Submitted:
08 September 2023
Posted:
12 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Conversion of methane to methanol routes
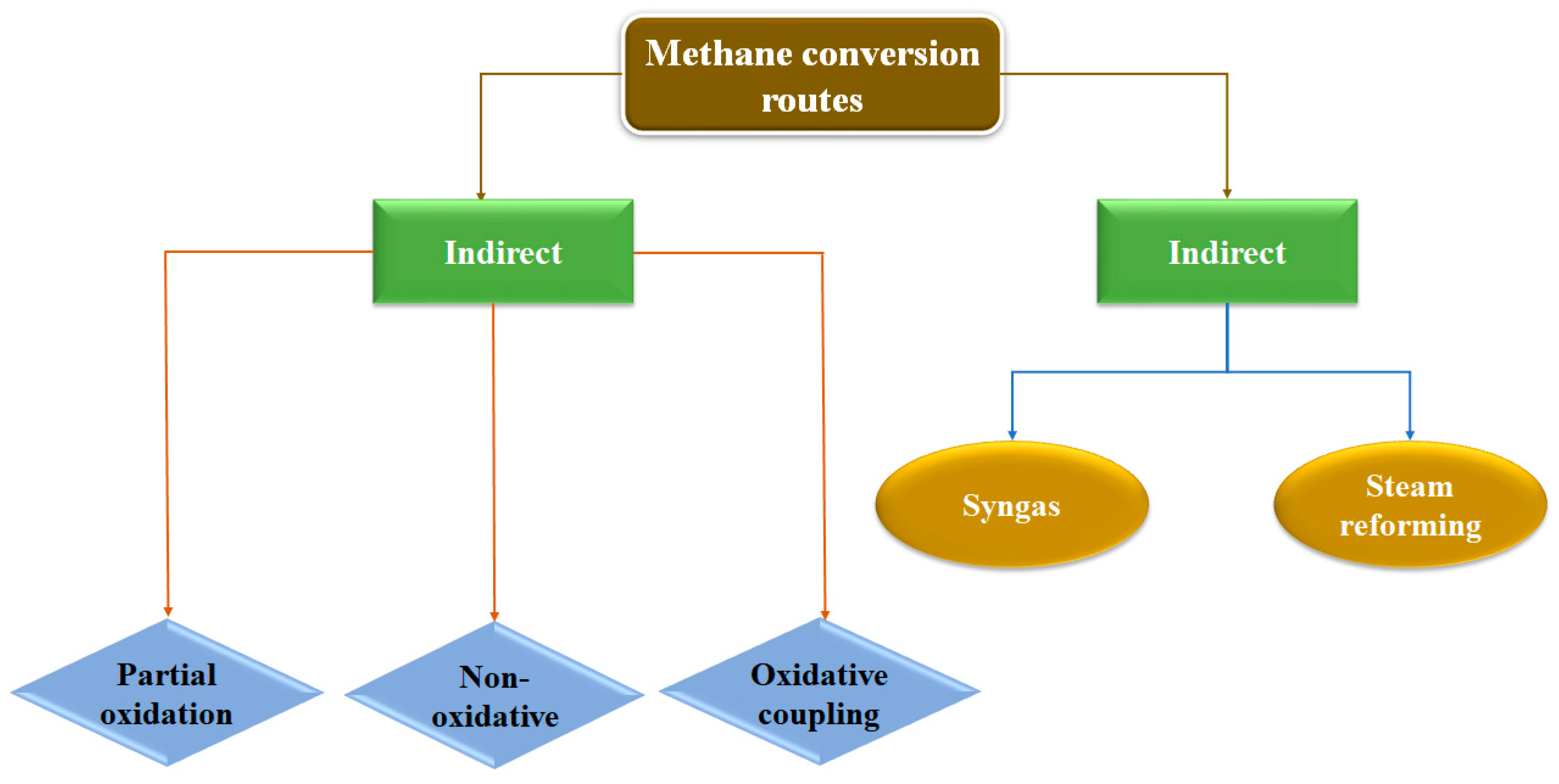
2.1. Direct and indirect routes
2.2. Challenging parameters in methane to methanol catalysis
2.2.1. Activation of C-H bonds and its connection to selectivity
2.2.2. Activation of catalyst
2.2.3. Temperature and pressure
| Catalyst | Reaction time (min) |
Temp. (˚C) |
Pressure (bar) |
Oxidant | Methanol yield (µmol/gcat) |
Selectivity (%) |
Side products |
Ref. |
| ZSM-5 | 60 | 600-700 | 0.01 | O2 | - | 10 | CH2O CO2 O2 |
[36] |
| FeHZSM-5 | 2.5 s (Contact time) |
630 | atmosphere | O2 | - | 16.51 | CO 2 HCHO |
[37] |
| FeNaZSM-5 | 0.5 s (Contact time) |
390 | atmosphere | O2 | - | 74.37 | CO 2 HCHO |
[37] |
| FeZSM-5 | 8-165 | 160 | 0.1 | N2O | 160 34 |
76 95 |
C2H5OH C2H4O |
[38] |
| Fe-ZSM-5 (84) | 30 | 50 | 30.5 | H2O2 | 74.4 | 10 | HCOOH CH3OOH |
[42] |
| ZSM-5 (86) | 30 | 50 | 30.5 | H2O2 | 5.55 | 72 | HCOOH CH3OOH |
[42] |
| Fe-silicalite-1 (86) | 30 | 50 | 30.5 | H2O2 | 65.18 | 19 | HCOOH CH3OOH |
[42] |
| Fe-Cu-ZSM-5 (30) | Steady state = 60 min | 50 | 20 | H2O2 | 81 (µmol gcat-1 h-1) |
92.2 | CO 2 | [40] |
| Cu-SSZ-13 | 60 | 200 | 0.3 | N2O | 13.1 | 24 | CO 2 HCHO |
[58] |
| Cu-MOR | 30 | 200 | 36 | O2 | 56 | 100 | - | [52] |
| Cu-MOR | 30 | 200 | 7 | H2O | 0.204 mol/molCu |
97 | H2O H2 |
[25] |
| Cu-ZSM-5-Cl | 30 | 50 | 30 | H2O2 H2O |
5866 | 79.93 | CH3OOH HOCH2OOH |
[59] |
| Cu-ZSM-5-N | 30 | 50 | 30 | H2O2 H2O |
3216 | 73.31 | CH3OOH HOCH2OOH |
[59] |
| Cu-ZSM-5-Ac | 30 | 50 | 30 | H2O2 H2O |
2851 | 74.78 | CH3OOH HOCH2OOH |
[59] |
| Cu-Fe(2/0.1)/ZSM-5 | 30 | 50 | 30 | H2O2 | 431mol/molFe | 80 | HOCH2OOH CH3OOHCO 2 |
[46] |
3. Traditional catalysts
4. Nanoparticles-based novel catalysts
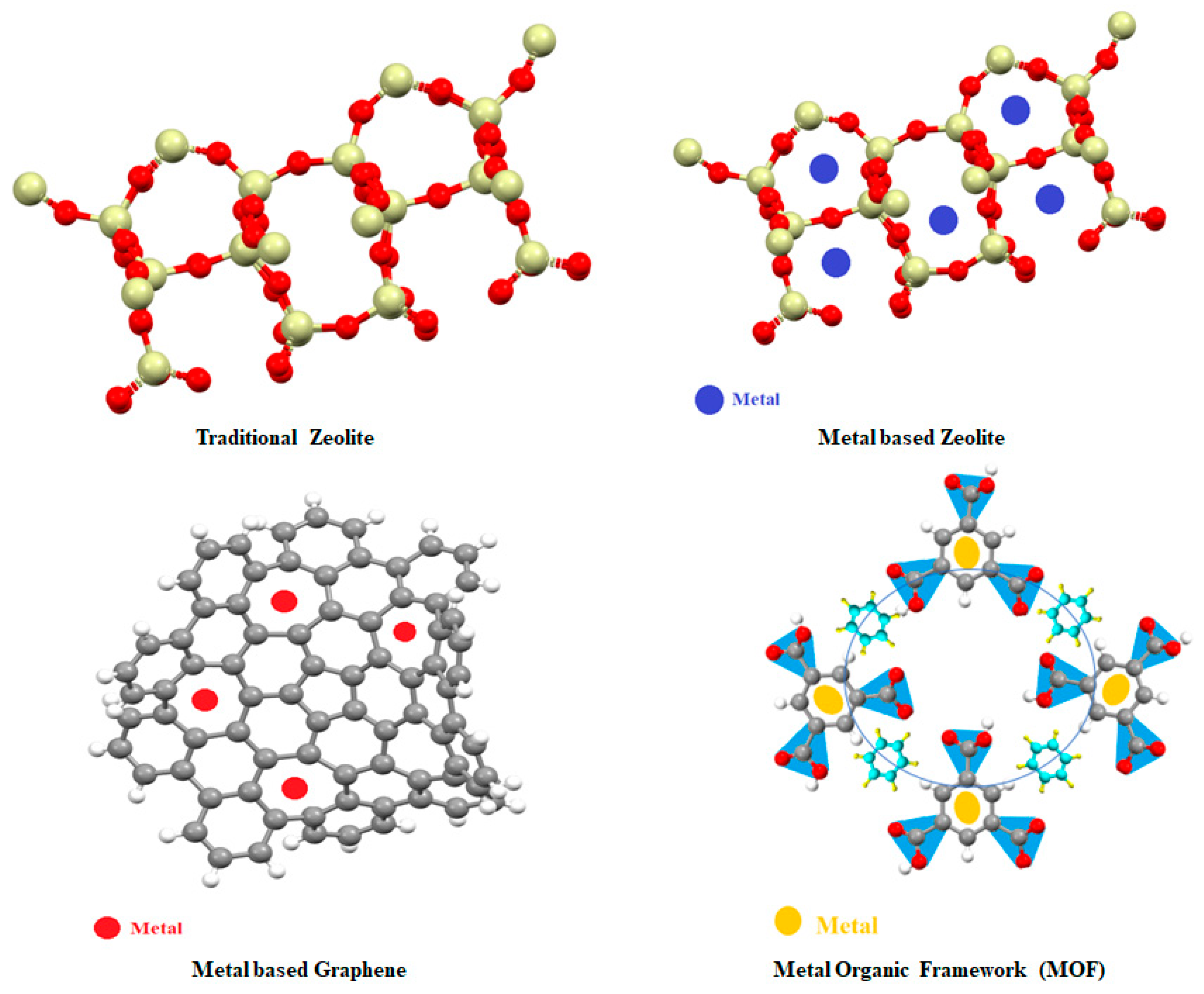
4.1. Nanomaterials used with zeolite
4.2. Graphene-based catalysts
4.3. Nanomaterials used with MOFs
4.3.1. General characteristics
4.3.2. Potentials and limitations
| Catalyst | Reaction time (min) |
Temp. (˚C) |
Pressure (bar) |
Oxidant | Methanol yield (µmol/gcat) |
Methanol selectivity(%) |
Side products |
Ref |
| Rh-ZSM-5 | 60 | 150 | 30 | O2 | 1224 | 8.78 | CH3COOH HCOOH |
[65] |
| 1%Pd/HZS-5 (30) | 30 | 50 | 30.5 | H2O2 | 51.1 | 33.6 | CH3OOH HCOOHCO2 |
[66] |
| MIL-53 (Fe, Al) | 60 | ≤60 | 30.5 | H2O2 | - | - | CH3OOH CH2O 2 CO2 |
[126] |
| CuxOy@UiO-bpy | 180 | 200 | 1 | O2 | 24 | 88.1 | C2H5OH | [127] |
| Uio-67-Pt-Z | 120 | 60 | 50 | H2O2 | - | 12.4 | C2H5OH CH3COOH |
[128] |
| MOF derived IrO2/CuO | 180 | 150 | 3 | H2O | 872 | 95 | C2H5OH CH3COOH |
[129] |
| AuPd@ZIF-8 | 30 | 90 | 15 | H2O2/O2 | 10.85 | 21.9 | CH3OOH HCOOH |
[130] |
| Au@ZIF-8 | 30 | 90 | 15 | H2O2/O2 | 0.7 | - | CH3OOH HCOOH |
[130] |
| Pd@ZIF-8 | 30 | 90 | 15 | H2O2/O2 | 1.2 | - | CH3OOH HCOOH |
[130] |
| MOF-808-His-Cu | 60 | 150 | - | N2O | 31.7 | 100 | - | [10] |
| MOF-808-Iza-Cu | 60 | 150 | - | N2O | 61.8 | 100 | - | [10] |
| MOF-808-Bzz-Cu | 60 | 150 | - | N2O | 71.8 | 100 | - | [10] |
| CU-NU-1000 | 30-180 | 150-200 | 1-40 | O2 | 1.5 -15.81 | 70-90 | C2H5OH CO2 |
[131] |
| CU-NU-1000 | 180 | 200 | 1 | O2 | 17.7 | ≤46 | C2H5OH CO2 |
[132] |
| MIL-100(Fe) | 120 | 200 | 0.015 | N2O | 0.2 | ≥98 | CO2 | [133] |
| Fe-ZSM-5@ZIF-8 | 300 | 150 | 1 | - | 0.12 | - | - | [134] |
5. Stability and reusability of catalysts
6. Reactors used for methane to methanol catalysis
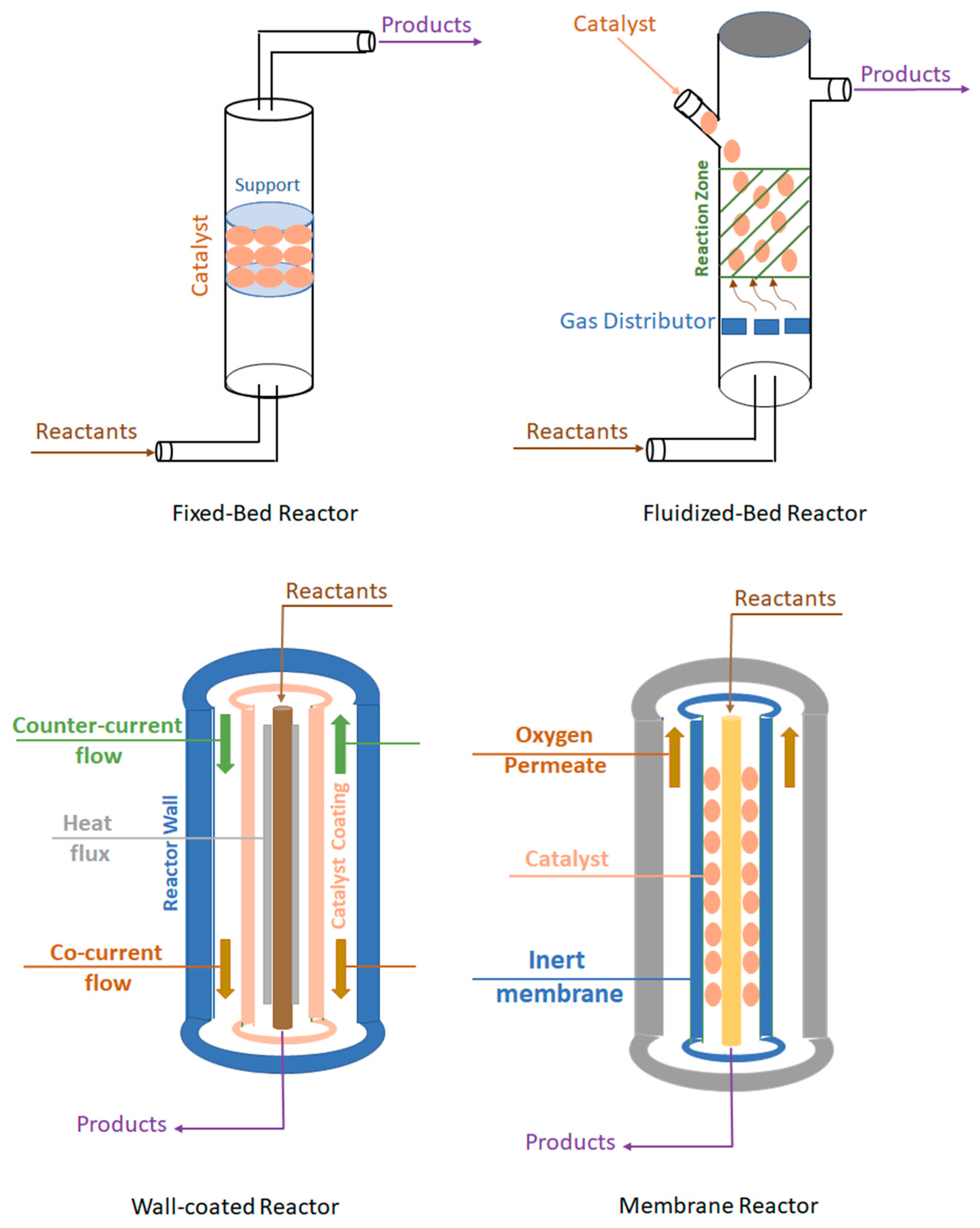
6.1. Fixed-bed reactor
6.2. Fluidized-bed reactor
6.3. Wall-coated reactors
6.3.1. Tubular reactor type
6.3.2. Monolithic reactor type
6.3.3. Plate-type reactor type
6.3.4. Microchannel plate type reactor
6.4. Membrane reactor
7. Conclusions
Author credit statement
Acknowledgments
References
- Karl, T.R.; Trenberth, K.E. Modern Global Climate Change. Science 2003, 302, 1719–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradforf MCJ, Vannice MA. CO2 Reforming of CH4. Catal Rev 1999, 41, 1–42. [CrossRef]
- Bitter JH, Seshan K, Lercher JA. Mono and Bifunctional Pathways of CO2/CH4 Reforming over Pt and Rh Based Catalysts. J Catal 1998, 176, 93–101. [CrossRef]
- Pakhare, D.; Spivey, J. A review of dry (CO2) reforming of methane over noble metal catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7813–7837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arutyunov, V. Low-scale direct methane to methanol – Modern status and future prospects. Catal. Today 2013, 215, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Guo, Y. Nanostructured perovskite oxides as promising substitutes of noble metals catalysts for catalytic combustion of methane. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 29, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihlar, J.; Vrba, R.; Castkova, K. Effect of transition metal on stability and activity of La-Ca-M-(Al)-O (M = Co, Cr, Fe and Mn) perovskite oxides during partial oxidation of methane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 19920–19934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Chen, W.; Pan, L.; Wang, X.; Dai, X. Tuning the adsorption behaviors and conversions of CHx species on metal embedded graphene surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 390, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckner, M.; Dailly, A. A pilot study of activated carbon and metal–organic frameworks for methane storage. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.; Rungtaweevoranit, B.; Pei, X.; Park, M.; Fakra, S.C.; Liu, Y.-S.; Matheu, R.; Alshmimri, S.A.; Alshehri, S.; Trickett, C.A.; et al. Bioinspired Metal–Organic Framework Catalysts for Selective Methane Oxidation to Methanol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 18208–18216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aseem, A.; Jeba, G.G.; Conato, M.T.; Rimer, J.D.; Harold, M.P. Oxidative coupling of methane over mixed metal oxide catalysts: Steady state multiplicity and catalyst durability. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, R.; Jamshidi, E.; Zhang, G. Transformation of methane to synthesis gas over metal oxides without using catalyst. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2009, 18, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Higashimoto, S.; Takahashi, S.; Nagai, Y.; Anpo, M. Selective photooxidation of methane into methanol by nitric oxide over V-MCM-41 mesoporous molecular sieves. Catal. Lett. 2005, 100, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliaguine, S.; Shelimov, B.; Kazansky, V. Reactions of methane and ethane with hole centers O$minus; J. Catal. 1978, 55, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.D.; Brazdil, J.F.; Mehandru, S.P.; Anderson, A.B. Methane photoactivation on copper molybdate: an experimental and theoretical study. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 6515–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Jin, R.; Li, A.; Bi, Y.; Ruan, Q.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S.; Sankar, G.; Ma, D.; et al. Highly selective oxidation of methane to methanol at ambient conditions by titanium dioxide-supported iron species. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlquist, M.; Nielsen, R.J.; Periana, R.A.; Iii, W.A.G. Product Protection, the Key to Developing High Performance Methane Selective Oxidation Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17110–17115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Wang, Y. Direct conversion of methane into oxygenates. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2001, 222, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirajuddin, S.; Rosenzweig, A.C. Enzymatic Oxidation of Methane. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 2283–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.J.; Luque, R.; Budarin, V.L.; Clark, J.H.; Macquarrie, D.J. Supported metal nanoparticles on porous materials. Methods and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 38, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Wu, Z.; Zones, S.I.; Iglesia, E. Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of Metal Clusters Encapsulated within Small-Pore (SOD, GIS, ANA) Zeolites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17688–17695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.-L.; Xu, Q. Immobilization of Ultrafine Metal Nanoparticles to High-Surface-Area Materials and Their Catalytic Applications. Chem 2016, 1, 220–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomkins, P.; Ranocchiari, M.; van Bokhoven, J.A. Direct Conversion of Methane to Methanol under Mild Conditions over Cu-Zeolites and beyond. Accounts Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, C.; Forde, M.M.; Ab Rahim, M.H.; Thetford, A.; He, Q.; Jenkins, R.L.; Dimitratos, N.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.A.; Dummer, N.F.; Murphy, D.M.; et al. Direct Catalytic Conversion of Methane to Methanol in an Aqueous Medium by using Copper-Promoted Fe-ZSM-5. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5129–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sushkevich, V.L.; Palagin, D.; Ranocchiari, M.; Van Bokhoven, J.A. Selective anaerobic oxidation of methane enables direct synthesis of methanol. Science 2017, 356, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Wang, L.; Zuidema, E.; Mondal, K.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Meng, X.; Yang, H.; Mesters, C.; et al. Hydrophobic zeolite modification for in situ peroxide formation in methane oxidation to methanol. Science 2020, 367, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawdhury, P.; Bhargavi, K.V.S.S.; Subrahmanyam, C. A single-stage partial oxidation of methane to methanol: a step forward in the synthesis of oxygenates. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2021, 5, 3351–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogukkanli S, Moteki T, Ogura M. Selective methanol formation via CO-assisted direct partial oxidation of methane over copper-containing CHA-type zeolites prepared by one-pot synthesis. Green Chem 2021, 23, 2148–2154. [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Luo, J.; Li, H.; Ren, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, A.; Li, W.-X.; Zeng, J. Water enables mild oxidation of methane to methanol on gold single-atom catalysts. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, D.; Bao, X. Catalysis for Selected C1 Chemistry. Chem 2020, 6, 2497–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikbal, S.A.; Colomban, C.; Zhang, D.; Delecluse, M.; Brotin, T.; Dufaud, V.; Dutasta, J.-P.; Sorokin, A.B.; Martinez, A. Bioinspired Oxidation of Methane in the Confined Spaces of Molecular Cages. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 7220–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, K.T.; Sullivan, M.M.; Serna, P.; Meyer, R.J.; Dincă, M.; Román-Leshkov, Y. Viewpoint on the Partial Oxidation of Methane to Methanol Using Cu- and Fe-Exchanged Zeolites. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 8306–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunsalus, N.J.; Koppaka, A.; Park, S.H.; Bischof, S.M.; Hashiguchi, B.G.; Periana, R.A. Homogeneous Functionalization of Methane. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8521–8573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marenich, A.V.; Jerome, S.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Charge Model 5: An Extension of Hirshfeld Population Analysis for the Accurate Description of Molecular Interactions in Gaseous and Condensed Phases. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latimer AA, Kakekhani A, Kulkarni AR, Nørskov JK. Direct Methane to Methanol, The Selectivity-Conversion Limit and Design Strategies. ACS Catal 2018, 8, 6894–6907.
- Kudo, H.; Ono, T. Partial oxidation of CH4 over ZSM-5 catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1997, 121-122, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalkiewicz, B. Partial oxidation of methane to formaldehyde and methanol using molecular oxygen over Fe-ZSM-5. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2004, 277, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starokon, E.V.; Parfenov, M.V.; Arzumanov, S.S.; Pirutko, L.V.; Stepanov, A.G.; Panov, G.I. Oxidation of methane to methanol on the surface of FeZSM-5 zeolite. J. Catal. 2013, 300, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenov, M.V.; Starokon, E.V.; Pirutko, L.V.; Panov, G.I. Quasicatalytic and catalytic oxidation of methane to methanol by nitrous oxide over FeZSM-5 zeolite. J. Catal. 2014, 318, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Armstrong, R.D.; Shaw, G.; Dummer, N.F.; Freakley, S.J.; Taylor, S.H.; Hutchings, G.J. Continuous selective oxidation of methane to methanol over Cu- and Fe-modified ZSM-5 catalysts in a flow reactor. Catal. Today 2015, 270, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starokon, E.V.; Parfenov, M.V.; Pirutko, L.V.; Abornev, S.I.; Panov, G.I. Room-Temperature Oxidation of Methane by α-Oxygen and Extraction of Products from the FeZSM-5 Surface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 2155–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, C.; Dimitratos, N.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.A.; Jenkins, R.L.; Whiting, G.; Kondrat, S.A.; ab Rahim, M.H.; Forde, M.M.; Thetford, A.; Hagen, H.; et al. Aqueous-Phase Methane Oxidation over Fe-MFI Zeolites; Promotion through Isomorphous Framework Substitution. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Wang, Y.; Nishitoba, T.; Kondo, J.N.; Yokoi, T. Selective oxidation of methane to methanol with H2O2 over an Fe-MFI zeolite catalyst using sulfolane solvent. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 2896–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang J, Park ED. Selective oxidation of methane over Fe-Zeolites by In situ generated H2O2. Catal 2020, 10, 299.
- Fang, Z.; Murayama, H.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, B.; Jiang, F.; Xu, Y.; Tokunaga, M.; Liu, X. Selective mild oxidation of methane to methanol or formic acid on Fe–MOR catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 6946–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Li, Z.; Lin, L.; Chu, S.; Su, Y.; Song, W.; Wang, A.; Weckhuysen, B.M.; Luo, W. Highly Selective Oxidation of Methane into Methanol over Cu-Promoted Monomeric Fe/ZSM-5. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 6684–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Lee, I.; Khare, R.; Jentys, A.; Fulton, J.L.; Sanchez-Sanchez, M.; Lercher, J.A. Speciation of Cu-Oxo Clusters in Ferrierite for Selective Oxidation of Methane to Methanol. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 4355–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koishybay, A.; Shantz, D.F. Water Is the Oxygen Source for Methanol Produced in Partial Oxidation of Methane in a Flow Reactor over Cu-SSZ-13. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 11962–11966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.R.; Jung, H.; Kang, J.; Han, J.W.; Park, E.D. Continuous Synthesis of Methanol from Methane and Steam over Copper-Mordenite. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le H, v. Le H v., Parishan S, Sagaltchik A, Ahi H, Trunschke A, Schomäcker R, et al. Stepwise Methane-to-Methanol Conversion on CuO/SBA-15. Chem Eur J 2018, 24, 12592–12599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, J.; Hirayama, A.; Tsuchimura, Y.; Kondou, N.; Yoshida, H.; Machida, M.; Nishimura, S.; Kato, K.; Miyazato, I.; Takahashi, K. Catalytic direct oxidation of methane to methanol by redox of copper mordenite. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 3437–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomkins, P.; Mansouri, A.; Bozbag, S.E.; Krumeich, F.; Park, M.B.; Alayon, E.M.C.; Ranocchiari, M.; van Bokhoven, J.A. Isothermal Cyclic Conversion of Methane into Methanol over Copper-Exchanged Zeolite at Low Temperature. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5467–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, M.; Marín, P.; Ordóñez, S. Harnessing of Diluted Methane Emissions by Direct Partial Oxidation of Methane to Methanol over Cu/Mordenite. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 9409–9417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knorpp, A.J.; Pinar, A.B.; Newton, M.A.; Sushkevich, V.L.; van Bokhoven, J.A. Copper-Exchanged Omega (MAZ) Zeolite: Copper-concentration Dependent Active Sites and its Unprecedented Methane to Methanol Conversion. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 5593–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knorpp, A.J.; Newton, M.A.; Pinar, A.B.; van Bokhoven, J.A. Conversion of Methane to Methanol on Copper Mordenite: Redox Mechanism of Isothermal and High-Temperature-Activation Procedures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 12036–12039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, K.T.; Sullivan, M.M.; Narsimhan, K.; Serna, P.; Meyer, R.J.; Dincă, M.; Román-Leshkov, Y. Continuous Partial Oxidation of Methane to Methanol Catalyzed by Diffusion-Paired Copper Dimers in Copper-Exchanged Zeolites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 11641–11650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Sushkevich, V.L.; Knorpp, A.J.; Newton, M.A.; Mizuno, S.C.M.; Wakihara, T.; Okubo, T.; Liu, Z.; van Bokhoven, J.A. Cu-Erionite Zeolite Achieves High Yield in Direct Oxidation of Methane to Methanol by Isothermal Chemical Looping. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 1448–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipek, B.; Lobo, R.F. Catalytic conversion of methane to methanol on Cu-SSZ-13 using N2O as oxidant. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 13401–13404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Huang, M.; Liu, B.; Jiang, F.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X. Identifying the crucial role of water and chloride for efficient mild oxidation of methane to methanol over a [Cu2(μ-O)]2+-ZSM-5 catalyst. J. Catal. 2021, 405, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Li, J.; Zhang, T. Heterogeneous single-atom catalysis. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenya, BR. Synthesis and catalytic properties of metal nanoparticles, Size, shape, support, composition, and oxidation state effects. Thin Solid Films 2010, 581, 3127–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ji, S.; Liu, Y.; Cao, X.; Tian, S.; Chen, Y.; Niu, Z.; Li, Y. Well-Defined Materials for Heterogeneous Catalysis: From Nanoparticles to Isolated Single-Atom Sites. Chem. Rev. 2019, 120, 623–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisz, P.B. Molecular Diffusion in Microporous Materials: Formalisms and Mechanisms. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1995, 34, 2692–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Ke, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Chen, J. Encapsulating Palladium Nanoparticles Inside Mesoporous MFI Zeolite Nanocrystals for Shape-Selective Catalysis. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 9324–9328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; Li, M.; Allard, L.F.; Lee, S.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Mild oxidation of methane to methanol or acetic acid on supported isolated rhodium catalysts. Nature 2017, 551, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Bara-Estaun, A.; Agarwal, N.; Freakley, S.J.; Morgan, D.J.; Hutchings, G.J. The Direct Synthesis of H2O2 and Selective Oxidation of Methane to Methanol Using HZSM-5 Supported AuPd Catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 3066–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Xiao, F.-S. Metal@Zeolite Hybrid Materials for Catalysis. ACS Central Sci. 2020, 6, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehling, T.O.; Novoselov, K.S.; Morozov, S.V.; Vdovin, E.E.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Geim, A.K.; Lichtenstein, A.I. Molecular Doping of Graphene. Nano Lett. 2007, 8, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, P.; Hill, E.W.; Neto, A.H.C.; Novoselov, K.S.; Jiang, D.; Yang, R.; Booth, T.J.; Geim, A.K. Making graphene visible. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 063124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, A.; Feng, X.L.; Wang, X.; Zhi, L.J.; Müllen, K.; Koch, N.; Rabe, J.P. Electronic and structural properties of graphene-based transparent and conductive thin film electrodes. Appl. Phys. A 2008, 94, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, A.V.; Muraliganth, T.; Manthiram, A. Rapid, Facile Microwave-Solvothermal Synthesis of Graphene Nanosheets and Their Polyaniline Nanocomposites for Energy Strorage. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 5004–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, E.; Kim, J.; Hosono, E.; Zhou, H.-S.; Kudo, T.; Honma, I. Large Reversible Li Storage of Graphene Nanosheet Families for Use in Rechargeable Lithium Ion Batteries. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2277–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yu, D.; Dai, L.; Chang, D.W.; Baek, J.-B. Polyelectrolyte-Functionalized Graphene as Metal-Free Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6202–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo B, Fang L, Zhang B, Gong JR. Graphene Doping, A Review. Insciences J. 2011, 1, 80–89.
- Wang, D.-W.; Su, D. Heterogeneous nanocarbon materials for oxygen reduction reaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 7, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakou, G.; Boucher, M.B.; Jewell, A.D.; Lewis, E.A.; Lawton, T.J.; Baber, A.E.; Tierney, H.L.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M.; Sykes, E.C.H. Isolated Metal Atom Geometries as a Strategy for Selective Heterogeneous Hydrogenations. Science 2012, 335, 1209–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses-Debusk M, Yoon M, Allard LF, Mullins DR, Wu Z, Yang X, et al. CO oxidation on supported single Pt atoms, Experimental and ab initio density functional studies of CO interaction with Pt atom on θ-Al2O3 surface. J Am Chem Soc 2013, 135, 12634–12645. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-G.; Wen, M.; Wu, Q.-S.; Fang, H. Ni/graphene Nanostructure and Its Electron-Enhanced Catalytic Action for Hydrogenation Reaction of Nitrophenol. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 6307–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.J.G.; Ayuela, A.; Fagan, S.B.; Filho, J.M.; Azevedo, D.L.; Filho, A.G.S.; Sánchez-Portal, D. Switching on magnetism in Ni-doped graphene: Density functional calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 195420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, J.-M.; Xu, K.-W.; Ji, V. A first-principles study on gas sensing properties of graphene and Pd-doped graphene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 343, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, G.; Gauquelin, N.; Chen, N.; Zhou, J.; Yang, S.; Chen, W.; Meng, X.; Geng, D.; Banis, M.N.; et al. Single-atom Catalysis Using Pt/Graphene Achieved through Atomic Layer Deposition. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1775–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, G.; Chen, W.; Chen, Z. CO Catalytic Oxidation on Iron-Embedded Graphene: Computational Quest for Low-Cost Nanocatalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 6250–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esrafili, M.D.; Saeidi, N.; Nematollahi, P. Si-doped graphene: A promising metal-free catalyst for oxidation of SO2. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2016, 649, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, X.-C.; Liu, Y.-J.; Zhao, J.-X.; Cai, Q.-H.; Wang, X.-Z. Can Si-doped graphene activate or dissociate O2 molecule? J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2013, 39, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wei, Z.; Gou, X.; Xu, W. Phosphorus-doped graphene nanosheets as efficient metal-free oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 9978–9984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; He, K.; Robertson, A.W.; Kirkland, A.I.; Kim, D.; Ihm, J.; Yoon, E.; Lee, G.-D.; Warner, J.H. Atomic Structure and Dynamics of Metal Dopant Pairs in Graphene. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 3766–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usachov D, Vilkov O, Grüneis A, Haberer D, Fedorov A, Adamchuk VK, et al. Nitrogen-doped graphene, Efficient growth, structure, and electronic properties. Nano Lett 2011, 11, 5401–5407. [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L.; Yu, G. Synthesis of N-Doped Graphene by Chemical Vapor Deposition and Its Electrical Properties. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattel, S.; Atanassov, P.; Kiefer, B. Stability, Electronic and Magnetic Properties of In-Plane Defects in Graphene: A First-Principles Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 8161–8166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.J.; Kim, H.S.; Baik, S.Y.; Myung, Y.; Jung, C.S.; Kim, C.H.; Park, J.; Kang, H.S. Selective Nitrogen-Doping Structure of Nanosize Graphitic Layers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 3737–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L. Conversion of Methane to Methanol on Cobalt-Embedded Graphene: A Theoretical Perspective. Catal. Lett. 2021, 152, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impeng, S.; Khongpracha, P.; Warakulwit, C.; Jansang, B.; Sirijaraensre, J.; Ehara, M.; Limtrakul, J. Direct oxidation of methane to methanol on Fe–O modified graphene. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 12572–12578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impeng S, Khongpracha P, Sirijaraensre J, Jansang B, Ehara M, Limtrakul J. Methane activation on Fe- and FeO-embedded graphene and boron nitride sheet, Role of atomic defects in catalytic activities. RSC Adv 2015, 5, 97918–97927. [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Suib, S.L.; Alpay, S.P. Graphene Supported Single Atom Transition Metal Catalysts for Methane Activation. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 3229–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, J. A high performance catalyst for methane conversion to methanol: graphene supported single atom Co. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 2284–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Liu, C.-Y.; Sun, Y.-C. Effective methane conversion to methanol on bi-functional graphene-oxide-supported platinum nanoclusters (Pt5) – a DFT study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 4967–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Hua, L.; Li, H.; Han, X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, F.; He, L.; et al. Room-Temperature Methane Conversion by Graphene-Confined Single Iron Atoms. Chem 2018, 4, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Luan, C.; Fang, Y.; Feng, X.; Peng, X.; Yang, G.; Tsubaki, N. Low-temperature direct conversion of methane to methanol over carbon materials supported Pd-Au nanoparticles. Catal. Today 2019, 339, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deria, P.; Mondloch, J.E.; Karagiaridi, O.; Bury, W.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. ChemInform Abstract: Beyond Post-Synthesis Modification: Evolution of Metal-Organic Frameworks via Building Block Replacement. ChemInform 2014, 45, no. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, N.; Biswas, S. Synthesis of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs): Routes to Various MOF Topologies, Morphologies, and Composites. Chem. Rev. 2011, 112, 933–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, R.J.; Forgan, R.S. Postsynthetic Modification of Zirconium Metal-Organic Frameworks. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 2016, 4310–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, S.M.J.; Bavykina, A.; Hajek, J.; Garcia, H.; Olivos-Suarez, A.I.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A.; Vimont, A.; Clet, G.; Bazin, P.; Kapteijn, F.; et al. Metal–organic and covalent organic frameworks as single-site catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3134–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranchemontagne DJ, Tranchemontagne JL, O’keeffe M, Yaghi OM. Secondary building units, nets and bonding in the chemistry of metal–organic frameworks. Chem Soc Rev 2009, 38, 1257–1283. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai Y, Dou Y, Xie LH, Rutledge W, Li JR, Zhou HC. Zr-based metal-organic frameworks, Design, synthesis, structure, and applications. Chem Soc Rev 2016, 45, 2327–2367. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Wei, Z.; Gu, Z.-Y.; Liu, T.-F.; Park, J.; Park, J.; Tian, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Iii, T.G.; et al. Tuning the structure and function of metal–organic frameworks via linker design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5561–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoedel, A.; Li, M.; Li, D.; O’keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Structures of Metal–Organic Frameworks with Rod Secondary Building Units. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12466–12535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheetham, A.K.; Bennett, T.D.; Coudert, F.-X.; Goodwin, A.L. Defects and disorder in metal organic frameworks. Dalton Trans. 2015, 45, 4113–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholl DS, Lively RP. Defects in Metal-Organic Frameworks, Challenge or Opportunity? J Phys Chem Lett 2015, 6, 3437–3444. [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Bueken, B.; De Vos, D.E.; Fischer, R.A. Defektmanipulierte Metall-organische Gerüste. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 7340–7362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissegna, S.; Epp, K.; Heinz, W.R.; Kieslich, G.; Fischer, R.A. Metal-Organic Frameworks: Defective Metal-Organic Frameworks (Adv. Mater. 37/2018). Adv. Mater. 2018, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtch, N.C.; Jasuja, H.; Walton, K.S. Water Stability and Adsorption in Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10575–10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Demir, N.K.; Chen, J.P.; Li, K. Applications of water stable metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5107–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva P, Vilela SMF, Tomé JPC, Almeida Paz FA. Multifunctional metal-organic frameworks, From academia to industrial applications. Chem Soc Rev 2015, 44, 6774–6803. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Martinez, M.; Avci-Camur, C.; Thornton, A.W.; Imaz, I.; Maspoch, D.; Hill, M.R. New synthetic routes towards MOF production at scale. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3453–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Dyosiba, X.; Musyoka, N.M.; Langmi, H.W.; Mathe, M.; Liao, S. Review on the current practices and efforts towards pilot-scale production of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Co-ord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 352, 187–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chrzanowski, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, S. Applications of metal-organic frameworks featuring multi-functional sites. Co-ord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 307, 106–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang YB, Liang J, Wang XS, Cao R. Multifunctional metal-organic framework catalysts, Synergistic catalysis and tandem reactions. Chem Soc Rev 2017, 46, 126–157. [CrossRef]
- Herbst A, Janiak C. MOF catalysts in biomass upgrading towards value-addedfine chemicals. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 4092–4117. [CrossRef]
- Trickett CA, Helal A, Al-Maythalony BA, Yamani ZH, Cordova KE, Yaghi OM. The chemistry of metal-organic frameworks for CO2 capture, regeneration and conversion. Nat Rev Mater 2017, 2, 17045. [CrossRef]
- Maina, J.W.; Pozo-Gonzalo, C.; Kong, L.; Schütz, J.; Hill, M.; Dumée, L.F. Metal organic framework based catalysts for CO2 conversion. Mater. Horizons 2017, 4, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K.E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. The Chemistry and Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 1230444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; García, H.; Xamena, F.X.L. Engineering Metal Organic Frameworks for Heterogeneous Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4606–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee J, Farha OK, Roberts JM, Scheidt KA, Nguyen ST, Hupp JT. Metal – organic framework materials as catalysts. Chem Soc Rev 2009, 38, 1450–1459. [CrossRef]
- Farrusseng, D.; Aguado, S.; Pinel, C. Metal-Organic Frameworks: Opportunities for Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7502–7513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang Q, Xu Q, Jiang HL. Metal-organic frameworks meet metal nanoparticles, Synergistic effect for enhanced catalysis. Chem Soc Rev 2017, 46, 4774–4808. [CrossRef]
- Osadchii, D.Y.; Olivos-Suarez, A.I.; Szécsényi, A.; Li, G.; Nasalevich, M.A.; Dugulan, I.A.; Crespo, P.S.; Hensen, E.J.M.; Veber, S.L.; Fedin, M.V.; et al. Isolated Fe Sites in Metal Organic Frameworks Catalyze the Direct Conversion of Methane to Methanol. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 5542–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren M, Shi Q, Mi L, Liang W, Yuan M, Wang L, et al. Isothermal conversion of methane to methanol over CuxOy@UiO-bpy. Mater Today Sustain 2021, 11–12, 100061.
- Xia, M.; Qiu, L.; Li, Y.; Shen, T.; Sui, Z.; Feng, L.; Chen, Q. A metal-organic frameworks composite catalyst containing platinum and polyoxometalate for direct conversion of methane. Mater. Lett. 2021, 307, 131078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang L, Huang J, Ma R, You R, Zeng H, Rui Z. Metal-Organic Framework-Derived IrO2/CuO Catalyst for Selective Oxidation of Methane to Methanol. ACS Energy Lett 2019, 4, 2945–2951. [CrossRef]
- Xu G, Yu A, Xu Y, Sun C. Selective oxidation of methane to methanol using AuPd@ZIF-8. Catal Commun 2021, 158, 106338. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Ye, J.; Ortuño, M.A.; Fulton, J.L.; Gutiérrez, O.Y.; Camaioni, D.M.; Motkuri, R.K.; Li, Z.; Webber, T.E.; Mehdi, B.L.; et al. Selective Methane Oxidation to Methanol on Cu-Oxo Dimers Stabilized by Zirconia Nodes of an NU-1000 Metal–Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 9292–9304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuno, T.; Zheng, J.; Vjunov, A.; Sanchez-Sanchez, M.; Ortuño, M.A.; Pahls, D.R.; Fulton, J.L.; Camaioni, D.M.; Li, Z.; Ray, D.; et al. Methane Oxidation to Methanol Catalyzed by Cu-Oxo Clusters Stabilized in NU-1000 Metal–Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 10294–10301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall JN, Bollini P. Low-Temperature, Ambient Pressure Oxidation of Methane to Methanol Over Every Tri-Iron Node in a Metal–Organic Framework Material. Chem Eur J 2020, 26, 16639–16643. [CrossRef]
- Imyen, T.; Znoutine, E.; Suttipat, D.; Iadrat, P.; Kidkhunthod, P.; Bureekaew, S.; Wattanakit, C. Methane Utilization to Methanol by a Hybrid Zeolite@Metal–Organic Framework. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 23812–23821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, Z.; Kamarudin, S. Direct conversion technologies of methane to methanol: An overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 65, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Smet, C.; de Croon, M.; Berger, R.; Marin, G.; Schouten, J. Design of adiabatic fixed-bed reactors for the partial oxidation of methane to synthesis gas. Application to production of methanol and hydrogen-for-fuel-cells. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 4849–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Fan, Y.; Bellettre, J.; Yue, J.; Luo, L. A review on catalytic methane combustion at low temperatures: Catalysts, mechanisms, reaction conditions and reactor designs. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 119, 109589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosiewski, K.; Pawlaczyk, A.; Jaschik, M. Energy recovery from ventilation air methane via reverse-flow reactors. Energy 2015, 92, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhang, L.; Guo, M.; Ran, J. Experiment and modeling of low-concentration methane catalytic combustion in a fluidized bed reactor. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 93, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhang, L.; Guo, M.; Ran, J. Experiment and modeling of low-concentration methane catalytic combustion in a fluidized bed reactor. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 93, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.-S.; Yu, S.-P.; Cho, S.-J.; Song, K.-S. The catalytic heat exchanger using catalytic fin tubes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismagilov, Z.; Pushkarev, V.; Podyacheva, O.; Koryabkina, N.; Veringa, H. A catalytic heat-exchanging tubular reactor for combining of high temperature exothermic and endothermic reactions. Chem. Eng. J. 2001, 82, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender S, Friedrich HB. Monoliths, A review of the basics, preparation methods and their relevance to oxidation. Catalysts 2017, 7, 62. [CrossRef]
- Lyubovsky, M.; Karim, H.; Menacherry, P.; Boorse, S.; LaPierre, R.; Pfefferle, W.C.; Roychoudhury, S. Complete and partial catalytic oxidation of methane over substrates with enhanced transport properties. Catal. Today 2003, 83, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolios, G.; Gritsch, A.; Morillo, A.; Tuttlies, U.; Bernnat, J.; Opferkuch, F.; Eigenberger, G. Heat-integrated reactor concepts for catalytic reforming and automotive exhaust purification. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2007, 70, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Fan, Y.; Luo, L. Multi-channel heat exchanger-reactor using arborescent distributors: A characterization study of fluid distribution, heat exchange performance and exothermic reaction. Energy 2014, 69, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’connell, M.; Kolb, G.; Zapf, R.; Men, Y.; Hessel, V. Bimetallic catalysts for the catalytic combustion of methane using microreactor technology. Catal. Today 2009, 144, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.M.; Ribeiro, M.F.; Fernandes, E.C. Catalytic activity of electrodeposited cobalt oxide films for methane combustion in a micro-channel reactor. Fuel 2018, 232, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Singh, S.; Ganguly, S.; Patwardhan, A.V. Steam reforming of methane and methanol in simulated macro & micro-scale membrane reactors: Selective separation of hydrogen for optimum conversion. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2014, 18, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Zhou, H.; Peng, H.; Jiang, H. Nitrogen Production by Efficiently Removing Oxygen From Air Using a Perovskite Hollow-Fiber Membrane With Porous Catalytic Layer. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, M.A.; Nemitallah, M.A. Design of an ion transport membrane reactor for application in fire tube boilers. Energy 2015, 81, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





