Submitted:
19 September 2023
Posted:
21 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Analytical Target Profile (ATP)
2.2. Critical Quality Attributes (CQA)
2.3. Risk Management (QRM)
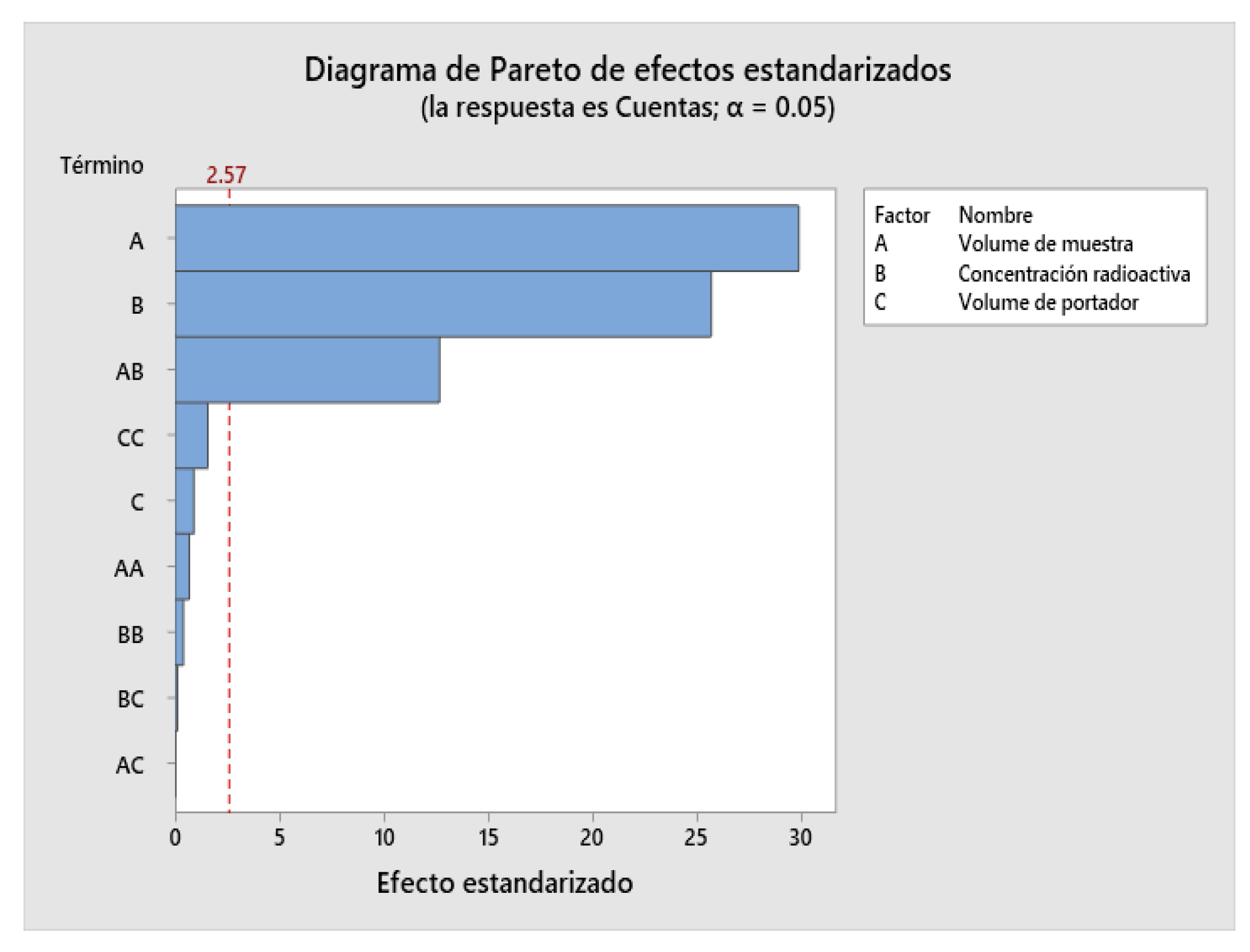
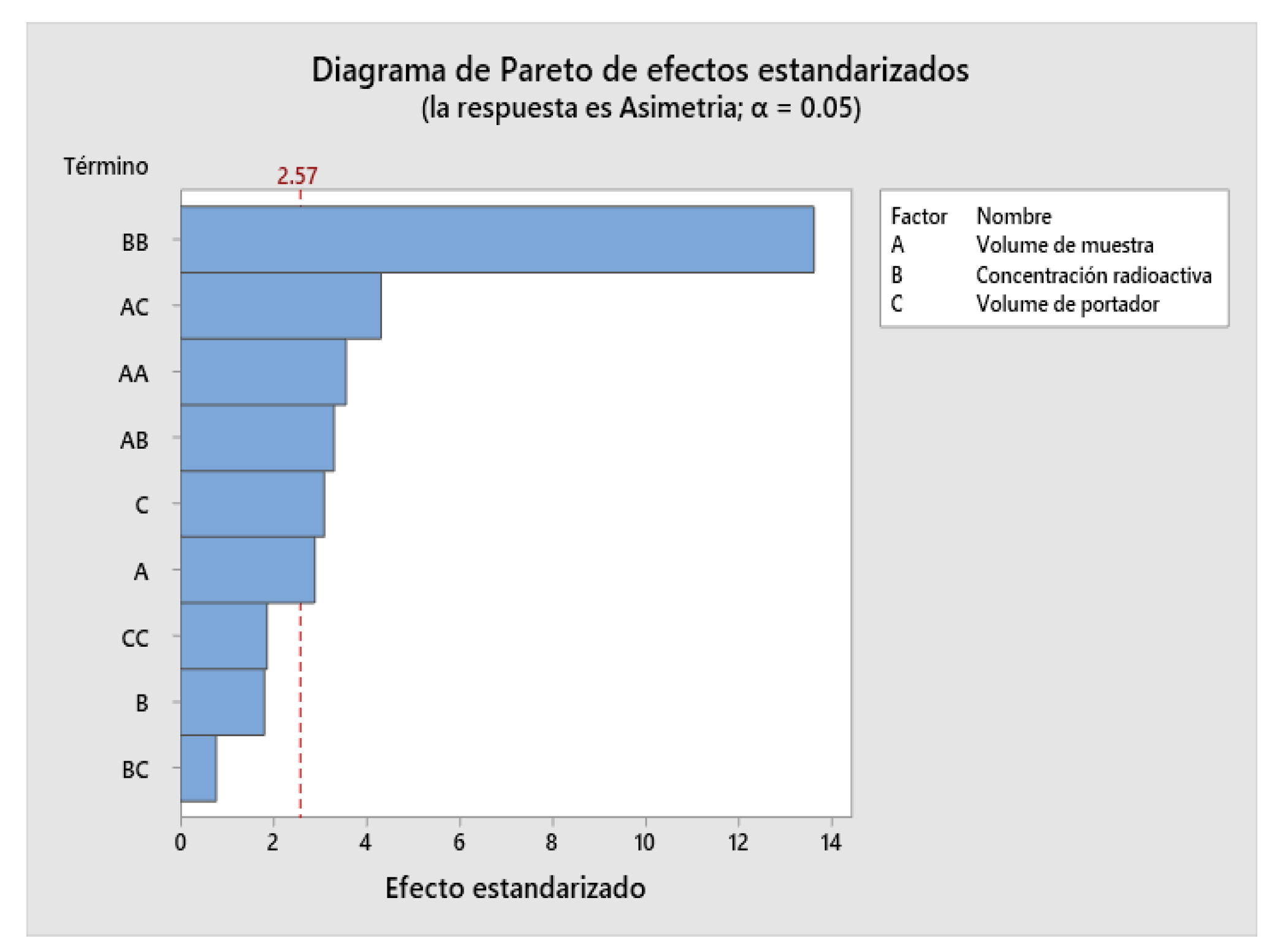
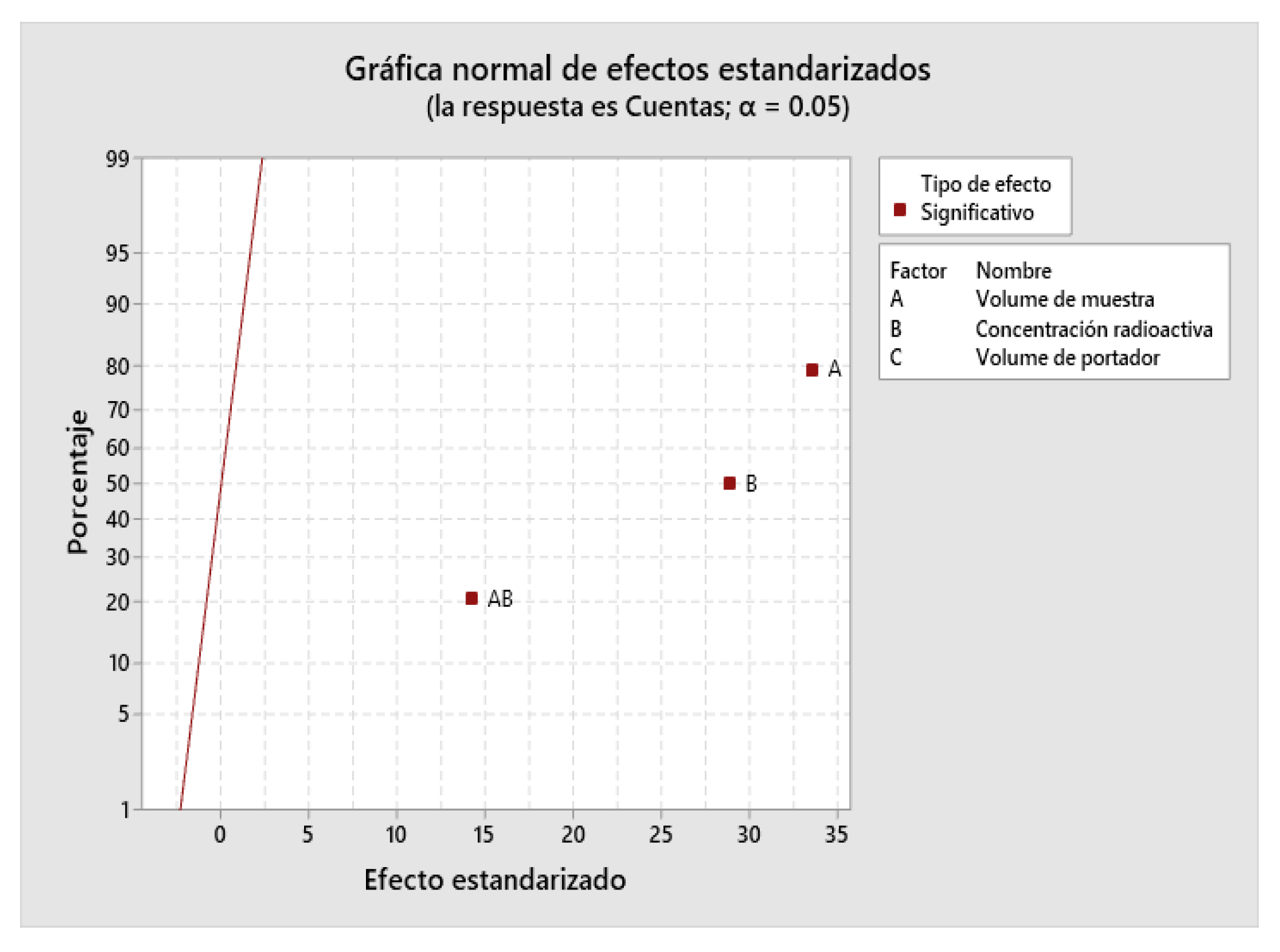
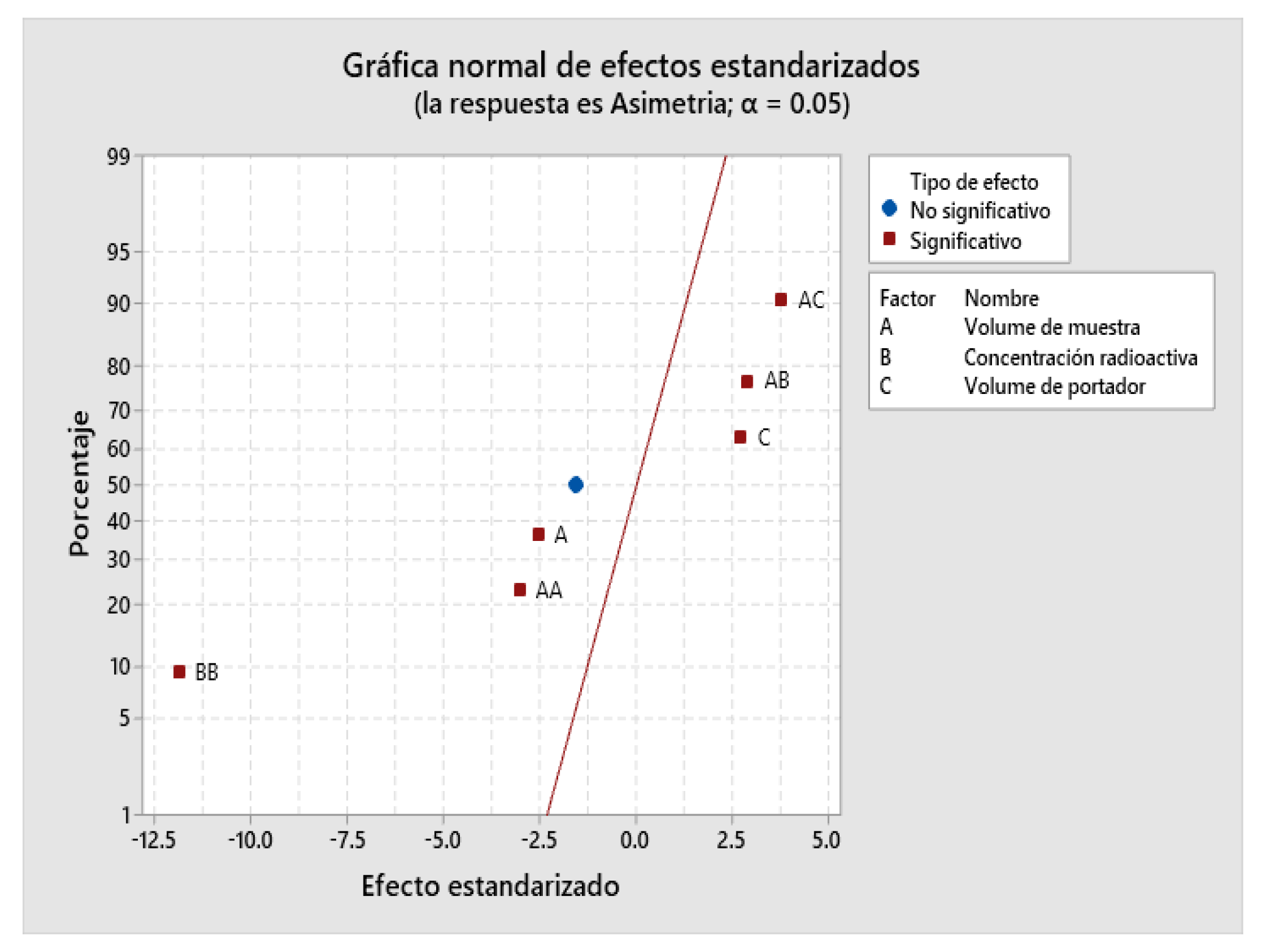
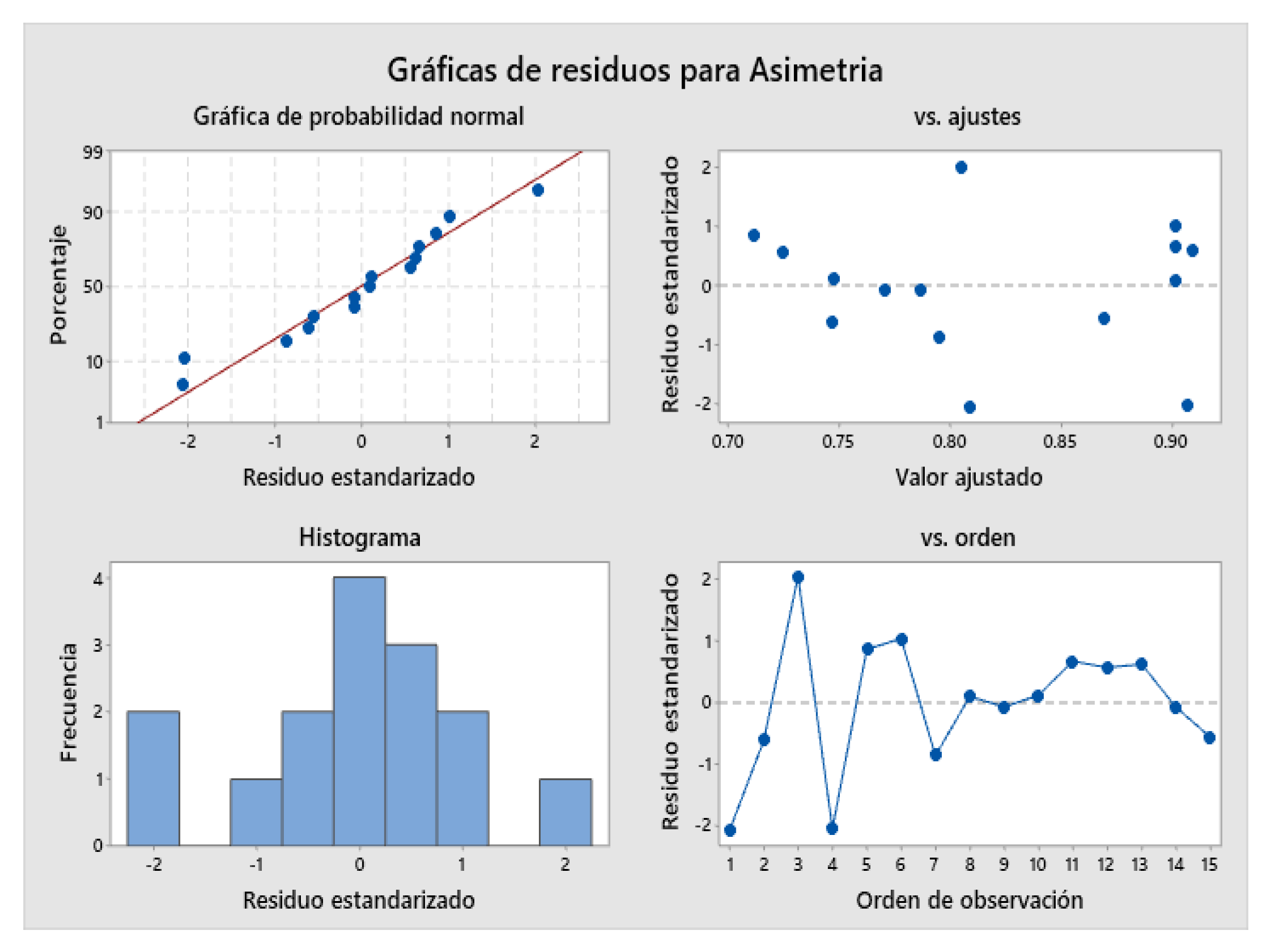
2.4. Design of Experiments (DOE)
| Factor | Name | Low | High |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Injection volume | 1 | 3 |
| B | Radioactive concentration | 5 | 15 |
| C | Carrier volume | 10 | 40 |
| S | R-quad. |
R-quad. (adjusted) |
R-quad. (pred) |
| 2229.99 | 99.71% | 99.18% | 96.19% |
| S | R-quad. |
R-quad. (adjusted) |
R-quad. (pred) |
| 0.0176392 | 97.98% | 94.36% | 70.19% |
| S | R-quad. |
R-quad. (adjusted) |
R-quad. (pred) |
| 1984.49 | 99.49% | 99.35% | 98.91% |
| S | R-quad. |
R-quad. (adjusted) |
R-quad. (pred) |
| 0.0200620 | 96.35% | 92.70% | 76.07% |
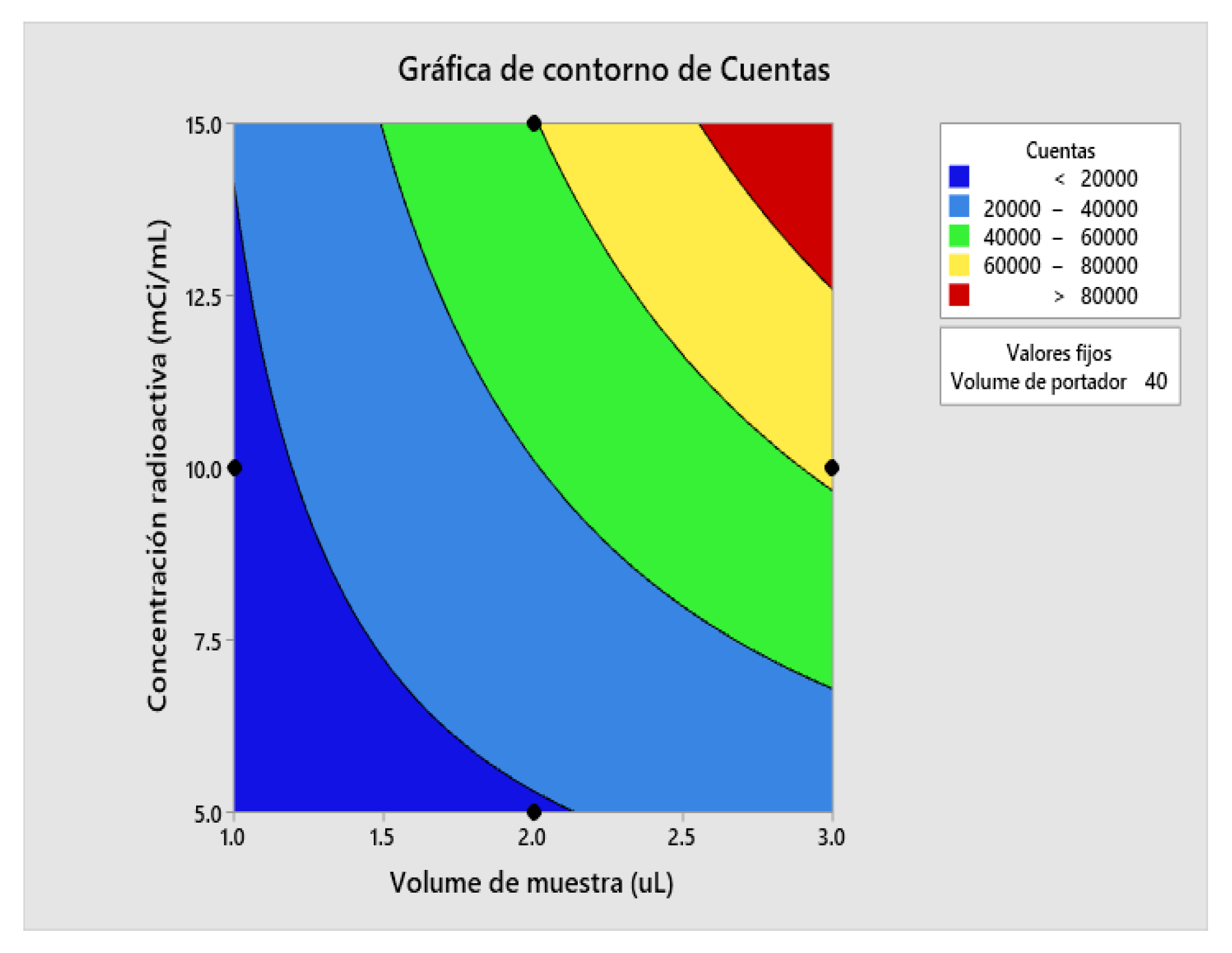
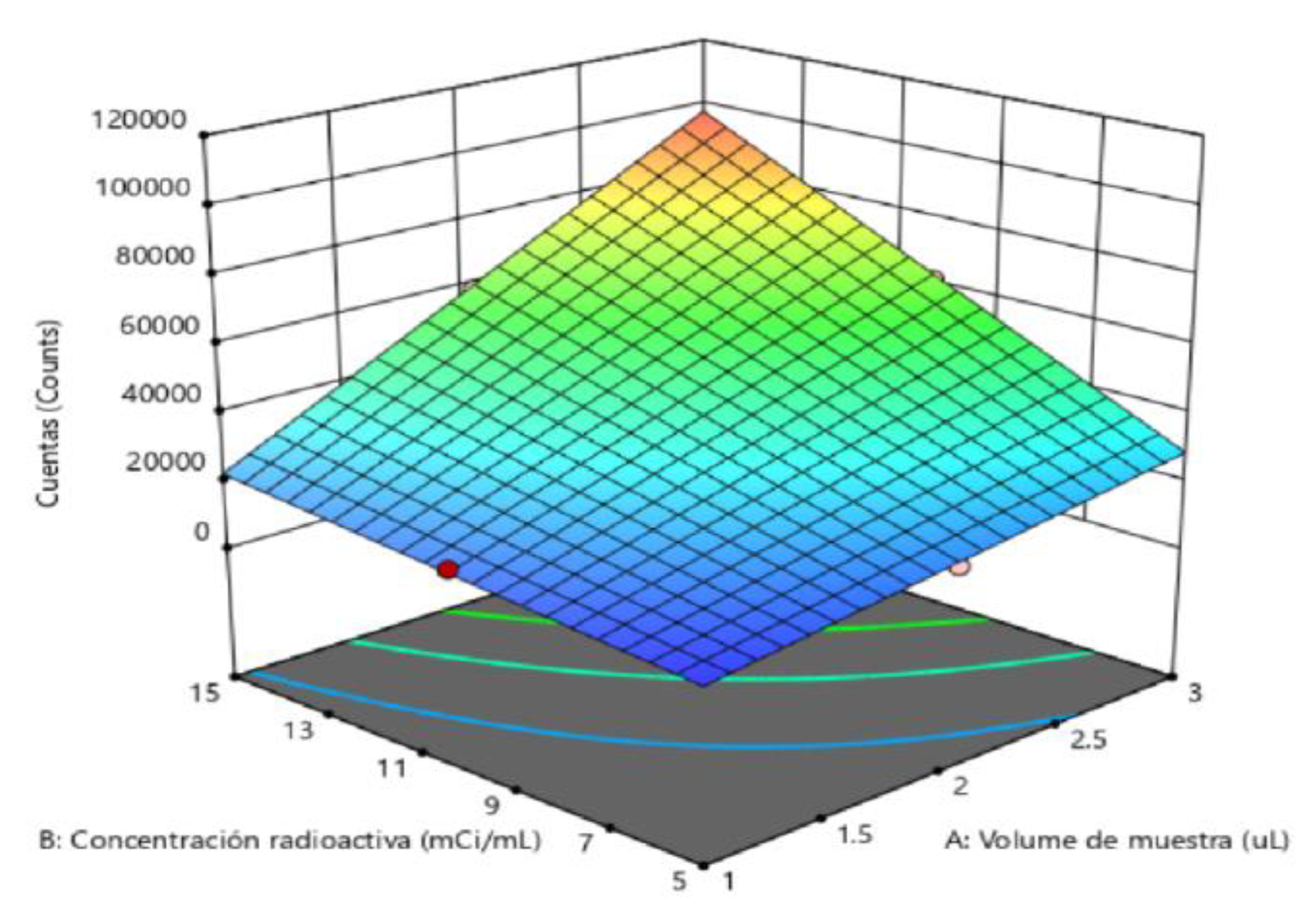
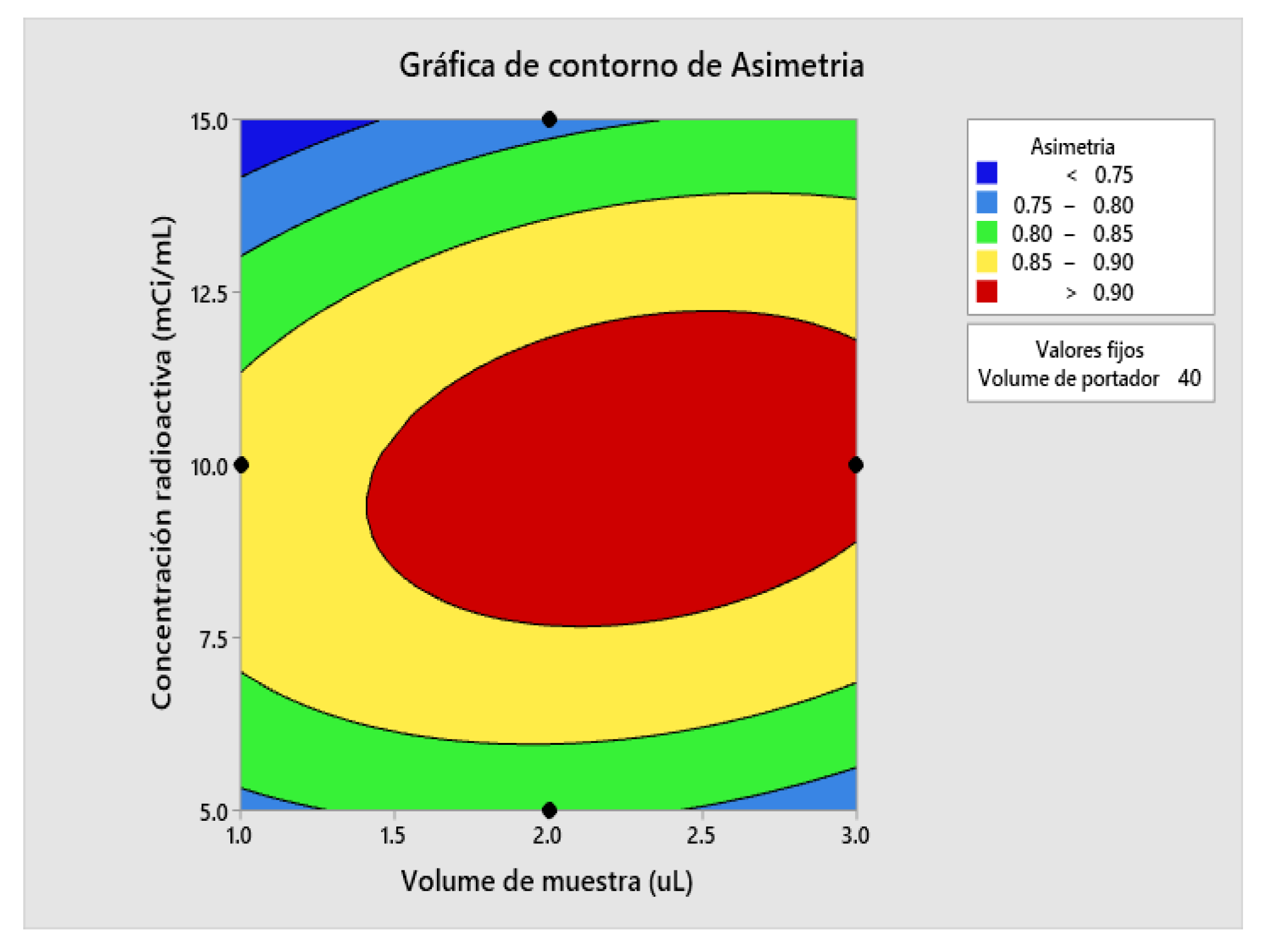
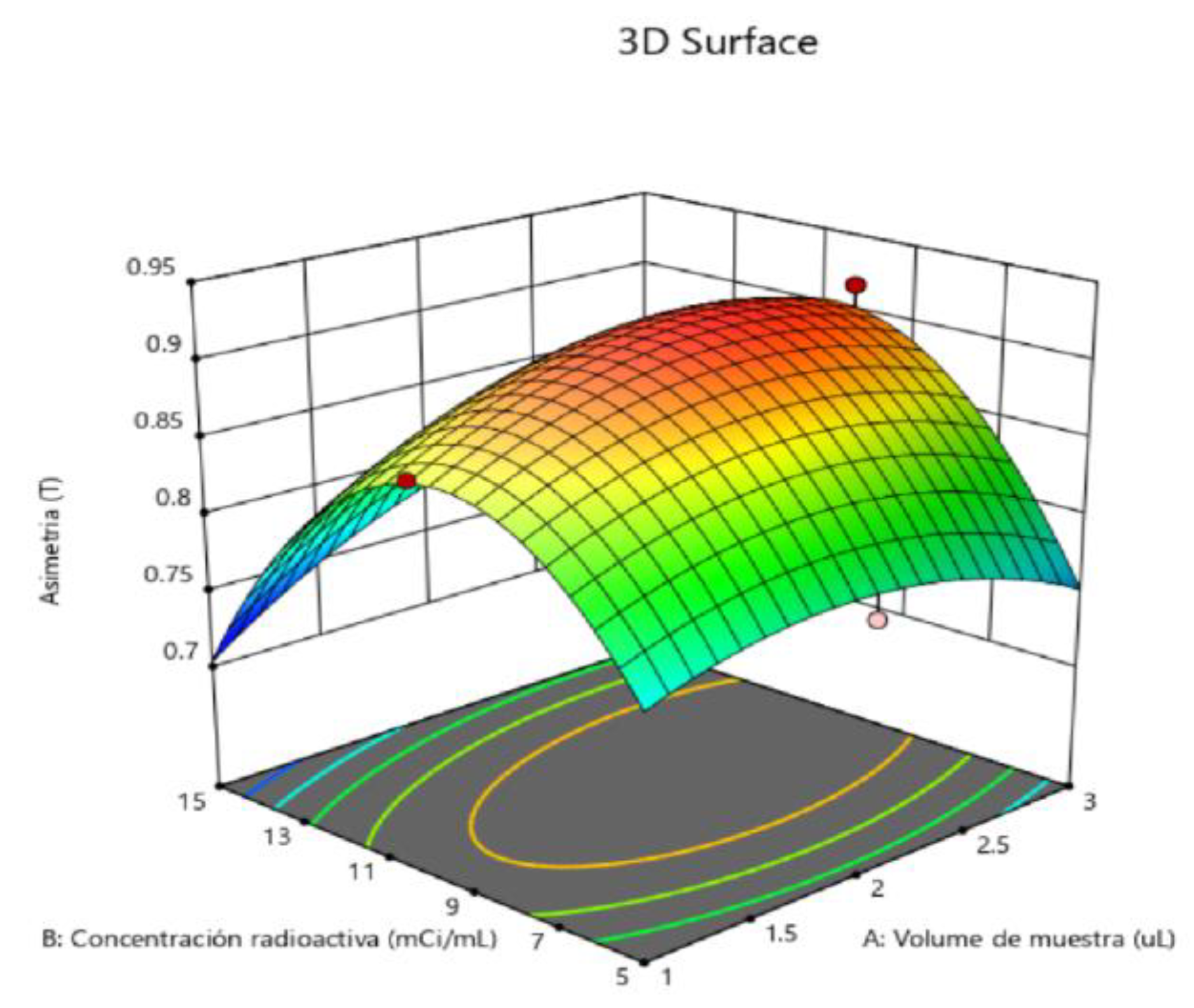
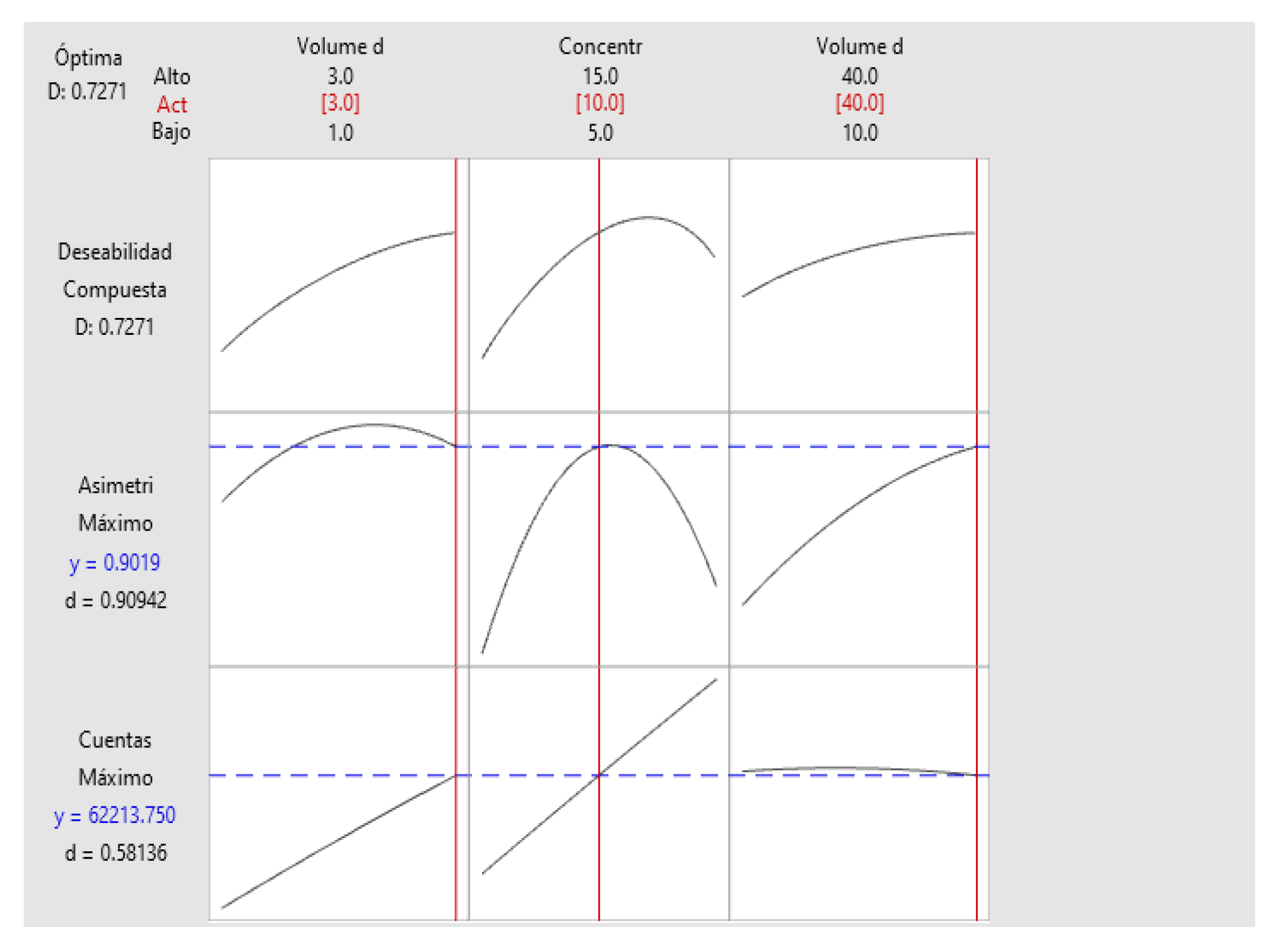
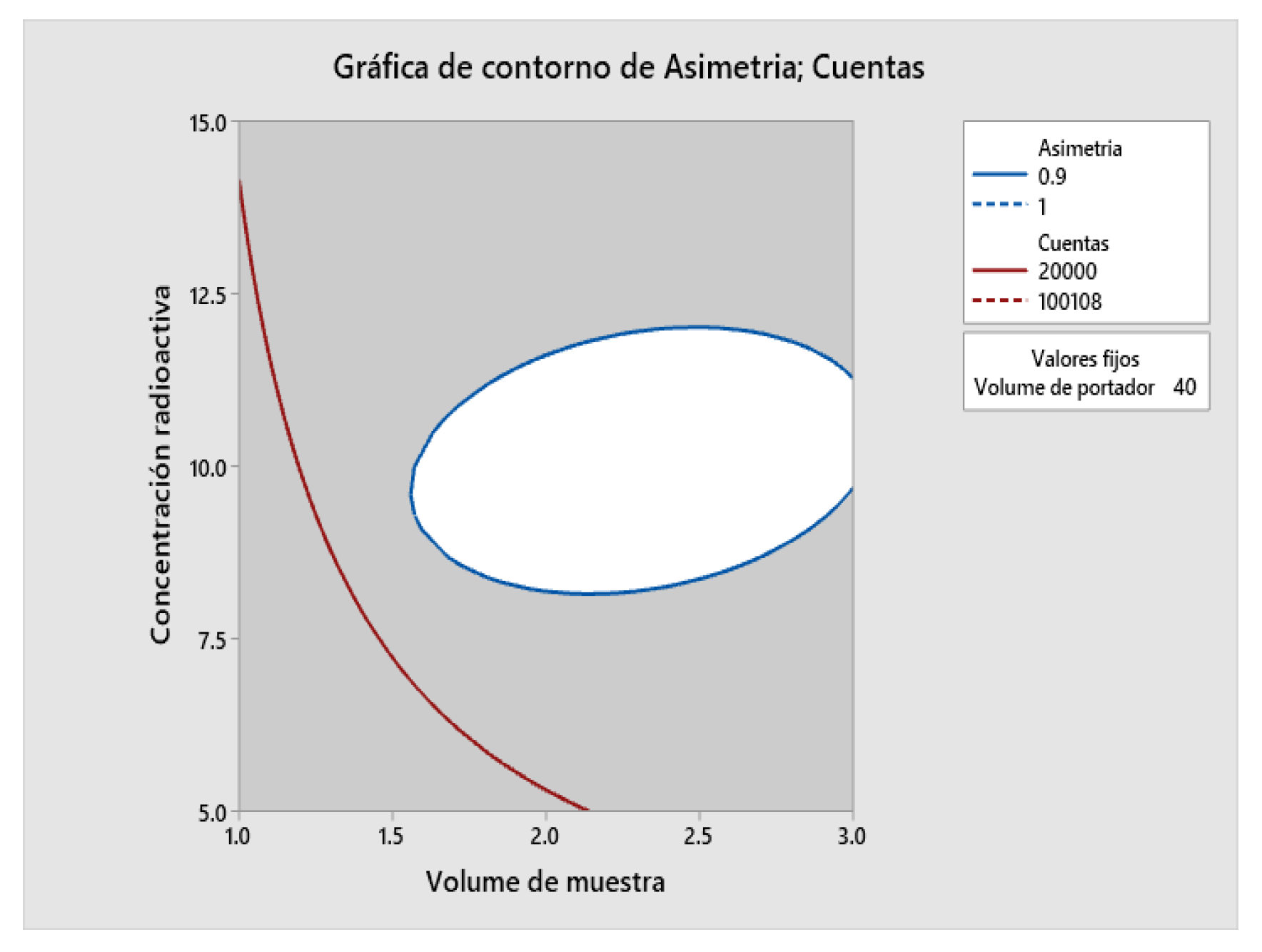
2.5. Determination of Method Operable Design Region (MODR).
| Variable | Setting Value |
| Sample Volume | 3 |
| Radioactive concentration | 10 |
| Carrier volume | 40 |
| Response | Adjustment |
EE of adjustment |
95% CI | 95% PI |
| Asymmetry | 0.9019 | 0.0153 | (0.8627; 0.9412) | (0.8420; 0.9619) |
| Counts | 62214 | 1931 | (57249; 67178) | (54631; 69797) |
| Solution | Sample volume | Radioactive concentration | Carrier Volume | Asymmetry adjustment | Counts Adjustment | Compound desirability |
| 1 | 3 | 10 | 40 | 0.901938 | 62213.8 | 0.727118 |
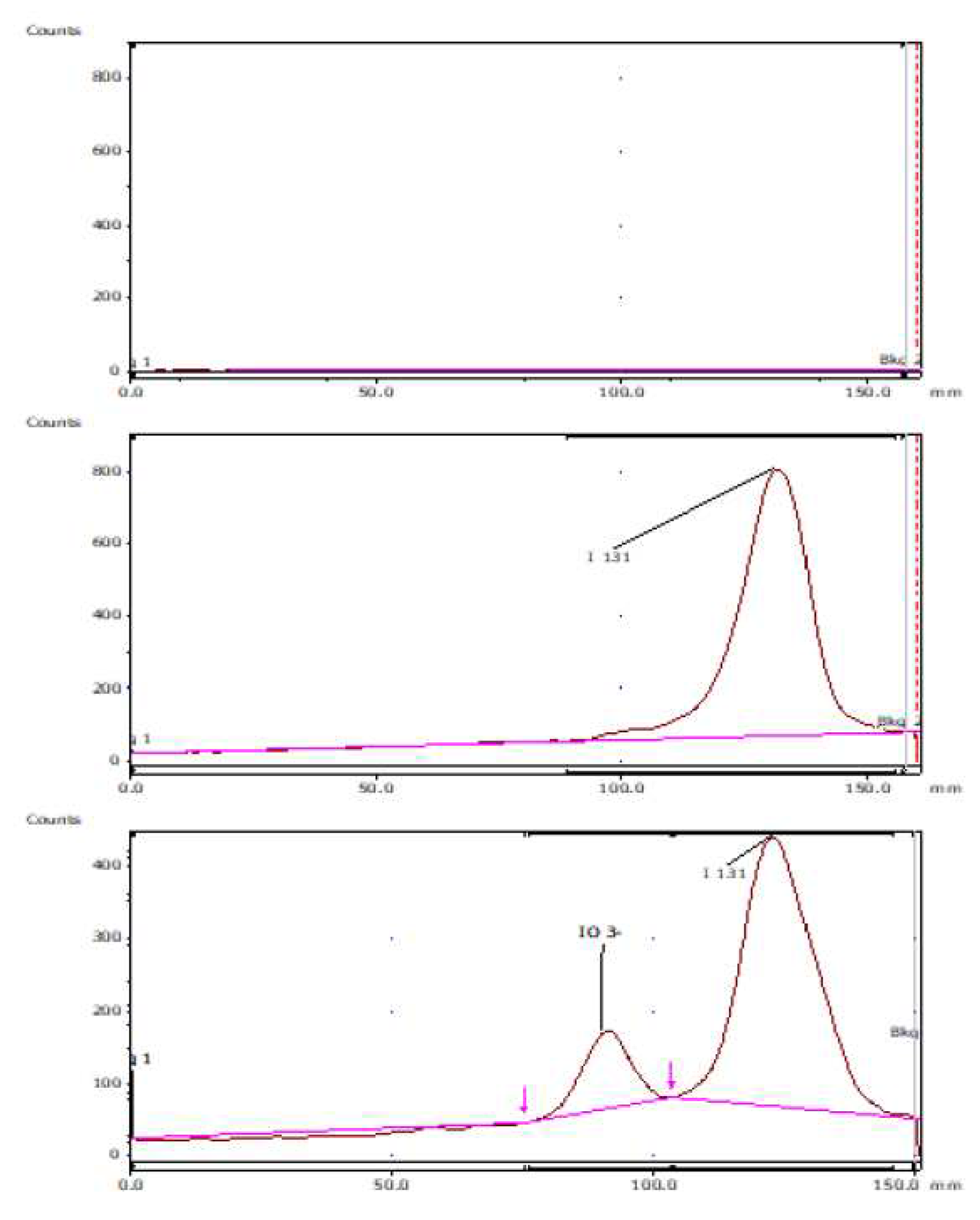
2.6. Selectivity Determination
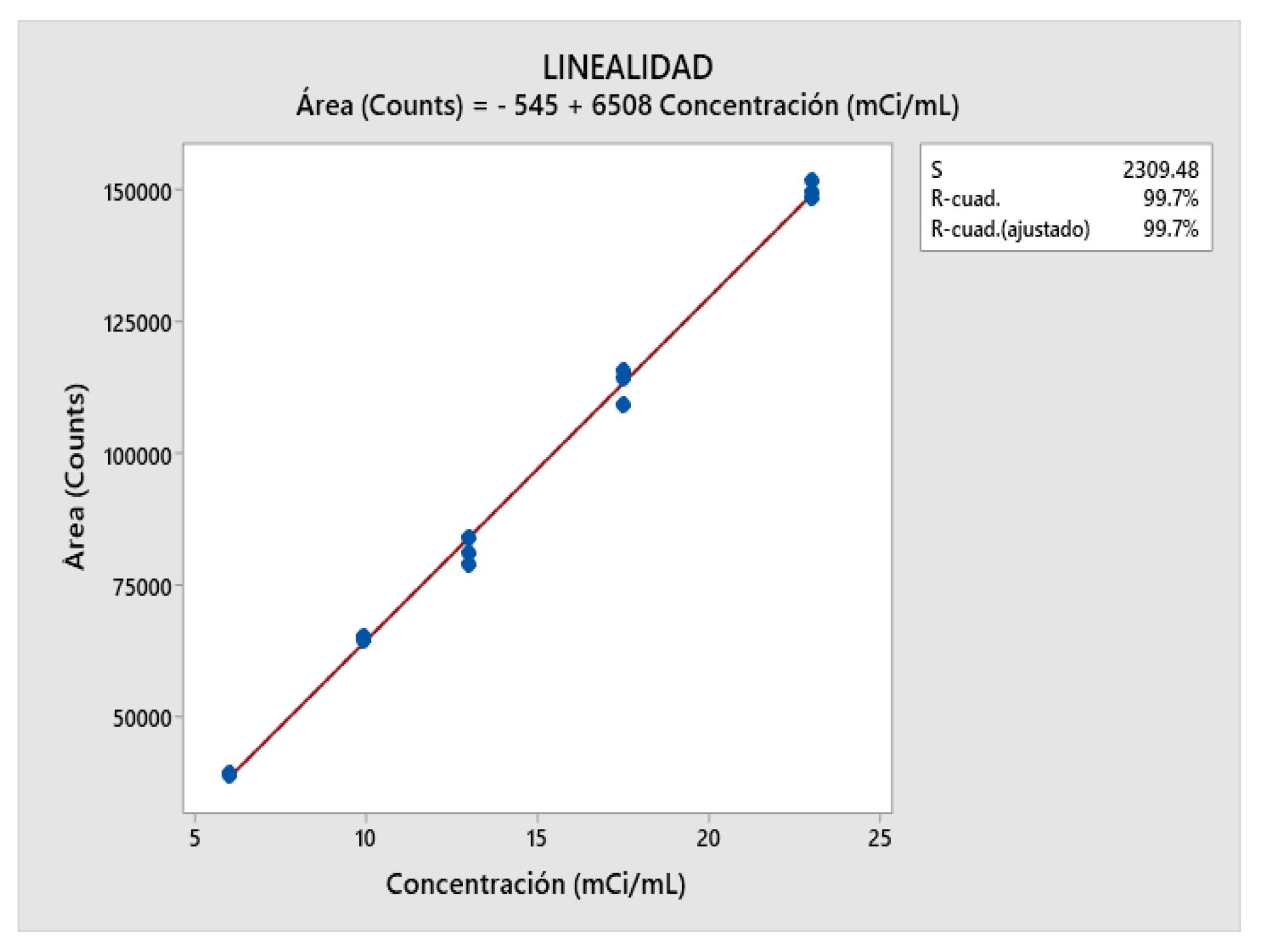
2.7. Linearity Determination
| Levels (mCi/mL) | Area (Counts) Average |
|---|---|
| 6.00 | 39143.333 ± 0.7825 |
| 10.00 | 65067.333 ± 0.6271 |
| 13.00 | 81480.666 ± 3.0296 |
| 17.50 | 113205.33 ± 2.9852 |
| 23.00 | 150009.00 ± 1.1630 |
2.8. Determination of Precision
| Analyst Equipment |
Area Counts |
PRQ (%) |
RSD (%) |
%RSD Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyst 1 | 64930 | 101,05 | 1,1375 | 0,624 |
| Equipment 1 | 65526 | 98,185 | ||
| 66521 | 99,327 | |||
| 63468 | 98,392 | |||
| 65784 | 98,015 | |||
| 63891 | 99,102 | |||
| Analyst 2 | 11235 | 99,902 | 2,6032 | |
| Equipment 2 | 11766 | 99,958 | ||
| 11845 | 99,890 | |||
| 11716 | 99,923 | |||
| 12126 | 99,844 | |||
| 11992 | 99,825 |
2.9. Robustness Determination
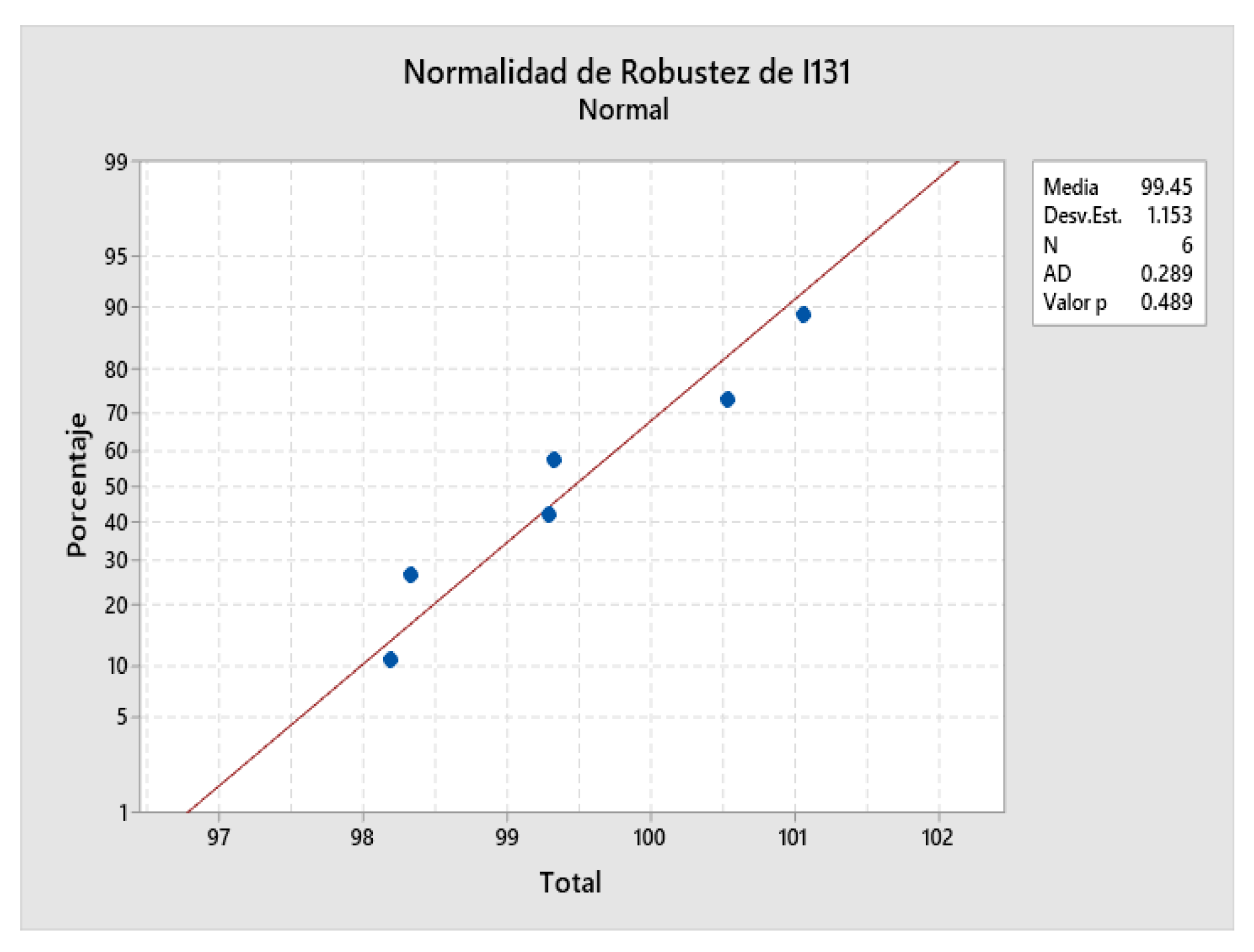
2.10. Determination of the Limit of Detection and Quantitation
2.11. Rank Determination
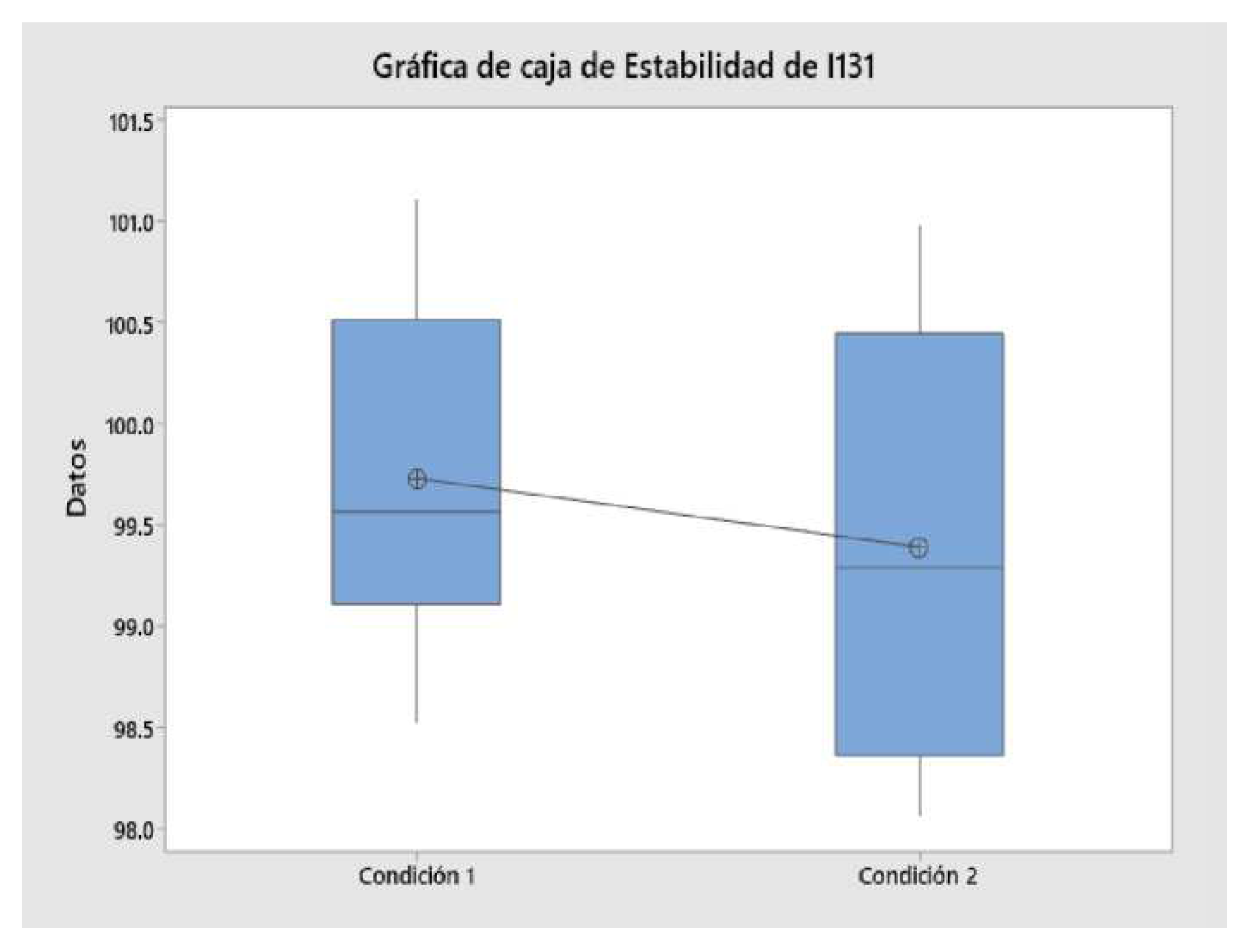
2.12. Sample Solution Stability Determination
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Process Description
3.2. Sampling Plan
3.3. Analytical Method
3.3.1. Equipment, Materials and Reagents
- Chromatographic paper No. 1 of 10 x 200 mm.
- Chambers or chromatographic tanks.
- Micropipette from 2 to 20 µL Code: TH80AC and micropipette from 20 to 200 µL Code: TH82AC.
- Radio-TLC scanner: Code: PM05AC, Brand: Scan-RAM.
- Single channel gamma spectrometry chain: Code: PM03AC, Brand: Canberra.
- Dose calibrator: Code: CA10AC, Brand: Capintec.
- Radiation Monitor: Code: DP28JP, Brand: Technical Associates.
- 131I radiochemical fume hood.
- Handheld Dosimeter.
- Body dosimeter.
- Methanol ACS, Brand: Merck.
- Potassium iodide ACS, Brand: Merck.
- ACS sodium bicarbonate, Brand: Merck.
- Starch SR, Brand: Merck.
- Potassium Iodate, Brand: J.T.Baker.
- Hydrogen Peroxide, Brand: Merck.
3.3.2. Chromatographic System for Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
- Detector: NaI (sodium iodide).
- Mobile phase: 70% methanol
- Stationary phase: Chromatographic Paper No. 1
- Volume: 3 µL.
- Time: 90 minutes approx.
3.4. Analytical Quality by Design
3.5. Implementation of the AQbD Approach
3.6. Validation of the AQbD Method
3.7. Parameters
3.8. Work Solutions
3.9. Procedure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raman, N.V.V.S.S., Mallu U. R., Bapatu, H. R. Analytical Quality by Design Approach to Test Method Development and Validation in Drug Substance Manufacturing. Journal of Chemistry, 2015, vol. 2015. Article ID435129, 8 pages, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Peraman, R., Bhadraya, K., & Padmanabha Reddy, Y. Analytical Quality by Design: A Tool for Regulatory Flexibility and Robust Analytics. International Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2015, Vol. 2015. Article ID 868727, 9 pages, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Alhakeem, M. A., Ghica, M. V., Pirvu, C. D., Anuta, V., & Popa, L. Analytical Quality by Design with the Lifecycle Approach: A Modern Epitome for Analytical Method Development. Acta Marisiensis-Serie Medica, 2019; 65(2): 37-44. [CrossRef]
- Programa ARCAL. Manual de protocolos de calidad de radiofármacos. ARCAL XV Producción y control de radiofármacos. Organismo Internacional de Energía Atómica. Viena. Austria. 1999.
- Soriano, B., Mendarte, L. & San Martín, E. Agentes de diagnóstico y radiofarmacia. Farmacia Hospitalaria. Tomo II. Pág. 758 - 759. Universidad de Belgrano. Madrid. España. 2002.
- Chain, C. Y. & Illanes, L. Radiofármacos en medicina nuclear. Fundamentos y aplicación clínica. 1era Edición. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas. Universidad Nacional de la Plata. Buenos Aires. Argentina. 2015.
- USP 43 NF 38 – Farmacopea de los Estados Unidos de América. Monografía Oficial del Ioduro de Sodio I 131 Solución. 2020. p. 2367-2368.
- Priyanka P. Pande, Sadikali F. Sayyad, Machindra J. Chavan, Sanjay R. Chaudhari. Quality by design in analytical method development and validation. Journal of Environment and Life Sciences. 2017. Vol. 2 (2), pp. 39 – 45.
- ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline – International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. Pharmaceutical Development. Q8 (R2). 2009.
- ICH Harmonised Guideline – International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requeriments for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. Analytical Procedure Development (Q14). 2022.
- ICH Harmonised Guideline – International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. Validation of Analytical Procedures. Q2 (R2). 2022.
- USP 43 NF 38 – Farmacopea de los Estados Unidos de América. Capitulo General Validación de Procedimientos Farmacopéicos <1225>. 2020.
- Bhusnure O. G., Fasmale R. N., Gandge N. V., Gholve S. B., Giram P. S. QbD Approach for Analytical Method Development and Validation of serotonin by Spectroscopic Method. Interntional Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, Vol. 10 (1), pp. 98 – 117.
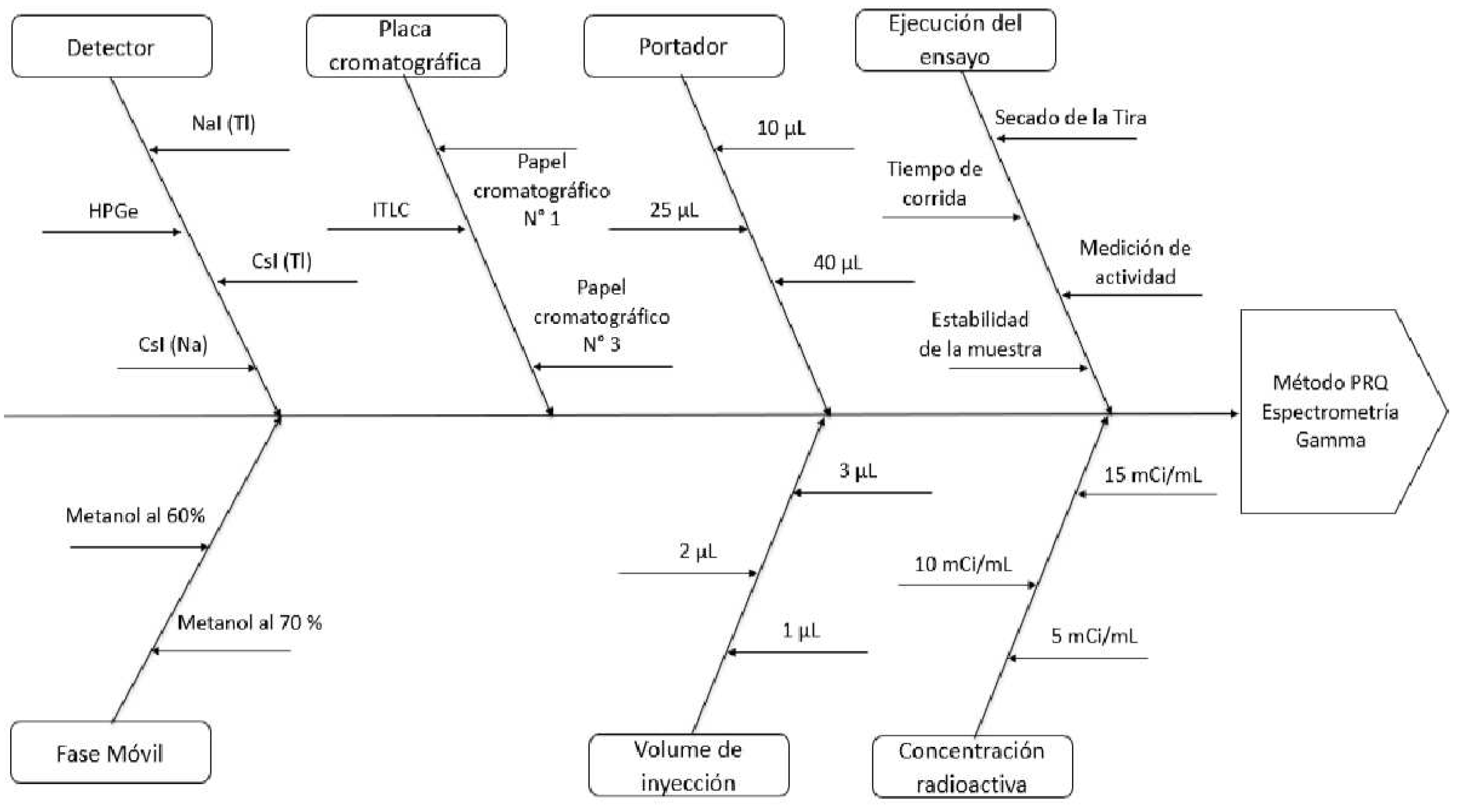
| Analytical Target Profile (ATP) Element | Target / Requirement | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Profile | Determination of the Radiochemical Purity of the Radiopharmaceutical Sodium Iodide I131 Oral Solution Capable of Detecting Radiochemical Impurities and Interferences. | To determine the purity of the radioactive iodide I131 in the radiopharmaceutical Sodium iodide I131 Oral Solution. |
| Instrumentation/ Method Type / Detection Mode / Chromatography | TLC-Scanner, Gamma Spectroscopy, NaI scintillation radiation detector (Tl), thin layer chromatography. | A gamma ray interacts with a scintillator and produces a light pulse that is converted into an electric pulse by a photomultiplier tube (PMT). |
| Specificity | Blank, placebo, and no interference from radiochemical impurities should be observed. | The method must be specific and must be able to distinguish radioactive impurities from radioactive iodide I131. |
| Intermediate Precision / Instrumental and Method Repeatability | The overall RSD with all results below 3%. | ICH Q2 (R2) guideline requirements |
| Linearity | The correlation coefficient and the determination should not be less than 0.99. | Linearity must be obtained at different levels of radioactive concentration. ICH Q2 (R2) guideline requirements. |
| Robustness | The overall RSD with all results below 2%. | The test results should not be affected by small changes in the method parameters. |
| Sample Stability | The overall RSD with all results below 3%. | Test results should not be affected by preparation time when processed. |
| Detection Limit / Quantitation Limit | Minimum quantity that can be detected and can be determined precisely. | ICH Q2 (R2) guideline requirements. |
| Critical Method Variables (CMV) | Critical Analytical Attributes (CAA) |
|---|---|
| Injection volume | Counts |
| Sample Concentration | Delay Factor (RF) |
| Carrier | Asymmetry (T) |
| Mobile Phase | |
| Stationary phase Counting Speed Development Time Detection |
| CAA | Detector | Chromatography Plate | Carrier | Mobile Phase | Injection volume | Radioactive concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Counts | High | Low | Medium | Low | High | High |
| Delay Factor | Low | Medium | High | High | Low | Low |
| Asymmetry | Low | Medium | High | Low | Medium | Low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





