Submitted:
02 September 2023
Posted:
05 September 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Comparison of the demographic characteristics of patients with type 1 diabetes and healthy controls and vitamin D levels
| Variable | Control group n = 23 | T1DM group n = 30 | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c (%) | 5.126± 0.4158 | 8.957 ±1.353 | <0.0001 |
| IA2 (IU/mL) | 0 | 140.4 (14.45–511.0) | - |
| GAD65A (IU/mL) | 2.62 (0.4–4.7) | 79.55 (18.77–264.3) | - |
| Age (years) | 9.296 ±3.006 | 10.71 ± 6.072 | 0.3098 |
| Sex: male/female | 11/12 | 15/15 | - |
| BMI | 21.86 ±3.250 | 22.31±4.248 | 0.6775 |
| Vitamin D | 43.18±50.89 | 24.37±17.14 | 0.0045 |

2.2. The expression of CYP27B1 mRNA but not CYP24A1 was downregulated in PBMCs from T1DM as compared with healthy controls
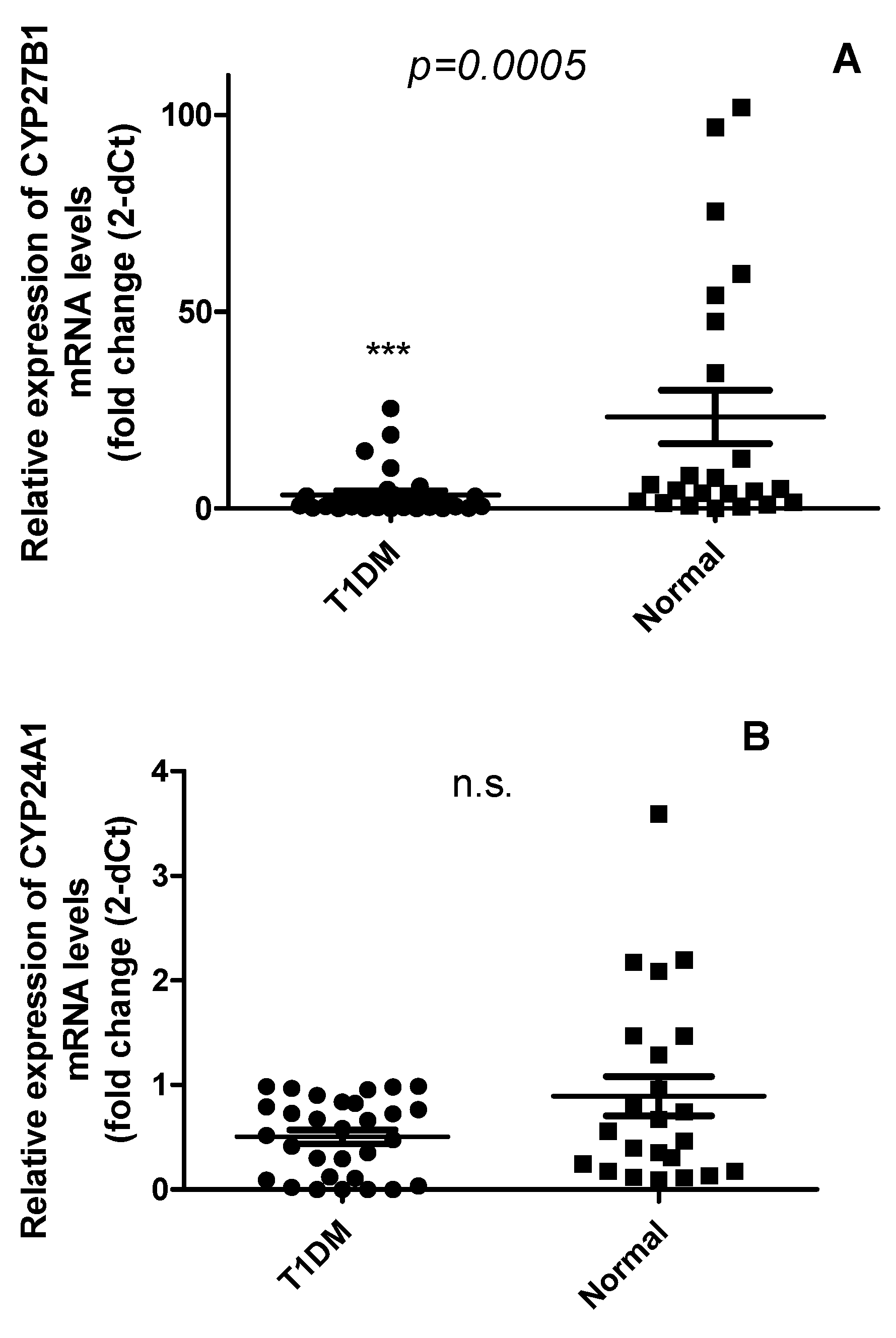
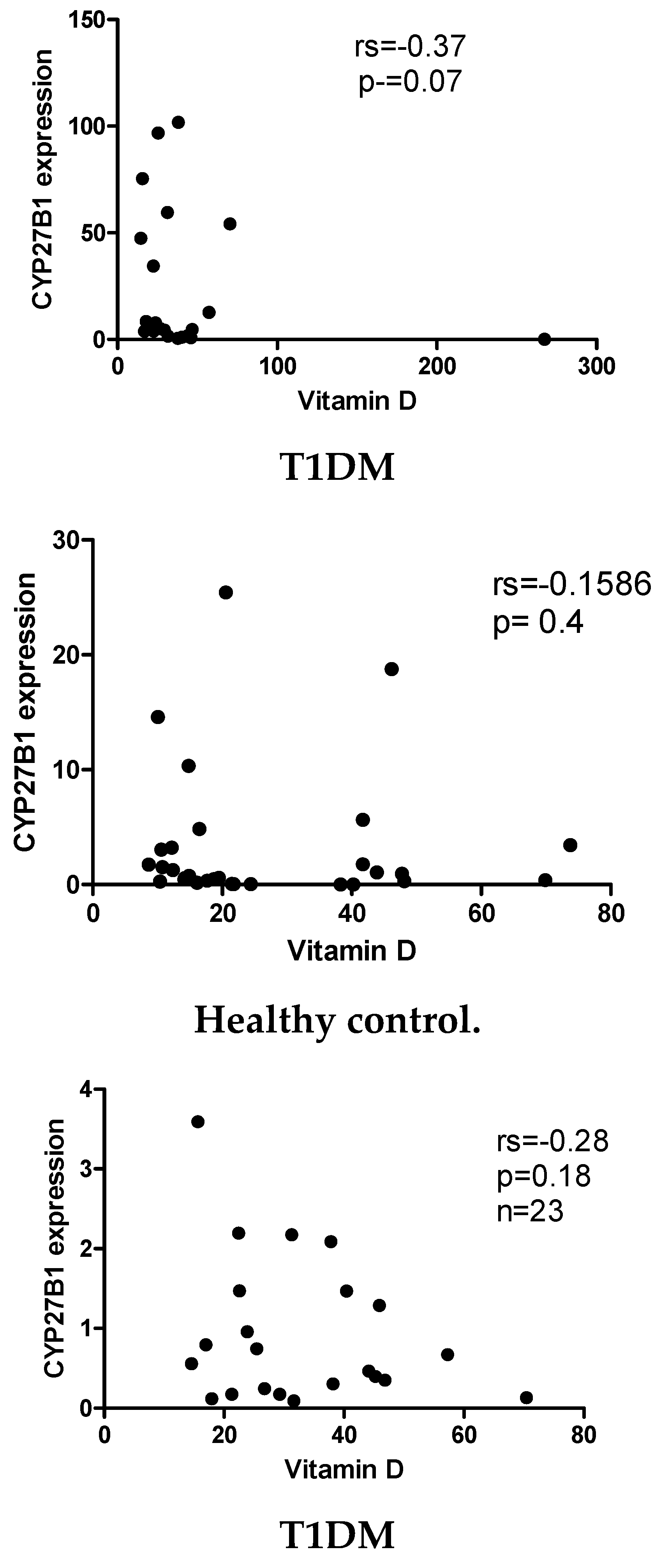
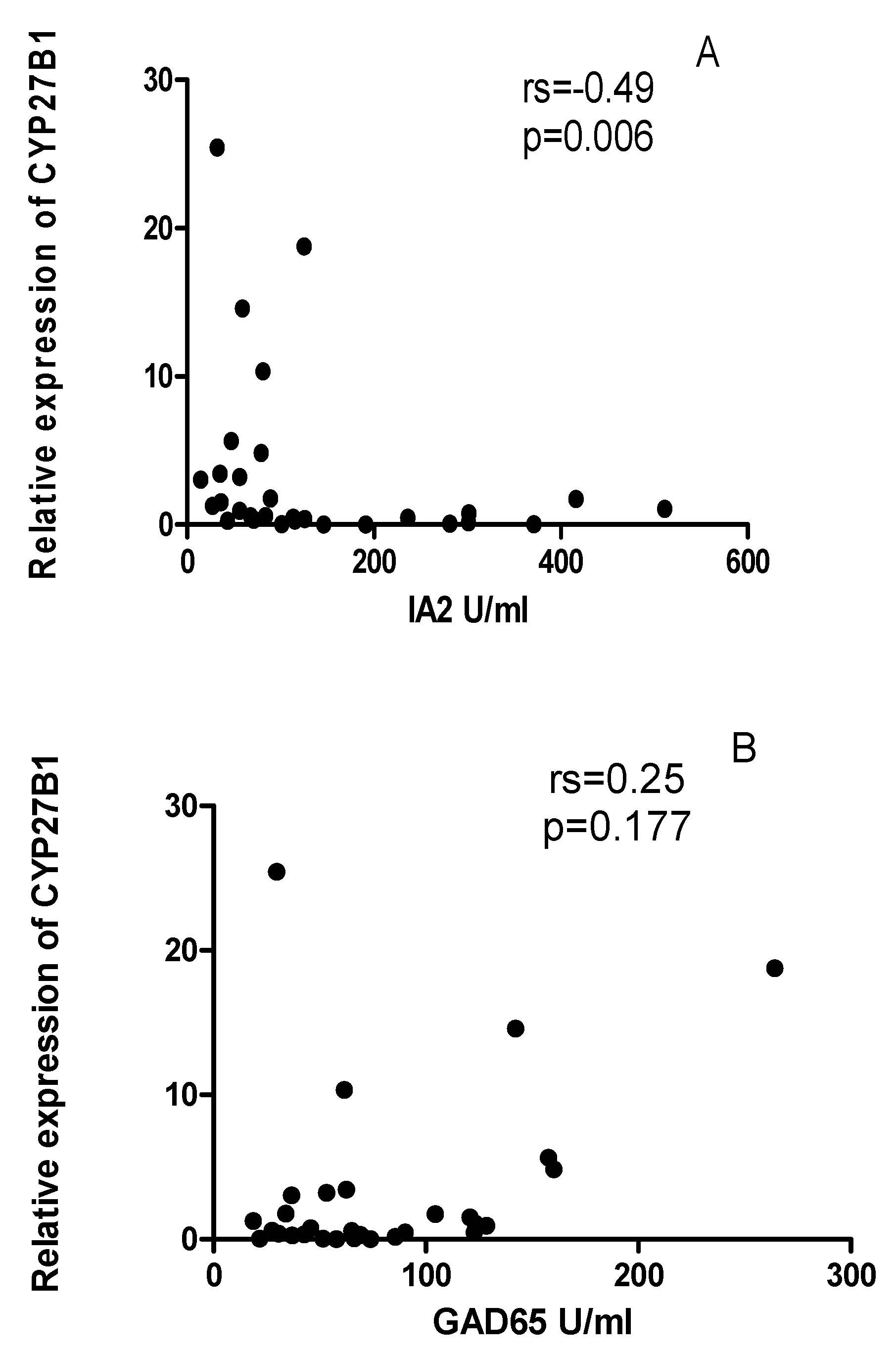
2.3. Vitamin D does not correlate with the expression levels of CYP24A1 and CYP27B1 mRNA levels

2.4. Circulating Levels of has-miR-21 and has-miR-216b-5p but not has-miR-125b are differentially expressed in PBMCs of T1D patients compared with healthy controls
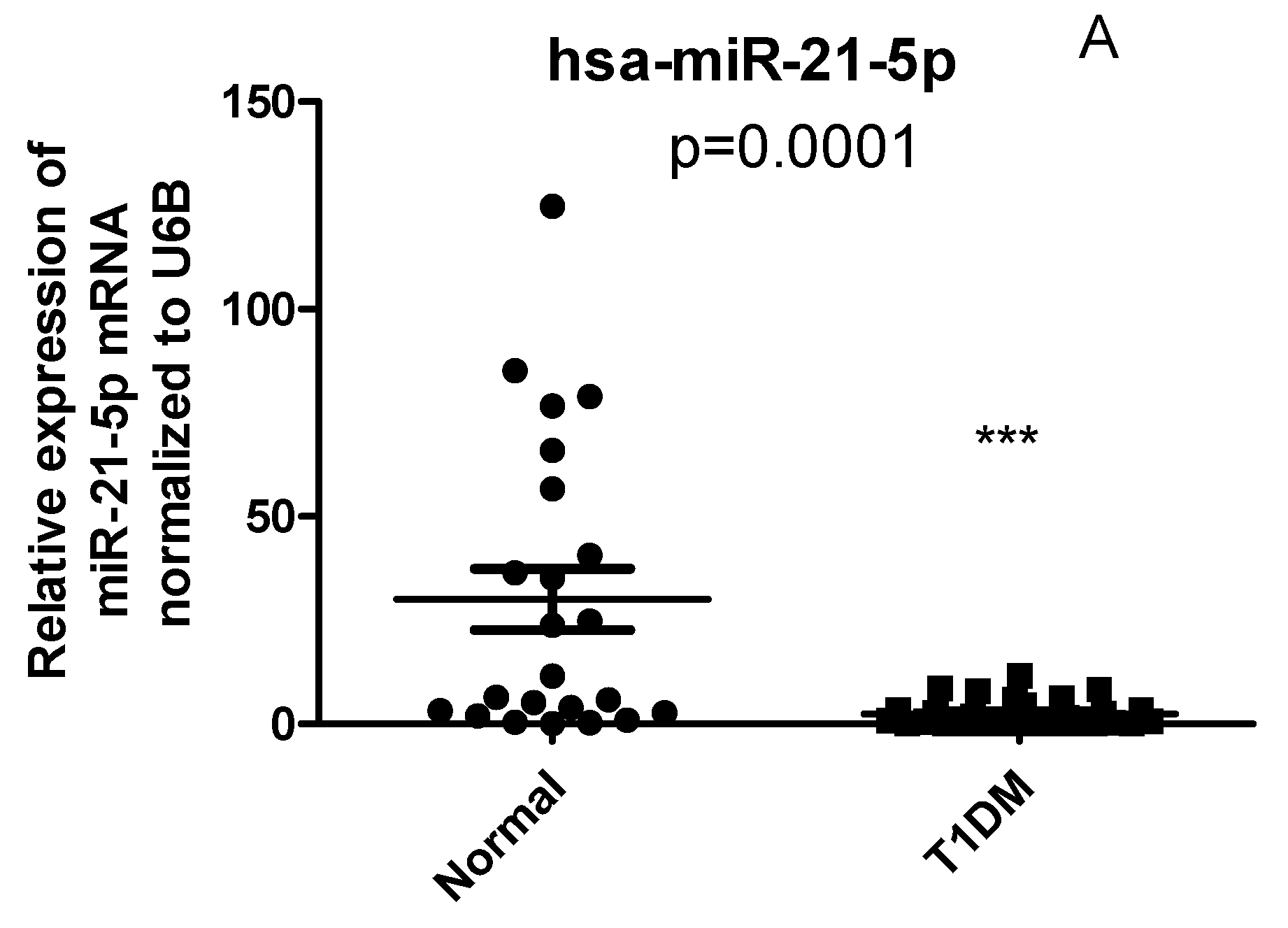
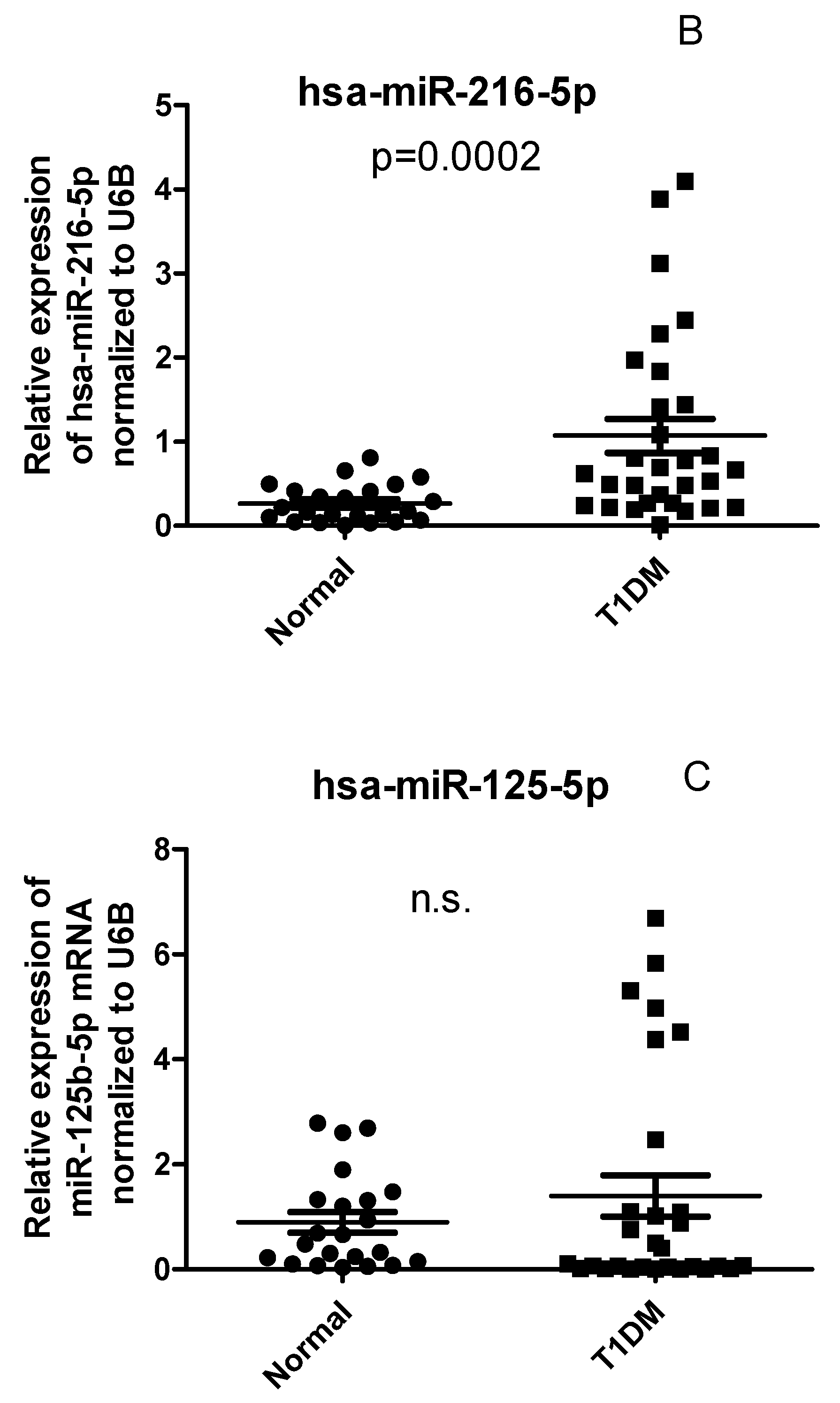
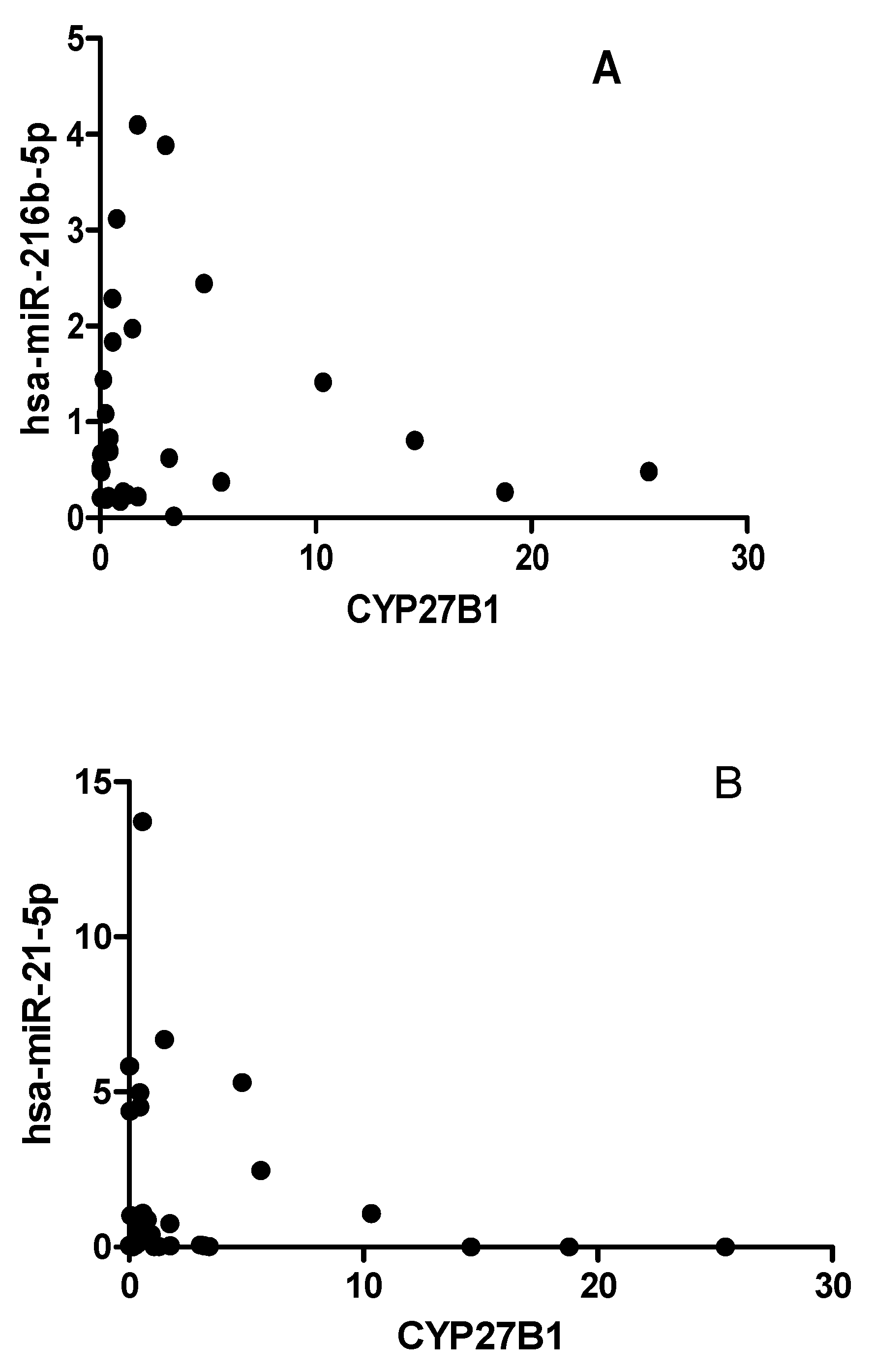
2.5. CYP27B1 not correlated with has-miR-216 and has-miR-21 in T1DM
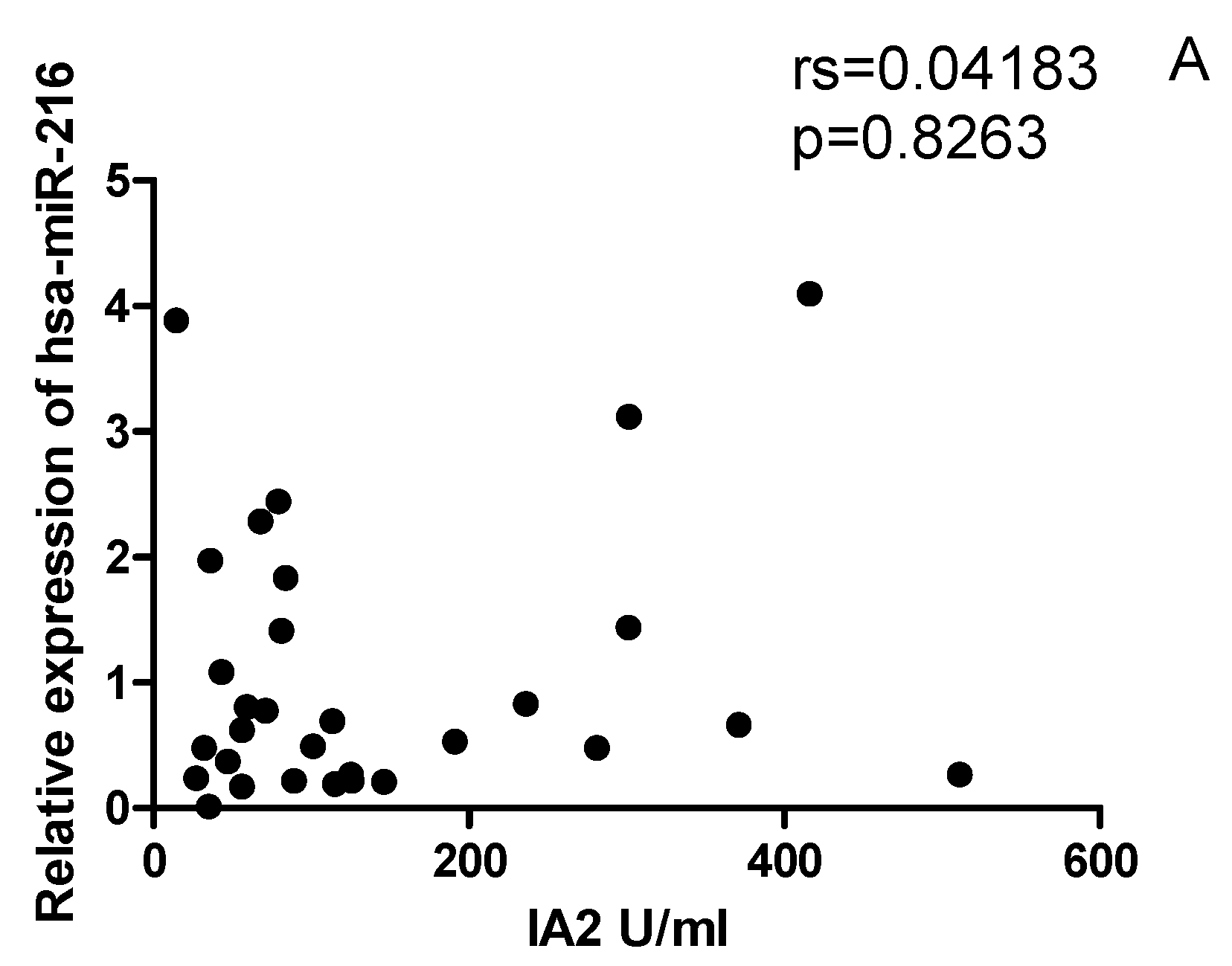
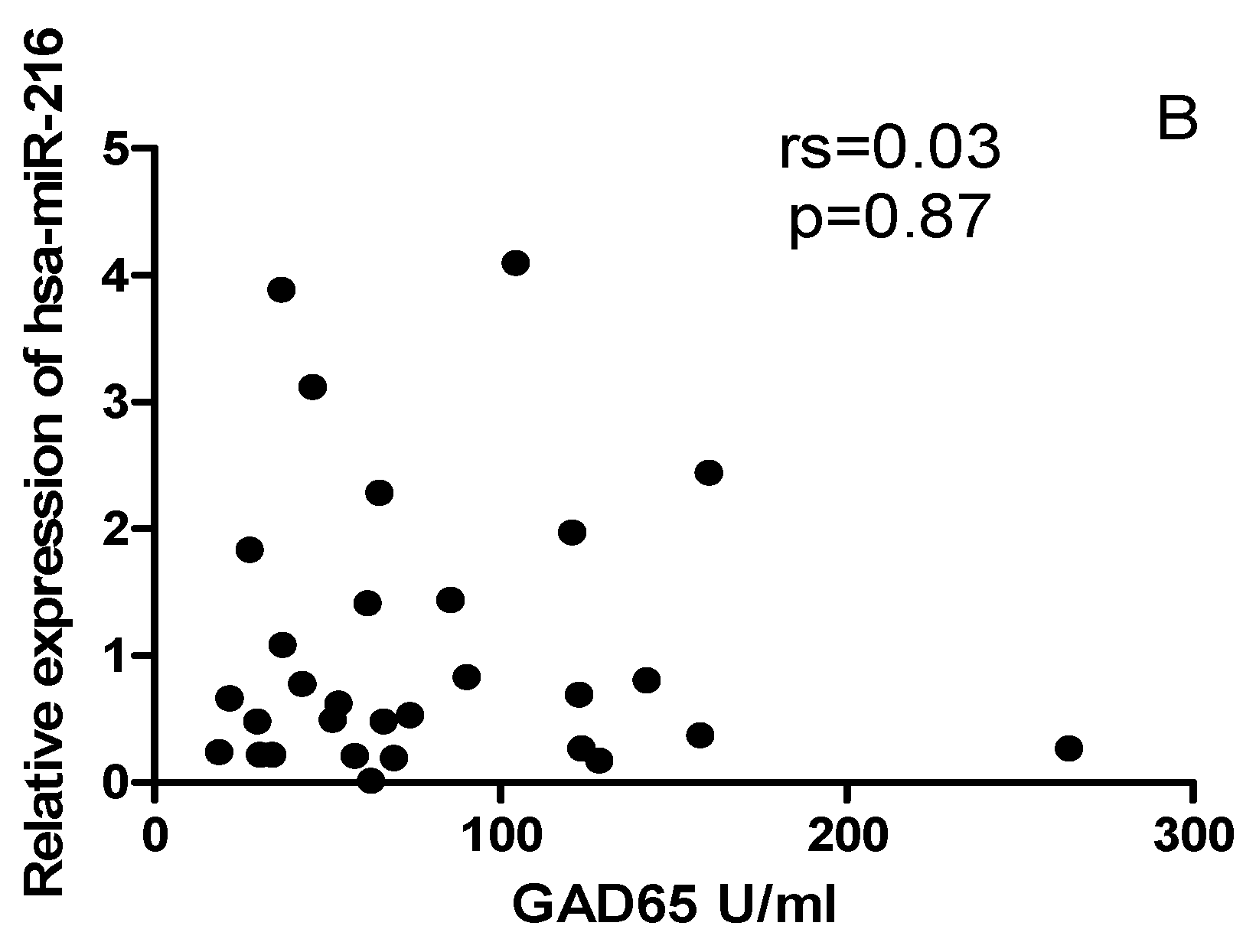
2.6. The correlation between miRNAs, and CYP27B1 islet autoantibodies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics and Consent
4.2. Study Design, T1DM patients' recruitment, inclusion and exclusion criteria
4.3. Isolation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs)
4.4. RNA and miRNA extraction from PBMCs
4.5. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.6. Serum sample collection and vitamin D level measurement
4.7. Serological analysis
4.8. Target gene identification and bioinformatic analysis
4.9. Statistical analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- J.-W. Yoon and H.-S. Jun, “Autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells.,” American journal of therapeutics, vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 580–591, 2005. [CrossRef]
- P. Pozzilli et al., “Low levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in patients with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes.,” Hormone and metabolic research = Hormon- und Stoffwechselforschung = Hormones et metabolisme, vol. 37, no. 11, pp. 680–683, Nov. 2005. [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, High Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency Among Saudi Children And Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes In Albaha Region, Saudi Arabia, vol. 12. 2017. [CrossRef]
- J. Feng, W. Xing, and L. Xie, “Regulatory Roles of MicroRNAs in Diabetes,” International Journal of Molecular Sciences, vol. 17, no. 10, p. 1729, Oct. 2016. [CrossRef]
- K. Tashiro, T. Abe, N. Oue, W. Yasui, and M. Ryoji, “Characterization of vitamin D-mediated induction of the CYP 24 transcription.,” Molecular and cellular endocrinology, vol. 226, no. 1–2, pp. 27–32, Oct. 2004. [CrossRef]
- S. Komagata, M. Nakajima, S. Takagi, T. Mohri, T. Taniya, and T. Yokoi, “Human CYP24 Catalyzing the Inactivation of Calcitriol Is Post-Transcriptionally Regulated by miR-125b,” Molecular Pharmacology, 2009. [CrossRef]
- S. Essa et al., “VDR microRNA expression and epigenetic silencing of vitamin D signaling in melanoma cells.,” The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology, vol. 121, no. 1–2, pp. 110–113, Jul. 2010. [CrossRef]
- T. Mohri, M. Nakajima, S. Takagi, S. Komagata, and T. Yokoi, “MicroRNA regulates human vitamin D receptor.,” International journal of cancer, vol. 125, no. 6, pp. 1328–1333, Sep. 2009. [CrossRef]
- G. Sebastiani, F. A. Grieco, I. Spagnuolo, L. Galleri, D. Cataldo, and F. Dotta, “Increased expression of microRNA miR-326 in type 1 diabetic patients with ongoing islet autoimmunity,” Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, vol. 27, no. 8, pp. 862–866, 2011. [CrossRef]
- L. Adorini and G. Penna, “Control of autoimmune diseases by the vitamin D endocrine system.,” Nature clinical practice. Rheumatology, vol. 4, no. 8, pp. 404–412, Aug. 2008. [CrossRef]
- G. M. Gager et al., “Expression Patterns of MiR-125a and MiR-223 and Their Association with Diabetes Mellitus and Survival in Patients with Non-ST-Segment Elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome,” Biomedicines, vol. 11, no. 4, 2023. [CrossRef]
- P. T. Liu et al., “MicroRNA-21 targets the vitamin D-dependent antimicrobial pathway in leprosy.,” Nature medicine, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 267–273, Jan. 2012. [CrossRef]
- P. Wang et al., “miR-216a-targeting theranostic nanoparticles promote proliferation of insulin-secreting cells in type 1 diabetes animal model.,” Scientific reports, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 5302, Mar. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. H. El-Samahy et al., “Urinary miRNA-377 and miRNA-216a as biomarkers of nephropathy and subclinical atherosclerotic risk in pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes,” Journal of Diabetes and its Complications, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 185–192, 2018. [CrossRef]
- K. Margaritis et al., “Micro-RNA Implications in Type-1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Literature.,” International journal of molecular sciences, vol. 22, no. 22, Nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. G. Scherm and C. Daniel, “miRNA-Mediated Immune Regulation in Islet Autoimmunity and Type 1 Diabetes.,” Frontiers in endocrinology, vol. 11, p. 606322, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zheng, Z. Wang, and Z. Zhou, “miRNAs: novel regulators of autoimmunity-mediated pancreatic β-cell destruction in type 1 diabetes,” Cellular &Amp; Molecular Immunology, vol. 14, p. 488, Mar. 2017, [Online]. [CrossRef]
- F. Salas-Pérez, E. Codner, E. Valencia, C. Pizarro, E. Carrasco, and F. Pérez-Bravo, “MicroRNAs miR-21a and miR-93 are down regulated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from patients with type 1 diabetes,” Immunobiology, vol. 218, no. 5, pp. 733–737, 2013. [CrossRef]
- G. Sebastiani, F. A. Grieco, I. Spagnuolo, L. Galleri, D. Cataldo, and F. Dotta, “Increased expression of microRNA miR-326 in type 1 diabetic patients with ongoing islet autoimmunity,” Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, vol. 27, no. 8, pp. 862–866, Nov. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Z. Azhir, F. Dehghanian, and Z. Hojati, “Increased expression of microRNAs, miR-20a and miR-326 in PBMCs of patients with type 1 diabetes.,” Molecular biology reports, vol. 45, no. 6, pp. 1973–1980, Dec. 2018. [CrossRef]
- K. Rak and M. Bronkowska, “Immunomodulatory Effect of Vitamin D and Its Potential Role in the Prevention and Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus-A Narrative Review.,” Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), vol. 24, no. 1, Dec. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Li, L.-J. Song, and X.-Y. Qin, “Advances in the cellular immunological pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes.,” Journal of cellular and molecular medicine, vol. 18, no. 5, pp. 749–758, May 2014. [CrossRef]
- L. L. Ritterhouse et al., “B lymphocyte stimulator levels in systemic lupus erythematosus: higher circulating levels in African American patients and increased production after influenza vaccination in patients with low baseline levels.,” Arthritis and rheumatism, vol. 63, no. 12, pp. 3931–3941, Dec. 2011. [CrossRef]
- S. Piantoni et al., “Phenotype modifications of T-cells and their shift toward a Th2 response in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus supplemented with different monthly regimens of vitamin D.,” Lupus, vol. 24, no. 4–5, pp. 490–498, Apr. 2015. [CrossRef]
- R. Lin, “Crosstalk between Vitamin D Metabolism, VDR Signalling, and Innate Immunity.,” BioMed research international, vol. 2016, p. 1375858, 2016. [CrossRef]
- N. Charoenngam and M. F. Holick, “Immunologic Effects of Vitamin D on Human Health and Disease.,” Nutrients, vol. 12, no. 7, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- R. Cheung et al., “Glucose-Dependent miR-125b Is a Negative Regulator of β-Cell Function.,” Diabetes, vol. 71, no. 7, pp. 1525–1545, Jul. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Januszewski et al., “Insulin micro-secretion in Type 1 diabetes and related microRNA profiles.,” Scientific reports, vol. 11, no. 1, p. 11727, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Shen et al., “miR-34a and miR-125b are upregulated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus,” Exp Ther Med, vol. 14, no. 6, pp. 5589–5596, 2017. [CrossRef]
- G. E. Grieco et al., “Serum Levels of miR-148a and miR-21-5p Are Increased in Type 1 Diabetic Patients and Correlated with Markers of Bone Strength and Metabolism.,” Non-coding RNA, vol. 4, no. 4, Nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- P. Morales-Sánchez et al., “Circulating miRNA expression in long-standing type 1 diabetes mellitus.,” Scientific reports, vol. 13, no. 1, p. 8611, May 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Chakhtoura and S. T. Azar, “The role of vitamin d deficiency in the incidence, progression, and complications of type 1 diabetes mellitus.,” International journal of endocrinology, vol. 2013, p. 148673, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Bener et al., “High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in type 1 diabetes mellitus and healthy children.,” Acta diabetologica, vol. 46, no. 3, pp. 183–189, Sep. 2009. [CrossRef]
- E. Ramos-Lopez, P. Brück, T. Jansen, J. M. Pfeilschifter, H. H. Radeke, and K. Badenhoop, “CYP2R1-, CYP27B1- and CYP24-mRNA expression in German type 1 diabetes patients,” The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, vol. 103, no. 3, pp. 807–810, 2007. [CrossRef]
- R. Singh, V. Yadav, S. kumar, and N. Saini, “MicroRNA-195 inhibits proliferation, invasion and metastasis in breast cancer cells by targeting FASN, HMGCR, ACACA and CYP27B1,” Scientific Reports, vol. 5, no. 1, p. 17454, 2015. [CrossRef]
- L. P. Garo and G. Murugaiyan, “Contribution of MicroRNAs to autoimmune diseases.,” Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, vol. 73, no. 10, pp. 2041–2051, May 2016. [CrossRef]
- T. S. Assmann, M. Recamonde-Mendoza, B. M. De Souza, and D. Crispim, “MicroRNA expression profiles and type 1 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and bioinformatic analysis.,” Endocrine connections, vol. 6, no. 8, pp. 773–790, Nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Martin et al., “The microRNA miR-148a functions as a critical regulator of B cell tolerance and autoimmunity.,” Nature immunology, vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 433–440, Apr. 2016. [CrossRef]
- L. Abuhatzira, H. Xu, G. Tahhan, A. Boulougoura, A. A. Schäffer, and A. L. Notkins, “Multiple microRNAs within the 14q32 cluster target the mRNAs of major type 1 diabetes autoantigens IA-2, IA-2β, and GAD65.,” FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, vol. 29, no. 10, pp. 4374–4383, Oct. 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. C. Ongagna, M. Pinget, and A. Belcourt, “Vitamin D-binding protein gene polymorphism association with IA-2 autoantibodies in type 1 diabetes,” Clinical Biochemistry, vol. 38, no. 5, pp. 415–419, 2005. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





