Submitted:
04 September 2023
Posted:
06 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
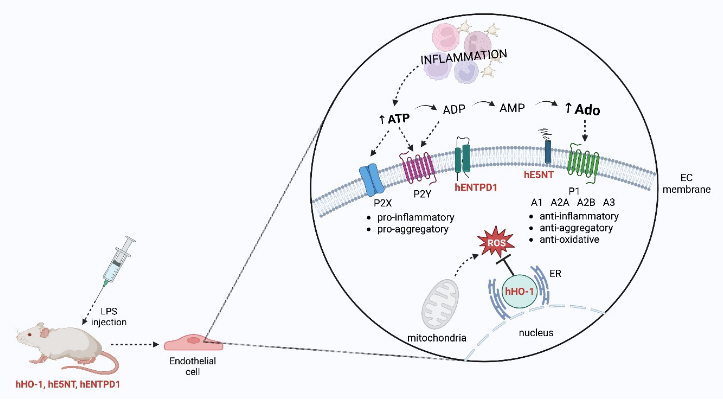
1. Introduction
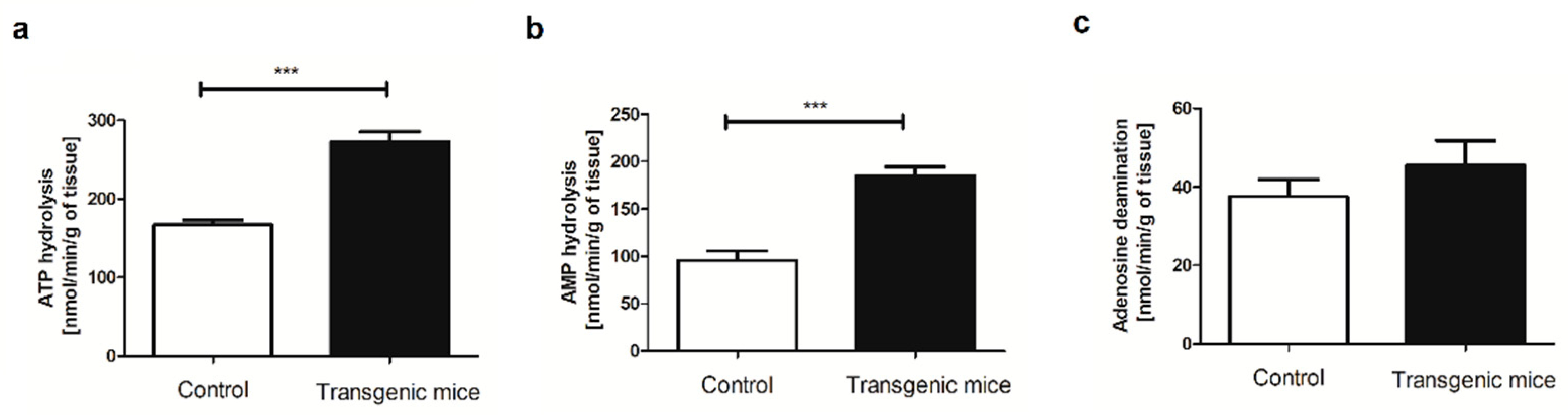
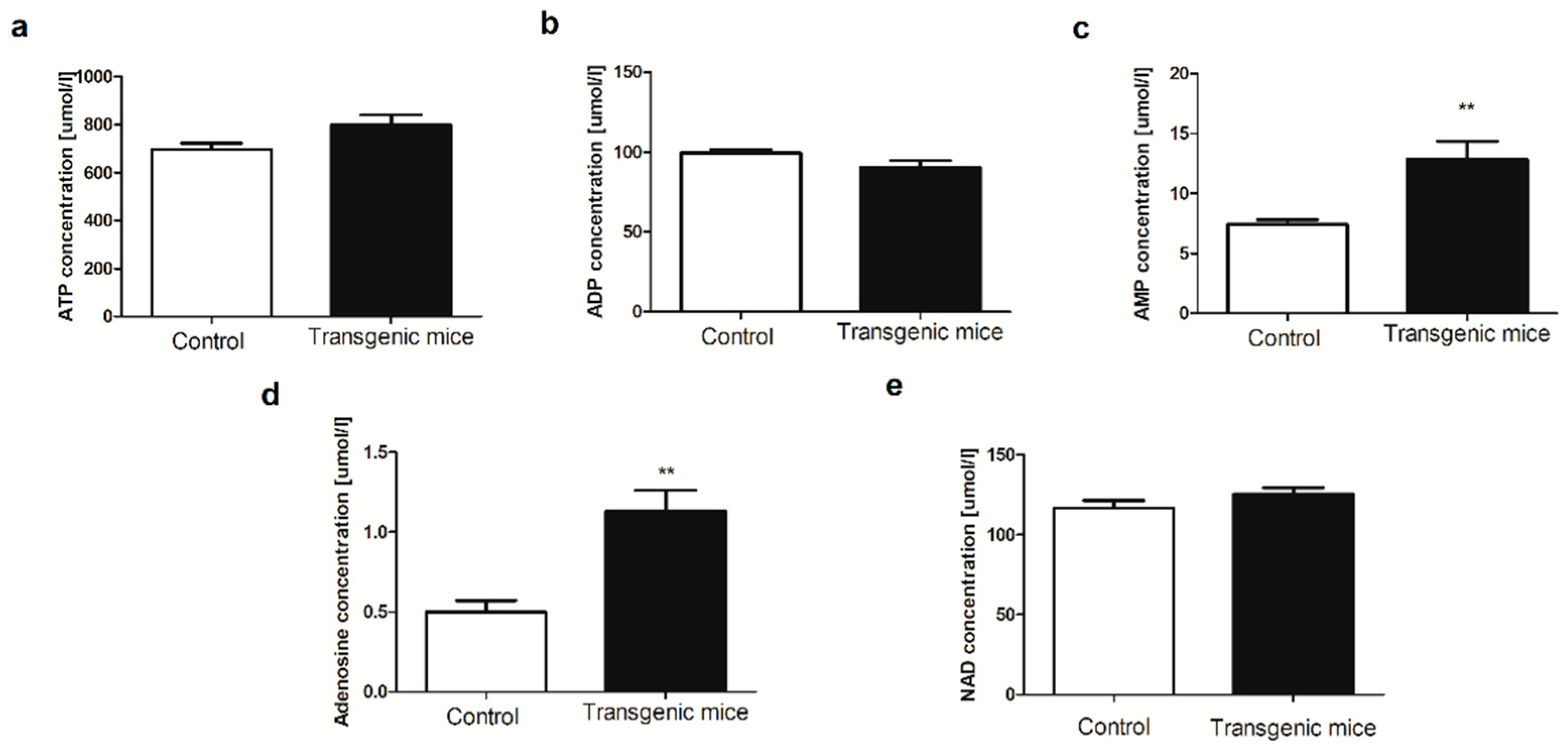
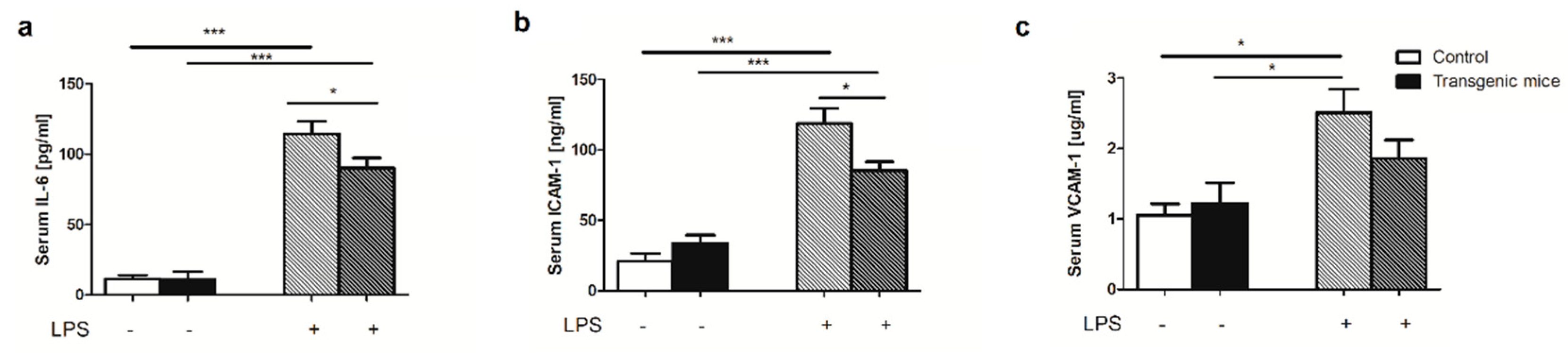
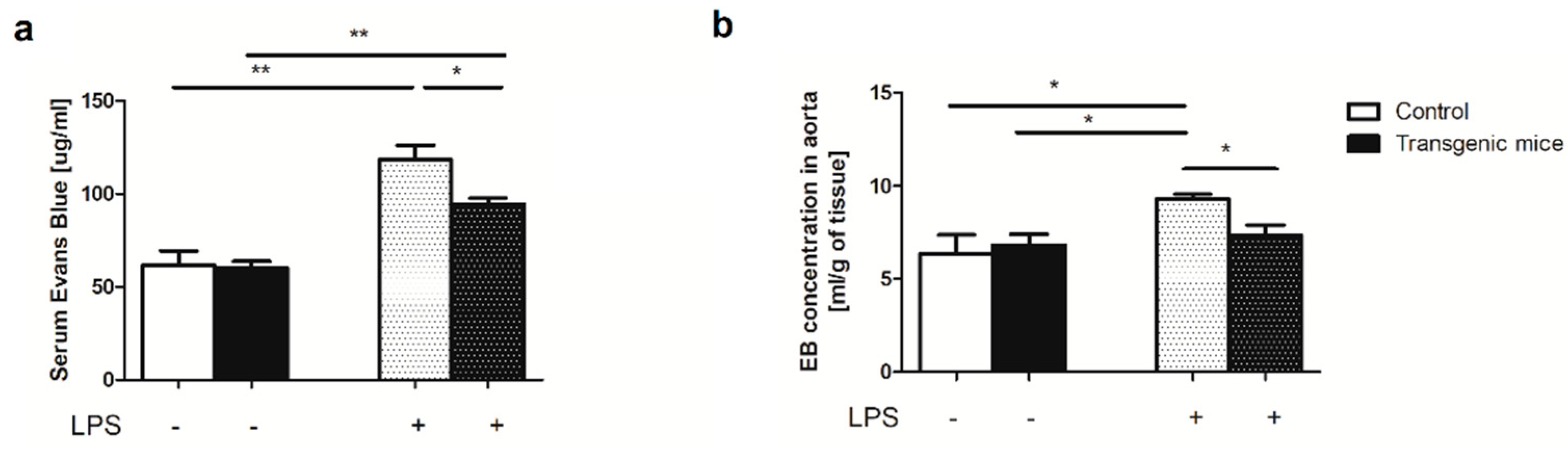
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Triple cistronic plasmid construction and transgenic mice production
4.3. Animal maintenance and treatment
4.4. Evaluation of extracellular catabolism of adenine nucleotides on the aortic surface
4.5. Determination of blood nucleotides and metabolites concentration
4.6. Determination of amino acids and derivatives concentration
4.7. Intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), vascular adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), interleukin 6 (IL-6) measurements
4.8. Evaluation of Endothelial Permeability
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lei, T.; Chen, L.; Wang, K.; Du, S.; Gonelle-Gispert, C.; Wang, Y.; Buhler, L.H. Genetic Engineering of Pigs for Xenotransplantation to Overcome Immune Rejection and Physiological Incompatibilities: The First Clinical Steps. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 1031185. [CrossRef]
- Sykes, M.; Sachs, D.H. Progress in Xenotransplantation: Overcoming Immune Barriers. Nat Rev Nephrol 2022, 18, 745–761. [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.K.C.; Ekser, B.; Ramsoondar, J.; Phelps, C.; Ayares, D. The Role of Genetically Engineered Pigs in Xenotransplantation Research. J Pathol 2016, 238, 288–299. [CrossRef]
- Banz, Y.; Rieben, R. Endothelial Cell Protection in Xenotransplantation: Looking after a Key Player in Rejection. Xenotransplantation 2006, 13, 19–30. [CrossRef]
- Kummer, L.; Zaradzki, M.; Vijayan, V.; Arif, R.; Weigand, M.A.; Immenschuh, S.; Wagner, A.H.; Larmann, J. Vascular Signaling in Allogenic Solid Organ Transplantation - The Role of Endothelial Cells. Front Physiol 2020, 11, 443. [CrossRef]
- Luft, T.; Dreger, P.; Radujkovic, A. Endothelial Cell Dysfunction: A Key Determinant for the Outcome of Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2021, 56, 2326–2335. [CrossRef]
- Cinti, A.; De Giorgi, M.; Chisci, E.; Arena, C.; Galimberti, G.; Farina, L.; Bugarin, C.; Rivolta, I.; Gaipa, G.; Smolenski, R.T.; et al. Simultaneous Overexpression of Functional Human HO-1, E5NT and ENTPD1 Protects Murine Fibroblasts against TNF-α-Induced Injury In Vitro. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0141933. [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Pacher, P.; Vizi, E.S.; Haskó, G. CD39 and CD73 in Immunity and Inflammation. Trends Mol Med 2013, 19, 355–367. [CrossRef]
- Mierzejewska, P.; Zabielska, M.A.; Kutryb-Zajac, B.; Tomczyk, M.; Koszalka, P.; Smolenski, R.T.; Slominska, E.M. Impaired L-Arginine Metabolism Marks Endothelial Dysfunction in CD73-Deficient Mice. Mol Cell Biochem 2019, 458, 133–142. [CrossRef]
- Koszalka, P.; Ozüyaman, B.; Huo, Y.; Zernecke, A.; Flögel, U.; Braun, N.; Buchheiser, A.; Decking, U.K.M.; Smith, M.L.; Sévigny, J.; et al. Targeted Disruption of Cd73/Ecto-5’-Nucleotidase Alters Thromboregulation and Augments Vascular Inflammatory Response. Circ Res 2004, 95, 814–821. [CrossRef]
- Huttinger, Z.M.; Milks, M.W.; Nickoli, M.S.; Aurand, W.L.; Long, L.C.; Wheeler, D.G.; Dwyer, K.M.; d’Apice, A.J.F.; Robson, S.C.; Cowan, P.J.; et al. Ectonucleotide Triphosphate Diphosphohydrolase-1 (CD39) Mediates Resistance to Occlusive Arterial Thrombus Formation after Vascular Injury in Mice. Am J Pathol 2012, 181, 322–333. [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.P.; Bach, F.H. Heme Oxygenase-1: From Biology to Therapeutic Potential. Trends Mol Med 2009, 15, 50–58. [CrossRef]
- Belcher, J.D.; Mahaseth, H.; Welch, T.E.; Otterbein, L.E.; Hebbel, R.P.; Vercellotti, G.M. Heme Oxygenase-1 Is a Modulator of Inflammation and Vaso-Occlusion in Transgenic Sickle Mice. J Clin Invest 2006, 116, 808–816. [CrossRef]
- De Giorgi, M.; Cinti, A.; Pelikant-Malecka, I.; Chisci, E.; Lavitrano, M.; Giovannoni, R.; Smolenski, R.T. Co-Expression of Functional Human Heme Oxygenase 1, Ecto-5’-Nucleotidase and Ecto-Nucleoside Triphosphate Diphosphohydrolase-1 by "Self-Cleaving" 2A Peptide System. Plasmid 2015, 79, 22–29. [CrossRef]
- Crikis, S.; Lu, B.; Murray-Segal, L.M.; Selan, C.; Robson, S.C.; D’Apice, A.J.F.; Nandurkar, H.H.; Cowan, P.J.; Dwyer, K.M. Transgenic Overexpression of CD39 Protects against Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion and Transplant Vascular Injury. Am J Transplant 2010, 10, 2586–2595. [CrossRef]
- Minor, M.; Alcedo, K.P.; Battaglia, R.A.; Snider, N.T. Cell Type- and Tissue-Specific Functions of Ecto-5’-Nucleotidase (CD73). Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2019, 317, C1079–C1092. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wan, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Meng, F.; Glaser, S.; Wu, N.; Zhou, T.; Li, S.; et al. The Emerging Role of Cellular Senescence in Renal Diseases. J Cell Mol Med 2020, 24, 2087–2097. [CrossRef]
- Behdad, A.; Sun, X.; Khalpey, Z.; Enjyoji, K.; Wink, M.; Wu, Y.; Usheva, A.; Robson, S.C. Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Expression of Ectonucleotidase CD39 (ENTPD1) Is Required for Neointimal Formation in Mice. Purinergic Signal 2009, 5, 335–342. [CrossRef]
- Zukowska, P.; Kutryb-Zajac, B.; Jasztal, A.; Toczek, M.; Zabielska, M.; Borkowski, T.; Khalpey, Z.; Smolenski, R.T.; Slominska, E.M. Deletion of CD73 in Mice Leads to Aortic Valve Dysfunction. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2017, 1863, 1464–1472. [CrossRef]
- Kutryb-Zajac, B.; Jablonska, P.; Serocki, M.; Bulinska, A.; Mierzejewska, P.; Friebe, D.; Alter, C.; Jasztal, A.; Lango, R.; Rogowski, J.; et al. Nucleotide Ecto-Enzyme Metabolic Pattern and Spatial Distribution in Calcific Aortic Valve Disease; Its Relation to Pathological Changes and Clinical Presentation. Clin Res Cardiol 2020, 109, 137–160. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.F.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Ibla, J.C.; Van De Wiele, C.J.; Resta, R.; Morote-Garcia, J.C.; Colgan, S.P. Crucial Role for Ecto-5’-Nucleotidase (CD73) in Vascular Leakage during Hypoxia. J Exp Med 2004, 200, 1395–1405. [CrossRef]
- Cronstein, B.N.; Levin, R.I.; Belanoff, J.; Weissmann, G.; Hirschhorn, R. Adenosine: An Endogenous Inhibitor of Neutrophil-Mediated Injury to Endothelial Cells. J Clin Invest 1986, 78, 760–770. [CrossRef]
- Kara, F.M.; Chitu, V.; Sloane, J.; Axelrod, M.; Fredholm, B.B.; Stanley, E.R.; Cronstein, B.N. Adenosine A1 Receptors (A1Rs) Play a Critical Role in Osteoclast Formation and Function. FASEB J 2010, 24, 2325–2333. [CrossRef]
- Haskó, G.; Pacher, P.; Deitch, E.A.; Vizi, E.S. Shaping of Monocyte and Macrophage Function by Adenosine Receptors. Pharmacol Ther 2007, 113, 264–275. [CrossRef]
- Barczyk, K.; Ehrchen, J.; Tenbrock, K.; Ahlmann, M.; Kneidl, J.; Viemann, D.; Roth, J. Glucocorticoids Promote Survival of Anti-Inflammatory Macrophages via Stimulation of Adenosine Receptor A3. Blood 2010, 116, 446–455. [CrossRef]
- Allard, B.; Longhi, M.S.; Robson, S.C.; Stagg, J. The Ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73: Novel Checkpoint Inhibitor Targets. Immunol Rev 2017, 276, 121–144. [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, T.; Bouïs, D.; Liao, H.; Visovatti, S.H.; Pinsky, D.J. Ecto-5’ Nucleotidase (CD73)-Mediated Adenosine Generation and Signaling in Murine Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy. Circ Res 2008, 103, 1410–1421. [CrossRef]
- St Hilaire, C.; Ziegler, S.G.; Markello, T.C.; Brusco, A.; Groden, C.; Gill, F.; Carlson-Donohoe, H.; Lederman, R.J.; Chen, M.Y.; Yang, D.; et al. NT5E Mutations and Arterial Calcifications. N Engl J Med 2011, 364, 432–442. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-C.; Lee, H.; Oh, K.B.; Hwang, I.-S.; Yang, H.; Park, M.-R.; Ock, S.-A.; Woo, J.-S.; Im, G.-S.; Hwang, S. Production and Breeding of Transgenic Cloned Pigs Expressing Human CD73. Dev Reprod 2017, 21, 157–165. [CrossRef]
- Detmer, S.A.; Chan, D.C. Functions and Dysfunctions of Mitochondrial Dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007, 8, 870–879. [CrossRef]
- Köhler, D.; Eckle, T.; Faigle, M.; Grenz, A.; Mittelbronn, M.; Laucher, S.; Hart, M.L.; Robson, S.C.; Müller, C.E.; Eltzschig, H.K. CD39/Ectonucleoside Triphosphate Diphosphohydrolase 1 Provides Myocardial Protection during Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Circulation 2007, 116, 1784–1794. [CrossRef]
- Pinsky, D.J.; Broekman, M.J.; Peschon, J.J.; Stocking, K.L.; Fujita, T.; Ramasamy, R.; Connolly, E.S.; Huang, J.; Kiss, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Elucidation of the Thromboregulatory Role of CD39/Ectoapyrase in the Ischemic Brain. J Clin Invest 2002, 109, 1031–1040. [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Tu, L.; Guignabert, C.; Merkus, D.; Zhou, Z. Purinergic Dysfunction in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J Am Heart Assoc 2020, 9, e017404. [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.S.; Mazza, L.F.; Yalavarthi, S.; Sule, G.; Ali, R.A.; Hodgin, J.B.; Kanthi, Y.; Pinsky, D.J. Ectonucleotidase-Mediated Suppression of Lupus Autoimmunity and Vascular Dysfunction. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 1322. [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, H.; Yao, J.; Zhong, H.; Kuang, Y.; Li, X.; Bian, W. HO-1 Knockdown Upregulates the Expression of VCAM-1 to Induce Neutrophil Recruitment during Renal Ischemia-reperfusion Injury. Int J Mol Med 2021, 48. [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Hillestad, M.L.; Grande, J.P.; Croatt, A.J.; Barry, M.A.; Farrugia, G.; Katusic, Z.S.; Nath, K.A. Induction and Functional Significance of the Heme Oxygenase System in Pathological Shear Stress in Vivo. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2015, 308, H1402-13. [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, A.; Oda, Y.; Yachie, A.; Koizumi, S.; Nakanishi, I. Heme Oxygenase-1 Deficiency: The First Autopsy Case. Hum Pathol 2002, 33, 125–130. [CrossRef]
- Ollinger, R.; Bilban, M.; Erat, A.; Froio, A.; McDaid, J.; Tyagi, S.; Csizmadia, E.; Graça-Souza, A. V; Liloia, A.; Soares, M.P.; et al. Bilirubin: A Natural Inhibitor of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation. Circulation 2005, 112, 1030–1039. [CrossRef]
- Tulis, D.A.; Keswani, A.N.; Peyton, K.J.; Wang, H.; Schafer, A.I.; Durante, W. Local Administration of Carbon Monoxide Inhibits Neointima Formation in Balloon Injured Rat Carotid Arteries. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 2005, 51, 441–446.
- Singh, A.K.; Griffith, B.P.; Goerlich, C.E.; Ayares, D.; Mohiuddin, M.M. The Road to the First FDA-Approved Genetically Engineered Pig Heart Transplantation into Human. Xenotransplantation 2022, 29. [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3--New Capabilities and Interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res 2012, 40, e115. [CrossRef]
- Kutryb-Zajac, B.; Mateuszuk, L.; Zukowska, P.; Jasztal, A.; Zabielska, M.A.; Toczek, M.; Jablonska, P.; Zakrzewska, A.; Sitek, B.; Rogowski, J.; et al. Increased Activity of Vascular Adenosine Deaminase in Atherosclerosis and Therapeutic Potential of Its Inhibition. Cardiovasc Res 2016, 112, 590–605. [CrossRef]
- Smolenski, R.T.; Lachno, D.R.; Ledingham, S.J.; Yacoub, M.H. Determination of Sixteen Nucleotides, Nucleosides and Bases Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Its Application to the Study of Purine Metabolism in Hearts for Transplantation. J Chromatogr 1990, 527, 414–420. [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Jeffers, L.A.; Koval, M. Measurement of Lung Vessel and Epithelial Permeability In Vivo with Evans Blue. Methods Mol Biol 2021, 2367. [CrossRef]
| Amino acid [μmol/L] | Control | Transgenic | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arginine | 84.06±5.18 | 92.65±3.25 | 0.075 |
| ADMA | 0.91±0.05 | 0.78±0.04 | 0.112 |
| SDMA | 0.52±0.09 | 0.50±0.06 | 0.868 |
| L-NMMA | 0.36±0.01 | 0.28±0.02 | 0.043* |
| Ornithine | 140.20±16.48 | 147.70±17.73 | 0.777 |
| Citrulline | 89.46±2.98 | 98.48±6.12 | 0.246 |
| Ornithine/Arginine | 1.85±0.05 | 1.32±0.12 | 0.012* |
| Ornithine/CItrulline | 1.71±0.13 | 1.32±0.17 | 0.131 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





