Submitted:
05 September 2023
Posted:
07 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
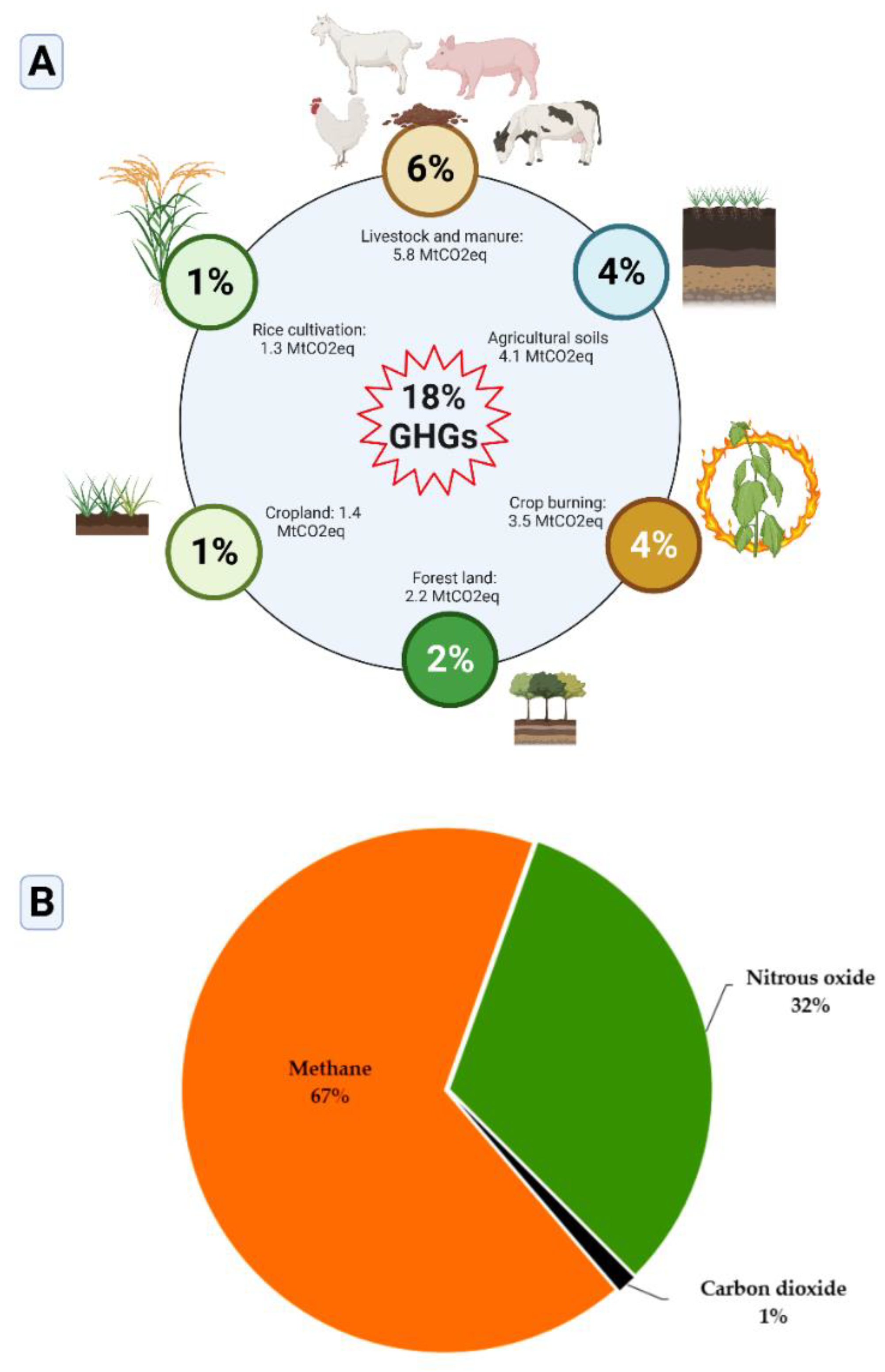
2. Major sources of greenhouse gases in agriculture
2.1. Agricultural Land Use and Management of Crop Residues
2.2. Farming Practices and Fertilizers
2.3. Livestock production
3. Mechanisms of greenhouse gases production and emission from crop cultivation
3.1. Methanogenesis and Methanotrophy
3.2. Nitrous Oxide generation and emission
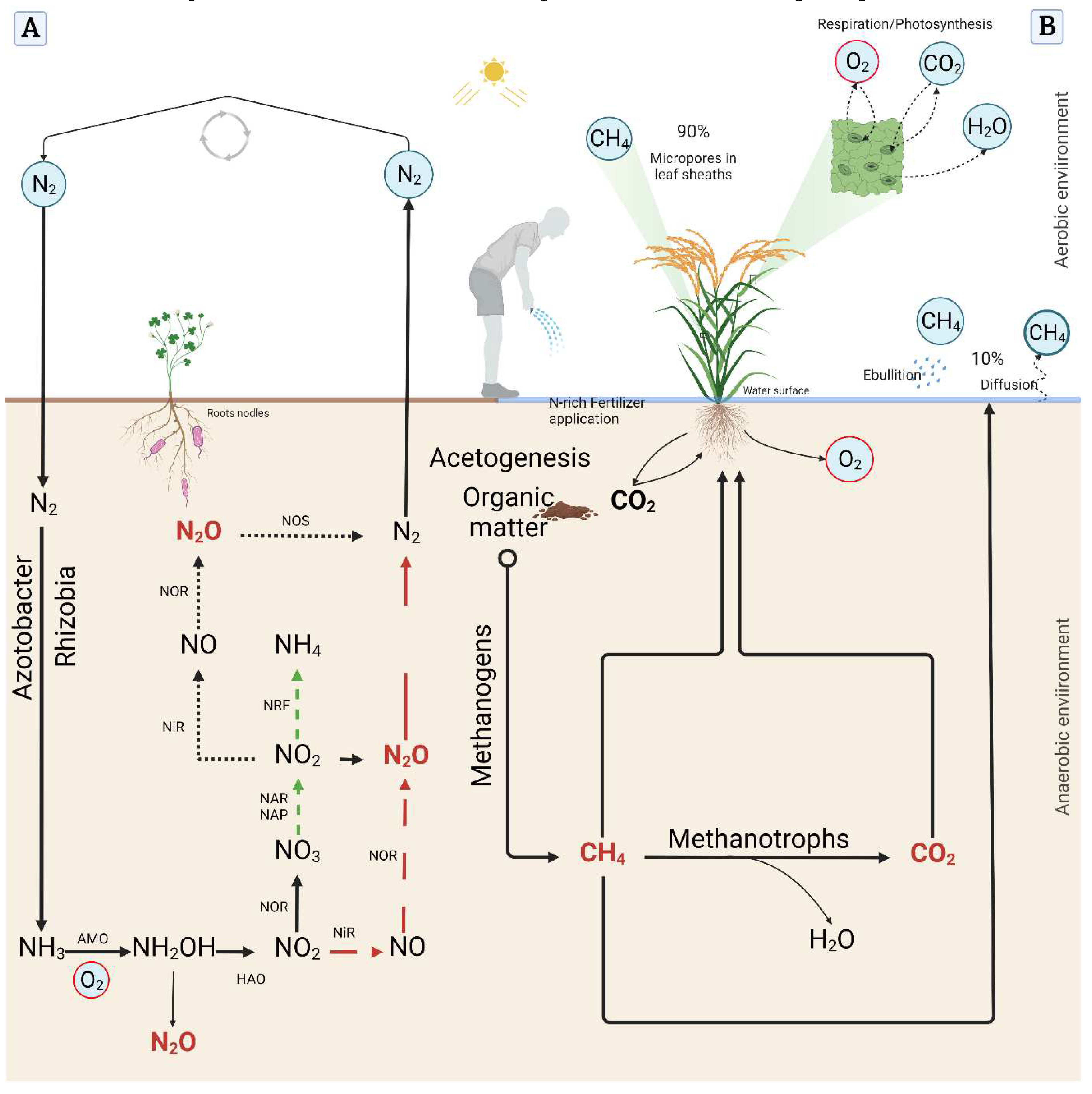
3.3. Carbon dioxide emission and sequestration
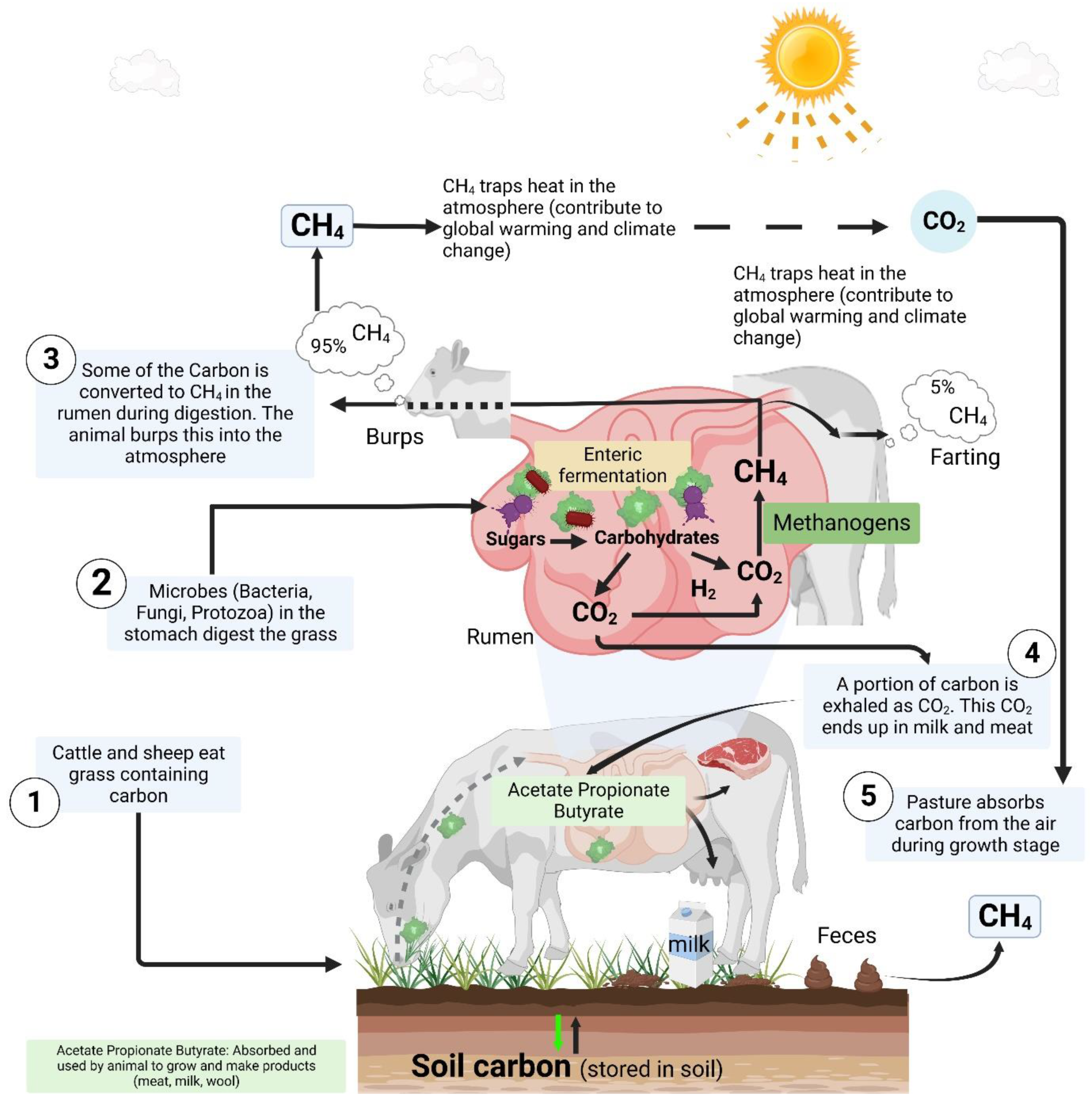
4. Mechanisms of GHG production and emission from livestock
5. Approaches to Reduce GHG Emissions in Agriculture
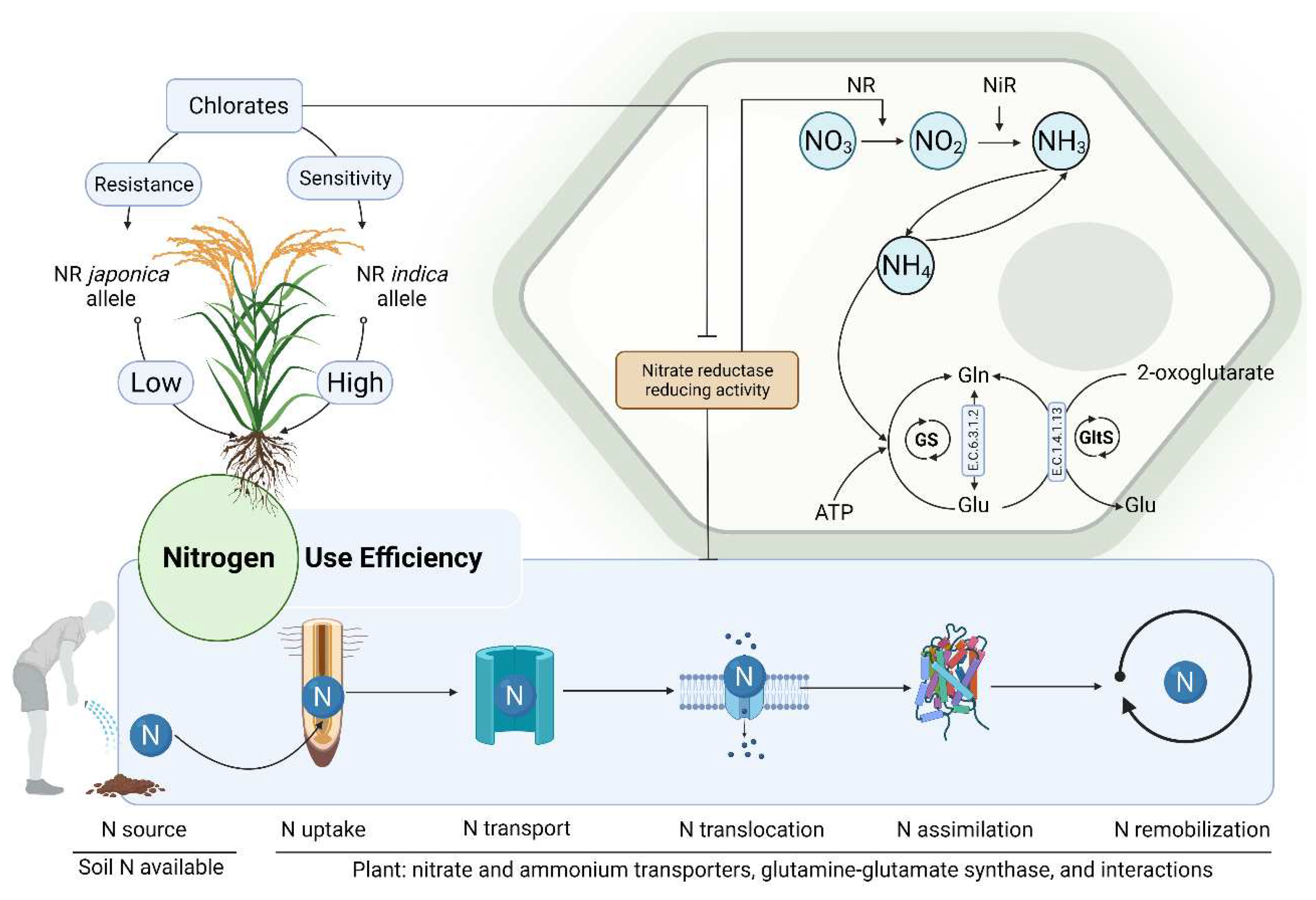
5.1. Enhancing Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Plants
5.2. Improving Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants
5.3. Exploring Radial Oxygen Loss and Intermittent Drainage
5.4. Biochar reduces mineral fertilizers use, improves soil properties and mitigate GHG emissions
5.5. Enhancing Sink Strength
5.6. Use of Nitrification Inhibitors or Low GHG-Emitting Crop Cultivars
5.7. Improving Management of Crop Residues
5.8. Improving Livestock Production and Feeding Efficiency
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holden, E.; Linnerud, K.; Banister, D.J.G.e.c. Sustainable development: Our common future revisited. 2014, 26, 130-139.
- Sam, S.J.E. The people, planet, prosperity, peace and partnership: why the sustainable development goals should matter to everyone. 2016, 30, 7-12.
- Mpabanga, D.; Sesa, L.J.A.J.o.P.A. ; Management. Imperatives: The Five P’s: People, Planet, Prosperity, Peace and Partnerships and Sustainable Development Goals-The Need to Transform Public Administration and Management. 2020, 17, 44–58. [Google Scholar]
- Papoulis, D.; Kaika, D.; Bampatsou, C.; Zervas, E.J.C. Public perception of climate change in a period of economic crisis. 2015, 3, 715-726.
- Adger, W.N.; Kelly, P.M.J.M.; change, a.s.f.g. Social vulnerability to climate change and the architecture of entitlements. 1999, 4, 253-266.
- Otto, I.M.; Reckien, D.; Reyer, C.P.; Marcus, R.; Le Masson, V.; Jones, L.; Norton, A.; Serdeczny, O.J.R.e.c. Social vulnerability to climate change: A review of concepts and evidence. 2017, 17, 1651-1662.
- Hasegawa, T.; Fujimori, S.; Havlík, P.; Valin, H.; Bodirsky, B.L.; Doelman, J.C.; Fellmann, T.; Kyle, P.; Koopman, J.F.; Lotze-Campen, H.J.N.C.C. Risk of increased food insecurity under stringent global climate change mitigation policy. 2018, 8, 699-703.
- Ericksen, P.J.; Thornton, P.K.; Notenbaert, A.M.O.; Cramer, L.; Jones, P.G.; Herrero, M.T.J.C.r. Mapping hotspots of climate change and food insecurity in the global tropics. 2011.
- Crutzen, P.J.J.N. Methane's sinks and sources. 1991, 350, 380-381.
- Reay, D. Greenhouse gas sinks; CABI: 2007.
- Reay, D.; Smith, P.; Van Amstel, A. Methane sources and the global methane budget. In Methane and climate change; Earthscan London and Washington, DC: 2010; pp. 1-13.
- Ming, T.; Davies, P.; Liu, W.; Caillol, S.J.P.i.E.; Science, C. Removal of non-CO2 greenhouse gases by large-scale atmospheric solar photocatalysis. 2017, 60, 68-96.
- Schütz, H.; Holzapfel-Pschorn, A.; Conrad, R.; Rennenberg, H.; Seiler, W.J.J.o.G.R.A. A 3-year continuous record on the influence of daytime, season, and fertilizer treatment on methane emission rates from an Italian rice paddy. 1989, 94, 16405-16416.
- Colmer, T.J.P. , Cell; Environment. Long-distance transport of gases in plants: a perspective on internal aeration and radial oxygen loss from roots. 2003, 26, 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Schiermeier, Q. Study fails to catch plants making methane. 2009.
- Nisbet, R.; Fisher, R.; Nimmo, R.; Bendall, D.; PM, C.; Gallego-Sala, A.; Hornibrook, E. L {ó} pez-Juez. E., Lowry, D., Nisbet, P., Shuckburgh, E., Sriskantharajah, S., Howe, CJ, and Nisbet, EG: Emission of methane from plants, Proc. R. Soc 2009, 276, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Nouchi, I.; Mariko, S.; Aoki, K. Mechanism of methane transport from the rhizosphere to the atmosphere through rice plants. Plant Physiology 1990, 94, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassmann, R.; Aulakh, M.S. The role of rice plants in regulating mechanisms of methane missions. Biology and Fertility of Soils 2000, 31, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnet, K.N.; Megonigal, J.P.; Litchfield, C.; Taylor Jr, G.E. Physiological control of leaf methane emission from wetland plants. Aquatic Botany 2005, 81, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, A.R.; Fry, S.C.; Loake, G.J.; Messenger, D.J.; Reay, D.S.; Smith, K.A.; Yun, B.W. Ultraviolet radiation drives methane emissions from terrestrial plant pectins. New Phytologist 2008, 180, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putkinen, A.; Siljanen, H.M.; Laihonen, A.; Paasisalo, I.; Porkka, K.; Tiirola, M.; Haikarainen, I.; Tenhovirta, S.; Pihlatie, M. New insight to the role of microbes in the methane exchange in trees: evidence from metagenomic sequencing. New Phytologist 2021, 231, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, R.; Fisher, R.; Nimmo, R.; Bendall, D.; Crill, P.; Gallego-Sala, A.V.; Hornibrook, E.; López-Juez, E.; Lowry, D.; Nisbet, P.J.P.o.t.R.S.B.B.S. Emission of methane from plants. 2009, 276, 1347-1354.
- Li, L.; Wei, S.; Shen, W. The role of methane in plant physiology: a review. Plant cell reports 2020, 39, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Huang, D.; Li, C.; Deng, Y.; Li, W.; Yao, Y.; Liao, W. Regulatory roles of methane in plants. Scientia Horticulturae 2020, 272, 109492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP, U.J.U.E.P. Emissions gap report 2020. 2020.
- SUN, B.-f.; Hong, Z.; Lü, Y.-z.; Fei, L.; WANG, X.-k.J.J.o.i.a. The effects of nitrogen fertilizer application on methane and nitrous oxide emission/uptake in Chinese croplands. 2016, 15, 440-450.
- Xu, X.; Wu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Xiong, Z.J.S.r. Effects of nitrogen and biochar amendment on soil methane concentration profiles and diffusion in a rice-wheat annual rotation system. 2016, 6, 1-13.
- Nunes-Nesi, A.; Fernie, A.R.; Stitt, M.J.M.p. Metabolic and signaling aspects underpinning the regulation of plant carbon nitrogen interactions. 2010, 3, 973-996.
- Stokstad, E. The nitrogen fix. 2016.
- Tokarz, E.; Urban, D.J.J.o.E.E. Soil redox potential and its impact on microorganisms and plants of wetlands. 2015, 16, 20--30.
- Wilmoth, J.L.; Schaefer, J.K.; Schlesinger, D.R.; Roth, S.W.; Hatcher, P.G.; Shoemaker, J.K.; Zhang, X.J.G.C.B. The role of oxygen in stimulating methane production in wetlands. 2021, 27, 5831-5847.
- Morard, P.; Silvestre, J.J.P. ; soil. Plant injury due to oxygen deficiency in the root environment of soilless culture: a review. 1996, 184, 243–254. [Google Scholar]
- Duyen, D.V.; Kwon, Y.; Kabange, N.R.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-M.; Kang, J.-W.; Park, H.; Cha, J.-K.; Cho, J.-H.; Shin, D.J.P. Novel QTL Associated with Aerenchyma-Mediated Radial Oxygen Loss (ROL) in Rice (Oryza sativa L. ) under Iron (II) Sulfide. 2022, 11, 788. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, Y.; Johnson-Beebout, S.; Buresh, R.J.A.i.a. Crop residue management for lowland rice-based cropping systems in Asia. 2008, 98, 117-199.
- Dobermann, A.; Fairhurst, T.J.B.C.I. Rice straw management. 2002, 16, 7-11.
- Singh, D.; Dhiman, S.K.; Kumar, V.; Babu, R.; Shree, K.; Priyadarshani, A.; Singh, A.; Shakya, L.; Nautiyal, A.; Saluja, S.J.A. Crop Residue Burning and Its Relationship between Health, Agriculture Value Addition, and Regional Finance. 2022, 13, 1405.
- Andini, A.; Bonnet, S.; Rousset, P.; Hasanudin, U.J.C.S. Impact of open burning of crop residues on air pollution and climate change in Indonesia. 2018, 115, 2259-2266.
- Romasanta, R.R.; Sander, B.O.; Gaihre, Y.K.; Alberto, M.C.; Gummert, M.; Quilty, J.; Castalone, A.G.; Balingbing, C.; Sandro, J.; Correa Jr, T.J.A., ecosystems; et al. How does burning of rice straw affect CH4 and N2O emissions? A comparative experiment of different on-field straw management practices. 2017, 239, 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Baggs, E.M.; Philippot, L. Microbial terrestrial pathways to nitrous oxide. Nitrous oxide and climate change 2010, 256. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, K.; Mary, B.; Renault, P.J.S.B. ; Biochemistry. Nitrous oxide production by nitrification and denitrification in soil aggregates as affected by O2 concentration. 2004, 36, 687–699. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal, R.C.; Wang, W.; Robertson, G.P.; Parton, W.J.J.S.R. Nitrous oxide emission from Australian agricultural lands and mitigation options: a review. 2003, 41, 165-195.
- Dalal, R.; Allen, D.; Livesley, S.; Richards, G.J.P. ; Soil. Magnitude and biophysical regulators of methane emission and consumption in the Australian agricultural, forest, and submerged landscapes: a review. 2008, 309, 43–76. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Sharma, P.; Shu, S.; Lin, T.; Ciais, P.; Tubiello, F.; Smith, P.; Campbell, N.; Jain, A. Global greenhouse gas emissions from animal-based foods are twice those of plant-based foods. Nature Food 2 (9): 724–732. 2021.
- Bridgham, S.D.; Cadillo-Quiroz, H.; Keller, J.K.; Zhuang, Q. Methane emissions from wetlands: biogeochemical, microbial, and modeling perspectives from local to global scales. Global change biology 2013, 19, 1325–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Shao, N.; Akinyemi, T.; Whitman, W.B. Methanogenesis. Current Biology 2018, 28, R727–R732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, G.P.; Gogarten, J.P. Evolution of acetoclastic methanogenesis in Methanosarcina via horizontal gene transfer from cellulolytic Clostridia. Journal of bacteriology 2008, 190, 1124–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveit, A.T.; Hestnes, A.G.; Robinson, S.L.; Schintlmeister, A.; Dedysh, S.N.; Jehmlich, N.; von Bergen, M.; Herbold, C.; Wagner, M.; Richter, A.J.P.o.t.N.A.o.S. Widespread soil bacterium that oxidizes atmospheric methane. 2019, 116, 8515-8524.
- Hanson, R.S.; Hanson, T.E.J.M.r. Methanotrophic bacteria. 1996, 60, 439-471.
- Kirschke, S.; Bousquet, P.; Ciais, P.; Saunois, M.; Canadell, J.G.; Dlugokencky, E.J.; Bergamaschi, P.; Bergmann, D.; Blake, D.R.; Bruhwiler, L.J.N.g. Three decades of global methane sources and sinks. 2013, 6, 813-823.
- Hink, L.; Nicol, G.W.; Prosser, J.I.J.E.m. Archaea produce lower yields of N2O than bacteria during aerobic ammonia oxidation in soil. 2017, 19, 4829-4837.
- Hink, L.; Lycus, P.; Gubry-Rangin, C.; Frostegård, Å.; Nicol, G.W.; Prosser, J.I.; Bakken, L.R.J.E.M. Kinetics of NH3-oxidation, NO-turnover, N2O-production and electron flow during oxygen depletion in model bacterial and archaeal ammonia oxidisers. 2017, 19, 4882-4896.
- Schmidt-Rohr, K.J.A.o. Oxygen is the high-energy molecule powering complex multicellular life: Fundamental corrections to traditional bioenergetics. 2020, 5, 2221-2233.
- Murrell, J. The aerobic methane oxidizing bacteria (methanotrophs). In Handbook of hydrocarbon and lipid microbiology; 2010.
- Reim, A.; Lüke, C.; Krause, S.; Pratscher, J.; Frenzel, P.J.T.I.j. One millimetre makes the difference: high-resolution analysis of methane-oxidizing bacteria and their specific activity at the oxic–anoxic interface in a flooded paddy soil. 2012, 6, 2128-2139.
- Stein, L.Y.; Roy, R.; Dunfield, P.F.J.e. Aerobic methanotrophy and nitrification: processes and connections. 2012.
- Walkiewicz, A.; Brzezińska, M.; Bieganowski, A.J.B.; Soils, F.o. Methanotrophs are favored under hypoxia in ammonium-fertilized soils. 2018, 54, 861-870.
- Ravishankara, A.; Daniel, J.S.; Portmann, R.W.J.s. Nitrous oxide (N2O): the dominant ozone-depleting substance emitted in the 21st century. 2009, 326, 123-125.
- Thomson, A.J.; Giannopoulos, G.; Pretty, J.; Baggs, E.M.; Richardson, D.J. Biological sources and sinks of nitrous oxide and strategies to mitigate emissions. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2012, 367, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bange, H.W.; Freing, A.; Kock, A.; Löscher, C.R. Marine pathways to nitrous oxide. Nitrous oxide and climate change 2010, 2, 36–62. [Google Scholar]
- Inatomi, M.; Hajima, T.; Ito, A.J.P.o. Fraction of nitrous oxide production in nitrification and its effect on total soil emission: A meta-analysis and global-scale sensitivity analysis using a process-based model. 2019, 14, e0219159.
- Liu, R.; Hu, H.; Suter, H.; Hayden, H.L.; He, J.; Mele, P.; Chen, D.J.F.i.m. Nitrification is a primary driver of nitrous oxide production in laboratory microcosms from different land-use soils. 2016, 7, 1373.
- Codispoti, L.; Christensen, J. Nitrification, denitrification and nitrous oxide cycling in the eastern tropical South Pacific Ocean. Marine chemistry 1985, 16, 277–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Buitenhuis, E.; Suntharalingam, P.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Ward, B.B. Global nitrous oxide production determined by oxygen sensitivity of nitrification and denitrification. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 2018, 32, 1790–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, D.J.; Kerkhof, L.J. Nitrous oxide reductase (nosZ) gene-specific PCR primers for detection of denitrifiers and three nosZ genes from marine sediments. FEMS Microbiology Letters 1998, 162, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwman, A.; Stehfest, E.; van Kessel, C. Nitrous oxide emissions from the nitrogen cycle in arable agriculture: estimation and mitigation. Nitrous oxide and climate change 2010, 85–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Q.; Babbin, A.R.; Jayakumar, A.; Oleynik, S.; Ward, B.B.J.G.R.L. Nitrous oxide production by nitrification and denitrification in the Eastern Tropical South Pacific oxygen minimum zone. 2015, 42, 10,755-710,764.
- Wrage, N.; Velthof, G.L.; Van Beusichem, M.L.; Oenema, O.J.S.b. ; Biochemistry. Role of nitrifier denitrification in the production of nitrous oxide. 2001, 33, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Mueller, C.; Cai, Z.J.S.B. ; Biochemistry. Heterotrophic nitrification of organic N and its contribution to nitrous oxide emissions in soils. 2015, 84, 199–209. [Google Scholar]
- Livesley, S.; Kiese, R.; Graham, J.; Weston, C.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Arndt, S.J.P. ; Soil. Trace gas flux and the influence of short-term soil water and temperature dynamics in Australian sheep grazed pastures of differing productivity. 2008, 309, 89–103. [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen, C.J.; Elberling, B.J.S.B. ; Biochemistry. Effects of flooding-induced N2O production, consumption and emission dynamics on the annual N2O emission budget in wetland soil. 2012, 53, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Mørkved, P.T.; Dörsch, P.; Bakken, L.R.J.S.B. ; Biochemistry. The N2O product ratio of nitrification and its dependence on long-term changes in soil pH. 2007, 39, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar]
- de Klein, C.A.; Eckard, R.J.; van der Weerden, T.J. Nitrous oxide emissions from the nitrogen cycle in livestock agriculture: estimation and mitigation. Nitrous oxide and climate change 2010, 107–144. [Google Scholar]
- Conen, F.; Neftel, A. Nitrous oxide emissions from land-use and land-management change. Nitrous Oxide and Climate Change 2010, 143–159. [Google Scholar]
- Well, R.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Indirect emissions of nitrous oxide from nitrogen deposition and leaching of agricultural nitrogen. Nitrous Oxide and Climate Change (ed Smith K), 2010; 162, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Gubry-Rangin, C.; Nicol, G.W.; Prosser, J.I.J.F.m.e. Archaea rather than bacteria control nitrification in two agricultural acidic soils. 2010, 74, 566-574.
- Stein, L.Y.J.C.o.i.c.b. Insights into the physiology of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms. 2019, 49, 9-15.
- Di, H.J.; Cameron, K.C.; Shen, J.-P.; Winefield, C.S.; O’Callaghan, M.; Bowatte, S.; He, J.-Z.J.N.G. Nitrification driven by bacteria and not archaea in nitrogen-rich grassland soils. 2009, 2, 621-624.
- Di, H.J.; Cameron, K.C.; Sherlock, R.R.; Shen, J.-P.; He, J.-Z.; Winefield, C.S.J.J.o.S. ; Sediments. Nitrous oxide emissions from grazed grassland as affected by a nitrification inhibitor, dicyandiamide, and relationships with ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea. 2010, 10, 943–954. [Google Scholar]
- Treusch, A.H.; Leininger, S.; Kletzin, A.; Schuster, S.C.; Klenk, H.P.; Schleper, C.J.E.m. Novel genes for nitrite reductase and Amo-related proteins indicate a role of uncultivated mesophilic crenarchaeota in nitrogen cycling. 2005, 7, 1985-1995.
- Leininger, S.; Urich, T.; Schloter, M.; Schwark, L.; Qi, J.; Nicol, G.W.; Prosser, J.I.; Schuster, S.; Schleper, C.J.N. Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. 2006, 442, 806-809.
- Offre, P.; Prosser, J.I.; Nicol, G.W.J.F.M.E. Growth of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in soil microcosms is inhibited by acetylene. 2009, 70, 99-108.
- He, J.z.; Shen, J.p.; Zhang, L.m.; Zhu, Y.g.; Zheng, Y.m.; Xu, M.g.; Di, H.J.E.m. Quantitative analyses of the abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea of a Chinese upland red soil under long-term fertilization practices. 2007, 9, 2364-2374.
- Shen, J.p.; Zhang, L.m.; Zhu, Y.g.; Zhang, J.b.; He, J.z.J.E.M. Abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea communities of an alkaline sandy loam. 2008, 10, 1601-1611.
- Freitag, A.; Rudert, M.; Bock, E.J.F.M.L. Growth of Nitrobacter by dissimilatoric nitrate reduction. 1987, 48, 105-109.
- Daims, H.; Lebedeva, E.V.; Pjevac, P.; Han, P.; Herbold, C.; Albertsen, M.; Jehmlich, N.; Palatinszky, M.; Vierheilig, J.; Bulaev, A.J.N. Complete nitrification by Nitrospira bacteria. 2015, 528, 504-509.
- Van Kessel, M.A.; Speth, D.R.; Albertsen, M.; Nielsen, P.H.; Op den Camp, H.J.; Kartal, B.; Jetten, M.S.; Lücker, S.J.N. Complete nitrification by a single microorganism. 2015, 528, 555-559.
- Zou, J.; Huang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Liu, S.; Shen, Q.; Pan, G.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Q.J.G.C.B. Changes in fertilizer-induced direct N2O emissions from paddy fields during rice-growing season in China between 1950s and 1990s. 2009, 15, 229-242.
- Ma, J.; Li, X.; Xu, H.; Han, Y.; Cai, Z.; Yagi, K.J.S.R. Effects of nitrogen fertiliser and wheat straw application on CH4 and N2O emissions from a paddy rice field. 2007, 45, 359-367.
- Davidson, E.A.J.N.G. The contribution of manure and fertilizer nitrogen to atmospheric nitrous oxide since 1860. 2009, 2, 659-662.
- Syakila, A.; Kroeze, C.J.G.g.m. ; management. The global nitrous oxide budget revisited. 2011, 1, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Prather, M.J.; Holmes, C.D.; Hsu, J.J.G.R.L. Reactive greenhouse gas scenarios: Systematic exploration of uncertainties and the role of atmospheric chemistry. 2012, 39. 39.
- Reay, D.S.; Grace, J. Carbon dioxide: importance, sources and sinks. In Greenhouse gas sinks; CABI Wallingford UK: 2007; pp. 1-10.
- Xu, X.; Sharma, P.; Shu, S.; Lin, T.-S.; Ciais, P.; Tubiello, F.N.; Smith, P.; Campbell, N.; Jain, A.K.J.N.F. Global greenhouse gas emissions from animal-based foods are twice those of plant-based foods. 2021, 2, 724-732.
- Chang, J.; Ciais, P.; Gasser, T.; Smith, P.; Herrero, M.; Havlík, P.; Obersteiner, M.; Guenet, B.; Goll, D.S.; Li, W.J.N.C. Climate warming from managed grasslands cancels the cooling effect of carbon sinks in sparsely grazed and natural grasslands. 2021, 12, 118.
- Adopted, I.J.I.G. , Szwitzerland. Climate change 2014 synthesis report. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Poore, J.; Nemecek, T.J.S. Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers. 2018, 360, 987-992.
- Casper, J.K. Agriculture: the food we grow and animals we raise; Infobase Publishing: 2007.
- Rakotoson, T.; Dusserre, J.; Letourmy, P.; Frouin, J.; Ratsimiala, I.R.; Rakotoarisoa, N.V.; Vom Brocke, K.; Ramanantsoanirina, A.; Ahmadi, N.; Raboin, L.-M.J.R.S. Genome-wide association study of nitrogen use efficiency and agronomic traits in upland rice. 2021, 28, 379-390.
- Bandyopadhyay, T.; Swarbreck, S.M.; Jaiswal, V.; Maurya, J.; Gupta, R.; Bentley, A.R.; Griffiths, H.; Prasad, M.J.J.o.A.R. GWAS identifies genetic loci underlying nitrogen responsiveness in the climate resilient C4 model Setaria italica (L. ). 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhatar, J.; Goyal, A.; Kaur, N.; Atri, C.; Mittal, M.; Singh, M.P.; Kaur, R.; Rialch, I.; Banga, S.S.J.S.r. Genome wide association analyses to understand genetic basis of flowering and plant height under three levels of nitrogen application in Brassica juncea (L. ) Czern & Coss. 2021, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Nazish, T.; Arshad, M.; Jan, S.U.; Javaid, A.; Khan, M.H.; Naeem, M.A.; Baber, M.; Ali, M.J.T.R. Transporters and transcription factors gene families involved in improving nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) and assimilation in rice (Oryza sativa L. ). 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Su, Q.; Nian, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, M.; Dong, G.; Hu, J.; Wang, R.; Wei, C.; Li, G.J.M.P. The Ghd7 transcription factor represses ARE1 expression to enhance nitrogen utilization and grain yield in rice. 2021, 14, 1012-1023.
- Han, M.-L.; Lv, Q.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, C.-X.; Tan, R.-J.; Wang, Y.-L.; Zhong, L.-Y.; Gao, Y.-Q.; Chao, Z.-F.J.M.P. Decreasing nitrogen assimilation under drought stress by suppressing DST-mediated activation of Nitrate Reductase 1. 2 in rice. 2022, 15, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chu, C.J.M.P. Nitrogen-use divergence between indica and japonica rice: variation at nitrate assimilation. 2020, 13, 6-7.
- Teng, W.; He, X.; Tong, Y.J.P. Genetic Control of Efficient Nitrogen Use for High Yield and Grain Protein Concentration in Wheat: A Review. 2022, 11, 492.
- Kabange, N.R.; Park, S.-Y.; Shin, D.; Lee, S.-M.; Jo, S.-M.; Kwon, Y.; Cha, J.-K.; Song, Y.-C.; Ko, J.-M.; Lee, J.-H.J.A. Identification of a novel QTL for chlorate resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L. ). 2020, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anas, M.; Liao, F.; Verma, K.K.; Sarwar, M.A.; Mahmood, A.; Chen, Z.-L.; Li, Q.; Zeng, X.-P.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.-R. Fate of nitrogen in agriculture and environment: agronomic, eco-physiological and molecular approaches to improve nitrogen use efficiency. Biological Research 2020, 53, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Shen, L.; Dai, L.; He, J.; Yang, L.; Li, P.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, Q.J.T.C.J. Genome-wide association study and transcriptome analysis reveal new QTL and candidate genes for nitrogen-deficiency tolerance in rice. 2022.
- Fan, X.; Naz, M.; Fan, X.; Xuan, W.; Miller, A.J.; Xu, G.J.J.o.E.B. Plant nitrate transporters: from gene function to application. 2017, 68, 2463-2475.
- Lea, P.J.; Miflin, B.J.J.P.P. ; Biochemistry. Glutamate synthase and the synthesis of glutamate in plants. 2003, 41, 555–564. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, L.R.V.; Mailapalli, D.R.J.C.i.S.S.; Analysis, P. Evaluation of nitrogen fertilization patterns using DSSAT for enhancing grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in rice. 2018, 49, 1401-1417.
- Nakidakida, T.; Hayashi, H. Nitrogen recovery and nitrogen use efficiency of potatoes in an integrated compost fertilization system in an Andosol soil. In Proceedings of the III International Symposium on Organic Matter Management and Compost Use in Horticulture 1146; 2015; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Hu, B.; Chu, C.J.J.o.E.B. Nitrogen use efficiency in crops: lessons from Arabidopsis and rice. 2017, 68, 2477-2488.
- Duan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, L.; Fan, X.; Xu, G.; Shen, Q.J.A.o.B. Responses of rice cultivars with different nitrogen use efficiency to partial nitrate nutrition. 2007, 99, 1153-1160.
- Djaman, K.; Mel, V.; Ametonou, F.; El-Namaky, R.; Diallo, M.; Koudahe, K.J.J.o.A.S.; Research, F. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer dose and application timing on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of irrigated hybrid rice under semi-arid conditions. 2018.
- Gallais, A.; Hirel, B.J.J.o.e.b. An approach to the genetics of nitrogen use efficiency in maize. 2004, 55, 295-306.
- Liu, X.; Hu, B.; Chu, C.J.J.o.G. ; Genomics. Nitrogen assimilation in plants: current status and future prospects. 2021.
- Hirel, B.; Tétu, T.; Lea, P.J.; Dubois, F.J.S. Improving nitrogen use efficiency in crops for sustainable agriculture. 2011, 3, 1452-1485.
- Yamaya, T.; Obara, M.; Nakajima, H.; Sasaki, S.; Hayakawa, T.; Sato, T.J.J.o.e.b. Genetic manipulation and quantitative-trait loci mapping for nitrogen recycling in rice. 2002, 53, 917-925.
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, L.; Shen, C.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Yu, J.; Yang, N.; He, Y.J.T.P.C. Natural allelic variation in a modulator of auxin homeostasis improves grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in rice. 2021, 33, 566-580.
- Kiba, T.; Kudo, T.; Kojima, M.; Sakakibara, H.J.J.o.e.b. Hormonal control of nitrogen acquisition: roles of auxin, abscisic acid, and cytokinin. 2011, 62, 1399-1409.
- Séguéla, M.; Briat, J.F.; Vert, G.; Curie, C.J.T.P.J. Cytokinins negatively regulate the root iron uptake machinery in Arabidopsis through a growth-dependent pathway. 2008, 55, 289-300.
- Maruyama-Nakashita, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Yamaya, T.; Takahashi, H.J.T.P.J. A novel regulatory pathway of sulfate uptake in Arabidopsis roots: implication of CRE1/WOL/AHK4-mediated cytokinin-dependent regulation. 2004, 38, 779-789.
- Wagner, B.M.; Beck, E.J.P. Cytokinins in the perennial herb Urtica dioica L. as influenced by its nitrogen status. 1993, 190, 511–518. [Google Scholar]
- Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; Martin, A.C.; Solano, R.; Rubio, V.; Leyva, A.; Paz-Ares, J.J.T.P.J. Mutations at CRE1 impair cytokinin-induced repression of phosphate starvation responses in Arabidopsis. 2002, 32, 353-360.
- Nacry, P.; Canivenc, G.; Muller, B.; Azmi, A.; Van Onckelen, H.; Rossignol, M.; Doumas, P.J.P.P. A role for auxin redistribution in the responses of the root system architecture to phosphate starvation in Arabidopsis. 2005, 138, 2061-2074.
- Vidal, E.A.; Araus, V.; Lu, C.; Parry, G.; Green, P.J.; Coruzzi, G.M.; Gutiérrez, R.A.J.P.o.t.N.A.o.S. Nitrate-responsive miR393/AFB3 regulatory module controls root system architecture in Arabidopsis thaliana. 2010, 107, 4477-4482.
- Chen, K.-E.; Chen, H.-Y.; Tseng, C.-S.; Tsay, Y.-F. Improving nitrogen use efficiency by manipulating nitrate remobilization in plants. Nature Plants 2020, 6, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, Y.; Yanagisawa, S. Transcription factor-based genetic engineering to increase nitrogen use efficiency. In Engineering Nitrogen Utilization in Crop Plants; Springer: 2018; pp. 37-55.
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.S.; Xia, J.Q.; Alfatih, A.; Song, Y.; Huang, Y.J.; Wan, G.Y.; Sun, L.Q.; Tang, H.; Liu, Y. Rice NIN-LIKE PROTEIN 4 plays a pivotal role in nitrogen use efficiency. Plant Biotechnology Journal 2021, 19, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Ding, G.; Yang, N.; White, P.J.; Ye, X.; Cai, H.; Lu, J.; Shi, L.; Xu, F. Comparative genome and transcriptome analysis unravels key factors of nitrogen use efficiency in Brassica napus L. Plant, cell & environment 2020, 43, 712–731. [Google Scholar]
- Heuermann, D.; Hahn, H.; Von Wirén, N.J.F.i.p.s. Seed yield and nitrogen efficiency in oilseed rape after ammonium nitrate or urea fertilization. 2021, 11, 2197.
- Ruffel, S.; Krouk, G.; Ristova, D.; Shasha, D.; Birnbaum, K.D.; Coruzzi, G.M.J.P.o.t.N.A.o.S. Nitrogen economics of root foraging: transitive closure of the nitrate–cytokinin relay and distinct systemic signaling for N supply vs. demand. 2011, 108, 18524–18529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Li, Z.; Mao, Y.; Struik, P.C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.J.P.S. Roles of nitrogen and cytokinin signals in root and shoot communications in maximizing of plant productivity and their agronomic applications. 2018, 274, 320-331.
- Azarakhsh, M.; Lebedeva, M.A.; Lutova, L.A.J.F.i.P.S. Identification and expression analysis of Medicago truncatula isopentenyl transferase genes (IPTs) involved in local and systemic control of nodulation. 2018, 9, 304. 9.
- Lin, J.; Roswanjaya, Y.P.; Kohlen, W.; Stougaard, J.; Reid, D.J.N.c. Nitrate restricts nodule organogenesis through inhibition of cytokinin biosynthesis in Lotus japonicus. 2021, 12, 1-12.
- Sasaki, T.; Suzaki, T.; Soyano, T.; Kojima, M.; Sakakibara, H.; Kawaguchi, M.J.N.c. Shoot-derived cytokinins systemically regulate root nodulation. 2014, 5, 1-9. 5.
- Singh, B.N.; Dwivedi, P.; Sarma, B.K.; Singh, G.S.; Singh, H.B.J.B. A novel function of N-signaling in plants with special reference to Trichoderma interaction influencing plant growth, nitrogen use efficiency, and cross talk with plant hormones. 2019, 9, 1-13.
- Mundim, F.M.; Pringle, E.G.J.F.i.p.s. Whole-plant metabolic allocation under water stress. 2018, 9, 852. 9.
- Rolly, N.K.; Yun, B.-W.J.P. Regulation of Nitrate (NO3) Transporters and Glutamate Synthase-Encoding Genes under Drought Stress in Arabidopsis: The Regulatory Role of AtbZIP62 Transcription Factor. 2021, 10, 2149.
- Rolly, N.K.; Mun, B.-G.; Yun, B.-W.J.G. Insights into the Transcriptional Regulation of Branching Hormonal Signaling Pathways Genes under Drought Stress in Arabidopsis. 2021, 12, 298.
- Sun, L.; Di, D.-W.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Kronzucker, H.J.; Shi, W.J.J.o.P.P. Transcriptome analysis of rice (Oryza sativa L. ) in response to ammonium resupply reveals the involvement of phytohormone signaling and the transcription factor OsJAZ9 in reprogramming of nitrogen uptake and metabolism. 2020, 246, 153137. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, L.; Chen, D.; Min, D.; Li, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, M.; Ma, Y. AtTGA4, a bZIP transcription factor, confers drought resistance by enhancing nitrate transport and assimilation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2015, 457, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.J. Plant Respiration and Internal Oxygen.
- Armstrong, W.; Armstrong, J. Plant internal oxygen transport (diffusion and convection) and measuring and modelling oxygen gradients. In Low-oxygen stress in plants; Springer: 2014; pp. 267-297.
- Kosmacz, M.; Weits, D.A. Oxygen perception in plants. In Low-Oxygen Stress in Plants; Springer: 2014; pp. 3-17.
- Guan, B.; Lin, Z.; Liu, D.; Li, C.; Zhou, Z.; Mei, F.; Li, J.; Deng, X.J.F.i.p.s. Effect of waterlogging-induced autophagy on programmed cell death in Arabidopsis roots. 2019, 10, 468.
- Armstrong, W. Advances in Botanical Research, Volume 7. Aeration in higher plants. Woolhouse HW. 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Sifton, H.J.T.B.R. Air-space tissue in plants. 1945, 11, 108-143.
- Roland, J.J.J.o.C.S. Cell wall differentiation and stages involved with intercellular gas space opening. 1978, 32, 325-336.
- Jeffree, C.; Dale, J.; Fry, S.J.P. The genesis of intercellular spaces in developing leaves ofPhaseolus vulgaris L. 1986, 132, 90-98.
- RAVEN, J.A.J.A.o.B. Into the voids: the distribution, function, development and maintenance of gas spaces in plants. 1996, 78, 137-142.
- Wegner, L.H. Oxygen transport in waterlogged plants. In Waterlogging signalling and tolerance in plants; Springer: 2010; pp. 3-22.
- Lai, W.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.-H.J.E.E. Radial oxygen loss, photosynthesis, and nutrient removal of 35 wetland plants. 2012, 39, 24-30.
- Mohammed, U.; Caine, R.; Atkinson, J.; Harrison, E.; Wells, D.; Chater, C.; Gray, J.; Swarup, R.; Murchie, E.J.S.r. Rice plants overexpressing OsEPF1 show reduced stomatal density and increased root cortical aerenchyma formation. 2019, 9, 1-13.
- Scheehle, E.A.; Kruger, D.J.T.E.J. Global anthropogenic methane and nitrous oxide emissions. 2006.
- Denmead, O.; Freney, J.; Simpson, J.J.S.S.S.o.A.J. Nitrous oxide emission during denitrification in a flooded field. 1979, 43, 716-718.
- Bodelier, P.L.; Pérez, G.; Veraart, A.J.; Krause, S. Methanotroph ecology, environmental distribution and functioning. In Methanotrophs; Springer: 2019; pp. 1-38.
- Trotsenko, Y.A.; Murrell, J.C.J.A.i.a.m. Metabolic aspects of aerobic obligate methanotrophy⋆. 2008, 63, 183-229.
- Saggar, S.; Tate, K.; Giltrap, D.; Singh, J.J.P. ; Soil. Soil-atmosphere exchange of nitrous oxide and methane in New Zealand terrestrial ecosystems and their mitigation options: a review. 2008, 309, 25–42. [Google Scholar]
- Schütz, H.; Seiler, W.; Rennenberg, H.J.S. ; effect., t.g. Soil and land use related sources and sinks of methane (CH4) in the context of the global methane budget. 1990, 269-285.
- Horwath, W. Greenhouse gas emissions from rice cropping systems. In Understanding greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural management; ACS Publications: 2011; pp. 67-89.
- Colmer, T.D.; Kotula, L.; Malik, A.I.; Takahashi, H.; Konnerup, D.; Nakazono, M.; Pedersen, O.J.P. , Cell; Environment. Rice acclimation to soil flooding: low concentrations of organic acids can trigger a barrier to radial oxygen loss in roots. 2019, 42, 2183–2197. [Google Scholar]
- Ejiri, M.; Shiono, K.J.F.i.p.s. Prevention of radial oxygen loss is associated with exodermal suberin along adventitious roots of annual wild species of Echinochloa. 2019, 10, 254.
- Abiko, T.; Kotula, L.; Shiono, K.; Malik, A.I.; Colmer, T.D.; Nakazono, M.J.P. , Cell; Environment. Enhanced formation of aerenchyma and induction of a barrier to radial oxygen loss in adventitious roots of Zea nicaraguensis contribute to its waterlogging tolerance as compared with maize (Zea mays ssp. mays). 2012, 35, 1618–1630. [Google Scholar]
- Ejiri, M.; Fukao, T.; Miyashita, T.; Shiono, K.J.B.s. A barrier to radial oxygen loss helps the root system cope with waterlogging-induced hypoxia. 2021, 71, 40-50.
- Peralta Ogorek, L.L.; Pellegrini, E.; Pedersen, O.J.N.P. Novel functions of the root barrier to radial oxygen loss–radial diffusion resistance to H2 and water vapour. 2021, 231, 1365-1376.
- Foyer, C.H.; Noctor, G.; Hodges, M.J.J.o.E.B. Respiration and nitrogen assimilation: targeting mitochondria-associated metabolism as a means to enhance nitrogen use efficiency. 2011, 62, 1467-1482.
- Maier, R.J. Nitrogen fixation and respiration: Two processes linked by the energetic demands of Nitrogenase. In Respiration in archaea and bacteria; Springer: 2004; pp. 101-120.
- Weger, H.G.; Turpin, D.H.J.P.p. Mitochondrial respiration Can support NO3− and NO2− reduction during photosynthesis: interactions between photosynthesis, respiration, and N assimilation in the N-limited green alga Selenastrum minutum. 1989, 89, 409-415.
- De Laulanié, H.J.T. Intensive rice farming in Madagascar. 2011, 29, 183-187.
- Sinclair, T.R.J.R.T. Agronomic UFOs waste valuable scientific resources. 2004, 3. 3.
- Pereira-Mora, L.; Terra, J.A.; Fernández-Scavino, A.J.A.S.E. Methanogenic community linked to organic acids fermentation from root exudates are affected by rice intensification in rotational soil systems. 2022, 176, 104498.
- Chan, K.Y.; Xu, Z.J.B.f.e.m.s. ; technology. Biochar: nutrient properties and their enhancement. 2009, 1, 67–84. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, J.; Cowie, A.; Masiello, C.A.; Kammann, C.; Woolf, D.; Amonette, J.E.; Cayuela, M.L.; Camps-Arbestain, M.; Whitman, T.J.N.G. Biochar in climate change mitigation. 2021, 14, 883-892.
- Roe, S.; Streck, C.; Beach, R.; Busch, J.; Chapman, M.; Daioglou, V.; Deppermann, A.; Doelman, J.; Emmet-Booth, J.; Engelmann, J.J.G.C.B. Land-based measures to mitigate climate change: Potential and feasibility by country. 2021, 27, 6025-6058.
- Yang, W.; Feng, G.; Miles, D.; Gao, L.; Jia, Y.; Li, C.; Qu, Z.J.S.o.t.T.E. Impact of biochar on greenhouse gas emissions and soil carbon sequestration in corn grown under drip irrigation with mulching. 2020, 729, 138752.
- Lyu, H.; Zhang, H.; Chu, M.; Zhang, C.; Tang, J.; Chang, S.X.; Mašek, O.; Ok, Y.S.J.L.D. ; Development. Biochar affects greenhouse gas emissions in various environments: A critical review. 2022, 33, 3327–3342. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Xie, Z.; Zheng, J.; Liu, Q.; Bei, Q.; Zhu, J.J.E.J.o.S.S. Effects of biochar application on greenhouse gas emissions, carbon sequestration and crop growth in coastal saline soil. 2015, 66, 329-338.
- Joseph, S.; Lehmann, J.J.B.f.e.m.S. ; technology. Biochar for environmental management: an introduction. 2015, 1.
- Lehmann, J.; Czimczik, C.; Laird, D.; Sohi, S.J.B.f.e.m.s. ; technology. Stability of biochar in soil. 2009, 183–206. [Google Scholar]
- Major, J.; Steiner, C.; Downie, A.; Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S.J.B.f.e.m.S. ; technology. Biochar effects on nutrient leaching. 2009, 271. [Google Scholar]
- Turunen, M.; Hyväluoma, J.; Heikkinen, J.; Keskinen, R.; Kaseva, J.; Hannula, M.; Rasa, K.J.B.E. Quantifying the pore structure of different biochars and their impacts on the water retention properties of Sphagnum moss growing media. 2020, 191, 96-106.
- Gaunt, J.; Cowie, A.J.B.f.e.m.S. ; technology. Biochar, greenhouse gas accounting and emissions trading. 2009, 317-340.
- Smernik, R.J.J.B.f.e.m.s. ; technology. Biochar and sorption of organic compounds. 2009, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Thies, J.E.; Rillig, M.C.J.B.f.e.m.S. ; technology. Characteristics of biochar: biological properties. 2009, 1, 85–105. [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca, T.H.; Gundale, M.J.; MacKenzie, M.D.; Jones, D.L.J.B.f.e.m.s. , technology; implementation. Biochar effects on soil nutrient transformations. 2015, 2, 421–454. [Google Scholar]
- Rondon, M.A.; Molina, D.; Hurtado, M.; Ramirez, J.; Lehmann, J.; Major, J.; Amezquita, E. Enhancing the productivity of crops and grasses while reducing greenhouse gas emissions through bio-char amendments to unfertile tropical soils. In Proceedings of the 18th world congress of soil science; 2006; pp. 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yanai, Y.; Toyota, K.; Okazaki, M.J.S.s.; nutrition, p. Effects of charcoal addition on N2O emissions from soil resulting from rewetting air-dried soil in short-term laboratory experiments. 2007, 53, 181-188.
- Joseph, S.; Cowie, A.L.; Van Zwieten, L.; Bolan, N.; Budai, A.; Buss, W.; Cayuela, M.L.; Graber, E.R.; Ippolito, J.A.; Kuzyakov, Y.J.G.B. How biochar works, and when it doesn't: A review of mechanisms controlling soil and plant responses to biochar. 2021, 13, 1731-1764.
- Joseph, S.; Peacocke, C.; Lehmann, J.; Munroe, P.J.B.f.e.m.s. ; technology. Developing a biochar classification and test methods. 2009, 1, 107–126. [Google Scholar]
- Borchard, N.; Schirrmann, M.; Cayuela, M.L.; Kammann, C.; Wrage-Mönnig, N.; Estavillo, J.M.; Fuertes-Mendizábal, T.; Sigua, G.; Spokas, K.; Ippolito, J.A.J.S.o.t.T.E. Biochar, soil and land-use interactions that reduce nitrate leaching and N2O emissions: a meta-analysis. 2019, 651, 2354-2364.
- Riley, W.; Ortiz-Monasterio, I.; Matson, P.J.N.C.i.A. Nitrogen leaching and soil nitrate, nitrite, and ammonium levels under irrigated wheat in Northern Mexico. 2001, 61, 223-236.
- Song, X.; Pan, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.J.E.H. ; Sustainability. Effects of biochar application on fluxes of three biogenic greenhouse gases: a meta-analysis. 2016, 2, e01202. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, M.; Du, Z.; Zhou, G.; Shao, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Hosseini Bai, S.J.G.B. Effects of biochar application on soil greenhouse gas fluxes: A meta-analysis. 2017, 9, 743-755.
- Kalu, S.; Kulmala, L.; Zrim, J.; Peltokangas, K.; Tammeorg, P.; Rasa, K.; Kitzler, B.; Pihlatie, M.; Karhu, K.J.F.i.E.S. Potential of biochar to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and increase nitrogen use efficiency in boreal arable soils in the long-term. 2022, 630.
- Sass, R.L.; Cicerone, R.J.J.P.o.t.N.A.o.S. Photosynthate allocations in rice plants: Food production or atmospheric methane? 2002, 99, 11993-11995.
- van Der Gon, H.D.; Kropff, M.; Van Breemen, N.; Wassmann, R.; Lantin, R.; Aduna, E.; Corton, T.; Van Laar, H.J.P.o.t.N.A.o.S. Optimizing grain yields reduces CH4 emissions from rice paddy fields. 2002, 99, 12021-12024.
- Su, J.; Hu, C.; Yan, X.; Jin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Guan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, D.; Jansson, C.; Wang, F.J.N. Expression of barley SUSIBA2 transcription factor yields high-starch low-methane rice. 2015, 523, 602-606.
- Stein, L.Y.; Klotz, M.G.J.B.S.T. Nitrifying and denitrifying pathways of methanotrophic bacteria. 2011, 39, 1826-1831.
- Canarini, A.; Kaiser, C.; Merchant, A.; Richter, A.; Wanek, W.J.F.i.P.S. Root exudation of primary metabolites: mechanisms and their roles in plant responses to environmental stimuli. 2019, 10, 157.
- Rougier, M.J.P.C.I.E.C. Secretory activity of the root cap. 1981, 542-574.
- Abbott, L.K.; Murphy, D.V. Soil biological fertility: a key to sustainable land use in agriculture; Springer Science & Business Media: 2003.
- Walker, T.S.; Bais, H.P.; Grotewold, E.; Vivanco, J.M.J.P.p. Root exudation and rhizosphere biology. 2003, 132, 44-51.
- Nardi, S.; Concheri, G.; Pizzeghello, D.; Sturaro, A.; Rella, R.; Parvoli, G.J.C. Soil organic matter mobilization by root exudates. 2000, 41, 653-658.
- Vives-Peris, V.; De Ollas, C.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; Pérez-Clemente, R.M.J.P.c.r. Root exudates: from plant to rhizosphere and beyond. 2020, 39, 3-17.
- De-la-Pena, C.; Badri, D.V.; Lei, Z.; Watson, B.S.; Brandao, M.M.; Silva-Filho, M.C.; Sumner, L.W.; Vivanco, J.M.J.J.o.B.C. Root secretion of defense-related proteins is development-dependent and correlated with flowering time. 2010, 285, 30654-30665.
- Chai, Y.N.; Schachtman, D.P.J.T.i.P.S. Root exudates impact plant performance under abiotic stress. 2022, 27, 80-91.
- Salem, M.A.; Wang, J.Y.; Al-Babili, S.J.F.i.P.S. Metabolomics of plant root exudates: From sample preparation to data analysis. 2022, 13, 5035.
- Narula, N.; Kothe, E.; Behl, R.K.J.J.o.A.B.; Quality, F. Role of root exudates in plant-microbe interactions. 2012, 82, 122-130.
- Kumar, R.; Bhatia, R.; Kukreja, K.; Behl, R.K.; Dudeja, S.S.; Narula, N.J.J.o.b.m. Establishment of Azotobacter on plant roots: chemotactic response, development and analysis of root exudates of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. ) and wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). 2007, 47, 436–439. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Wassmann, R.; Neue, H.; Huang, C.; Bueno, C.J.S.B. ; Biochemistry. Methanogenic responses to exogenous substrates in anaerobic rice soils. 2000, 32, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar]
- Moscôso, J.S.C.; Silva, L.S.d.; Pujol, S.B.; Giacomini, S.J.; Severo, F.F.; Marzari, L.B.; Molin, G.D.J.R.B.d.C.d.S. Methane emission induced by short-chain organic acids in lowland soil. 2019, 43. 43.
- Aulakh, M.S.; Wassmann, R.; Bueno, C.; Rennenberg, H.J.P. ; Soil. Impact of root exudates of different cultivars and plant development stages of rice (Oryza sativa L.) on methane production in a paddy soil. 2001, 230, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.R.; Rao, I.M.; Merchant, A.J.F.i.P.S. Source-sink relationships in crop plants and their influence on yield development and nutritional quality. 2018, 9, 1889.
- Andersen, C.P.J.N.p. Source–sink balance and carbon allocation below ground in plants exposed to ozone. 2003, 157, 213-228.
- Wingler, A.; Einig, W.; Schaeffer, C.; Wallenda, T.; Hampp, R.; Wallander, H.; NYLUND, J.E.J.N.p. Influence of different nutrient regimes on the regulation of carbon metabolism in Norway spruce [Picea abies (L. ) Karst.] seedlings. 1994, 128, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K.J.A.r.o.p.b. Carbohydrate-modulated gene expression in plants. 1996, 47, 509-540.
- Mathur, J.; Hülskamp, M.J.C.B. Microtubules and microfilaments in cell morphogenesis in higher plants. 2002, 12, R669-R676.
- Yao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, X.; Xie, B.; Mei, B.; Wang, R.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Zhu, J.J.P. ; Soil. Effects of organic matter incorporation on nitrous oxide emissions from rice-wheat rotation ecosystems in China. 2010, 327, 315–330. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, X.; Sass, R.L.J.G.b.c. A 3-year field measurement of methane and nitrous oxide emissions from rice paddies in China: Effects of water regime, crop residue, and fertilizer application. 2005, 19. 19.
- Eagle, A.J.; Bird, J.A.; Horwath, W.R.; Linquist, B.A.; Brouder, S.M.; Hill, J.E.; van Kessel, C.J.A.J. Rice yield and nitrogen utilization efficiency under alternative straw management practices. 2000, 92, 1096-1103.
- Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Xu, H.; Cai, Z.; Yagi, K.J.C. Effect of timing of joint application of hydroquinone and dicyandiamide on nitrous oxide emission from irrigated lowland rice paddy field. 2009, 75, 1417-1422.
- Akiyama, H.; Yan, X.; Yagi, K.J.G.C.B. Evaluation of effectiveness of enhanced-efficiency fertilizers as mitigation options for N2O and NO emissions from agricultural soils: meta-analysis. 2010, 16, 1837-1846.
- Majumdar, D.J.C.S. Methane and nitrous oxide emission from irrigated rice fields: proposed mitigation strategies. 2003, 1317-1326.
- Mahesh, M.; Mohini, M.J.A.i.D.R. Crop residues for sustainable livestock production. 2014, 1-2.
- Ritchie, H.; Rosado, P.; Roser, M.J.O.W.i.D. Meat and dairy production. 2017.
- Williams, P.J.N. ; Dietetics. Nutritional composition of red meat. 2007, 64, S113–S119. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, J.J.P.o.t.N.S. Milk as a source of lactose, vitamins and minerals. 1978, 37, 225-230.
- Shaheen, N.; Ahmed, M.K.; Islam, M.S.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Tukun, A.B.; Islam, S.; MA Rahim, A.T.J.E.s.; research, p. Health risk assessment of trace elements via dietary intake of ‘non-piscine protein source’foodstuffs (meat, milk and egg) in Bangladesh. 2016, 23, 7794-7806.
- McAfee, A.J.; McSorley, E.M.; Cuskelly, G.J.; Moss, B.W.; Wallace, J.M.; Bonham, M.P.; Fearon, A.M.J.M.s. Red meat consumption: An overview of the risks and benefits. 2010, 84, 1-13.
- Willett, W.C.; Ludwig, D.S.J.N.E.J.o.M. Milk and health. 2020, 382, 644-654.
- Tricarico, J.; de Haas, Y.; Hristov, A.; Kebreab, E.; Kurt, T.; Mitloehner, F.; Pitta, D.J.J.o.d.s. Symposium review: Development of a funding program to support research on enteric methane mitigation from ruminants. 2022.
- Nairobi., U.N.E.P.J. Nairobi., U.N.E.P.J. Emissions gap report 2022: The closing window—Climate crisis calls for rapid transformation of societies. 2022.
- Frank, S.; Beach, R.; Havlík, P.; Valin, H.; Herrero, M.; Mosnier, A.; Hasegawa, T.; Creason, J.; Ragnauth, S.; Obersteiner, M.J.N.c. Structural change as a key component for agricultural non-CO2 mitigation efforts. 2018, 9, 1060.
- Arndt, C.; Hristov, A.N.; Price, W.J.; McClelland, S.C.; Pelaez, A.M.; Cueva, S.F.; Oh, J.; Dijkstra, J.; Bannink, A.; Bayat, A.R.J.P.o.t.N.A.o.S. Full adoption of the most effective strategies to mitigate methane emissions by ruminants can help meet the 1. 5 C target by 2030 but not 2050. 2022, 119, e2111294119. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, G.J.A.N. Decreasing ruminal methane production through enhancing the sulfate reduction pathway. 2022.
- Haque, M.N.J.J.o.a.s. ; technology. Dietary manipulation: a sustainable way to mitigate methane emissions from ruminants. 2018, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Newbold, C.; El Hassan, S.; Wang, J.; Ortega, M.; Wallace, R.J.B.J.o.N. Influence of foliage from African multipurpose trees on activity of rumen protozoa and bacteria. 1997, 78, 237-249.
- Bodas, R.; Prieto, N.; García-González, R.; Andrés, S.; Giráldez, F.J.; López, S.J.A.F.S. ; Technology. Manipulation of rumen fermentation and methane production with plant secondary metabolites. 2012, 176, 78–93. [Google Scholar]
- Patra, A.K.; Saxena, J.J.A.v.L. Dietary phytochemicals as rumen modifiers: a review of the effects on microbial populations. 2009, 96, 363-375.
- Patra, A.; Saxena, J.J.N.r.r. The effect and mode of action of saponins on the microbial populations and fermentation in the rumen and ruminant production. 2009, 22, 204-219.
- Milich, L.J.G.E.C. The role of methane in global warming: where might mitigation strategies be focused? 1999, 9, 179-201.
- Benchaar, C.; Pomar, C.; Chiquette, J.J.C.J.o.A.S. Evaluation of dietary strategies to reduce methane production in ruminants: a modelling approach. 2001, 81, 563-574.
- Boadi, D.; Wittenberg, K.J.C.J.o.A.S. Methane production from dairy and beef heifers fed forages differing in nutrient density using the sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) tracer gas technique. 2002, 82, 201-206.
- Beauchemin, K.; Kreuzer, M.; O’mara, F.; McAllister, T.J.A.J.o.E.A. Nutritional management for enteric methane abatement: a review. 2008, 48, 21-27.
- Tamminga, S.; Bannink, A.; Dijkstra, J.; Zom, R. Feeding strategies to reduce methane loss in cattle; 1570-8616; Animal Sciences Group: 2007.
- O'mara, F.; Fitzgerald, J.; Murphy, J.; Rath, M.J.L.P.S. The effect on milk production of replacing grass silage with maize silage in the diet of dairy cows. 1998, 55, 79-87.
- Hassanat, F.; Gervais, R.; Julien, C.; Massé, D.; Lettat, A.; Chouinard, P.; Petit, H.; Benchaar, C.J.J.o.D.S. Replacing alfalfa silage with corn silage in dairy cow diets: Effects on enteric methane production, ruminal fermentation, digestion, N balance, and milk production. 2013, 96, 4553-4567.
- Martin, C.; Morgavi, D.P.; Doreau, M.J.A. Methane mitigation in ruminants: from microbe to the farm scale. 2010, 4, 351-365.
- Ferris, C.; Gordon, F.; Patterson, D.; Porter, M.; Yan, T.J.T.J.o.A.S. The effect of genetic merit and concentrate proportion in the diet on nutrient utilization by lactating dairy cows. 1999, 132, 483-490.
- Lovett, D.; Lovell, S.; Stack, L.; Callan, J.; Finlay, M.; Conolly, J.; O'Mara, F.J.L.P.S. Effect of forage/concentrate ratio and dietary coconut oil level on methane output and performance of finishing beef heifers. 2003, 84, 135-146.
- Johnson, K.A.; Johnson, D.E.J.J.o.a.s. Methane emissions from cattle. 1995, 73, 2483-2492.
- Murphy, M.; Baldwin, R.; Koong, L.J.J.o.A.S. Estimation of stoichiometric parameters for rumen fermentation of roughage and concentrate diets. 1982, 55, 411-421.
- Hindrichsen, I.; Wettstein, H.; Machmüller, A.; Jörg, B.; Kreuzer, M.J.E.m. ; assessment. Effect of the carbohydrate composition of feed concentratates on methane emission from dairy cows and their slurry. 2005, 107, 329–350. [Google Scholar]
- Hindrichsen, I.; Kreuzer, M.J.J.o.a.p.; nutrition, a. High methanogenic potential of sucrose compared with starch at high ruminal pH. 2009, 93, 61-65.
- Castillo, C.; Benedito, J.; Méndez, J.; Pereira, V.; Lopez-Alonso, M.; Miranda, M.; Hernández, J.J.A.F.S. ; Technology. Organic acids as a substitute for monensin in diets for beef cattle. 2004, 115, 101–116. [Google Scholar]
- McAllister, T.; Newbold, C.J.A.J.o.E.A. Redirecting rumen fermentation to reduce methanogenesis. 2008, 48, 7-13.
- Beauchemin, K.; McGinn, S.J.J.o.a.s. Methane emissions from beef cattle: Effects of fumaric acid, essential oil, and canola oil. 2006, 84, 1489-1496.
- Burt, S.J.I.j.o.f.m. Essential oils: their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—a review. 2004, 94, 223-253.
- Benchaar, C.; Calsamiglia, S.; Chaves, A.V.; Fraser, G.; Colombatto, D.; McAllister, T.A.; Beauchemin, K.A.J.A.F.S. ; Technology. A review of plant-derived essential oils in ruminant nutrition and production. 2008, 145, 209–228. [Google Scholar]
- Benchaar, C.; Greathead, H.J.A.F.S. ; Technology. Essential oils and opportunities to mitigate enteric methane emissions from ruminants. 2011, 166, 338–355. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, A.R.; Jouany, J.-P.; Newbold, J. Methane production by ruminants: its contribution to global warming. In Proceedings of the Annales de zootechnie; 2000; pp. 231–253. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, S.; McIntosh, F.; Wallace, R.; Newbold, C.J.A.F.S. ; Technology. Effect of adding acetogenic bacteria on methane production by mixed rumen microorganisms. 1999, 78, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- McAllister, T.; Beauchemin, K.; Alazzeh, A.; Baah, J.; Teather, R.; Stanford, K.J.C.J.o.A.S. The use of direct fed microbials to mitigate pathogens and enhance production in cattle. 2011, 91, 193-211.
- Newbold, C.J.; Rode, L. Dietary additives to control methanogenesis in the rumen. In Proceedings of the International congress series; 2006; pp. 138–147. [Google Scholar]
- Beauchemin, K.; Colombatto, D.; Morgavi, D.; Yang, W.J.J.o.A.S. Use of exogenous fibrolytic enzymes to improve feed utilization by ruminants. 2003, 81, E37-E47.
- Eun, J.-S.; Beauchemin, K.J.A.F.S. ; Technology. Assessment of the efficacy of varying experimental exogenous fibrolytic enzymes using in vitro fermentation characteristics. 2007, 132, 298–315. [Google Scholar]
- Hook, S.E.; Northwood, K.S.; Wright, A.-D.; McBride, B.W.J.A.; Microbiology, E. Long-term monensin supplementation does not significantly affect the quantity or diversity of methanogens in the rumen of the lactating dairy cow. 2009, 75, 374-380.
- Patra, A.K.J.E.M. ; Assessment. Enteric methane mitigation technologies for ruminant livestock: a synthesis of current research and future directions. 2012, 184, 1929–1952. [Google Scholar]
- McGinn, S.; Beauchemin, K.; Coates, T.; Colombatto, D.J.J.o.a.s. Methane emissions from beef cattle: Effects of monensin, sunflower oil, enzymes, yeast, and fumaric acid. 2004, 82, 3346-3356.
- Guan, H.; Wittenberg, K.; Ominski, K.; Krause, D.J.J.o.a.s. Efficacy of ionophores in cattle diets for mitigation of enteric methane. 2006, 84, 1896-1906.
- Clark, H.; Pinares-Patiño, C.; De Klein, C.J.G.A.G.R. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from grazed grasslands. 2005, 279, 293.
- Madsen, J.; Lassen, J.; Hvelplund, T.; Weisbjerg, M.J.E.p. A fast, easy, reliable and cheap method to measure the methane production from ruminants. 2010, 121-122.
- Eckard, R.; Grainger, C.; De Klein, C.J.L.s. Options for the abatement of methane and nitrous oxide from ruminant production: A review. 2010, 130, 47-56.

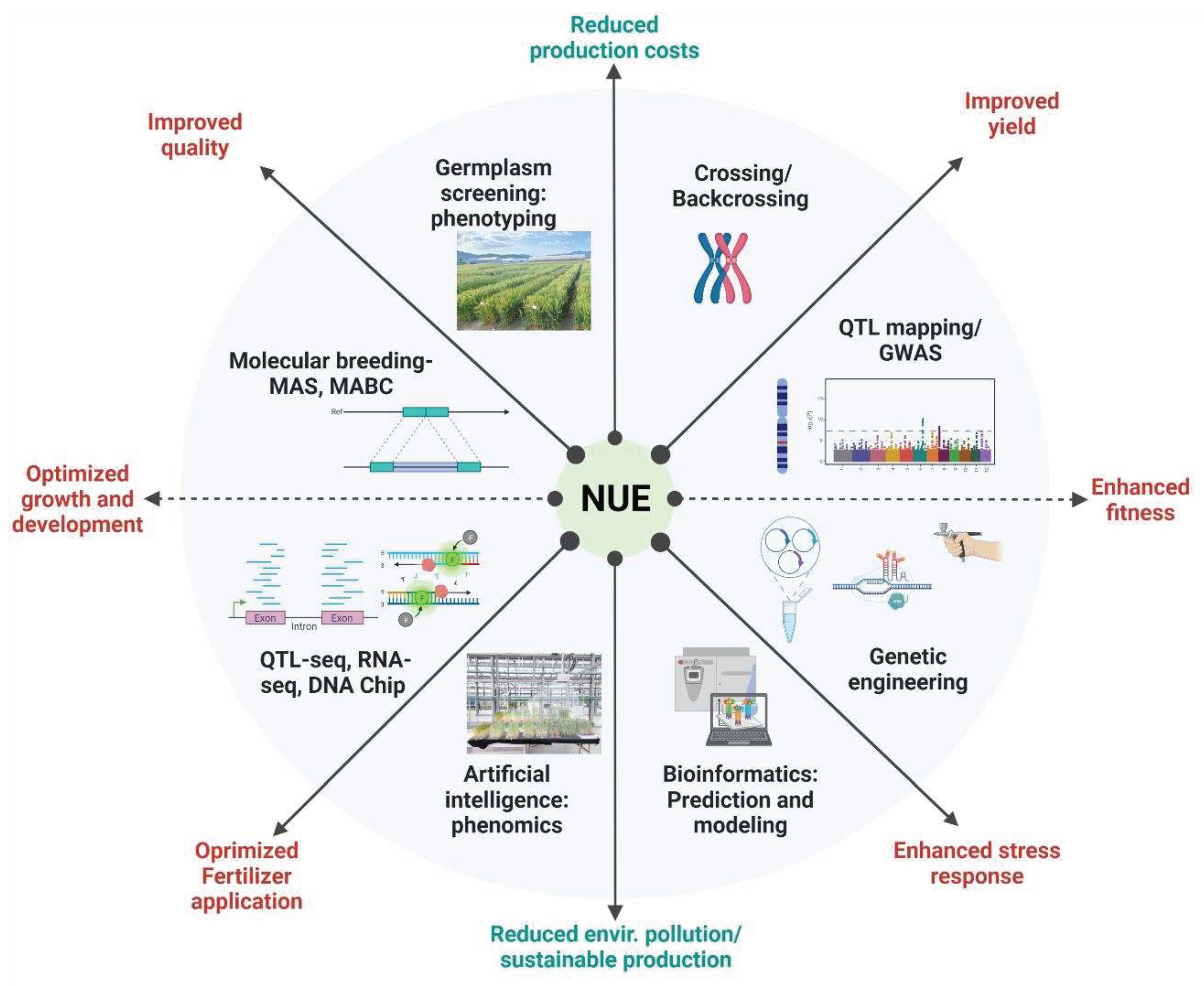
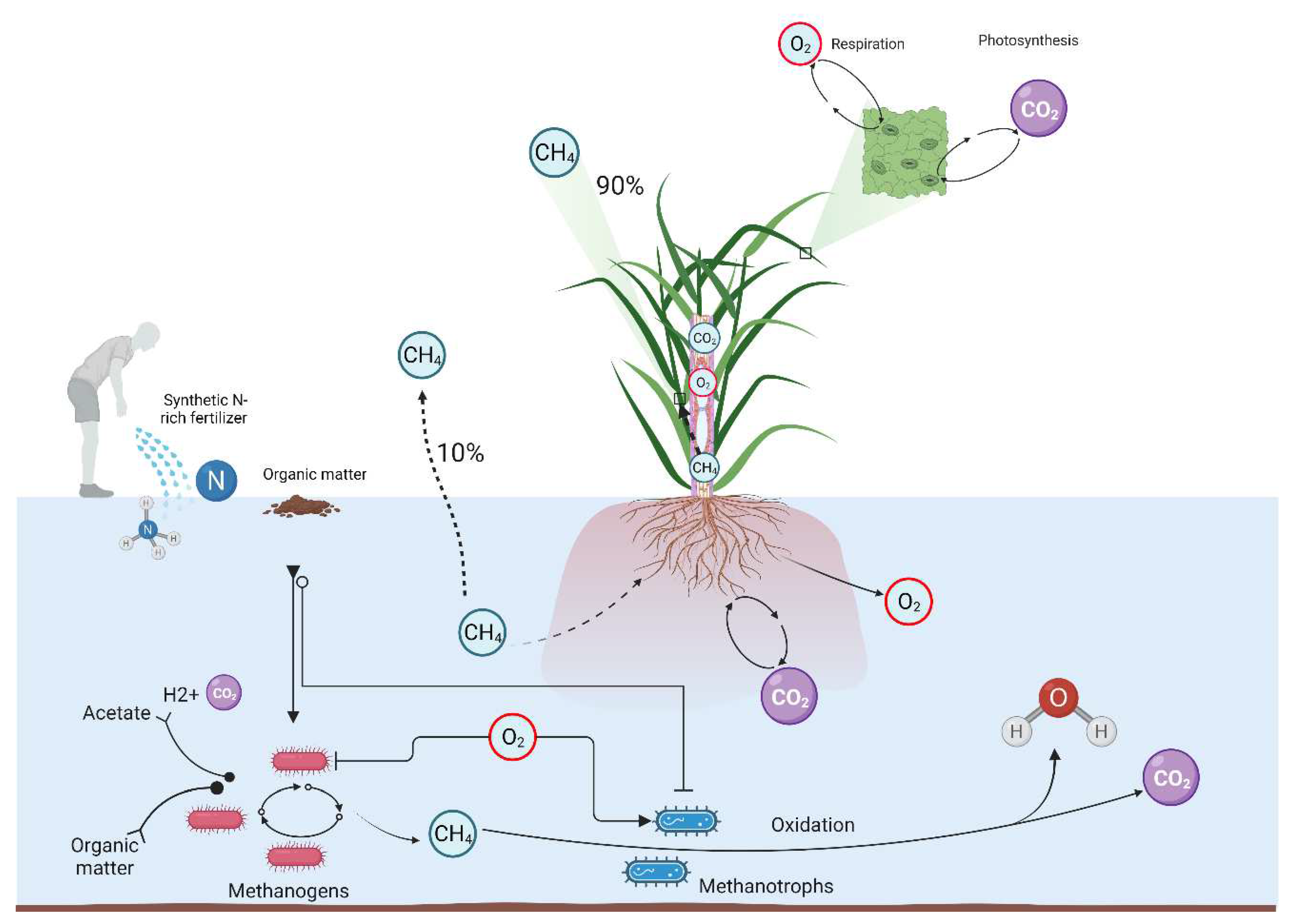
| Advantages | Prerequisite | Application | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen use efficiency | |||
|
|
|
|
| Radial oxygen loss (ROL) | |||
|
|
|
|
| Application of biochar | |||
|
|
|
|
| Best Agricultural Practices | |||
|
|
|
|
| Improving ruminant feeding efficiency and enhancing target-specific ruminal bacterial activity | |||
|
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





