Submitted:
28 October 2023
Posted:
30 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Limited Scope: Existing surveys predominantly focus either on short-term weather forecasting or medium-to-long-term climate predictions. There is a notable absence of comprehensive surveys that endeavour to bridge these two-time scales. In addition, current investigations tend to focus narrowly on specific methods, such as simple neural networks, thereby neglecting some combination of methods.
- Lack of Model details: Many extant studies offer only generalized viewpoints and lack a systematic analysis of the specific model employed in weather and climate prediction. This absence creates a barrier to researchers aiming to understand the intricacies and efficacy of individual methods.
- Neglect of Recent Advances: Despite rapid developments in machine learning and computational techniques, existing surveys have not kept pace with these advancements. The paucity of information on cutting-edge technologies stymies the progression of research in this interdisciplinary field.
- Comprehensive scope: Unlike research endeavors that restrict their inquiry to a singular temporal scale, our survey provides a comprehensive analysis that amalgamates short-term weather forecasting with medium- and long-term climate predictions. In total, 20 models were surveyed, from which a select subset of eight were chosen for an in-depth scrutiny.These models are discerned as the industry’s avant-garde, thereby serving as invaluable references for researchers. For instance, the PanGu model exhibits a remarkable congruence with actual observational results, thereby illustrating the caliber of models included in our analysis
- In-Depth Analysis: Breaking new ground, this study delves into the intricate operational mechanisms of the eight focal models. We have dissected the operating mechanisms of these eight models, distinguishing the differences in their approaches and summarizing the commonalities in their methods through comparison. This comparison helps readers gain a deeper understanding of the efficacy and applicability of each model and provides a reference for choosing the most appropriate model for a given scenario.
- Identification of Contemporary Challenges and Future Work: The survey identifies pressing challenges currently facing the field, such as limited dataset of chronological seasons and complex climate change effects, and suggests directions for future work, including simulating dataset and physics-Based Constraint model. These recommendations not only add a forward-looking dimension to our research but also act as a catalyst for further research and development in climate prediction.
2. Background
3. Related work
| Symbol | Definition |
| v | velocity vector |
| t | time |
| fluid density | |
| p | pressure |
| dynamic viscosity | |
| gravitational acceleration vector | |
| intensity of radiation at frequency | |
| s | distance along the ray path |
| absorption coefficient at frequency | |
| emission coefficient at frequency | |
| absorption coefficient at frequency | |
| density of the medium | |
| Planck function at frequency | |
| expectation under the variational distribution | |
| latent variable | |
| observed data | |
| joint distribution of observed and latent variables | |
| variational distribution | |
| variational parameters | |
| G, F | Generators for mappings from simulated to real domain and vice versa. |
| Discriminators for real and simulated domains. | |
| Cycle consistency loss and Generative Adversarial Network loss. | |
| X, Y | Data distributions for simulated and real domains. |
| Weighting factor for the cycle consistency loss. |
3.1. Statistical method
3.2. Physical Models
4. Taxonomy of climate prediction applications
4.1. Climate prediction Milestone based on machine-learning.
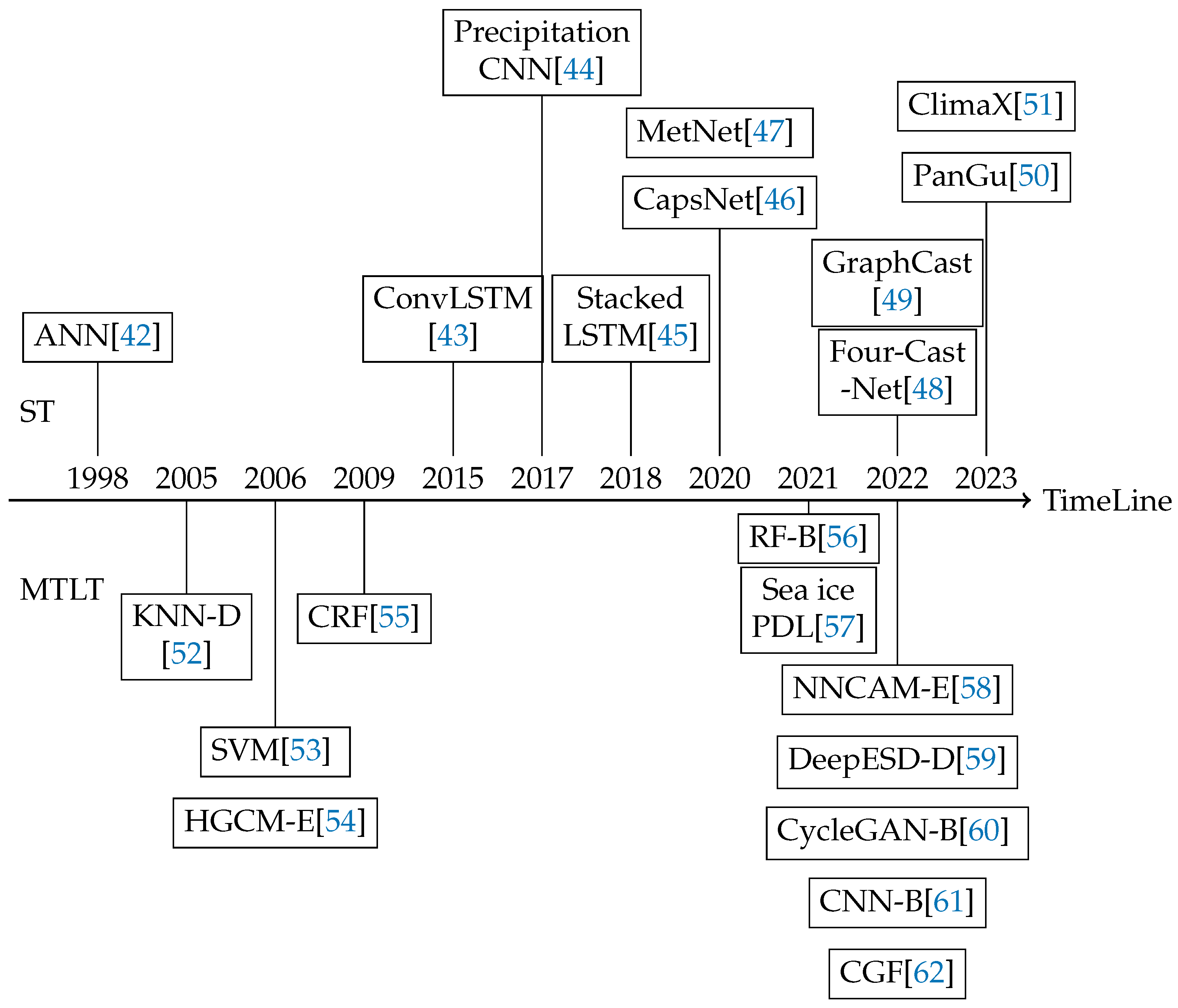
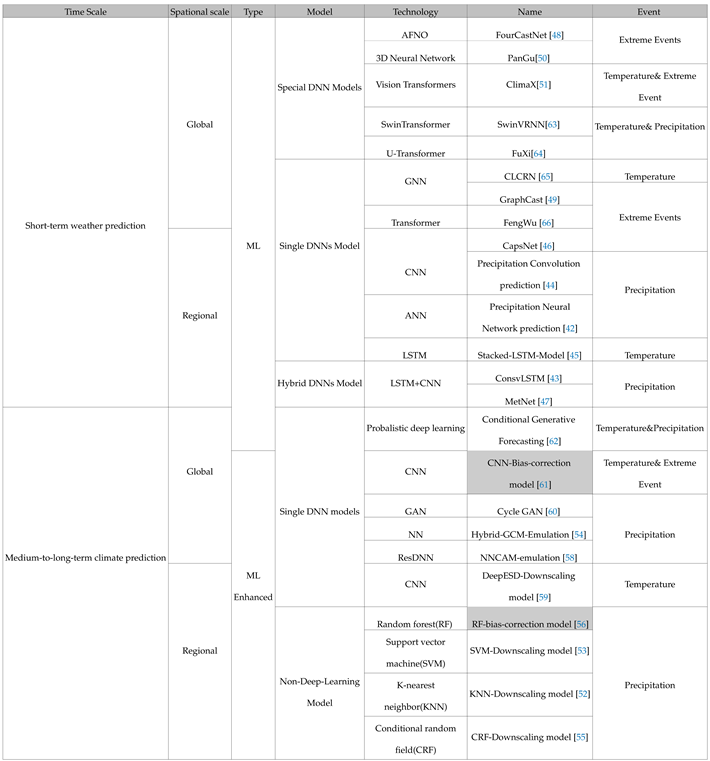
4.2. Classification of climate prediction methods
5. Short-term weather forecast
5.1. Model Design
- The Navier-Stokes Equations [74]: Serving as the quintessential descriptors of fluid motion, these equations delineate the fundamental mechanics underlying atmospheric flow.
- The Thermodynamic Equations [75]: These equations intricately interrelate the temperature, pressure, and humidity within the atmospheric matrix, offering insights into the state and transitions of atmospheric energy.
- Shortwave and Longwave Radiation Transfer Equations elucidate the absorption, scattering, and emission of both solar and terrestrial radiation, which in turn influence atmospheric temperature and dynamics.
- Empirical or Semi-empirical Convection Parameterization Schemes simulate vertical atmospheric motions initiated by local instabilities, facilitating the capture of weather phenomena like thunderstorms.
- Boundary-Layer Dynamics concentrate on the exchanges of momentum, energy, and matter between the Earth’s surface and the atmosphere, which are crucial for the accurate representation of surface conditions in the model.
- Land Surface and Soil/Ocean Interaction Modules simulate the exchange of energy, moisture, and momentum between the surface and the atmosphere, while also accounting for terrestrial and aquatic influences on atmospheric conditions.
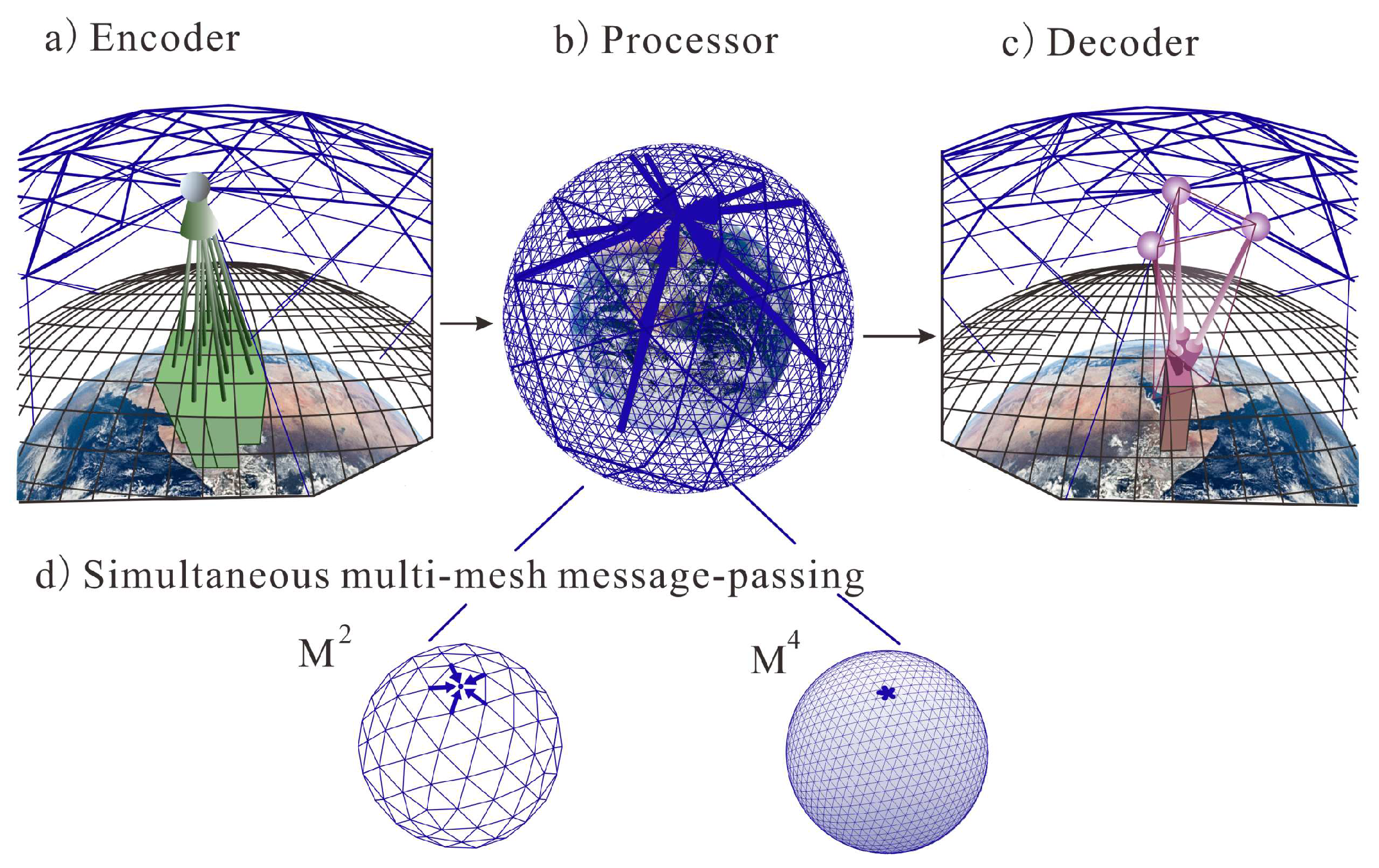
- Encoder: The encoder component maps the local region of the input data (on the original latitude-longitude grid) onto the nodes of the multigrid graphical representation. It maps two consecutive input frames of the latitude-longitude input grid, with numerous variables per grid point, into a multi-scale internal mesh representation. This mapping process helps the model better capture and understand spatial dependencies in the data, allowing for more accurate predictions of future weather conditions.
- Processor: This part performs several rounds of message-passing on the multi-mesh, where the edges can span short or long ranges, facilitating efficient communication without necessitating an explicit hierarchy. More specifically, the section uses a multi-mesh graph representation. It refers to a special graph structure that is able to represent the spatial structure of the Earth’s surface in an efficient way. In a multi-mesh graph representation, nodes may represent specific regions of the Earth’s surface, while edges may represent spatial relationships between these regions. In this way, models can capture spatial dependencies on a global scale and are able to utilize the power of GNNs to analyze and predict weather changes.
- Decoder: It then maps the multi-mesh representation back to the latitude-longitude grid as a prediction for the next time step.
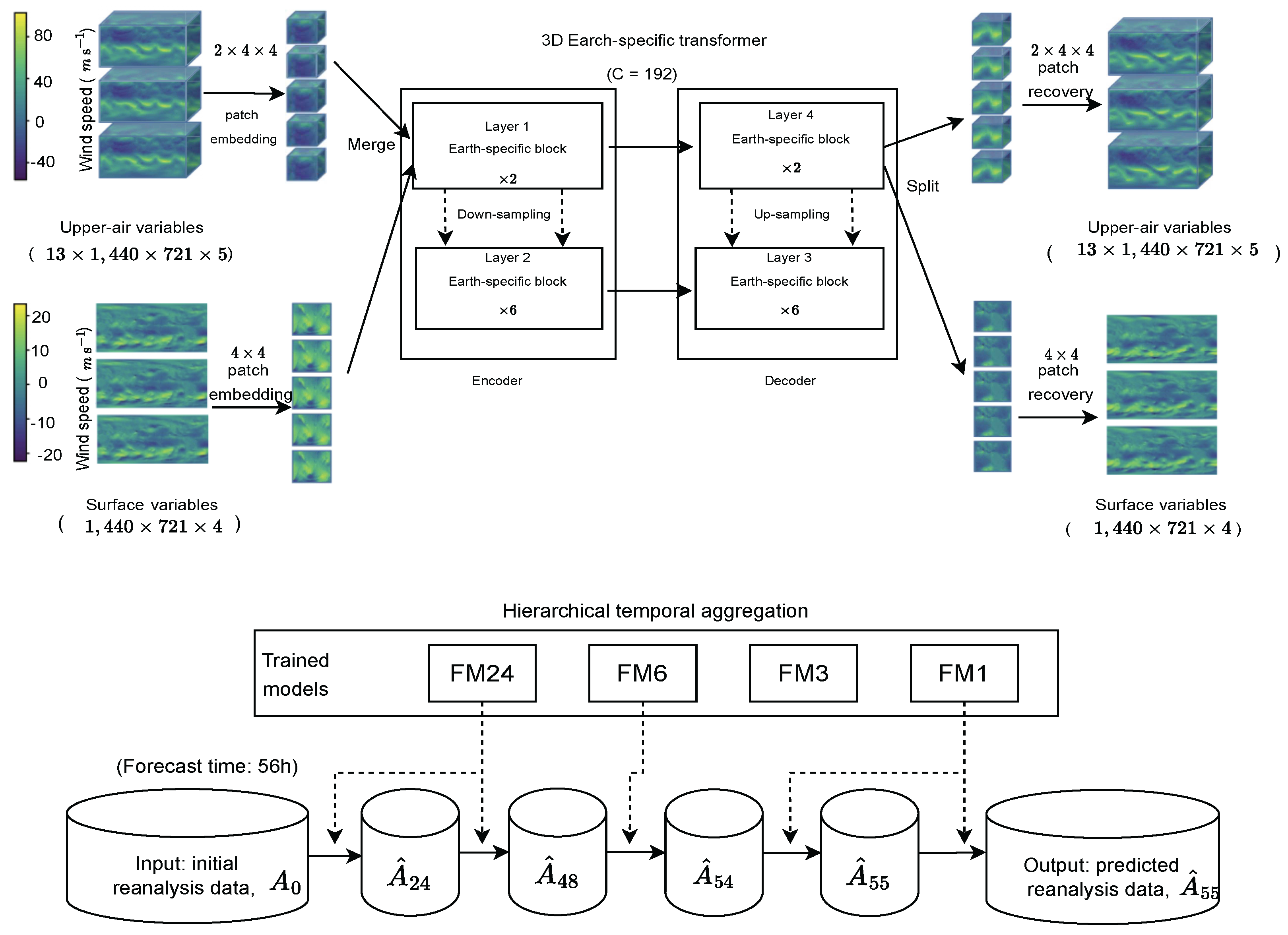
5.2. Result Analysis
6. Medium-to-long-term climate prediction
6.1. Model Design
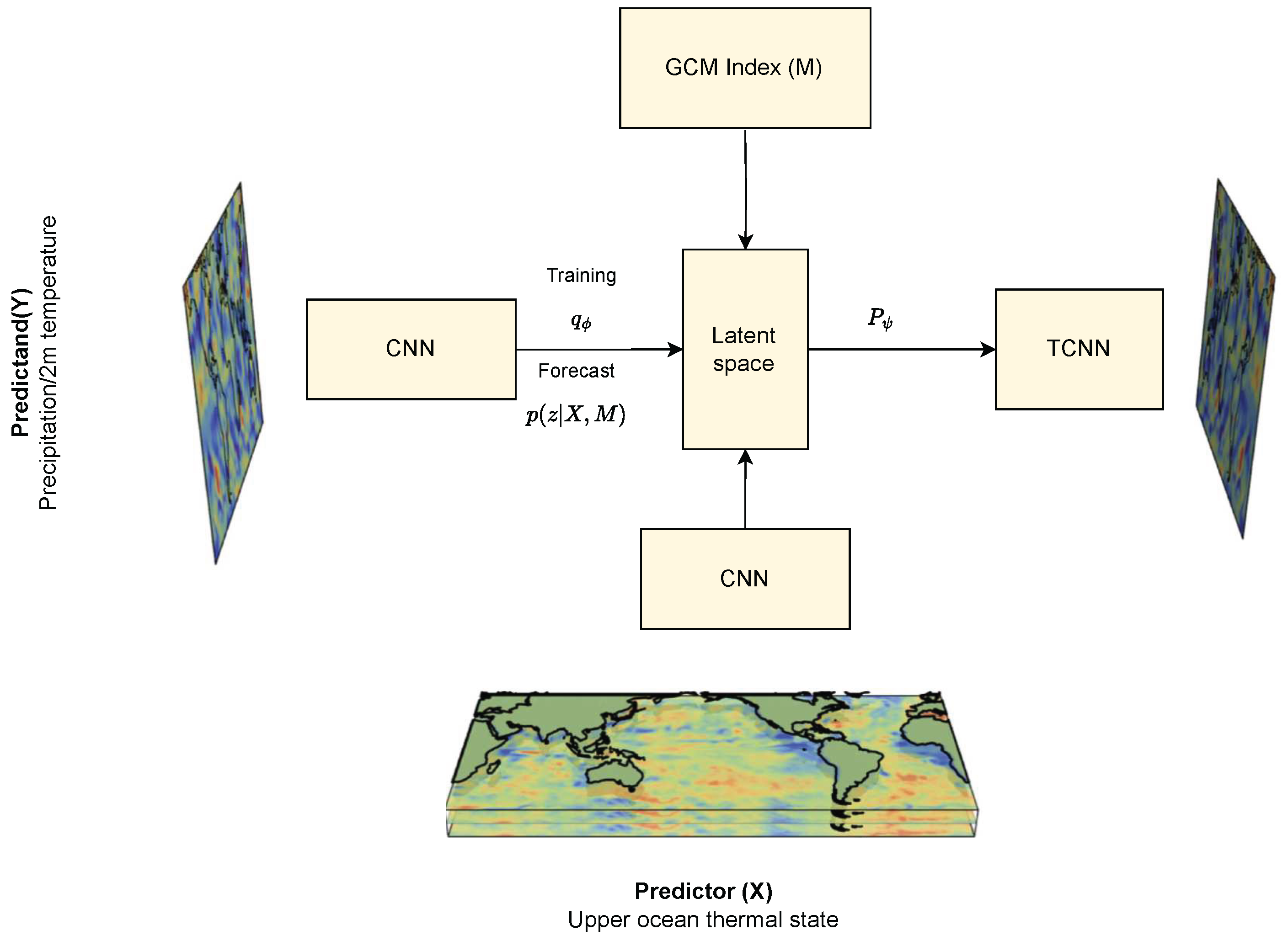
- Problem Definition: The goal is to approximate , a task challenged by high-dimensional geospatial data, data inhomogeneity, and a large dataset.
-
Model Specification:
- Random Variable z: A latent variable with a fixed standard Gaussian distribution.
- Parametric Functions : Neural networks for transforming z and approximating target and posterior distributions.
- Objective Function: Maximization of the Evidence Lower Bound (ELBO).
-
Training Procedure:
-
parametric functions .
- Training Objective (Maximize ELBO) [104]: The ELBO is defined as:with terms for reconstruction, regularization, and residual error.
- Optimization: Utilize variational inference, Monte Carlo reparameterization, and Gaussian assumptions.
-
- Forecasting: Generate forecasts by sampling , the likelihood of , and using the mean of for an average estimate.
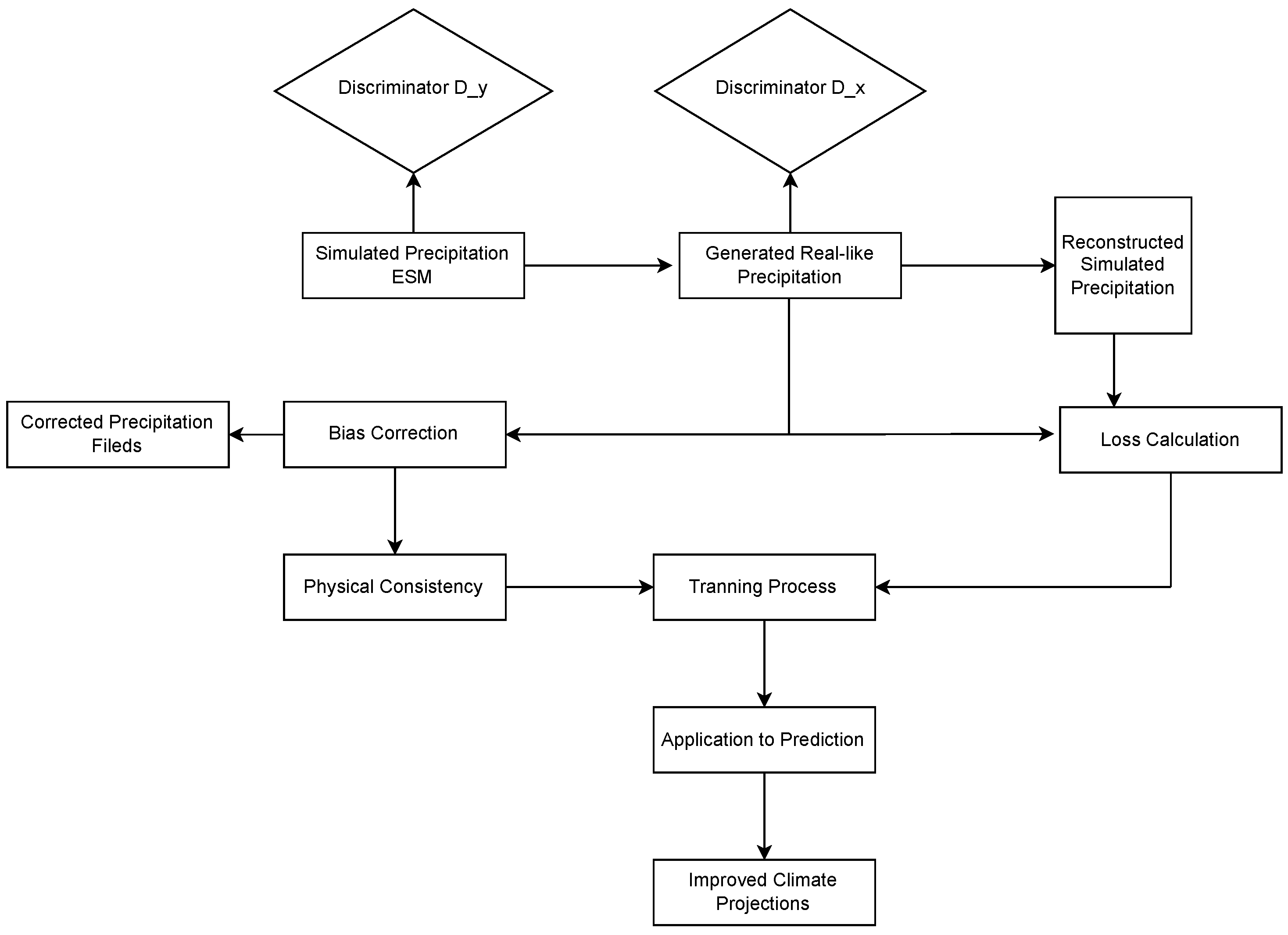
- Two Generators: The CycleGAN model includes two generators. Generator G learns the mapping from the simulated domain to the real domain, and generator F learns the mapping from the real domain to the simulated domain [106].
- Two Discriminators: There are two discriminators, one for the real domain and one for the simulated domain. Discriminator encourages generator G to generate samples that look similar to samples in the real domain, and discriminator encourages generator F to generate samples that look similar to samples in the simulated domain.
- Cycle Consistency Loss: To ensure that the mappings are consistent, the model enforces the following condition through a cycle consistency loss: if a sample is mapped from the simulated domain to the real domain and then mapped back to the simulated domain, it should get a sample similar to the original simulated sample. Similarly, if a sample is mapped from the real domain to the simulated domain and then mapped back to the real domain, it should get a sample similar to the original real sample.
- Training Process: The model is trained to learn the mapping between these two domains by minimizing the adversarial loss and cycle consistency loss between the generators and discriminators.
- Application to Prediction: Once trained, these mappings can be used for various tasks, such as transforming simulated precipitation data into forecasts that resemble observed data.
- Reference Model: SPCAM. SPCAM serves as the foundational GCM and is embedded with Cloud-Resolving Models (CRMs) to simulate microscale atmospheric processes like cloud formation and convection. SPCAM is employed to generate "target simulation data," which serves as the training baseline for the neural networks. The use of CRMs is inspired by recent advancements in data science, demonstrating that machine learning parameterizations can potentially outperform traditional methods in simulating convective and cloud processes.
- Neural Networks: ResDNNs. ResDNNs, a specialized form of deep neural networks, are employed for their ability to approximate complex, nonlinear relationships. The network comprises multiple residual blocks, each containing two fully connected layers with Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activations. ResDNNs are designed to address the vanishing and exploding gradient problems in deep networks through residual connections, offering a stable and effective gradient propagation mechanism. This makes them well-suited for capturing the complex and nonlinear nature of atmospheric processes.
- Subgrid-Scale Physical Simulator. Traditional parameterizations often employ simplified equations to model subgrid-scale processes, which might lack accuracy. In contrast, the ResDNNs are organized into a subgrid-scale physical simulator that operates independently within each model grid cell. This simulator takes atmospheric states as inputs and outputs physical quantities at the subgrid scale, such as cloud fraction and precipitation rate.
6.2. Result Analysis
7. Discussion
7.1. Overall comparison
7.2. Challenge
7.3. Future work
- Simulate the dataset using statistic methods or physical methods
- Combining statistical knowledge with machine learning methods to enhance the interpretability of patterns
- Consider the introduction of physics-based constraints into deep learning models to produce more accurate and reliable results.
- Accelerating Physical Model Prediction with machine learning knowledge
8. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbe, C. The physical basis of long-range weather forecasts. Mon. Weath. Rev. 1901, 29, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Capra, L.; Wolfson, O.; Yang, H. Urban computing: concepts, methodologies, and applications. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST) 2014, 5, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gneiting, T.; Raftery, A.E. Weather forecasting with ensemble methods. Science 2005, 310, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapiou, A. Remote sensing heritage in a petabyte-scale: satellite data and heritage Earth Engine applications. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2017, 10, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendre, M. R.; Thool, R. C.; Thool, V. R. Big data in precision agriculture: Weather forecasting for future farming. NGCT. IEEE 2015, 744–750. [Google Scholar]
- Zavala, V. M.; Constantinescu, E. M.; Krause, T. On-line economic optimization of energy systems using weather forecast information. Journal of Process Control 2009, 1725–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmi, Vaino, et al. "Economic value of weather forecasts on transportation–Impacts of weather forecast quality developments to the economic effects of severe weather." EWENT FP7 project, no.490 (2012).
- Russo Jr, J.A. The economic impact of weather on the construction industry of the United States. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 1966, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badorf, F.; Kai, H. The impact of daily weather on retail sales: An empirical study in brick-and-mortar stores. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services 2020, 101921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K. Environmental hazards: assessing risk and reducing disaster. Routledge 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, G. L.; et al. Advances in application of climate prediction in agriculture. Agricultural systems 2001, 515–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, Gilvan, Rodrigo Raad, and Lucélia Raad. "Welfare consequences of persistent climate prediction errors on insurance markets against natural hazards." Estudos Econômicos (São Paulo), no.49 (2019): 235-264.
- McNamara, D.E.; Andrew, K. A coupled physical and economic model of the response of coastal real estate to climate risk. Nature Climate Change 2013, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleerekoper, L.; Van Esch, M.; Salced, T.B. How to make a city climate-proof, addressing the urban heat island effect. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 2012, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaján, Eva, and Jarkko Saarinen. "Tourism, climate change and adaptation: A review." Current Issues in Tourism, no.16.2 (2013): 167-195.
- de Freitas, C.R. Tourism climatology: evaluating environmental information for decision making and business planning in the recreation and tourism sector. international Journal of Biometeorology 2003, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessai, Suraje, et al. "Climate prediction: a limit to adaptation." Adapting to climate change: thresholds, values, governance, no.64 (2009): 78.
- Reichstein, M.; Camps-Valls, G.; Stevens, B.; Jung, M.; Denzler, J.; Carvalhais, N. et al.; et al. Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science. Nature 2019, 566, 195–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, L.; Wain, A. Predicting the Future, Vol. V, pp. 1–195. Cambridge Univ. Press (1993).
- Hantson, S.; et al. The status and challenge of global fire modelling. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 3359–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racah, E.; Beckham, C.; Maharaj, T.; et al. ExtremeWeather: A large-scale climate dataset for semi-supervised detection, localization, and understanding of extreme weather events. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2017, 3402–3413. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Zhao, P.; Pan, B.; et al. A nowcasting model for the prediction of typhoon tracks based on a long short term memory neural network. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 2018, 37, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, Y. G.; Kim, J. H.; Luo, J. J. Deep learning for multi-year ENSO forecasts. Nature 2019, 573, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Li, X.; Ren, K.; Song, J.; Xu, Z.; Deng, K.; Wang, X. Deep Learning-Based Weather Prediction: A Survey. Big Data Research 2021, 23, 100178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichstein, M.; Camps-Valls, G.; Stevens, B.; et al. Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science. Nature 2019, 566, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockhause, M.; Lautenschlager, M. CMIP6 data citation of evolving data. Data Sci. J. 2017, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, W. W. Machine Learning Methods in the Environmental Sciences: Neural Networks and Kernels; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Krasnopolsky, V. M.; Fox-Rabinovitz, M. S.; Chalikov, D. V. New Approach to Calculation of Atmospheric Model Physics: Accurate and Fast Neural Network Emulation of Longwave Radiation in a Climate Model. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 1370–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnopolsky, V. M.; Fox-Rabinovitz, M. S.; Belochitski, A. A. Using ensemble of neural networks to learn stochastic convection parameterizations for climate and numerical weather prediction models from data simulated by a cloud resolving model. Adv. Artif. Neural Syst. 2013, 2013, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, F.; Morcrette, J-J.; Chéruy, F.; Scott, N.A. Use of a neural-network-based long-wave radiative-transfer scheme in the ECMWF atmospheric model. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society 2000, 126, 761–776. [Google Scholar]
- V.M. Krasnopolsky, M.S. Fox-Rabinovitz, Y.T. Hou, S.J. Lord, and A.A. Belochitski, Accurate and fast neural network emulations of model radiation for the NCEP coupled climate forecast system: Climate simulations and seasonal predictions, Monthly Weather Review, vol. 138, no. 5, pp. 1822–1842, 2010.
- H.L. Tolman, V.M. Krasnopolsky, and D.V. Chalikov, Neural network approximations for nonlinear interactions in wind wave spectra: direct mapping for wind seas in deep water, Ocean Modelling, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 253–278, 2005.
- Markakis, E.; Papadopoulos, A.; Perakakis, P. Spatiotemporal Forecasting: A Survey. arXiv preprint 2018, arXiv:1808.06571. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C.; Ljung, G.M. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Kolovos, A. Spatial and Spatio-Temporal Geostatistical Modeling and Kriging; Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Fan, Z.; Zhu, H. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Air Quality and Its Application in LASG/IAP Climate System Model. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters 2011, 4, 204–210. [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield, C. The Analysis of Time Series: An Introduction, 7th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Stull, R. Meteorology for Scientists and Engineers, 3rd ed.; Brooks/Cole: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yuval, J.; O’Gorman, P.A. Machine Learning for Parameterization of Moist Convection in the Community Atmosphere Model. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2020, 117, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Gagne, D.J.; Haupt, S.E.; Nychka, D.W. Machine Learning for Spatial Environmental Data. Meteorological Monographs 2020, 59, 9–1. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, Q.; Shi, X.; Zhu, Y. A Multi-Model Deep Learning Ensemble Method for Rainfall Prediction. Journal of Hydrology 2020, 584, 124579. [Google Scholar]
- Kuligowski, R. J.; Barros, A. P. Localized precipitation forecasts from a numerical weather prediction model using artificial neural networks. Weather and Forecasting 1998, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
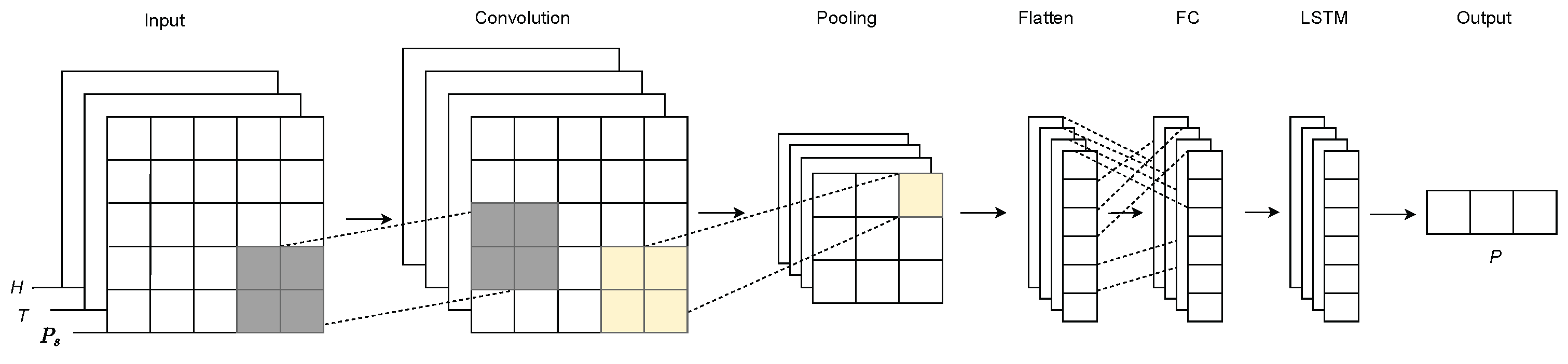
- Xingjian, S.; et al. Convolutional LSTM Network: A Machine Learning Approach for Precipitation Nowcasting. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.04214. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, M.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, K.; Huang, J.; Shi, X.; Wang, X.; Chu, W. A short-term rainfall prediction model using multi-task convolutional neural networks, in: Data Mining (ICDM), IEEE International Conference on, IEEE, 2017, pp. 395–404.
- Karevan, Z.; Suykens, J.A. Spatio-temporal stacked lstm for temperature prediction in weather forecasting. arXiv arXiv:1811.06341.
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Nabizadeh, E.; Hassanzadeh, P. Analog Forecasting of extreme-causing weather patterns using deep learning. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems 2020, 12, e2019MS001958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; et al. MetNet: A Neural Weather Model for Precipitation Forecasting. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.12140. [Google Scholar]
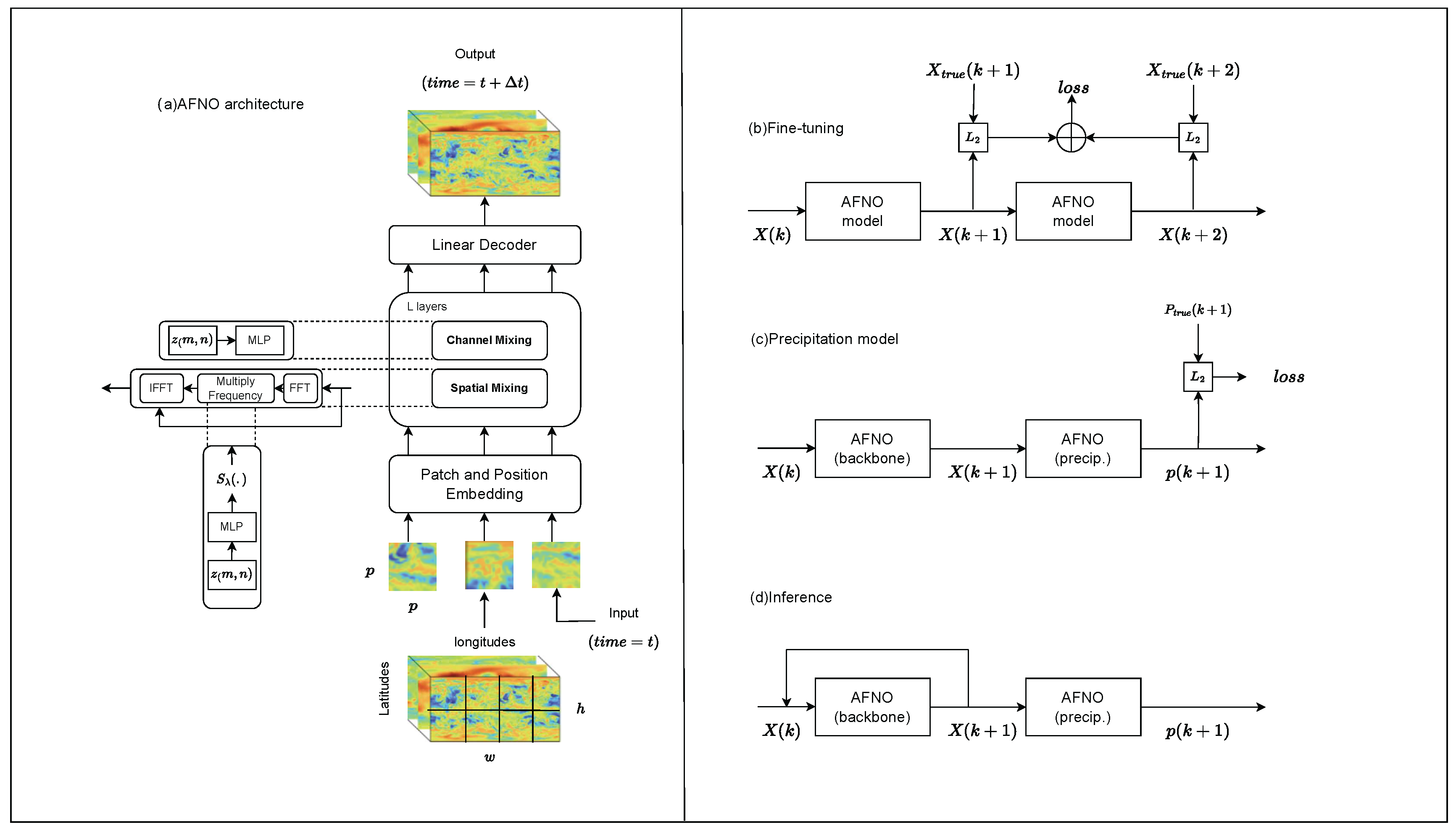
- J. Pathak et al., "FourCastNet: A Global Data-Driven High-Resolution Weather Model Using Adaptive Fourier Neural Operators," arXiv, February 22, 2022.
- Lam, R.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, A.; Willson, M.; et al. GraphCast: Learning skillful medium-range global weather forecasting. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.12794. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, K.; Xie, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Gu, X.; Tian, Q. Accurate Medium-Range Global Weather Forecasting with 3D Neural Networks. Nature 2023, 619, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Brandstetter, J.; Kapoor, A.; et al. ClimaX: A foundation model for weather and climate. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10343. [Google Scholar]
- Gangopadhyay, S.; Clark, M.; Rajagopalan, B. "Statistical downscaling using K-nearest neighbors," Water Resources Research 41, no. 2 (2005). Publisher: Wiley Online Library.
- Tripathi, S.; Srinivas, V.V.; Nanjundiah, R. S. Downscaling of precipitation for climate change scenarios: a support vector machine approach. Journal of hydrology 2006, 330, 621–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnopolsky, V. M.; Fox-Rabinovitz, M. S. Complex hybrid models combining deterministic and machine learning components for numerical climate modeling and weather prediction. Neural Networks 2006, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raje, D.; Mujumdar, P.P. "A conditional random field–based downscaling method for assessment of climate change impact on multisite daily precipitation in the Mahanadi basin," Water Resources Research 45, no. 10 (2009). Publisher: Wiley Online Library.
- Zarei, M.; Najarchi, M.; Mastouri, R. "Bias correction of global ensemble precipitation forecasts by Random Forest method," Earth Science Informatics 14 (2021): 677–689. Publisher: Springer.
- Andersson, T. R.; Hosking, J. S.; Pérez-Ortiz, M.; Paige, B.; Elliott, A.; Russell, C.; Law, S.; et al. Seasonal Arctic Sea Ice Forecasting with Probabilistic Deep Learning. Nature Communications 2021, 5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Xin and Han, Yilun and Xue, Wei and Yang, Guangwen and Zhang, Guang. Stable climate simulations using a realistic general circulation model with neural network parameterizations for atmospheric moist physics and radiation processes. Geoscientific Model Development 2022, 3923–3940.
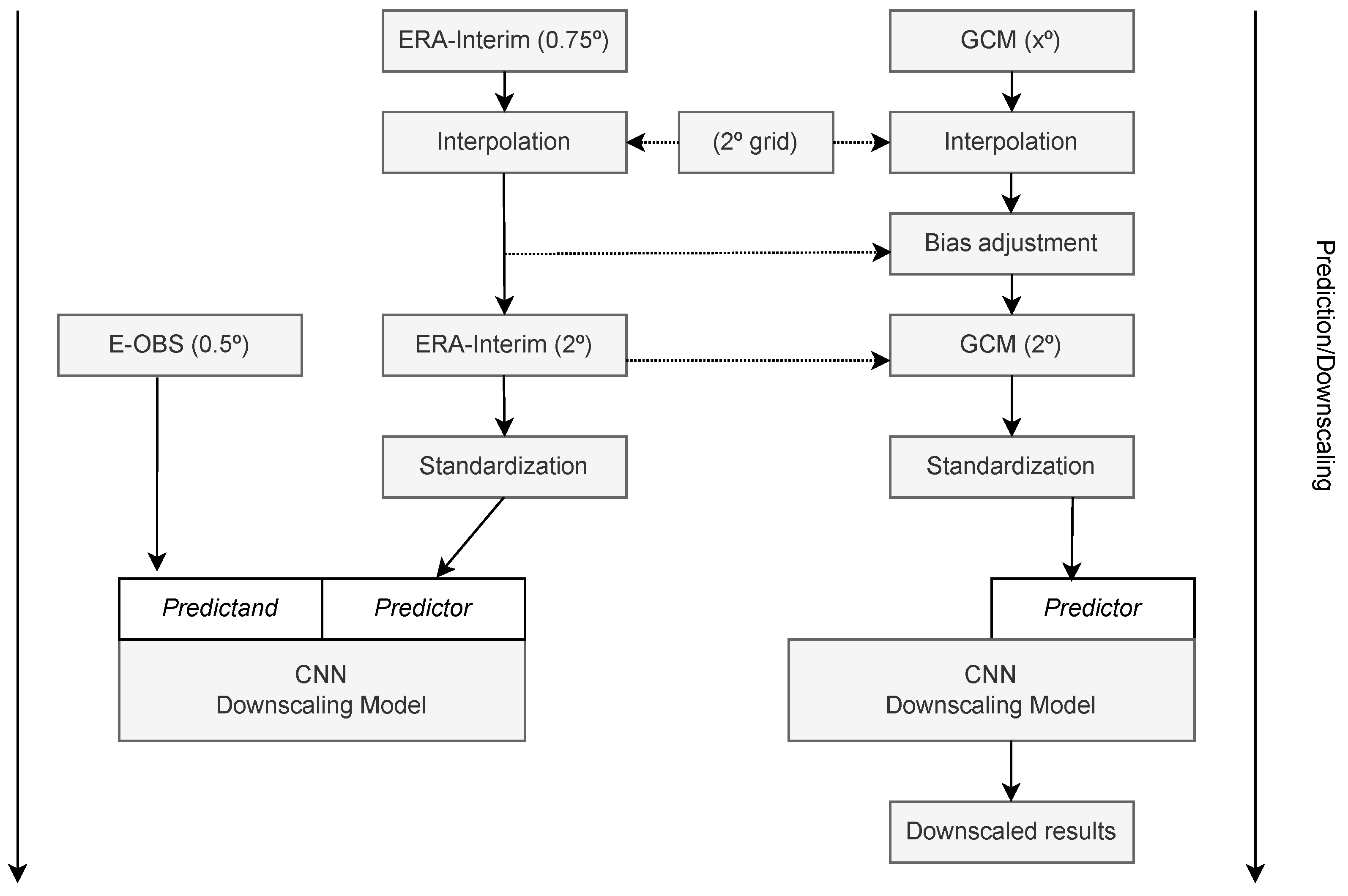
- Baño-Medina, J.; Manzanas, R.; Cimadevilla, E.; Fernández, J.; González-Abad, J.; Cofiño, A. S.; Gutiérrez, J. M. Downscaling Multi-Model Climate Projection Ensembles with Deep Learning (DeepESD): Contribution to CORDEX EUR-44. Geoscientific Model Development 2022, 15, 6747–6758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, P.; Lange, S.; Boers, N. Deep Learning for bias-correcting comprehensive high-resolution Earth system models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2301.01253. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Tian, D. "On deep learning-based bias correction and downscaling of multiple climate models simulations," Climate dynamics 59, no. 11-12 (2022): 3451–3468. Publisher: Springer.
- Pan, B.; Anderson, G. J.; Goncalves, A.; Lucas, D. D.; Bonfils, C. J. W.; Lee, J. Improving Seasonal Forecast Using Probabilistic Deep Learning. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems 2022, 14, e2021MS002766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; et al. SwinVRNN: A Data-Driven Ensemble Forecasting Model via Learned Distribution Perturbation. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems 2023, 15, e2022MS003211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, F.; et al. FuXi: A cascade machine learning forecasting system for 15-day global weather forecast. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.12873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Gao, Z.; Xu, Y.; et al. Conditional local convolution for spatio-temporal meteorological forecasting. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2022, 7470–7478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Han, T.; Gong, J.; et al. FengWu: Pushing the Skillful Global Medium-range Weather Forecast beyond 10 Days Lead. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.02948. [Google Scholar]
- C.O. de Burgh-Day and T. Leeuwenburg, Machine Learning for numerical weather and climate modelling: a review, EGUsphere, vol. 2023, pp. 1–48, 2023.
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2012, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, D.; Müller, A.; Behnke, S. Evaluation of pooling operations in convolutional architectures for object recognition. International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks 2010, 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Racah, E.; Correa, J.; Khosrowshahi, A.; Lavers, D.; Kunkel, K.; Wehner, M.; Collins, W. Application of deep convolutional neural networks for detecting extreme weather in climate datasets. arXiv preprint 2016, arXiv:1605.01156. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Warde-Farley, D.; Mirza, M.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Maxout networks. International Conference on Machine Learning 2013, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Marion, Martine, and Temam, Roger. Navier-Stokes equations: Theory and approximation. Handbook of numerical analysis, 6, 503–689 (1998). Elsevier.
- Iacono, M.J.; Mlawer, E.J.; Clough, S.A.; Jean-Jacques, M. Impact of an improved longwave radiation model, RRTM, on the energy budget and thermodynamic properties of the NCAR community climate model, CCM3. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 2000, 105, 14873–14890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Marinucci, M.R.; Bates, G.T. Development of a second-generation regional climate model (RegCM2). Part I: Boundary-layer and radiative transfer processes. Monthly Weather Review 1993, 121, 2794–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, G.W.; Carslaw, K.S.; Spracklen, D.V.; Ridley, D.A.; Manktelow, P.T.; Chipperfield, M.P.; Pickering, S.J.; Johnson, C.E. Description and evaluation of GLOMAP-mode: A modal global aerosol microphysics model for the UKCA composition-climate model. Geoscientific Model Development 2010, 3, 519–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y. Guo, C. Shao, and A. Su, “Comparative Evaluation of Rainfall Forecasts during the Summer of 2020 over Central East China,” Atmosphere, vol. 14, no. 6, Article 992, 2023. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/14/6/992.
- Y. Guo, C. Shao, and A. Su, “Investigation of Land–Atmosphere Coupling during the Extreme Rainstorm of 20 July 2021 over Central East China,” Atmosphere, vol. 14, no. 10, Article 1474, 2023. 20 July. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/14/10/1474.
- Bauer, P.; Alan, T.; Gilbert, B. The Quiet Revolution of Numerical Weather Prediction. Nature 2015, 525, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A. et al., Attention is All You Need, NeurIPS, 2017.
- Ho, J.; et al. Axial-DeepLab: Stand-Alone Axial-Attention for Panoptic Segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:2003.07853. [Google Scholar]
- Schmit, T. J.; et al. A closer look at the ABI on the GOES-R series. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 2017, 681–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Z. Li, N. Kovachki, K. Azizzadenesheli, B. Liu, K. Bhattacharya, A. Stuart, and A. Anandkumar, "Fourier Neural Operator for Parametric Partial Differential Equations," in International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2021a.
- J. Guibas, M. Mardani, Z. Li, A. Tao, A. Anandkumar, and B. Catanzaro, "Adaptive Fourier Neural Operators: Efficient token mixers for transformers," in International Conference on Representation Learning (to appear), 22. 20 April.
- Rasp, S.; et al. Weatherbench: a benchmark data set for data-driven weather forecasting. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems 2022, 12, e2020MS002203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasp, S.; Thuerey, N. Purely data-driven medium-range weather forecasting achieves comparable skill to physical models at similar resolution. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.08626. [Google Scholar]
- Weyn, J.A.; et al. Sub-seasonal forecasting with a large ensemble of deep-learning weather prediction models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.05107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasp, S.; et al. Weatherbench: a benchmark data set for data-driven weather forecasting. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems 2020, 12, e2020MS002203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Z. Liu et al., "Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows," in Proc. International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 10012–10022, IEEE, 2021.
- A. Dosovitskiy et al., "An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929, 2020.
- Váňa, F.; Düben, P.; Lang, S.; Palmer, T.; Leutbecher, M.; Salmond, D.; Carver, G. Single precision in weather forecasting models: An evaluation with the IFS. Monthly Weather Review 2017, 145, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC, 2013: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA.
- Flato, G., et al. 2013: Evaluation of Climate Models. In: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA.
- Washington, W. M., & Parkinson, C. L. (2005). An Introduction to Three-Dimensional Climate Modeling. University Science Books.
- Giorgi, F.; Gutowski, W. J. Regional Dynamical Downscaling and the CORDEX Initiative. Annual Review of Environment and Resources 2015, 40, 467–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, D. A.; et al. Climate Models and Their Evaluation. In Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, United Kingdom; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, K. E.; Stouffer, R. J.; Meehl, G. A. An overview of CMIP5 and the experiment design. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 2012, 93, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, Y.-G.; Kim, J.-H.; Luo, J.-J. Deep Learning for Multi-Year ENSO Forecasts. Nature 2019, 573, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Shen, Y.; Sun, J. Spatial–temporal ensemble forecasting (STEFS) of high-resolution temperature using machine learning models. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems 2019, 11, 2961–2973. [Google Scholar]
- Mukkavilli, S., Perone, C. S., Rangapuram, S. S., & Müller, K. R. (2020). Distribution regression forests for probabilistic spatio-temporal forecasting. In International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML).
- Mylonas, A.; Bontempi, G.; Panagakis, Y. Stochastic Deep Learning for Short-Term Load Forecasting. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, G.; Charlton-Perez, A.; Lee, R.; Inness, P. Challenges and progress in probabilistic forecasting of convective phenomena: The 2016 GFE/EUMETSAT/NCEP/SPC severe convective weather workshop. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 2016, 97, 1829–1835. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D. P.; Welling, M. Auto-encoding variational bayes. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Krasting, J. P., John, J. G., Blanton, C., McHugh, C., Nikonov, S., Radhakrishnan, A., ... Zhao, M. (2018). NOAA-GFDL GFDL-ESM4 model output prepared for CMIP6 CMIP. Earth System Grid Federation. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-Y., Park, T., Isola, P., & Efros, A. A. (2017). Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 2223–2232).
- Brands, S.; Herrera, S.; Fernández, J.; Gutiérrez, J. M. How well do CMIP5 Earth System Models simulate present climate conditions in Europe and Africa? Clim. Dynam. 2013, 41, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vautard, R.; Kadygrov, N.; Iles, C.; et al. Evaluation of the large EURO-CORDEX regional climate model ensemble. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2021, 126, e2019JD032344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boé, J.; Somot, S.; Corre, L.; Nabat, P. Large discrepancies in summer climate change over Europe as projected by global and regional climate models: causes and consequences. Clim. Dynam. 2020, 54, 2981–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baño-Medina, J.; Manzanas, R.; Gutiérrez, J. M. Configuration and intercomparison of deep learning neural models for statistical downscaling. Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 13, 2109–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y. Title, Journal, Year.
- Baño-Medina, J.; Manzanas, R.; Gutiérrez, J. M. Configuration and intercomparison of deep learning neural models for statistical downscaling. Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 13, 2109–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D. P.; Uppala, S. M.; Simmons, A. J.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornes, R. C.; van der Schrier, G.; van den Besselaar, E. J. M.; Jones, P. D. An Ensemble Version of the E-OBS Temperature and Precipitation Data Sets. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2018, 123, 9391–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baño-Medina, J.; Manzanas, R.; Gutiérrez, J. M. On the suitability of deep convolutional neural networks for continentalwide downscaling of climate change projections. Clim. Dynam. 2021, 57, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraun, D.; Widmann, M.; Gutiérrez, J. M.; et al. VALUE: A framework to validate downscaling approaches for climate change studies. Earths Future 2015, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrac, M.; Ayar, P. Influence of Bias Correcting Predictors on Statistical Downscaling Models. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2016, 56, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P. M.: Modelling Seasonality and Trends in Daily Rainfall Data, in: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 10, MIT Press, Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), 985–991, ISBN 0-262-10076-2, 1998.
- Cannon, A. J. Probabilistic Multisite Precipitation Downscaling by an Expanded Bernoulli–Gamma Density Network. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 1284–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoof, J. T.; Pryor, S. C. Downscaling temperature and precipitation: a comparison of regression-based methods and artificial neural networks. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 773–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraun, D.; Widmann, M. Statistical Downscaling and Bias Correction for Climate Research; Cambridge University Press: Online, 2018; ISBN 9781107588783. [Google Scholar]
- Vrac, M.; Stein, M.; Hayhoe, K.; Liang, X.-Z. A general method for validating statistical downscaling methods under future climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, L18701, L18701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Martín, D.; Manzanas, R.; Brands, S.; Herrera, S.; Gutiérrez, J. M. Reassessing Model Uncertainty for Regional Projections of Precipitation with an Ensemble of Statistical Downscaling Methods. J. Climate 2017, J. Climate, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Chacón, D.; Barfus, K.; Bernhofer, C. Climate change projections and extremes for Costa Rica using tailored predictors from CORDEX model output through statistical downscaling with artificial neural networks. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Time Scale | Domains | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | The timing for sowing and harvesting; Irrigation and fertilization plans. [5] |
|
| Energy | Predicts output for wind and solar energy. [6] | |
| Transportation | Road traffic safety; Rail transport; Aviation and maritime industries. [7] |
|
| Construction | Project plans and timelines; Safe operations. [8] | |
| Short Term | Retail and Sales | Adjusts inventory based on weather forecasts. [9] |
| Tourism and Entertainment |
Operations of outdoor activities and tourist attractions. [16] |
|
| Environment and Disaster Management |
Early warnings for floods, fires, and other natural disasters. [10] |
|
| Agriculture | Long-term land management and planning. [11] | |
| Insurance | Preparations for future increases in types of disasters, such as floods and droughts. [12] |
|
| Real Estate | Assessment of future sea-level rise or other climate-related factors. [13] |
|
| Medium - Long Term | Urban Planning | Water resource management. [14] |
| Tourism | Long-term investments and planning, such as deciding which regions may become popular tourist destinations in the future. [15] |
|
| Public Health | Long-term climate changes may impact the spread of diseases. [17] |
 |
| Model | Forecast- timeliness |
Z500 RMSE(7 days) | Z500 ACC(7 days) | Training-complexity | Forecasting-speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MetNet [47] | 8 hours | - | - | 256 Google- TPU-accelerators (16-days-training) |
Fewer seconds |
| FourCastNet [48] | 7 days | 595 | 0.762 | 4 A100-GPU | 24-hour forecast for 100 members in 7 seconds |
| GraphCast [49] | 9.75 days | 460 | 0.825 | 32 Cloud-TPU-V4 (21-days-training) | 10-days-predication within 1 minute |
| PanGu [50] | 7 days | 510 | 0.872 | 192 V100-GPU (16-days-training) | 24-hours-global- prediction in 1.4s for each GPU |
| IFS [92] | 8.5 days | 439 | 0.85 | - | - |
| Name | Categories | Metrics | ESM | This model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CycleGAN [60] | Bias correction | MAE | 0.241 | 0.068 |
| DeepESD [59] | Downscaling | Euclidean Distance to Observations in PDF | 0.5 | 0.03 |
| CGF[62] | Prediction | ACC | 0.31 | 0.4 |
| NNCAM [58] | Emulation | Speed | 1 | 30 times speed-up |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




