1. Introduction
Natural nootropics are organic substances that may act as a vasodilator in the brain, increase cellular energy, and/or protect the brain from oxidative stress (Malík & Tlustoš, 2022; Pranav, 2013). Nootropics may also improve cognitive function, reduce tiredness, improve reaction time, improve memory retention and recall, and reduce mental fatigue (Malík & Tlustoš, 2022; Pranav, 2013). The most widely consumed nootropic is caffeine and there is an abundance of research demonstrating improved attention and executive function, however in some individuals caffeine use can have undesirable affects such as a crash, jitteriness, anxiety, or elevated vital signs (Lorca et al., 2022; Temple et al., 2017). Therefore, natural substances that can provide similar cognitive enhancements without the side-effect profile of caffeine may be desirable for consumers. Methylliberine (trademark name DynamineTM) is a purine alkaloid metabolite of caffeine which may provide similar cognitive enhancements as caffeine with none of the hemodynamic effects (i.e., elevated blood pressure and jitteriness) (Cintineo et al., 2022). A few studies have examined the impact of the combination of caffeine, theacrine (as TeaCrine®), and methylliberine (CMT) (Cintineo et al., 2022; La Monica et al., 2021; Tartar et al., 2021) on cognitive tasks, but investigations examining methylliberine independently are scarce. To date, only two investigations have analyzed independent methylliberine ingestion in humans. These investigations conducted a safety profile (i.e., cardiovascular function and comprehensive hematological panel) of methylliberine supplementation alone and in conjunction with TeaCrine® and/or caffeine over an acute period of 48 hours and over a period of four weeks in healthy, young men and women (Bloomer et al., 2020; VanDusseldorp et al., 2020). Preceding human trials, methylliberine was shown to be safe in rats following chronic dosing (90 days) and after a 28 day follow-up (Murbach et al., 2019).
Several studies have examined the impact CMT has on cognitive performance. A previous study from La Monica et al. (2021) comparing placebo (PLA), caffeine, and CMT on gaming performance in a first-person shooter with recreational gamers showed that CMT, not CAFF, improved the time it took to eliminate a target vs. PLA. Simultaneously, caffeine increased jitteriness relative to baseline and was not able to maintain cognitive control vs. CMT and PLA (La Monica et al., 2021). It was also noted that CMT and CAFF elevated systolic blood pressure (SBP) slightly vs. PLA relative to baseline (La Monica et al., 2021). Notably, subjects perceived themselves to perform better during the gaming simulation under the CMT treatment vs. PLA relative to baseline (La Monica et al., 2021). Likewise, Tartar et al. (2021) compared CMT, caffeine, and PLA in amateur gamers and found that CMT and PLA improved inhibitory control on a Flanker test vs. caffeine. CMT also improved subjective alertness vs. PLA and improved reaction time on the Psychomotor Vigilance Task relative to baseline, whereas caffeine and PLA did not (Tartar et al., 2021). In addition, CMT (relative to caffeine) was associated with lower self-reported headaches (Tartar et al., 2021). Unique to Tartar et al. (2021) the investigation observed an increase in delta power during EEG recordings under the CMT treatment while caffeine showed a decrease in delta power relative to baseline (Tartar et al., 2021). The authors concluded that an increase in delta power along with a possible increase in theta power (in CMT) were associated with an increase in attention and cognitive control (Harmony et al., 1996; Nigbur et al., 2011; Tartar et al., 2021). Lastly, Cintineo et al. (2022) compared CMT, caffeine, and PLA on reaction time and marksmanship in tactical athletes and found that caffeine and CMT (as opposed to PLA) were able to improve reaction time on a vigilance task, however there were no differences in accuracy or reaction time between treatments within a marksmanship task. Also, caffeine elevated systolic and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) while CMT only elevated SBP (Cintineo et al., 2022). Unlike La Monica et al. (2021) and Tartar et al. (2021) where the caffeine content was matched to the caffeine in CMT, Cintineo et al. (2022) doubled the caffeine content in caffeine compared to CMT. Given the differences between caffeine and CMT shown in these previous investigations there are theoretical benefits to TeaCrine® and methylliberine that should be explored further.
The pharmacokinetics of methylliberine, TeaCrine®, and caffeine have been compared. A 100mg dose of methylliberine showed peak plasma concentrations at 0.8-0.9 hr and a half-life of 1.4-1.5 hr (Mondal et al., 2022; Y.-H. Wang et al., 2020). Although the half-life of caffeine and TeaCrine® differ depending on the dose, TeaCrine® has been shown to have a much longer half-life than caffeine (He et al., 2017) and both have an extended half-life compared to methylliberine (Y.-H. Wang et al., 2020). Methylliberine has been shown to reduce the oral clearance and extend the half-life of caffeine when co-administered, however caffeine does not appear to affect the pharmacokinetics of methylliberine, at least at a 100mg dose (Mondal et al., 2022). The conclusion is that caffeine and methylliberine likely differ in their affinity and selectivity for adenosine A1 and A2A receptors which may also result in different effects (Daley et al., 1983; Mondal et al., 2022; Ralevic & Burnstock, 1998). Currently, there have not been any studies conducted on the effects of independent methylliberine ingestion on cognitive function or indices of affect. Within the two studies that have investigated independent ingestion of methylliberine, neither one reported any influence on vital signs, respiratory rate, body temperature, or mood in men and women (Bloomer et al., 2020) nor did it negatively affect markers of health (VanDusseldorp et al., 2020). Thus, the purpose of this study was to assess the acute and potential accumulative effects of methylliberine supplementation on cognitive function and overall well-being including energy, sustained energy, mental stamina, focus, concentration, motivation to accomplish difficult tasks, drive, vigor, positive outlook, maintaining a healthy mood, feelings of well-being, and resilience to stress. Our hypothesis was that methylliberine ingestion would improve cognitive function, energy, mood and focus without negatively impacting heart rate or blood pressure.
2. Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
This was a double-blind, randomized, two-arm, within-subject crossover trial in which participants visited the laboratory on five occasions (one screening visit, two baseline visits, and two post supplement testing visits). This study was conducted according to the guidelines laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki of 1975 and all procedures involving human subjects were approved by the Genetic Alliance IRB on 9/30/22 (#CSI-08-2022-001). Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects prior to enrollment. The study was registered on clinicaltrials.gov (“Effects of Dynamine Ingestion on Various Indices of Sustained Energy”, #NCT06048640). This study was conducted at a contract research organization (CRO) in Northeast Ohio. During the initial screening visit each participant’s medical history and blood work (CBC, CMP, and lipid panel) were assessed, baseline diet was evaluated, and each participant underwent 3 sets of familiarization trials of the neuropsychological assessments [Stroop and Trail Making Test B (TMT-B)]. During the baseline visits (visits 2 and 4, which were prior to supplementation administration), subjects completed baseline testing which included subjective questionnaires [visual analog scales (VAS)] that assessed energy, sustained energy, mental stamina, focus, concentration, motivation to accomplish difficult tasks, drive, vigor, positive outlook, maintaining a healthy mood, feelings of well-being, and resilience to stress in addition to completing 3 sets of the neuropsychological assessments to assess mental processing, cognitive flexibility, and attention. After visits 2 and 4, participants were given their respective supplement to take for three days and return on the fourth day. Participants returned for visits 3 and 5 where they took a fourth dose of their respective supplement at the laboratory and repeated the testing outlined at visits 2 and 4 with timepoints consisting of baseline (prior to administration of the 4th dose), 1 hour post, 2 hours post, and 3 hours post ingestion.
2.2. Participants
25 healthy men and women completed all study visits (See
Table 1 for subject characteristics). All participants were in good health as determined by physical examination and medical history, between the ages of 21 and 55 years, and had a body mass index (BMI) of 18.5-27 kg•m
-2. Prior to participation, all participants indicated their willingness to comply with all aspects of the experimental and supplement protocol. Participants were excluded if they: (a) had a history of diabetes or pre-diabetes; (b) had a history of malignancy in the previous 5 years except for non-melanoma skin cancer (basal cell cancer or squamous cell cancer of the skin); (c) had prior gastrointestinal bypass surgery; (d) known gastrointestinal or metabolic diseases that might impact nutrient absorption or metabolism (e.g. short bowel syndrome, diarrheal illnesses, history of colon resection, gastro paresis, Inborn-Errors-of-Metabolism); (e) had any chronic inflammatory condition or disease; (f) had a known allergy to any of the ingredients in the supplement or the placebo; (g) had currently been participating in another research study with an investigational product or have been in another research study in the past 30 days; (h) had a caffeine intake of three or more cups of coffee or equivalent (>400 mg) per day; (i) used corticosteroids or testosterone replacement therapy (ingestion, injection, or transdermal); (j) had any other diseases or conditions that, in the opinion of the medical staff, could confound the primary endpoint or place the participant at increased risk of harm if they were to participate; or (k) did not demonstrate a verbal understanding of the informed consent document.
Participants were instructed to follow their normal diet and activity patterns throughout their participation in the study. Participants were required to complete a 24-hour diet record prior to arriving at the laboratory for their initial screening visit. Participants were given a copy of this dietary record and instructed to duplicate all food and fluid intake 24 hours prior to each subsequent laboratory visits. Prior to each subsequent visit participants were asked to verbally confirm their 24-hour prior diet adherence and ensure they had a normal night’s rest. In addition to replicating food and fluid intake for 24 hours prior, study participants were also asked to refrain from exercise and alcohol 24 hours prior, abstain from caffeine 12 hours prior, and arrive 8 hours fasted to all testing sessions which were all verbally confirmed at the beginning of each study visit.
2.3. Neuropsychological Assessments
The Stroop test requires individuals to read color-words printed in a different color ink (for example, the word “green” is printed in blue) and select the color of the ink instead of reading the word (therefore within the example, the answer is blue) (Scarpina & Tagini, 2017). This challenge requires participants to perform a less automated task (i.e., naming the ink color) while inhibiting the interference coming from a more automated task (i.e., reading the word) (Scarpina & Tagini, 2017). All participants in the study were assessed using the congruent standard condition of the Stroop for two minutes. The outcome variables associated with the Stroop test were total score, accuracy, and average time per score. The Stroop test measures the ability to inhibit cognitive interference, attention, processing speed, cognitive flexibility (Jensen & Rohwer, 1966), and working memory (Kane & Engle, 2003).
The TMT-B requires individuals to connect 25 encircled numbers and letters in numerical and alphabetical order (Bowie & Harvey, 2006). For example, the number “1” is followed by “A” which is then followed by “2” then “B” and so forth and so on (Bowie & Harvey, 2006). The outcome variable associated with TMT-B was time to completion. TMT-B measures cognitive flexibility with its visually interfering stimuli and distance between numbers/letters (Bowie & Harvey, 2006).
Participants consecutively completed the Stroop test and TMT-B with one minute of rest in between each test and each set. In total, participants underwent 3 sets of Stroop and TMT-B at each time point and the median value was taken as the value for each respective time point. During visits 2 and 4 participants completed the Stroop and TMT-B at baseline and once again after a 10-minute break. The two median values from visits 2 and 4 were averaged and used in the statistical analyses. During visits 3 and 5 participants completed the Stroop and TMT-B at baseline, 1-hour, 2-hours, and 3-hours post ingestion of their respective supplement.
2.4. Visual-Analog Scales
100-mm anchored VAS were completed before and after baseline testing, 1-hour, 2-hours, and 3-hours after ingestion of each acute supplement on visits 3 and 5 and before and after baseline cognitive testing on visits 2 and 4. VAS were anchored with “Not very focused”, “Very low initiative”, and “Lowest Possible” or “Highly focused”, “Very high initiative” and “Highest Possible” and assessed subjective ratings of energy, sustained energy, mental stamina, ability to focus, ability to concentrate, motivation to accomplish difficult tasks, drive, vigor, positive outlook, mood, feeling of well-being, and ability to tolerate stress. The two values (before and after testing) for each subjective rating on visits 2 and 4 were averaged and then used in statistical analyses. The validity and reliability of VAS to assess fatigue and energy have been previously established (Lee et al., 1991) and reported (Lopez et al., 2020; Ziegenfuss et al., 2018).
2.5. Supplement Protocol
Throughout the study protocol, all supplements were prepared in single capsule form for oral ingestion and packaged in coded generic containers for administration. Participants orally ingested a PLA (100mg cellulose) and 100 mg methylliberine (as Dynamine™). Using a cross-over design, half of the subjects were randomly assigned to receive the PLA first while the other half were assigned to receive methylliberine first. At the end of visits 2 and 4 participants were given a packet of three daily doses (1 dose/day) to consume prior to their visit 3 and 5, respectively. The fourth dose was consumed in the laboratory after their baseline testing timepoint in the presence of the medical staff. There were no less than 7 days in between each trial (i.e., in between visit 3 and 4).
2.6. Anthropometric and Other Resting Measures
Standing height was determined using a wall-mounted stadiometer and body weight was measured using a Seca 767TM Medical Scale (body weight was measured at each visit). Resting heart rate and blood pressure were measured using an automated blood pressure cuff (Omron HEM-780) before and after each timepoint (i.e., baseline, 1-hour, 2-hours, and 3-hours post after ingestion of each assigned supplement) during visits 3 and 5. Similarly, resting heart rate and blood pressure were measured before and after baseline testing during visits 2 and 4.
2.7. Statistical Analyses
Primary outcome measures included cognitive focus and attention (i.e., total score, accuracy, average time per score, and time to completion) determined by neuropsychological testing (Stroop and TMT-B) and VAS assessing objective and subjective changes in mental processing, cognitive flexibility, attention, energy, sustained energy, mental stamina, focus, concentration, motivation to accomplish difficult tasks, drive, vigor, positive outlook, maintaining a healthy mood, feelings of well-being, and resilience to stress. Secondary outcome measures included vital signs (blood pressure and heart rate) and side effect profile/adverse events monitoring. An a priori power analysis was conducted for the main outcome measures using G*Power (i.e., specifically energy). For a mixed factorial ANOVA with repeated measures, with two groups and four time points, within-between interaction, and a small effect of 0.25, a sample size of 24 was needed to achieve 80% power. All variables were tested for normality using results from a Shapiro-Wilk test. When a deviation from normality was identified, natural log transformations were employed. As such, transformations were employed for Stroop accuracy scores. In the case of scale (ratio) data, transformations were not possible. Data is presented as means ± standard deviation and the primary statistical approach employed was mixed factorial ANOVA with repeated measures on time to assess group (methylliberine vs. PLA), time, and group x time interaction effects. Specifically, these ANOVAs were used to compare baseline at visits 2 and 4 to the baseline timepoint on visits 3 and 5 (examining whether an accumulation over 3 daily doses had any effect on the primary outcomes) as well as comparing all timepoints within visits 3 and 5 (examining the acute effects on the primary outcomes). Factorial ANOVA with repeated measures on time were used to examine changes from baseline within each group with Bonferroni corrections applied to all pairwise comparisons. Changes from baseline (deltas) were calculated and independent t-tests were computed to evaluate between-group changes using 95% confidence intervals, p-values, and effect sizes. Non-normal data was first analyzed using the Friedman test (within-group changes), then the Wilcoxon signed rank test (paired differences within group) and then Mann-Whitney U test (between-group differences). A significance level of 0.05 was used for all statistical determinations while p-values between 0.051 and 0.10 were deemed a trend. All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS version 23.
3. Results
13 women and 12 men completed all study visits. See
Table 1.
Table 1.
Participant characteristics.
Table 1.
Participant characteristics.
| |
Men (N=12) |
Women (N=13) |
| Age (years) |
33.5 ± 10.7 |
33.5 ± 11.1 |
| Height (cm) |
180.6 ± 7.7 |
170.8 ± 7.2 |
| Weight (kg) |
79.0 ± 8.0 |
68.1 ± 11.1 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) |
24.9 ± 1.4 |
23.9 ± 2.6 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure (mm Hg) |
122.4 ± 8.7 |
113.3 ± 13.5 |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (mm Hg) |
78.6 ± 9.8 |
76.5 ± 7.8 |
| Resting Heart Rate (bpm) |
66.2 ± 8.7 |
70.0 ± 12.6 |
3.1. Stroop
There were no differences in total score between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation (group: p = 0.61; time: p = 0.44; group x time: p = 0.29). However, there was an acute improvement over time after the 4th dose regardless of group (group: p = 0.21; time: p < 0.001; group x time: p = 0.61).
There were no differences in accuracy between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation (group: p = 0.440; time: p = 0.850; group x time: p = 0.99). There were no acute differences in accuracy after the 4th dose (group: p = 0.56; time: p = 0.42; group x time: p = 0.93).
There were no differences in average time per score between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation (group: p = 0.45; time: p = 0.39; group x time: p = 0.45). However, there was an acute improvement over time after the 4
th dose regardless of group (group: p = 0.22; time: p < 0.001; group x time: p = 0.63). See
Table 2.
Table 2.
Stroop and Trail Making Test B (TMT-B) scores on Baseline (Day 0) and Testing Visits (Day 4).
Table 2.
Stroop and Trail Making Test B (TMT-B) scores on Baseline (Day 0) and Testing Visits (Day 4).
| |
Stroop Test |
TMT-B |
| |
Total Score (au) |
Accuracy (%) |
Average time per score (ms) |
Time to completion (s) |
| Time |
PLA |
ML |
PLA |
ML |
PLA |
ML |
PLA |
ML |
| Day 0 |
125.2 ± 18.4 |
125.0 ± 17.9 |
99.1 ± 1.2 |
99.2 ± 1.1 |
0.99 ± 0.14 |
0.98 ± 0.13 |
22.8 ± 6.1 |
24.3 ± 7.2 |
0 min
(Day 4) |
124.7 ± 19.2 |
127.4 ± 18.8 |
99.0 ± 1.1 |
99.2 ± 1.3 |
0.99 ± 0.17 |
0.96 ± 0.14 |
21.8 ± 5.5 |
21.6 ± 5.8⸸
|
60 min
(Day 4) |
128.5 ± 17.4 |
131.5 ± 17.5* |
99.0 ± 1.3 |
99.1 ± 1.8 |
0.95 ± 0.14 |
0.93 ± 0.12 |
21.7 ± 6.0 |
20.4 ± 5.2 |
120 min
(Day 4) |
131.3 ± 17.0* |
132.1 ± 16.3* |
98.8 ± 1.7 |
99.0 ± 1.2 |
0.93 ± 0.12 |
0.92 ± 0.11* |
21.1 ± 5.4 |
20.2 ± 4.1 |
180 min
(Day 4) |
131.7 ± 17.7 |
134.8 ± 17.7* |
98.8 ± 1.3 |
98.9 ± 1.8 |
0.92 ± 0.12* |
0.91 ± 0.11* |
19.3 ± 4.0* |
20.3 ± 3.8 |
3.2. TMT-B
There was a trend for a group x time interaction and a significant main effect of time for time to completion between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation (group: p = 0.56; time: p = 0.001; group x time: p = 0.06). Post hoc analyses showed that the baseline time point after 3 days of supplementation was ~11% lower (i.e., improved) vs. the baseline visit for methylliberine (p < 0.001). Additionally, there was an acute improvement over time after the 4
th dose regardless of group (group: p = 0.65; time: p = 0.009; group x time: p = 0.13). See
Table 2.
3.3. VAS
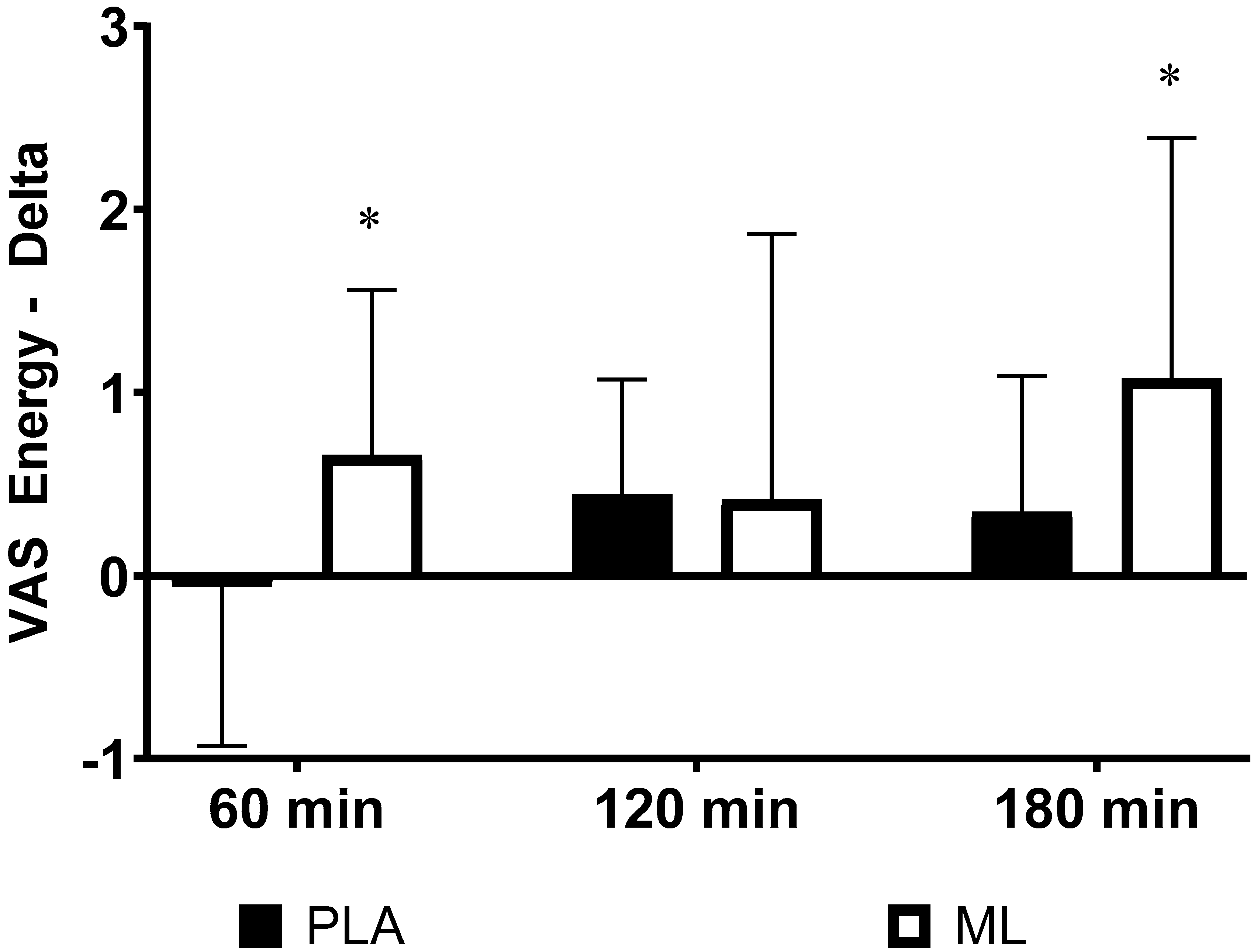
There were no differences in subjective ratings of energy between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation (group: p = 0.84; time: p = 0.26; group x time: p = 0.27). However, there was an acute improvement over time regardless of group after the 4
th dose (group: p = 0.14; time: p = 0.001; group x time: p = 0.23). Additionally, there were no differences in the deltas (p>0.050) from the baseline timepoint after the 4
th dose for energy (See
Table 3). There was a trend for a group x sex x time interaction (p=0.064) showing that the two sexes may have responded differently in energy between the two treatment conditions over time. Post hoc 2 x 4 (group x time) mixed factorial ANOVA with repeated measures showed that women had a significant group x time interaction (p=0.020) while the men did not (p = 0.810). Post hoc testing on the deltas showed that women had a greater change in energy from the baseline timepoint to 1 hour post supplementation (p=0.010, 95%CI: 0.21 to 1.23, d = 0.81) and from the baseline timepoint to 3 hours post supplementation (p=0.040, 95%CI: 0.06 to 1.40, d = 0.69) in methylliberine vs. PLA. See
Figure 1.
Table 3.
Feelings of Affect via VAS on Baseline (Day 0) and Testing Visits (Day 4).
Table 3.
Feelings of Affect via VAS on Baseline (Day 0) and Testing Visits (Day 4).
| |
|
Time |
| |
Group |
Day 0 |
0 min (Day 4) |
60 min (Day 4) |
120 min (Day 4) |
180 min (Day 4) |
| Energy (cm) |
PLA |
5.6 ± 1.9 |
5.6 ± 1.9 |
5.8 ± 2.0 |
6.1 ± 1.8 |
6.1 ± 1.9* |
| ML |
5.5 ± 2.0 |
5.8 ± 2.1 |
6.2 ± 1.9 |
6.2 ± 2.2 |
6.5 ± 1.9* |
| Sustained energy (cm) |
PLA |
5.7 ± 1.8 |
5.6 ± 1.9 |
5.8 ± 2.0 |
6.2 ± 1.7* |
6.1 ± 1.9* |
| ML |
5.6 ± 2.0 |
5.7 ± 2.1 |
6.2 ± 1.9* |
6.3 ± 2.2 |
6.5 ± 2.0* |
| Mental Stamina (cm) |
PLA |
5.8 ± 1.8 |
5.6 ± 2.0 |
6.0 ± 1.9 |
6.1 ± 1.7* |
6.0 ± 1.9* |
| ML |
5.7 ± 1.9 |
6.0 ± 1.9 |
6.3 ± 1.9 |
6.3 ± 2.1 |
6.6 ± 1.9 |
| Focus (cm) |
PLA |
5.9 ± 1.9 |
6.0 ± 1.9 |
6.0 ± 2.0 |
6.2 ± 1.8 |
6.2 ± 1.9 |
| ML |
5.9 ± 1.8 |
6.0 ± 2.0 |
6.4 ± 1.8 |
6.5 ± 2.0 |
6.7 ± 2.0 |
| Drive (cm) |
PLA |
5.7 ± 1.9 |
5.7 ± 2.0 |
6.0 ± 1.9 |
6.3 ± 1.7* |
6.0 ± 1.8 |
| ML |
5.8 ± 1.9 |
5.9 ± 1.9 |
6.1 ± 2.1 |
6.2 ± 2.0 |
6.4 ± 2.1 |
| Vigor (cm) |
PLA |
5.8 ± 1.8 |
5.7 ± 2.0 |
6.1 ± 2.0 |
6.3 ± 1.8* |
5.9 ± 1.8 |
| ML |
5.8 ± 2.0 |
5.8 ± 2.0 |
6.2 ± 2.0 |
6.3 ± 1.9 |
6.4 ± 2.0* |
| Positive Outlook (cm) |
PLA |
6.8 ± 1.7 |
6.4 ± 1.9⸸
|
6.7 ± 1.8 |
7.0 ± 1.7* |
6.8 ± 1.9 |
| ML |
6.6 ± 1.9 |
6.4 ± 2.0 |
6.8 ± 1.9 |
7.0 ± 1.7 |
7.0 ± 1.7* |
| Well-being (cm) |
PLA |
7.0 ± 1.7 |
6.6 ± 1.8 |
6.9 ± 1.8 |
7.0 ± 1.6 |
6.9 ± 1.8 |
| ML |
6.8 ± 2.0 |
6.4 ± 1.7 |
6.8 ± 1.7 |
7.3 ± 1.6* |
7.2 ± 1.6* |
| Ability to Tolerate Stress (cm) |
PLA |
6.1 ± 1.9 |
5.8 ± 2.1 |
6.0 ± 2.0 |
6.1 ± 2.0 |
5.8 ± 2.0 |
| ML |
6.1 ± 2.0 |
5.7 ± 2.0 |
6.2 ± 2.1 |
6.4 ± 1.9* |
6.4 ± 1.9 |
Figure 1.
The change in Energy relative to the baseline time point (0 min) for women between groups. *Significantly different from PLA (p ≤ 0.05).
Figure 1.
The change in Energy relative to the baseline time point (0 min) for women between groups. *Significantly different from PLA (p ≤ 0.05).
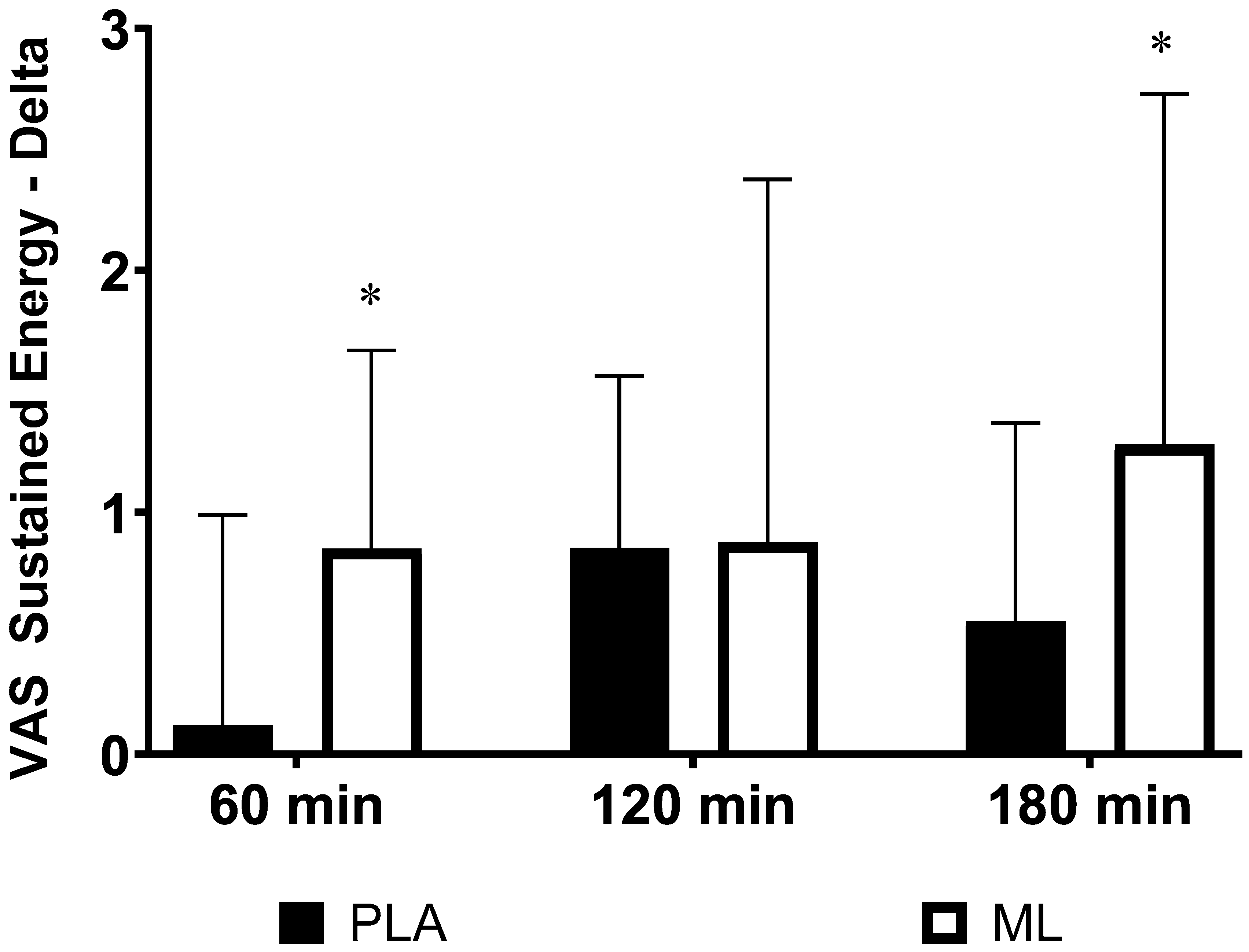
There were no differences in subjective ratings of sustained energy between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation (group: p = 0.75; time: p = 0.97; group x time: p = 0.38). However, there was an acute improvement over time regardless of group after the 4
th dose (group: p = 0.24; time: p < 0.001; group x time: p = 0.33). Additionally, there were no differences in the deltas (p>0.050) from the baseline timepoint after the 4
th dose the 4
th dose for sustained energy (See
Table 3). There was a significant group x sex x time interaction (p=0.034) showing that the two sexes responded differently in sustained energy between the two treatment conditions over time. Post hoc 2 x 4 (group x time) mixed factorial ANOVA with repeated measures showed that women had a significant group x time interaction (p=0.022) while the men did not (p = 0.68). Post hoc testing on the deltas showed that women had a greater change in sustained energy from the baseline timepoint to 1 hour post supplementation (p=0.030, 95%CI: 0.10 to 1.38, d = 0.86) and from the baseline timepoint to 3 hours post supplementation (p=0.040, 95%CI: 0.04 to 1.41, d = 0.62) in methylliberine vs. PLA. See
Figure 2.
Figure 2.
The change in Sustained Energy relative to the baseline time point (0 min) for women between groups. *Significantly different from PLA (p ≤ 0.05).
Figure 2.
The change in Sustained Energy relative to the baseline time point (0 min) for women between groups. *Significantly different from PLA (p ≤ 0.05).
There were no differences in subjective ratings of mental stamina between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation (group: p = 0.32; time: p = 0.74; group x time: p = 0.11). However, there was an acute improvement over time regardless of group after the 4
th dose (group: p = 0.15; time: p = 0.003; group x time: p = 0.41). Additionally, there were no differences in the deltas (p>0.050) from the baseline timepoint after the 4
th dose for mental stamina. See
Table 3.
There were no differences in subjective ratings of focus between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation (group: p = 0.61; time: p = 0.58; group x time: p = 0.91). However, there was an acute improvement over time regardless of group after the 4
th dose (group: p = 0.18; time: p = 0.03; group x time: p = 0.33). There was a trend for a difference in deltas from the baseline timepoint to 3-hour post showing that methylliberine may have had a greater increase in focus relative to baseline vs. PLA (p = 0.08, mean difference = 0.44 ± 0.24 cm, 95%CI: -0.06 to 0.93, d = 0.38). See
Table 3.
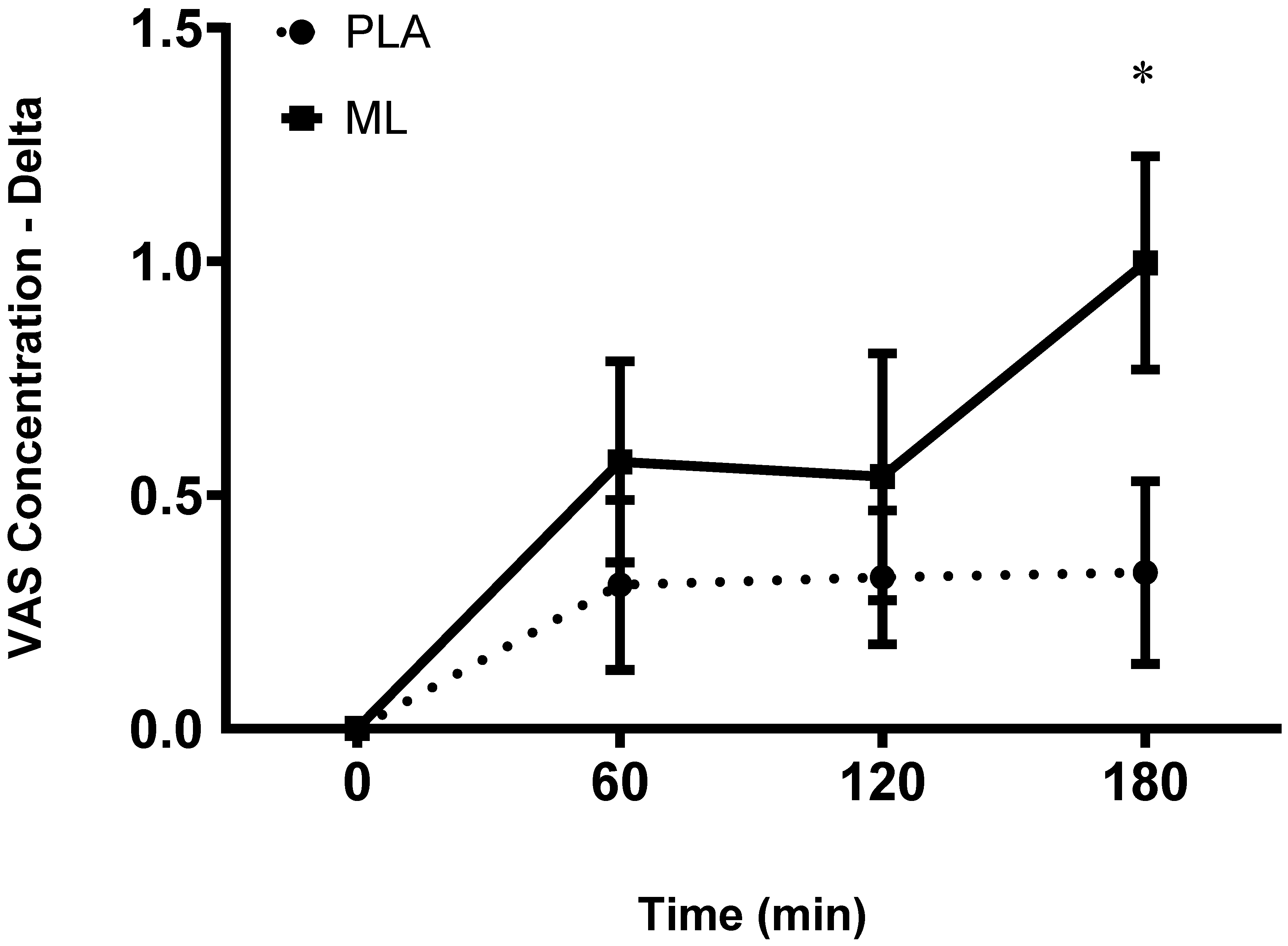
There were no differences in subjective ratings of concentration between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation (group: p = 0.89; time: p = 0.91; group x time: p = 0.98). There was a group x time interaction and a significant time effect after the 4
th dose (group: p = 0.17; time: p = 0.002 group x time: p = 0.03). Post hoc analysis showed improvements in concentration over time for methylliberine, but not for PLA. Specifically, for methylliberine, 1 hour (~10.2%, p = 0.045) and 3-hour (~15.3%, p = 0.004) post were significantly greater than the baseline time point. Also, the delta from baseline to 3-hours post was significantly larger in methylliberine vs. PLA (p = 0.006, mean difference = 0.70 ± 0.23 cm, 95%CI: 0.22 to 1.18, d = 0.68). See
Figure 3.
Figure 3.
The change in Concentration relative to the baseline time point (0 min) between groups. PLA: Placebo. ML: Methylliberine. *Significantly different from PLA (p ≤ 0.05).
Figure 3.
The change in Concentration relative to the baseline time point (0 min) between groups. PLA: Placebo. ML: Methylliberine. *Significantly different from PLA (p ≤ 0.05).
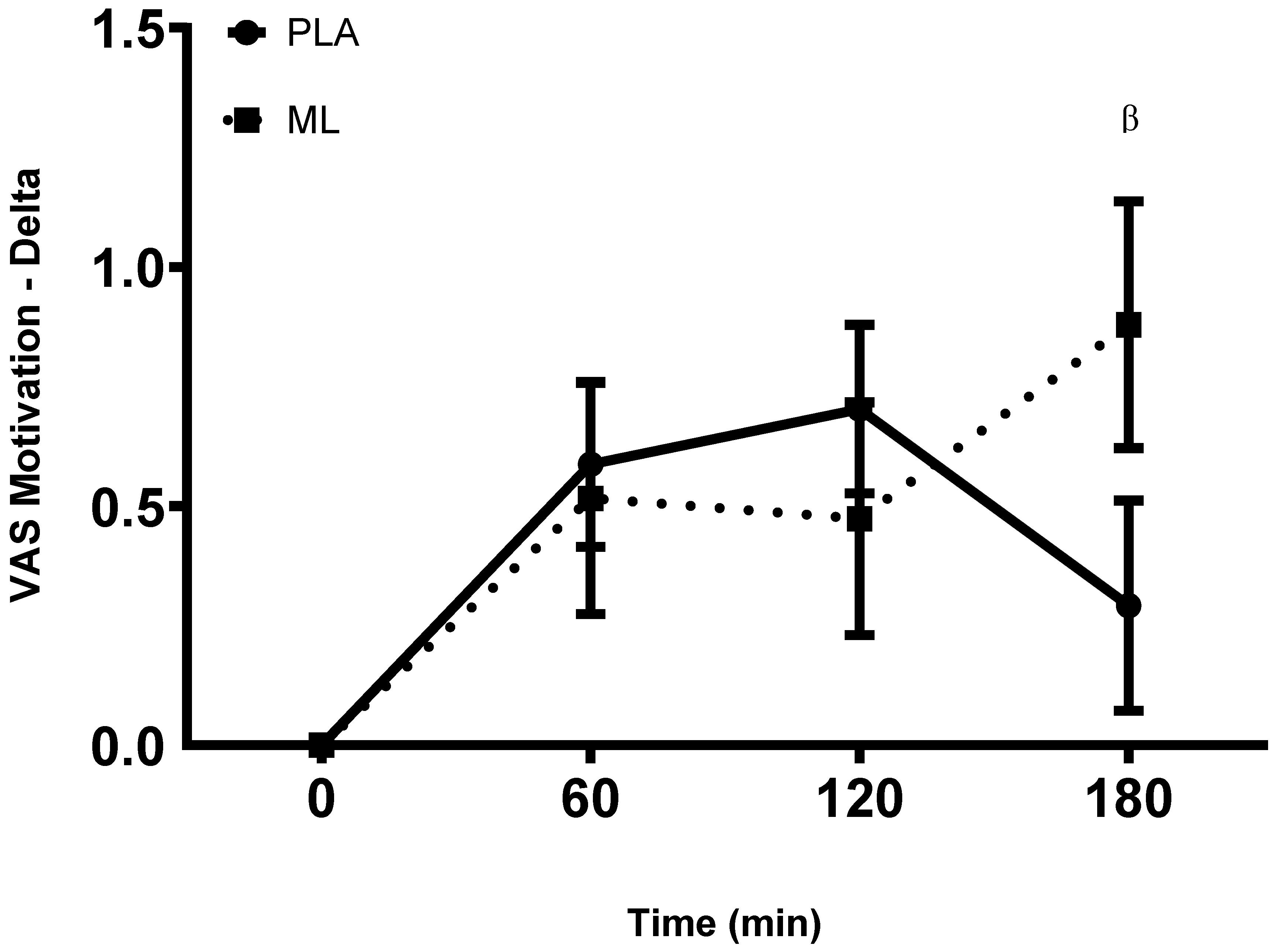
There were no differences in subjective ratings of motivation between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation (group: p = 0.45; time: p = 0.29; group x time: p = 0.63). There was a group x time interaction and a significant time effect after the 4
th dose (group: p = 0.19; time: p < 0.001, group x time: p = 0.02). Post hoc analysis showed greater motivation at 1 hour (~10.9%, p = 0.010) and 2-hours (~12.7%, p = 0.003) post vs. baseline within PLA and greater motivation at 3-hour post vs. baseline in methylliberine (~15.8%, p = 0.004). Also, the delta from baseline to 3-hours post may have been larger in methylliberine vs. PLA (p = 0.06, mean difference = 0.53 ± 0.27 cm, 95%CI: -0.02 to 1.08, d = 0.50). See
Figure 4.
Figure 4.
The change in Motivation relative to the baseline time point (0 min) between groups. PLA: Placebo. ML: Methylliberine. βStatistical trend from PLA (p ≤ 0.1).
Figure 4.
The change in Motivation relative to the baseline time point (0 min) between groups. PLA: Placebo. ML: Methylliberine. βStatistical trend from PLA (p ≤ 0.1).
There were no differences in subjective ratings of drive between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation (group: p = 0.37; time: p = 0.65; group x time: p = 0.97). However, there was a positive impact over time regardless of group after the 4
th dose (group: p = 0.45; time: p = 0.02; group x time: p = 0.36). Additionally, there were no differences in the deltas (p > 0.050) from the baseline timepoint after the 4
th dose for drive. See
Table 3.
There were no differences in subjective ratings of vigor between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation (group: p = 0.83; time: p = 0.97; group x time: p = 0.78). However, there was a trend for a group x time interaction and a significant time effect after the 4
th dose (group: p = 0.470; time: p = 0.002; group x time: p = 0.10). Post hoc analysis showed greater vigor 2 hours post vs. baseline within PLA (~10.5%, p < 0. 009) and greater vigor 3 hours post vs. baseline within methylliberine (~10.3%, p = 0.009). Additionally, there were no differences in the deltas (p > 0.050) from the baseline timepoint after the 4
th dose for vigor. See
Table 3.
There was a significant main effect of time between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation for positivity (group: p = 0.64; time: p = 0.01; group x time: p = 0.62) which showed a decrease in subjective ratings of positive outlook regardless of group. There was a trend for a group x time interaction and a significant time effect (group: p = 0.62; time: p < 0.001; group x time: p = 0.08) after the 4
th dose showing an increase in positive outlook regardless of group. Post hoc analysis showed greater positivity 2 hours post vs. baseline within PLA (~9.4%, p < 0.001) and greater positivity 3 hours post vs. baseline within methylliberine (~9.4%, p = 0.002). There was a trend for a delta showing positivity increasing to a greater degree from baseline to 3 hours post in methylliberine vs. PLA (p = 0.100, mean difference = 0.46 ± 0.27 cm, 95%CI: -0.09 to 1.01, d = 0.43). See
Table 3.
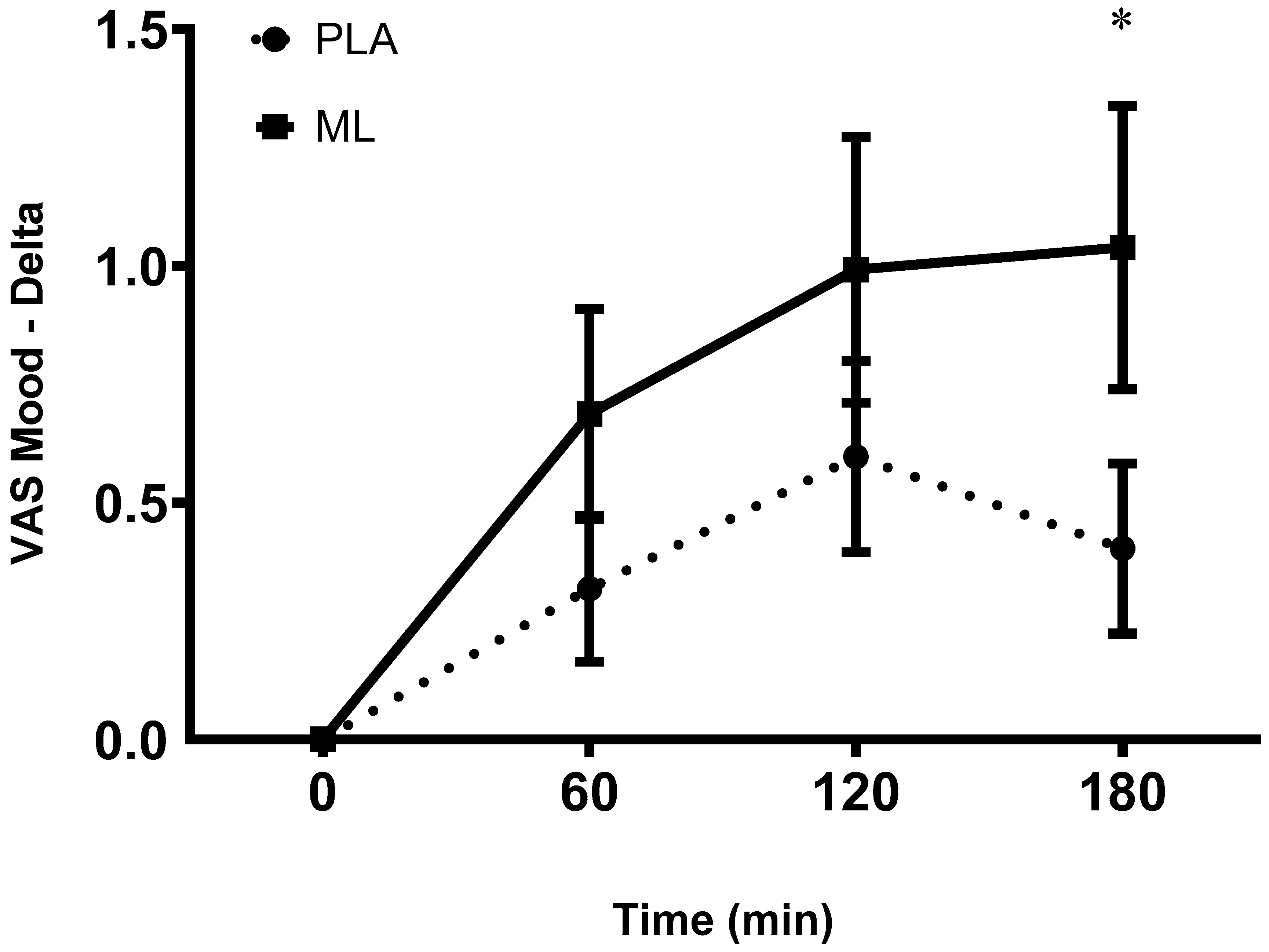
There was a significant main effect of time between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation for mood (group: p = 0.54; time: p = 0.01; group x time: p = 0.70) which showed a decrease in subjective ratings of mood regardless of group. There was a group x time interaction and a significant time effect (group: p = 0.48; time: p < 0.001; group x time: p = 0.04) after the 4
th dose. Post hoc analysis showed a more positive mood at 1-hour (~9.8%, p = 0.020), 2-hours (~14.8%, p = 0.004), and 3-hours (~16.4%, p = 0.004) post vs. baseline within methylliberine and at 2-hours post vs. baseline within PLA (~9.7%, p = 0.047). Also, the delta from baseline to 1 hour post (p = 0.05, mean difference = 0.38 ± 0.18 cm, 95%CI: -0.01 to 0.76, d = 0.43) and the delta from baseline to 3-hours post (p = 0.03, mean difference = 0.72 ± 0.30 cm, 95%CI: 1.35 to 2.37, d = 0.65) were significantly greater in methylliberine vs. PLA showing that methylliberine improved mood to a greater degree at 1 hour and 3 hours post ingestion. See
Figure 5.
Figure 5.
The change in Mood relative to the baseline time point (0 min) between groups. PLA: Placebo. *Significantly different from PLA (p ≤ 0.05).
Figure 5.
The change in Mood relative to the baseline time point (0 min) between groups. PLA: Placebo. *Significantly different from PLA (p ≤ 0.05).
There was a significant main effect of time between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation for well-being (group: p = 0.15; time: p = 0.01; group x time: p = 0.92) which showed a decrease in subjective ratings of well-being regardless of group. There was a trend for a group x time interaction and a significant time effect (group: p = 0.75; time: p < 0.001; group x time: p = 0.09) after the 4
th dose. Post hoc analysis showed a more positive rating of well-being at 2-hours (~14.1%, p = 0.013) and 3-hours (12.5%, p = 0.027) vs. baseline within methylliberine. Also, the delta from baseline to 3-hours post (p = 0.050, mean difference = 0.54 ± 1.34 cm, 95%CI: -0.01 to 1.10, d = 0.52) was significantly greater in methylliberine vs. PLA showing that well-being improved to a greater degree in methylliberine. See
Table 3.
There was a significant main effect of time between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation for the ability to tolerate stress (group: p = 0.89; time: p = 0.002; group x time: p = 0.90) which showed a decrease in the ability to tolerate stress regardless of group. There was a trend for a group x time interaction and a significant time effect (group: p = 0.29; time: p = 0.03; group x time: p = 0.08). Post hoc analysis showed a more positive rating in the ability to tolerate stress at 2-hours post vs. baseline within methylliberine (~12.3%, p = 0.010). Also, the delta from baseline to 3-hours post (p = 0.040, mean difference = 0.67 ± 0.30 cm, 95%CI: 0.04 to 1.29, d = 0.54) was significantly greater in methylliberine vs. PLA showing that the ability to tolerate stress was improved to a greater degree in methylliberine. See
Table 3.
3.4. Hemodynamics
There were no differences in heart rate levels between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation (group: p = 0.38; time: p = 0. 59; group x time: p = 0.58). There was a significant time effect (group: p = 0.501; time: p < 0.001; group x time: p = 0.421) after the 4th dose showing a decrease in heart rate regardless of group. There were no differences in deltas between groups at 60 min (p = 0.250), 120 min (p = 0.920), and 180 min (p = 0.230) post ingestion. See
Table 4.
Table 4.
Vitals on Baseline (Day 0) and Testing Visits (Day 4).
Table 4.
Vitals on Baseline (Day 0) and Testing Visits (Day 4).
| |
Heart Rate (bpm) |
SBP (mmHg) |
DBP (mmHg) |
| Time |
PLA |
ML |
PLA |
ML |
PLA |
ML |
| Day 0 |
71.8 ± 13.7 |
71.4 ± 11.9 |
122.0 ± 12.2 |
118.6 ± 12.9 |
77.1 ± 7.1 |
76.6 ± 10.2 |
0 min
(Day 4) |
71.6 ± 11.4 |
69.8 ± 11.2 |
120.6 ± 12.8 |
121.4 ± 16.0 |
75.3 ± 9.3 |
77.3 ± 10.0 |
60 min
(Day 4) |
66.5 ± 13.5 |
66.4 ± 11.8 |
118.2 ± 12.5 |
117.9 ± 12.9 |
76.2 ± 9.2 |
76.9 ± 8.8 |
120 min
(Day 4) |
66.4 ± 13.5 |
64.7 ± 9.9 |
119.2 ± 11.9 |
120.6 ± 13.5 |
79.5 ± 11.7* |
75.6 ± 9.1 |
180 min
(Day 4) |
65.7 ± 12.0 |
66.0 ± 10.9 |
121.6 ± 11.7 |
120.0 ± 12.5 |
77.8 ± 9.8 |
77.2 ± 9.1 |
There was a significant condition effect for systolic blood pressure levels between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation (group: p = 0.03; time: p = 0.72; group x time: p = 0.13). There were no acute differences after the 4
th dose (group: p = 0.914; time: p = 0.101; group x time: p = 0.495). There were no differences in deltas between groups at 60 min (p = 0.660), 120 min (p = 0.790), and 180 min (p = 0.300) post ingestion. See
Table 4.
There were no differences in diastolic blood pressure levels between the baseline visit and the baseline timepoint after 3 days of supplementation (group: p = 0.55; time: p = 0. 56; group x time: p = 0.25). When acute changes across time were evaluated in response to day 4 supplementation, a group x time interaction (p = 0.004) was present while the main effects for time (p = 0.367) and condition were not significant (p = 0.624). Post-hoc analysis using independent t-tests of the observed changes from baseline revealed no significant differences between groups after 60 min (p = 0.450) and 180 min (p = 0.120) however a significantly greater diastolic blood pressure was observed in PLA vs. methylliberine after 120 min (p = 0.001, mean difference = 5.84 ± 1.55 mmHg, 95% CI: 2.63, 9.05 mmHg, d = -0.84). See
Table 4.
4. Discussion
This investigation sought to examine the ingestion of methylliberine on cognitive performance and subjective feelings of well-being. Acute ingestion of methylliberine improved concentration, motivation, and mood more profoundly and sustained positive effects longer than PLA. Furthermore, acute ingestion of methylliberine may have improved well-being and the ability to tolerate stress while short-term supplementation of methylliberine (i.e., after 3 days) may have improved time to completion on the TMT-B. On the other hand, there were no acute differences in the cognitive performance measures between PLA and methylliberine. Interestingly, methylliberine had a positive impact on energy and sustained energy for women as compared to men which may have been driven by differences in body size/weight. There were negligible differences between treatments in vital signs apart from a higher diastolic blood pressure 2-hours post-ingestion during the PLA treatment. Lastly, both treatments were very well tolerated without any adverse events reported.
To our knowledge this is the first study evaluating the impact of independent ingestion of methylliberine on common cognitive function tests. The Stroop test measures working memory and attention control (Kane & Engle, 2003) while the TMT-B measures processing speed, sequencing, mental flexibility and visual–motor skills (Bowie & Harvey, 2006). Consistent with PLA, methylliberine did not significantly impact the neuropsychological assessments performed in this study (i.e., the Stroop test and TMT-B). Neither treatment improved Stroop test total score, accuracy, or reaction time, however there was a potential ~11% improvement in the TMT-B time to completion after 3 daily doses of methylliberine. This may suggest that longer periods of methylliberine use may be needed to optimize cognitive enhancements. Comparatively, independent ingestion of TeaCrine® (a closely related methylurate) was not able to improve cognitive measures of performance against PLA during a simulated soccer match (Bello et al., 2019), however caffeine was shown to decrease reaction times in a Stroop test interspersed with intermittent exercise in soccer players (C. Wang et al., 2020). Meanwhile, the combination of CMT has been reported to improve cognitive performance after gaming and go/no go tasks (Cintineo et al., 2022; La Monica et al., 2021; Tartar et al., 2021). These findings imply an additive/synergistic effect of combining caffeine (a methylxanthine) with Methylliberine and TeaCrine® (which are methylurates).
Methylliberine had a significant positive impact on mood, motivation, and concentration. Notably, an acute 100mg dose of methylliberine uniquely improved concentration by approximately 10.2% one-hour post-ingestion and approximately 15.3% three hours post-ingestion. Although PLA improved motivation 1- and 2-hours post ingestion and mood 2 hours post ingestion, methylliberine increased motivation 3 hours post ingestion and improved mood 1-, 2-, and 3 hours post ingestion. Methylliberine also had a larger positive change in mood from baseline to 1 hour and 3 hours post ingestion. The consistent improvements in methylliberine at the 3 hour mark is notable and unexpected given its short half-life of 1.5 ± 0.8hr (Y.-H. Wang et al., 2020). Other potential benefits observed with methylliberine include a more positive state of well-being 2- and 3-hours post ingestion, an enhanced ability to tolerate stress 2 hours post ingestion, and greater vigor and positivity 3 hours post ingestion. In opposition, a previous investigation did not report any influence after an acute 100mg dose methylliberine on attentiveness, energy, motivation, irritability, focus, and mood (Bloomer et al., 2020). However, the study treatments in the previous investigation (Bloomer et al., 2020) did not include a PLA treatment for comparison, therefore the impact methylliberine had on subjective feelings of affect are not definitive. A previous pilot study employing a 100mg and a 150mg dose of methylliberine alone or in conjunction with TeaCrine® vs. a PLA, observed significant main effects of time for alertness, productivity, and motivation to perform mental tasks after 1, 2, and 4 weeks of supplementation (Stratton et al., 2018). However, in addition to having a longer supplementation period than the current study the results of Stratton et al. (2018) provide vague differences over time regardless of group and do not indicate a positive or negative influence from either investigational product. In comparison, there have been mixed results observed with an acute dose of TeaCrine® showing increased energy, reduced fatigue, and possibly improved concentration (Ziegenfuss et al., 2017) while an 8-week dose regimen increased vigor (via POMS), but had negligible effects on focus, concentration, and energy (Taylor et al., 2016). Meanwhile, acute ingestion of CMT did not impact energy, alertness, focus, creativity, or decision making compared to PLA and caffeine (La Monica et al., 2021), but positively impacted mood compared to PLA in egamers (Tartar et al., 2021). Also, CMT did not differ from caffeine, TeaCrine®, or methylliberine alone or compared to combinations of TeaCrine® + methylliberine or methylliberine + caffeine in subjective energy, attentiveness, motivation, focus, or moodiness over a 48 hour period (Bloomer et al., 2020). Therefore, this is the first study demonstrating beneficial effects of methylliberine ingestion alone on several indices of overall well-being.
An interesting observation in the current investigation was the notable increases in energy and sustained energy that were unique to women. After an acute dose of methylliberine women had a greater increase in sustained energy and a potential increase in energy 1- and 3 hours post ingestion relative to baseline vs. PLA. Similarly, Taylor et al. (2016) noted increased levels of vigor from week 4 to week 8 during daily TeaCrine® ingestion that was unique to women. Previous observations on caffeine have observed sex specific impacts in physical performance (Mielgo-Ayuso et al., 2019) and memory (Zhang & Madan, 2021) potentially mediated by sex hormones’ influence on caffeine metabolism (Sisti et al., 2015). Meanwhile, there have not been any reported sex specific differences with CMT consumption. The observed differences in the current investigation could be due to men having a larger frame and greater body weight than women. On average, men ingested 1.27 mg/kg and women ingested a 1.47mg/kg of methylliberine. Future research on methylliberine may need to consider dosing relative to body weight, similar to how caffeine recommendations are often structured based on body weight (Guest et al., 2021).
Methylliberine had minimal effects on vitals. In fact, an increase in DBP was noted 2 hours after PLA ingestion while there were no changes over time under methylliberine. Therefore, the current investigation corroborates with previous findings showing no effect on hemodynamics with methylliberine ingestion (Bloomer et al., 2020; VanDusseldorp et al., 2020). Likewise, TeaCrine® did not impact hemodynamics over 8 weeks (Taylor et al., 2016) or in combination with methylliberine (VanDusseldorp et al., 2020) under acute or chronic conditions. An investigation assessing methylliberine, TeaCrine®, caffeine, and various combinations of the three, observed higher blood pressure only when caffeine was included in the treatment (Bloomer et al., 2020). However, it should be noted that the observed increases were small, transient, and within normal clinical limits.
Given that caffeine and TeaCrine® both act as adenosine receptor antagonists and increase dopamine transmission (Feduccia et al., 2012) which can impact behavioral activation and effort-related processes (Salamone et al., 2009, 2018), one would expect caffeine, TeaCrine®, and methylliberine to have similar physiological and performance impacts, however previous research (Bloomer et al., 2020; VanDusseldorp et al., 2020) and the current investigation have shown otherwise. Unfortunately, due to the limited scope of research on the novel compound (i.e., methylliberine) we cannot mechanistically deduce the observed effects. Therefore, additional studies on methylliberine should be undertaken to explore the potential of this unique compound. Given the observed differences in women with perceptions of energy status, future studies should also investigate sex effects and doses relative to body weight. Nonetheless, methylliberine may offer a viable non-habitual alternative for those sensitive to caffeine and looking for a positive impact on well-being.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.L., J.S., B.R.; project administration, B.R.; data curation, M.L, B.R., K.M., S.H., J.G., A.G.; formal analysis, M.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L.; writing—review and editing, M.L, J.S., B.R., K.M., S.H., J.G., A.G.; funding acquisition, J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded in part by Compound Solutions.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Genetic Alliance IRB on 9/30/22 (#CSI-08-2022-001) for human studies.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank all the participants that volunteered for this study and Dr. Chad Kersick for his constructive criticism of the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results. This study was conducted at The Center for Applied Health Sciences in Ohio, where Tim N. Ziegenfuss, PhD is a principal owner. While Dr. Ziegenfuss had no direct involvement in the data collection or statistical analyses of this study, he does have several granted patents on methylliberine. He is disclosing his intellectual property interests to maintain research integrity and transparency.
References
- Bello, M. L., Walker, A. J., McFadden, B. A., Sanders, D. J., & Arent, S. M. (2019). The effects of TeaCrine® and caffeine on endurance and cognitive performance during a simulated match in high-level soccer players. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 16(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-019-0287-6. [CrossRef]
- Bloomer, R., Butawan, M., & Pence, J. (2020). Acute impact of a single dose of Dynamine®, TeaCrine, caffeine, and their combination on systemic hemodynamics and associated measures in men and women. Medical Research Archives, 8(4). https://doi.org/10.18103/mra.v8i4.2062. [CrossRef]
- Bowie, C., & Harvey, P. (2006). Administration and interpretation of Trail Making Test. Nature Protocols, 1, 2277–2281. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.390. [CrossRef]
- Cintineo, H. P., Bello, M. L., Chandler, A. J., Cardaci, T. D., McFadden, B. A., & Arent, S. M. (2022). Effects of caffeine, methylliberine, and theacrine on vigilance, marksmanship, and hemodynamic responses in tactical personnel: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 19(1), 543–564. https://doi.org/10.1080/15502783.2022.2113339. [CrossRef]
- Daley, Butts-Lamb, P., & Padgett, W. (1983). Subclasses of adenosine receptors in the central nervous system: Interaction with caffeine and related methylxanthines. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00734999. [CrossRef]
- Feduccia, A. A., Wang, Y., Simms, J. A., Yi, H. Y., Li, R., Bjeldanes, L., Ye, C., & Bartlett, S. E. (2012). Locomotor activation by theacrine, a purine alkaloid structurally similar to caffeine: Involvement of adenosine and dopamine receptors. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 102(2), 241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2012.04.014. [CrossRef]
- Guest, N. S., VanDusseldorp, T. A., Nelson, M. T., Grgic, J., Schoenfeld, B. J., Jenkins, N. D. M., Arent, S. M., Antonio, J., Stout, J. R., Trexler, E. T., Smith-Ryan, A. E., Goldstein, E. R., Kalman, D. S., & Campbell, B. I. (2021). International society of sports nutrition position stand: Caffeine and exercise performance. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 18(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-020-00383-4. [CrossRef]
- Harmony, T., Fernández, T., Silva, J., Bernal, J., Díaz-Comas, L., Reyes, A., Marosi, E., Rodríguez, M., & Rodríguez, M. (1996). EEG delta activity: An indicator of attention to internal processing during performance of mental tasks. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 24(1), 161–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8760(96)00053-0. [CrossRef]
- He, H., Ma, D., Crone, L. B., Butawan, M., Meibohm, B., Bloomer, R. J., & Yates, C. R. (2017). Assessment of the Drug–Drug Interaction Potential Between Theacrine and Caffeine in Humans. Journal of Caffeine Research, 7(3), 95–102. https://doi.org/10.1089/jcr.2017.0006. [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A. R., & Rohwer, W. D. (1966). The stroop color-word test: A review. Acta Psychologica, 25, 36–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6918(66)90004-7. [CrossRef]
- Kane, M. J., & Engle, R. W. (2003). Working-memory capacity and the control of attention: The contributions of goal neglect, response competition, and task set to Stroop interference. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 132, 47–70. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.132.1.47. [CrossRef]
- La Monica, M. B., Listman, J. B., Donovan, I., Johnson, T. E., Heeger, D. J., & Mackey, W. E. (2021). Effects of TeaCrine® (Theacrine), DynamineTM (Methylliberine), and Caffeine on Gamer Psychomotor Performance in a First-Person Shooter Video Game Scenario. Journal of Exercise and Nutrition, 4(2). https://www.journalofexerciseandnutrition.com.
- Lee, K. A., Hicks, G., & Nino-Murcia, G. (1991). Validity and reliability of a scale to assess fatigue. Psychiatry Research, 36(3), 291–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1781(91)90027-M. [CrossRef]
- Lopez, H. L., Cesareo, K. R., Raub, B., Kedia, A. W., Sandrock, J. E., Kerksick, C. M., & Ziegenfuss, T. N. (2020). Effects of Hemp Extract on Markers of Wellness, Stress Resilience, Recovery and Clinical Biomarkers of Safety in Overweight, But Otherwise Healthy Subjects. Journal of Dietary Supplements, 17(5), 561–586. https://doi.org/10.1080/19390211.2020.1765941. [CrossRef]
- Lorca, C., Mulet, M., Arévalo-Caro, C., Sanchez, M. Á., Perez, A., Perrino, M., Bach-Faig, A., Aguilar-Martínez, A., Vilella, E., Gallart-Palau, X., & Serra, A. (2022). Plant-derived nootropics and human cognition: A systematic review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 0(0), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2021.2021137. [CrossRef]
- Malík, M., & Tlustoš, P. (2022). Nootropics as Cognitive Enhancers: Types, Dosage and Side Effects of Smart Drugs. Nutrients, 14(16), Article 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163367. [CrossRef]
- Mielgo-Ayuso, J., Marques-Jiménez, D., Refoyo, I., Del Coso, J., León-Guereño, P., & Calleja-González, J. (2019). Effect of Caffeine Supplementation on Sports Performance Based on Differences Between Sexes: A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 11(10), Article 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102313. [CrossRef]
- Mondal, G., Wang, Y.-H., Yates, R., Bloomer, R., & Butawan, M. (2022). Caffeine and Methylliberine: A Human Pharmacokinetic Interaction Study: Original Research. Journal of Exercise and Nutrition, 5(3). https://doi.org/10.53520/jen2022.103124. [CrossRef]
- Murbach, T. S., Glávits, R., Endres, J. R., Clewell, A. E., Hirka, G., Vértesi, A., Béres, E., & Szakonyiné, I. P. (2019). A Toxicological Evaluation of Methylliberine (Dynamine®). Journal of Toxicology, 2019, e4981420. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4981420. [CrossRef]
- Nigbur, R., Ivanova, G., & Stürmer, B. (2011). Theta power as a marker for cognitive interference. Clinical Neurophysiology, 122(11), 2185–2194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2011.03.030. [CrossRef]
- Pranav, J. (2013). A Review on Natural Memory Enhancers (Nootropics). Unique Journal of Engineering and Advanced Sciences, 1(1), 8–18.
- Ralevic, V., & Burnstock, G. (1998). Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacology Reviews, 50, 413–492.
- Salamone, J. D., Correa, M., Ferrigno, S., Yang, J.-H., Rotolo, R. A., & Presby, R. E. (2018). The Psychopharmacology of Effort-Related Decision Making: Dopamine, Adenosine, and Insights into the Neurochemistry of Motivation. Pharmacological Reviews, 70(4), 747–762. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.117.015107. [CrossRef]
- Salamone, J. D., Farrar, A. M., Font, L., Patel, V., Schlar, D. E., Nunes, E. J., Collins, L. E., & Sager, T. N. (2009). Differential actions of adenosine A1 and A2A antagonists on the effort-related effects of dopamine D2 antagonism. Behavioural Brain Research, 201(1), 216–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.02.021. [CrossRef]
- Scarpina, F., & Tagini, S. (2017). The Stroop Color and Word Test. Frontiers in Psychology, 8. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00557.
- Sheng, Y.-Y., Xiang, J., Wang, Z.-S., Jin, J., Wang, Y.-Q., Li, Q.-S., Li, D., Fang, Z.-T., Lu, J.-L., Ye, J.-H., Liang, Y.-R., & Zheng, X.-Q. (2020). Theacrine From Camellia kucha and Its Health Beneficial Effects. Frontiers in Nutrition, 7. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2020.596823.
- Sisti, J. S., Hankinson, S. E., Caporaso, N. E., Gu, F., Tamimi, R. M., Rosner, B., Xu, X., Ziegler, R., & Eliassen, A. H. (2015). Caffeine, Coffee, and Tea Intake and Urinary Estrogens and Estrogen Metabolites in Premenopausal Women. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 24(8), 1174–1183. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-15-0246. [CrossRef]
- Stratton, M. T., Holmes, A. J., Bailly, A. R., Modjeski, A. S., Barie, M., Serafini, P., Feito, Y., Mangine, G. T., Tuggle, K. R., Esmat, T. A., Hester, G. M., & VanDusseldorp, T. A. (2018). A72 Effect of DynamineTM with and without Teacrine® over four weeks of continuous use on cardiovascular function and psychometric parameters: A pilot study. Proceedings of the Fifteenth International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN) Conference and Expo, 15(Suppl 1):A72, 34. https://doi.org/doi: 10.1186/s12970-018-0256-5. [CrossRef]
- Tartar, J. L., Banks, J. B., Marang, M., Pizzo, F., Antonio, J., Tartar, J. L., Banks, J. B., Marang, M., Pizzo, F., & Antonio, J. (2021). A Combination of Caffeine, TeaCrine® (Theacrine), and Dynamine® (Methylliberine) Increases Cognitive Performance and Reaction Time Without Interfering With Mood in Adult Male Egamers. Cureus, 13(12). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.20534. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L., Mumford, P., Roberts, M., Hayward, S., Mullins, J., Urbina, S., & Wilborn, C. (2016). Safety of TeaCrine®, a non-habituating, naturally-occurring purine alkaloid over eight weeks of continuous use. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 13(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-016-0113-3. [CrossRef]
- Temple, J. L., Bernard, C., Lipshultz, S. E., Czachor, J. D., Westphal, J. A., & Mestre, M. A. (2017). The Safety of Ingested Caffeine: A Comprehensive Review. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 8. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00080.
- VanDusseldorp, T. A., Stratton, M. T., Bailly, A. R., Holmes, A. J., Alesi, M. G., Feito, Y., Mangine, G. T., Hester, G. M., Esmat, T. A., Barcala, M., Tuggle, K. R., Snyder, M., & Modjeski, A. S. (2020). Safety of Short-Term Supplementation with Methylliberine (Dynamine®) Alone and in Combination with TeaCrine® in Young Adults. Nutrients, 12(3), Article 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030654. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C., Zhu, Y., Dong, C., Zhou, Z., & Zheng, X. (2020). Effects of Various Doses of Caffeine Ingestion on Intermittent Exercise Performance and Cognition. Brain Sciences, 10(9), Article 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090595. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H., Mondal, G., Butawan, M., Bloomer, R. J., & Yates, C. R. (2020). Development of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) method for characterizing caffeine, methylliberine, and theacrine pharmacokinetics in humans. Journal of Chromatography B, 1155, 122278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2020.122278. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.-C., & Madan, C. R. (2021). How does caffeine influence memory? Drug, experimental, and demographic factors. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 131, 525–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.09.033. [CrossRef]
- Ziegenfuss, T. N., Habowski, S. M., Sandrock, J. E., Kedia, A. W., Kerksick, C. M., & Lopez, H. L. (2017). A Two-Part Approach to Examine the Effects of Theacrine (TeaCrine®) Supplementation on Oxygen Consumption, Hemodynamic Responses, and Subjective Measures of Cognitive and Psychometric Parameters. Journal of Dietary Supplements, 14(1), 9–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/19390211.2016.1178678. [CrossRef]
- Ziegenfuss, T. N., Kedia, A. W., Sandrock, J. E., Raub, B. J., Kerksick, C. M., & Lopez, H. L. (2018). Effects of an Aqueous Extract of Withania somnifera on Strength Training Adaptations and Recovery: The STAR Trial. Nutrients, 10(11), Article 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111807. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).