Submitted:
12 September 2023
Posted:
14 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
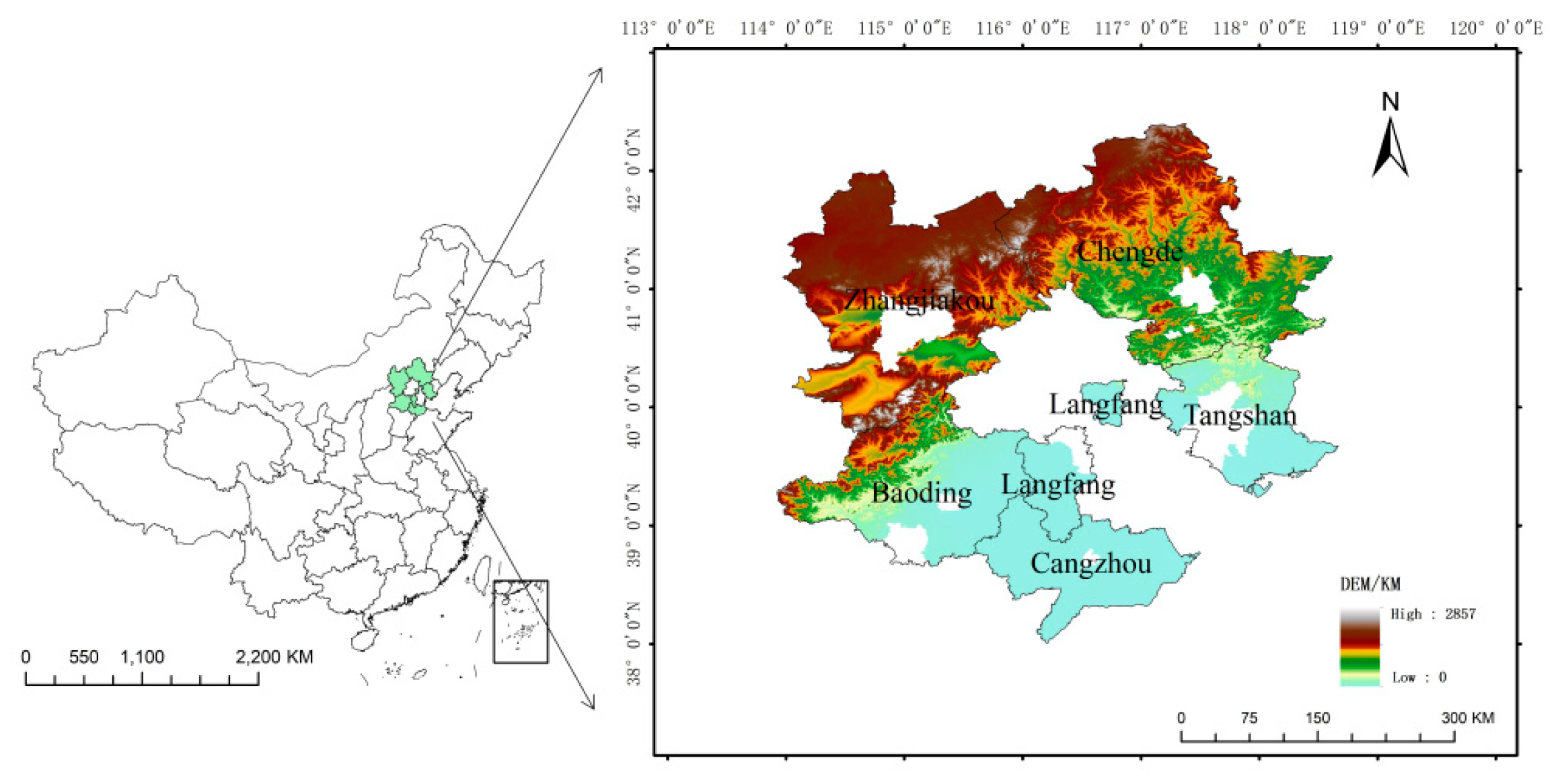
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
3. Research Methodology
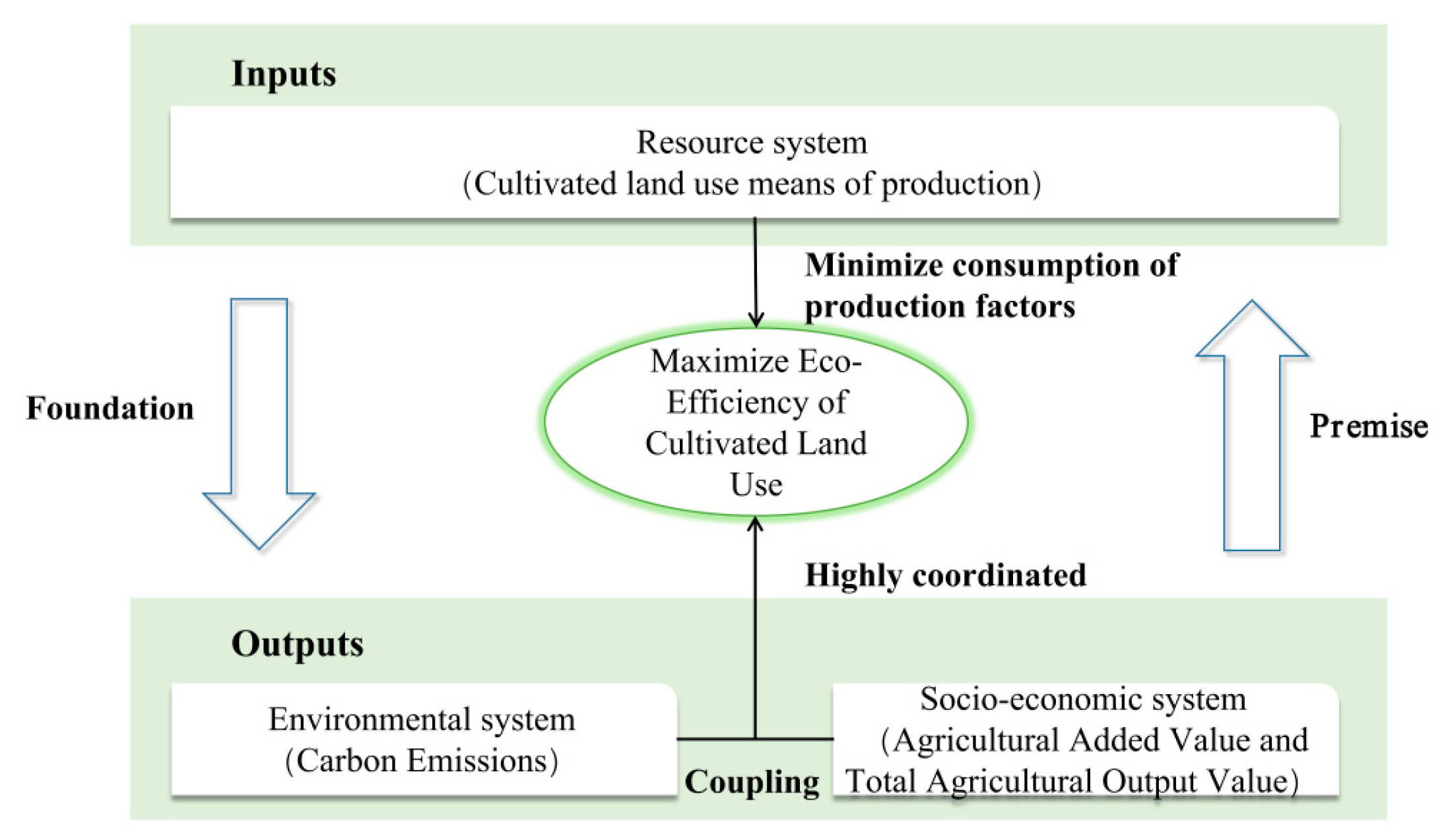
3.1. Connotation of the ECLU
3.2. Index System Construction
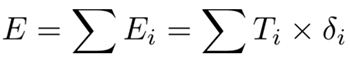
3.3. Super-EBM Model
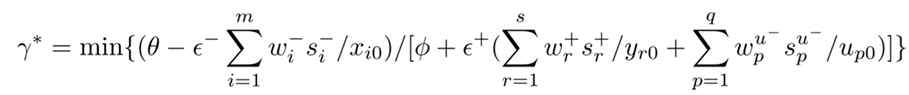
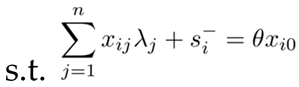
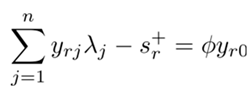
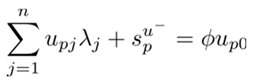
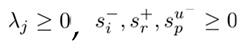
3.4. Kernel Density Estimation
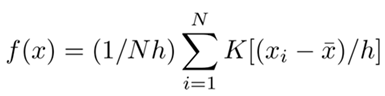
3.5. Markov Chain Model
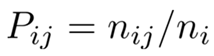
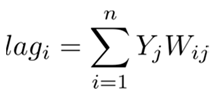
4. Results and Analysis
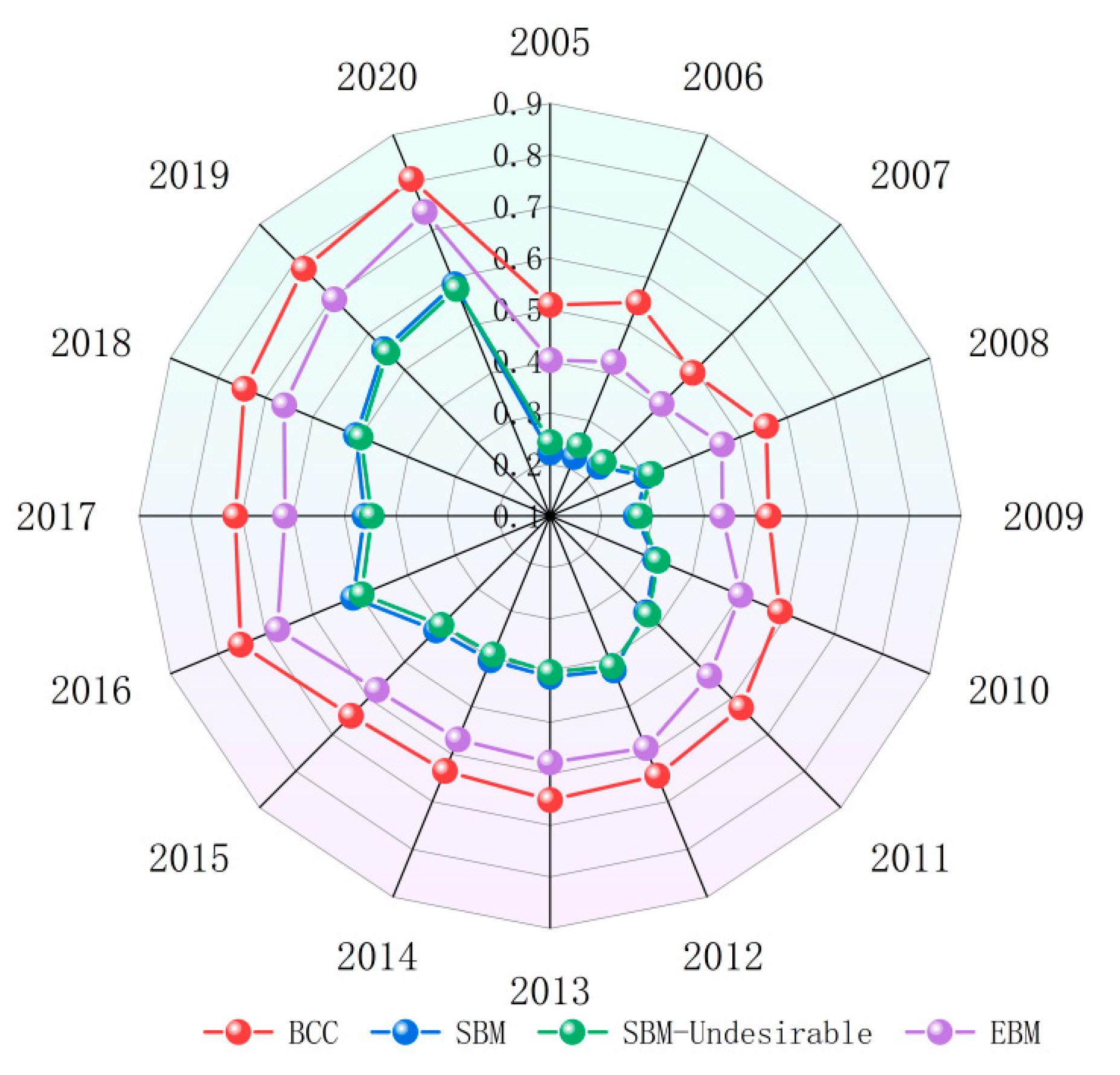
4.1. Results of the Determination of the ECLU Based on the Super-EBM Model
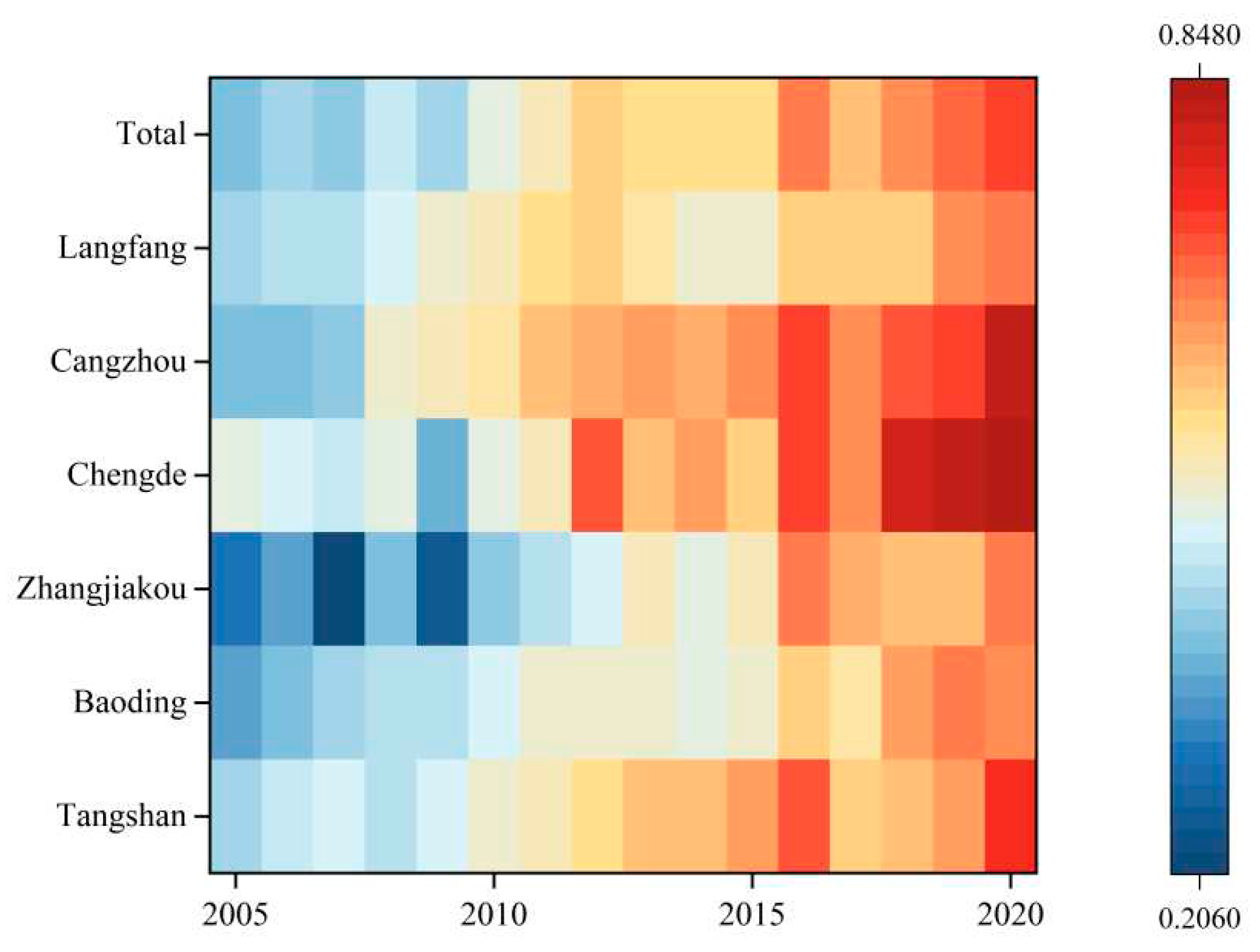
4.1.1. Analysis of Annual Change Features of the ECLU
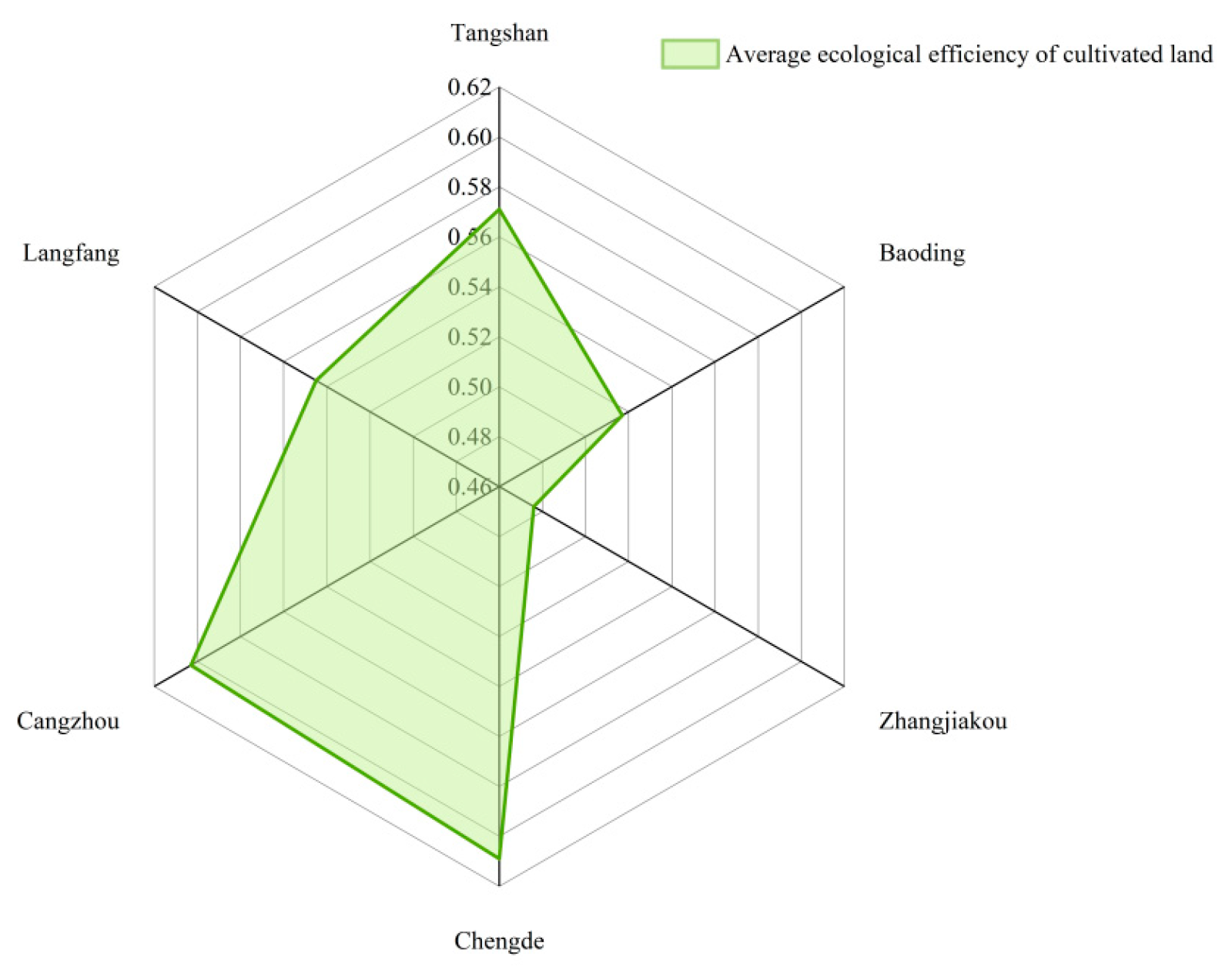
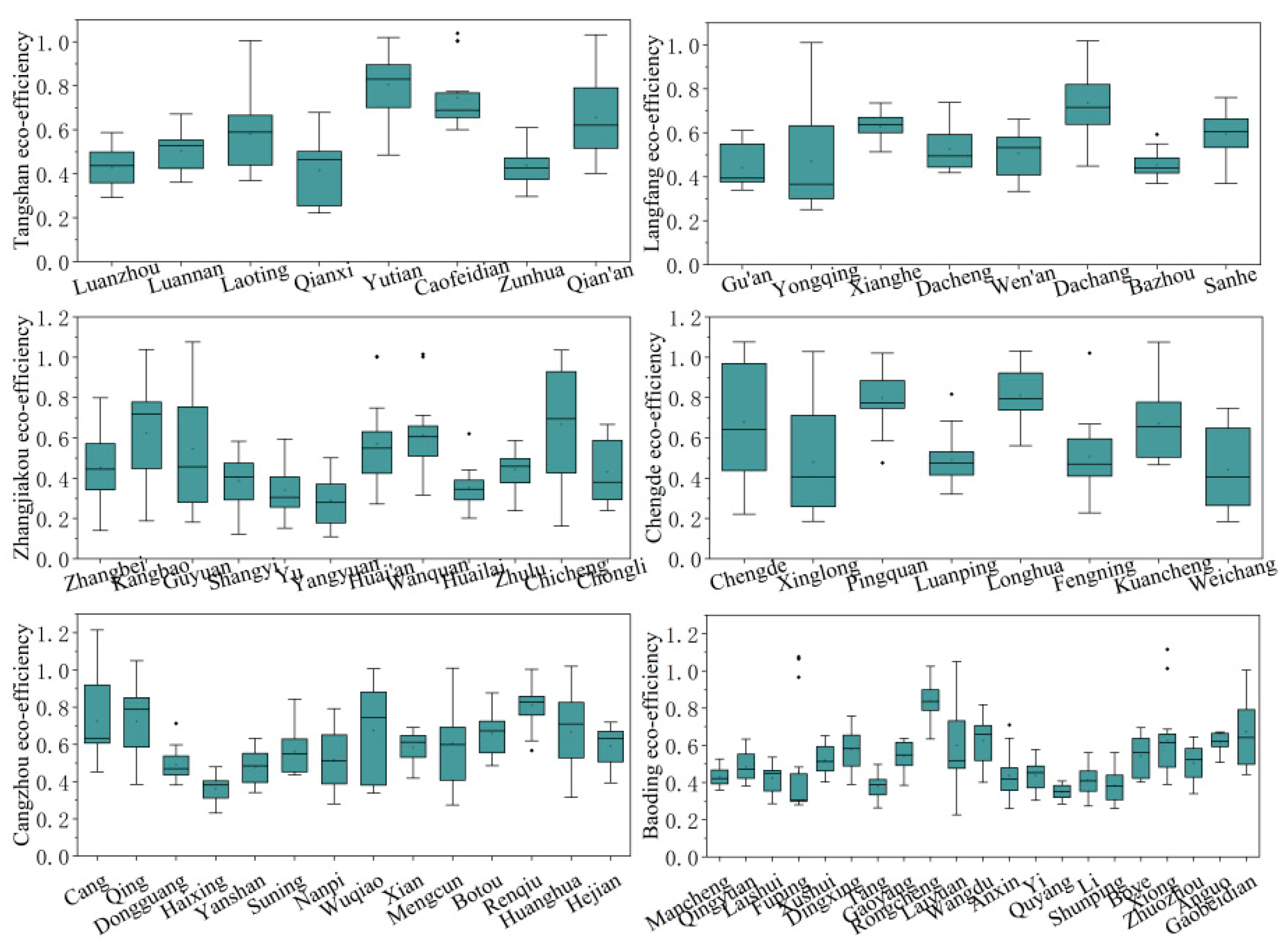
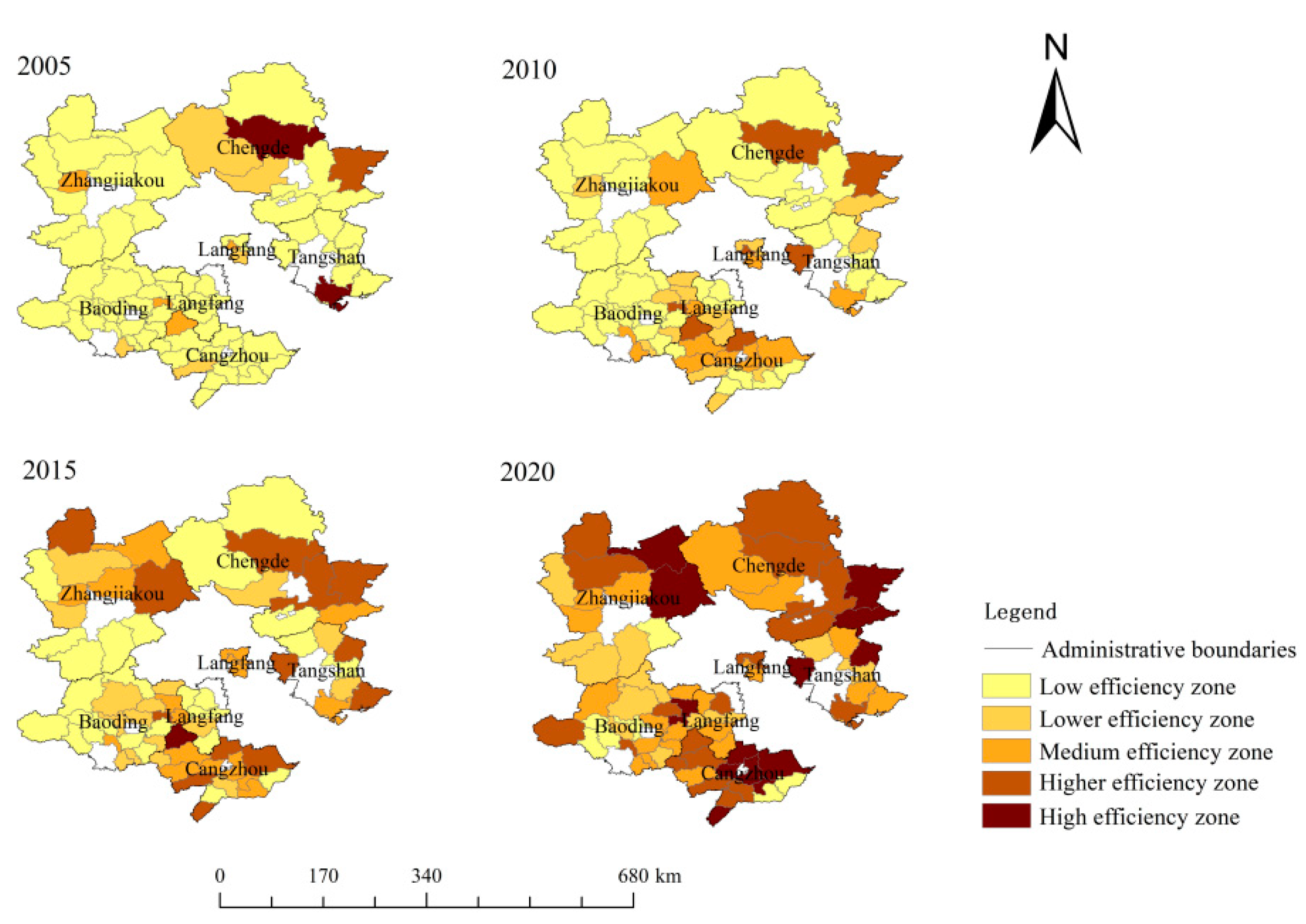
4.1.2. Study on the spatial distribution features of the ECLU
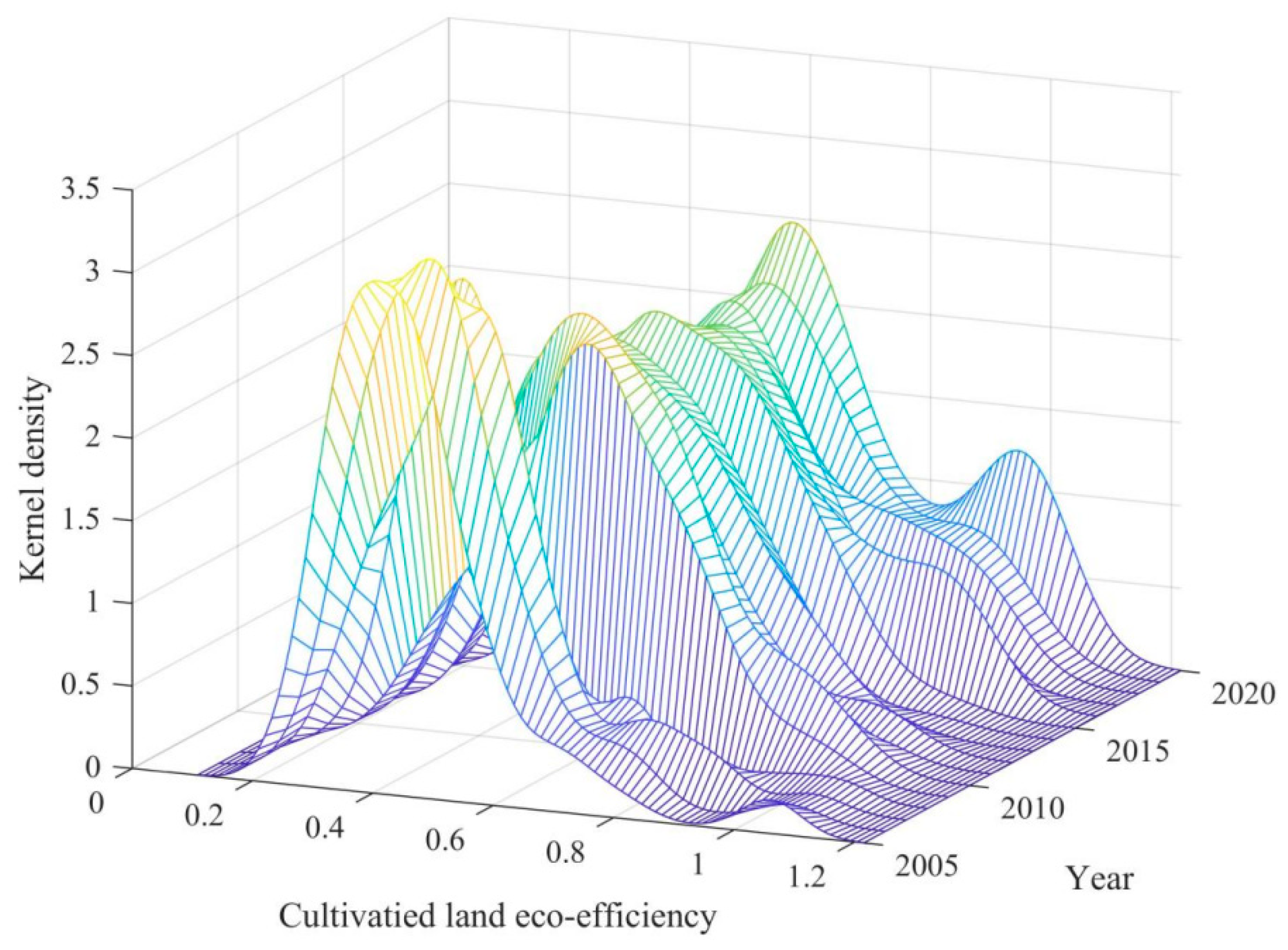
4.2. Study on Temporal Evolution Features
4.3. Spatial Evolution Characterization
4.3.1. Traditional Markov Chain Analysis
4.3.2. Spatial Markov Chain Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. Understanding of Results of the ECLU
5.2. Implications of Characteristics of the Temporal Evolution of the ECLU
5.3. Insights into Characteristics of the Spatial Evolution of the ECLU
6. Conclusions and Suggestions
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. Strategic adjustment of land use policy under the economic transformation. Land use policy, 2018, 74, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Huang, J.; Rozelle, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Impact of urbanization on cultivated land changes in China. Land use policy 2015, 45, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkesford, M. J. Reducing the reliance on nitrogen fertilizer for wheat production. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 59(3), 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaltegger, S.; Sturm, A. Ökologische rationalität: ansatzpunkte zur ausgestaltung von ökologieorientierten managementinstrumenten. Die Unternehm. 1990, 44(3), 273–290. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Hou, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, D. Detection and attribution of changes in cultivated land use ecological efficiency: A case study on Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlström, K.; Ekins, P. Eco-efficiency trends in the UK steel and aluminum industries. J. Ind. Ecol. 2005, 9(4), 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, R.; Booth, A. Eco-efficiency and SMEs in nova scotia, Canada. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14(6-7), 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gössling, S.; Peeters, P.; Ceron, J. P.; Dubois, G.; Patterson, T. The eco-efficiency of tourism. Ecol. Econ. 2005, 54(4), 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, U.; Li, Q. L.; Akmal, M. A.; Mohammed, S.; Wasim, I. Nexus between agro-eco-efficiency and carbon emission transfer: evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 18995–19007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutinho, V.; Robaina, M.; Macedo, P. Economic-environmental efficiency of European agriculture–a generalized maximum entropy approach. Agric. Econ. 2018, 64(10), 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, P. Impacts of Dynamic Agglomeration Externalities on Eco-Efficiency: Empirical Evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15(10), 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130(3), 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. Data envelopment analysis as a Kaizen tool: SBM variations revisited. Bul. Math. Sci. Appl. 2016, 16(3), 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K.; Tsutsui, M. An epsilon-based measure of efficiency in DEA–a third pole of technical efficiency. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 207(3), 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, N.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; Kuang, B.; Jiang, B. Regional disparities and influencing factors of eco-efficiency of arable land utilization in China. Land 2022, 11(2), 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhou, H. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of agricultural land eco-efficiency: a case study of 128 cities in the Yangtze River Basin. Water 2022, 14(3), 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Hou, J. Spatial Distribution Evolution and Optimization Path of Eco-Efficiency of Cultivated Land Use: A Case Study of Hubei Province, China. Sustainability 2022, 14(18), 11417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Wang, Y.H.; Huang, Q.Q.; Yang, Q.Y. How Much Is the Eco-Efficiency of Agricultural Production in West China? Evidence from the Village Level Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, M. Impact of urbanization on the eco-efficiency of cultivated land utilization: A case study on the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tong, L.; Mei, L. Spatiotemporal characteristics and influencing factors of agricultural eco-efficiency in Jilin agricultural production zone from a low carbon perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29(20), 29854–29869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Wang, Z.; Zou, L.; Zou, L.; Zhang, H. Exploring the eco-efficiency of cultivated land utilization and its influencing factors in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt, 2001-2018. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 294, 112939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Deng, C.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, P.; Lu, H. Spatial-temporal pattern and evolution trend of the cultivated land use eco-efficiency in the National Pilot Zone for ecological conservation in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19(1), 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, Y.; Ma, L.; Shi, Z.; Gong, M. Agricultural Eco-Efficiency Response and Its Influencing Factors from the Perspective of Rural Population Outflowing: A Case Study in Qinan County, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20(2), 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H. Detection and attribution of changes in agricultural eco-efficiency within rapid urbanized areas: A case study in the Urban agglomeration in the middle Reaches of Yangtze River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T. Spatio-temporal characteristics and typical patterns of eco-efficiency of cultivated land use in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Spatiotemporal characteristics and driving mechanisms of arable land in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region during 1990-2015. Socio-Economic Plan. Sci. 2020, 70, 100720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development). Eco-efficiency. 1998.
- Tan, J.; Duan, Q.; Xiao, C.; He, C.; Yan, X. A brief review of the coupled human-Earth system modeling: Current state and challenges. The Anthropocene Rev. 2023, 20530196221149121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sarwar, S.; Jin, T. Spatiotemporal evolution and improvement potential of agricultural eco-efficiency in Jiangsu province. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 746405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhou, W.; Wu, T.; Wang, X.; Xu, J. Spatial-temporal characteristics of cultivated land utilization eco-efficiency under carbon constraints and its relationship with landscape pattern dynamics. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X. Assessment and analysis of agricultural non-point source pollution loads in China: 1978–2017. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 263, 110400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, N. Modeling the eco-efficiency of Chinese prefecture-level cities with regional heterogeneities: A comparative perspective. Ecol. Model. 2019, 402, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhang, H.; Ke, N. Cultivated Land Transfer, Management Scale, and Cultivated Land Green Utilization Efficiency in China: Based on Intermediary and Threshold Models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Yu, C.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wu, K.; Ma, X. Spatial differentiation characteristics and driving factors of agricultural eco-efficiency in Chinese provinces from the perspective of ecosystem services. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K. G.; Anderson, S.; Gonzales-Chang, M.; Costanza, R.; Courville, S.; Dalgaard, T.; Dominati, E.; Kubiszewski, I.; Ogilvy, S.; Porfirio, L.; Ratna, N.; Sandhu, H.; Sutton, P.C.; Svenning, J.; Turner, G. M.; Varennes, Y.; Voinov k, A.; Wratten d., S; Wratten, S. A review of methods, data, and models to assess changes in the value of ecosystem services from land degradation and restoration. Ecol. Model. 2016, 319, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.; Guo, Q.; Mi, L.; Wang, G.; Song, W. Spatial distribution of agricultural eco-efficiency and agriculture high-quality development in China. Land 2022, 11(5), 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zou, L.; Wang, Y. Spatial-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of agricultural eco-efficiency in China in recent 40 years. Land Use Policy 2020, 97, 104794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, K.; Krabben, E.v.d. Rapid urbanization, land pooling policies & the concentration of wealth. Land Use Policy 2022, 116, 106050. [Google Scholar]
- Ajzen, I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Dec. 1991, 50(2), 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Huang, X.; Song, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Tan, Q. Response to urban land scarcity in growing megacities: Urban containment or inter-city connection? Cities 2020, 96, 102399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Indicator | Variable | Unit | Calculation method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inputs | The average number of agricultural machinery power | kw/ha | Total power of agricultural machinery/crop sown area |
| Average number of people employed in primary industry | person/ha | Number of people employed in primary industry/crop sown area | |
| The average amount of fertilizer used on the land | t/ha | Fertilizer use / crop sown area | |
| Local average use of pesticides | t/ha | Amount of pesticides used/crop sown area | |
| Local average use of agricultural film | t/ha | Amount of agricultural film used/crop sown area | |
| Desirable output | Local average agricultural value added | 104 yuan/ha | Value added of agriculture/crop sown area |
| Local average food production | t/ha | Total food production/crop sown area | |
| Undesirable output | Local average carbon emissions | t/ha | Carbon emissions/crop sown area |
| Local Status | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 0.715 | 0.250 | 0.025 | 0.011 |
| Ⅱ | 0.094 | 0.610 | 0.238 | 0.058 |
| Ⅲ | 0.023 | 0.088 | 0.635 | 0.254 |
| Ⅳ | 0.000 | 0.033 | 0.172 | 0.795 |
| Spatial lag | Local Status | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | Ⅰ | 0.741 | 0.235 | 0.012 | 0.012 |
| Ⅱ | 0.200 | 0.543 | 0.214 | 0.043 | |
| Ⅲ | 0.037 | 0.259 | 0.444 | 0.259 | |
| Ⅳ | 0.000 | 0.130 | 0.174 | 0.696 | |
| Ⅱ | Ⅰ | 0.802 | 0.173 | 0.025 | 0.000 |
| Ⅱ | 0.060 | 0.655 | 0.262 | 0.024 | |
| Ⅲ | 0.000 | 0.067 | 0.700 | 0.233 | |
| Ⅳ | 0.000 | 0.026 | 0.179 | 0.795 | |
| Ⅲ | Ⅰ | 0.459 | 0.432 | 0.081 | 0.027 |
| Ⅱ | 0.066 | 0.632 | 0.226 | 0.075 | |
| Ⅲ | 0.015 | 0.076 | 0.664 | 0.244 | |
| Ⅳ | 0.000 | 0.016 | 0.163 | 0.822 | |
| Ⅳ | Ⅰ | 0.250 | 0.750 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Ⅱ | 0.000 | 0.529 | 0.294 | 0.176 | |
| Ⅲ | 0.071 | 0.048 | 0.571 | 0.310 | |
| Ⅳ | 0.000 | 0.038 | 0.189 | 0.774 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




