Submitted:
04 January 2024
Posted:
04 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell culture
2.2. Development of hybridomas
2.3. Production of recombinant mAbs
2.4. Flow cytometry
2.5. ADCC reporter bioassay
2.6. Immunohistochemical analysis
2.7. ELISA
2.8. Determination of KD via surface plasmon resonance (SPR)
3. Results
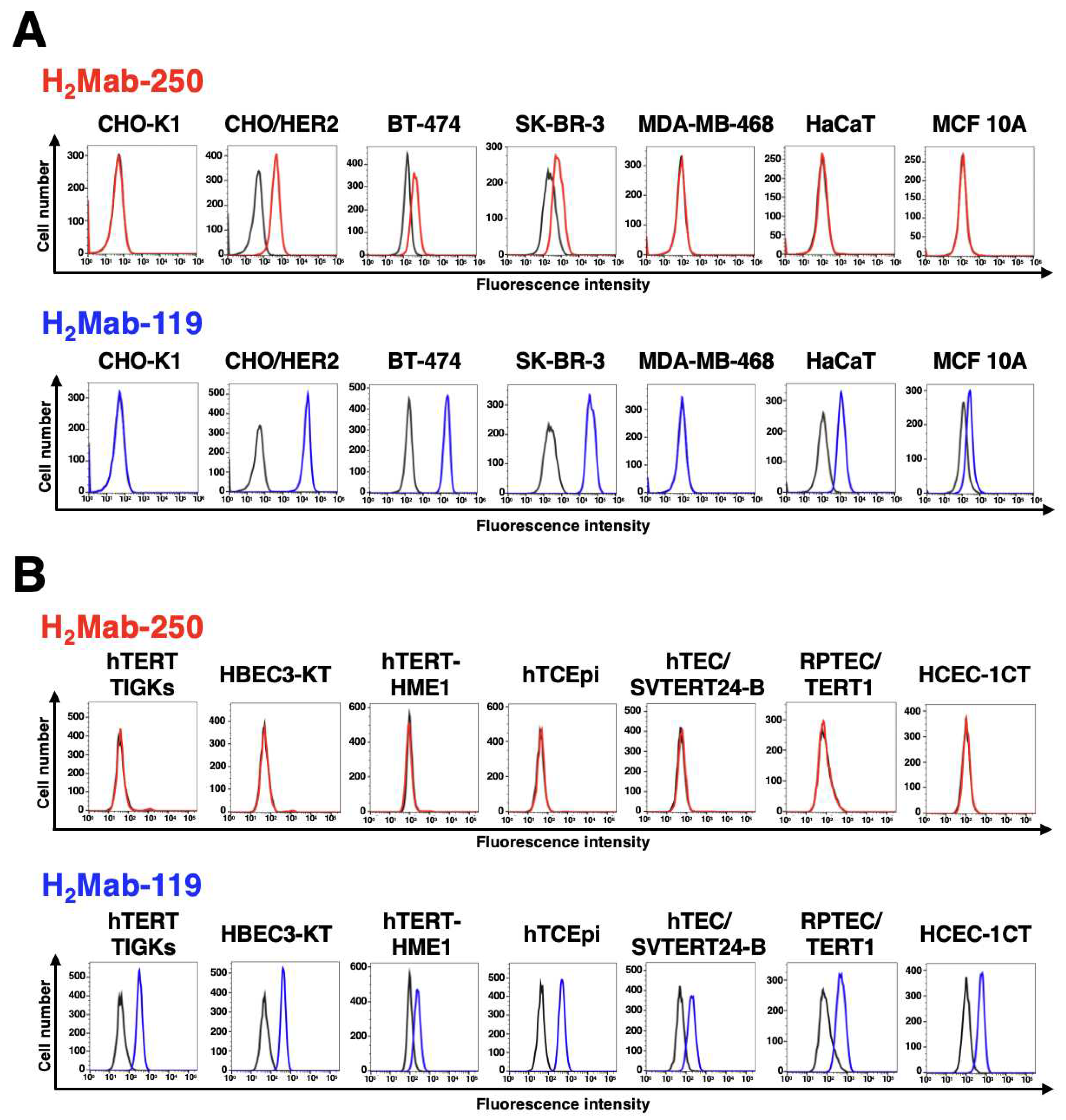
3.1. Establishment of H2Mab-250
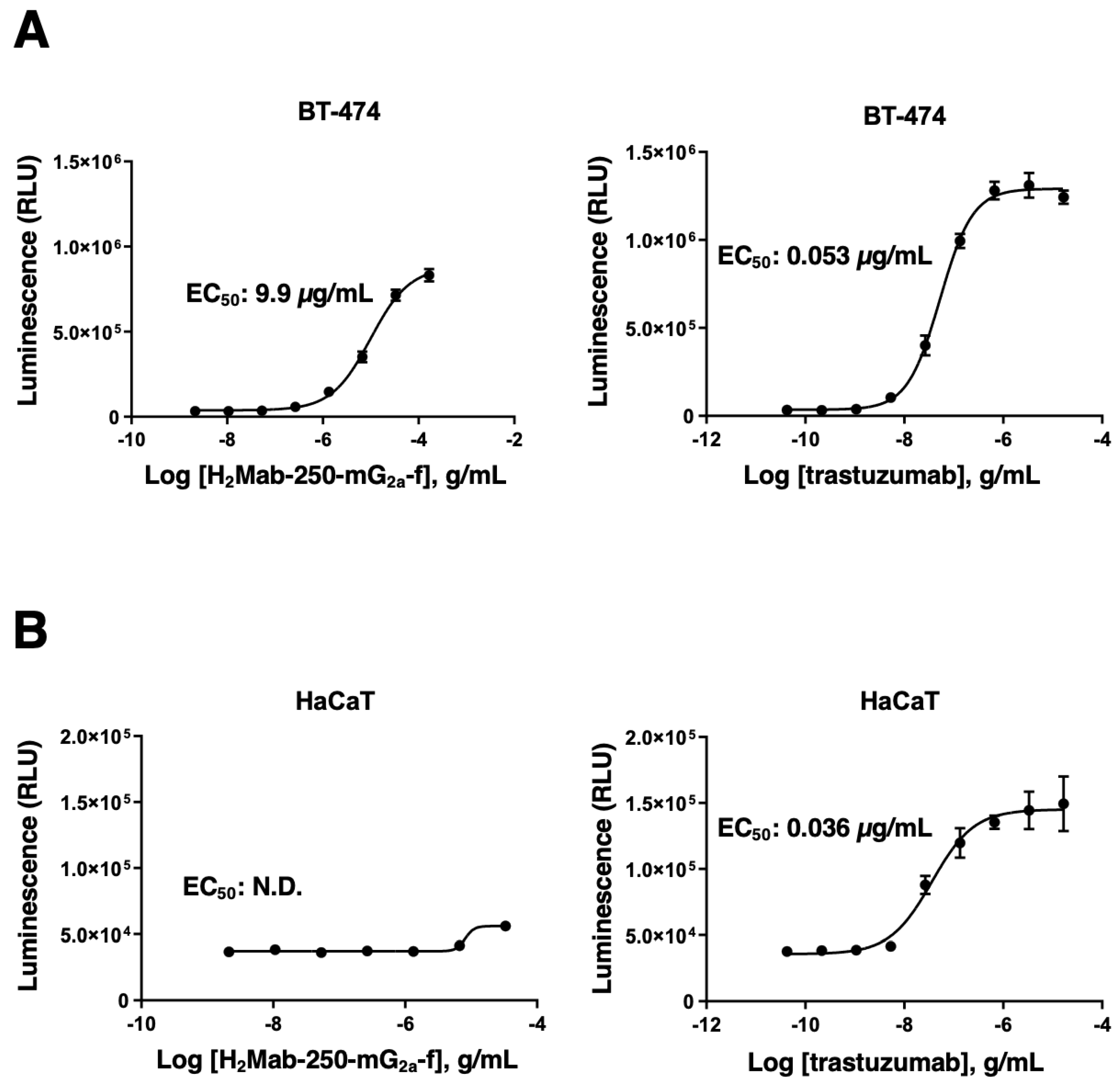
3.2. The ability of effector cell activation by H2Mab-250 and trastuzumab
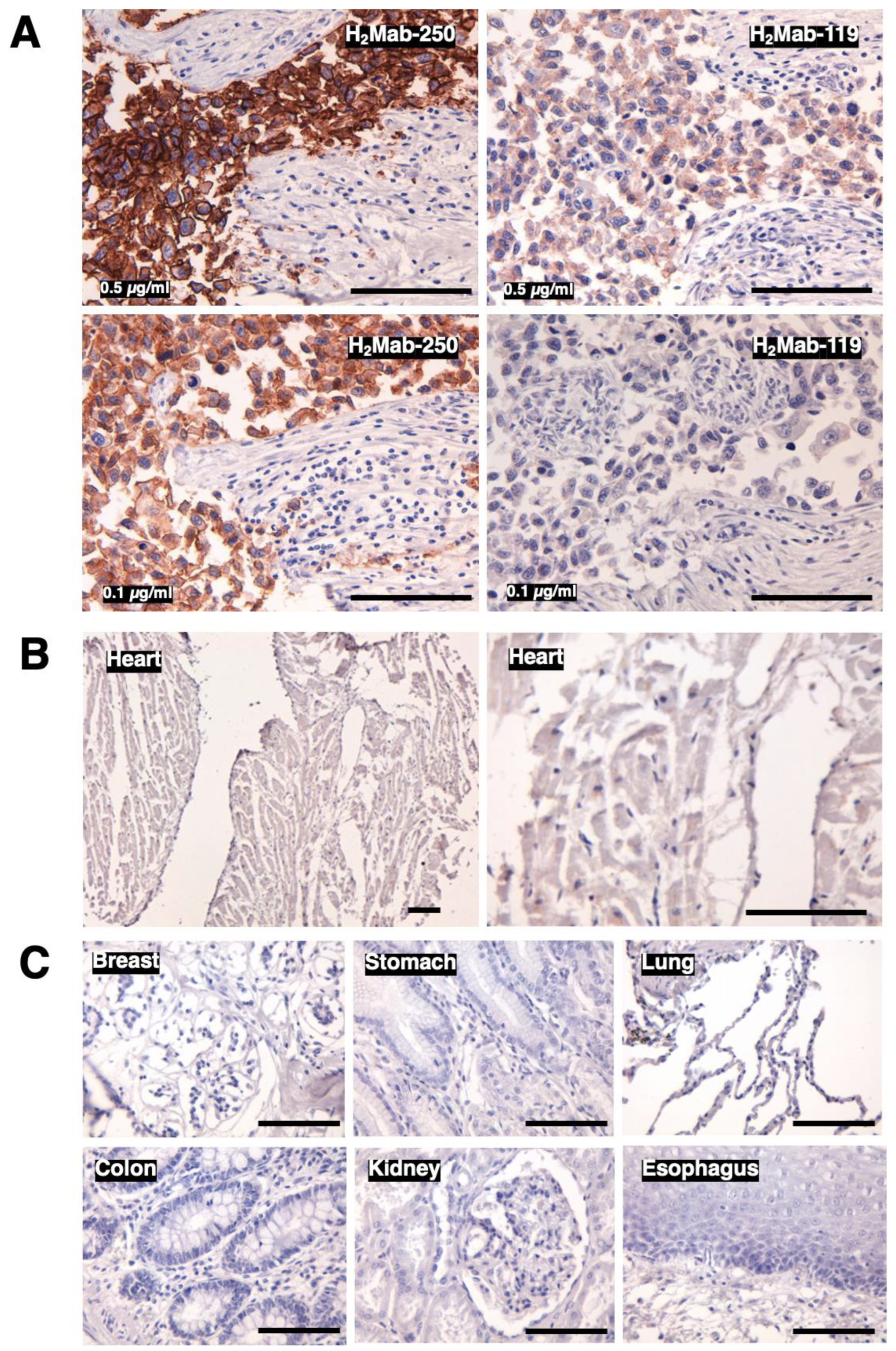
3.3. Immunohistochemical analysis of H2Mab-250 in breast cancer and normal epithelium
3.4. Epitope identification for H2Mab-250
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
References
- Yarden, Y.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slamon, D.J.; Clark, G.M.; Wong, S.G.; Levin, W.J.; Ullrich, A.; McGuire, W.L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 1987, 235, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Bang, Y.J.; Feng-Yi, F.; Xu, J.M.; Lee, K.W.; Jiao, S.C.; Chong, J.L.; López-Sanchez, R.I.; Price, T.; Gladkov, O.; et al. HER2 screening data from ToGA: targeting HER2 in gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer. Gastric Cancer 2015, 18, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.S.; Mason, K.; Ramyar, K.X.; Stanley, A.M.; Gabelli, S.B.; Denney, D.W., Jr.; Leahy, D.J. Structure of the extracellular region of HER2 alone and in complex with the Herceptin Fab. Nature 2003, 421, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, L.C.; Force, J.; Hartman, Z.C. Mechanisms of Therapeutic Antitumor Monoclonal Antibodies. Cancer Res 2021, 81, 4641–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essadi, I.; Benbrahim, Z.; Kaakoua, M.; Reverdy, T.; Corbaux, P.; Freyer, G. HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: Available Treatments and Current Developments. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slamon, D.J.; Leyland-Jones, B.; Shak, S.; Fuchs, H.; Paton, V.; Bajamonde, A.; Fleming, T.; Eiermann, W.; Wolter, J.; Pegram, M.; et al. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med 2001, 344, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, Y.J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Feyereislova, A.; Chung, H.C.; Shen, L.; Sawaki, A.; Lordick, F.; Ohtsu, A.; Omuro, Y.; Satoh, T.; et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maadi, H.; Soheilifar, M.H.; Choi, W.S.; Moshtaghian, A.; Wang, Z. Trastuzumab Mechanism of Action; 20 Years of Research to Unravel a Dilemma. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland-Halperin, R.S.; Liu, J.E.; Yu, A.F. Cardiotoxicity of HER2-targeted therapies. Curr Opin Cardiol 2019, 34, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.F.; Simon, H.; Chen, H.; Bates, B.; Hung, M.C.; Hauser, C. Requirement for neuregulin receptor erbB2 in neural and cardiac development. Nature 1995, 378, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crone, S.A.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Fan, L.; Gu, Y.; Minamisawa, S.; Liu, Y.; Peterson, K.L.; Chen, J.; Kahn, R.; Condorelli, G.; et al. ErbB2 is essential in the prevention of dilated cardiomyopathy. Nat Med 2002, 8, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei, J.; Kaneko, M.K.; Ohishi, T.; Kawada, M.; Harada, H.; Kato, Y. H2Mab-19, an anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 monoclonal antibody exerts antitumor activity in mouse oral cancer xenografts. Exp Ther Med 2020, 20, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tateyama, N.; Asano, T.; Ohishi, T.; Takei, J.; Hosono, H.; Nanamiya, R.; Tanaka, T.; Sano, M.; Saito, M.; Kawada, M.; et al. An Anti-HER2 Monoclonal Antibody H2Mab-41 Exerts Antitumor Activities in Mouse Xenograft Model Using Dog HER2-Overexpressed Cells. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itai, S.; Fujii, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Yamada, S.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Saidoh, N.; Chang, Y.W.; Handa, S.; Takahashi, M.; et al. H2Mab-77 is a Sensitive and Specific Anti-HER2 Monoclonal Antibody Against Breast Cancer. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2017, 36, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Itai, S.; Nakamura, T.; Chang, Y.W.; Harada, H.; Suzuki, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Establishment of H(2)Mab-119, an Anti-Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Monoclonal Antibody, Against Pancreatic Cancer. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2017, 36, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, M.K.; Yamada, S.; Itai, S.; Kato, Y. Development of an Anti-HER2 Monoclonal Antibody H2Mab-139 Against Colon Cancer. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2018, 37, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei, J.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Sano, M.; Hosono, H.; Nanamiya, R.; Tateyama, N.; Saito, M.; Suzuki, H.; Harada, H.; et al. Development of a Novel Anti-HER2 Monoclonal Antibody H(2)Mab-181 for Gastric Cancer. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Suzuki, H.; Ohishi, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Antitumor activities against breast cancers by an afucosylated anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody H2Mab-77-mG2a-f. Preprint 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimori, T.; Mihara, E.; Suzuki, H.; Ohishi, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Takagi, J.; Kato, Y. Locally misfolded HER2 expressed on cancer cells is a promising target for development of cancer-specific antibodies Cell Press Community Review 2023. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Ohishi, T.; Nanamiya, R.; Kawada, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Defucosylated Monoclonal Antibody (H2Mab-139-mG2a-f) Exerted Antitumor Activities in Mouse Xenograft Models of Breast Cancers against Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 7734–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kuno, A.; Uchiyama, N.; Amano, K.; Chiba, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Hirabayashi, J.; Narimatsu, H.; Mishima, K.; et al. Inhibition of tumor cell-induced platelet aggregation using a novel anti-podoplanin antibody reacting with its platelet-aggregation-stimulating domain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006, 349, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvin, D.; Stecha, P.; Gilden, J.; Wang, J.; Grailer, J.; Hartnett, J.; Fan, F.; Cong, M.; Cheng, Z.J. Determining ADCC Activity of Antibody-Based Therapeutic Molecules using Two Bioluminescent Reporter-Based Bioassays. Curr Protoc 2021, 1, e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwanji, D.; Trenker, R.; Thaker, T.M.; Wang, F.; Agard, D.A.; Verba, K.A.; Jura, N. Structures of the HER2-HER3-NRG1β complex reveal a dynamic dimer interface. Nature 2021, 600, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.; Saura, C.; Yamashita, T.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, S.B.; Tamura, K.; Andre, F.; Iwata, H.; Ito, Y.; Tsurutani, J.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med 2020, 382, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitara, K.; Bang, Y.J.; Iwasa, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Ryu, M.H.; Sakai, D.; Chung, H.C.; Kawakami, H.; Yabusaki, H.; Lee, J.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Positive Gastric Cancer. N Engl J Med 2020, 382, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.T.; Smit, E.F.; Goto, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Udagawa, H.; Mazières, J.; Nagasaka, M.; Bazhenova, L.; Saltos, A.N.; Felip, E.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in HER2-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med 2022, 386, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, S.; Jacot, W.; Yamashita, T.; Sohn, J.; Vidal, M.; Tokunaga, E.; Tsurutani, J.; Ueno, N.T.; Prat, A.; Chae, Y.S.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Low Advanced Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med 2022, 387, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercogliano, M.F.; Bruni, S.; Mauro, F.L.; Schillaci, R. Emerging Targeted Therapies for HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, L.R.; Vilbert, M.; Rosa, V.D.L.; Oliveira, J.L.; Deus, M.M.; Freitas-Junior, R. Incidence of interstitial lung disease and cardiotoxicity with trastuzumab deruxtecan in breast cancer patients: a systematic review and single-arm meta-analysis. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 101613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
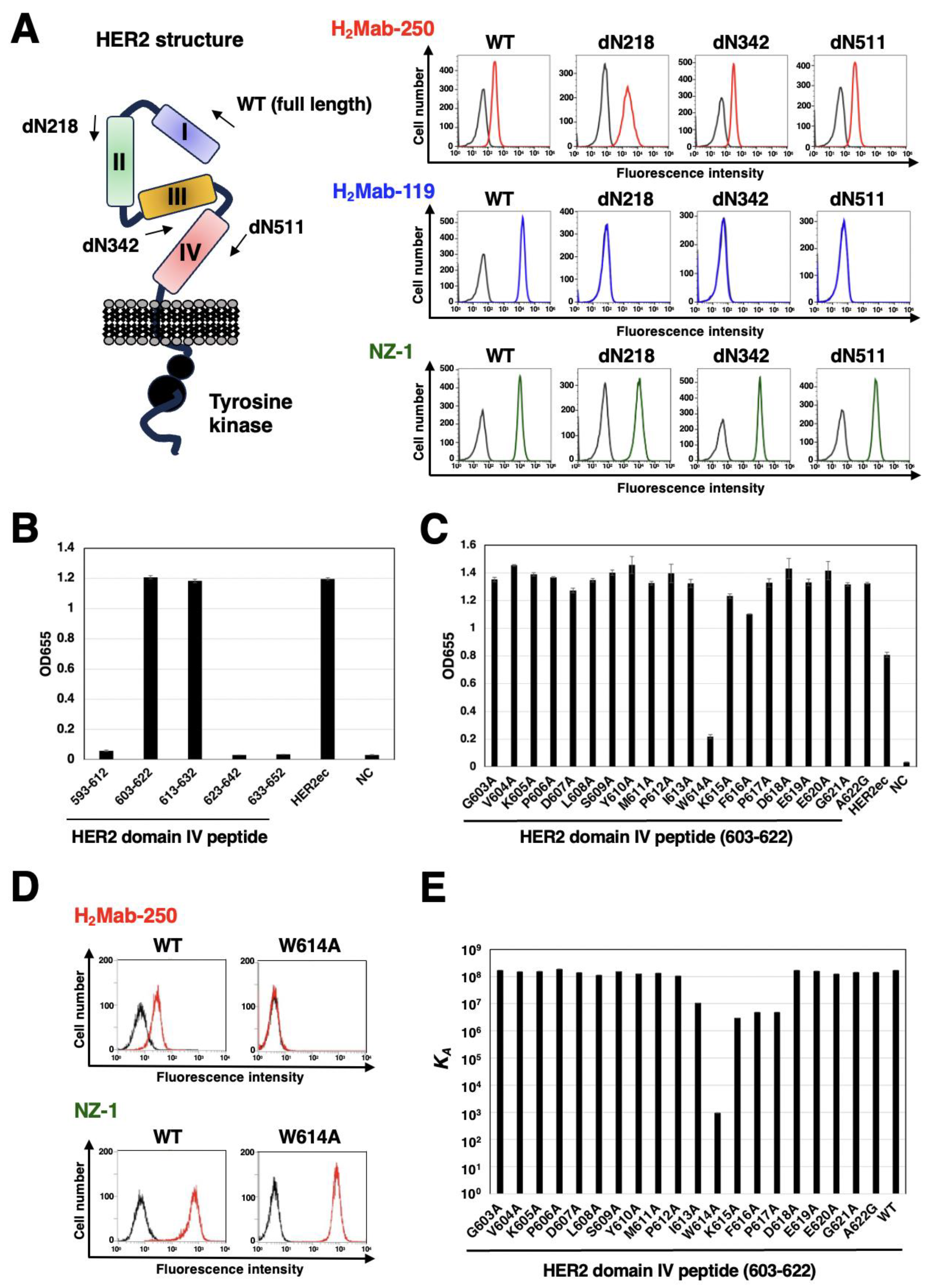
| Peptide | Sequence | KD (M) |
|---|---|---|
| 603-622 (WT) | GVKPDLSYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 5.8 × 10-9 |
| G603A | AVKPDLSYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 5.9 × 10-9 |
| V604A | GAKPDLSYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 6.5 × 10-9 |
| K605A | GVAPDLSYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 6.5 × 10-9 |
| P606A | GVKADLSYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 5.3 × 10-9 |
| D607A | GVKPALSYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 7.1 × 10-9 |
| L608A | GVKPDASYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 8.8 × 10-9 |
| S609A | GVKPDLAYMPIWKFPDEEGA | 6.5 × 10-9 |
| Y610A | GVKPDLSAMPIWKFPDEEGA | 7.9 × 10-9 |
| M611A | GVKPDLSYAPIWKFPDEEGA | 7.5 × 10-9 |
| P612A | GVKPDLSYMAIWKFPDEEGA | 9.5 × 10-9 |
| I613A | GVKPDLSYMPAWKFPDEEGA | 9.4 × 10-8 |
| W614A | GVKPDLSYMPIAKFPDEEGA | 1.1 × 10-3 |
| K615A | GVKPDLSYMPIWAFPDEEGA | 3.4 × 10-7 |
| F616A | GVKPDLSYMPIWKAPDEEGA | 2.0 × 10-7 |
| P617A | GVKPDLSYMPIWKFADEEGA | 2.1 × 10-7 |
| D618A | GVKPDLSYMPIWKFPAEEGA | 5.8 × 10-9 |
| E619A | GVKPDLSYMPIWKFPDAEGA | 6.3 × 10-9 |
| E620A | GVKPDLSYMPIWKFPDEAGA | 8.0 × 10-9 |
| G621A | GVKPDLSYMPIWKFPDEEAA | 6.9 × 10-9 |
| A622G | GVKPDLSYMPIWKFPDEEGG | 6.9 × 10-9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





