Submitted:
21 September 2023
Posted:
22 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Etiopathogenesis of PKAN
2.1. CoA deficiency in PKAN
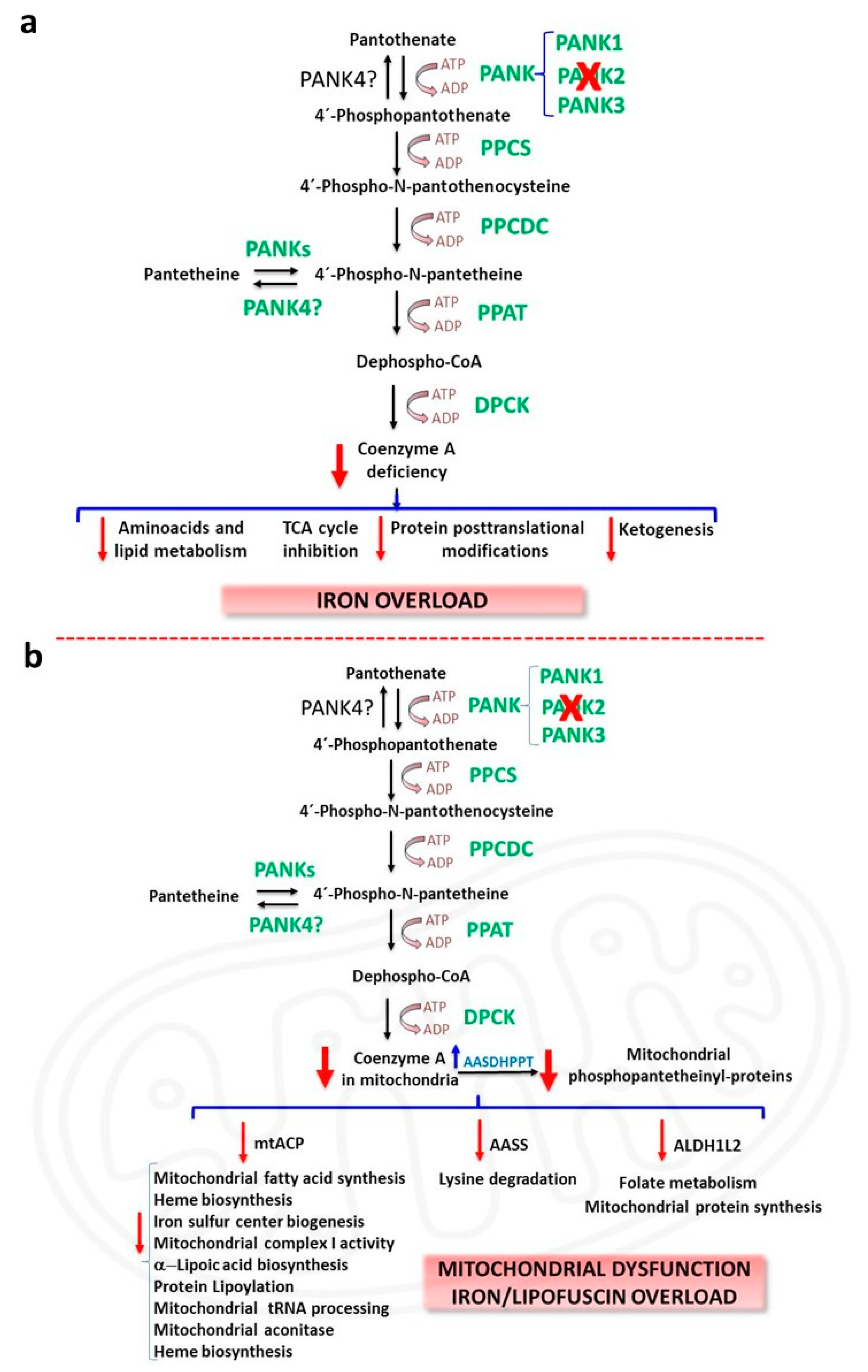
2.2. Iron/lipofuscin accumulation in PKAN
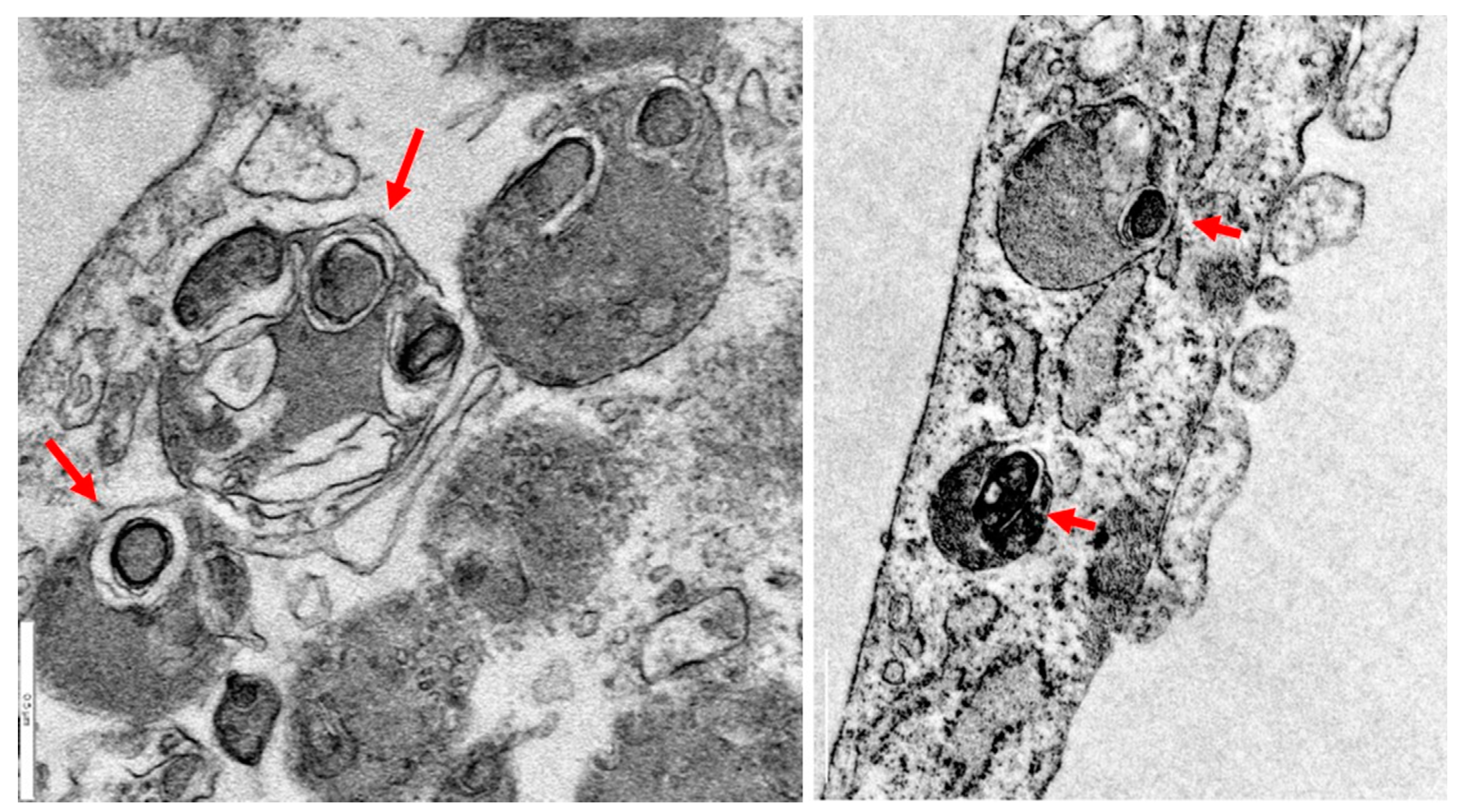
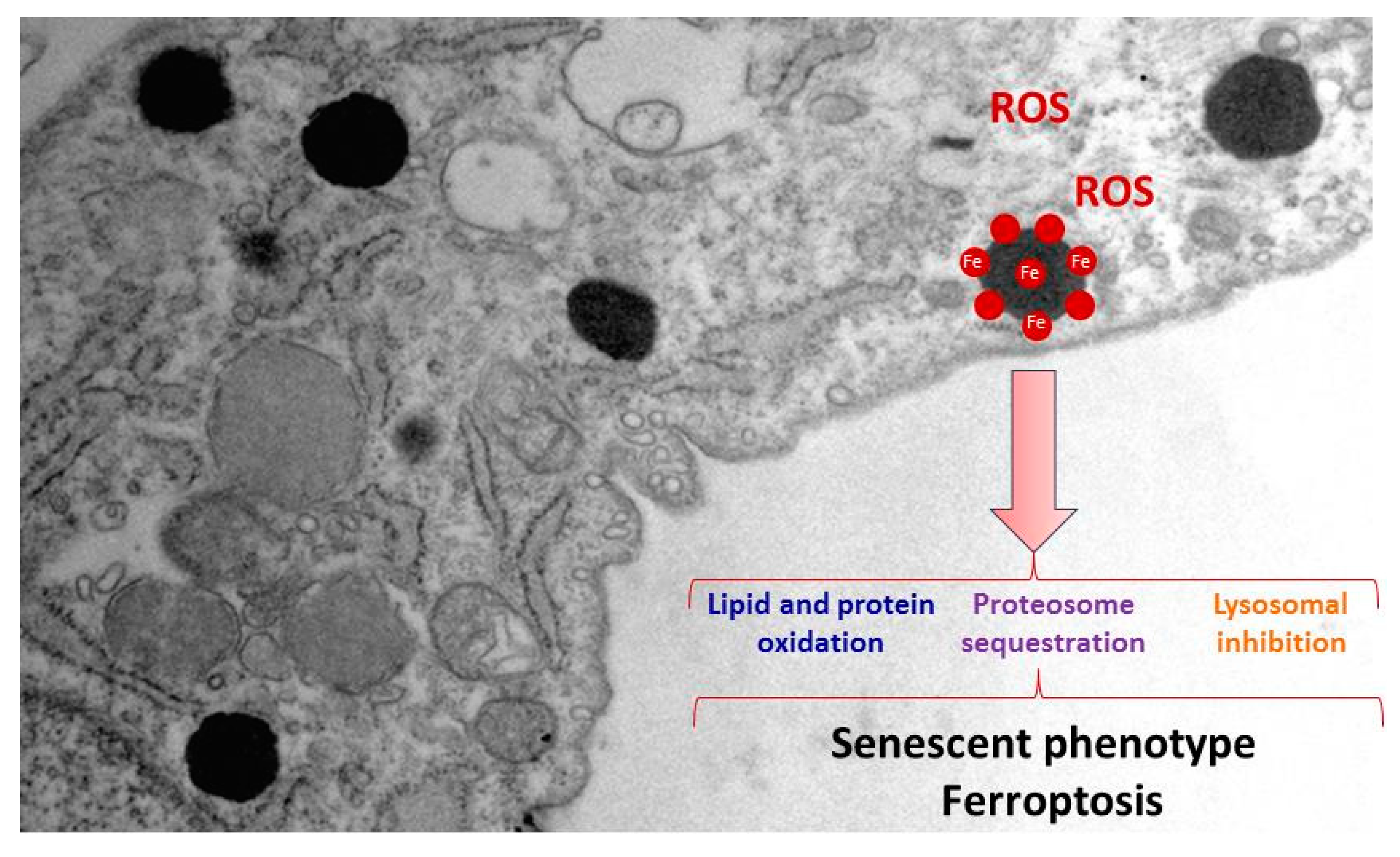
3. PKAN disease modeling
3.1. Modeling PKAN disease in biological models
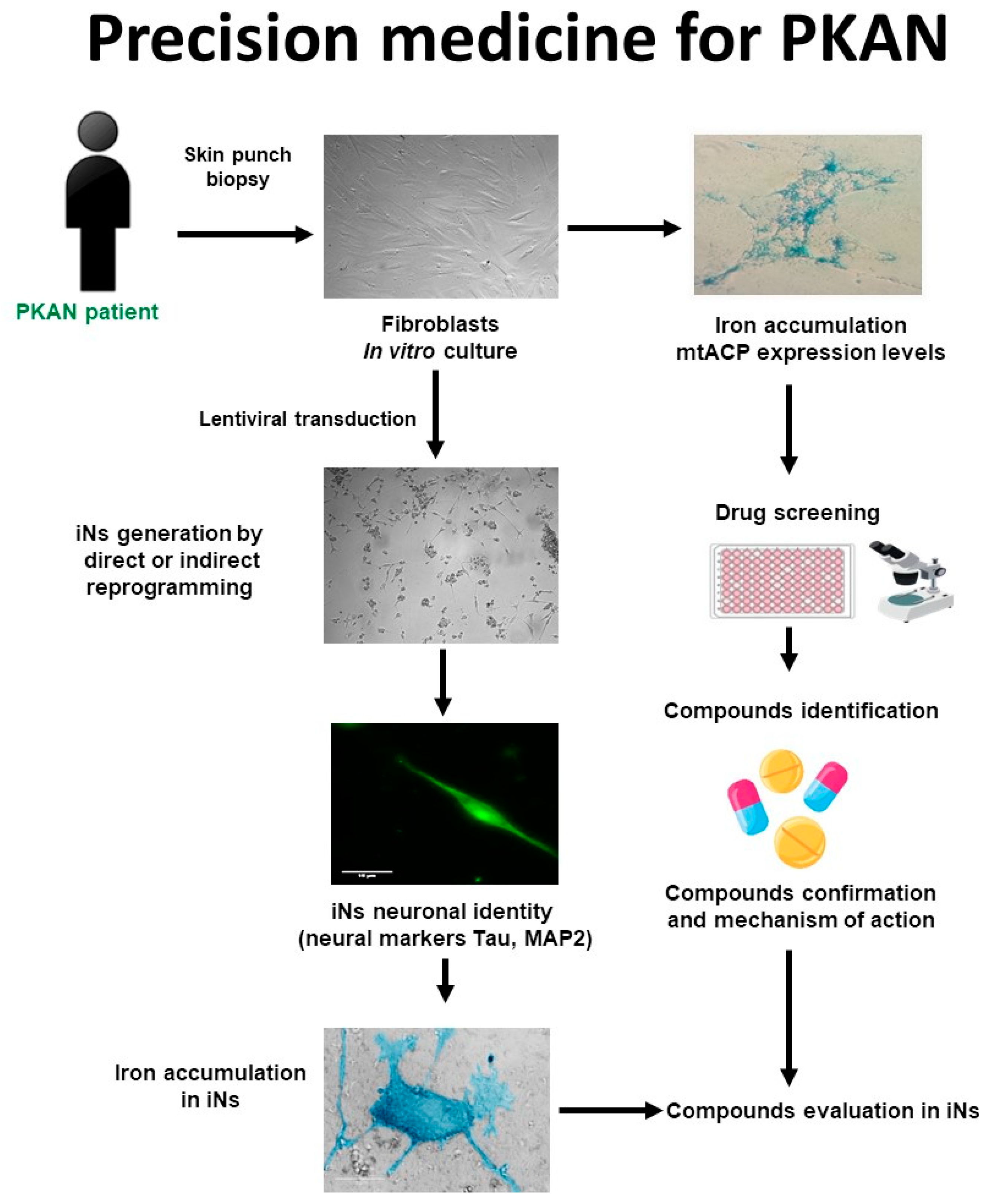
3.2. Patient-derived cellular models
3.3. Induced neurons
3.4. Alterations in cellular models of PKAN
4. Therapeutic strategies for PKAN
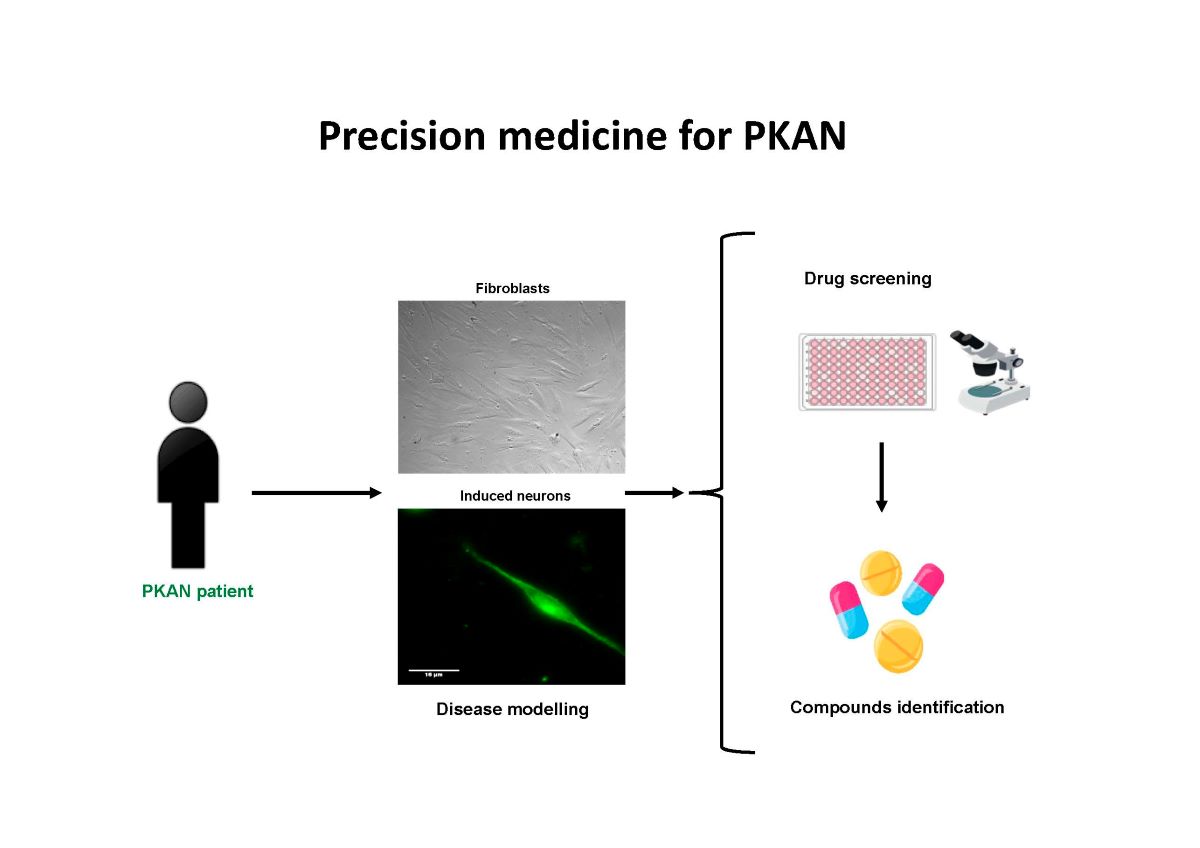
4.1. Strategy for finding alternative treatments for PKAN using patient-derived cellular models
4.2. Precision medicine in PKAN
5. Polytarget therapy in PKAN
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hogarth, P.; Kurian, M.A.; Gregory, A.; Csanyi, B.; Zagustin, T.; Kmiec, T.; Wood, P.; Klucken, A.; Scalise, N.; Sofia, F.; et al. Consensus clinical management guideline for pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration (PKAN). Molecular genetics and metabolism 2017, 120, 278-287. [CrossRef]
- Gregory, A.; Polster, B.J.; Hayflick, S.J. Clinical and genetic delineation of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Journal of medical genetics 2009, 46, 73-80. [CrossRef]
- Levi, S.; Tiranti, V. Neurodegeneration with Brain Iron Accumulation Disorders: Valuable Models Aimed at Understanding the Pathogenesis of Iron Deposition. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2019, 12. [CrossRef]
- Levi, S.; Finazzi, D. Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation: update on pathogenic mechanisms. Frontiers in pharmacology 2014, 5, 99. [CrossRef]
- Hayflick, S.J. Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation: from genes to pathogenesis. Seminars in pediatric neurology 2006, 13, 182-185. [CrossRef]
- Hayflick, S.J.; Westaway, S.K.; Levinson, B.; Zhou, B.; Johnson, M.A.; Ching, K.H.; Gitschier, J. Genetic, clinical, and radiographic delineation of Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome. The New England journal of medicine 2003, 348, 33-40. [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, R.; Zhang, Y.M.; Lykidis, A.; Rock, C.O.; Jackowski, S. Localization and regulation of mouse pantothenate kinase 2. FEBS Lett 2007, 581, 4639-4644. [CrossRef]
- Jackowski, S., Rock, C. O. CoA regulation and metabolic control. Biochem (Lond) 2015, 37.
- Huang, L.; Khusnutdinova, A.; Nocek, B.; Brown, G.; Xu, X.; Cui, H.; Petit, P.; Flick, R.; Zallot, R.; Balmant, K.; et al. A family of metal-dependent phosphatases implicated in metabolite damage-control. Nat Chem Biol 2016, 12, 621-627. [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Subramanian, C.; Rock, C.O.; Jackowski, S. Human pantothenate kinase 4 is a pseudo-pantothenate kinase. Protein Sci 2019, 28, 1031-1047. [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, R.; Zhang, Y.M.; Rock, C.O.; Jackowski, S. Coenzyme A: back in action. Progress in lipid research 2005, 44, 125-153. [CrossRef]
- Cavestro, C.; Diodato, D.; Tiranti, V.; Di Meo, I. Inherited Disorders of Coenzyme A Biosynthesis: Models, Mechanisms, and Treatments. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [CrossRef]
- Gregory, A.; Hayflick, S.J. Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Folia neuropathologica / Association of Polish Neuropathologists and Medical Research Centre, Polish Academy of Sciences 2005, 43, 286-296.
- Kurian, M.A.; Hayflick, S.J. Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration (PKAN) and PLA2G6-associated neurodegeneration (PLAN): review of two major neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA) phenotypes. International review of neurobiology 2013, 110, 49-71. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Moretti, I.F.; Grzeschik, N.A.; Sibon, O.C.M.; Schepers, H. Coenzyme A levels influence protein acetylation, CoAlation and 4'-phosphopantetheinylation: Expanding the impact of a metabolic nexus molecule. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2021, 1868, 118965. [CrossRef]
- Arber, C.; Angelova, P.R.; Wiethoff, S.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Mazzacuva, F.; Preza, E.; Bhatia, K.P.; Mills, K.; Gout, I.; Abramov, A.Y.; et al. iPSC-derived neuronal models of PANK2-associated neurodegeneration reveal mitochondrial dysfunction contributing to early disease. PloS one 2017, 12, e0184104. [CrossRef]
- Dusi, S.; Valletta, L.; Haack, T.B.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Venco, P.; Pasqualato, S.; Goffrini, P.; Tigano, M.; Demchenko, N.; Wieland, T.; et al. Exome sequence reveals mutations in CoA synthase as a cause of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. American journal of human genetics 2014, 94, 11-22. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.; Leonardi, R.; Zhang, Y.M.; Rehg, J.E.; Jackowski, S. Germline deletion of pantothenate kinases 1 and 2 reveals the key roles for CoA in postnatal metabolism. PloS one 2012, 7, e40871. [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Cordoba, M.; Fernandez Khoury, A.; Villanueva-Paz, M.; Gomez-Navarro, C.; Villalon-Garcia, I.; Suarez-Rivero, J.M.; Povea-Cabello, S.; de la Mata, M.; Cotan, D.; Talaveron-Rey, M.; et al. Pantothenate Rescues Iron Accumulation in Pantothenate Kinase-Associated Neurodegeneration Depending on the Type of Mutation. Molecular neurobiology 2019, 56, 3638-3656. [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, R.A.; Schepers, H.; Yu, Y.; van der Zwaag, M.; Autio, K.J.; Vieira-Lara, M.A.; Bakker, B.M.; Tijssen, M.A.; Hayflick, S.J.; Grzeschik, N.A.; et al. CoA-dependent activation of mitochondrial acyl carrier protein links four neurodegenerative diseases. EMBO Mol Med 2019, 11, e10488. [CrossRef]
- Beld, J.; Sonnenschein, E.C.; Vickery, C.R.; Noel, J.P.; Burkart, M.D. The phosphopantetheinyl transferases: catalysis of a post-translational modification crucial for life. Nat Prod Rep 2014, 31, 61-108. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.K.; Zhang, L.; Rangan, V.S.; Smith, S. Cloning, expression, and characterization of a human 4'-phosphopantetheinyl transferase with broad substrate specificity. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 33142-33149. [CrossRef]
- Bunkoczi, G.; Pasta, S.; Joshi, A.; Wu, X.; Kavanagh, K.L.; Smith, S.; Oppermann, U. Mechanism and substrate recognition of human holo ACP synthase. Chemistry & biology 2007, 14, 1243-1253. [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Witkowski, A.; Joshi, A.K. Structural and functional organization of the animal fatty acid synthase. Progress in lipid research 2003, 42, 289-317. [CrossRef]
- Smith, S. The animal fatty acid synthase: one gene, one polypeptide, seven enzymes. FASEB J 1994, 8, 1248-1259.
- Sackmann, U.; Zensen, R.; Rohlen, D.; Jahnke, U.; Weiss, H. The acyl-carrier protein in Neurospora crassa mitochondria is a subunit of NADH:ubiquinone reductase (complex I). European journal of biochemistry / FEBS 1991, 200, 463-469. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Joshi, A.K.; Smith, S. Cloning, expression, characterization, and interaction of two components of a human mitochondrial fatty acid synthase. Malonyltransferase and acyl carrier protein. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 40067-40074. [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.; Brors, B.; Massow, M.; Weiss, H. Mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis: a relic of endosymbiontic origin and a specialized means for respiration. FEBS Lett 1997, 407, 249-252. [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.; Massow, M.; Lisowsky, T.; Weiss, H. Different respiratory-defective phenotypes of Neurospora crassa and Saccharomyces cerevisiae after inactivation of the gene encoding the mitochondrial acyl carrier protein. Current genetics 1995, 29, 10-17. [CrossRef]
- Hiltunen, J.K.; Schonauer, M.S.; Autio, K.J.; Mittelmeier, T.M.; Kastaniotis, A.J.; Dieckmann, C.L. Mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis type II: more than just fatty acids. J Biol Chem 2009, 284, 9011-9015. [CrossRef]
- Kotzbauer, P.T.; Truax, A.C.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Altered neuronal mitochondrial coenzyme A synthesis in neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation caused by abnormal processing, stability, and catalytic activity of mutant pantothenate kinase 2. J Neurosci 2005, 25, 689-698. [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Cordoba, M.; Talaveron-Rey, M.; Villalon-Garcia, I.; Povea-Cabello, S.; Suarez-Rivero, J.M.; Suarez-Carrillo, A.; Munuera-Cabeza, M.; Salas, J.J.; Sanchez-Alcazar, J.A. Down regulation of the expression of mitochondrial phosphopantetheinyl-proteins in pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration: pathophysiological consequences and therapeutic perspectives. Orphanet journal of rare diseases 2021, 16, 201. [CrossRef]
- Cronan, J.E. Assembly of Lipoic Acid on Its Cognate Enzymes: an Extraordinary and Essential Biosynthetic Pathway. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2016, 80, 429-450. [CrossRef]
- Mayr, J.A.; Feichtinger, R.G.; Tort, F.; Ribes, A.; Sperl, W. Lipoic acid biosynthesis defects. J Inherit Metab Dis 2014, 37, 553-563. [CrossRef]
- Van Vranken, J.G.; Nowinski, S.M.; Clowers, K.J.; Jeong, M.Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Berg, J.A.; Gygi, J.P.; Gygi, S.P.; Winge, D.R.; Rutter, J. ACP Acylation Is an Acetyl-CoA-Dependent Modification Required for Electron Transport Chain Assembly. Molecular cell 2018, 71, 567-580 e564. [CrossRef]
- Vinothkumar, K.R.; Zhu, J.; Hirst, J. Architecture of mammalian respiratory complex I. Nature 2014, 515, 80-84. [CrossRef]
- Cory, S.A.; Van Vranken, J.G.; Brignole, E.J.; Patra, S.; Winge, D.R.; Drennan, C.L.; Rutter, J.; Barondeau, D.P. Structure of human Fe-S assembly subcomplex reveals unexpected cysteine desulfurase architecture and acyl-ACP-ISD11 interactions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2017, 114, E5325-E5334. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.Y.; Hogarth, P.; Placzek, A.; Gregory, A.M.; Fox, R.; Zhen, D.; Hamada, J.; van der Zwaag, M.; Lambrechts, R.; Jin, H.; et al. 4'-Phosphopantetheine corrects CoA, iron, and dopamine metabolic defects in mammalian models of PKAN. EMBO Mol Med 2019, 11, e10489. [CrossRef]
- Van Vranken, J.G.; Jeong, M.Y.; Wei, P.; Chen, Y.C.; Gygi, S.P.; Winge, D.R.; Rutter, J. The mitochondrial acyl carrier protein (ACP) coordinates mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis with iron sulfur cluster biogenesis. eLife 2016, 5. [CrossRef]
- Chen, O.S.; Hemenway, S.; Kaplan, J. Inhibition of Fe-S cluster biosynthesis decreases mitochondrial iron export: evidence that Yfh1p affects Fe-S cluster synthesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2002, 99, 12321-12326. [CrossRef]
- Orellana, D.I.; Santambrogio, P.; Rubio, A.; Yekhlef, L.; Cancellieri, C.; Dusi, S.; Giannelli, S.G.; Venco, P.; Mazzara, P.G.; Cozzi, A.; et al. Coenzyme A corrects pathological defects in human neurons of PANK2-associated neurodegeneration. EMBO Mol Med 2016, 8, 1197-1211. [CrossRef]
- Santambrogio, P.; Dusi, S.; Guaraldo, M.; Rotundo, L.I.; Broccoli, V.; Garavaglia, B.; Tiranti, V.; Levi, S. Mitochondrial iron and energetic dysfunction distinguish fibroblasts and induced neurons from pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration patients. Neurobiology of disease 2015, 81, 144-153. [CrossRef]
- Nunez, M.T.; Urrutia, P.; Mena, N.; Aguirre, P.; Tapia, V.; Salazar, J. Iron toxicity in neurodegeneration. Biometals : an international journal on the role of metal ions in biology, biochemistry, and medicine 2012, 25, 761-776. [CrossRef]
- Lan, A.P.; Chen, J.; Chai, Z.F.; Hu, Y. The neurotoxicity of iron, copper and cobalt in Parkinson's disease through ROS-mediated mechanisms. Biometals : an international journal on the role of metal ions in biology, biochemistry, and medicine 2016, 29, 665-678. [CrossRef]
- Salvador, G.A.; Uranga, R.M.; Giusto, N.M. Iron and mechanisms of neurotoxicity. International journal of Alzheimer's disease 2010, 2011, 720658. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xin, W.; Anderson, G.J.; Li, R.; Gao, L.; Chen, S.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S. Double-edge sword roles of iron in driving energy production versus instigating ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis 2022, 13, 40. [CrossRef]
- Kruer, M.C. The neuropathology of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. International review of neurobiology 2013, 110, 165-194. [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Cordoba, M.; Villanueva-Paz, M.; Villalon-Garcia, I.; Povea-Cabello, S.; Suarez-Rivero, J.M.; Talaveron-Rey, M.; Abril-Jaramillo, J.; Vintimilla-Tosi, A.B.; Sanchez-Alcazar, J.A. Precision medicine in pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration. Neural Regen Res 2019, 14, 1177-1185. [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, T.; Kotamraju, S.; Kalivendi, S.V.; Dhanasekaran, A.; Joseph, J.; Kalyanaraman, B. Ceramide-induced intracellular oxidant formation, iron signaling, and apoptosis in endothelial cells: protective role of endogenous nitric oxide. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 28614-28624. [CrossRef]
- Perry, T.L.; Norman, M.G.; Yong, V.W.; Whiting, S.; Crichton, J.U.; Hansen, S.; Kish, S.J. Hallervorden-Spatz disease: cysteine accumulation and cysteine dioxygenase deficiency in the globus pallidus. Annals of neurology 1985, 18, 482-489. [CrossRef]
- Biosa, A.; Arduini, I.; Soriano, M.E.; Giorgio, V.; Bernardi, P.; Bisaglia, M.; Bubacco, L. Dopamine Oxidation Products as Mitochondrial Endotoxins, a Potential Molecular Mechanism for Preferential Neurodegeneration in Parkinson's Disease. ACS chemical neuroscience 2018, 9, 2849-2858. [CrossRef]
- Hare, D.J.; Double, K.L. Iron and dopamine: a toxic couple. Brain 2016, 139, 1026-1035. [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, A.; Crescenzi, O.; Pezzella, A.; Prota, G. Generation of the neurotoxin 6-hydroxydopamine by peroxidase/H2O2 oxidation of dopamine. Journal of medicinal chemistry 1995, 38, 917-922.
- Zhang, L.; Yagnik, G.; Jiang, D.; Shi, S.; Chang, P.; Zhou, F. Separation of intermediates of iron-catalyzed dopamine oxidation reactions using reversed-phase ion-pairing chromatography coupled in tandem with UV-visible and ESI-MS detections. Journal of chromatography. B, Analytical technologies in the biomedical and life sciences 2012, 911, 55-58. [CrossRef]
- Pezzella, A.; d'Ischia, M.; Napolitano, A.; Misuraca, G.; Prota, G. Iron-mediated generation of the neurotoxin 6-hydroxydopamine quinone by reaction of fatty acid hydroperoxides with dopamine: a possible contributory mechanism for neuronal degeneration in Parkinson's disease. Journal of medicinal chemistry 1997, 40, 2211-2216. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dryhurst, G. Irreversible inhibition of mitochondrial complex I by 7-(2-aminoethyl)-3,4-dihydro-5-hydroxy-2H-1,4-benzothiazine-3-carboxyli c acid (DHBT-1): a putative nigral endotoxin of relevance to Parkinson's disease. Journal of neurochemistry 1997, 69, 1530-1541. [CrossRef]
- Berman, S.B.; Hastings, T.G. Dopamine oxidation alters mitochondrial respiration and induces permeability transition in brain mitochondria: implications for Parkinson's disease. Journal of neurochemistry 1999, 73, 1127-1137.
- Zhang, F.; Dryhurst, G. Effects of L-cysteine on the oxidation chemistry of dopamine: new reaction pathways of potential relevance to idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Journal of medicinal chemistry 1994, 37, 1084-1098.
- Double, K.L.; Dedov, V.N.; Fedorow, H.; Kettle, E.; Halliday, G.M.; Garner, B.; Brunk, U.T. The comparative biology of neuromelanin and lipofuscin in the human brain. Cell Mol Life Sci 2008, 65, 1669-1682. [CrossRef]
- Jolly, R.D.; Douglas, B.V.; Davey, P.M.; Roiri, J.E. Lipofuscin in bovine muscle and brain: a model for studying age pigment. Gerontology 1995, 41 Suppl 2, 283-295. [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.; Bader, N.; Grune, T. Lipofuscin: formation, distribution, and metabolic consequences. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2007, 1119, 97-111. [CrossRef]
- Konig, J.; Ott, C.; Hugo, M.; Jung, T.; Bulteau, A.L.; Grune, T.; Hohn, A. Mitochondrial contribution to lipofuscin formation. Redox biology 2017, 11, 673-681. [CrossRef]
- Frolova, M.S.; Surin, A.M.; Braslavski, A.V.; Vekshin, N.L. [Degradation of Mitochondria to Lipofuscin upon Heating and Illumination]. Biofizika 2015, 60, 1125-1131.
- Brunk, U.T.; Terman, A. Lipofuscin: mechanisms of age-related accumulation and influence on cell function. Free radical biology & medicine 2002, 33, 611-619. [CrossRef]
- Salmonowicz, H.; Passos, J.F. Detecting senescence: a new method for an old pigment. Aging cell 2017, 16, 432-434. [CrossRef]
- Gorgoulis, V.; Adams, P.D.; Alimonti, A.; Bennett, D.C.; Bischof, O.; Bishop, C.; Campisi, J.; Collado, M.; Evangelou, K.; Ferbeyre, G.; et al. Cellular Senescence: Defining a Path Forward. Cell 2019, 179, 813-827. [CrossRef]
- Powell, S.R.; Wang, P.; Divald, A.; Teichberg, S.; Haridas, V.; McCloskey, T.W.; Davies, K.J.; Katzeff, H. Aggregates of oxidized proteins (lipofuscin) induce apoptosis through proteasome inhibition and dysregulation of proapoptotic proteins. Free radical biology & medicine 2005, 38, 1093-1101. [CrossRef]
- Hohn, A.; Grune, T. Lipofuscin: formation, effects and role of macroautophagy. Redox biology 2013, 1, 140-144. [CrossRef]
- Kurz, T.; Terman, A.; Gustafsson, B.; Brunk, U.T. Lysosomes and oxidative stress in aging and apoptosis. Biochimica et biophysica acta 2008, 1780, 1291-1303. [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Banerjee, K.; Lehmann, G.L.; Almeida, D.; Hajjar, K.A.; Benedicto, I.; Jiang, Z.; Radu, R.A.; Thompson, D.H.; Rodriguez-Boulan, E.; et al. Lipofuscin causes atypical necroptosis through lysosomal membrane permeabilization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2021, 118. [CrossRef]
- Reeg, S.; Grune, T. Protein Oxidation in Aging: Does It Play a Role in Aging Progression? Antioxidants & redox signaling 2015, 23, 239-255. [CrossRef]
- Campanella, A.; Privitera, D.; Guaraldo, M.; Rovelli, E.; Barzaghi, C.; Garavaglia, B.; Santambrogio, P.; Cozzi, A.; Levi, S. Skin fibroblasts from pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration patients show altered cellular oxidative status and have defective iron-handling properties. Human molecular genetics 2012, 21, 4049-4059. [CrossRef]
- Luckenbach, M.W.; Green, W.R.; Miller, N.R.; Moser, H.W.; Clark, A.W.; Tennekoon, G. Ocular clinicopathologic correlation of Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome with acanthocytosis and pigmentary retinopathy. American journal of ophthalmology 1983, 95, 369-382. [CrossRef]
- Lill, R.; Srinivasan, V.; Muhlenhoff, U. The role of mitochondria in cytosolic-nuclear iron-sulfur protein biogenesis and in cellular iron regulation. Current opinion in microbiology 2014, 22, 111-119. [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Cortopassi, G. Frataxin knockdown causes loss of cytoplasmic iron-sulfur cluster functions, redox alterations and induction of heme transcripts. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics 2007, 457, 111-122. [CrossRef]
- Poli, M.; Derosas, M.; Luscieti, S.; Cavadini, P.; Campanella, A.; Verardi, R.; Finazzi, D.; Arosio, P. Pantothenate kinase-2 (Pank2) silencing causes cell growth reduction, cell-specific ferroportin upregulation and iron deregulation. Neurobiology of disease 2010, 39, 204-210. [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.L.; Lane, D.J.; Richardson, D.R. Mitochondrial mayhem: the mitochondrion as a modulator of iron metabolism and its role in disease. Antioxidants & redox signaling 2011, 15, 3003-3019. [CrossRef]
- Bosveld, F.; Rana, A.; van der Wouden, P.E.; Lemstra, W.; Ritsema, M.; Kampinga, H.H.; Sibon, O.C. De novo CoA biosynthesis is required to maintain DNA integrity during development of the Drosophila nervous system. Human molecular genetics 2008, 17, 2058-2069. [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, D.; Dusi, S.; Giordano, C.; Lamperti, C.; Morbin, M.; Fugnanesi, V.; Marchet, S.; Fagiolari, G.; Sibon, O.; Moggio, M.; et al. Pantethine treatment is effective in recovering the disease phenotype induced by ketogenic diet in a pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration mouse model. Brain 2014, 137, 57-68. [CrossRef]
- Chiu, J.E.; Thekkiniath, J.; Mehta, S.; Muller, C.; Bracher, F.; Ben Mamoun, C. The yeast pantothenate kinase Cab1 is a master regulator of sterol metabolism and of susceptibility to ergosterol biosynthesis inhibitors. J Biol Chem 2019, 294, 14757-14767. [CrossRef]
- Khatri, D.; Mignani, L.; Zizioli, D.; Ritelli, M.; Monti, E.; Finazzi, D. Abnormal Vasculature Development in Zebrafish Embryos with Reduced Expression of Pantothenate Kinase 2 Gene. Bulletin of experimental biology and medicine 2020, 170, 58-63. [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.M.; Duncan, J.L.; Westaway, S.K.; Yang, H.; Nune, G.; Xu, E.Y.; Hayflick, S.J.; Gitschier, J. Deficiency of pantothenate kinase 2 (Pank2) in mice leads to retinal degeneration and azoospermia. Human molecular genetics 2005, 14, 49-57. [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Seinen, E.; Siudeja, K.; Muntendam, R.; Srinivasan, B.; van der Want, J.J.; Hayflick, S.; Reijngoud, D.J.; Kayser, O.; Sibon, O.C. Pantethine rescues a Drosophila model for pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2010, 107, 6988-6993. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.K.; Subramanian, C.; Yun, M.K.; Frank, M.W.; White, S.W.; Rock, C.O.; Lee, R.E.; Jackowski, S. A therapeutic approach to pantothenate kinase associated neurodegeneration. Nature communications 2018, 9, 4399. [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, C.; Yao, J.; Frank, M.W.; Rock, C.O.; Jackowski, S. A pantothenate kinase-deficient mouse model reveals a gene expression program associated with brain coenzyme a reduction. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2020, 1866, 165663. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, C.; Lv, S.; Zhou, B. Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration: insights from a Drosophila model. Human molecular genetics 2009, 18, 3659-3672. [CrossRef]
- Zizioli, D.; Tiso, N.; Guglielmi, A.; Saraceno, C.; Busolin, G.; Giuliani, R.; Khatri, D.; Monti, E.; Borsani, G.; Argenton, F.; et al. Knock-down of pantothenate kinase 2 severely affects the development of the nervous and vascular system in zebrafish, providing new insights into PKAN disease. Neurobiology of disease 2016, 85, 35-48. [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, D.; Dusi, S.; Morbin, M.; Uggetti, A.; Moda, F.; D'Amato, I.; Giordano, C.; d'Amati, G.; Cozzi, A.; Levi, S.; et al. Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration: altered mitochondria membrane potential and defective respiration in Pank2 knock-out mouse model. Human molecular genetics 2012, 21, 5294-5305. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.A.; Kuo, Y.M.; Westaway, S.K.; Parker, S.M.; Ching, K.H.; Gitschier, J.; Hayflick, S.J. Mitochondrial localization of human PANK2 and hypotheses of secondary iron accumulation in pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2004, 1012, 282-298. [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.M.; Hayflick, S.J.; Gitschier, J. Deprivation of pantothenic acid elicits a movement disorder and azoospermia in a mouse model of pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration. J Inherit Metab Dis 2007, 30, 310-317. [CrossRef]
- Munshi, M.I.; Yao, S.J.; Ben Mamoun, C. Redesigning therapies for pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration. J Biol Chem 2022, 298, 101577. [CrossRef]
- Afshar, K.; Gonczy, P.; DiNardo, S.; Wasserman, S.A. fumble encodes a pantothenate kinase homolog required for proper mitosis and meiosis in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 2001, 157, 1267-1276.
- Olzhausen, J.; Schubbe, S.; Schuller, H.J. Genetic analysis of coenzyme A biosynthesis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae: identification of a conditional mutation in the pantothenate kinase gene CAB1. Current genetics 2009, 55, 163-173. [CrossRef]
- Ceccatelli Berti, C.; Gilea, A.I.; De Gregorio, M.A.; Goffrini, P. Exploring Yeast as a Study Model of Pantothenate Kinase-Associated Neurodegeneration and for the Identification of Therapeutic Compounds. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 22. [CrossRef]
- Connolly, G.P. Fibroblast models of neurological disorders: fluorescence measurement studies. Trends in pharmacological sciences 1998, 19, 171-177. [CrossRef]
- Colman, A.; Dreesen, O. Pluripotent stem cells and disease modeling. Cell stem cell 2009, 5, 244-247. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Bendriem, R.M.; Wu, W.W.; Shen, R.F. 3D brain Organoids derived from pluripotent stem cells: promising experimental models for brain development and neurodegenerative disorders. J Biomed Sci 2017, 24, 59. [CrossRef]
- Dolmetsch, R.; Geschwind, D.H. The human brain in a dish: the promise of iPSC-derived neurons. Cell 2011, 145, 831-834. [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Harada, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Dai, P. Chemical compound-based direct reprogramming for future clinical applications. Biosci Rep 2018, 38. [CrossRef]
- Ladewig, J.; Koch, P.; Brustle, O. Leveling Waddington: the emergence of direct programming and the loss of cell fate hierarchies. Nature reviews 2013, 14, 225-236. [CrossRef]
- Vierbuchen, T.; Ostermeier, A.; Pang, Z.P.; Kokubu, Y.; Südhof, T.C.; Wernig, M. Direct conversion of fibroblasts to functional neurons by defined factors. Nature 2010, 463, 1035-1041. [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.P.; Yang, N.; Vierbuchen, T.; Ostermeier, A.; Fuentes, D.R.; Yang, T.Q.; Citri, A.; Sebastiano, V.; Marro, S.; Sudhof, T.C.; et al. Induction of human neuronal cells by defined transcription factors. Nature 2011, 476, 220-223. [CrossRef]
- Yoo, A.S.; Sun, A.X.; Li, L.; Shcheglovitov, A.; Portmann, T.; Li, Y.; Lee-Messer, C.; Dolmetsch, R.E.; Tsien, R.W.; Crabtree, G.R. MicroRNA-mediated conversion of human fibroblasts to neurons. Nature 2011, 476, 228-231. [CrossRef]
- Drouin-Ouellet, J.; Lau, S.; Brattas, P.L.; Rylander Ottosson, D.; Pircs, K.; Grassi, D.A.; Collins, L.M.; Vuono, R.; Andersson Sjoland, A.; Westergren-Thorsson, G.; et al. REST suppression mediates neural conversion of adult human fibroblasts via microRNA-dependent and -independent pathways. EMBO Mol Med 2017, 9, 1117-1131. [CrossRef]
- Ladewig, J.; Mertens, J.; Kesavan, J.; Doerr, J.; Poppe, D.; Glaue, F.; Herms, S.; Wernet, P.; Kogler, G.; Muller, F.J.; et al. Small molecules enable highly efficient neuronal conversion of human fibroblasts. Nature methods 2012, 9, 575-578. [CrossRef]
- Pfisterer, U.; Ek, F.; Lang, S.; Soneji, S.; Olsson, R.; Parmar, M. Small molecules increase direct neural conversion of human fibroblasts. Scientific reports 2016, 6, 38290. [CrossRef]
- Mertens, J.; Paquola, A.C.M.; Ku, M.; Hatch, E.; Bohnke, L.; Ladjevardi, S.; McGrath, S.; Campbell, B.; Lee, H.; Herdy, J.R.; et al. Directly Reprogrammed Human Neurons Retain Aging-Associated Transcriptomic Signatures and Reveal Age-Related Nucleocytoplasmic Defects. Cell stem cell 2015, 17, 705-718. [CrossRef]
- Huh, C.J.; Zhang, B.; Victor, M.B.; Dahiya, S.; Batista, L.F.; Horvath, S.; Yoo, A.S. Maintenance of age in human neurons generated by microRNA-based neuronal conversion of fibroblasts. eLife 2016, 5. [CrossRef]
- Horvath, S. DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell types. Genome Biol 2013, 14, R115. [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Okada, Y.; Aoi, T.; Okada, A.; Takahashi, K.; Okita, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Koyanagi, M.; Tanabe, K.; Ohnuki, M.; et al. Variation in the safety of induced pluripotent stem cell lines. Nature biotechnology 2009, 27, 743-745. [CrossRef]
- Torper, O.; Pfisterer, U.; Wolf, D.A.; Pereira, M.; Lau, S.; Jakobsson, J.; Björklund, A.; Grealish, S.; Parmar, M. Generation of induced neurons via direct conversion in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2013, 110, 7038-7043.
- Torper, O.; Pfisterer, U.; Wolf, D.A.; Pereira, M.; Lau, S.; Jakobsson, J.; Bjorklund, A.; Grealish, S.; Parmar, M. Generation of induced neurons via direct conversion in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013, 110, 7038-7043. [CrossRef]
- Rivetti di Val Cervo, P.; Romanov, R.A.; Spigolon, G.; Masini, D.; Martin-Montanez, E.; Toledo, E.M.; La Manno, G.; Feyder, M.; Pifl, C.; Ng, Y.H.; et al. Induction of functional dopamine neurons from human astrocytes in vitro and mouse astrocytes in a Parkinson's disease model. Nat Biotechnol 2017, 35, 444-452. [CrossRef]
- Masserdotti, G.; Gascon, S.; Gotz, M. Direct neuronal reprogramming: learning from and for development. Development 2016, 143, 2494-2510. [CrossRef]
- Ripamonti, M.; Santambrogio, P.; Racchetti, G.; Cozzi, A.; Di Meo, I.; Tiranti, V.; Levi, S. PKAN hiPS-Derived Astrocytes Show Impairment of Endosomal Trafficking: A Potential Mechanism Underlying Iron Accumulation. Frontiers in cellular neuroscience 2022, 16, 878103. [CrossRef]
- Santambrogio, P.; Ripamonti, M.; Cozzi, A.; Raimondi, M.; Cavestro, C.; Di Meo, I.; Rubio, A.; Taverna, S.; Tiranti, V.; Levi, S. Massive iron accumulation in PKAN-derived neurons and astrocytes: light on the human pathological phenotype. Cell Death Dis 2022, 13, 185. [CrossRef]
- Villalon-Garcia, I.; Alvarez-Cordoba, M.; Povea-Cabello, S.; Talaveron-Rey, M.; Villanueva-Paz, M.; Luzon-Hidalgo, R.; Suarez-Rivero, J.M.; Suarez-Carrillo, A.; Munuera-Cabeza, M.; Salas, J.J.; et al. Vitamin E prevents lipid peroxidation and iron accumulation in PLA2G6-Associated Neurodegeneration. Neurobiology of disease 2022, 165, 105649. [CrossRef]
- Drouin-Ouellet, J.; Legault, E.M.; Nilsson, F.; Pircs, K.; Bouquety, J.; Petit, F.; Shrigley, S.; Birtele, M.; Pereira, M.; Storm, P.; et al. Age-related pathological impairments in directly reprogrammed dopaminergic neurons derived from patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Stem Cell Reports 2022, 17, 2203-2219. [CrossRef]
- Pircs, K.; Drouin-Ouellet, J.; Horvath, V.; Gil, J.; Rezeli, M.; Garza, R.; Grassi, D.A.; Sharma, Y.; St-Amour, I.; Harris, K.; et al. Distinct subcellular autophagy impairments in induced neurons from patients with Huntington's disease. Brain 2022, 145, 3035-3057. [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Paz, M.; Povea-Cabello, S.; Villalon-Garcia, I.; Suarez-Rivero, J.M.; Alvarez-Cordoba, M.; de la Mata, M.; Talaveron-Rey, M.; Jackson, S.; Sanchez-Alcazar, J.A. Pathophysiological characterization of MERRF patient-specific induced neurons generated by direct reprogramming. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2019, 1866, 861-881. [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.S.; Huang, Y.W.; Ho, C.S.; Huang, T.S.; Lee, T.H.; Wu, T.Y.; Huang, Z.D.; Wang, T.J. Impact of Mitochondrial A3243G Heteroplasmy on Mitochondrial Bioenergetics and Dynamics of Directly Reprogrammed MELAS Neurons. Cells 2022, 12. [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Cordoba, M.; Reche-Lopez, D.; Cilleros-Holgado, P.; Talaveron-Rey, M.; Villalon-Garcia, I.; Povea-Cabello, S.; Suarez-Rivero, J.M.; Suarez-Carrillo, A.; Munuera-Cabeza, M.; Pinero-Perez, R.; et al. Therapeutic approach with commercial supplements for pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration with residual PANK2 expression levels. Orphanet journal of rare diseases 2022, 17, 311. [CrossRef]
- Talaveron-Rey, M.; Alvarez-Cordoba, M.; Villalon-Garcia, I.; Povea-Cabello, S.; Suarez-Rivero, J.M.; Gomez-Fernandez, D.; Romero-Gonzalez, A.; Suarez-Carrillo, A.; Munuera-Cabeza, M.; Cilleros-Holgado, P.; et al. Alpha-lipoic acid supplementation corrects pathological alterations in cellular models of pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration with residual PANK2 expression levels. Orphanet journal of rare diseases 2023, 18, 80. [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Klopstock, T.; Jackowski, S.; Kuscer, E.; Tricta, F.; Videnovic, A.; Jinnah, H.A. Rational Design of Novel Therapies for Pantothenate Kinase-Associated Neurodegeneration. Mov Disord 2021. [CrossRef]
- Hayflick, S.J.; Jeong, S.Y.; Sibon, O.C.M. PKAN pathogenesis and treatment. Molecular genetics and metabolism 2022, 137, 283-291. [CrossRef]
- Nixon, R.A. The role of autophagy in neurodegenerative disease. Nature medicine 2013, 19, 983-997. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wan, Z.; Tang, Y.; Xu, J.; Laboret, B.; Nallamothu, S.; Yang, C.; Liu, B.; Lu, R.O.; Lu, B.; et al. Pantothenate kinase 2 interacts with PINK1 to regulate mitochondrial quality control via acetyl-CoA metabolism. Nature communications 2022, 13, 2412. [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, G.; Cabeza de Vaca, I.; Poziello, A.; Monti, M.C.; Guallar, V.; Cubellis, M.V. Conformational response to ligand binding in phosphomannomutase2: insights into inborn glycosylation disorder. J Biol Chem 2014, 289, 34900-34910. [CrossRef]
- Goldin, E.; Zheng, W.; Motabar, O.; Southall, N.; Choi, J.H.; Marugan, J.; Austin, C.P.; Sidransky, E. High throughput screening for small molecule therapy for Gaucher disease using patient tissue as the source of mutant glucocerebrosidase. PloS one 2012, 7, e29861. [CrossRef]
- Newton, C.L.; Whay, A.M.; McArdle, C.A.; Zhang, M.; van Koppen, C.J.; van de Lagemaat, R.; Segaloff, D.L.; Millar, R.P. Rescue of expression and signaling of human luteinizing hormone G protein-coupled receptor mutants with an allosterically binding small-molecule agonist. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2011, 108, 7172-7176. [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, G.; Guarracino, M.R.; Cammisa, M.; Correra, A.; Cubellis, M.V. Prediction of the responsiveness to pharmacological chaperones: lysosomal human alpha-galactosidase, a case of study. Orphanet journal of rare diseases 2010, 5, 36. [CrossRef]
- Hay Mele, B.; Citro, V.; Andreotti, G.; Cubellis, M.V. Drug repositioning can accelerate discovery of pharmacological chaperones. Orphanet journal of rare diseases 2015, 10, 55. [CrossRef]
- Rigat, B.; Mahuran, D. Diltiazem, a L-type Ca(2+) channel blocker, also acts as a pharmacological chaperone in Gaucher patient cells. Molecular genetics and metabolism 2009, 96, 225-232. [CrossRef]
- Maitra, R.; Hamilton, J.W. Altered biogenesis of deltaF508-CFTR following treatment with doxorubicin. Cell Physiol Biochem 2007, 20, 465-472. [CrossRef]
- Porto, C.; Ferrara, M.C.; Meli, M.; Acampora, E.; Avolio, V.; Rosa, M.; Cobucci-Ponzano, B.; Colombo, G.; Moracci, M.; Andria, G.; et al. Pharmacological enhancement of alpha-glucosidase by the allosteric chaperone N-acetylcysteine. Mol Ther 2012, 20, 2201-2211. [CrossRef]
- Bendikov-Bar, I.; Maor, G.; Filocamo, M.; Horowitz, M. Ambroxol as a pharmacological chaperone for mutant glucocerebrosidase. Blood Cells Mol Dis 2013, 50, 141-145. [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.M.; Chen, P.C.; Devaraneni, P.; Shyng, S.L. Pharmacological rescue of trafficking-impaired ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Front Physiol 2013, 4, 386. [CrossRef]
- Maegawa, G.H.; Tropak, M.; Buttner, J.; Stockley, T.; Kok, F.; Clarke, J.T.; Mahuran, D.J. Pyrimethamine as a potential pharmacological chaperone for late-onset forms of GM2 gangliosidosis. J Biol Chem 2007, 282, 9150-9161. [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Okuyama, S.; Kumano, S.; Iida, K.; Hamana, H.; Murakoshi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Usami, S.; Ikeda, K.; Haga, Y.; et al. Salicylate restores transport function and anion exchanger activity of missense pendrin mutations. Hear Res 2010, 270, 110-118. [CrossRef]
- Strafella, C.; Caputo, V.; Galota, M.R.; Zampatti, S.; Marella, G.; Mauriello, S.; Cascella, R.; Giardina, E. Application of Precision Medicine in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Frontiers in neurology 2018, 9, 701. [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Jiang, T.; Tan, L.; Yu, J.T. Toward precision medicine in neurological diseases. Annals of translational medicine 2016, 4, 104. [CrossRef]
- Didiasova, M.; Banning, A.; Tikkanen, R. Development of precision therapies for rare inborn errors of metabolism: Functional investigations in cell culture models. J Inherit Metab Dis 2023. [CrossRef]
- Schee Genannt Halfmann, S.; Mahlmann, L.; Leyens, L.; Reumann, M.; Brand, A. Personalized Medicine: What's in it for Rare Diseases? Advances in experimental medicine and biology 2017, 1031, 387-404. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Basak, J.M.; Holtzman, D.M. The role of apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer's disease. Neuron 2009, 63, 287-303. [CrossRef]
- Frasier, M.; Fiske, B.K.; Sherer, T.B. Precision medicine for Parkinson's disease: The subtyping challenge. Frontiers in aging neuroscience 2022, 14, 1064057. [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, C.; Yun, M.K.; Yao, J.; Sharma, L.K.; Lee, R.E.; White, S.W.; Jackowski, S.; Rock, C.O. Allosteric Regulation of Mammalian Pantothenate Kinase. J Biol Chem 2016, 291, 22302-22314. [CrossRef]
- Di Meo, I.; Carecchio, M.; Tiranti, V. Inborn errors of coenzyme A metabolism and neurodegeneration. J Inherit Metab Dis 2019, 42, 49-56. [CrossRef]
- Zano, S.P.; Pate, C.; Frank, M.; Rock, C.O.; Jackowski, S. Correction of a genetic deficiency in pantothenate kinase 1 using phosphopantothenate replacement therapy. Molecular genetics and metabolism 2015, 116, 281-288. [CrossRef]
- Balibar, C.J.; Hollis-Symynkywicz, M.F.; Tao, J. Pantethine rescues phosphopantothenoylcysteine synthetase and phosphopantothenoylcysteine decarboxylase deficiency in Escherichia coli but not in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of bacteriology 2011, 193, 3304-3312. [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Rumberger, J.A.; Azumano, I.; Napolitano, J.J.; Citrolo, D.; Kamiya, T. Pantethine, a derivative of vitamin B5, favorably alters total, LDL and non-HDL cholesterol in low to moderate cardiovascular risk subjects eligible for statin therapy: a triple-blinded placebo and diet-controlled investigation. Vasc Health Risk Manag 2014, 10, 89-100. [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yao, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y. Pilot trial on the efficacy and safety of pantethine in children with pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration: a single-arm, open-label study. Orphanet journal of rare diseases 2020, 15, 248. [CrossRef]
- Girotti, A.W. Lipid hydroperoxide generation, turnover, and effector action in biological systems. Journal of lipid research 1998, 39, 1529-1542.
- Yin, H.; Xu, L.; Porter, N.A. Free radical lipid peroxidation: mechanisms and analysis. Chemical reviews 2011, 111, 5944-5972. [CrossRef]
- Van der Paal, J.; Neyts, E.C.; Verlackt, C.C.W.; Bogaerts, A. Effect of lipid peroxidation on membrane permeability of cancer and normal cells subjected to oxidative stress. Chem Sci 2016, 7, 489-498. [CrossRef]
- Ayala, A.; Munoz, M.F.; Arguelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2014, 2014, 360438. [CrossRef]
- Villalon-Garcia, I.; Povea-Cabello, S.; Alvarez-Cordoba, M.; Talaveron-Rey, M.; Suarez-Rivero, J.M.; Suarez-Carrillo, A.; Munuera-Cabeza, M.; Reche-Lopez, D.; Cilleros-Holgado, P.; Pinero-Perez, R.; et al. Vicious cycle of lipid peroxidation and iron accumulation in neurodegeneration. Neural Regen Res 2023, 18, 1196-1202. [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.W.; Joyce, A.; Ingold, K.U. First proof that vitamin E is major lipid-soluble, chain-breaking antioxidant in human blood plasma. Lancet 1982, 2, 327. [CrossRef]
- Traber, M.G. Vitamin E: necessary nutrient for neural development and cognitive function. The Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 2021, 80, 319-326. [CrossRef]
- Ricciarelli, R.; Argellati, F.; Pronzato, M.A.; Domenicotti, C. Vitamin E and neurodegenerative diseases. Molecular aspects of medicine 2007, 28, 591-606. [CrossRef]
- Ulatowski, L.M.; Manor, D. Vitamin E and neurodegeneration. Neurobiology of disease 2015, 84, 78-83. [CrossRef]
- Pena-Bautista, C.; Vento, M.; Baquero, M.; Chafer-Pericas, C. Lipid peroxidation in neurodegeneration. Clinica chimica acta; international journal of clinical chemistry 2019, 497, 178-188. [CrossRef]
- Espinos, C.; Galindo, M.I.; Garcia-Gimeno, M.A.; Ibanez-Cabellos, J.S.; Martinez-Rubio, D.; Millan, J.M.; Rodrigo, R.; Sanz, P.; Seco-Cervera, M.; Sevilla, T.; et al. Oxidative Stress, a Crossroad Between Rare Diseases and Neurodegeneration. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020, 9. [CrossRef]
- Heshmati, J.; Morvaridzadeh, M.; Maroufizadeh, S.; Akbari, A.; Yavari, M.; Amirinejad, A.; Maleki-Hajiagha, A.; Sepidarkish, M. Omega-3 fatty acids supplementation and oxidative stress parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Pharmacol Res 2019, 149, 104462. [CrossRef]
- Avallone, R.; Vitale, G.; Bertolotti, M. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Neurodegenerative Diseases: New Evidence in Clinical Trials. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [CrossRef]
- Calon, F.; Cole, G. Neuroprotective action of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids against neurodegenerative diseases: evidence from animal studies. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2007, 77, 287-293. [CrossRef]
- Eckert, G.P.; Lipka, U.; Muller, W.E. Omega-3 fatty acids in neurodegenerative diseases: focus on mitochondria. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2013, 88, 105-114. [CrossRef]
- da Silva, E.P., Jr.; Nachbar, R.T.; Levada-Pires, A.C.; Hirabara, S.M.; Lambertucci, R.H. Omega-3 fatty acids differentially modulate enzymatic anti-oxidant systems in skeletal muscle cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 2016, 21, 87-95. [CrossRef]
- Calviello, G.; Su, H.M.; Weylandt, K.H.; Fasano, E.; Serini, S.; Cittadini, A. Experimental evidence of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid modulation of inflammatory cytokines and bioactive lipid mediators: their potential role in inflammatory, neurodegenerative, and neoplastic diseases. Biomed Res Int 2013, 2013, 743171. [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, C.; Afonso, C.; Bandarra, N.M. Dietary DHA and health: cognitive function ageing. Nutr Res Rev 2016, 29, 281-294. [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.; Hughes, C.F.; Ward, M.; Hoey, L.; McNulty, H. Diet, nutrition and the ageing brain: current evidence and new directions. The Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 2018, 77, 152-163. [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.B.; Negrato, C.A. Alpha-lipoic acid as a pleiotropic compound with potential therapeutic use in diabetes and other chronic diseases. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2014, 6, 80. [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Berkay Yilmaz, Y.; Antika, G.; Boyunegmez Tumer, T.; Fawzi Mahomoodally, M.; Lobine, D.; Akram, M.; Riaz, M.; Capanoglu, E.; Sharopov, F.; et al. Insights on the Use of alpha-Lipoic Acid for Therapeutic Purposes. Biomolecules 2019, 9. [CrossRef]
- Solmonson, A.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Lipoic acid metabolism and mitochondrial redox regulation. J Biol Chem 2018, 293, 7522-7530. [CrossRef]
- Moura, F.A.; de Andrade, K.Q.; dos Santos, J.C.; Goulart, M.O. Lipoic Acid: its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory role and clinical applications. Curr Top Med Chem 2015, 15, 458-483. [CrossRef]
- Tibullo, D.; Li Volti, G.; Giallongo, C.; Grasso, S.; Tomassoni, D.; Anfuso, C.D.; Lupo, G.; Amenta, F.; Avola, R.; Bramanti, V. Biochemical and clinical relevance of alpha lipoic acid: antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity, molecular pathways and therapeutic potential. Inflamm Res 2017, 66, 947-959. [CrossRef]
- Molz, P.; Schroder, N. Potential Therapeutic Effects of Lipoic Acid on Memory Deficits Related to Aging and Neurodegeneration. Front Pharmacol 2017, 8, 849. [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, S.M.; Romeiro, C.F.R.; Rodrigues, C.A.; Cerqueira, A.R.L.; Monteiro, M.C. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Beneficial or Harmful in Alzheimer's Disease? Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2019, 2019, 8409329. [CrossRef]
- Perham, R.N. Swinging arms and swinging domains in multifunctional enzymes: catalytic machines for multistep reactions. Annu Rev Biochem 2000, 69, 961-1004. [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.R.; Shenvi, S.V.; Widlansky, M.; Suh, J.H.; Hagen, T.M. Lipoic acid as a potential therapy for chronic diseases associated with oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem 2004, 11, 1135-1146. [CrossRef]
- Rezaei Zonooz, S.; Hasani, M.; Morvaridzadeh, M.; Beatriz Pizarro, A.; Heydari, H.; Yosaee, S.; Rezamand, G.; Heshmati, J. Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on oxidative stress parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Functional Foods 2021, 87. [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.H.; Moreau, R.; Heath, S.H.; Hagen, T.M. Dietary supplementation with (R)-alpha-lipoic acid reverses the age-related accumulation of iron and depletion of antioxidants in the rat cerebral cortex. Redox Rep 2005, 10, 52-60. [CrossRef]
- Camiolo, G.; Tibullo, D.; Giallongo, C.; Romano, A.; Parrinello, N.L.; Musumeci, G.; Di Rosa, M.; Vicario, N.; Brundo, M.V.; Amenta, F.; et al. alpha-Lipoic Acid Reduces Iron-induced Toxicity and Oxidative Stress in a Model of Iron Overload. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [CrossRef]
- Liufu, T.; Wang, Z. Treatment for mitochondrial diseases. Reviews in the neurosciences 2020. [CrossRef]
- Modanloo, M.; Shokrzadeh, M. Analyzing Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis: Potential Role of L-carnitine. Iranian journal of kidney diseases 2019, 13, 74-86.
- Infante, J.P.; Huszagh, V.A. Secondary carnitine deficiency and impaired docosahexaenoic (22:6n-3) acid synthesis: a common denominator in the pathophysiology of diseases of oxidative phosphorylation and beta-oxidation. FEBS Lett 2000, 468, 1-5. [CrossRef]
- Mantle, D.; Hargreaves, I.P. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neurodegenerative Disorders: Role of Nutritional Supplementation. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [CrossRef]
- Lonsdale, D. A review of the biochemistry, metabolism and clinical benefits of thiamin(e) and its derivatives. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2006, 3, 49-59. [CrossRef]
- Marsac, C.; Benelli, C.; Desguerre, I.; Diry, M.; Fouque, F.; De Meirleir, L.; Ponsot, G.; Seneca, S.; Poggi, F.; Saudubray, J.M.; et al. Biochemical and genetic studies of four patients with pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 alpha deficiency. Human genetics 1997, 99, 785-792. [CrossRef]
- Naito, E.; Ito, M.; Takeda, E.; Yokota, I.; Yoshijima, S.; Kuroda, Y. Molecular analysis of abnormal pyruvate dehydrogenase in a patient with thiamine-responsive congenital lactic acidemia. Pediatric research 1994, 36, 340-346. [CrossRef]
- Naito, E.; Ito, M.; Yokota, I.; Saijo, T.; Chen, S.; Maehara, M.; Kuroda, Y. Concomitant administration of sodium dichloroacetate and thiamine in west syndrome caused by thiamine-responsive pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency. Journal of the neurological sciences 1999, 171, 56-59. [CrossRef]
- Naito, E.; Ito, M.; Yokota, I.; Saijo, T.; Matsuda, J.; Ogawa, Y.; Kitamura, S.; Takada, E.; Horii, Y.; Kuroda, Y. Thiamine-responsive pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency in two patients caused by a point mutation (F205L and L216F) within the thiamine pyrophosphate binding region. Biochimica et biophysica acta 2002, 1588, 79-84. [CrossRef]
- Naito, E.; Ito, M.; Yokota, I.; Saijo, T.; Matsuda, J.; Osaka, H.; Kimura, S.; Kuroda, Y. Biochemical and molecular analysis of an X-linked case of Leigh syndrome associated with thiamin-responsive pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis 1997, 20, 539-548. [CrossRef]
- Polster, B.J.; Yoon, M.Y.; Hayflick, S.J. Characterization of the human PANK2 promoter. Gene 2010, 465, 53-60. [CrossRef]
- Ekstrand, M.I.; Falkenberg, M.; Rantanen, A.; Park, C.B.; Gaspari, M.; Hultenby, K.; Rustin, P.; Gustafsson, C.M.; Larsson, N.G. Mitochondrial transcription factor A regulates mtDNA copy number in mammals. Human molecular genetics 2004, 13, 935-944. [CrossRef]
- Puigserver, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1 alpha): transcriptional coactivator and metabolic regulator. Endocrine reviews 2003, 24, 78-90. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Puigserver, P.; Andersson, U.; Zhang, C.; Adelmant, G.; Mootha, V.; Troy, A.; Cinti, S.; Lowell, B.; Scarpulla, R.C.; et al. Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell 1999, 98, 115-124. [CrossRef]
- Talevi, A. Multi-target pharmacology: possibilities and limitations of the "skeleton key approach" from a medicinal chemist perspective. Frontiers in pharmacology 2015, 6, 205. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, X.J. [Multi-target therapeutics and new drug discovery]. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2009, 44, 226-230.
- Zimmermann, G.R.; Lehar, J.; Keith, C.T. Multi-target therapeutics: when the whole is greater than the sum of the parts. Drug discovery today 2007, 12, 34-42. [CrossRef]
- Keith, C.T.; Borisy, A.A.; Stockwell, B.R. Multicomponent therapeutics for networked systems. Nature reviews. Drug discovery 2005, 4, 71-78. [CrossRef]
- Borisy, A.A.; Elliott, P.J.; Hurst, N.W.; Lee, M.S.; Lehar, J.; Price, E.R.; Serbedzija, G.; Zimmermann, G.R.; Foley, M.A.; Stockwell, B.R.; et al. Systematic discovery of multicomponent therapeutics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2003, 100, 7977-7982. [CrossRef]
- Butcher, E.C. Can cell systems biology rescue drug discovery? Nature reviews. Drug discovery 2005, 4, 461-467. [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.T.; Beal, M.F. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 2006, 443, 787-795. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Gabr, M.T. Multitarget therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer's disease. Neural Regen Res 2019, 14, 437-440. [CrossRef]
- Maramai, S.; Benchekroun, M.; Gabr, M.T.; Yahiaoui, S. Multitarget Therapeutic Strategies for Alzheimer's Disease: Review on Emerging Target Combinations. Biomed Res Int 2020, 2020, 5120230. [CrossRef]
- Bawa, P.; Pradeep, P.; Kumar, P.; Choonara, Y.E.; Modi, G.; Pillay, V. Multi-target therapeutics for neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Drug discovery today 2016, 21, 1886-1914. [CrossRef]
- Jackowski, S. Proposed Therapies for Pantothenate-Kinase-Associated Neurodegeneration. J Exp Neurosci 2019, 13, 1179069519851118. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




