1. Introduction
Many promising unmanned aerial vehicles have an integral layout that combines the fuselage and lift surfaces. The modes of motion of such aircraft are characterized by relatively low flight speeds (small Mach numbers). The requirements for providing high lift and lift-to-drag ratio (aerodynamic quality), as well as a large internal volume, determine the interest in the flow around thick low aspect ratio wings and various methods for controlling their aerodynamic characteristics [
1].
The traditional approach to aerodynamic design requires increasing the aspect ratio of the wing to achieve maximum lift-to-drag ratio and transport efficiency [
2,
3]. The use of an adaptive wing is one of the solutions to improve the takeoff and landing characteristics of an aircraft. Variable airfoil curvature changes the pressure distribution over the wing, providing the ability to control aerodynamic forces and moments. The use of boundary layer suction makes it possible to transform the flow pattern around a thick airfoil from detached to practically non-separated, which leads to an increase in lift and lift-to-drag ratio. In this case, the drag coefficient includes additional resistance due to energy costs (power for air suction).
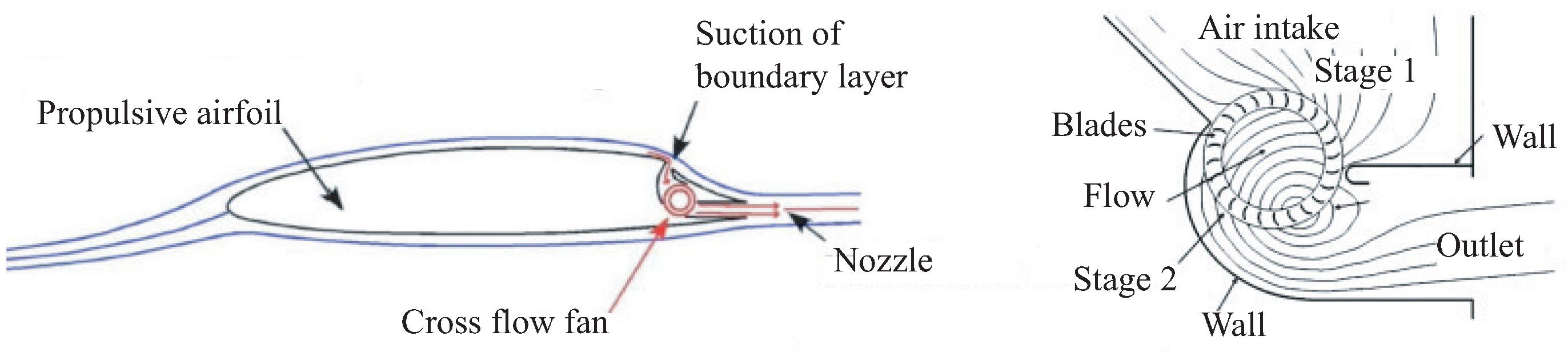
The development of the technology of propulsive (creating thrust) airfoils leads to the creation of new types of shaping of the lift surfaces of an aircraft [
4] (Griffith–Goldschmied airfoil concept). Air bled from the upper surface is expelled through the trailing edge of the wing, creating additional thrust. Due to the suction of air from the upper critical point of the airfoil and its ejection through the trailing edge, the super-circulation of the wing is actively controlled [
5]. In the absence of air extraction, such airfoils are a poorly streamlined body, and with the necessary air flow in the internal channel, the tail section of the airfoil creates thrust. The technical implementation of air extraction is carried out using a transverse (tangential) fan (Cross Flow Fan, CFF) [
6,
7,
8]. Changing the rotation speed of the fan blades prevents separation of the boundary layer [
9].
The design of airfoils and the modification of the contour of existing airfoils to increase their aerodynamic characteristics are considered in many studies. Various types of airfoils have been developed with an internal channel and energy principles for increasing lift and creating thrust by taking air from a critical point on the trailing edge of the wing. In a jet-slotted wing, air is taken from the upper surface of the wing through slots in the middle part of the airfoil and at the trailing edge and blown tangentially onto the upper surface of the wing through a slot at the leading edge. The presence of an internal channel in which air flows in the direction of flight leads to an increase in circulation and wing lift [
10].
In the literature, quite a lot of attention is paid to the control of the flow around airfoils due to the deliberate formation of large-scale vortex structures [
2,
3]. The use of vortex cells makes it possible to change the flow pattern, stabilize the flow, giving it a close to non-separated character, and significantly improve the aerodynamic characteristics [
11]. Vortex cells are curvilinear caverns in the contours of bodies, and to intensify the flow circulating in them, a distributed or concentrated (slotted) suction or boundary movement (rotation of the central body) [
12] is used. Under certain conditions, the flow in the vortex cell (cavity) is unstable [
13], and to increase the efficiency of the vortex cell, boundary layer suction [
14] is used.
Placement of a vortex cell on the surface of a semicircular airfoil with slit suction and ejection into the near wake leads to the reconstruction of the unsteady separation pattern of low-velocity flow around the airfoil [
15]. In this case, the flow separation point shifts to the trailing edge of the airfoil, the lift from ultra-low negative becomes positive, and the drag is halved. The static pressure drops two to three times on the upper surface and doubles on the lower surface, and the level of pressure fluctuations decreases by an order of magnitude. The use of longitudinal slotted cuts provides a restructuring of the flow pattern around the body with a reduction or elimination of separation zones and a significant improvement in the integral characteristics [
16].
Passive (without suction) vortex cells are not effective, since the intensity of the separated flow in them is low, and the effect on the external flow is weak. In practice, the aerodynamic characteristics of the airfoil with passive vortex cells coincide with those of the airfoil without cells. The use of vortex cells generates a number of technological requests in the field of flight dynamics and control, integrated aerodynamic configurations and power plants of aircraft, and design methods.
The propulsion airfoils in the tail section have a section that actually functions as a nozzle contour and creates thrust when air is taken from the surface [
17]. Thrust is created by the engine doing work to take air from the surface and pump it in the channels. As a result, pressure increases on the traction section of the airfoil, which creates additional traction. The key feature of propulsion airfoils is their ability to prevent separation flow, reducing drag, increasing lift and lift-to-drag ratio at acceptable energy costs.
In this study, the problem of creating high-lift airfoils with energy methods for increasing the lift force. is considered. A method of mathematical modelling of the flow around airfoils is developed with the method of solving the inverse problem of aerodynamics for given flow properties, taking into account the laminar-turbulent transition. The accuracy of various turbulence models is compared as applied to the flow around a model airfoil at low Reynolds numbers. The dependence of the lift properties of airfoils on the flow rate of air taken from their surface is studied. Conclusions are drawn about the possibility of using propulsion airfoils in the structures of the wings and fuselages of unmanned aerial vehicles.
2. Choice of airfoil
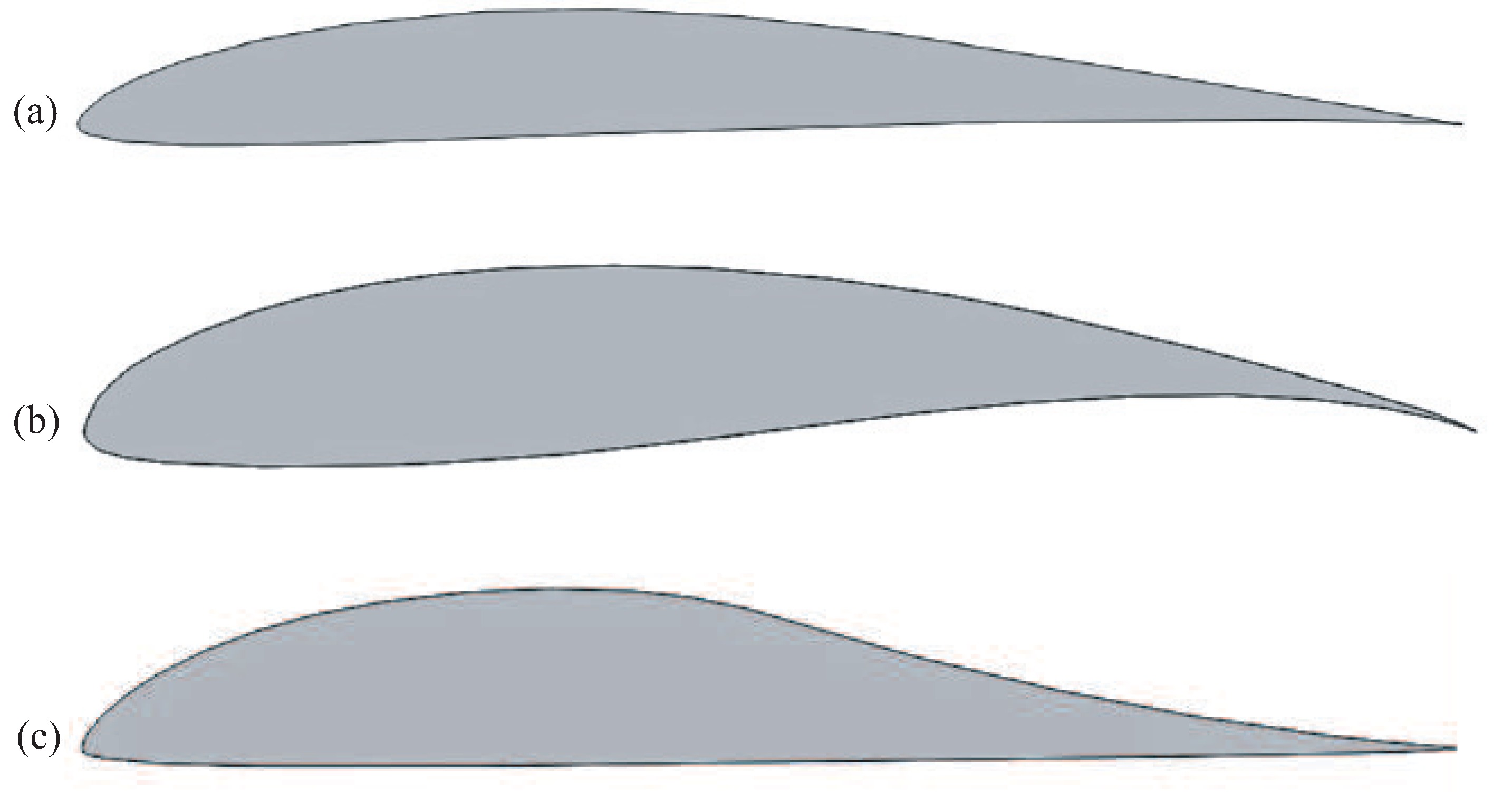
At low Reynolds numbers, the airfoils shown in
Figure 1 find wide practical application. The E387 airfoil with a flat surface adjacent to the trailing edge provides a fairly smooth pressure recovery. airfoils FX63-137 and M06-13-12 have convex and concave surfaces adjacent to the rear except for different aerodynamic characteristics. In contrast to the concave surface, the convex surface of the airfoil makes it possible to provide high (negative) moments and smooth changes in aerodynamic characteristics when the flow is stalled from the rear except for the airfoil. A comparison of the aerodynamic characteristics of the given airfoils is given in [
18] for Reynolds numbers up to
.
The evolution of the ideas of vortex cells (Glauert vortex cell) has led to the concept of a propulsion wing, in which air is taken in by a transverse fan (
Figure 2). The use of traditional axial fans for flow control is not suitable, since axial fans are sensitive to flow unevenness inside the boundary layer and do not work well at high back pressure [
19]. When the pressure drop on the fan is more than 1.15, the efficiency drops sharply, and when air is taken from the airfoil surface, pressure drops of 1.5–2 and higher must be realized. Boundary layer air extraction with CFF ensures laminar flow on the upper surface, which reduces friction drag. The ejection of air taken from the surface through a slotted nozzle eliminates the defect in the velocity airfoil in the wing wake. Increased pressure in the section of the airfoil from the selection slot to the nozzle creates a positive thrust.
The CFF efficiency reaches about 80%, which is less than that of axial fans, but this is compensated by the convenience of the layout, less sensitivity to flow inhomogeneity in the boundary layer and large counter-pressure [
8]. When the boundary layer is blown off, air is taken from the high-pressure area in the lower part of the airfoil, and the CFF plays the role of an energy slat [
20].
3. Simulation of flowfield
One of the stages of the numerical study of the aerodynamic characteristics of advanced aircraft is a comparative analysis of the results obtained with various semi-empirical turbulence models. The accuracy of one or another turbulence model is determined, as a rule, by solving problems with low-intensity turbulent eddy and separated flows [
21].
SST (Shear-Stress Transport) model proposed in [
22] and the Menter model of shear stress transport proposed in [
23] are widely used to model separated flows. The SST model is a generalization of two turbulence models: the
k–
model in the shear flow region far from the wall and the
k–
model in the near-wall region. SST model has significant advantages over the models of the
k–
family (RNG and Realizable versions), Spalart–Allmaras eddy viscosity model (the vorticity model or the modulus of the strain rate tensor is used to calculate the eddy viscosity), and the four-parameter model V2F [
24]. In the range of angles of attack from
to
, the pulsations of the longitudinal force are approximately 30% of the maximum load on the airfoil, and the maximum pulsations of the transverse force at an angle of attack of
are of the same order with the largest transverse force acting on the airfoil.
The flow around the airfoils of such a wing occurs at low Reynolds numbers (
). At such Reynolds numbers, a laminar-turbulent transition may occur in the vicinity of the airfoils, accompanied by flow separation, an abrupt change in the aerodynamic characteristics of the airfoil, and deterioration in flight performance. With the Reynolds number
, the recirculation zone occupies approximately 20–30% of the airfoil length [
25]. Comparison of aerodynamic characteristics of different airfoils is given in [
18,
26]. A catalog of high-carrying airfoils for low flight speeds is constructed in [
26] using the inverse multi-point method of conformal mappings.
One of the problems of airfoil modelling at low Reynolds numbers is the large extent of the laminar boundary layer region [
27]. Many semi-empirical turbulence models are unsuitable for reliable prediction of the transition from laminar flow to turbulent [
28,
29], significantly underestimating the intensity of separated flow due to predicting a false eddy viscosity field. The available empirical models, based on the processing of physical experiment data, relate the critical Reynolds number of the transition to such characteristics of the boundary layer as the pressure gradient and the level of turbulence. The transition occurs in that section of the boundary layer in which the local Reynolds number exceeds the critical value.
When a certain thickness of the boundary layer is reached, instability arises in it and Tollmien–Schlichting waves are formed, the amplitude of which increases according to the exponential dependence
. It is assumed that in the absence of external disturbances, the transition begins at
, and ends at
. The
method is based on the concepts of a two-dimensional boundary layer, which complicates its generalization to three-dimensional problems [
30].
In external flow problems, turbulence models do not allow achieving satisfactory accuracy in a wide range of angles of attack and Reynolds numbers [
31]. There are a number of semi-empirical turbulence models that take into account the possibility of a laminar-turbulent transition [
32]. In particular, the
–
model is based on the use of external empirical correlations to trigger a laminar-turbulent transition at critical values of local near-wall flow quantities [
33,
34]. In addition to the equations of the SST model, the transfer equation for the intermittency parameter and the critical Reynolds number [
35] is used. To close the equations, about ten empirical correlations and a dozen and a half constants are required. The results of numerical simulation of external and internal turbulent separated flows show the advantages of the
–
model over other semi-empirical turbulence models [
32,
36].
4. Mathematical model
The use of special wing airfoils, which make it possible to implement a laminar flow regime in the boundary layer, makes it possible to improve the lift-to-drag ratio. The state of the boundary layer has a significant effect on the accuracy of calculating the friction forces acting on the aerodynamic surface; therefore, the design of laminarized airfoils requires reliable calculation methods that allow one to reliably determine the position of the laminar-turbulent transition.
To solve the problem of a two-dimensional turbulent flow of viscous incompressible fluid around a airfoil, a mathematical model is used based on solving the Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS) equations. The following turbulence models are used to close the RANS: Spalart–Allmaras model (SA), k– SST (SST model) and its various modifications such as -SST and the SST model modified for low Reynolds numbers.
The model includes four differential equations: transport equation for turbulent kinetic energy, transport equation for the specific dissipation rate of turbulent energy, transport equation for intermittency, and transport equation for the Reynolds number corresponding to the onset of the laminar-turbulent transition.
The equations for the kinetic energy of turbulence and the specific rate of its dissipation have the form
Here,
k is kinetic energy of turbulence,
is specific rate of turbulence dissipation. The source terms
and
take into account the generation and dissipation of the kinetic energy of turbulence, and the source terms
and
take into account the generation and dissipation of the specific dissipation rate.
In addition to the equations (
1) and (2), equations are solved for the intermittency parameter
and the Reynolds number
, which is found from the loss thickness momentum, which implies integration across the boundary layer. Additional equations have the form
The source terms
and
take into account the generation and dissipation of the intermittency parameter, and the source term
is the generation of the Reynolds number.
The transport equations for
k and
are almost identical to the corresponding equations for the
k–
SST model written as (
1) and (2), except for the representation source terms
and
and the mixing function
, which are modified to take into account the intermittency of the medium.
The source term
in the equation (
1), which takes into account the generation of kinetic energy of turbulence, is replaced by a source term of the form
where
is the source term of the original SST model. The intermittency parameter changes in the interval
. Turbulence generation does not occur in a laminar boundary layer (
), so
. In a completely turbulent flow (
),
. At intermediate values of
, there is a transition from laminar to turbulent flow.
The source term
in the equation (2), which describes turbulence dissipation, is replaced by the source term
where
is the source term of the original SST model. In a laminar boundary layer (
) it is assumed that the minimum value of the dissipative term is 10% of its value in a turbulent flow, so
. Despite the laminar nature of the flow, the lower non-zero value of the source term takes into account the damping effect of the wall. In a completely turbulent flow (
),
.
Calculations show that the generation of kinetic energy of turbulence in the case of separation caused by a laminar-turbulent transition occurs rather slowly, which leads to the reattachment of the flow far downstream. To take this effect into account, the effective intermittency
is introduced, which takes the value 2 inside the recirculation region. This approach results in faster turbulence generation and earlier flow reattachment. The effective intermittency is found from the relation
where
The
parameter determines the size of the recirculation area. The constant factor relating
and
corresponds to the value
, while for the boundary layer on a flat plate the constant factor equals 2.193 at
. The function
limits the value of
in the boundary layer. The empirical function
prevents high values of
from occurring when
is large enough, causing a stream to reattach. The
function is defined by the relation
where
is ratio of eddy and molecular viscosity. The Reynolds number
is found from the magnitude of the velocity shift
where
y is distance to the wall,
is vorticity value.
In the original version of the SST model, the
function switches from the
k–
turbulence model used in the free flow region (
) to the
k–
model, which is used in the inlet area (
). In order to eliminate the appearance of computational errors and prevent switching from one model to another in the laminar region of the boundary layer, the function
is defined as follows
The
function corresponds to the SST model, and the
function is defined as follows
The source term
in the equation (
3) has a significant effect on the length of the laminar-turbulent transition, and the source term
makes it possible to take into account flow relaminarization. There is no turbulence generation in the laminar region, therefore
. In the transition region, the source term increases, reaching a maximum value in the turbulent region. The source member is defined by the expression
where
and
are empirical functions. The
function determines the point at which the intermittency parameter growth starts, and the
function controls the growth rate (the higher the growth rate, the shorter the transition section).
To implement the model, additional Reynolds numbers and are introduced. The parameter is the local value of the Reynolds number at which the intermittency parameter begins to increase (turbulence intensity grows), and the parameter is the local value of the Reynolds number at which the laminar-turbulent transition occurs (the velocity airfoil starts to deviate from distribution in a laminar boundary layer).
Using the equation (4),
is found in the free flow and then in the wall region. On the wall it is assumed that
. The source term
in the equation (4) is given by
The
function is identical to the function used in the original version of the SST model. While in a free flow
and the source term is equal to zero, in the boundary layer
.
To close the model, an empirical relation is used to determine , where I is turbulence intensity, is longitudinal pressure gradient.
Under conditions of developed separation, the laminar-turbulent transition is difficult to model within the framework of a two-dimensional problem statement even using the most complex turbulence models, which leads to the use of empirical data from databases on separated flows in calculations [
37]. The turbulence model
–
does not reproduce the physics of the laminar-turbulent transition [
32]. However, the selection of appropriate correlation relations allows obtaining a fairly good agreement between the calculated and experimental data for some types of flows [
38]. The original empirical functions are given for a boundary layer on a flat plate in the presence of a pressure gradient, when the degree of turbulence in the undisturbed flow varies in the range 0.3-5%.
5. Computational domain and mesh
The flow around a airfoil with the analytical assignment of the coordinates of the points of the upper and lower surfaces is considered. The chord length L is chosen as a characteristic linear scale. The solution of the problem is constructed in the flow coordinate system , which has its origin in the middle of the chord, and the x axis is oriented along the direction of the undisturbed flow. The inclination of the airfoil chord with respect to the undisturbed flow velocity vector V is given by the angle of attack . The flow of an incompressible viscous fluid around a airfoil is solved in a rectangular computational domain, the boundaries of which are located at a sufficient distance from the airfoil, and the inlet boundary is perpendicular to the velocity V. The boundaries of the rectangular computational domain with dimensions are located at a considerable distance from the airfoil. The distance from the center of the coordinate system to the entrance is 12, and to the upper border is 11.
At the initial moment of time, it is considered that the airfoil moving with the speed V suddenly slows down, and then the process of step-by-step formation of its vortex flow around it takes place depending on the Reynolds number determined from the speed V, the length L and the kinematic viscosity of the medium. The Reynolds number is calculated from the airfoil chord m and is set equal to . The oncoming flow velocity is selected based on the given value of the Reynolds number ( m/s). Fixing the Reynolds number in the calculations is not associated with fundamental methodological limitations, as well as with the desire to save computing resources. It is due to the need to process a large amount of information on non-stationary processes of airfoil flow.
The nodes of the computational grid near the airfoil surface are concentrated according to the law of geometric progression in such a way that . At the inlet boundary of the computational domain, the parameters of the free flow are set. When performing calculations, parameters are set corresponding to the average level of flow turbulence intensity. At the inlet boundary, the degree of turbulence is set equal to 5%, with the ratio of eddy viscosity to laminar viscosity equal to 10. Outflow boundary conditions are set at the outlet boundary. On the surface of the body, the no-slip and no-penetration conditions are used for the normal and tangential velocity components. To simulate a two-dimensional flow at the boundaries of the computational domain in the direction of the z axis, the symmetry condition is used.
As the initial conditions, the state of impact of a uniform flow on a suddenly stopped thick airfoil, which is initially carried away with the speed of the flow, is taken. The calculations are carried out in the range of angles of attack . The convergence criterion is the achievement of the level of by the value of the root-mean-square residual.
Calculations of unsteady flows lead to chaotic oscillatory processes, the processing of which is carried out by statistical methods. A quasi-periodic mode of changing the flow characteristics around the airfoil is achieved. The change in characteristics is obtained on the period of oscillation of the integral parameter, for example, lift.
6. Numerical method
To discretize the governing equations, the finite volume method on unstructured meshes is used [
39]. Time integration is carried out by the Runge–Kutta method of the 3rd order. Discretization of inviscid fluxes is carried out using the MUSCL scheme (Monotonic Upstream Schemes for Conservation Laws), and viscous flows are found with the central scheme of the 2nd order of accuracy. The MUSCL scheme makes it possible to increase the order of approximation in spatial variables without losing the monotonicity of the solution, satisfies the TVD (Total Variation Diminishing) condition, and is a combination of 2nd order central finite differences and a dissipative term, which are switched between by a flow limiter built on the basis of characteristic variables .
The calculation of unsteady flow around a thick airfoil is completed when the self-oscillating regime is reached with a periodic change in local and integral characteristics in time. The time step is chosen to be 0.01. The self-oscillating regime is reached in about 50 dimensionless units.
7. Characteristics of model airfoil
To test various turbulence models and select a airfoil for further research, the flow around the M06-13-128 airfoil is considered (
Figure 3), for which there are experimental data [
18]. The angle of attack varies from 0 to 15 degrees. The Reynolds number is assumed to be equal to the experimental value
. The airfoil chord is
m. The incoming flow velocity is selected based on the given Reynolds number and is
m/s.
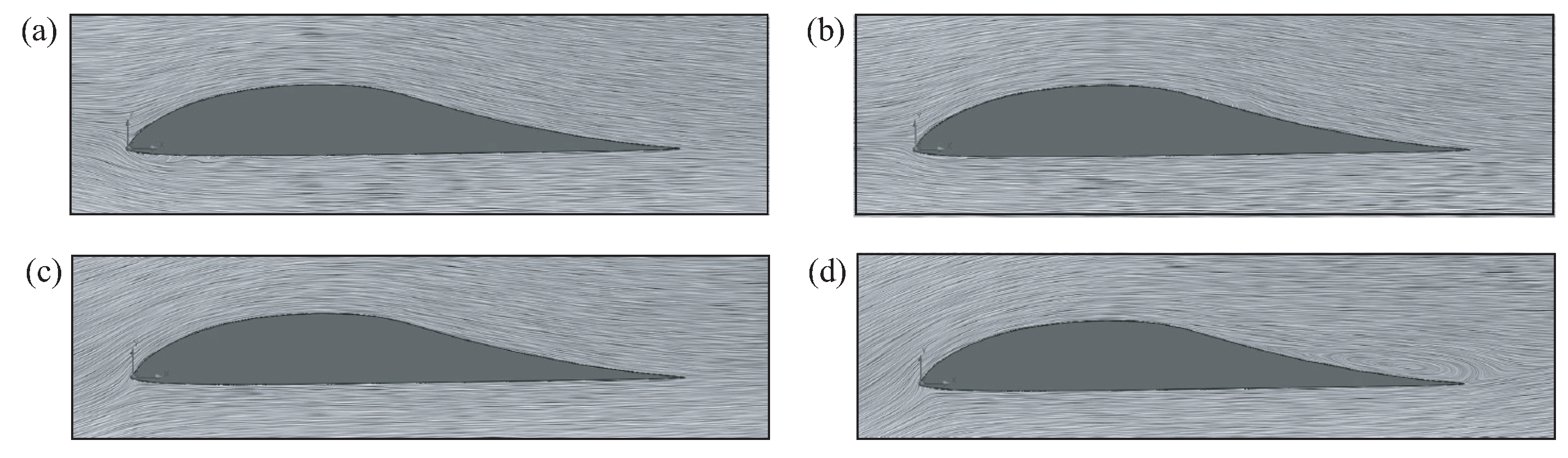
Streamlines near the airfoil at different angles of attack are shown in
Figure 4. Flow separation near the leading edge of the airfoil on its lower surface occurs at low angles of attack. There is also a separation of the flow on the upper surface of the airfoil.
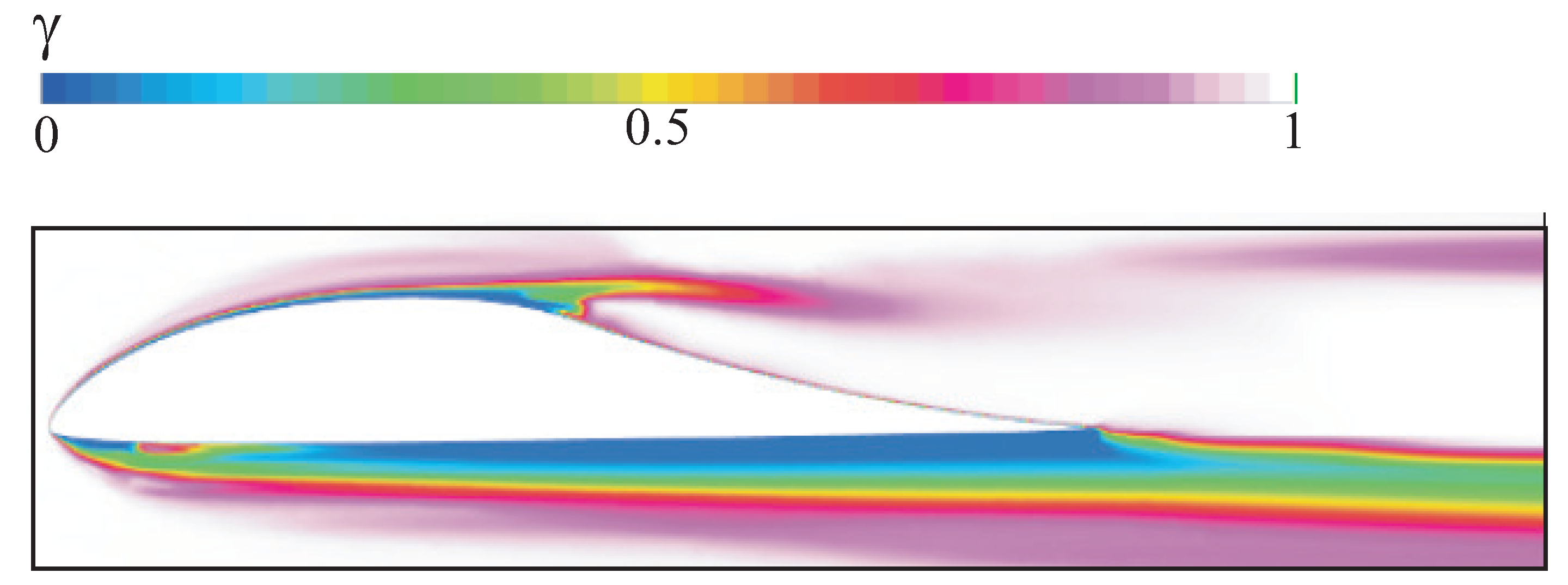
Figure 5 shows the flow pattern in the boundary layer in the laminar-turbulent transition zone. An intermittency factor equal to 0 corresponds to a laminar flow, and an intermittency factor equal to 1 corresponds to a turbulent flow. The calculated velocity airfoils show that as the intermittency coefficient increases, the velocity airfoil in the boundary layer changes its character from laminar (smooth increase in velocity from zero) to turbulent (jump-like change in velocity), which causes a sharp increase in friction resistance. Comparison of calculations for a completely turbulent flow and under conditions of a free laminar-turbulent transition shows that the state of the boundary layer has the greatest influence on the drag coefficient.
On the entire upper surface of the airfoil there is a thin layer, colored in blue-green colors, which indicates the laminar nature of the flow. On the lower surface, the laminar-turbulent transition point is located, depending on the angle of attack, at a distance of 0.55–0.6L from the front critical point.
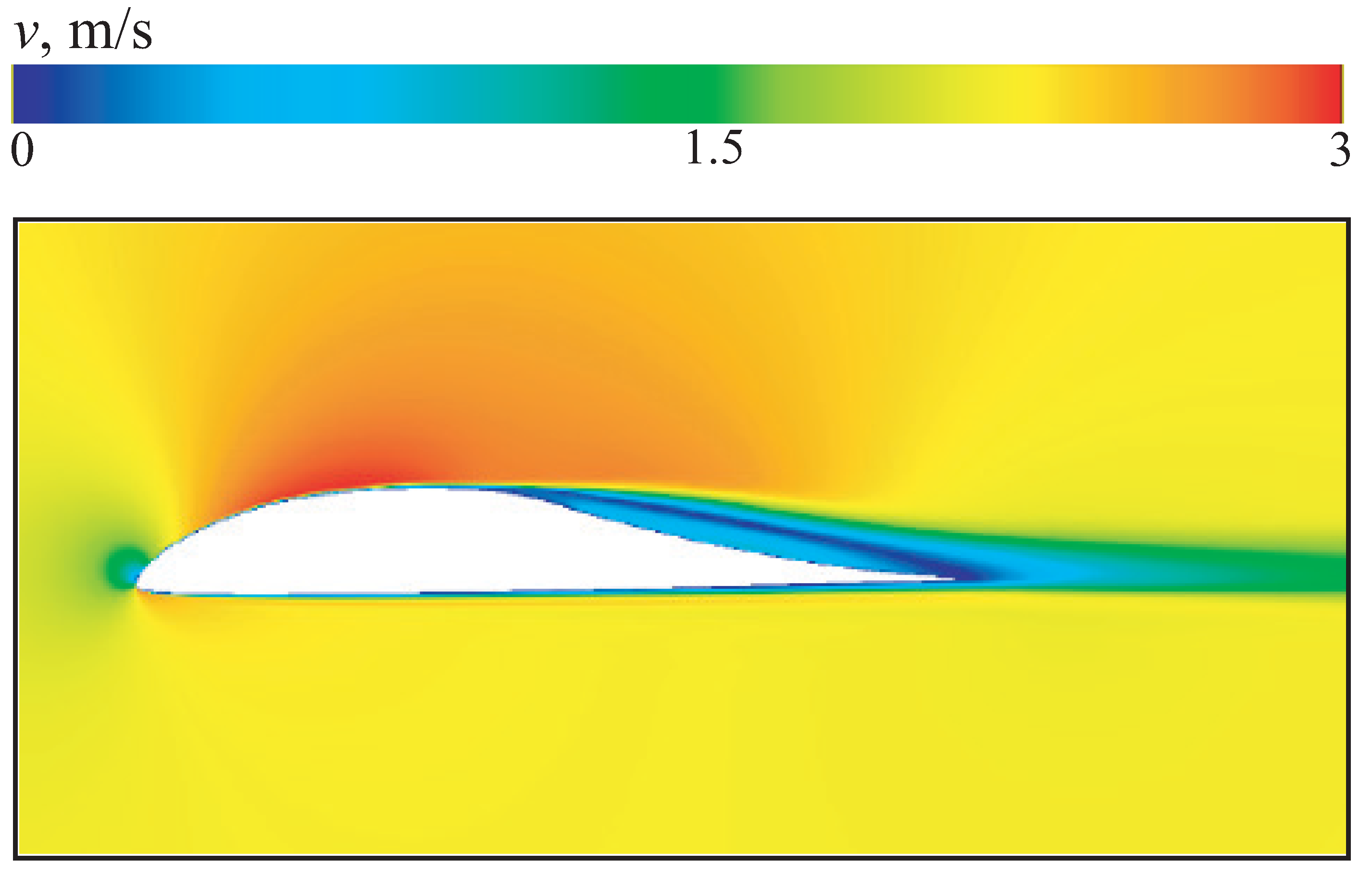
The velocity contours near the airfoil are shown in
Figure 6. Almost along the entire lower surface of the airfoil and on the front upper bearing surface, which has a negative curvature, the flow is laminar.
The results of numerical calculations of aerodynamic characteristics are shown in
Figure 7,
Figure 8 and
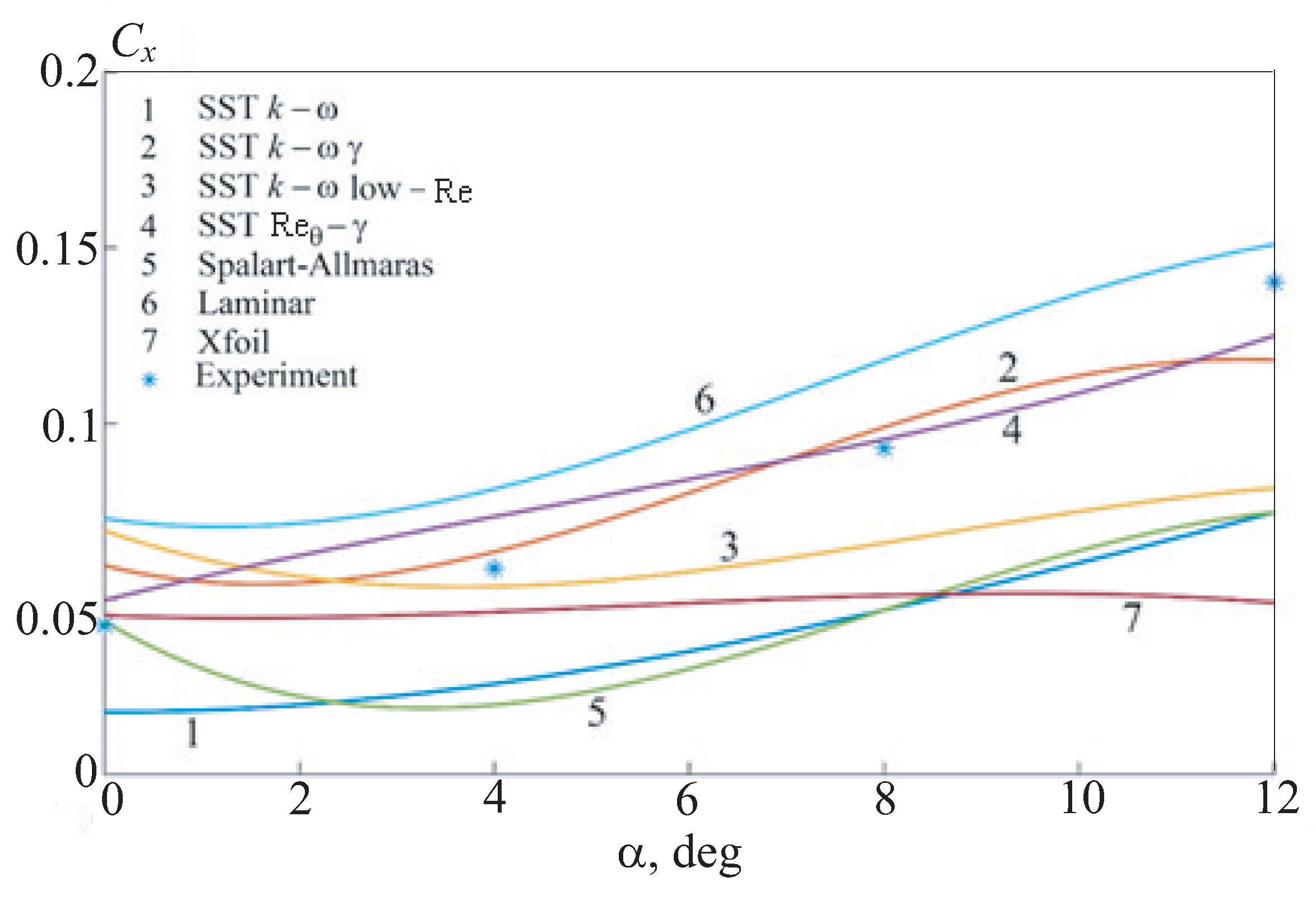
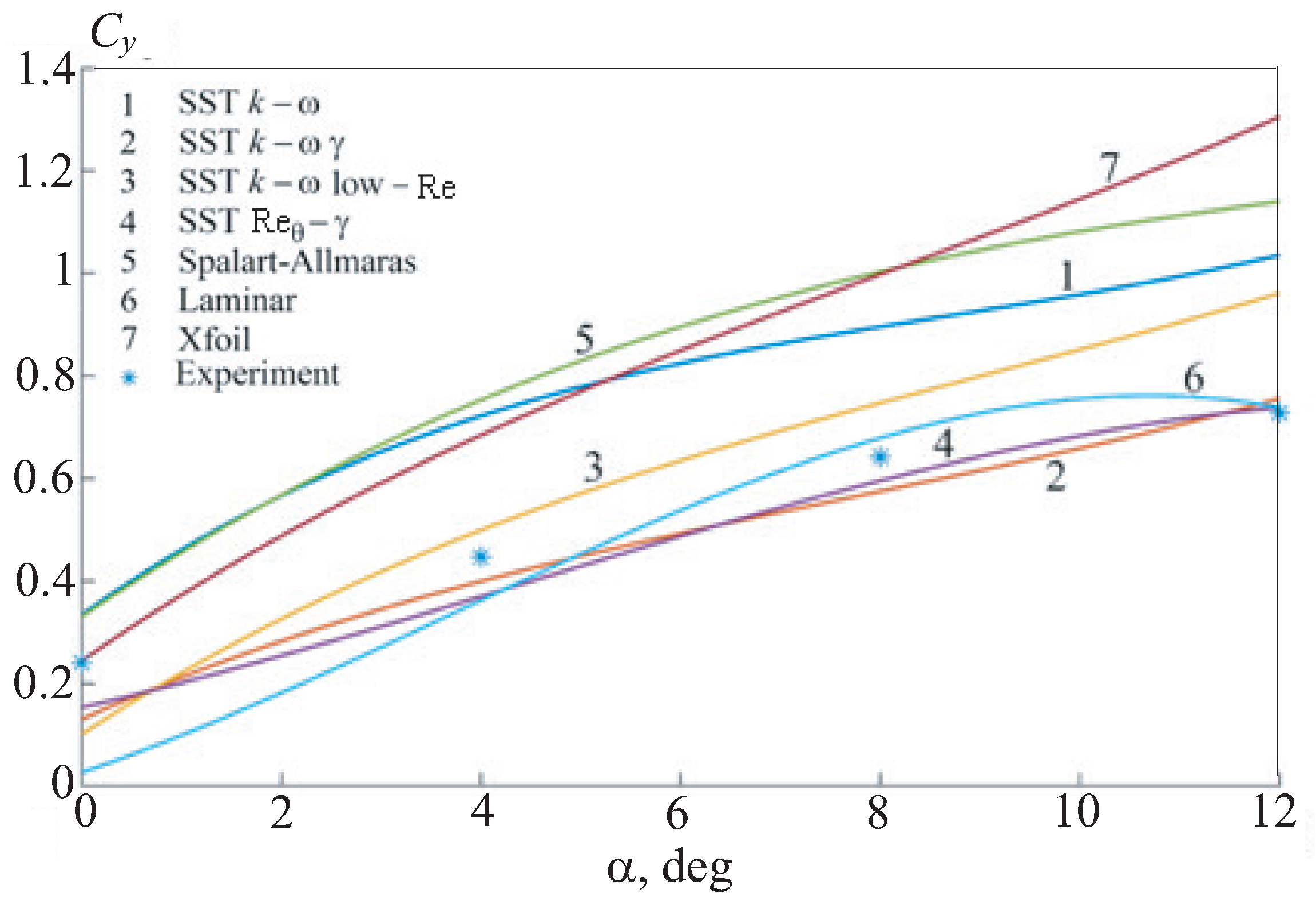
Figure 9. The qualitative behavior of the drag coefficient depending on the angle of attack for a thick airfoil differs little from the similar behavior for a thin airfoil: at large positive and negative angles of attack, the drag increases as the angle of attack modulus increases.
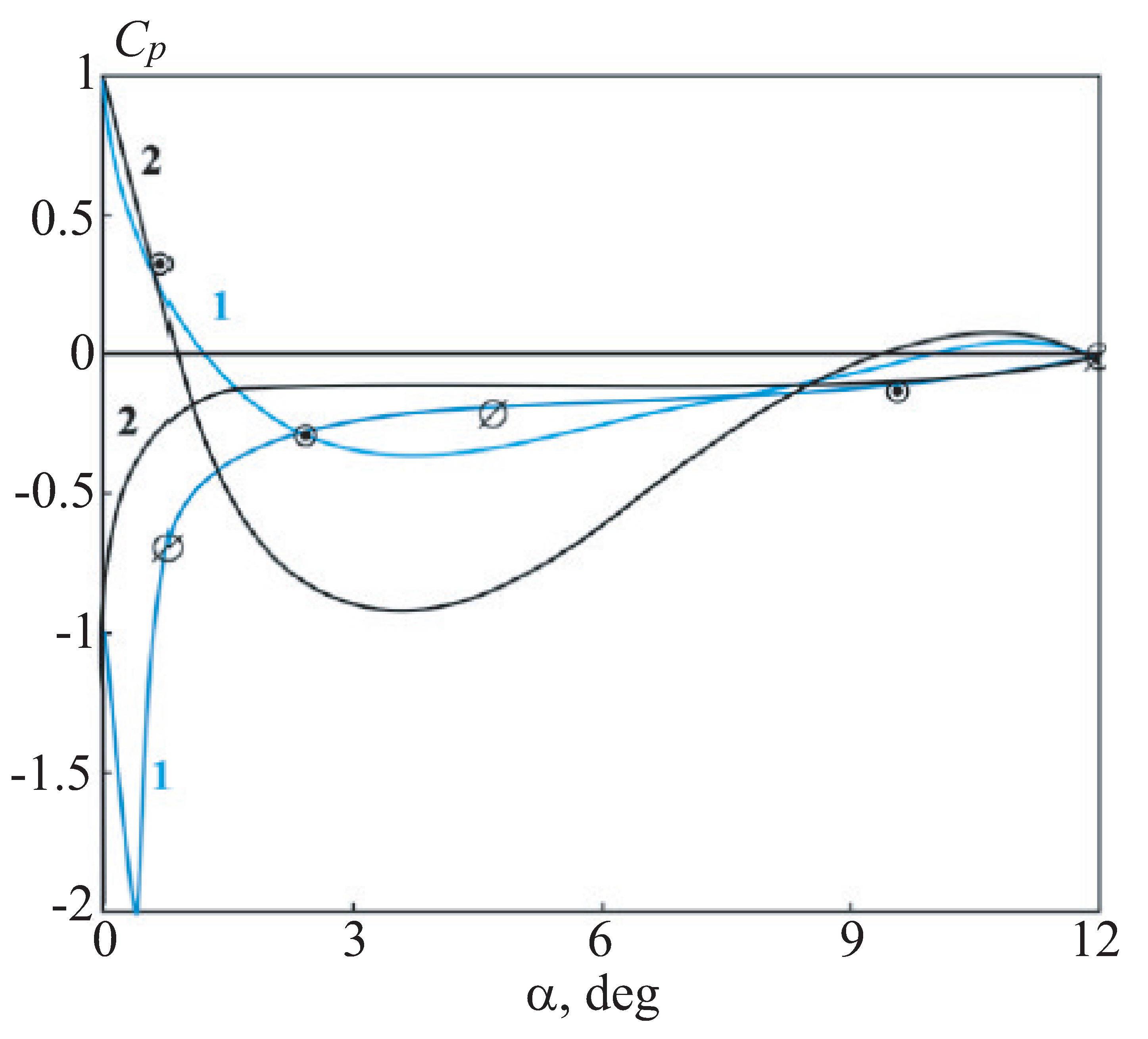
Figure 10 shows the pressure distribution over the airfoil surface in comparison with the experiment [
18] at zero angle of attack. The results show that the tSST model more accurately reproduces the pressure distribution over the airfoil surface and reproduces the presence of separation zones on the upper and lower airfoil surfaces.
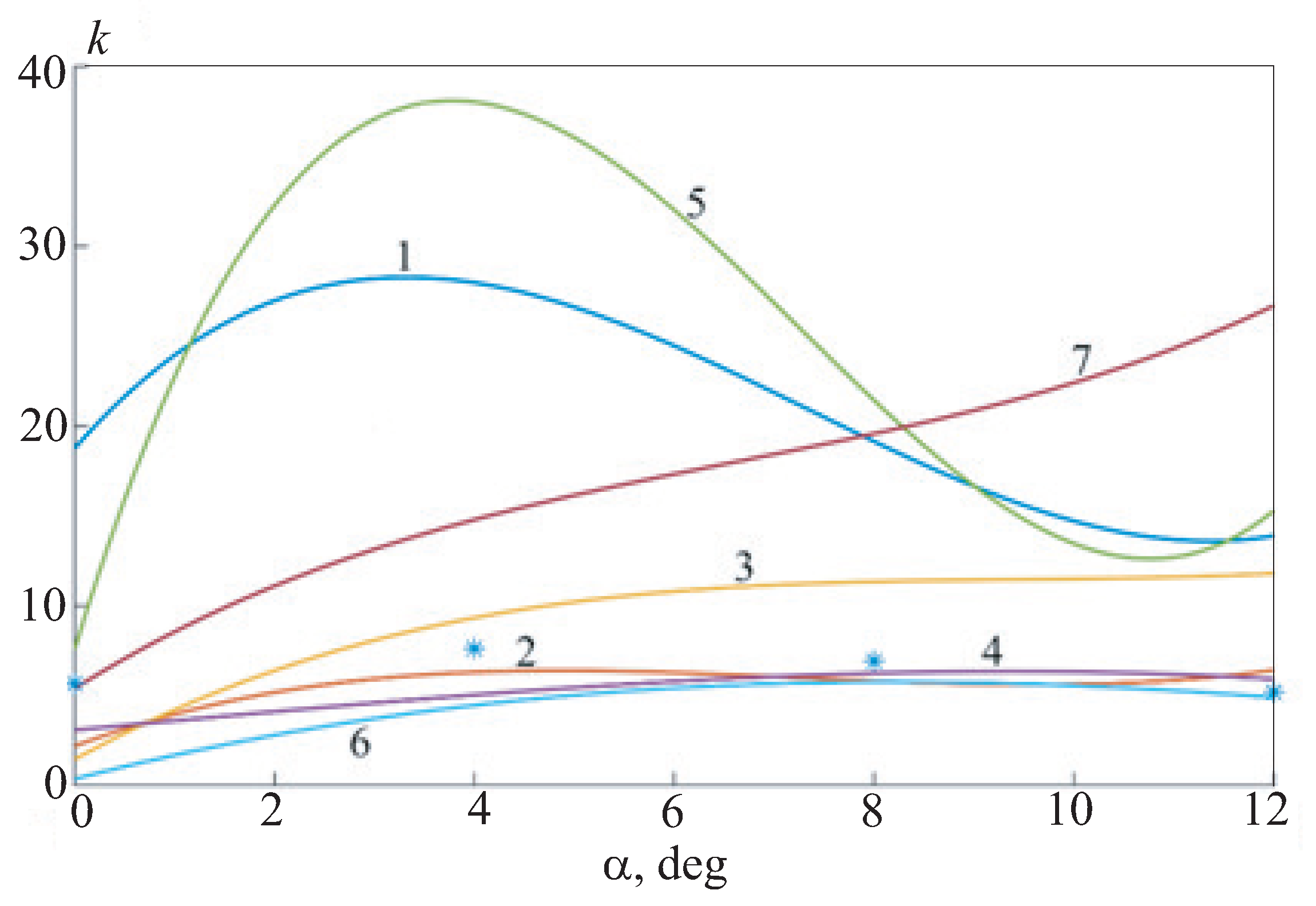
The choice of one or another turbulence model has a significant impact on the calculation results. The aerodynamic airfoil coefficients vary in a fairly wide range of values. The use of turbulence models that do not take into account the laminar-turbulent transition leads to a significant underestimation of the drag coefficient. Calculations using the SST and SA models give the values of the aerodynamic coefficients, which are 2-–3 times lower than the experimental ones. The use of the laminar model leads to an overestimation of the drag coefficient by about 20–-30%. The model with the intermittency parameter shows a fairly adequate agreement with the experiment both in numerical values and in the nature of the change in the values of the coefficient with varying the angle of attack.
Separation of the boundary layer from the surface of the airfoil under these conditions occurs even at zero angle of attack. However, only the use of models with the possibility of taking into account the laminar-turbulent transition makes it possible to detect this effect and evaluate its influence on the aerodynamic characteristics of the airfoil. At an angle of attack of 12 degrees, the application of the SST model makes it possible to obtain a flow pattern with a large separation zone. The external flow around the airfoil using the – model is accompanied by a larger separation zone, which has a non-stationary character, which also affects the calculated characteristics.
8. Results and discussion
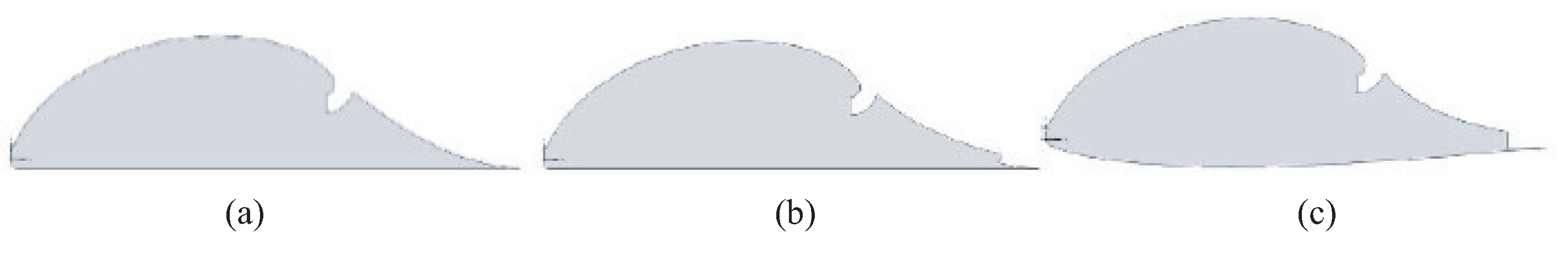
The calculations consider several propulsion airfoils shown in
Figure 11. A series of propulsion airfoils was obtained by a combination of solving the inverse problem of aerodynamics and stochastic methods of global optimization [
40]. Airfoil 1 has a flat lower surface, and there is no air blowing through the trailing edge (
Figure 11a). Airfoil 2 also has a flat lower surface, but air is blown through the trailing edge through the trailing edge (
Figure 11b). Airfoil 3 has a airfoil lower surface and an increased thickness, and air is blown through the trailing edge of the airfoil (
Figure 11c).
The airfoils have a large relative thickness and a favorable pressure gradient along most of the upper surface, which leads to the preservation of the laminar nature of the flow in this area and, consequently, to a decrease in frictional resistance. The suction slot, located upstream of the trailing edge, is used to provide burst pressure build-up at the top of the airfoil. On the tail section, the pressure is greater than on the front. The pressure difference leads to the appearance of static thrust, which negates a significant part of the frictional resistance. In the absence of air extraction, such airfoils are a poorly streamlined body, and with the necessary air flow in the internal channel, the tail section of the airfoil creates thrust.
Airfoil 1 corresponds to the airfoil studied by [
1], for which there are experimental data in the range of angles of attack from 0 to 10 degrees. In this case, the geometry of the air sampling slot changes somewhat, as well as the section from the slot to the tail edge of the airfoil, since the flow near the sampling slot in the original airfoil is accompanied by flow separation.
Airfoil 2 is equipped with a slotted nozzle on the trailing edge, which has a bottom plate extended downstream to compensate for the pitching moment. This surface can serve as an elevator and be used for pitch control.
Airfoil 3 is a modification of airfoil 2 and has an increased thickness. The profiling of the lower surface makes it possible to provide the greatest increase in lift due to the ground effect at an angle of attack of and a distance from the surface of 10–30% of the airfoil chord. Compared to the original airfoil, the area of the nozzle is increased by 50%, which makes it possible to reduce the speed of the jet to increase its propulsive action. The nozzle in the trailing edge at zero angle of attack creates a reactive force directed at an angle of . This is done so that at the cruising angle of attack the reactive force is directed parallel to the velocity vector.
The free flow velocity is assumed to be 70 m/s, which corresponds to the Reynolds number . In the air extraction slot, the degree of flow rarefaction is set, where is pressure at the edge of the slot, p is local pressure. In calculations, the degree of flow rarefaction varies from 0 to atm. For each pressure value in the slot and each angle of attack, the dimensionless air flow is calculated, taken from the airfoil surface, where Q is volumetric air flow, V is speed of the external flow, b is airfoil chord, l is length of the wing section, taken in the calculations equal to 1 m.
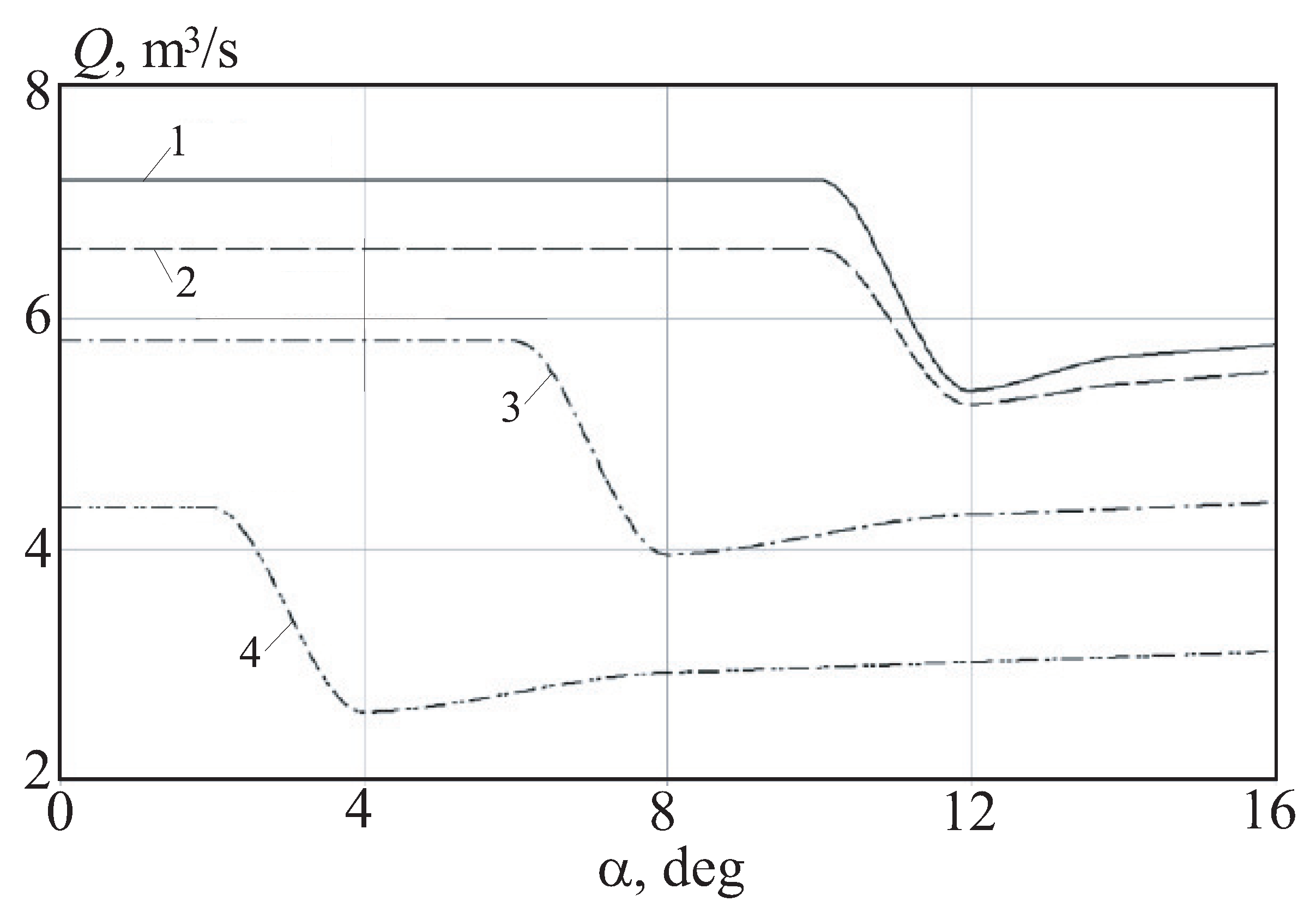
The flow rate of the bleed air at a given degree of rarefaction remains constant until the separation of the boundary layer occurs, after which the flow rate decreases (
Figure 12). This is caused by the formation of a circulation flow zone on the traction section of the airfoil, the pressure in which is lower than in the case of continuous flow. The decrease in pressure drop is accompanied by a decrease in the bleed air flow.
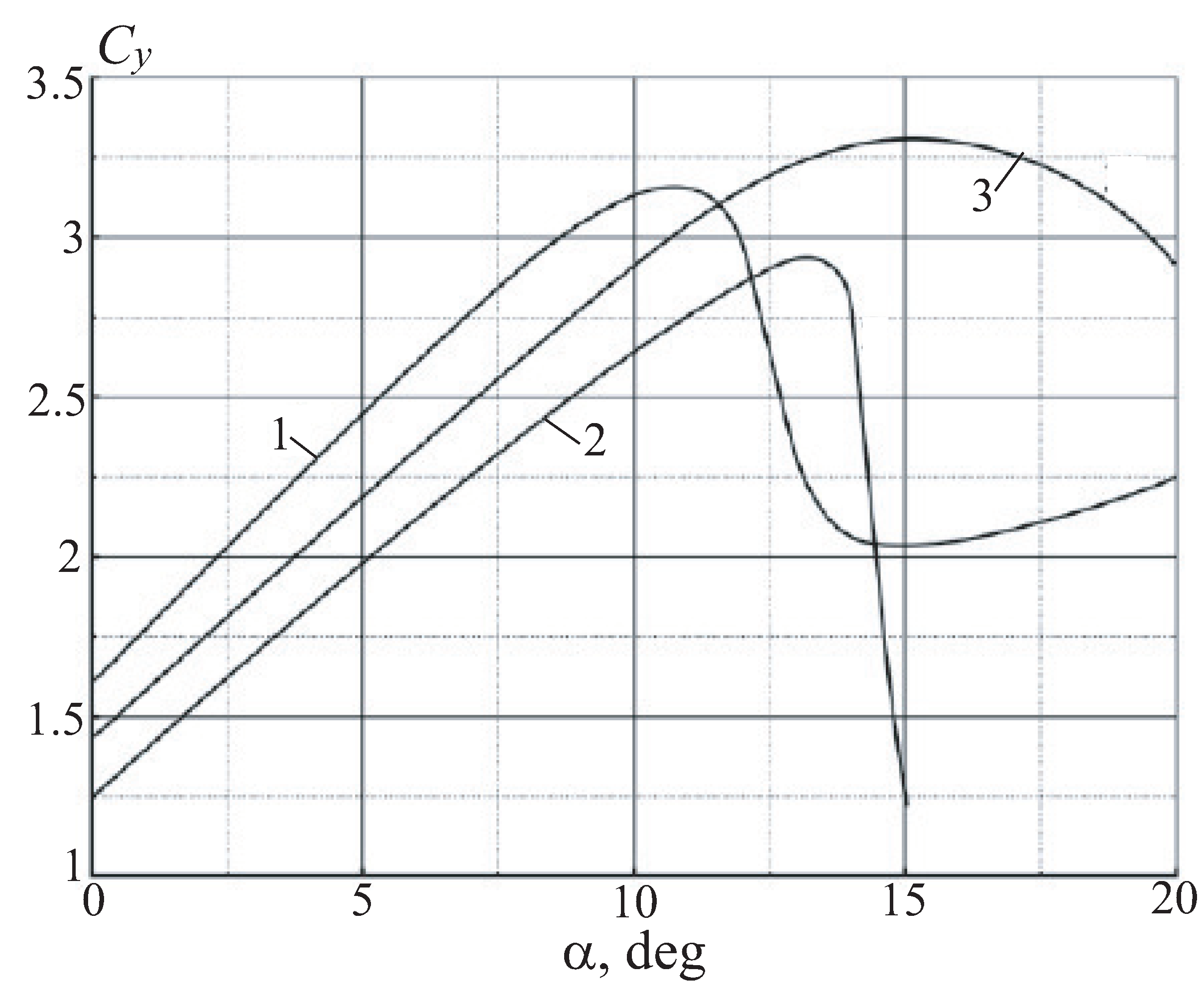
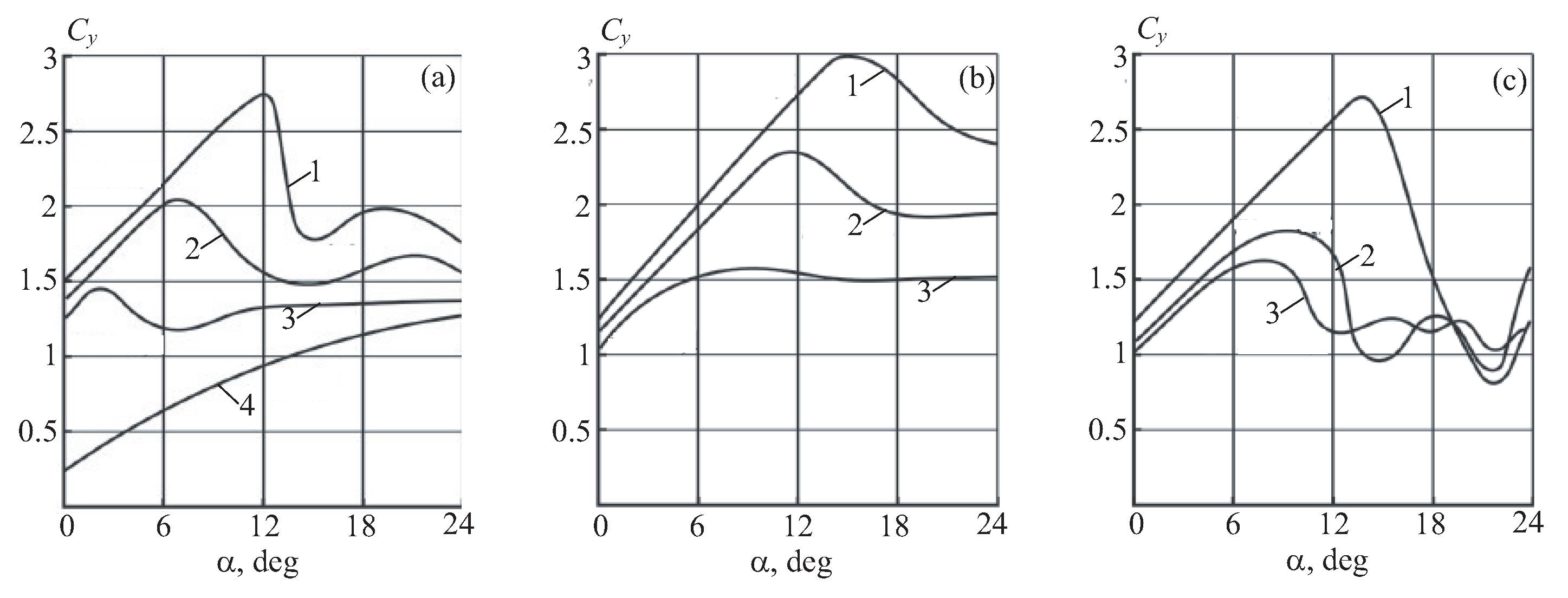
Comparison of the lift coefficients is given in
Figure 13 depending on the angle of attack of the airfoil and the degree of rarefaction in the slot. The airfoils are relatively thick and have a favorable pressure gradient along most of the upper surface, which leads to the preservation of the laminar nature of the flow in this area and the reduction of frictional drag. The suction slot is located upstream of the trailing edge and is used to provide a burst pressure increase on the top of the airfoil. As a result, the pressure on the tail is greater than on the front. This difference results in a static thrust, which compensates for a significant part of the frictional drag.
With an increase in the degree of rarefaction, the lift coefficient of airfoil 1 increases, and the limiting angle of attack of the continuous flow increases (
Figure 13a). In this case, the dependencies corresponding to the degrees of rarefaction
atm and
atm practically coincide, therefore it is considered that at
atm the limiting characteristics of airfoil 1 are achieved.
For airfoil 2, the amount of ejected air is assumed to be equal to the amount taken through the slot. The ejection of the jet delays the onset of stalled supercritical flow regimes. At the same time, the maximum lift coefficient is almost 10% higher than the value corresponding to airfoil 1 (
Figure 13b).’
For airfoil 3, it is also assumed that the amount of air ejected through the nozzle is equal to the amount taken through the slot. At the same time, the upgraded airfoil 3 is slightly inferior to airfoil 2 in terms of the maximum lift coefficient. Airfoil 3 has a nozzle set at an angle of , which reduces the lift force of the airfoil. Calculations show that at , an increase in the air flow rate ejected through the nozzle in the trailing edge from 50 to 200% of the air flow rate taken through the slot leads to a monotonous increase in lift, starting from the angle of attack (angle of attack at which the vertical component of the thrust vector becomes equal to zero). At lower degrees of rarefaction, the effect of the flow rate of air ejected through the nozzle at the trailing edge on the lift force is less pronounced.
There is an optimal flow rate of air taken from the surface, at which the resistance of viscous friction is minimal. This is explained by the fact that the laminar section of the flow reaches its maximum length at the optimal air extraction rate, and with a further increase in the extraction rate, the resistance in the laminar boundary layer increases, because its speed increases.
The change in air flow is achieved by controlling the degree of rarefaction in the slot . For each angle of attack, increases as long as the lift coefficient increases. Practical convergence is achieved at atm.
Figure 14.
Lift coefficient dependencies for airfoil 1 (a), airfoil 2 (b), airfoil 3 (c).
Figure 14.
Lift coefficient dependencies for airfoil 1 (a), airfoil 2 (b), airfoil 3 (c).
Up to an angle of attack of , the lift coefficient increases almost linearly, reaching a value of 3–3.3. The lift force increases with an increase in the degree of rarefaction created in the slot for air sampling, approaching the limit value at a rarefaction of 0.5 atm. At maximum vacuum, air ejection through the trailing edge increases the lift force the stronger, the greater the flow rate. At low rarefaction, the situation is ambiguous; in particular, the exhaust jet can also reduce lift. There is a preferred location of the slot near the trailing edge of the airfoil. Further displacement of the slot towards the trailing edge leads to the establishment of unsteady separated flow regime and the deterioration of its aerodynamic characteristics.
9. Conclusion
To obtain optimal airfoils, taking into account gas extraction from its surface and blowing through the trailing edge, a method is used to solve the inverse problem of aerodynamics (designing the airfoil shape according to given flow parameters near the airfoil). The calculations performed show a significant effect of the laminar-turbulent transition on the aerodynamic characteristics of the airfoil at low Reynolds numbers. The calculations were performed using the – turbulence model, which takes into account the transition from a laminar flow regime to a turbulent one.
The aerodynamic characteristics of airfoils using air extraction at the upper critical point to increase the lift force have been studied. The section of the upper surface of the airfoils from the air intake slot to the trailing edge creates traction even if there is no air outlet slot in the trailing edge. The lift force increases with an increase in the degree of rarefaction created in the slot for air sampling, approaching the limit value at a certain degree of rarefaction. At maximum vacuum, air ejection through the trailing edge increases the lift force the stronger, the greater the flow rate. At low rarefaction, the situation is ambiguous; in particular, the exhaust jet can also reduce lift.
The studied airfoils have a large relative thickness (up to 38%) and carrying capacity, creating thrust in the absence of blowing through the trailing edge. These properties allow them to be used in the design of the airframe of aircraft, for which the volume of internal compartments is important.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology and software, validation, N.Prodan; formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, P.Chernyshov; visualization, K.Volkov; supervision, P.Bulat; project administration, P.Bulat. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of Russian Federation during the implementation of the project «Fundamentals of mechanics, control and management systems for unmanned aerial systems with shape-forming structures, deeply integrated with power plants, and unique properties that are not used today in manned aircraft», No. FEFM-2020-0001.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Ilyinsky, N.B.; Abzalilov, D.F. Mathematical problems of designing wing profiles: complicated flow patterns; construction and optimization of the shape of wing profiles; Kazan: Publishing house of KSU, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Petrov, A.V. Energy methods for increasing the lift force of the wing; Fizmatlit: Moscow, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Petrov, A.V. Aerodynamics of short takeoff and landing transport aircraft with energy methods for increasing lift; Innovative engineering: Moscow, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo-Mosquera, P.D.; Catalano, F.M.; Zingg, D.W. Unconventional aircraft for civil aviation: a review of concepts and design methodologies. Progress in Aerospace Sciences 2022, 131, 100813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dygert, R.K.; Dang, T.Q. Experimental investigation of embedded cross-flow fan for airfoil propulsion/circulation control. AIAA Paper 2007, 2007-3568. [Google Scholar]
- Harloff, G.; Wilson, D. Cross-flow propulsion fan experimental development and finite-element modeling. Journal of Aircraft 1980, 18, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gologan, C.; + Mores, S.; Steiner, H.; Seitz, A. Potential of the cross-flow fan for powered-lift regional aircraft applications. AIAA Paper 2009, 2009-7098. [Google Scholar]
- Himeur, R.M.; Khelladi, S.; Chikh, M.A.A.; Vanaei, H.R. Towards an accurate aerodynamic performance analysis methodology of cross-flow fans. Energies 2022, 15, 5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummer, J.D.; Dang, T.Q. High-lift propulsive airfoil with integrated cross-flow fan. Journal of Aircraft 2006, 43, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsop, C.; Forster, M.; Crowther, W.J. Supercritical Coanda based circulation control and fluidic thrust vectoring. AIAA Paper 2019, 2019-0044. [Google Scholar]
-
Flow control around bodies with vortex cells in application to integrated aircraft (numerical and physical modeling)/A.V. Ermishina, S.A. Isaev; MGU: Moscow, 2003.
-
Aerodynamics of thickened bodies with vortex cells. Numerical and physical and modeling / S.A. Isaev; Publishing House of the Polytechnic University: St Petersburg, 2016.
- Iollo, A.; Zannetti, L. Trapped vortex optimal control by suction and blowing at the wall. European Journal of Mechanics B 2001, 20, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelli, R.; Chernyshenko, S.; Iannelli, P.; Iollo, A.; Zannetti, L. Flow models for a vortex cell. AIAA Journal 2009, 47, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaev, S.A.; Baranov, P.A.; Smurov, M.Yu.; Sudakov, A.G.; Shebelev, A.V. Flow control around a thick airfoil with a vortex cell with slotted air suction and near wake ejection. Thermophysics and Aeromechanics 2016, 23, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.; Ogbonna, I.; Volkov, K. Improvement of self-starting capabilities of vertical axis wind turbines with new design of turbine blades. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, A.T.; Ansell, P.J.; Kerho, M.; Ananda, G.; D’Urso, S. Design, analysis, and evaluation of a propulsive wing concept. AIAA Paper 2016, 2016-4178. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, T.J. The influence of laminar separation and transition on low Reynolds number airfoil hysteresis. Journal of Aircraft 1985, 22, 763–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, T.; Nagano, S. Effects of inlet distortions on a multi-stage compressor. AIAA Paper 1979, 79-7003. [Google Scholar]
- Karpuk, S.V.; Kazarin, P.; Gudmundsson, S.; Golubev, V.V. Preliminary feasibility study of a multi-purpose aircraft concept with a leading-edge embedded cross-flow fan. AIAA Paper 2018, 2018-1744. [Google Scholar]
- Menter, F.R.; Langtry, R.; Volker, S. Transition modelling for general purpose CFD codes. Flow, Turbulence and Combustion 2006, 77, 277–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F.R. Zonal two equation k–ω turbulence models for aerodynamic flows. AIAA Paper 1993, 93-2906. [Google Scholar]
- Menter, F.R.; Kuntz, M.; Langtry, R. Ten years of industrial experience with the SST turbulence model. Turbulence, Heat and Mass Transfer / K. Hajalic, Y. Nogano, M. Tummers. Begell House 2003, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, S.; + Ogbonna, I.; Volkov, K. Aerodynamic characteristics of a single aerofoil for vertical axis wind turbine blades and performance prediction of wind turbines. Fluids 2021, 6, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissaman, P. Low-Reynolds-number airfoils. Annual Review of Flluid Mechanics 1983, 15, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selig, M.S.; Guglielmo, J.J.; Broern, A.P.; Giguere, P. Experiments on airfoils at low Reynolds numbers. AIAA Paper 1996, 1996-0062. [Google Scholar]
- Holman, J.; Furst, J. Numerical simulation of separation induced laminar to turbulent transition over an airfoil. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 2021, 394, 113530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desert, T.; Jardin, T.; Bezard, H.; Moschetta, J.M. Numerical predictions of low Reynolds number compressible aerodynamics. Aerospace Science and Technology 2019, 92, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogowski, K.; Krolak, G.; Bangga, G. Numerical study on the aerodynamic characteristics of the NACA0018 airfoil at low Reynolds number for Darrieus wind turbines using the Transition SST model. Processes 2021, 9, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drela, M. Flight vehicle aerodynamics; MIT Press: Cambridge, 2014; 279 p. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Jiang, K. Comparative assessment of transitional turbulence models for airfoil aerodynamics in the low Reynolds number range. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics 2021, 217, 104726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauters, J.; Degroote, J. On the study of transitional low-Reynolds number flows over airfoils operating at high angles of attack and their prediction using transitional turbulence models. Progress in Aerospace Sciences 2018, 103, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langtry, R.B.; Menter, F.R. Correlation-based transition modeling for unstructured parallelized computational fluid dynamics codes. AIAA Journal 2009, 47, 2894–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coder, J.G.; Maughmer, M.D. Computational fluid dynamics compatible transition modeling using an amplification factor transport equation. AIAA Journal 2014, 52, 2506–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F.R.; Smirnov, P.E.; Liu, T.; Avancha, R. A one-equation local correlation-based transition model. Flow, Turbulence and Combustion 2015, 95, 583–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, S.; Seddighi, M.; Ariyaratne, C.; Vardy, A.E.; O’Donoghue, T.; Pokrajac, D.; He, S. A comparative study of turbulence models in a transient channel flow. Computers and Fluids 2014, 83, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, D.; Lengani, D.; Dellacasagrande, M.; Kubacki, S.; Dick, E. An accurate database on laminar-to-turbulent transition in variable pressure gradient flows. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow 2019, 77, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Kwon, O.J. Recent improvement of a correlation-based transition model for simulating three-dimensional boundary layers. AIAA Journal 2017, 55, 2103–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, K. Numerical analysis of Navier–Stokes equations on unstructured meshes. Handbook on Navier–Stokes Equations: Theory and Analysis / D. Campos. Nova Science, 2016, 365–442.
- Prodan, N.V.; Kurnukhin, A.A. Application of mathematical optimization methods for designing an airfoil with viscosity taken into account. Russian Aeronautics 2021, 4, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
Figure 1.
Aerodynamics airfoils E387 (a), FX63-137 (b), M06-13-128 (c).
Figure 1.
Aerodynamics airfoils E387 (a), FX63-137 (b), M06-13-128 (c).
Figure 2.
The concept of a propulsion airfoil with suction of the boundary layer from the upper surface and its ejection through the trailing edge (a) using a crossflow transverse fan (b).
Figure 2.
The concept of a propulsion airfoil with suction of the boundary layer from the upper surface and its ejection through the trailing edge (a) using a crossflow transverse fan (b).
Figure 3.
Aerodynamic airfoil M06-13-128.
Figure 3.
Aerodynamic airfoil M06-13-128.
Figure 4.
Streamlines around airfoil M06-13-128 at angles of attack (a), (b), (c), (d).
Figure 4.
Streamlines around airfoil M06-13-128 at angles of attack (a), (b), (c), (d).
Figure 5.
Contours of intermittency parameter in the boundary layer at ).
Figure 5.
Contours of intermittency parameter in the boundary layer at ).
Figure 6.
Velocity contours around the airfoil at .
Figure 6.
Velocity contours around the airfoil at .
Figure 7.
Dependence of the drag coefficient on the angle of attack.
Figure 7.
Dependence of the drag coefficient on the angle of attack.
Figure 8.
Dependence of the lift coefficient on the angle of attack.
Figure 8.
Dependence of the lift coefficient on the angle of attack.
Figure 9.
Dependence of the lift-to-drag ratio on the angle of attack.
Figure 9.
Dependence of the lift-to-drag ratio on the angle of attack.
Figure 10.
Pressure coefficient distributions over the airfoil surface obtained using the tSST model (line 1) and SST model (line 2) in comparison with physical experiment [
18] (symbols ⨂ and ⨀ refer to the top and bottom surfaces of the airfoil).
Figure 10.
Pressure coefficient distributions over the airfoil surface obtained using the tSST model (line 1) and SST model (line 2) in comparison with physical experiment [
18] (symbols ⨂ and ⨀ refer to the top and bottom surfaces of the airfoil).
Figure 11.
Propulsion airfoils: airfoil 1 (a), airfoil (b), airfoil 3 (c).
Figure 11.
Propulsion airfoils: airfoil 1 (a), airfoil (b), airfoil 3 (c).
Figure 12.
Dependence of the air consumption taken from the airfoil surface on the degree of rarefaction at different angles of attack and atm (1), atm (2), atm (3), atm (4).
Figure 12.
Dependence of the air consumption taken from the airfoil surface on the degree of rarefaction at different angles of attack and atm (1), atm (2), atm (3), atm (4).
Figure 13.
Dependencies of the lift coefficient on the degree of rarefaction at different angles of attack for airfoil 1 (a), airfoil 2 (b), airfoil 3 (c) at atm (1), atm (2), atm (3), 0 atm (4).
Figure 13.
Dependencies of the lift coefficient on the degree of rarefaction at different angles of attack for airfoil 1 (a), airfoil 2 (b), airfoil 3 (c) at atm (1), atm (2), atm (3), 0 atm (4).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).