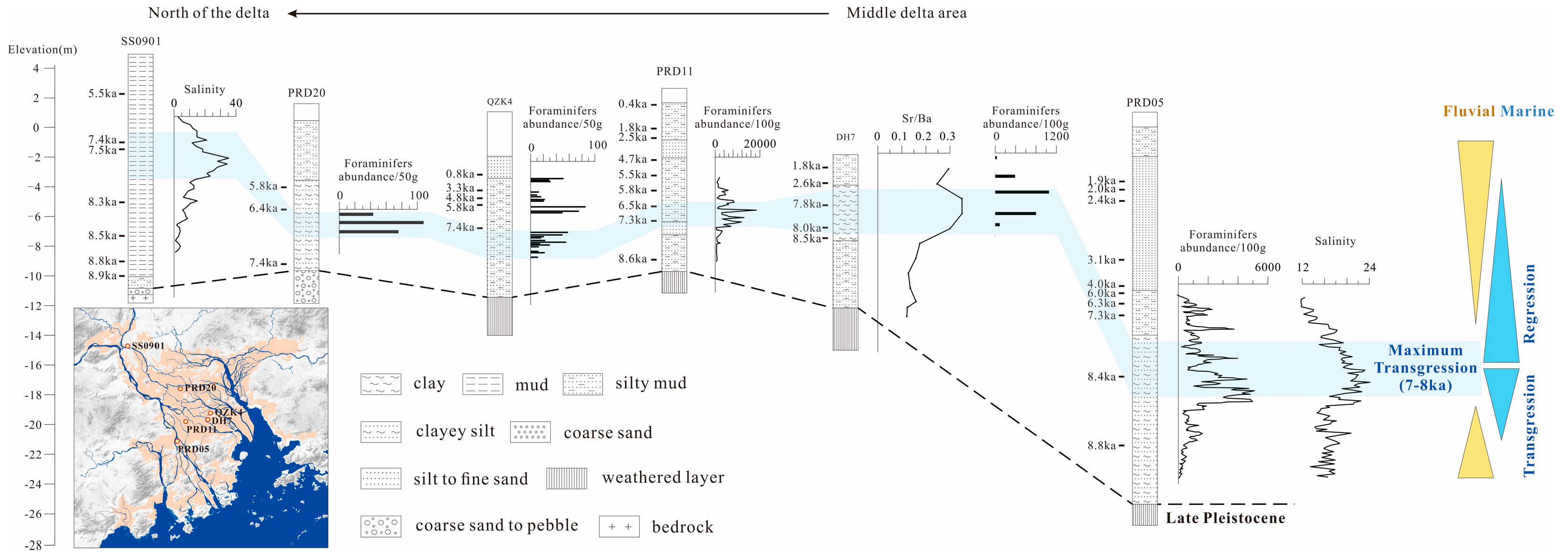
4.1. Holocene stratigraphy and lithofacies changes
4.1.1. Late glacial to Early Holocene deposits
4.1.2. Mid-Holocene marine deposits
4.1.3. Increasing alluvial deposits during the Late Holocene
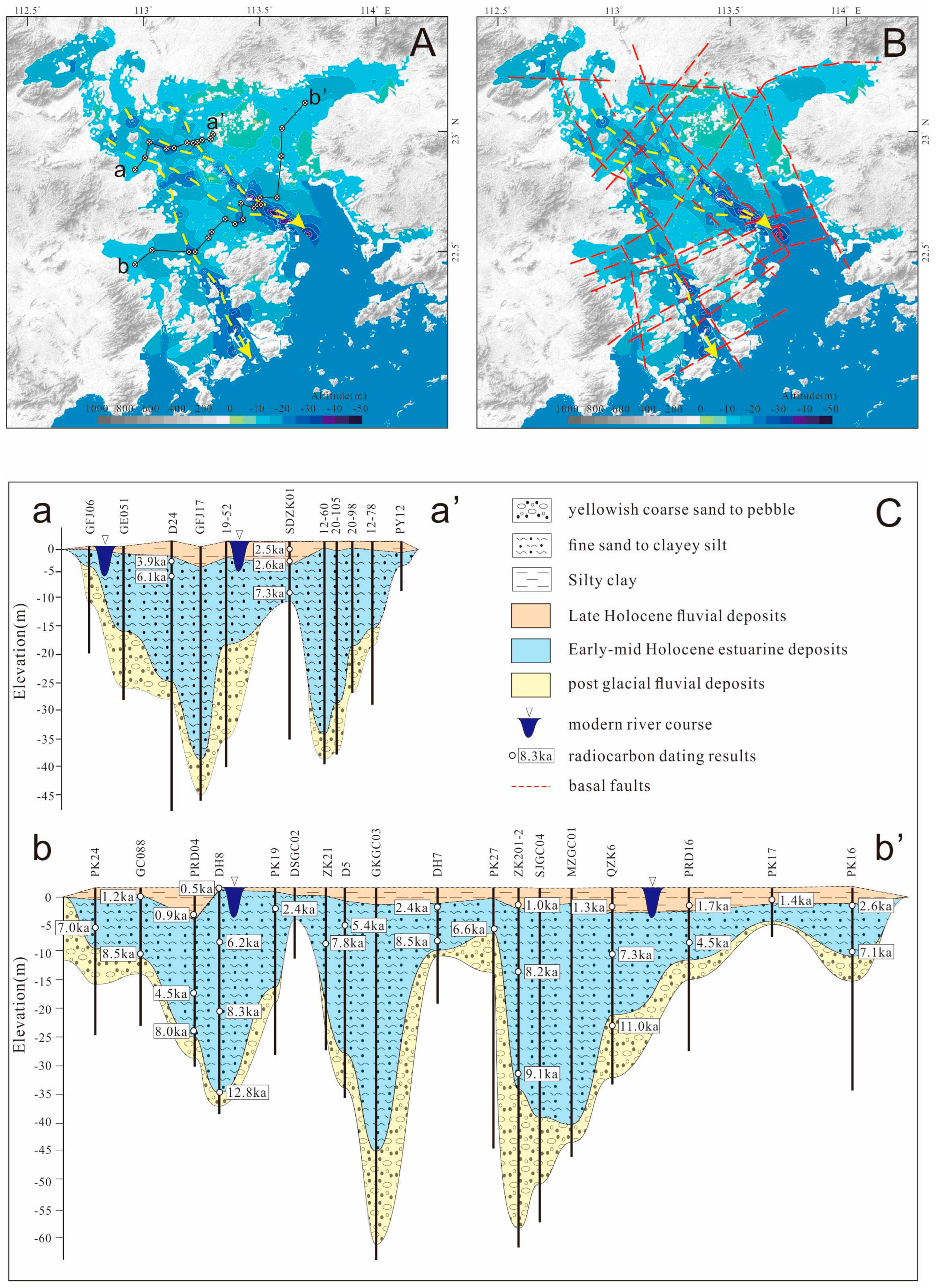
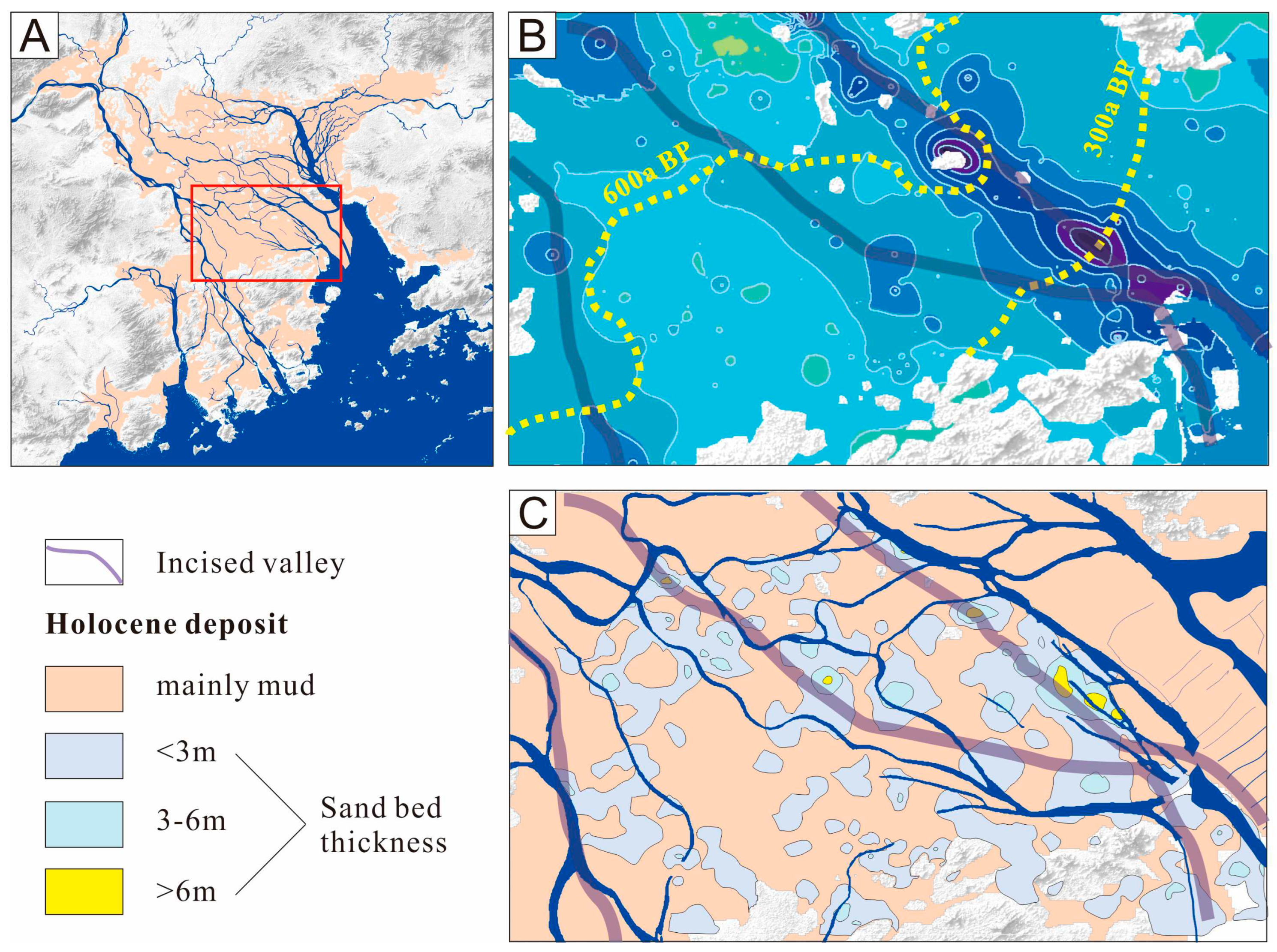
4.2. Holocene sediment isobaths and underlying deep incised-valley
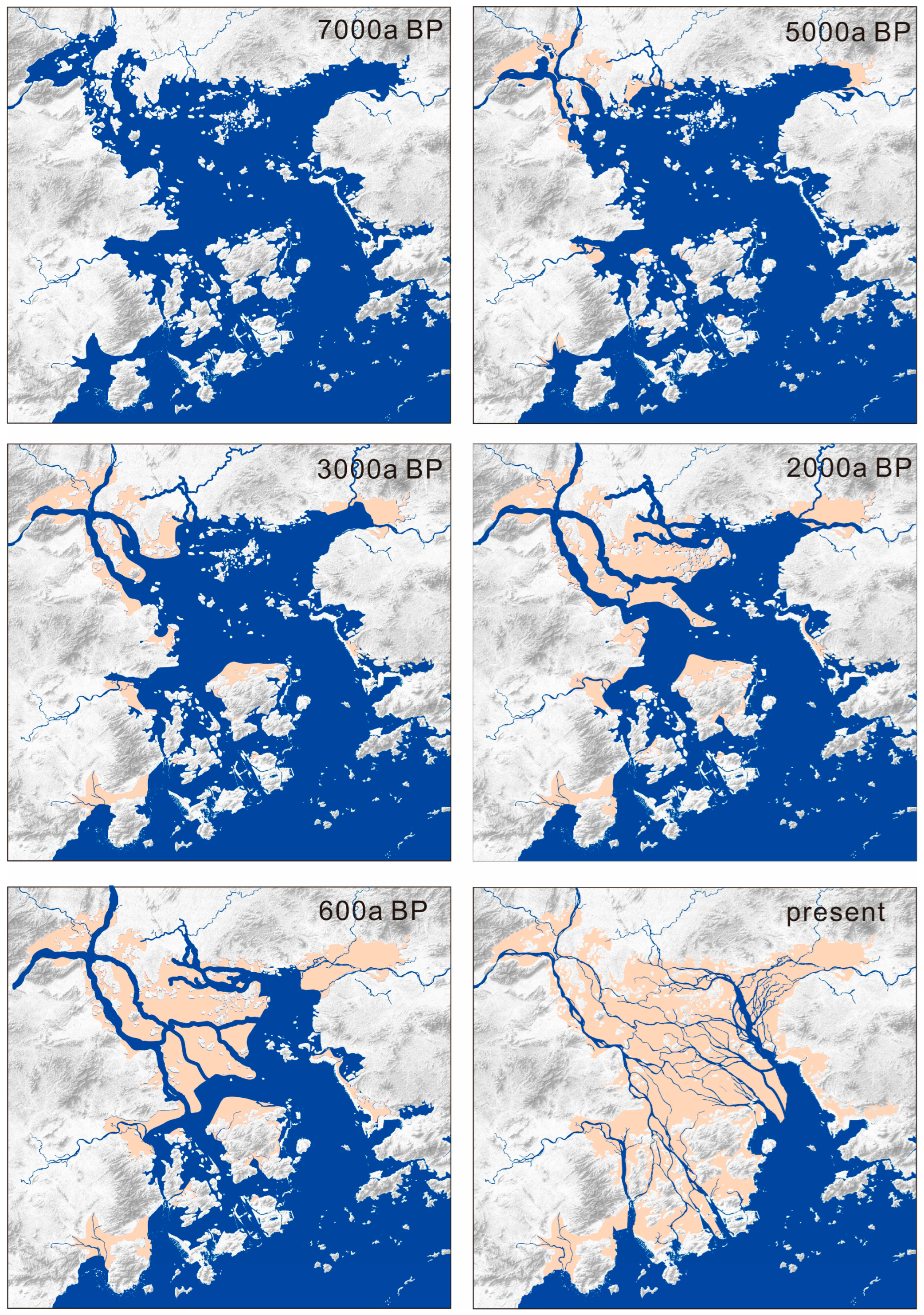
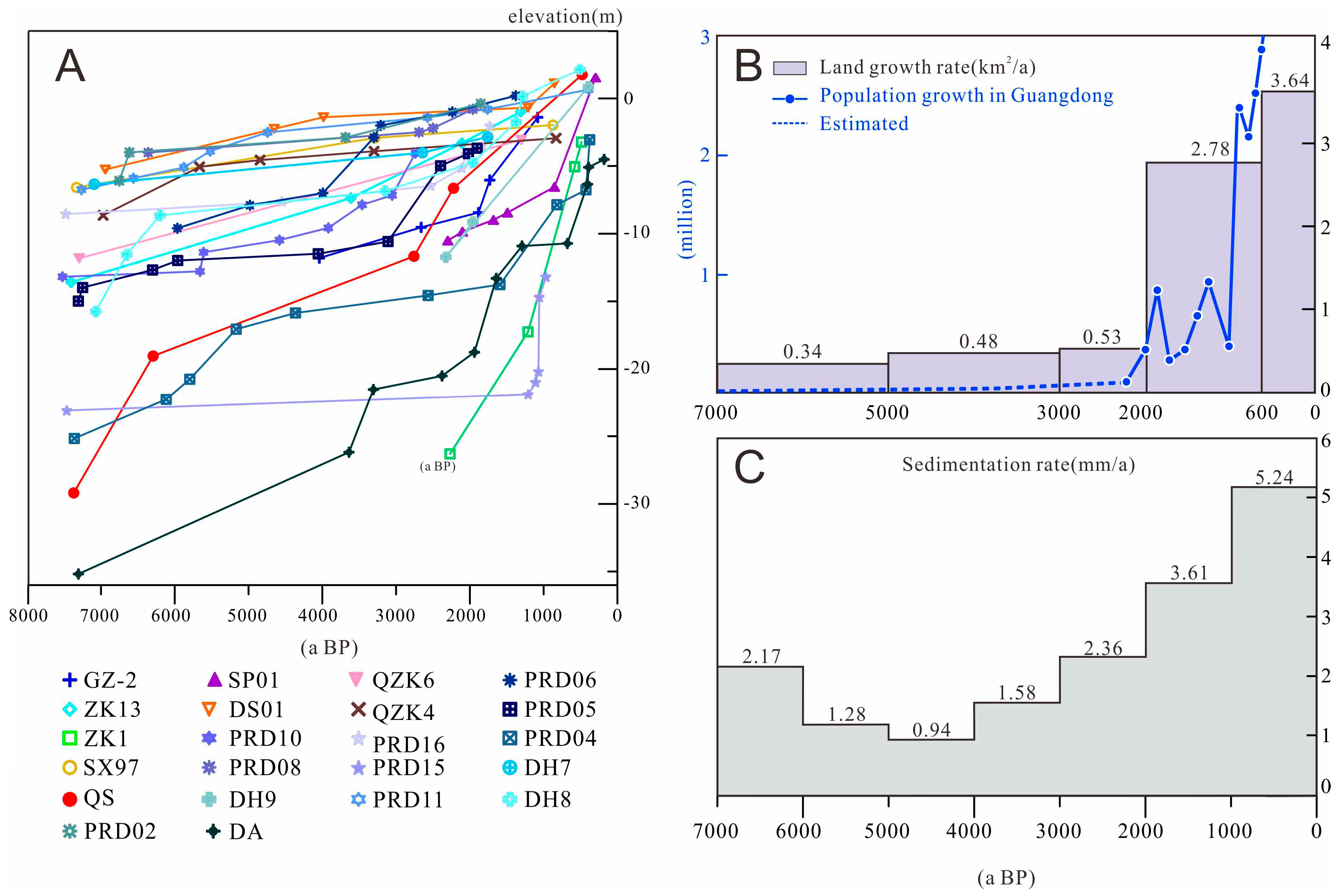
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dalrymple, R.W.; Choi, K. Morphologic and facies trends through the fluvial-marine transition in tide-dominated depositional systems: A schematic framework for environmental and sequence-stratigraphic interpretation. Earth. Sci. Rev. 2007, 81, 135–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorosi, A.; Dinelli, E.; Rossi, V.; Vaiani, S.C.; Sacchetto, M. Late Quaternary palaeoenvironmental evolution of the Adriatic coastal plain and the onset of Po River Delta. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2008, 268, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, M.; Martin, J.; Milliken, K.; Garvin, M. Paleovalley systems: Insights from Quaternary analogs and experiments. Earth. Sci. Rev. 2013, 116, 128–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miall, A.D. The valuation of unconformities. Earth. Sci. Rev. 2016, 163, 22–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, J.; Cohen, K.M.; Thrana, C.; Busschers, F.S.; Martinius, A.W.; Stouthamer, E.; Middelkoop, H. Preservation of Last Interglacial and Holocene transgressive systems tracts in the Netherlands and its applicability as a North Sea Basin reservoir analogue. Earth. Sci. Rev. 2019, 188, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Zong, Y.; Huang, G.; Fu, S. Human drivers accelerated the advance of Pearl River deltaic shoreline in the past 7500 years. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 246, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Li, K.; Qiao, P. The formation and development of Pearl River delta. General Scientific Press Guangzhou, China, 1982. (In Chinese).
- Chen, G.; Zhang, K.; Li, L.; Shao, R.; Zhuang, W.; Lin, X. Development of The Pearl River Delta In SE China and Its Relations to Reactivation of Basement Faults. J. Geosci. China 2002, 4, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Zhan, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhan, M.; Sun, J. Neotectonics and its Relations to the Evolution of the Pearl River Delta, Guangdong, China. J. Coastal Res. 2013, 66, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Huang, G.; Switzer, A.D.; Yu, F.; Yim, W.W.-S. An evolutionary model for the Holocene formation of the Pearl River delta, China. Holocene 2009, 19, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, K.; Sun, Y.; Wang, N.; Tang, M.; Huang, G. Changes in sea level, water salinity and wetland habitat linked to the late agricultural development in the Pearl River delta plain of China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 70, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wu, C. Holocene delta evolution and sequence stratigraphy of the Pearl River Delta in South China. Sci. China Earth 2011, 54, 1523–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, K.; Han, Z.; Zong, Y.; Li, P.; Tan, H. Environmental Changes Inferred from Spatial-temporal Distribution of Holocene Buried Peat Layers in Lower Reaches of the Xijiang and Beijiang and the River Confluence of Pearl River Delta. Trop. Geogr. 2016, 36, 4–16. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, H.; Zong, Y.; Qian, P.; Huang, G.; Fu, S. Holocene sea-level history of the northern coast of South China Sea. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2018, 194, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Rolett, B.; Zheng, Z.; Zong, Y. Holocene coastal evolution preceded the expansion of paddy field rice farming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2020, 117, 24138–24143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Cai, S.; Zhan, W. Impact of anthropogenic activities on morphological and deposition flux changes in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Ma, T.; Roberts, P.; Li, Z.; Yue, Y.; Peng, H.; Huang, K.; Han, Z.; Wan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Satio, Y. Anthropogenic impacts on Late Holocene land-cover change and floristic biodiversity loss in tropical southeastern Asia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2021, 118, e2022210118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Z. Holocene sedimentary environment transform and onset time of Pearl River Delta progradation. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2020, 40, 107–117, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Chen, F.; Jing, X.; Chen, C.; Waniek, J.J. Increasing terrigenous pollen input in the late Holocene: indications of intensive human activity and accelerated delta plain progradation. Mar. Geol. 2021, 439, 106547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Milliman, J.D.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, J.; Yao, C. Recent geomorphic change in LingDing Bay, China, in response to economic and urban growth on the Pearl River Delta, Southern China. Estuar. Coast Shelf S 2018, 209, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Xing, W. Characterizing the seasonal changing patterns of hydrological variables in the East River, southern China. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2016, 21, 05016031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G. Geological Hazards and Engineering Geological Condition in Seabed of the Northern Parts of South China Sea. Hohai University Press Nanjing, China, 1996, 31-49. (In Chinese).
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Ouyang, T. The human impacts on the river networks of the Pearl River delta. Quat. Sci. 2004, 24, 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Ta, T.K.O.; Nguyen, V.L.; Tateishi, M.; Kobayashi, I.; Tanabe, S.; Saito, Y. Holocene delta evolution and sediment discharge of the Mekong River, southern Vietnam. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2002, 21, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S.; Hori, K.; Saito, Y.; Haruyama, S.; Vu, V.P.; Kitamura, A. Song Hong (Red River) delta evolution related to millennium-scale Holocene sea-level changes. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2003, 22, 2345–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanebuth, T.J.J.; Saito, Y.; Tanabe, S.; Vu, Q.L.; Ngo, Q.T. Sea levels during late marine isotope stage 3 (or older?) reported from the Red River delta (northern Vietnam) and adjacent regions. Quat. Int. 2006, 145-146, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Yim, W.W.-S.; Yu, F.; Huang, G. Late Quaternary environmental changes in the Pearl River mouth region, China. Quat. Int. 2009, 206, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Bao, Y.; Ren, J.; Lei, Y.; Shi, H.; He, Z. A numerical simulation and morphodynamic analysis on the evolution of the Zhujiang River Delta in China: 6000-2500a BP. Acta. Oceanol. Sin. 2006, 28, 64–80, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Zeng, E.; Ji, R.; Wang, C. Effects of in-channel sand excavation on the hydrology of the Pearl River delta, China. J. Hydrol. 2007, 343, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, A.; Reuter, H.I.; Nelson, A.; Guevara, E. Hole-filled seamless SRTM data V4. International Centre for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT), 2008, Available from: http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org (accessed 10 November 2020). /, 10 November.
- Gunnink, J.L.; Maljers, D.; van Gessel, S.F.; Menkovic, A.; Hummelman, H.J. Digital Geological Model (DGM): a 3D raster model of the subsurface of the Netherlands. Neth. J. Geosci. 2013, 92, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, B.T.; Sturt, F.; Wilson, P.; Rowland, J.; Brown, A.G. The fluvial evolution of the Holocene Nile delta. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 170, 212–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Gao, Q.; Grapes, R.; Peng, Z.; Chen, G. Late Pleistocene loess-like deposits in the coastal area of south China. Catena 2018, 167, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, K. Quaternary stratigraphy in the Zhujiang delta. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 1984, 4, 133–142, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P. Quaternary stratigraphic divisions in the Pearl River Delta. Pearl River 1987, 6, 18–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lan, X. Paleogeography of the Pearl River Delta since the Late Quaternary. Bull. Mineral Petrol. Geochem. 1995, 2, 109–111. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zong, Y.; Huang, G.; Li, X.; Sun, Y. Late Quaternary Tectonics, Sea-Level Change and Lithostratigraphy along the Northern Coast of the South China Sea. Geological Society of London Special Publications 2015, Sp429.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxi, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Tao, H. Major and Trace Elements Geochemistry and Paleoenvironmental Implications of Borehole ZK19 in the Lingdingyang Bay of the Pearl River Estuary. Trop. Geogr. 2016, 36, 343–354, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Wu, C.; Ni, P.; Mo, W. Holocene delta evolution and sediment flux of the Pearl River, southern China. J. Quat. Sci. 2016, 31, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Franz, T.F.; Wu, J.; Dong, Y.; Yang, T.; Yin, J. Late Quaternary palaeoenvironmental changes documented by microfaunas and shell stable isotopes in the southern Pearl River Delta plain, South China. J. Palaeogeog. English 2013, 2, 344–361. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Wu, C. Long-term process-based morphodynamic modeling of the Pearl River Delta. Ocean Dynam. 2014, 64, 1753–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, B.; Zong, Y.; Wu, J. Evolution of the first mouth bar, distributaries and floodplains of the Pearl River Delta. Geomorphology 2023, 431, 108690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, X.; Hang, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhang, K. Holocene microfaunal records in the central Pearl River Delta and implications for palaeoenvironmental changes. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2019, 39, 31–43, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Zhao, X.; Sun, R.; Huang, C.; Zeng, M.; Liu, F.; Chen, W.; Shao, L. Micorpaleontological records of late Quaternary transgression in the modern Pearl River Delta region, Guangdong province, S. China. Acta. Palaeontol. Sin. 2015, 32, 292–307, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Liu, C.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Y. Foraminiferal records and paleoenvironmental changes since the Late Pleistocene in central Pearl River Delta. J. Palaeogeog. 2016, 18, 677–690, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bridge, J.S. Rivers and Floodplains: Forms, Processes, and the Sedimentary Record. Blackwell Science Publishing, Oxford. 2003, 1-491.
- Lambeck, K.; Rouby, H.; Purcell, A.; Sun, Y.; Sambridge, M. Sea level and global ice volumes from the Last Glacial Maximum to the Holocene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2014, 111, 15296–15303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. The Evolution of the Pearl River Estuaries. China Ocean Press, Beijing. 1990, 1-357. (In Chinese)
- Zong, Y.; Huang, K.; Yu, F.; Zheng, Z.; Switzer, A.; Huang, G.; Ning, W.; Min, T. The role of sea-level rise, monsoonal discharge and the palaeo-landscape in the early Holocene evolution of the Pearl River delta, southern China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2012, 54, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Huang, K.; Tang, Y.; Ma, T.; Wan, Q.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, B.; Zhang, S. Holocene environmental evolution and early agricultural development along the southeast coast of China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Harff, J.; Meyer, M. Reconstruction of paleocoastlines for the northwestern South China Sea since the Last Glacial Maximum. Sci. China Earth 2009, 52, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Wei, H.; Zhou, Y.; Nishimura, A.; Yokota, S. Delta progradation and chenier formation in the huanghe (yellow river) delta, china. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2000, 18, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S.; Saito, Y.; Vu, Q.L.; Hanebuth, T.J.J.; Ngo, Q.L.; Kitamura, A. Holocene evolution of the Song Hong (Red River) delta system, northern Vietnam. Sediment Geol. 2006, 187, 29–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wu, C.; Cai, S.; Zhan, W. Long-term morphodynamic evolution of the Pearl River Delta from the perspective of energy flux and dissipation changes. Quat. Int. 2020, 553, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wei, X. From drowned valley to delta: Discrimination and analysis on issues of the formation and evolution of the Zhujiang River Delta. Acta. Oceanol. Sin. 2021, 43, 1–26, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Xiong, H.; Zong, Y.; Huang, G. Reasons for the low sedimentation and slow progradation in the Pearl River delta, southern China, during the middle Holocene. Mar. Geol. 2020, 423, 106133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xie, P. Excavation and Significance of the Xiantouling Site in Shenzhen. Cultural Relics in Southern China 2011, 2, 122–131. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Ma, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wei, J.; Fuller D., Q. New radiocarbon evidence on early rice consumption and farming in South China. Holocene 2017, 27, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangdong Provincial Local Historical Records Compilation Committee. Guangdong Provincial Record of Population. Guangdong People's Publishing House Press, China, (In Chinese). 1995; 1–332.
- Yang, W.; He, B.; Nima, Y.; Ye, S.; Long, G. Quaternary sedimentary characteristics and palaeo-channel evolution in the central and southern Pearl River Delta. Geol. Chem. Minerals 2022, 44, 328–334, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
| Unit* | Age | Litho-facies | Huang et al. [7] | Zong et al. [27] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qh3 | Holocene | Fluvial silt and clay | Denglongsha Formation | M1b |
| Qh2 | Deltaic silt and clay | Wanqingsha Formation | ||
| Henglan Formation | ||||
| Qh1 | Fluvial-estuarine channel sand, silt | Xingtan Formation | M1a | |
| Qpsj | Pleistocene | Terrestrial sand, gravel and mottled clay | Sanjiao Formation | T1 |
| Qpxn | Shallow marine silt and clay | Xinan Formation | M2 | |
| Qpsj | Terrestrial silt, sand, gravel | Shipai Formation | T2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





