Submitted:
25 September 2023
Posted:
25 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extraction and Field Virus Detection
2.3. PCR for Meq Oncogene
2.4. Cloning and Sequencing
2.5. Genetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Profiles of Collected Samples
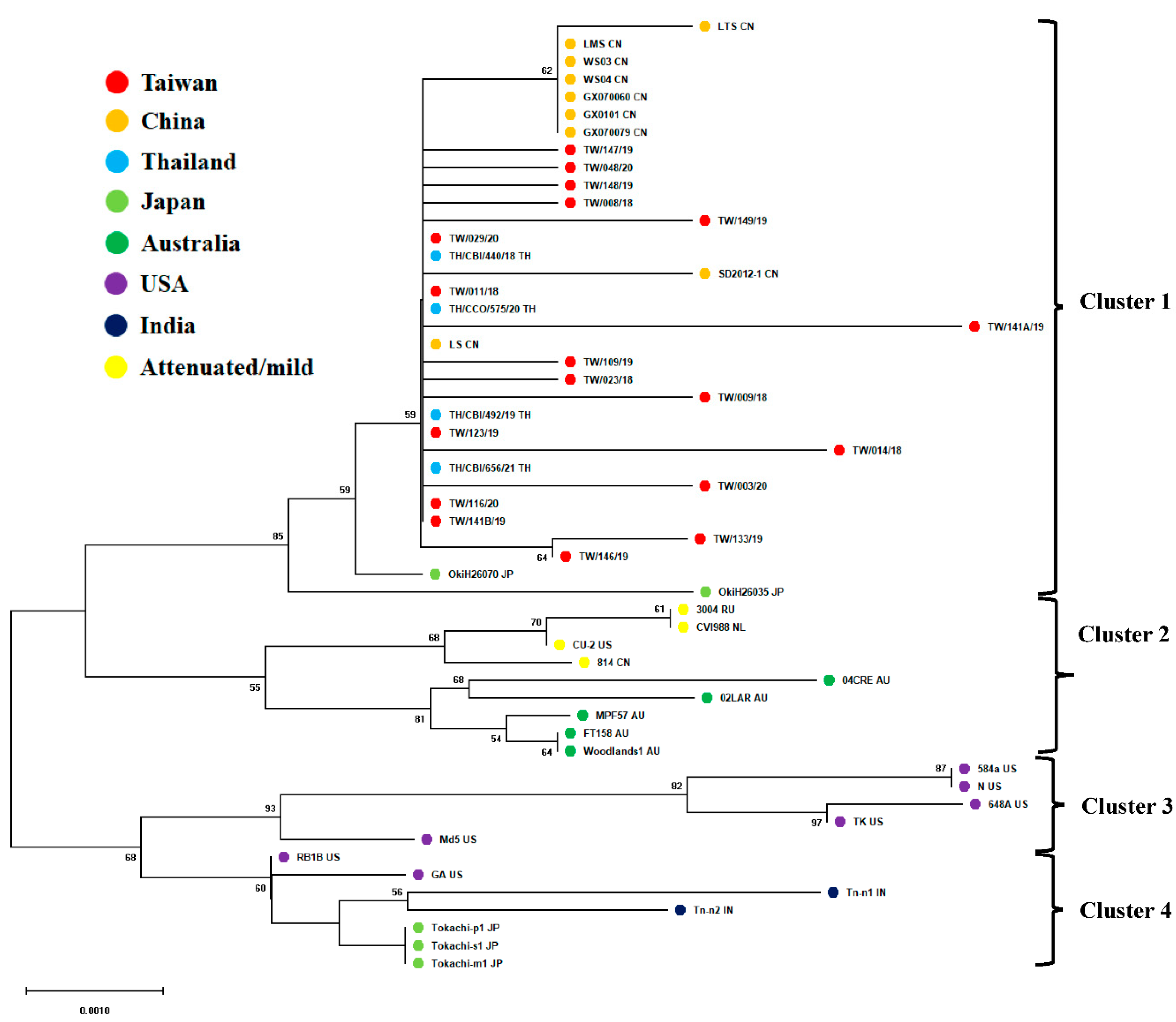
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of Meq Oncogenes of Taiwanese MDV-1 Isolates
3.3. Molecular Characterization of Meq Oncoproteins of Taiwanese MDV-1 Isolates
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethics Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calnek, B.W. Pathogenesis of Marek’s disease virus infection. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2001, 255, 25-55;. [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D. A.; Cairns, C.; Jones, M. J.; Bell, A.; Salathé, R. M.; Baigent, S. J.; Nair, V. K.; Dunn, P. A.; Read, A. F. Industry-wide surveillance of Marek’s disease virus on commercial poultry farms. Avian Dis. 2017, 61, 153-164;. [CrossRef]
- Bulow, V. V.; Biggs, P. M. Differentiation between strains of Marek’s disease virus and turkey herpesvirus by immunofluorescence assay. Avian Pathol. 1975, 4, 133-146;. [CrossRef]
- Jarosinski, K. W.; Tischer, B. K.; Trapp, S.; Osterrieder, N. Marek’s disease virus: lytic replication, oncogenesis and control. Expert Rev. Vaccines. 2006, 5, 761-772;. [CrossRef]
- Witter, R. L. Increased virulence of Marek’s disease virus field isolates. Avian Dis. 1997, 41, 149-163.
- Witter, R. L.; Calnek, B. W.; Buscaglia, C.; Gimeno, I. M.; Schat, K. A. Classification of Marek’s disease viruses according to pathotype: philosophy and methodology. Avian Pathol. 2005, 34: 75-90;. [CrossRef]
- Bertzbach, L. D.; Conradie, A. M.; You, Y.; Kaufer, B. B. Latest insights into Marek’s disease virus pathogenesis and tumorigenesis. Cancers (Basel). 2020, 12, 647;. [CrossRef]
- Yehia, N.; El-Sayed, H. S.; Omar, S. E.; Erfan, A.; Amer, F. Genetic evolution of Marek’s disease virus in vaccinated poultry farms. Vet. World. 2021, 14, 1342-1353;. [CrossRef]
- Ongor, H.; Timurkaan, N.; Abayli, H.; Karabulut, B.; Kalender, H.; Tonbak, S.; Eroksuz, H.; Cetinkaya, B. First report of serotype-1 Marek’s disease virus (MDV-1) with oncogenic form in backyard turkeys in Turkey: a molecular analysis study. BMC Vet Res. 2022, 18: 30;. [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Lee, L.; Liu, J. L.; Kung, H. J.; Tillotson, J. K. Marek’s disease virus encodes a basic-leucine zipper gene resembling the fos/jun oncogenes that is highly expressed in lymphoblastoid tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1992, 89, 4042-4046;. [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Li, X.; Shen, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Shao, D.; Jin, Y.; Chen, H.; Ding, C.; Li, L.; Chen, P.; Ma, Z. The Meq oncoproteins of Marek’s disease virus interacts with p53 and inhibits its transcriptional and apoptotic activities. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 348;. [CrossRef]
- Shamblin, C. E.; Greene, N.; Arumugaswami, V.; Dienglewicz, R. L.; Parcells, M. S. Comparative analysis of Marek’s disease virus (MDV) glycoprotein-, lytic antigen pp38- and transformation antigen Meq-encoding genes: association of meq mutations with MDVs of high virulence. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 102, 147-167;. [CrossRef]
- Renz, K. G.; Cooke, J.; Clarke, N.; Cheetham, B. F.; Hussain, Z.; Islam, A. F. M. F.; Tannock, G. A.; Walkden-Brown, S. W. Pathotyping of Australian isolates of Marek’s disease virus and association of pathogenicity with meq gene polymorphism. Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 161-176;. [CrossRef]
- Mescolini, G.; Lupini, C.; Felice, V.; Guerrini, A.; Silveira, F.; Cecchinato, M.; Catelli, E. Molecular characterization of the meq gene of Marek’s disease viruses detected in unvaccinated backyard chickens reveals the circulation of low- and high-virulence strains. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 3130-3137;. [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J. R.; Pyrkosz, A. B.; Steep, A.; Cheng, H. H. Identification of Marek’s disease virus genes associated with virulence of US strains. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1132-1139;. [CrossRef]
- Bayoumi, M.; El-Saied, M.; Ahmed, B.; El-Mahdy, M.; Amer, H. Gallid Alphaherpesvirus 2 in the Egyptian turkeys: Molecular characterization and establishment of a universal system for phylogenetic classification. Intervirology. 2021, 64, 156-164;. [CrossRef]
- Murata, S.; Machida, Y.; Isezaki, M.; Maekawa, N.; Okagawa, T.; Konnai, S.; Ohashi, K. Genetic characterization of a Marek’s disease virus strain isolated in Japan. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 186;. [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zeb, J.; Hussain, S.; Aziz, M. U.; Circella, E.; Casalino, G.; Camarda, A.; Yang, G.; Buchon, N.; Sparagano, O. A review on the Marek’s disease outbreak and its virulence-related meq genovariation in Asia between 2011-2021. Animals (Basel). 2022, 12, 540;. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z-H.; Teng, M.; Luo, J.; Wang, X-W.; Ding, K.; Yu, L-L.; Su, J-W.; Chi, J-Q.; Zhao, P.; Hu, B.; Zhang, G-P.; Liu, J-X. Molecular characteristics and evolutionary analysis of field Marek’s disease virus prevalent in vaccinated chick flocks in recent years in China. Virus Genes. 2013, 47, 282-291;. [CrossRef]
- Kannaki, T. R.; Priyanka, E.; Nishitha, Y.; Krishna, S. V.; Haunshi, S.; Subbiah, M. Molecular detection and phylogenetic analysis of Marek’s disease virus virulence-associated genes from vaccinated flocks in southern India reveals circulation of virulent MDV genotype. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 244-253;. [CrossRef]
- Ghalyanhilangeroudi, A.; Hosseini, H.; Nazarpak, H. H.; Molouki, A.; Dezfoulian, O.; Morshed, R. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of Marek’s disease virus in Iran. Avian Dis. 2022, 66, 1-5;. [CrossRef]
- Abd-Ellatieff, H. A.; Rawash, A. A. A.; Ellakany, H.; Goda, W. M.; Suzuki, T.; Yanai, T. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of a virulent Marek’s disease virus field strain in broiler chickens in Japan. Avian Pathol. 2018, 47, 47-57;. [CrossRef]
- Wannaratana, S.; Tunterak, W.; Prakairungnamthip, D.; Sasipreeyajan, J.; Thontiravong, A. Genetic characterization of Marek’s disease virus in chickens in Thailand reveals a high genetic diversity of circulating strains. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 3771-3779;. [CrossRef]
- Lin, J. A.; Chen, C. P. First isolation and characterization of very virulent Marek’s disease virus in Taiwan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1996, 58, 1011-1015;. [CrossRef]
- World Organization for Animal Health (OIE). Chapter 3.3.13: Marek’s disease. In Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals; OIE, 2018, pp. 952-963; URL: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/3.03.13_MAREK_DIS.pdf.
- Murata, S.; Chang, K-S.; Lee, S-I.; Konnai, S.; Onuma, M.; Ohashi, K. Development of a nested polymerase chain reaction method to detect oncogenic Marek’s disease virus from feather tips. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2007, 19, 471-478;. [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, M. M.; Khalafalla, A. I. Detection by PCR of multiple subgroups of Avian leukosis virus (ALV) in broilers in the Sudan. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2005, 4, 407-413; URL: http://medwelljournals.com/abstract/?doi=javaa.2005.407.413.
- Lin, M. Y.; Liu, H. J.; Ke, G. M. Genetic and antigenic analysis of Newcastle disease viruses from recent outbreaks in Taiwan. Avian Pathol. 2003, 32, 345-350;. [CrossRef]
- Caterina, K. M.; Frasca Jr, S.; Girshick, T.; Khan, M. I. Development of a multiplex PCR for detection of avian adenovirus, avian reovirus, infectious bursal disease virus, and chicken anemia virus. Mol. Cell. Probes. 2004, 18, 293-298;. [CrossRef]
- Handberg, K. J.; Nielsen, O.; Pedersen, M. W.; Jørgensen, P. H. Detection and strain differentiation of infectious bronchitis virus in tracheal tissues from experimentally infected chickens by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Comparison with an immunohistochemical technique. Avian Pathol. 1999, 28, 327-335;. [CrossRef]
- Meulemans, G.; Boschmans, M.; Berg, T. P.; Decaesstecker, M. Polymerase chain reaction combined with restriction enzyme analysis for detection and differentiation of fowl adenoviruses. Avian Pathol. 2001, 30, 655-660;. [CrossRef]
- Lauerman, L. H.; Hoerr, F. J.; Sharpton, A. R.; Shah, S. M.; van Santen, V. L. Development and application of a polymerase chain reaction assay for Mycroplasma synoviae. Avian Dis. 1993, 37, 829-834.
- Lee, L. H.; Lee, K. H. Application of the polymerase chain reaction for the diagnosis of fowl poxvirus infection. J. Virol. Methods. 1997, 63, 113-119;. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J. D.; Higgins, D. G.; Gibson, T. J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673-4680;. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547-1549;. [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zou, N.; Liu, C.; Liu, P.; Cao, S.; Wen, X.; Huang, Y. Comparative analysis of oncogenic genes revealed unique evolutionary features of field Marek’s disease virus prevalent in recent years in China. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 121;. [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Zhuang, G.; Xu, X.; Sun, A.; Su, S. Molecular and biological characterization of a Marek’s disease virus field strain with reticuloendotheliosis virus LTR insert. Virus Genes. 2010, 40, 236-243;. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y-P.; Li, Z-J.; Bao, K-Y.; Lv, H-C.; Gao, Y-L.; Gao, H-L.; Qi, X-L.; Cui, H-Y.; Wang, Y-Q.; Ren, X-G.; Wang, X-M. Pathogenic characteristics of Marek’s disease virus field strains prevalent in China and the effectiveness of existing vaccines against them. Vet Microbiol. 2015, 177: 62-8;. [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Zhang, K.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Qiu, Y.; Li, I.; Hou, G.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Shan, Hu. Effect of vaccination with different types and dosages against a very virulent Marek’s disease virus strain. J. Mol. Genet. Med. 2014, 8:4.
- Lachheb, J.; Mastour, H.; Nsiri, J.; Kaboudi, K.; Choura, I.; Ammouna, F.; Amara, A.; Ghram, A. Newly detected mutations in the Meq oncogene and molecular pathotyping of very virulent Marek’s disease herpesvirus in Tunisia. Arch Virol. 2020, 165, 2589-2597;. [CrossRef]
- Murata, S.; Hayashi, Y.; Kato, A.; Isezaki, M.; Takasaki, S.; Onuma, M.; Osa, Y.; Asakawa, M.; Konnai, S.; Ohashi, K. Surveillance of Marek’s disease virus in migratory and sedentary birds in Hokkaido, Japan. Vet. J. 2012, 192, 538-540;. [CrossRef]
- Mescolini, G.; Lupini, C.; Davidson, I.; Massi, P.; Tosi, G.; Catelli, E. Marek’s disease viruses circulating in commercial poultry in Italy in the years 2015-2018 are closely related by their meq gene phylogeny. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 98-107;. [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, G.; Bao, K.; Gao, Y.; Qi, X.; Cui, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Gao, L.; Pan, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, C. Genetic evolution of Gallid herpesvirus 2 isolated in China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 51, 263-274;. [CrossRef]
- Conradie, A. M.; Bertzbach, L. D.; Trimpert, J.; Patria, J. N.; Murata, S.; Parcells, M. S.; Kaufer, B. B. District polymorphisms in a single herpesvirus gene are capable of enhancing virulence and mediating vaccinal resistance. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009104;. [CrossRef]
- Padhi, A.; Parcells, M. S. Positive selection derives rapid evolution of the meq oncogene of Marek’s disease virus. PLoS One. 2016, 11, e0162180;. [CrossRef]
- Davison, F.; Nair, V. Use of Marek’s disease vaccines: Could they be driving the virus to increasing virulence? Expert Rev. Vaccines. 2005, 4, 77-88;. [CrossRef]
- Read, A. F.; Baigent, S. J.; Powers, C.; Kgosana, L. B.; Blackwell, L.; Smith, L. P.; Kennedy, D. A.; Walkden-Brown, S. W.; Nair, V. K. Imperfect vaccination can enhance the transmission of highly virulent pathogens. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002198. [CrossRef]
- Landman, W. J. M.; Verschuren, S. B. E. Titration of Marek’s disease cell-associated vaccine virus (CVI 988) of reconstituted vaccine and vaccine ampoules from Dutch hatcheries. Avian Dis. 2003, 47, 1458-65;. [CrossRef]
- López de Juan Abad, B. A.; Cortes, A. L.; Correa, M.; Gimeno, I. M. Evaluation of factors that influence dose variability of Marek’s disease vaccines. Avian Dis. 2019, 63, 591-598;. [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y. W.; Kang, C. Y.; Chiao, K. H.; Tsai, Y. L.; Lien, Y. Y.; Cheng, M. C. Detection of vaccine strain virus (serotype 1) in layer chicks feather tips after immunization against Marek’s disease. Presented at the 3rd joint meeting of veterinary science in east Asia, Pingtung, Taiwan, 1st May 2023.
- Sun, G-R.; Zhang, Y-P.; Zhou, L-Y.; Lv, H-C.; Zhang, F.; Li, K.; Gao, Y-L; Qi, X-L.; Cui, H-Y.; Wang, Y-Q.; Gao, L.; Pan, Q.; Wang, X-M.; Liu, C-J. Co-infection with Marek’s disease virus and reticuloendotheliosis virus increases illness severity and reduces Marek’s disease vaccine efficacy. Viruses. 2017, 9, 158;. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, N.; Han, N.; Wu, J.; Cui, Z.; Su, S. Depression of vaccinal immunity to Marek’s disease by infection with Chicken infectious anemia virus. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1863;. [CrossRef]
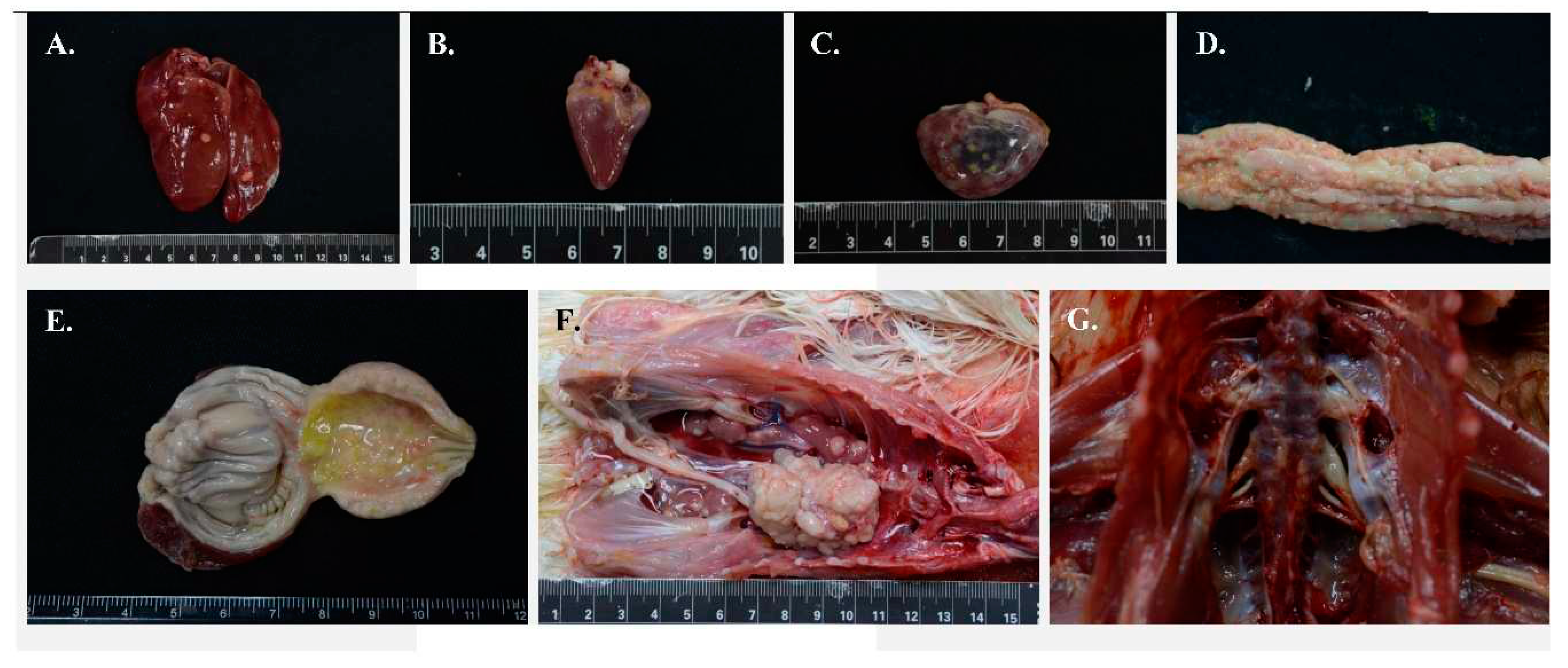
| Flock ID | Location | Year | Age (weeks) | Genetic line | Vaccine types | pathogen | Isolate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P107-008 | Changhua | 2018 | 20 | Hy-Line | CVI988 | MDV, CAV | TW/008/18 |
| P107-009 | Pingtung | 2018 | 17 | Hy-Line | CVI988 | MDV, CAV | TW/009/18 |
| P107-011 | Pingtung | 2018 | 19 | Hy-Line | CVI988 | MDV, CAV | TW/011/18 |
| P107-014 | NA | 2018 | 26 | Hy-Line | CVI988 | MDV | TW/014/18 |
| P107-023 | Pingtung | 2018 | 35 | Hy-Line | CVI988 | MDV, CAV | TW/023/18 |
| P108-109 | Tainan | 2019 | 31 | Native Chicken | CVI988 + HVT | MDV, CAV | TW/109/19 |
| P108-123 | Pingtung | 2019 | NA | HENDRIX | CVI988 + HVT | MDV | TW/123/19 |
| P108-133 | Pingtung | 2019 | 10 | Layer, NA | CVI988 + HVT | MDV | TW/133/19 |
| P108-141 | Chiayi | 2019 | 14, 18 | HENDRIX | CVI988 + HVT | MDV, IBV, CAV, IBDV | TW/141A/19TW/141B/19 |
| P108-146 | Chiayi | 2019 | 19 | Layer, NA | CVI988 + HVT | MDV, CAV | TW/146/19 |
| P108-147 | Tainan | 2019 | 23 | Layer, NA | CVI988 + HVT | MDV | TW/147/19 |
| P108-148 | Kaohsiung | 2019 | 19 | Layer, NA | CVI988 + HVT | MDV, CAV | TW/148/19 |
| P108-149 | Chiayi | 2019 | 23 | Layer, NA | CVI988 + HVT | MDV, CAV | TW/149/19 |
| P109-003 | Taitung | 2020 | 27 | HENDRIX | CVI988 + HVT | MDV | TW/003/20 |
| P109-029 | Chiayi | 2020 | 8 | HENDRIX | CVI988 + HVT | MDV, NDV | TW/029/20 |
| P109-048 | Pingtung | 2020 | 18 | Hy-Line | CVI988 | MDV, FAV | TW/048/20 |
| P109-116 | Chiayi | 2020 | 29 | HENDRIX | CVI988 + HVT | MDV, IBV, CAV, MS, FPV | TW/116/20 |
| Strain/Isolate | Pathotype | 71 | 77 | 80 | 88 | 93 | 110 | 115 | 119 | 139 | 153 (PPPP) |
176 (PPPP) |
180 | 217/276b (PPPP) |
218/277b (PPPP) |
277/336b | 283/342b | 326/385b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 648A (USA) | vv+MDV | A | K | D | A | Q | C | V | R | T | Q | A | A | A | P | P | A | T |
| N (USA) | vv+MDV | A | K | D | A | Q | C | V | R | T | Q | A | A | A | P | P | A | T |
| Md5 (USA) | vvMDV | A | K | D | A | Q | C | V | C | T | P | P | T | A | P | L | V | T |
| RB1B (USA) | vvMDV | A | K | D | A | Q | C | V | C | T | P | P | T | P | P | L | A | T |
| GA (USA) | vMDV | A | K | D | A | Q | C | V | C | T | P | P | T | P | P | L | A | T |
| 571 (USA) | vMDV | A | E | D | A | Q | C | V | C | T | P | H | T | P | P | L | A | T |
| CU-2 (USA) | mMDV | S | E | D | A | Q | S | V | C | T | P | P | T | P | P | L | A | I |
| CVI988/Rispens (NL) | attMDV | S | E | D | A | Q | S | V | C | T | P | P | T | P | P | L | A | I |
| SD2012-1 (CN) | vv+MDV | A | E | Y | T | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| LTS | vv+MDV | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | A | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| GX0101 (CN) | vvMDV | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | A | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| LS (CN) | vvMDV | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TH/CBI/656/21 (THA) | NAa | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| OkiH26035 (JP) | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | P | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/008/18 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/009/18 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/011/18 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/014/18 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/023/18 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/109/19 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/123/19 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/133/19 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/141A/19 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/141B/19 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/146/19 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/147/19 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/148/19 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/149/19 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/003/20 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/029/20 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/048/20 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| TW/116/20 | NA | A | E | Y | A | Q | C | A | C | T | P | R | T | A | P | L | A | T |
| Strain/Isolate | Pathotype | Size of Meq (a. a.) |
Insertion size (a. a.) | Proline contents (%) | Number of PPPPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVI988/Rispens (NL) | attMDV | 398 | 59 | 23.1 | 7 |
| CU-2 (USA) | mMDV | 398 | 59 | 23.1 | 7 |
| 648A (USA) | vv+MDV | 339 | Nilb | 20.9 | 2 |
| N (USA) | vv+MDV | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 2 |
| Md5 (USA) | vvMDV | 339 | Nil | 21.3 | 4 |
| RB1B (USA) | vvMDV | 339 | Nil | 21.5 | 5 |
| GA (USA) | vMDV | 339 | Nil | 21.5 | 5 |
| 571 (USA) | vMDV | 339 | Nil | 21.2 | 4 |
| SD2012-1 (CN) | vv+MDV | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| LTS (CN) | vv+MDV | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| GX0101 (CN) | vvMDV | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| LS (CN) | vvMDV | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| TH/CBI/656/21 (THA) | NAa | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| OkiH26035 (JP) | NA | 339 | Nil | 21.2 | 4 |
| TW/008/18 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| TW/009/18 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| TW/011/18 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| TW/014/18 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.6 | 3 |
| TW/023/18 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| TW/109/19 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| TW/123/19 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| TW/133/19 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.6 | 3 |
| TW/141A/19 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| TW/141B/19 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| TW/146/19 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| TW/147/19 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| TW/148/19 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| TW/149/19 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| TW/003/20 | NA | 339 | Nil | 21.3 | 3 |
| TW/029/20 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| TW/048/20 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
| TW/116/20 | NA | 339 | Nil | 20.9 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





