Submitted:
24 October 2023
Posted:
24 October 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
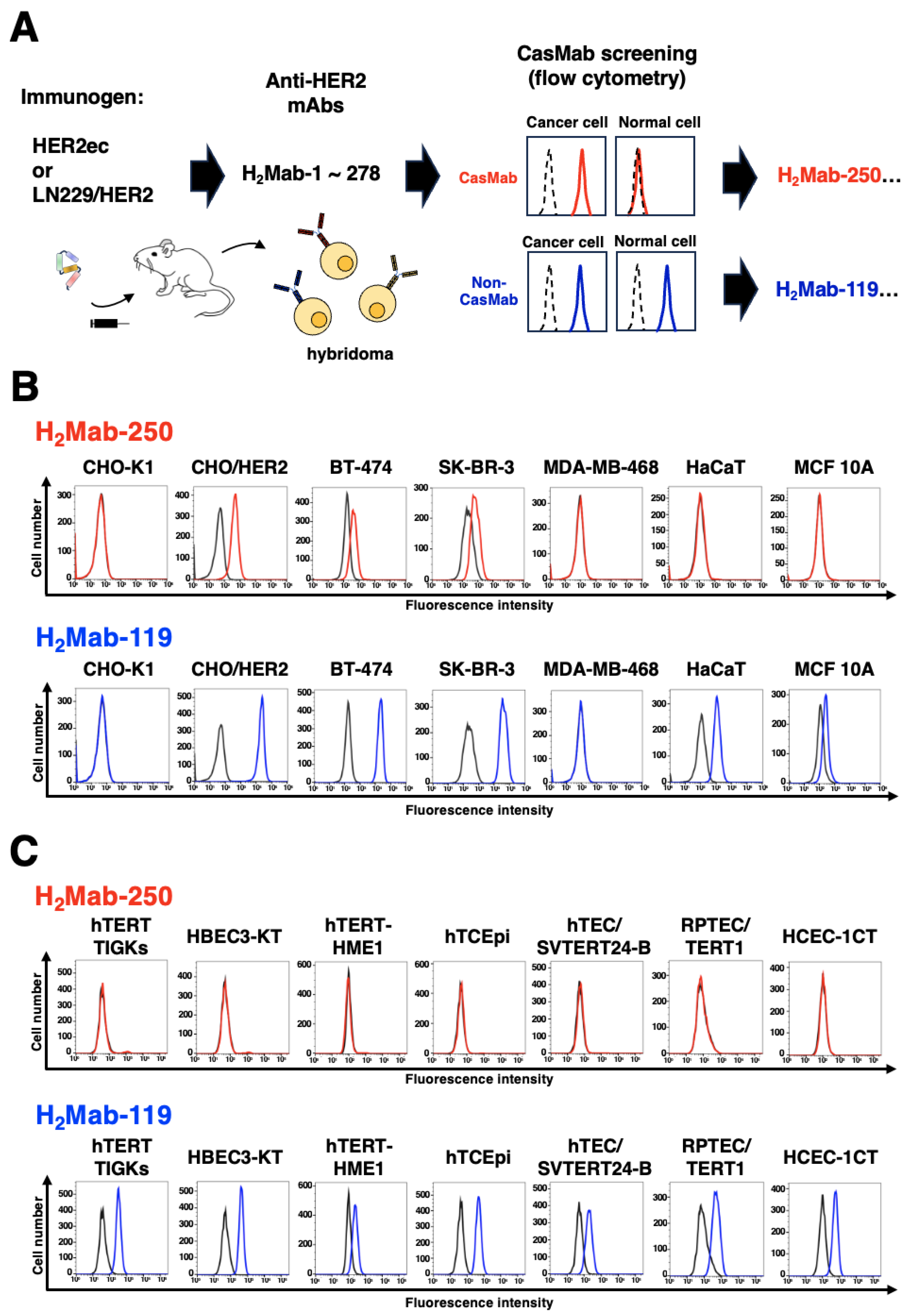
2.2. CasMab Screening
2.3. Recombinant mAb Production
2.4. Flow Cytometry
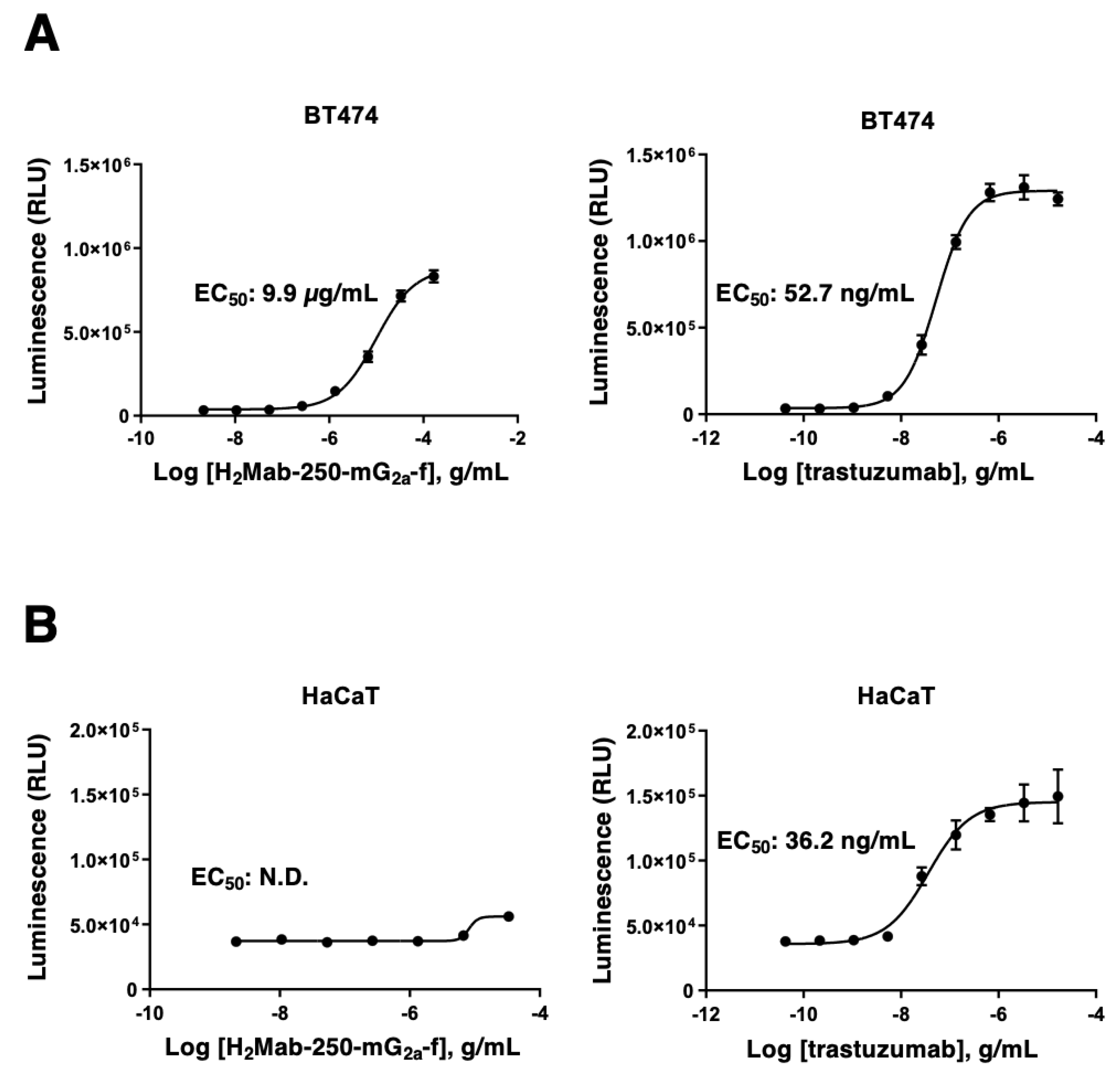
2.5. ADCC Reporter Bioassay
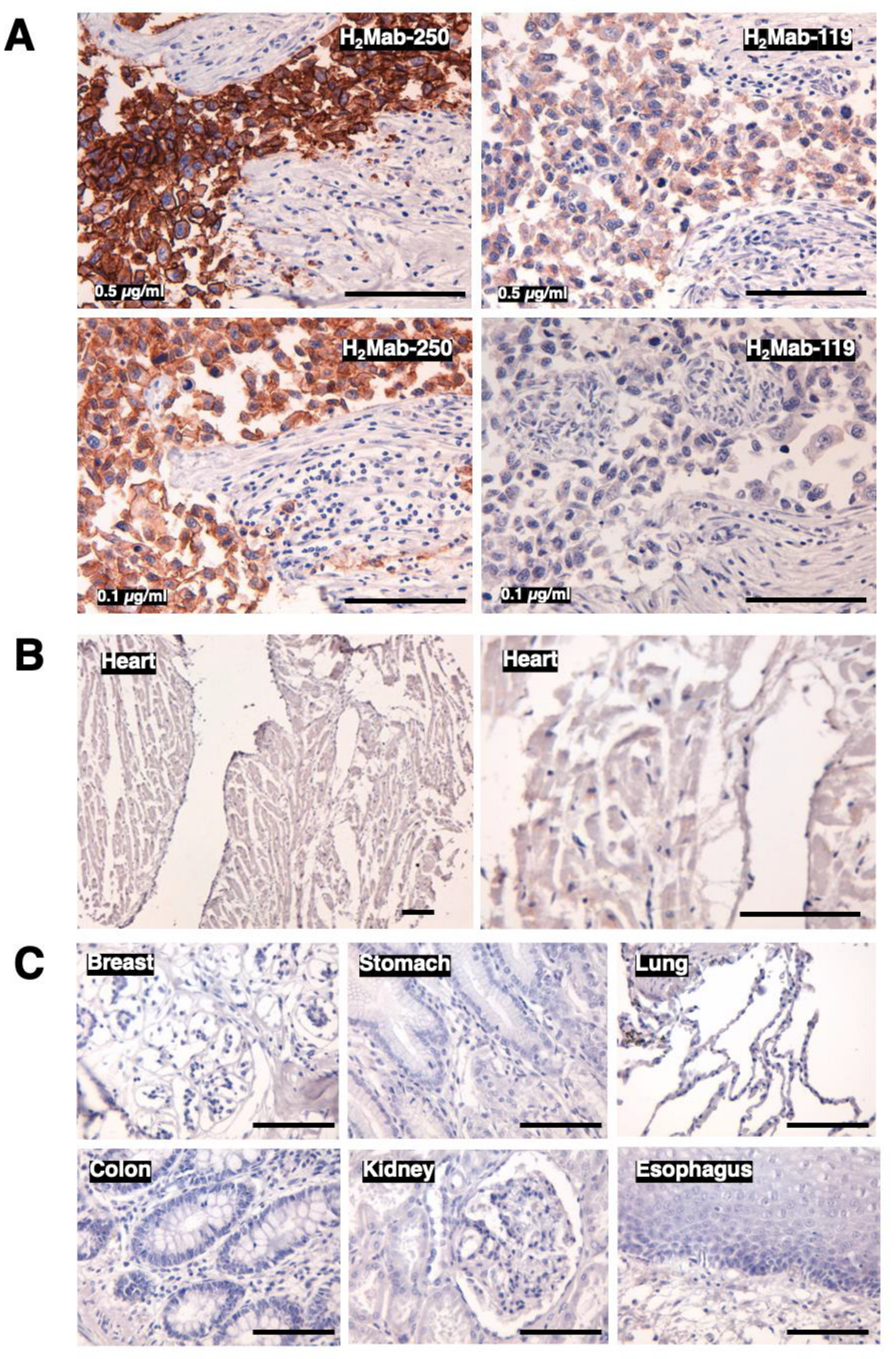
2.6. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.8. Determination of Dissociation Constant (KD) via Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
3. Results
3.1. Selection of H2Mab-250 Possessing the Cancer-Specific HER2 Recognition
3.2. The Ability of Effector Cell Activation by H2Mab-250 and Trastuzumab
3.3. Immunohistochemical Analysis of H2Mab-250 in Breast Cancer and Normal Epithelium
3.4. Epitope Identification for H2Mab-250
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yarden, Y.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slamon, D.J.; Clark, G.M.; Wong, S.G.; Levin, W.J.; Ullrich, A.; McGuire, W.L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 1987, 235, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Bang, Y.J.; Feng-Yi, F.; Xu, J.M.; Lee, K.W.; Jiao, S.C.; Chong, J.L.; López-Sanchez, R.I.; Price, T.; Gladkov, O.; et al. HER2 screening data from ToGA: targeting HER2 in gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer. Gastric Cancer 2015, 18, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.S.; Mason, K.; Ramyar, K.X.; Stanley, A.M.; Gabelli, S.B.; Denney, D.W., Jr.; Leahy, D.J. Structure of the extracellular region of HER2 alone and in complex with the Herceptin Fab. Nature 2003, 421, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, L.C.; Force, J.; Hartman, Z.C. Mechanisms of Therapeutic Antitumor Monoclonal Antibodies. Cancer Res 2021, 81, 4641–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essadi, I.; Benbrahim, Z.; Kaakoua, M.; Reverdy, T.; Corbaux, P.; Freyer, G. HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: Available Treatments and Current Developments. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slamon, D.J.; Leyland-Jones, B.; Shak, S.; Fuchs, H.; Paton, V.; Bajamonde, A.; Fleming, T.; Eiermann, W.; Wolter, J.; Pegram, M.; et al. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med 2001, 344, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, Y.J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Feyereislova, A.; Chung, H.C.; Shen, L.; Sawaki, A.; Lordick, F.; Ohtsu, A.; Omuro, Y.; Satoh, T.; et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maadi, H.; Soheilifar, M.H.; Choi, W.S.; Moshtaghian, A.; Wang, Z. Trastuzumab Mechanism of Action; 20 Years of Research to Unravel a Dilemma. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland-Halperin, R.S.; Liu, J.E.; Yu, A.F. Cardiotoxicity of HER2-targeted therapies. Curr Opin Cardiol 2019, 34, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.F.; Simon, H.; Chen, H.; Bates, B.; Hung, M.C.; Hauser, C. Requirement for neuregulin receptor erbB2 in neural and cardiac development. Nature 1995, 378, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crone, S.A.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Fan, L.; Gu, Y.; Minamisawa, S.; Liu, Y.; Peterson, K.L.; Chen, J.; Kahn, R.; Condorelli, G.; et al. ErbB2 is essential in the prevention of dilated cardiomyopathy. Nat Med 2002, 8, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itai, S.; Fujii, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Yamada, S.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Saidoh, N.; Chang, Y.W.; Handa, S.; Takahashi, M.; et al. H2Mab-77 is a Sensitive and Specific Anti-HER2 Monoclonal Antibody Against Breast Cancer. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2017, 36, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Itai, S.; Nakamura, T.; Chang, Y.W.; Harada, H.; Suzuki, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Establishment of H(2)Mab-119, an Anti-Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Monoclonal Antibody, Against Pancreatic Cancer. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2017, 36, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.K.; Yamada, S.; Itai, S.; Kato, Y. Development of an Anti-HER2 Monoclonal Antibody H2Mab-139 Against Colon Cancer. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2018, 37, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Suzuki, H.; Ohishi, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Antitumor activities against breast cancers by an afucosylated anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody H2Mab-77-mG2a-f. Preprint 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimori, T.; Mihara, E.; Suzuki, H.; Ohishi, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Takagi, J.; Kato, Y. Locally misfolded HER2 expressed on cancer cells is a promising target for development of cancer-specific antibodies Cell Press Community Review 2023.
- Suzuki, H.; Ohishi, T.; Nanamiya, R.; Kawada, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Defucosylated Monoclonal Antibody (H2Mab-139-mG2a-f) Exerted Antitumor Activities in Mouse Xenograft Models of Breast Cancers against Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 7734–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, M.K.; Ohishi, T.; Kawada, M.; Kato, Y. A cancer-specific anti-podocalyxin monoclonal antibody (60-mG(2a)-f) exerts antitumor effects in mouse xenograft models of pancreatic carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Rep 2020, 24, 100826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Ogasawara, S.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. LpMab-23: A Cancer-Specific Monoclonal Antibody Against Human Podoplanin. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2017, 36, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Kaneko, M.K. A cancer-specific monoclonal antibody recognizes the aberrantly glycosylated podoplanin. Sci Rep 2014, 4, 5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kuno, A.; Uchiyama, N.; Amano, K.; Chiba, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Hirabayashi, J.; Narimatsu, H.; Mishima, K.; et al. Inhibition of tumor cell-induced platelet aggregation using a novel anti-podoplanin antibody reacting with its platelet-aggregation-stimulating domain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006, 349, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvin, D.; Stecha, P.; Gilden, J.; Wang, J.; Grailer, J.; Hartnett, J.; Fan, F.; Cong, M.; Cheng, Z.J. Determining ADCC Activity of Antibody-Based Therapeutic Molecules using Two Bioluminescent Reporter-Based Bioassays. Curr Protoc 2021, 1, e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, S.; Saura, C.; Yamashita, T.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, S.B.; Tamura, K.; Andre, F.; Iwata, H.; Ito, Y.; Tsurutani, J.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med 2020, 382, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shitara, K.; Bang, Y.J.; Iwasa, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Ryu, M.H.; Sakai, D.; Chung, H.C.; Kawakami, H.; Yabusaki, H.; Lee, J.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Positive Gastric Cancer. N Engl J Med 2020, 382, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.T.; Smit, E.F.; Goto, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Udagawa, H.; Mazières, J.; Nagasaka, M.; Bazhenova, L.; Saltos, A.N.; Felip, E.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in HER2-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med 2022, 386, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, S.; Jacot, W.; Yamashita, T.; Sohn, J.; Vidal, M.; Tokunaga, E.; Tsurutani, J.; Ueno, N.T.; Prat, A.; Chae, Y.S.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Low Advanced Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med 2022, 387, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercogliano, M.F.; Bruni, S.; Mauro, F.L.; Schillaci, R. Emerging Targeted Therapies for HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, L.R.; Vilbert, M.; Rosa, V.D.L.; Oliveira, J.L.; Deus, M.M.; Freitas-Junior, R. Incidence of interstitial lung disease and cardiotoxicity with trastuzumab deruxtecan in breast cancer patients: a systematic review and single-arm meta-analysis. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 101613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
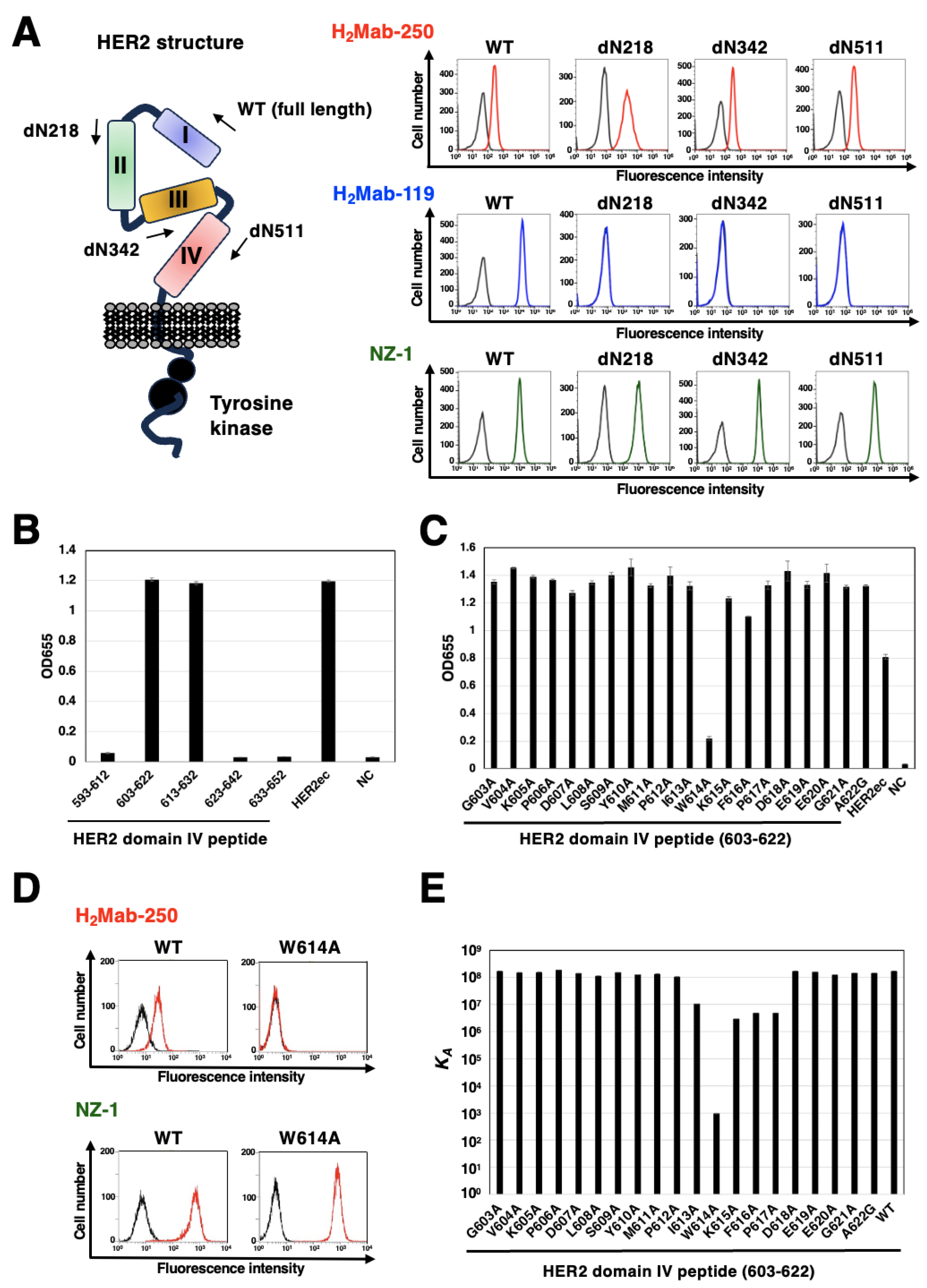
| Peptide | Sequence | KD (M) |
|---|---|---|
| 603-622 (WT) | GVKPDLSYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 5.8 × 10-9 |
| G603A | AVKPDLSYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 5.9 × 10-9 |
| V604A | GAKPDLSYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 6.5 × 10-9 |
| K605A | GVAPDLSYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 6.5 × 10-9 |
| P606A | GVKADLSYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 5.3 × 10-9 |
| D607A | GVKPALSYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 7.1 × 10-9 |
| L608A | GVKPDASYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 8.8 × 10-9 |
| S609A | GVKPDLAYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 6.5 × 10-9 |
| Y610A | GVKPDLSAMPIWKFPDEEGA | 7.9 × 10-9 |
| M611A | GVKPDLSYAPIWKFPDEEGA | 7.5 × 10-9 |
| P612A | GVKPDLSYMAIWKFPDEEGA | 9.5 × 10-9 |
| I613A | GVKPDLSYMPAWKFPDEEGA | 9.4 × 10-8 |
| W614A | GVKPDLSYMPIAKFPDEEGA | 1.1 × 10-3 |
| K615A | GVKPDLSYMPIWAFPDEEGA | 3.4 × 10-7 |
| F616A | GVKPDLSYMPIWKAPDEEGA | 2.0 × 10-7 |
| P617A | GVKPDLSYMPIWKFADEEGA | 2.1 × 10-7 |
| D618A | GVKPDLSYMPIWKFPAEEGA | 5.8 × 10-9 |
| E619A | GVKPDLSYMPIWKFPDAEGA | 6.3 × 10-9 |
| E620A | GVKPDLSYMPIWKFPDEAGA | 8.0 × 10-9 |
| G621A | GVKPDLSYMPIWKFPDEEAA | 6.9 × 10-9 |
| A622G | GVKPDLSYMPIWKFPDEEGG | 6.9 × 10-9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





