1. Introduction
Underground sewer system is one of the biggest infrastructure in modern cities around the world. However, many city’s sewer systems are deteriorating due to various structural defects on pipe walls, such as crack, fracture, surface damage and deformation [
1]. The most critical step to avoid sewer pipe deterioration is to assess sewer condition regularly and properly. The daily sewer condition assessment work mainly consists of three parts, including sewer pipe structural and functional data acquisition by inspection technologies such as Closed-Circuit TV (CCTV) and Quick View (QV), defects identification and severity level evaluation according to a condition assessment protocol, and assessment report generation for rehabilitation [
2]. It is well recognized that which condition assessment protocol is used plays a most important role in this process [
3,
4,
5,
6]. However, some previous studies have found different protocols may generate significantly different results, and detailed explanations have not been reported in previous studies. This situation causes great confusion for some countries or cities which are planning to make their own condition assessment protocols.
Since the Water Research Center (WRc) in UK released the world’s first manual for condition assessment of drainage pipelines in 1980, the technology of sewer inspection and evaluation has developed rapidly [
7]. Currently, there are many sewer condition assessment protocols in different countries and regions, such as the fourth edition of Sewer Rehabilitation Manual (SRM-4) in UK, the Pipeline Assessment and Certification Program (PACP) in USA, Sewer Physical Condition Grading Protocols (SPCCM) in Canada, and the Technical Specification for Inspection and Evaluation of Urban Sewer (TSIEUR) in China. The main purpose of these protocols is to guide municipal authorities to formulate work plans for the daily maintenance and repair of drainage network by properly identifying sewer defect types and ranking severity levels based on certain rules [
8]. Previous studies have noticed different protocols are likely to give significantly different results even when evaluating the same sewer pipe sections. Khazraeializadeh et al. [
9] used SRM-4, PACP and SPCCM to assess 20 pipe sections with various defects in the City of Edmonton, Canada, and obtained very different results. No pipe segment received the same grade from the three protocols. Shin et al. [
10] compared two protocols in the South Korea: one is the old sewer pipeline condition assessment protocol formulated by the Ministry of Environment of Korea (MOE); and the other is a newly developed sewer condition assessment and rehabilitation decision-making (SCARD) system based on the MOE protocol. Although the two protocols share the same defect types, there are still great differences in assessment results. For example, 45% of the total investigated pipes received the severity level of Grade 5 as per the MOE protocol, which was much higher than the value of 0.6% by the SCARD protocol. For the same sewer pipeline, its defects would not change with the inspection methods or assessment protocols used. Therefore, when analyzing defects’ types and their severity levels from CCTV or QV images, it is expected that different protocols should give similar assessment results.
In order to provide some references for some countries or cities which are planning to make new or update their protocols in the future, in this study, the four most widely-used sewer condition assessment protocols including SRM-4, PACP, SPCCM and TSIEUR were compared by evaluating 182 sewer pipe segments with various types of defects, based on field data in the City of Wuhu, China. The comparisons among the protocols were organized into two stages. In the first stage, the defect definition, defect weight, assessment methods and internal condition grades (ICGs) of the four protocols were qualitatively compared, and the equivalent definitions of structural defects between the protocols was realized. In the second stage, detailed assessments on the 182 sewer pipe segments using the four protocols were conducted, and assessment results are quantitatively compared and analyzed. Main reasons for the differences in the assessment results were revealed and discussed.
2. The Four Protocols
To better compare the assessment results of the four protocols (SRM-4, PACP, SPCCM and TSIEUR), a brief introduction of the protocols is given below.
The first edition of Sewerage Rehabilitation Manual (SRM) was released in UK in 1980, and its fourth edition (SRM-4) was a major update and published in 2004 [
11]. As the first drainage pipeline condition assessment system, SRM is well-known and played an important reference role in the development of sewer condition assessment agreements in other countries and regions. In SRM-4, sewer pipeline defects are divided into structural defects and functional defects, and the description or coding method for a pipeline defect consists of two parts. The first part describes the category that the defect belongs to, such as crack, collapse and joint; and the second part provides information related to the direction and location of the defect, such as longitudinal, circular and multiple defects. Then, SRM-4 assigns a score between 1 and 165 to each defect and calls it “Deduct Value”. Since a sewer pipeline may have many defects, by calculating the peak score of all defects in the pipeline and comparing it with the predetermined thresholds of different internal condition grades (ICGs, Grade 1 to Grade 5), the condition level of the pipeline can be determined.
The National Association of Sewer Service Companies (NASSCO) in the United States established the Pipeline Assessment and Certification Program (PACP) in 2004 with assistance from the WRc [
12]. Although PACP is the North American localized SRM, it formulates defect levels and designs a new coding system from the perspective of structure, function and external factors [
13]. In PACP, pipeline defects are divided into four families, including structural, operational and maintenance, construction features, and others. The coding method for a defect consists of two or three parts. The first part gives the defect category, the second part provides information related to the direction and location of the defect, and the third part is the supplementary description of some categories of the defect, which usually quantitatively describes the severity of the defect. Then, a grade of one to five is assigned to each defect in the pipeline, and ICG of the pipeline is obtained by calculating the average grade of all defects.
The Sewer Physical Condition Grading Protocol (SPCCM) was developed from the second edition of the WRc protocol in 1996 and adapted to the characteristics of some Canadian cities’ sewage collection systems, such as Edmonton [
14]. Therefore, the coding method for a defect in SPCCM similarly consists of two parts as the SRM. However, SPCCM assigns a Deduct Value (score) between 1 and 115 for a defect (vs. 1 to 165 in SRM). Then, the total score, mean score and peak score of all defects in a pipeline are calculated and compared with the correspondingly predetermined thresholds for five ICGs, and the highest grade determined by the three values is taken as the condition level of the pipeline.
Technical Specification for Inspection and Evaluation of Urban Sewer (TSIEUR) is an industry standard issued by China in 2012. This protocol was compiled with reference to the relevant standards of Denmark, UK, and Japan. In TSIEUR, pipeline defects are divided into structural defects and functional defects. A defect is not only given a score of 0.5 to 10, but also a grade of 1 to 4. By calculating the mean score and peak score of all defects in a pipeline and comparing it with the predetermined thresholds, the condition level of the pipeline is determined. However, in TSIEUR, the pipeline condition is graded into 4 levels, which is different from the above three protocols.
From the above information, it can be seen that the four protocols have different condition assessment methods. In the following, we will systematically compare these protocols qualitatively and quantitatively. The focus of the comparison in this study is on structural defects and structural condition grades, considering that the main purpose of the current inspection and repair of drainage sewer pipelines is to protect its structural safety.
3. Qualitative Comparison of The Protocols
Qualitative comparison is the comparison of the same structural defects in different protocols through the descriptions provided by the protocol. The purpose of this part is (a) to understand the different calculating methods in the severity levels of different protocols for the same structural defect, and (b) to find the equivalent definitions of the defect codes in different protocols.
3.1. Equivalent Definitions of Structural Defects in Protocols
The sewer condition assessment protocols determine the condition of a pipeline on the basis of different defect categories and severity of each defect [
15]. Considering that each protocol is designed for a specific country or region, they have developed new functions to adapt to these countries or regions. The unique function of a protocol is likely to have some structural defects that other protocols do not have. For example, both SRM-4 and PACP define the category of structural defects in brick sewers, but SPCCM and TSIEUR do not define it because there are no brick pipes in in Canada and China. In addition to these special cases, each protocol includes the most common structural defects items, such as Crack, Fracture, Broken, Hole, Deformed, Collapsed, Joint, and Surface Damage, but they may have different names in different protocols.
Table 1 lists all the structural defects’ categories contained in the four assessment protocols. There are 26 different structural defects categories in total in the four protocols, including 16 categories in PACP, 13 categories in SRM-4, 11 categories in SPCCM and 10 categories in TSIEUR. In order to pick out the same defect in different protocols, we referred to the detailed definition or description for each structural defect in each protocol, and found that PACP has the most detailed descriptions. By comparison, equivalent definitions were obtained, and the results are summarized in
Table 2. For better understanding, detailed explanations of 8 major and common defects are given below.
Crack. In PACP, a crack is defined as a “visible crack line” on the surface, which is not visibly open. There are four sub-categories in Crack. If the crack is parallel to the joint, it is defined as Circumferential Crack and coded as CC; if the crack is parallel to the pipeline axis, it is defined as Longitudinal Crack and coded as CL; if the position of a single crack changes along the pipeline, it is regarded as Spiral Crack and coded as CS; and when Circumferential Crack and Longitudinal Crack appear at the same location, they are regarded as Multiple Crack and coded as CM. All these subcategories in PACP have equivalent items in SRM-4. In SPCCM, Circumferential Crack is regarded as Crack light and coded as CL. Longitudinal Crack and Spiral Crack both are regarded as Crack Moderate and coded as CM. Multiple Crack is regarded as Crack Severe and Coded as CS. In TSIEUR, Crack has not been classified as detailed above. According to the defect description, they are equivalent to be level I PL in TSIEUR.
Fracture. In PACP, Fracture means that a clear gap has been formed at the defect, but the shape of the pipe has not been affected and no material has fallen off. It can be regarded as a crack that is visibly open. There are also four sub-categories in Fracture. All the Fracture subcategories in PACP have the same equivalent items in SRM-4. In SPCCM, Circumferential Fracture is regarded as Fracture light. Longitudinal Fracture and Spiral Fracture both are regarded as Fracture Moderate. Multiple Fracture is regarded as Fracture Severe. In TSIEUR, Crack has not been classified as detailed above. According to the defect description, they are equivalent to be level Ⅱ PL in TSIEUR.
Broken. In PACP, Broken refers to a pipe that its pieces are noticeably displaced and have moved from their original position. Both SRM-4 and SPCCM have the same defect category. The level III PL in TSIEUR is similar to the severity of this defect.
Collapse. In PACP, pipe has collapsed when it completely loses its structural integrity for about 40% of the cross-sectional area and the camera is blocked. SRM-4 has the same defect category. In SPCCM, if a pipe loses 25% of its cross-sectional area, it is a Collapse Pipe. According to the defect description, Collapse can be equivalent to be level Ⅳ PL in TSIEUR.
Deformed. Deformed is one of the most common structural defects in sewers. The four protocols all have such defect definitions and are divided into sub-categories according to the severity of the deformation. According to the descriptions of these sub-categories, we found they are equivalent in four protocols.
Surface Damage. Surface damage is also one of the most common defects. The four protocols all have such defects defined to describe the failure and damage of the inner wall of the pipeline. Different from the other three protocols, PACP does not divide the defect according to the severity but describes the causes of these surface damages in detail.
Joint. In PACP, Joint defects are divided into three categories, including Offset Joint, Separated Joint and Angular Joint. The Offset Joint and Separated Joint have similar descriptions and definitions in the other three protocols, and their sub-categories are also divided as per defect severity. According to the descriptions of the sub-categories, we found their equivalences in the four protocols.
Sag. This is a structural defect defined only in TSIEUR and SPCCM. The defect refers to the displacement of a pipe at the joint, which causes the vertical position of the pipe change and accumulate water at low places.
3.2. Deduct Values and ICGs
Deduct Values is a concept firstly proposed in SRM, which is used to describe the severity of defects and calculate the ICG of a sewer pipe. Four protocols specify different Deduct Values ranges for structural defects, as shown in
Table 3. Because the Deduct Value range of each protocol is not the same, the defect severity cannot be directly compared. Therefore, the weight of defect, which is defined as the ratio of defect’s Deduct Value to the maximum value, is introduced to make the comparison applicable and easy.
Table 4 compares the Deduct Values of the structural defects and their corresponding weights in the four protocols. After the Deduct Value and the condition level of each defect in a pipe are determined, the condition assessment or the ICGs of the pipeline can be calculated according to the structural rating thresholds of the four protocols, as shown in
Table 5. ICGs are the data that directly reflect the status of the pipe in the condition assessment report [
16]. Different protocols use different predetermined thresholds for ICGs. For PACP, the mean Deduct Value is used for determining the ICGs of the pipe, SRM-4 uses the peak Deduct Value, while SPCCM uses the mean, peak and total Deduct Values at the same time. TSIEUR takes the larger of the mean and the peak Deduct Values.
Table 6 shows the ICGs of the four sewer condition assessment protocols, with Grade 1 being the best and Grade 5 being the worst pipe condition. Among them, only TSIEUR divides the structural condition into four grades. The description of the Grade 1 in TSIEUR is similar to the description of Grade 1 and Grade 2 in other protocols. Therefore, to facilitate subsequent quantitative comparisons among the four protocols, the obtained assessment results of Grade 1 and Grade 2 as per SRM-4, PACP and SPCCM will be assigned to be Grade 1.
4. Quatitative Comparison among The Protocols
4.1. Quantitative Comparison
182 sewer pipelines condition assessment reports from Wuhu city in China were collected for the quantitative comparison among protocols. The quantitative comparison is to compare the assessment results of 182 sewer pipes by using the four protocols, and to further reveal major reasons causing the differences. Of the 182 sewer segments, 90 segments are sanitary pipes and the other 92 segments are storm-water pipes. Diameters of the pipes range from 300 mm to 800 mm and the pipes’ materials include reinforced concrete and PVC.
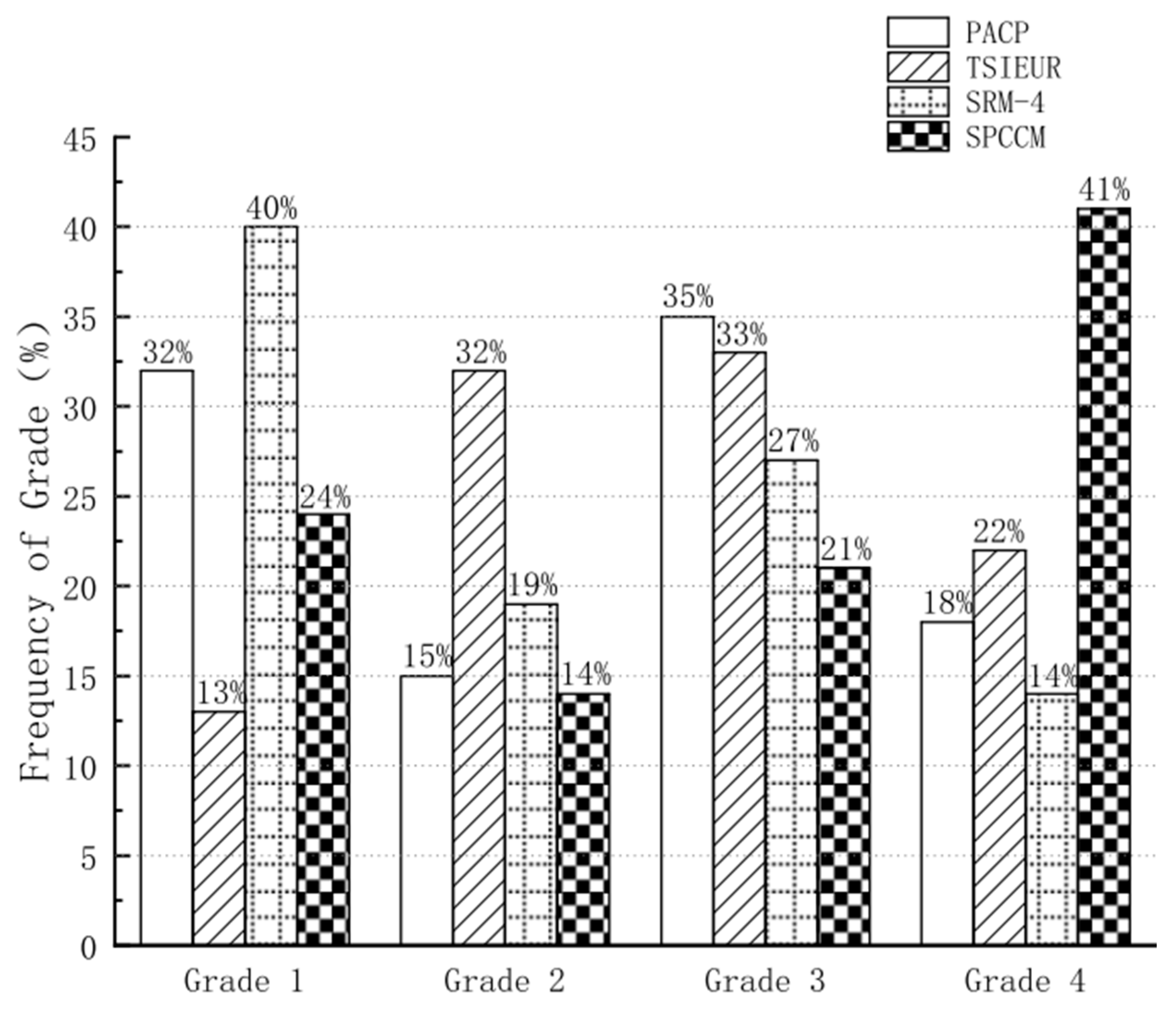
Figure 1 shows the evaluation results on the total 182 segments using the four protocols. According to the evaluation results, it was found that no pipe segment of these 182 segments received the same grade based on the four protocols. To better show the comparison process,
Table 7 shows an example of the condition assessment results on the same one pipe segment by the four protocols. The pipeline in the example is a 300 mm sewage pipe with 34.91 meters of length. As shown in
Table 7, although TEIEUR and PACP both assigned the pipe segment Grade 3, SRM-4 and SPCCM assigned it Grade 4.
As shown in
Figure 1, most pipes are assigned Grade 2 (32%) and Grade 3 (33%) as per TSIEUR. However, most pipes are assigned Grade 1 (32% for PACP, and 40% for SRM-4) and Grade 3 (35% for PACP, and 27% for SRM-4) by PACP and SRM-4. SPCCM gives the most different evaluation results with 41% pipes being Grade 4. In this experiment, the evaluation results obtained from SRM-4 are the most optimistic with 59% pipes being Grade 1 and Grade 2, while SPCCM gives the most pessimistic results with 62% pipes being Grade 3 and Grade 4. SRM-4 results show that 40% of the pipes are in good condition and belong to Grade 1, while SPCCM results suggest that 41% are Grade 4 pipes that need rapid repair. These assessment results are different from the results of Khazraeializadeh et al. [
9], who found that the assessment results from PACP were most optimistic and the results from SRM-4 and SPCCM were similar. The reasons for the significant differences in the evaluation results of the four protocols are further analyzed in the section below.
4.2. Explanations For Different Results Among Protocols
As stated earlier, each protocol may bring some structural defects that other protocols do not have, and thus cause assessment results. The selected 182 pipe segments do not have unique structural defects, and therefore, it is not the reason for the different evaluation results.
It is found that the weight of the defect, defined as the ratio of the defect value to the maximum value (
Table 4), has important influences on the evaluation results. For the same defect, the weight of the defect in PACP is often higher than those of the other three defects. For example, the defect type of “deformed” will be only assigned as Grade 4 or Grade 5 in PACP, and its weight or severity is 80% or 100%. In other protocols, “deformed” has subcategories with lower severity, such as the weight of Deformation Light in SPCCM is only 2%. When these two protocols are used to evaluate the condition of a pipe segment with a slight deformation, it is likely to result in two very different results: PACP evaluates that this pipe needs urgent repair, while SPCCM considers that the repair priority is not high. Actually, SPCCM usually gives less than 10% severity to some low and medium severity defects, and it is also the only protocol that does not give a 100% severity for deformations exceeding 10% of the cross-section. From the perspective of deduct values, it is found that PACP is the strictest of the four protocols for the evaluation of a single defect, while SPCCM is less strict. However, as indicated in
Section 4.1, the evaluation results on 182 experimental pipe segments obtained from SRM-4 are the most optimistic, while SPCCM gives the most pessimistic results. This implies that in addition to the severity of a single defect, there are other factors that affect the ICGs results of sewer pipes [
17].
Because PACP uses the mean deduct value of all defects to calculate ICG of a pipe segment, it means that when a pipe has multiple defects, it is easy for a serious defect to be diluted (averaged) by other low-risk defects. This explains the evaluation results on pipe segments are not so pessimistic (
Figure 1), although PACP is the strictest for a single defect among all the four protocols. It must be noticed that PACP is the only protocol in which the deduct value range coincides with the ICGs (both ranges 1-5), and the dilution phenomenon relies heavily on this fact. When using the peak defect value to determine the pipe’s ICG as in SRM-4, the focus is more on the impact of the worst defect on the pipeline condition and does not encounter the dilution problem. In this experiment, the main reason for the most optimistic evaluation results from SRM-4 is due to its wide Deduct Value range (1-165) with defects score larger than 80 being regarded as Grade 3 or Grade 4. TSIEUR uses the higher of the mean and peak defect value to obtain the ICGs of a pipe. SPCCM uses the mean deduct value, the peak value and the total value respectively to compare with predetermined thresholds, and take the worst condition as the final ICGs evaluation result. Although SPCCM also has a wide deduct value range (1-115), it is found that the mean or peak value determines the pipe’s ICG result in most cases due to their narrow predetermined thresholds. As shown in
Table 5, when the mean value is beyond 1.5, the ICG results will be Grade 4 at least. And if the pipe has any defect with a value greater than or equal to 5, SPCCM will assign the pipe’s ICG to be Grade 5. This means that even if the defect weight is only 4% (the ratio of 5 to 115), this deduct value is enough to make the pipe to be regarded as Grade 5. This causes SPCCM to give the most pessimistic evaluation results compared with other three protocols.
5. Conclusion
In this study, a comparative analysis of four widely-used sewer condition assessment protocols including PACP, TSIEUR, SRM-4 and SPCCM was conducted. This comparison includes a qualitative analysis of the defects, deduct values and assessment methods of the protocols, and a quantitative analysis to evaluate 182 real pipe segments in the City of Wuhu, China. The results show that for the same pipes, the evaluation results of the four protocols are significantly different. The evaluation result of SRM-4 is the most optimistic of the four protocols, while the result of SPCCM is the most pessimistic. Main reasons for the significant difference in results is the different weights of defects and evaluation methods used in the four protocols. Future research needs to develop objective assessment protocols that can truly reflect the condition of drainage pipelines for more regions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Guang-xue Cao. and Shuai Guo; methodology, Guang-xue Cao; data resources, Jun Wei; writing—original draft preparation, Guang-xue Cao.; writing—review and editing, Shuai Guo.; visualization, Guang-xue Cao; supervision, Shuai Guo; project administration, Rong-min Huang; funding acquisition, Mei Li. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Major Special Foundation of Science and Technology of Anhui Province (grant number 202003a07020010) and Yangtze Ecology and Environment Co. Ltd. (No. HB/AH2021039).
Data Availability Statement
All data, models, and code generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Salihu, C.; Hussein, M.; Mohandes, S.R.; Zayed, T. Towards a comprehensive review of the deterioration factors and modeling for sewer pipelines: A hybrid of bibliometric, scientometric, and meta-analysis approach. Journal of Cleaner Production 2022, 351, 131460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Wang, B.; Guo, S.; Zhang, W.M.; Edwini-Bonsu, S. Statistical analysis of sewer odour based on 10-year complaint data. Water Science and Technology 2020, 81, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chughtai, F.; Zayed, T. Integrating WRc and CERIU Condition Assessment Models and Classification Protocols for Sewer Pipelines. Journal of Infrastructure Systems 2011, 17, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opila, M.C.; Attoh-Okine, N. Novel Approach in Pipe Condition Scoring. Journal of Pipeline Systems Engineering and Practice 2011, 2, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowski, D.; James, F. Developing a Focused CIP to Optimize Resources Using Pipeline Renewal Models. Pipelines 2019: Condition Assessment, Construction, and Rehabilitation. Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers 2019, 140–149.
- Tade, O.; O'Neill, S.; Smith, K.G.; Williams, T.; Ali, A.; Bayyati, A.; See, H. Modified sewer asset management to accommodate london's future sustainable development. Structural Survey 2019, 37, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Wang, H.X.; Dang, L.M.; Song, H.K.; Moon, H. Vision-Based Defect Inspection and Condition Assessment for Sewer Pipes: A Comprehensive Survey. Sensors 2022, 22, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phyu, H.E.; Khaodhiar, S. Inspection and Understanding of Sewer Network Condition in Dindaeng District, Bangkok, Thailand. Applied Environmental Research 2021, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazraeializadeh, S.; Gay, L.F.; Bayat, A. Comparative analysis of sewer physical condition grading protocols for the City of Edmonton. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering 2014, 41, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Han, S.; Hwang, H. Comparison of two sewer condition assessment protocols in S. Korea. Desalination and Water Treatment 2016, 57, 29384–29392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WRC (Water Research Center). Manual of sewer condition classification. Water Research Centre, UK 2004.
- Irvin, G. Pipeline assessment and certification program. New Pipeline Technologies, Security, and Safety 2003, 822–825.
- Vladeanu, G.; Matthews, J. Wastewater Pipe Condition Rating Model Using Multicriteria Decision Analysis. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management 2019, 145, 04019058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonton. Sewer Physical Condition Classification Manual. Transportation Department, Drainage Engineering Section, City of Edmonton, Canada 1996.
- Daher, S.; Zayed, T.; Elmasry, M.; Hawari, A. Determining Relative Weights of Sewer Pipelines’ Components and Defects. Journal of Pipeline Systems Engineering and Practice 2018, 9, 04017026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.Z.; Ayed, T.; Moselhi, O. Structural Condition Assessment of Sewer Pipelines. Journal of performance of constructed facilities 2010, 24, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altarabsheh, A.; Mario, V.; Amr, K. New approach for Critical Pipe Prioritization in Wastewater Asset Management Planning. American Society of Civil Engineers 2018, 32, 04018044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).