Submitted:
17 September 2023
Posted:
19 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
3. Results and Discussion
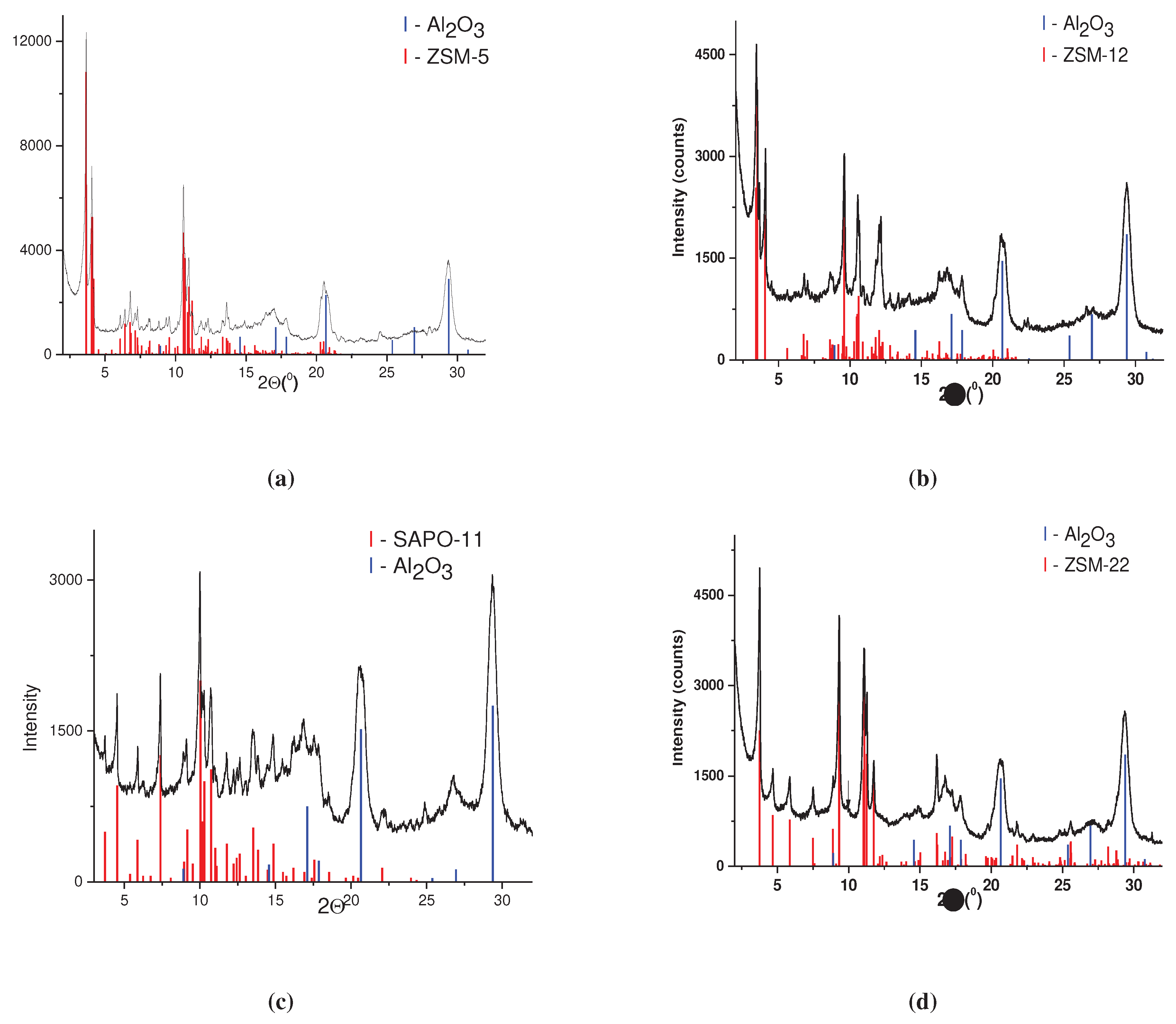
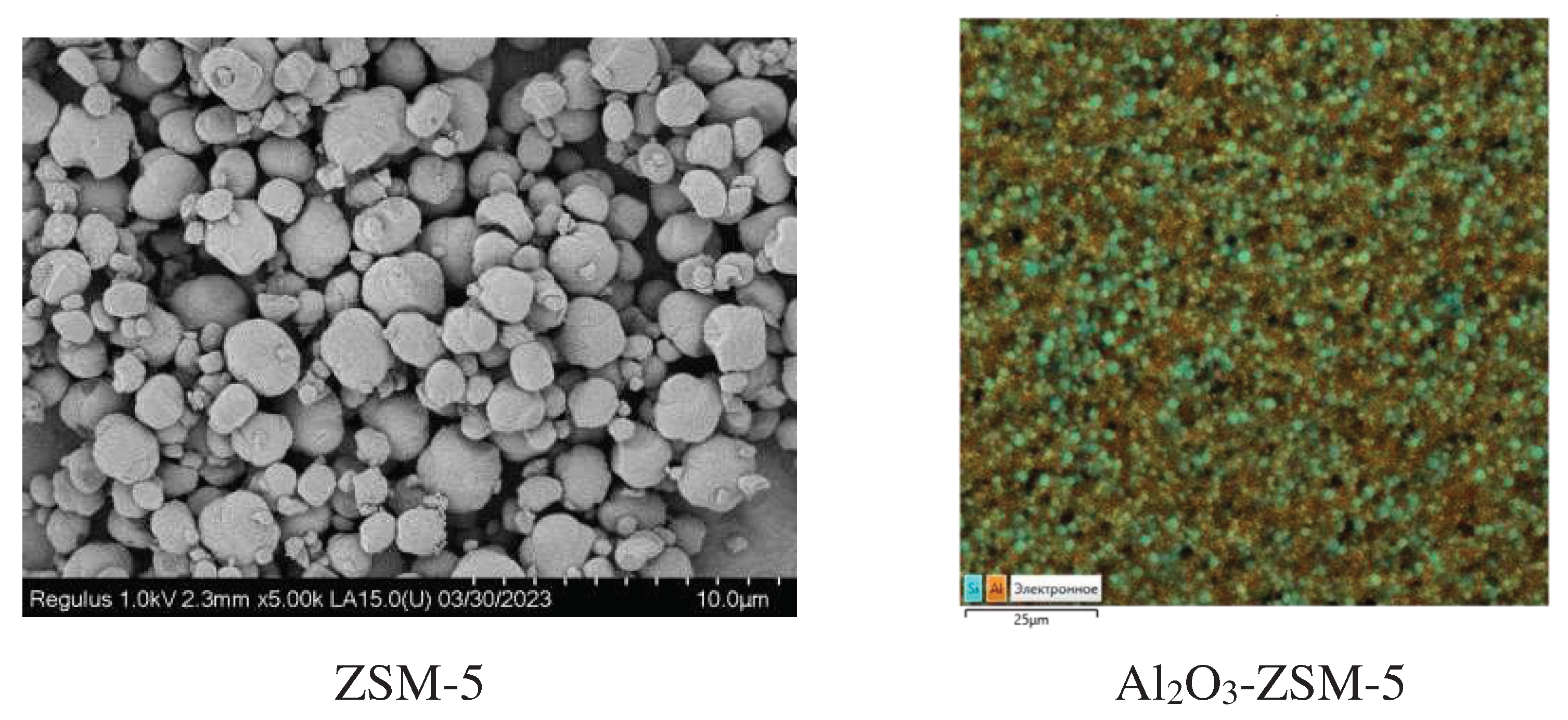
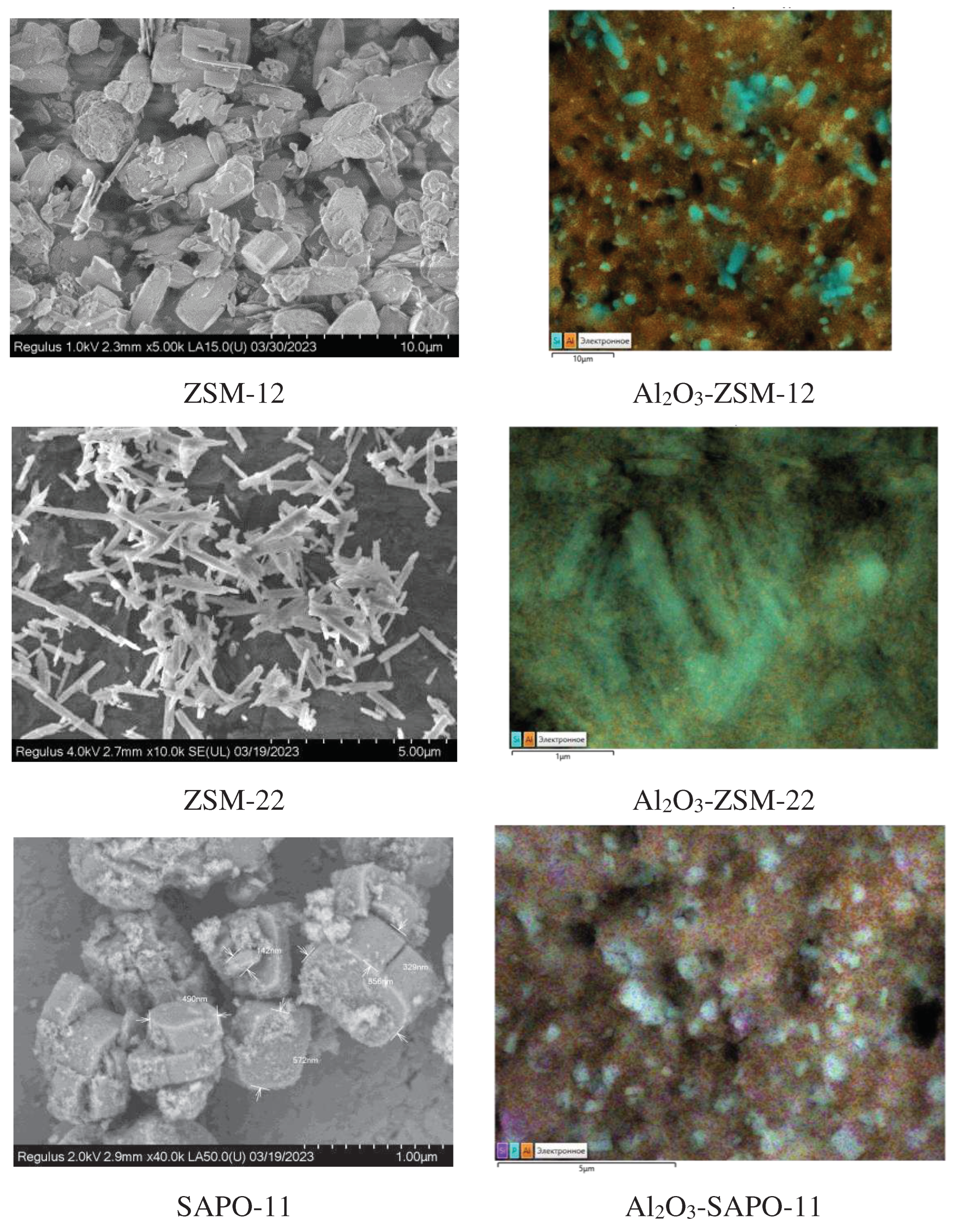
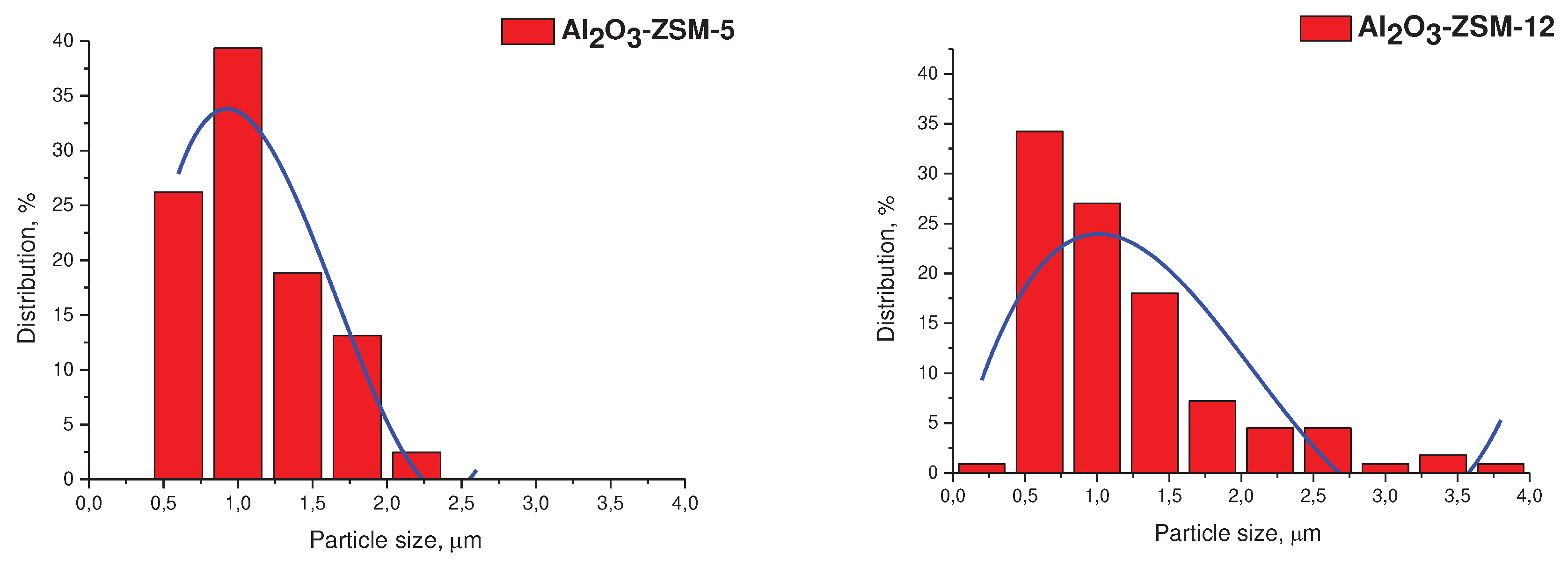
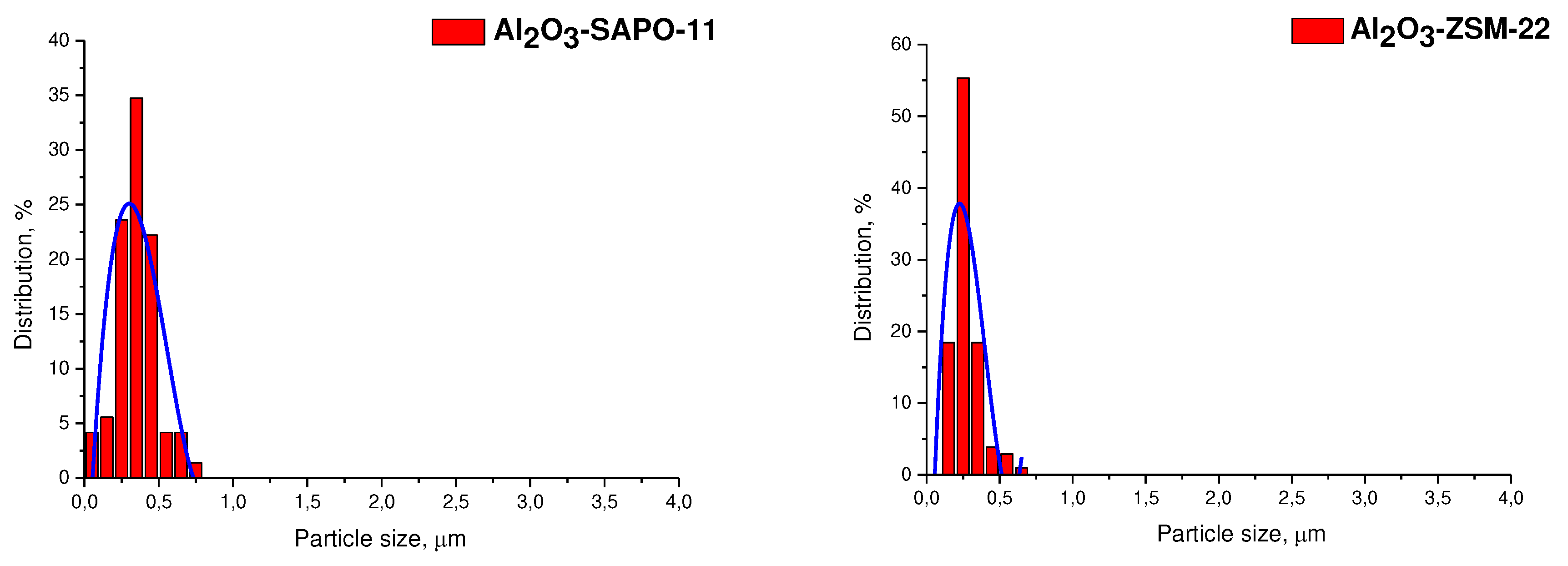
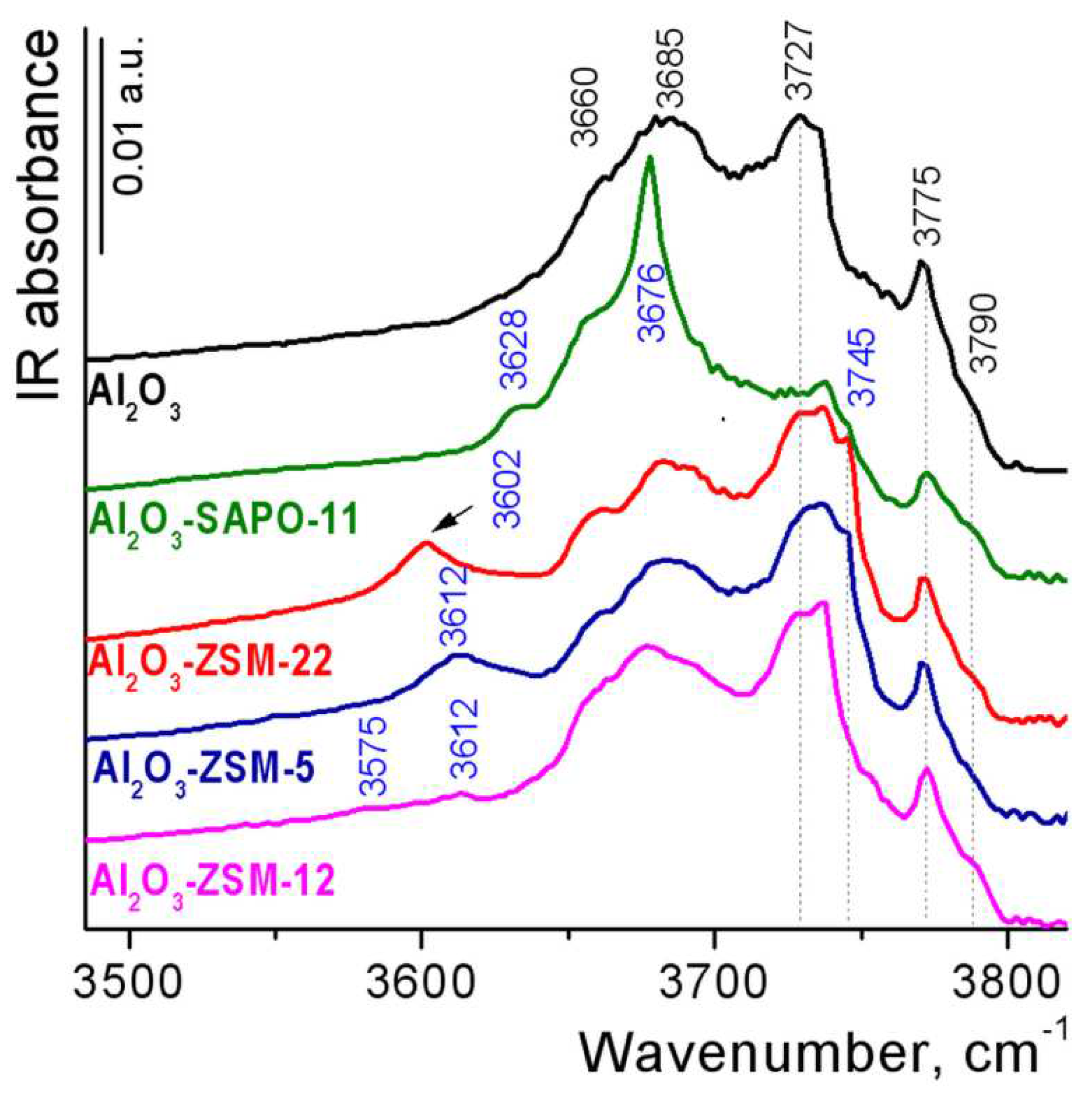
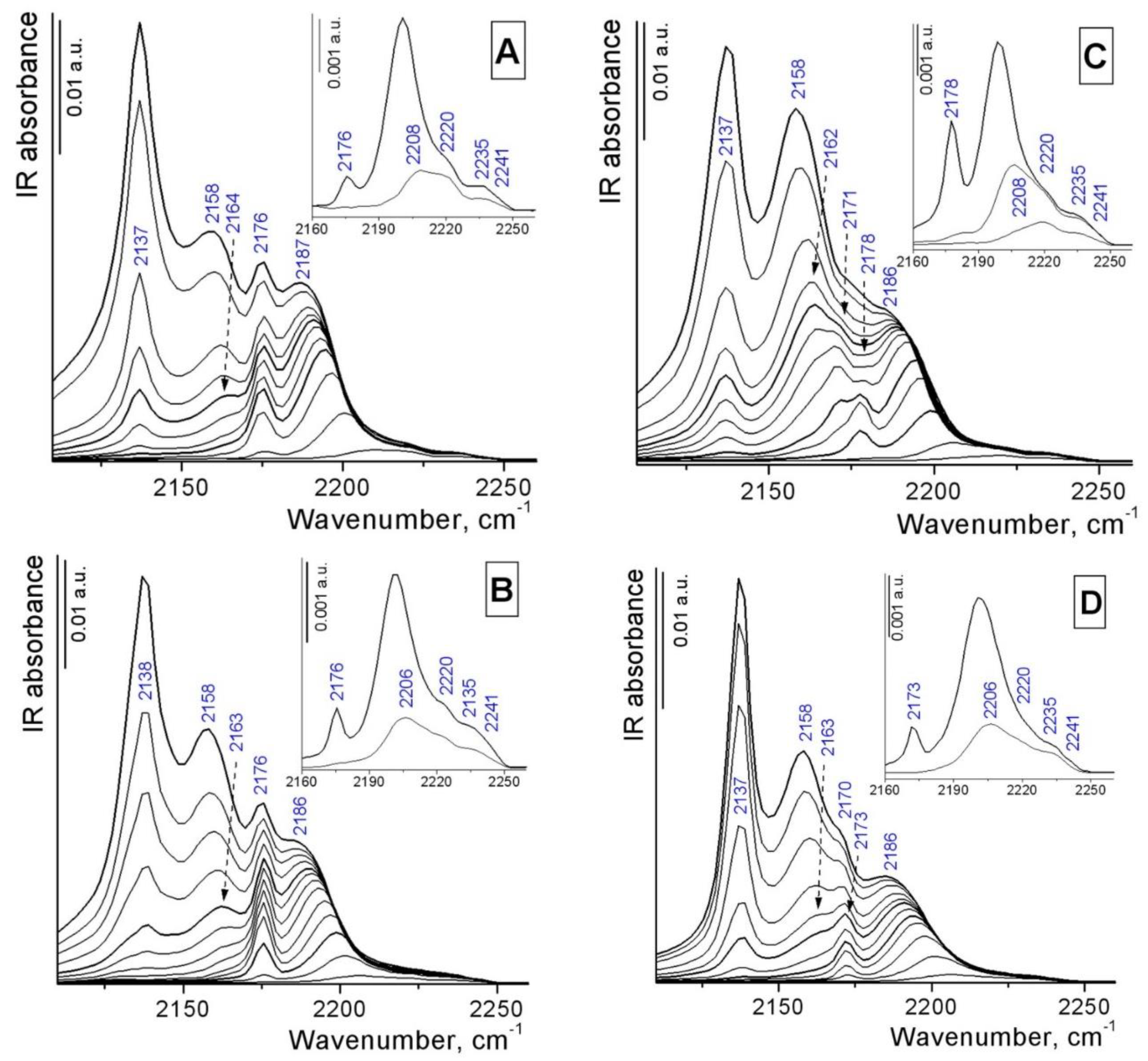
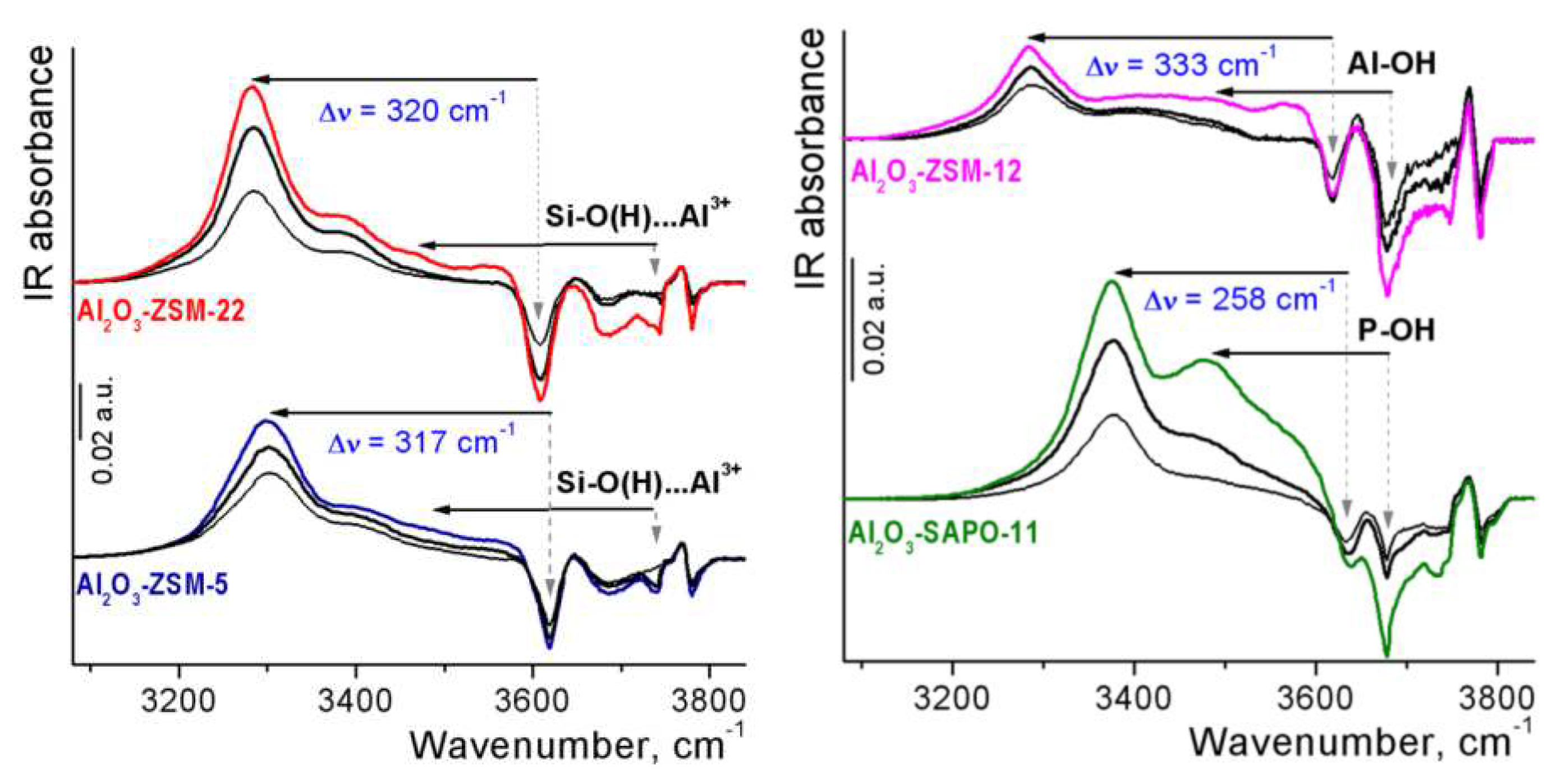
3.1. Catalyst characterization
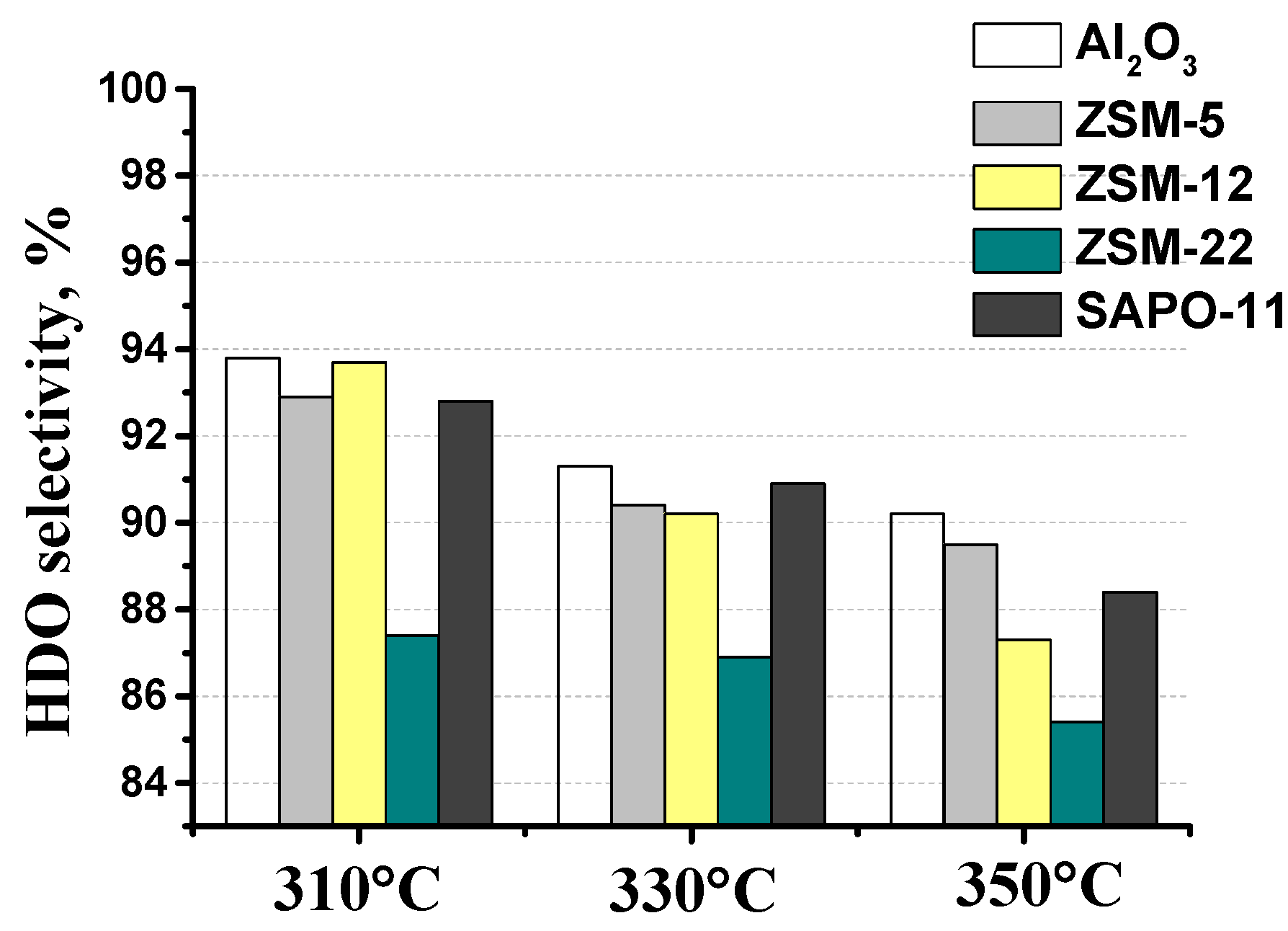
3.2. The effect of zeolite type on hydrodeoxygenation of methyl palmitate
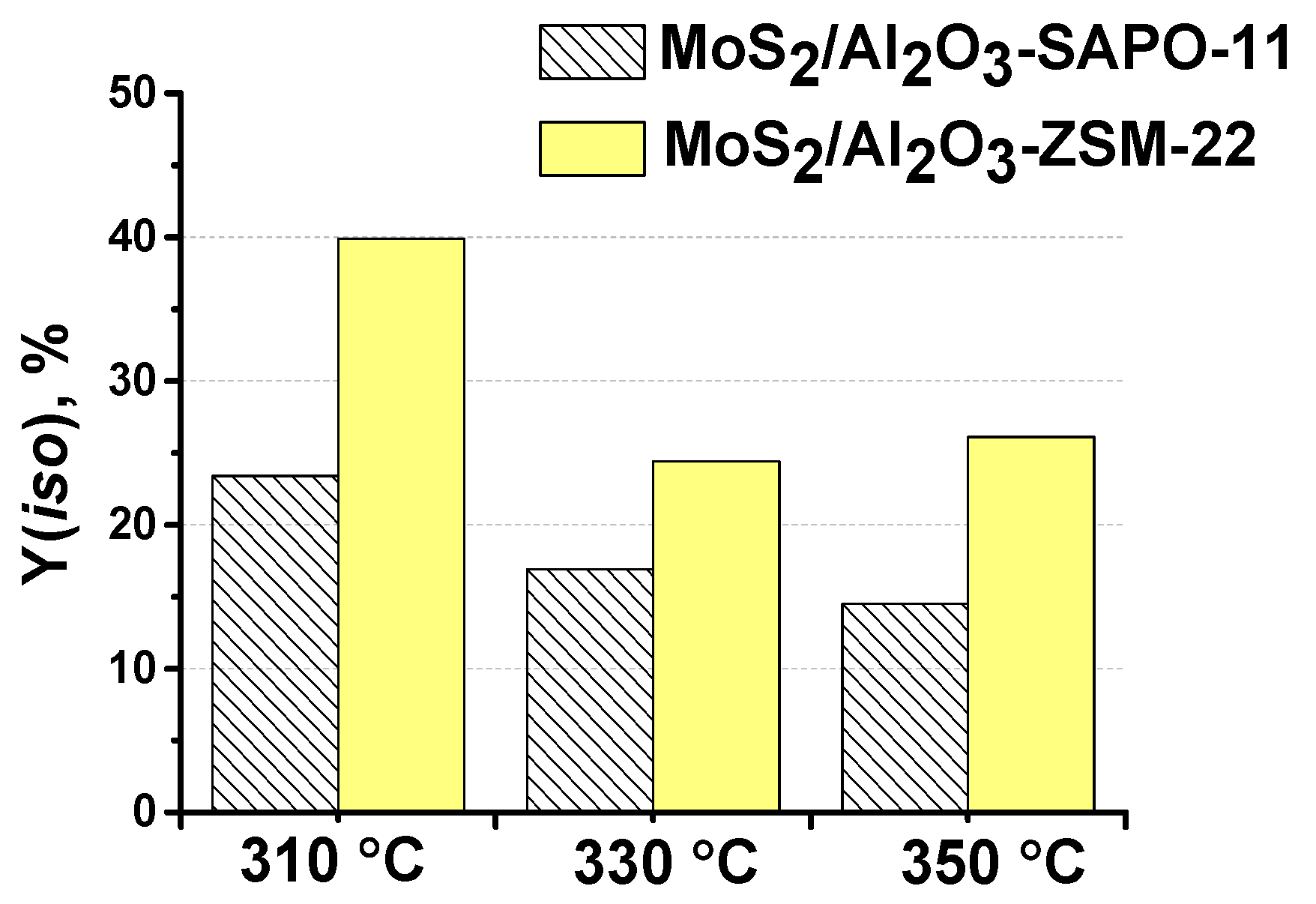
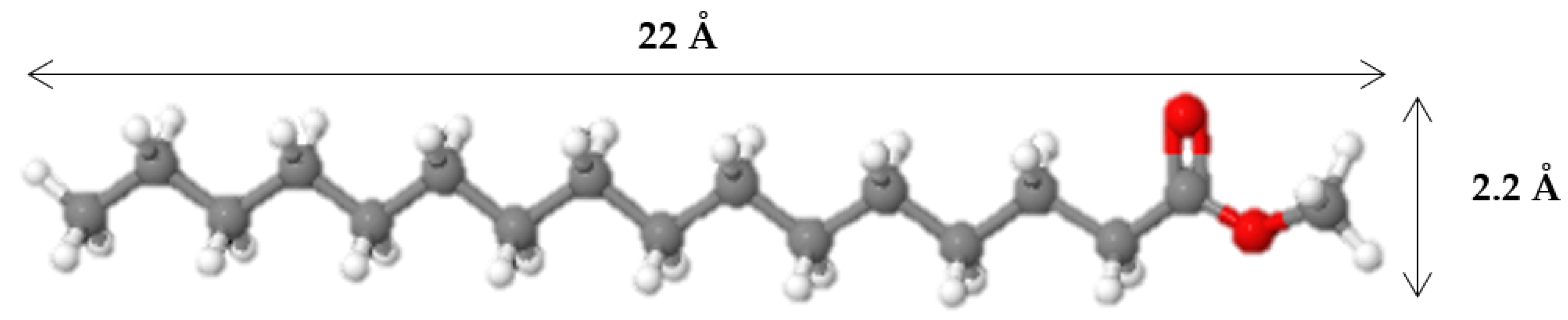
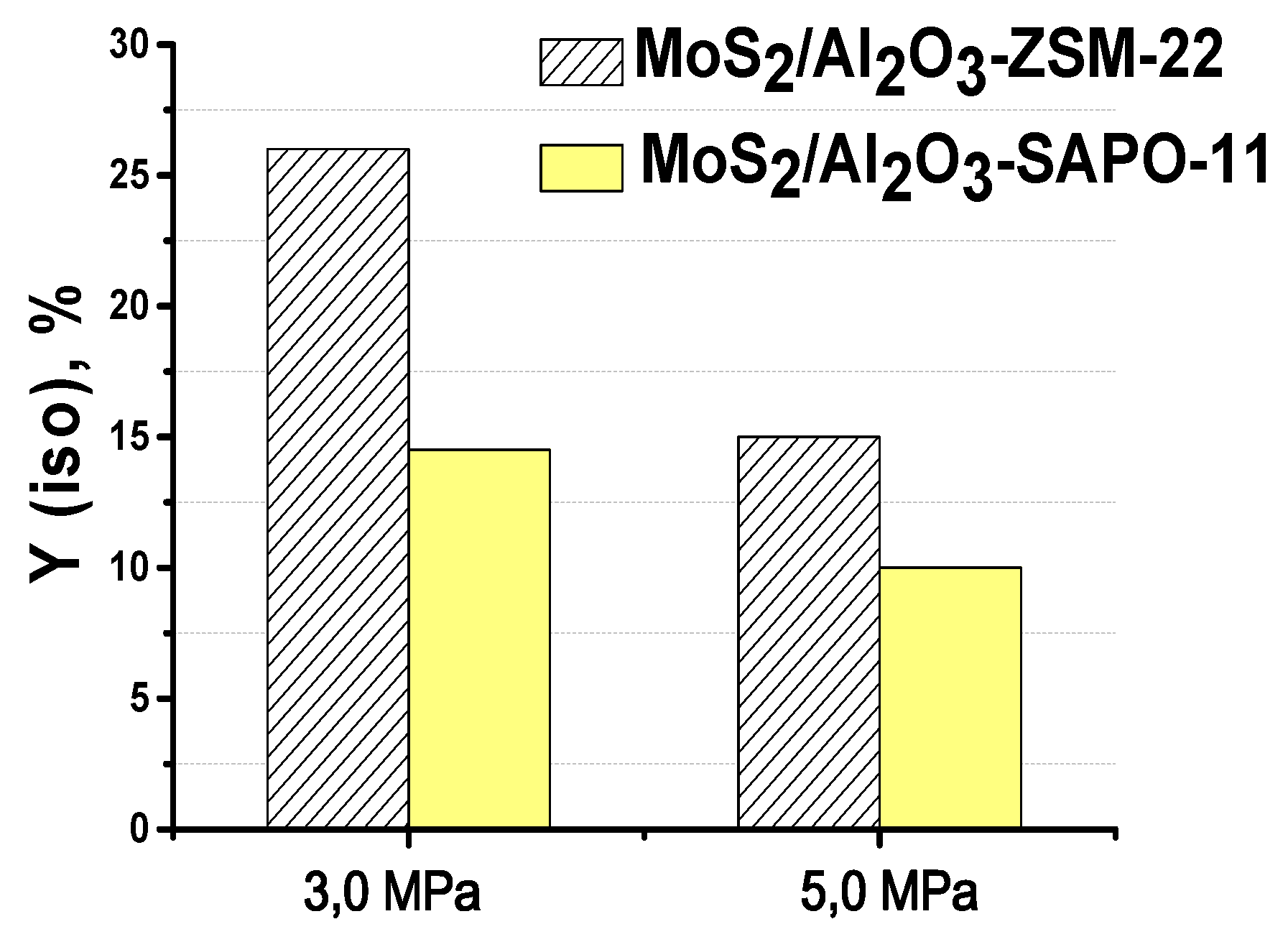
3.3. The effect of zeolite type on hydroisomerization of methyl palmitate
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Support preparation
4.2. Catalyst preparation
4.3. Support and catalyst characterization
4.4. Catalytic experiments
4.5. Product analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panoutsou, C.; Germer, S.; Karka, P.; Papadokostantakis, S.; Kroyan, Y.; Wojcieszyk, M.; Maniatis, K.; Marchand, P.; Landalv, I. Advanced biofuels to decarbonise European transport by 2030: Markets, challenges, and policies that impact their successful market uptake. Energy Strategy Reviews 2021, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douvartzides, S.L.; Charisiou, N.D.; Papageridis, K.N.; Goula, M.A. Green Diesel: Biomass Feedstocks, Production Technologies, Catalytic Research, Fuel Properties and Performance in Compression Ignition Internal Combustion Engines. Energies 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelbach, M. Fuels from oils and fats: Recent developments and perspectives. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology 2015, 117, 1832–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, M.C.; Silva, E.E.; Castillo, E.F. Hydrotreatment of vegetable oils: A review of the technologies and its developments for jet biofuel production. Biomass & Bioenergy 2017, 105, 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, B.H.H.; Chong, C.T.; Ge, Y.; Ong, H.C.; Ng, J.-H.; Tian, B.; Ashokkumar, V.; Lim, S.; Seljak, T.; Józsa, V. Progress in utilisation of waste cooking oil for sustainable biodiesel and biojet fuel production. Energy Conversion and Management 2020, 223, 113296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki-Arvela, P.; Martinez-Klimov, M.; Murzin, D.Y. Hydroconversion of fatty acids and vegetable oils for production of jet fuels. Fuel 2021, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, F.; Liu, W.G.; Jiang, X.; Zhai, Q.L.; Cao, X.C.; Jiang, J.C.; Xu, J.M. State-of-the-art technologies for biofuel production from triglycerides: A review. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews 2021, 148. [Google Scholar]
- Yeletsky, P.M.; Kukushkin, R.G.; Yakovlev, V.A.; Chen, B.H. Recent advances in one-stage conversion of lipid-based biomass-derived oils into fuel components - aromatics and isomerized alkanes. Fuel 2020, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hari, T.K.; Yaakob, Z. Production of diesel fuel by the hydrotreatment of jatropha oil derived fatty acid methyl esters over gamma-Al2O3 and SiO2 supported NiCo bimetallic catalysts. Reaction Kinetics Mechanisms and Catalysis 2015, 116, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezergianni, S.; Dimitriadis, A.; Chrysikou, L.P. Quality and sustainability comparison of one- vs. two-step catalytic hydroprocessing of waste cooking oil. Fuel 2014, 118, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.W.; Chang, Y.H.; Wang, W.C. Techno-economic analysis of used cooking oil to jet fuel production under uncertainty through three-, two-, and one-step conversion processes. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmedov, V.M.; Al-Khowaiter, S.H. Recent advances and future aspects in the selective isomerization of high n-alkanes. Catalysis Reviews-Science and Engineering 2007, 49, 33–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, E.W.; Chen, N.; Gong, S. Role of support in deoxygenation and isomerization of methyl stearate over nickel-molybdenum catalysts. Journal of Molecular Catalysis a-Chemical 2014, 387, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fan, Q.; Wu, Y.; Lin, X.; Ma, S.; Li, S.; Ye, Y.; Wang, D.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, Z. Enhancing hydrodeoxygenation-isomerization of FAME over M-SAPO-11 in one-step process: Effect of in-situ isomorphic substitution of transition metals and synergy of PtxSny alloy. Chemical Engineering Journal 2023, 452, 139528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.G.; Li, H.W.; Fu, J.Y.; Miao, C.L.; Lv, P.M.; Yuan, Z.H. Catalytic hydroprocessing of fatty acid methyl esters to renewable alkane fuels over Ni/HZSM-5 catalyst. Catalysis Today 2016, 259, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Z.T.; Liu, J.F.; Zhou, J.H. Continuous hydroprocessing of microalgae biodiesel to jet fuel range hydrocarbons promoted by Ni/hierarchical mesoporous Y zeolite catalyst. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HYDROGEN ENERGY 2019, 44, 11765–11773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.F.; Zhou, J.H.; Cen, K.F. Hydrodeoxygenation and hydrocracking of microalgae biodiesel to produce jet biofuel over H3PW12O40-Ni/hierarchical mesoporous zeolite Y catalyst. Fuel 2019, 245, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, Y.X.; Guo, H.; Yang, W.J. Jet fuel range hydrocarbons production through competitive pathways of hydrocracking and isomerization over HPW-Ni/MCM-41 catalyst. Fuel 2020, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.F.; Huang, R.; Zhou, J.H. Jet range hydrocarbons converted from microalgal biodiesel over mesoporous zeolite-based catalysts. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HYDROGEN ENERGY 2018, 43, 9988–9993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Shang, J.; Zhai, M.; Qiao, C. Hydrodeoxygenation of fatty acid methyl esters and simultaneous products isomerization over bimetallic Ni-Co/SAPO-11 catalysts. International Journal of Energy Research 2021, 45, 9648–9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, M.; Chu, Y.; Chen, J. Hydroconversion of Methyl Laurate as a Model Compound to Hydrocarbons on Bifunctional Ni2P/SAPO-11: Simultaneous Comparison with the Performance of NUSAPO-11. Energy & Fuels 2014, 28, 7122–7132. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, P.; Ma, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, K.; Jiang, L. In situ generation of dispersed MoS2 catalysts from oil-soluble Mo-based ionic liquids for highly effective biolipids hydrodeoxygenation. Journal of Catalysis 2023, 423, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliy, I.V.; Vlasova, E.N.; Nuzhdin, A.L.; Gerasimov, E.Y.; Bukhtiyarova, G.A. Hydrodeoxygenation of methyl palmitate over sulfided Mo/Al2O3, CoMo/Al2O3 and NiMo/Al2O3 catalysts. Rsc Advances 2014, 4, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaluza, L.; Kubicka, D. The comparison of Co, Ni, Mo, CoMo and NiMo sulfided catalysts in rapeseed oil hydrodeoxygenation. Reaction Kinetics Mechanisms and Catalysis 2017, 122, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, C.; Lemeur, R.; Daudin, A.; Raybaud, P. Hydrodeoxygenation pathways catalyzed by MoS2 and NiMoS active phases: A DFT study. Journal of Catalysis 2011, 279, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubickova, I.; Kubicka, D. Utilization of Triglycerides and Related Feedstocks for Production of Clean Hydrocarbon Fuels and Petrochemicals: A Review. Waste and Biomass Valorization 2010, 1, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergwerff, J.A.; Jansen, M.; Visser, T.; de Jong, K.P.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Influence of the preparation method on the hydrotreating activity of MoS2/Al2O3 extrudates: A Raman microspectroscopy study on the genesis of the active phase. Journal of Catalysis 2006, 243, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G. Structural, surface, and catalytic properties of aluminas. In Advances in catalysis; Elsevier, 2014; Volume 57, pp. 319–404. [Google Scholar]
- Meriaudeau, P.; Tuan, V.; Nghiem, V.T.; Lai, S.; Hung, L.; Naccache, C. SAPO-11, SAPO-31, and SAPO-41 molecular sieves: Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic properties inn-octane hydroisomerization. Journal of Catalysis 1997, 169, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morterra, C.; Magnacca, G.; Demaestri, P. Surface characterization of modified aluminas: III. Surface-features of PO4-doped Al2O3. Journal of Catalysis 1995, 152, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verboekend, D.; Chabaneix, A.M.; Thomas, K.; Gilson, J.-P.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. Mesoporous ZSM-22 zeolite obtained by desilication: Peculiarities associated with crystal morphology and aluminium distribution. CrystEngComm 2011, 13, 3408–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustov, L.; Kazanskii, V.; Beran, S.; Kubelkova, L.; Jiru, P. Adsorption of carbon monoxide on ZSM-5 zeolites: Infrared spectroscopic study and quantum-chemical calculations. Journal of Physical Chemistry 1987, 91, 5247–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, L.; Mihaylov, M.; Hadjiivanov, K.; Mavrodinova, V. Catalytic properties and acidity of ZSM-12 zeolite with different textures. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 2011, 143, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrienko, A.A.; Danilova, I.G.; Arzumanov, S.S.; Toktarev, A.V.; Freude, D.; Stepanov, A.G. Strong acidity of silanol groups of zeolite beta: Evidence from the studies by IR spectroscopy of adsorbed CO and 1H MAS NMR. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 2010, 131, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morterra, C.; Bolis, V.; Magnacca, G. IR spectroscopic and microcalorimetric characterization of Lewis acid sites on (transition phase) Al2O3 using adsorbed CO. Langmuir 1994, 10, 1812–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecchina, A.; Bordiga, S.; Spoto, G.; Scarano, D.; Petrini, G.; Leofanti, G.; Padovan, M.; Otero Areàn, C. Low-temperature Fourier-transform Infrared Investigation of the Interaction of CO with Nanosized ZSM5 and Silicalite. J. CHEM. SOC. FARADAY TRANS. 1992, 88, 2959–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrienko, A.A.; Danilova, I.G.; Arzumanov, S.S.; Freude, D.; Stepanov, A.G. Does the Zn2+ Species Introduced into H-ZSM-5 Zeolite Affect the Strength of Brønsted Acid Sites? Chemcatchem 2020, 12, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.H. Spectroscopic characterization of the surface hydroxyls of zeolitic catalysts. 2014.
- Hadjiivanov, K. Identification and characterization of surface hydroxyl groups by infrared spectroscopy. In Advances in Catalysis; Elsevier, 2014; Volume 57, pp. 99–318. [Google Scholar]
- Chakarova, K.; Hadjiivanov, K. Problems in the IR measuring the acidity of zeolite bridging hydroxyls by low-temperature CO adsorption. Chemical Communications 2011, 47, 1878–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höchtl, M.; Jentys, A.; Vinek, H. Acidity of SAPO and CoAPO molecular sieves and their activity in the hydroisomerization of n-heptane. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 1999, 31, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazimov, D.; Klimov, O.; Danilova, I.; Trukhan, S.; Saiko, A.; Cherepanova, S.; Chesalov, Y.A.; Martyanov, O.; Noskov, A. Effect of alumina polymorph on the dehydrogenation activity of supported chromia/alumina catalysts. Journal of Catalysis 2020, 391, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brimont, M.R.; Dupont, C.; Daudin, A.; Geantet, C.; Raybaud, P. Deoxygenation mechanisms on Ni-promoted MoS2 bulk catalysts: A combined experimental and theoretical study. Journal of Catalysis 2012, 286, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasova, E.N.; Bukhtiyarova, G.A.; Deliy, I.V.; Aleksandrov, P.V.; Porsin, A.A.; Panafidin, M.A.; Gerasimov, E.Y.; Bukhtiyarov, V.I. The effect of rapeseed oil and carbon monoxide on SRGO hydrotreating over sulfide CoMo/Al2O3 and NiMo/Al2O3 catalysts. Catalysis Today 2020, 357, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumans, A.E.; Hensen, E.J.M. A model compound (methyl oleate, oleic acid, triolein) study of triglycerides hydrodeoxygenation over alumina-supported NiMo sulfide. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental 2017, 201, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoosuk, B.; Sanggam, P.; Wiengket, S.; Prasassarakich, P. Hydrodeoxygenation of oleic acid and palmitic acid to hydrocarbon-like biofuel over unsupported Ni-Mo and Co-Mo sulfide catalysts. Renewable Energy 2019, 139, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.M.; Tsang, C.W.; Liang, C.H. Shape Selectivity in Hydroisomerization of Hexadecane over Pt Supported on 10-Ring Zeolites: ZSM-22, ZSM-23, ZSM-35, and ZSM-48. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 2016, 55, 6069–6078. [Google Scholar]
- Lanzafame, P.; Perathoner, S.; Centi, G.; Heracleous, E.; Iliopoulou, E.F.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Lappas, A.A. Effect of the Structure and Mesoporosity in Ni/Zeolite Catalysts for n-Hexadecane Hydroisomerisation and Hydrocracking. Chemcatchem 2017, 9, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtchev, V.; Majano, G.; Mintova, S.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. Tailored crystalline microporous materials by post-synthesis modification. Chemical Society Reviews 2013, 42, 263–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ramírez, J.; Christensen, C.H.; Egeblad, K.; Christensen, C.H.; Groen, J.C. Hierarchical zeolites: Enhanced utilisation of microporous crystals in catalysis by advances in materials design. Chemical Society Reviews 2008, 37, 2530–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwieger, W.; Machoke, A.G.; Weissenberger, T.; Inayat, A.; Selvam, T.; Klumpp, M.; Inayat, A. Hierarchy concepts: Classification and preparation strategies for zeolite containing materials with hierarchical porosity. Chemical Society Reviews 2016, 45, 3353–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, W.J.; Nachtigall, P.; Morris, R.E.; Cejka, J. Two-dimensional zeolites: Current status and perspectives. Chemical Reviews 2014, 114, 4807–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.-G.; Min, H.-K.; Lee, J.K.; Hong, S.B.; Seo, G. SAPO-34 and ZSM-5 nanocrystals’ size effects on their catalysis of methanol-to-olefin reactions. Applied Catalysis A: General 2012, 437, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.7889 (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Available online: https://avogadro.cc/ (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Cai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yu, P.; Ding, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, K.; Jiang, L. Direct production of isomerized biodiesel over MoS2/ZrPOx under solvent-free conditions. Fuel 2023, 337, 127175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://asia.iza-structure.org (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Fyfe, C.; Gies, H.; Kokotailo, G.; Marler, B.; Cox, D. Crystal structure of silica-ZSM-12 by the combined use of hgh-resolution solid-state MAS NMR spectroscopy and synchrotron x-ray powder diffraction. Journal of Physical Chemistry 1990, 94, 3718–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borade, R.B.; Clearfield, A. A comparative study of acidic properties of SAPO-5,− 11,− 34 and− 37 molecular sieves. Journal of molecular catalysis 1994, 88, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dik, P.; Klimov, O.; Danilova, I.; Leonova, K.; Pereyma, V.Y.; Budukva, S.; Uvarkina, D.; Kazakov, M.; Noskov, A. Hydroprocessing of hydrocracker bottom on Pd containing bifunctional catalysts. Catalysis Today 2016, 271, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
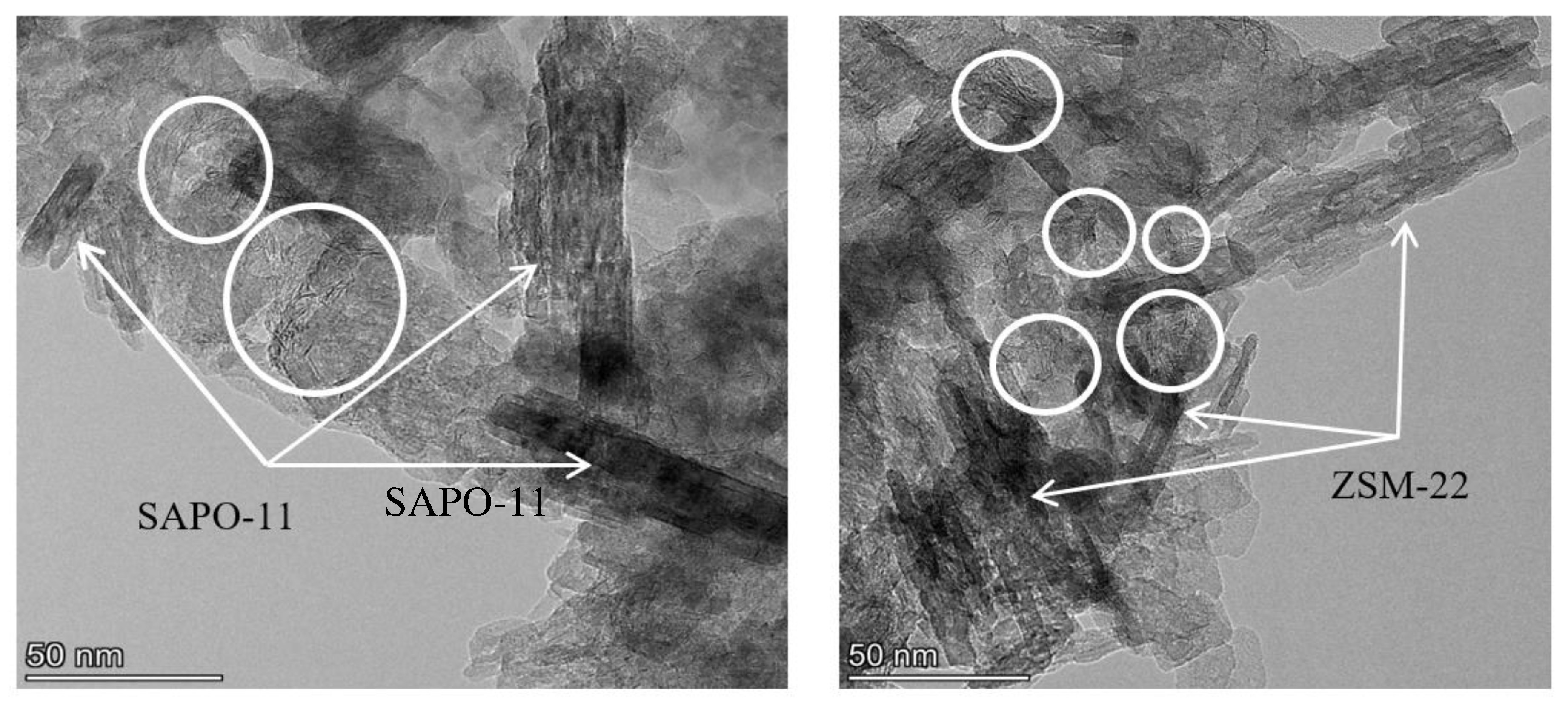
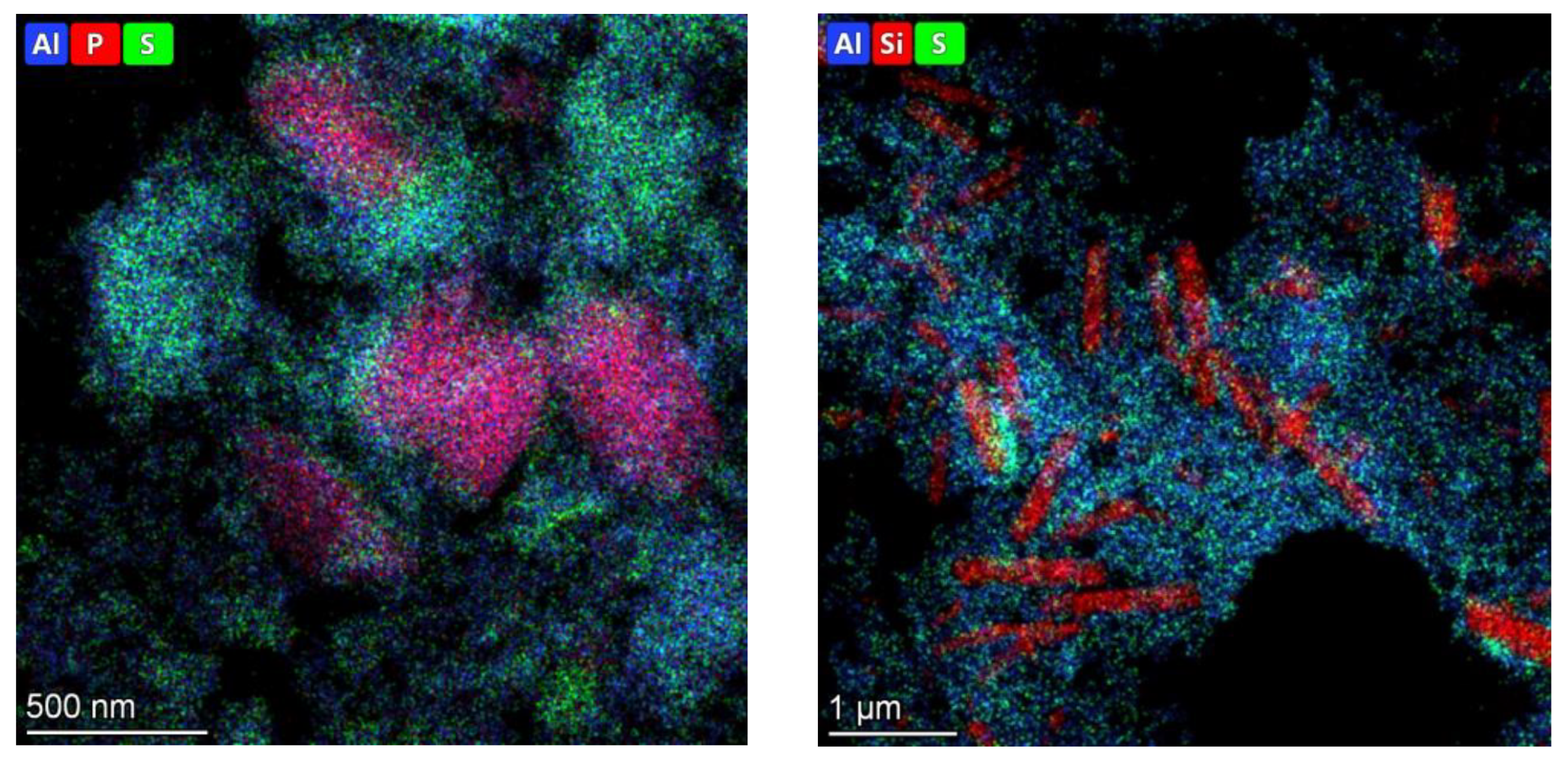
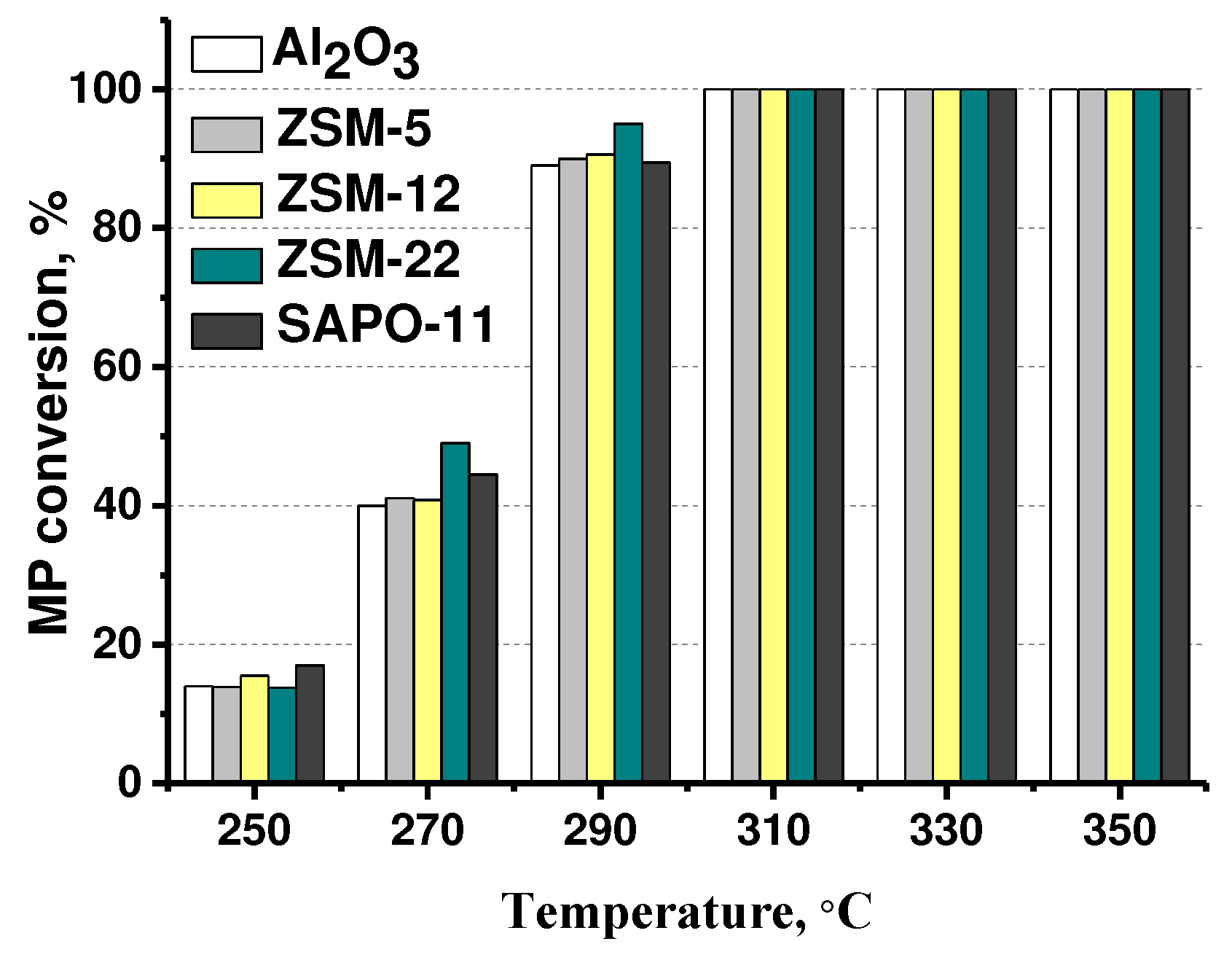
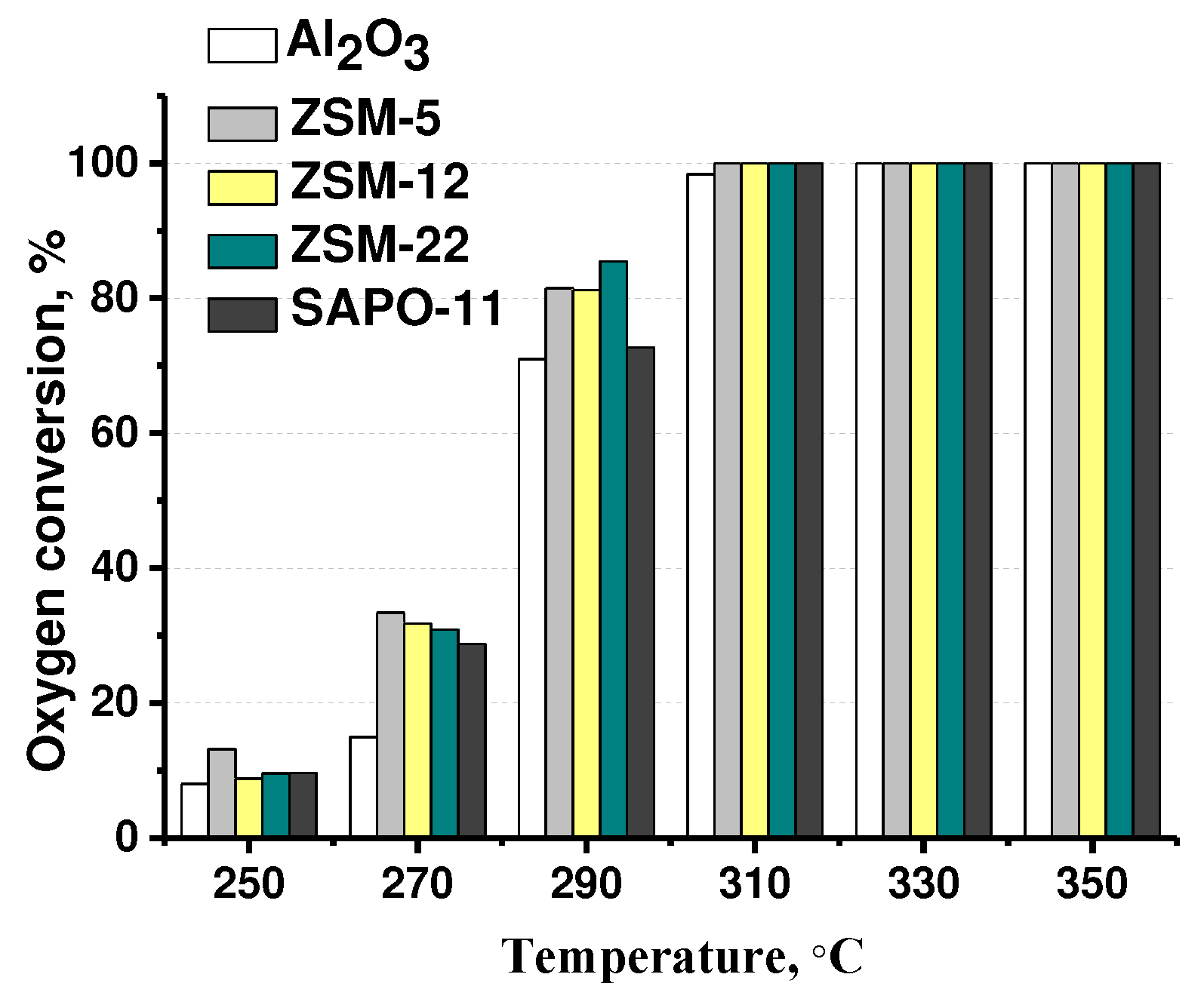
| Catalysts | Mo, wt.% | Support | Textural properties of the support | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface area, m2/g | Pore volume, cm3/g | Pore diameter, nm | |||
| Mo/Al2O3 | 6.95 | Al2O3 | 133 | 0.66 | 25.1 |
| Mo/Al2O3-ZSM-5 | 6.90 | Al2O3-ZSM-5 | 202 | 0.48 | 25.6 |
| Mo/ Al2O3-ZSM-12 | 6.96 | Al2O3-ZSM-12 | 165 | 0.49 | 22.8 |
| Mo/ Al2O3-ZSM-22 | 6.90 | Al2O3-ZSM-22 | 175 | 0.53 | 25.5 |
| Mo/ Al2O3-SAPO-11 | 6.97 | Al2O3-SAPO-11 | 177 | 0.42 | 22.6 |
| Al2O3-zeolite composites | Type of zeolite sites | IR frequency shift / cm–1 | BAS concentration (μmol g−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔνOH…COa | ΔνCOb | |||
| Al2O3-ZSM-5 | Framework Si-O(H)-Al groups Extra-framework Si-O(H)…Al3+ groups |
–317 –(260÷270) |
+33 |
8.1 1.8 |
| Al2O3-ZSM-22 | Framework Si-O(H)-Al groups Extra-framework Si-O(H)…Al3+ groups |
–320 –(260÷270) |
+33 |
11.4 1.0 |
| Al2O3-ZSM-12 | Framework Si-O(H)-Al groups Extra-framework Al-OH groups |
–333 –(200÷196) |
+35 +28 |
2.7 2.6 |
| Al2O3-SAPO-11 | Framework Si-O(H)-Al groups P-OH groups |
–258 –(202÷198) |
+30 +27 |
7.4 ~4c |
| Material | SiO2/Al2O3 Mole Ratio |
Framework Type | Channels | Size of channels |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZSM-5 | 280 | MFI | 3D, 10 MR | 5.3 x 5.6 Å [010] 5,1 х 5,5 Å [100] [57] |
| ZSM-12 | 280 | MTW | 1D, 12 MR | 5.6 x 7.7 Å [010] [58] |
| ZSM-22 | 97 | TON | 1D, 10 MR | 4.6 x 5.7 Å [001] [57] |
| SAPO-11 | SiO2/Al2O3/P2O5= 0.25/1.0/0.8 |
AEL | 1D, 10 MR | 3.9 x 6.3 Å [001] [59] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





