1. Introduction
Drop attack (DA) is defined as the sudden loss of postural tone that generally causes falls, and which, unlike epilepsy or syncope, is not associated with loss of consciousness(3-6, 10).Its etiology can be explained by vertebrobasilar insufficiency, epilepsy or vestibular instability, (the latter are also known as Tumarkin’s otolithic crises (1, 3, 4, 10, 11) and their physiopathology includes the sudden imbalance of the vestibular reflexes induced, for instance, by pathologies such as Ménière's disease (MD) in which fluctuations in vestibular tone are typical (5). Turmakin otolitic crises as a complication of Ménière's disease were first described in 1936 (16), and even today it is difficult to establish their true incidence. Although new studies would be necessary in order to establish it, a recently published meta-analysis shows a 3 to 19% DA frequency of in patients diagnosed with MD, although this varies greatly according to the criteria used for its diagnosis (16).
We know that MD is a condition of the inner ear that is characterized by episodic vertigo, auditory fluctuations, and ear fullness. Its epidemiology is better known, and it affects approximately 50-200 people per 100,000 inhabitants, and it predominates in patients between the age of 40 and 60. Its pathophysiology can be explained by the fluctuating endolymphatic hydrops that characterizes it, which is an ideal terrain for the development of sudden pressure changes in the inner ear (1, 4, 5, 7, 9). Vestibular DA is due to a sudden change in endolymphatic flow, which results in inadequate otolithic stimulation (1, 4).Patients describe feeling like they were pushed to the ground or like the surroundings moved (3).This is what causes the fall which, sometimes, even leads to serious injuries (4, 13). This significantly affects the individual’s quality of life, and this makes an early diagnosis essential in order to provide a timely treatment. The neurologist should always suspect and be prepared to consider a DA of vestibular origin as a differential diagnosis of the loss of postural tone or instability.
For the treatment of DA (as well as for the control of MD) we have hygienic-dietary measures such as salt restriction, pharmacological measures such as betahistine and vestibular sedatives (4), and, if these strategies fail, intratympanic injections gentamicin can be administered (4).We present a series of 43 patients treated at our institution with a diagnosis of DA, of which 33 presented a diagnosis of MD. The purpose of this study is to analyze the characteristics of the treated patients and their response to the established treatment in order to find predictors of good or bad evolution, which may be useful at the moment of deciding when to escalate in the treatment. Bearing in mind that the natural evolution of untreated or insufficiently treated MD is towards hearing loss, it is of vital importance to have these predictors that can help us carry out timely therapeutic interventions, sparing our patients a long-term disability.
2. Materials and Methods
An analytical, observational, cross-sectional study was carried out, with retrospective data collection that included the review of medical recordsbetween 2015 and 2022 in the database of the San Lucas Foundation for Neuroscience, a neuro-otology center of reference located in the city of Rosario, Argentina.Patients who presented DA were recorded, and those of vestibular origin were differentiated, especially in the context of Ménière's disease; these were treated with betahistine 48 mg daily (24 mg twice daily) The diagnosis of MD was made according to the diagnostic criteria jointly developed by the Committee for the Classification of Vestibular Disorders of the Bárány Society, the Japan Society for Equilibrium Research, the European Academy of Otology and Neurotology (EAONO), the Balance Committee from the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS), and the Korean Balance Society (17). Although there are different degrees of DA depending on the degree of imbalance suffered by the patient, all the patients included in the series presented severe DA, that is, they caused the patient to fall. Demographic data such as age and sex, symptoms such as hearing loss, vertigo, headache, instability, pulsion, in addition to the vestibular physical examination of the patient, disease evolution time and response to betahistine were recorded for all patients, For those patients that, despite treatment with the maximum dose of the drug, did not achieve adequate AD control, BTH was considered a therapeutic failure. A descriptive analysis of the qualitative andquantitative variables was performed. The former were represented in the tables as frequencies and percentages,while the quantitative variables were summarized as means and standard deviations or, in the case of asimmetricaldistributions, as medians and interquartile range (IR) (P25 - P75).
The Chi-square, Chi-square test with continuity correction or Fisher's test was applied according to application criteria, to compare qualitative variables between two groups (with and without response to BTH).Student's T-test was used once the requirements of randomization, independence, normality, and equality of variance were validated.If the normality requirement was not met, the Mann-Whitney U test was used.When significant differences were detected, 95% confidence intervals (CI) were determined.Initially, a univariate logistic regression analysis was performed, and subsequently, a multivariate logistic regression model was performed to express the strength of association between the lack of response to BTH and the variables studied.The OR (odds ratio) and the CI were estimated at 95%.In all hypothesis contrasts, a significance level of p<0.05 was considered.
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 22.0 software (IBM Corporation, NY, United States).
3. Results
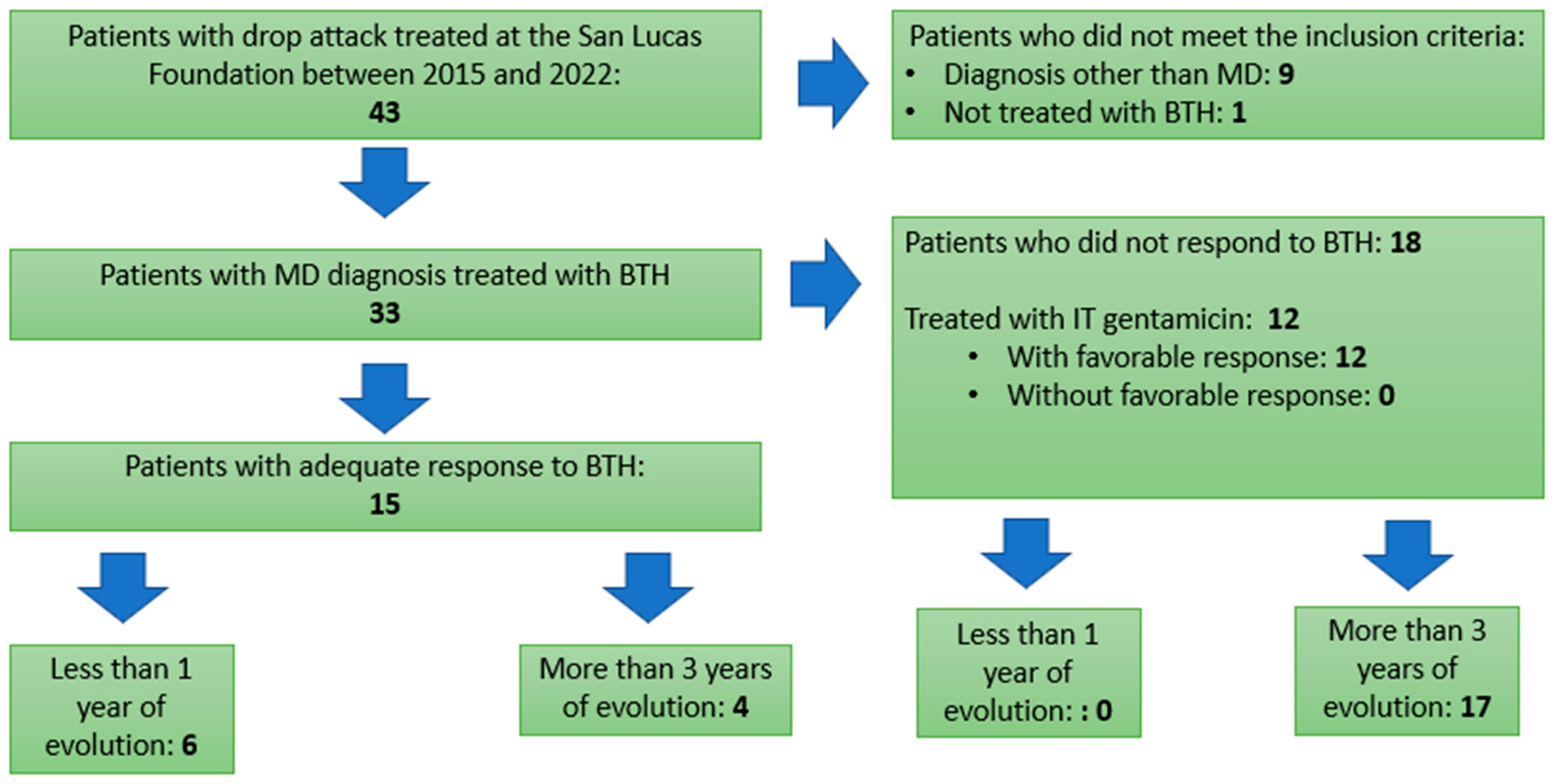
In a thorough review of the database of patients treated at the San Lucas Foundation between 2015 and 2022, 43 patients with a diagnosis of drop attack were found, 10 of which were excluded as they did not meet the inclusion criteria for this study. (9 presented drop attacks of idiopathic etiology and 1 patient had not adequately completed the treatment with betahistine).Therefore, the study population was made up of 33 patients who presented drop attacks of vestibular origin with a diagnosis of Ménière's disease, all of whom were treated with betahistine. As shown in Picture 1, 15 patients had an adequate response to BTH; in this group, 6 of them had less than 1 year of evolution of the disease, while 4 of them had more than 3 years of evolution. As for the 18 patients who did not respond to BTH, it should be noted that none of them had less than 1 year of evolution, and almost the whole group (17 patients) presented a disease that had progressed for more than 3 years. It is important to point out that, in this last group, and given the lack of response to BTH, 12 patients were treated with intratympanic gentamicin with a more than acceptable success rate of 100% with 1 or several applications.
Picture 1.
- Patient's Flow Chart.
Picture 1.
- Patient's Flow Chart.
The general characteristics of the 33 patients, as well as their clinical symptoms and comorbidities associated with the drop attack, and the disease evolution time are shown in
Table 1.
Table 1.
- General Characteristics of the 33 Patients.
Table 1.
- General Characteristics of the 33 Patients.
| Characteristics |
N=33 |
| Average Age (±ED) |
62 (±16.327) |
| Sex, M n° (%) |
15 (45.5%) |
| Hearing Loss (%) |
27 (81.8%) |
| Vertigo (%) |
27 (81.8%) |
| Instability (%) |
4 (12.1%) |
| Pulsion (%) |
10 (30.3%) |
| Headache (%) |
6 (18.2%) |
| Abnormal Physical Examination (%) |
24 (72.7%) |
| Active Disease (%) |
25 (75.8%) |
| Migraine (%) |
5 (15.2%) |
| Evolution: |
|
| Less than 1 year (%) |
6 (18.2%) |
| More than 3 years (%) |
21 (63.6%) |
| Response to betahistine (%) |
15 (45.5%) |
Picture 2 shows the differences in the different variables between those patients who showed an adequate response to treatment with BTH and those who did not. It should be noted, on the one hand, that significant differences were found in those patients who presented alterations in the physical examination (here, we are referring to patients with alterations in the vestibulospinal or oculomotor physical examination in intercritical periods), 53.3% in the group with response to BTH as compared to 88.9% in the group without response to BTH (p=0.047).On the other hand, response to BTH was found in 40% of the patients with less than 1 year of evolution of the disease; in contrast, none of the patients in the group that did not respond to BTH had less than 1 year of evolution (p= 0.005).Also, in relation to the disease evolution time, it was found with good statistical significance (p=<0.001) that, of the patients who responded to BTH, only 26.7% had suffered from the disease for more than 3 years, in the group of patients who did not respond to BTH, 94.4% had an evolution of more than 3 years.
Table 2.
Distribution of variables according to response to betahistine.
Table 2.
Distribution of variables according to response to betahistine.
| VARIABLES |
With response (n=15) |
Without response (n=18) |
p |
| Age, median (IR) |
65 (56;73.5) |
63.5 (48;73) |
0.971 |
| Sex, M n° (%) |
5 (33.3) |
10 (55.6) |
0.296 |
| Hearing Loss (%) |
10 (66.7) |
17 (94.4) |
0.070 |
| Vertigo (%) |
11 (73.3) |
16 (88.9) |
0.375 |
| Instability |
1 (6.7) |
3 (16.7) |
0.607 |
| Pulsion |
7 (46.7) |
3 (16.7) |
0.125 |
| Headache |
2 (13.3) |
4 (22.2) |
0.665 |
| Abnormal Physical Examination |
8 (53.3) |
16 (88.9) |
0.047 |
| Active Disease |
11 (73.3%) |
14 (77.8) |
1.000 |
| Associated Migraine |
2 (13.3) |
3 (16.7) |
1.000 |
| Evolution: |
|
|
|
| Less than one year |
6 (40) |
0 (0) |
0.005 |
| More than three years |
4 (26.7%) |
17 (94.4) |
<0.001 |
Picture 3 shows the results of the univariate logistic regression in relation to the lack of response to BTH in the patients studied.In this model, it can be seen with good statistical power that the presence of an abnormal physical examination predicts a lack of response to BTH (OR:7.000; CI 1.173 – 41.759; p=0.033).Likewise, the history of a disease with more than 3 years of evolution strongly predicts a failure of BTH for the treatment of drop attacks due to Ménière's disease according to this model (OR:46.750; CI:4.600 – 475.161; p=0.001).
A multivariate logistic regression analysis was also performed between those variables that showed statistical significance in the univariate model. It is worth mentioning that only the evolution of the disease for more than 3 years maintained statistical power in this analysis, with an OR:31.682; CI:2.350 – 427.066; p=0.009.
Table 3.
Results of the univariate logistic regression analysis to establish the predictive capacity of the different variables in relation to the lack of response to betahistine.
Table 3.
Results of the univariate logistic regression analysis to establish the predictive capacity of the different variables in relation to the lack of response to betahistine.
| Variables |
Response to betahistine |
p |
| OR |
CI |
| Age |
1.000 |
0.959 – 1.044 |
0.983 |
| Sex |
2.500 |
0.604-10.440 |
0.206 |
| Hearing Loss |
8.500 |
0.865-83.493 |
0.066 |
| Vertigo |
2.909 |
0.452-18.742 |
0.261 |
| Instability |
2.800 |
0.260-30.178 |
0.396 |
| Pulsion |
0.229 |
0.046-1.340 |
0.071 |
| Headache |
1.857 |
0.290-11.902 |
0.514 |
| Abnormal Physical Examination |
7.000 |
1.173-41.759 |
0.033 |
| Active Disease |
1.273 |
0.258-6.273 |
0.767 |
| Associated Migraine |
1.300 |
0.187-9.021 |
0.791 |
| More than three years of evolution |
46.750 |
4.600-475.161 |
0.001 |
4. Discussion
First of all, we must say that, in terms of the general characteristics of the population, the average age is somewhat higher compared to that described for patients with MD (40 to 60 years), although we can find that it can occur between the third and the seventh decade of life (17) this may be due to the idiosyncratic characteristics of the population cared for in a specialized reference center such as the San Lucas Foundation. Audiol.Res.2023, 13, FOR PEER REVIEW 6
As regards distribution by sex, and in agreement with the literature, a subtle prevalence is observed in the female sex (17). 81.8% of the sample presented the two typical symptoms of the disease, i.e., hearing loss and episodic vertigo, consistent with the literature. 12.1% of the patients presented instability, and more than 30% of them presented pulsion, symptoms which, although they are not part of the diagnostic criteria, are grounds to suspect the disease (17).
It should be noted that a large proportion of the sample (72.2%) presented an abnormal vestibulo-spinal or oculomotor physical examination, although it is fair to note that the examination was carried out by highly trained neurootologists, given that San Lucas Foundation is a center of reference on this matter, and this may not be the case in evaluations performed in emergency rooms or general practitioners’ offices.
On the other hand, 75.8% of the patients in the sample had active MD, that is, they had had one or more episodes of vertigo or fluctuating hearing loss in the previous month. As regards the frequency of migraine, we must say that our sample presents an incidence similar to that of the general population, although it is known that the frequency of this disease is higher in patients suffering from MD (18)
It was possible to make an early diagnosis of MS, that is, before one year of symptoms evolution in18.2% of the patients; in an identical percentage, diagnosis was made between the first and third year of evolution of the disease, and, in 63.6% of the cases, the disease presented over a three-year evolution, and, in general, they were patients who had made multiple previous consultations. This situation shows us the importance of maintaining a high level of suspicion in the face of symptoms that are so frequent in general medical and specialized neurological consultations, as it is the case with episodic vertigo. Also, we should not forget to always ask these patients about hearing loss. These two points would allow us to reach an earlier diagnosis, which is of vital importance, taking into account that the time of evolution of the disease, according to the results previously mentioned, seems to be one of the factors that determine the pharmacological response to BTH, at least in terms of DAs. It is therefore worth redoubling our efforts to reach a diagnosis as early as possible.
This study was designed to evaluate factors that may predict a poor initial response to BTH in patients treated for drop attacks of vestibular origin secondary to Ménière's disease.When the variables are individually analyzed, it can be seen that the presence of an abnormal vestibular physical examination, or the history of a disease with more than 3 years of evolution is associated to a poor response to treatment with BTH.We can also say that these two variables show predictive capacity for the failure of BTH as therapy according to the univariate logistic regression model, although it is fair to say that, when analyzing the variables as a whole, only a disease of more than 3 years of evolution predicts a poor therapeutic response to BTH for the treatment of drop attacks secondary to Ménière's disease(15).
It should be noted that no significant differences were found in the variables sex, age, nor for accompanying symptoms such as hearing loss, vertigo, pulsion, instability, or headache; the history of associated migraine was not related to the therapeutic response to BTH either.
In specialized neuro-otology consultations due to drop attack, we observed that 79% of them were of vestibular origin and had a diagnosis of Ménière disease. Of them, 39.4% showed a favorable response to betahistine. We have found that those patients who have alterations in the vestibulospinal or oculomotor physical examination in intercritical periods showed an unfavorable response to the control of the disease with betahistine, as well as those who have 3 years or more of symptoms evolution.
Although the mechanism of action of BTH is not completely known, we know that it is a histamine H1 receptor agonist and H3 antagonist, which exerts its beneficial effects on MS at two levels, 1) increasing blood flow at the vestibular level through an improvement in the microcirculation of the stria vascularis in the cochlea, and 2) improving the central compensation of vestibular imbalances through the stimulation of histamine synthesis in the vestibular nuclei. Since MD is a pathology of the inner ear, characterized by fluctuating hydrops, it may be possible that the evolution of the pathology itself could produce structural changes in it which affect the capacity of the stria vascularis to achieve better vascularization in the inner ear in response to BTH, and thus decrease endo-lymphatic pressure. In the same way, these structural changes that would occur over time, would reveal alterations in the vestibulo-spinal or oculomotor examination that could be objectified in a possible consultation, regardless of whether or not the patient is experiencing a crisis at that time.
An interesting fact of the present series of patients is the high response to treatment with intratympanic gentamicin in those patients who did not respond to BTH (8, 12, 14). A noteworthy fact is that DA control was achieved in 100% of the patients treated with IT gentamicin, either with one or more applications (a maximum of 3 IT gentamicin applications were performed) (8, 12, 14)
5. Conclusions:
One of the main issues that this experience reveals is the great importance of making an early MD diagnosis, though it is well known that it is an under-diagnosed disease, and for which there is a significant delay in diagnosis, maybe because it is a rare disease which requires sub-specialists. This situation is even more serious if we take into account the fact that, apparently and consistently with the results of our multivariable logistic regression model, there is a moment beyond the three years in which pharmacological response is already very poor. In contrast, before the year of symptoms evolution, therapeutic response to BTH is very good. This situation emphasized the importance of maximizing the efforts to reach an early diagnosis, always taking MD into account among the differential diagnoses when we care for patients with vertigo, dizziness, instability or fluctuating drive, especially if these are accompanied by hearing symptoms or loss of cochlear function. Another interesting point to highlight is the importance of carrying out an adequate vestibulo-spinal and oculomotor physical examination. In our series, we found, as previously mentioned, a high rate of patients with altered physical examination in the intercritical period, which leads us to think, first, that it is more frequent than reported, and once again, it emphasizes the importance of a correct physical examination for the diagnosis of neurootological pathologies. On the other hand, with the exception that in our case the physical examination was carried out by experts, this also appears strong enough in the univariate logistic regression analysis to predict a poor response to BTH.
The present study supports us, then, with the sufficient strength given by the statistical methods used, to state that in patients who present severe DA secondary to MD, the response to pharmacological treatment with BTH is conditioned, on the one hand, by the duration of symptoms evolution, being the response a very good one in patients who present symptoms of less than a year of evolution, and a very bad one when symptoms have been present for more than three years. On the other hand, another strong predictive factor of a bad response to BTH is the presence of an altered vestibulo-spinal or oculomotor physical examination, although, to be rigorous, we may only sustain this last statement when it is carried out by people with expertise in this matter.
The conclusions we were able to obtain open the door to different questions. Bearing in mind that we have found strong predictors of a poor response to BTH, such as abnormal vestibular physical examination and a disease with an evolution of more than 3 years, is it possible to directly consider treatment with intratympanic gentamicin in those patients who present all these characteristics? In case a treatment with BTH is attempted in these patients, for how long do we apply it before considering it a therapeutic failure? (8, 15). We think that one of the next challenges would be to adapt therapeutic behaviors to these new prognostic factors in order not to unnecessarily waste time, always with the goal of improving our patients’ quality of life.
It would also be necessary to carry out a similar experience with an exhaustive statistical analysis in all the patients with MD in order to determine if the relationships found at the time of controlling the vestibular DA have the same implications for the control of the symptoms and the evolution of the disease, which would expand the number of patients who would possibly benefit from these findings.
References
- Ilmari Pyykko¨a, Nora Pyykko¨b,c and Vinaya Manchaiah, Vestibular drop attacks in Ménière's disease, Journal of Vestibular Research xx (2021).
- Ilmari Pyykko¨a, Nora Pyykko¨b,c and Vinaya Manchaiah, Jing Zou, Hilla Levo and Erna Kentala, Association between Syncope and Tumarkin Atttacks in Ménière´s Disease. J Int Adv Otol. 2019, 15, 135–140.
- Thomas Brandt, Vertigo, Its multisensory Syndrome, Second Edition. Springer 1999.Chapter 5, Ménière's Disease. Pages 83-95.
- Nicholas Senofsky, Justin Faber , Dolores Bozovic, Vestibular Drop Attacks and Meniere's Disease as Results of Otolithic Membrane Damage-A Numerical Model. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 2023, 24, 107–115.
- Mansur A Kutlubaev, Ying Xu, Vinaya Manchaiah, Jing Zou, Ilmari Pyykkö Vestibular drop attacks in Ménière's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of frequency, correlates and consequences. J Vestib Res. 2022, 32, 171–182. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilmari Pyykkö 1, Vinaya Manchaiah 2, Jing Zou 1, Hilla Levo 3, Erna Kentala. Association between Syncope and Tumarkin Attacks in Ménière's Disease. J Int Adv Otol. 2019, 15, 135–140. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- F O Black, M Z Effron, D S Burns. Diagnosis and management of drop attacks of vestibular origin: Tumarkin's otolithic crisis. 1982, 90, 256–262.
- Bo Liu, Yangming Leng, Renhong Zhou, Jingjing Liu, Dongdong Liu, Su-Lin Zhang, Wei-Jia Kong. Intratympanic steroids injection is effective for the treatment of drop attacks with Ménière's disease and delayed endolymphatic hydrops: A retrospective study. 2016, 95, e5767.
- R Gürkov, I Pyykö, J Zou, E Kentala. What is Menière's disease? A contemporary re-evaluation of endolymphatic hydrops. J Neurol. 2016, 263 Suppl. 1, S71–S81. [CrossRef]
- Ilmari Pyykkö, Vinaya Manchaiah, Jing Zou, Hilla Levo, Erna Kentala. Vestibular syncope: A disorder associated with drop attack in Ménière's disease. Auris Nasus Larynx 2018, 45, 234–241. [CrossRef]
- C Morales Angulo, J Gallo-Terán. [Vestibular drop attacks or Tumarkin's otolithic crisis in patients with Meniere's disease]. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 2005, 56, 469–471.
- Yann Lelonge, Alexandre Karkas, Roland Peyron, Pierre Reynard, Philippe Convers, Pierre Bertholon. Clinical Features and Management of Drop Attacks in Menière's Disease. Special Emphasis on the Possible Occurrence of Vertigo After the Drop Attacks. Otol Neurotol 2021, 42, 1269–1274. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- S Rapoport. The management of drop attacks. The management of drop attacks. Dis Mon. 1986, 32, 121–62. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas M Viana, Fayez Bahmad Jr, Steven D Rauch Intratympanic gentamicin as a treatment for drop attacks in patients with Meniere's disease. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 2151–4. [CrossRef]
- Katie E Webster , Kevin Galbraith , Natasha A Harrington-Benton , Owen Judd , Diego Kaski , Otto R Maarsingh, Samuel MacKeith, Jaydip Ray , Vincent A Van Vugt, Martin J Burton. Systemic pharmacological interventions for Ménière's disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023, 2, CD015171.
- TUMARKIN, M. B, THE OTOLITHIC CATASTROPHE A NEW SYNDROME. The British Medical Journal 1936, 57, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- José, A. Lopez-Escamez a,∗, John Carey b, Won-Ho Chung c, Joel A. Goebel d,Måns Magnussone, Marco Mandalàf, David E. Newman-Toker g, Michael Strupp h, Mamoru Suzukii, Franco Trabalzinif y Alexandre Bisdorffj Criterios diagnósticos de enfermedad de Menière. Documento de consenso de la Bárány Society, la Japan Society for Equilibrium Research, la European Academy of Otology and Neurotology (EAONO), la American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS) y la Korean Balance Society. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 2015.
- L. Pérez López, A. Belinchón de Diego, A. Bermell Carrión, H. Pérez Garrigues, C. Morera Pérez. Enfermedad de Ménière y migraña. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 2006, 57, 126–129.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).