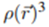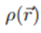1. Generalization of the boltzmann´s constant in curved space-time
Equation of state of an ideal gas as a function of the Boltzmann´ constant.
Where, P is the absolute pressure, V is the volume, N is the number of particles, KB is Boltzmann's constant, and T is the absolute temperature.
Boltzmann's constant is defined for 1 mole of carbon 12 and corresponds to 6.0221 10²³ atoms.
Equation (1) applies for atoms, molecules and for normal conditions of pressure, volume and temperature.
We will analyse what happens with equation (1) when we work in a degenerate state of matter.
We will consider an ideal neutron star, only for neutrons.
We will analyse the condition:
This condition tells us that the number of particles remains constant, under normal conditions of pressure, volume and temperature
However, in an ideal neutron star, the smallest units of particles are neutrons and not atoms.
This leads us to suppose that number of neutrons would fit in the volume of a carbon 12 atom, this amount can be represented by the symbol Dn.
In an ideal neutron star,
Where Dn represents the number of neutrons in a carbon 12 atom.
However, equation (3) is not constant, with respect to equation (2), the number of particles increased by a factor Dn, to make it constant again, I must divide it by the factor Dn.
Where N' = (Dn N), is the new number of particles if we take neutrons into account and not atoms as the fundamental unit.
Where Kʙ' = (Kʙ / Dn), is the new Boltzmann´s constant if we take neutrons into account and not atoms as the fundamental unit.
We can say that equation (2) is equal to equation (5), equal to a constant
Generalizing, it is the state in which matter is found that will determine Boltzmann's constant.
A white dwarf star a will have a Boltzmann´s constant Kʙe, a neutron star will have a Boltzmann´s constant Kʙn, and a black hole will have a Boltzmann´s constant Kʙq.
There is a Boltzmann´s constant KB that we all know for normal conditions of pressure, volume and temperature, for a flat space-time.
There is an effective Boltzmann´s constant, which will depend on the state of matter, for curved space-time.
The theory of general relativity tells us that in the presence of mass or energy space-time curves but it does not tell us how to quantify the curvature of space-time.
Here we put forward the hypothesis that there is an effective Boltzmann´ constant that depends on the state of matter and through the value that the Boltzmann´ constant takes we can measure or quantify the curvature of space-time.
2. Why is the theory of the generalization of the boltzmann´s constant correct?
There is confusion about the concepts of heat and work. We believe that such confusion is caused by the amalgamation of axiomatic and empirical definitions and ideas that get mixed up when thermodynamics is explained to someone.
Temperature definition:
Temperature is a measure of the average of one kind of energy, the translational kinetic energy.
Molecules have different components in their energy. Molecules can generally do three things:
- i)
A molecule can move. Then we will have that its kinetic energy will be, (1/2)mv² (kinetic energy of its centre of mass).
- ii)
A molecule can rotate. Molecules generally have a three-dimensional structure and can have different rotations in different directions in space, which contributes energy.
- iii)
A molecule can vibrate. Molecules are a collection of atoms that are held together by chemical bonds. These links are not rigid, but rather behave like "springs" and the molecule can undergo vibrations.
What we measure with temperature is the average translational kinetic energy of a set of molecules.
The temperature does not take into account the rest of the components, so measuring the temperature is not the same as measuring the internal energy of a system. Or put another way, two systems with the same temperature need not have the same internal energy.
When averaging generally, the result has the same dimensions and units as the concept of averaging, and here "generally" is used ironically. So, shouldn't we measure temperature in units of energy? The answer is yes, but historically we didn't realize that temperature was a measure of an energetic component of systems until relatively recently (since the work of Boltzmann and Gibbs).
In summary, we have a historical problem with the units of temperature and this is where the Boltzmann´s constant (Kʙ) comes in, which is nothing more than the appropriate conversion factor to pass the temperature in degrees (whatever), which is a “unnatural” measure, for units of energy, like Joules, for example.
Boltzmann's constant is: 1.380 6488 (13) × 10⁻²³ J/K (in the international system and with the absolute temperature scale).
As we have seen, Boltzmann's constant is simply a proportionality factor between the temperature measured in units of "temperature" and units of energy. In other words, what the constant actually does is correct the misunderstanding of the units we assign to temperature.
In school we learned that an ideal gas obeys a very simple equation that relates the pressure, volume, and temperature of the gas to its content in moles.
In this equation we have an empirical constant (determined by experimental methods), the gas constant R. This constant is nothing more than the Boltzmann constant multiplied by Avogadro's number.
That is, the Boltzmann´ constant and the gas constant are essentially the same, only one refers to a mole and the other does not.
Therefore, the equation of state for ideal gases can be written:
The number of moles n times Avogadro's number Nᴀ is a dimensionless quantity that simply tells you the number of particles you have in the gas. One mole is equivalent to the number of components of one Avogadro; Actually, a mole is not a unit and neither is a radian, it is just a useful name to simplify the concepts.
If we now study the dimensions of factor PV and factor KʙT, we will see how both have energy dimensions and everything is dimensionally consistent.
By this we wanted to show that Boltzmann's constant is not a universal constant in the sense of revealing a general characteristic of the universe, like the speed of light or Planck's constant. This constant is just an artifact of a poor choice of temperature units.
So far, we have analysed the conceptual importance of the Boltzmann´s constant, we are going to continue analysing and we are going to discover the true meaning of the Boltzmann´s constant.
We continue with the generalization of the Boltzmann´s constant.
The ideal gas law is the equation of state of the ideal gas, a hypothetical gas formed by point particles with no attraction or repulsion between them and whose collisions are perfectly elastic (conservation of momentum and kinetic energy). Kinetic energy is directly proportional to temperature in an ideal gas. The real gases that most closely approximate ideal gas behaviour are monatomic gases under conditions of low pressure and high temperature.
Molecular kinetic theory:
This theory was developed by Ludwig Boltzmann and Maxwell. It tells us the properties of an ideal gas at the molecular level.
Every ideal gas is made up of N small point particles (atoms or molecules).
Gaseous molecules move at high speeds, in a straight and disorderly way.
An ideal gas exerts a continuous pressure on the walls of the container that contains it, due to the collisions of the particles with the walls of this.
Molecular collisions are perfectly elastic. There is no loss of kinetic energy.
Molecular attraction and repulsion interactions are not taken into account.
The average kinetic energy of the translation of a molecule is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas.
If we analyse the kinetic theory of gases, we see that equation (8) applies to atoms and molecules and also to normal conditions of pressure, volume and temperature, that is, conditions that we are used to working with, in which the particles points are atoms and molecules. Now let us ask ourselves, what happens with equation (8) in a neutron star or in a plasma of quarks and gluons, where, in both cases, the point particles do not correspond to atoms or molecules?
Next, we will analyse these two situations:
- i)
Equation of state of ideal gases and neutron stars.
Idealizing, we are going to assume that neutron stars are formed solely by neutrons, that is, in this case the point particles would be neutrons.
In quantum field theory, atoms are not represented by perfect spheres of radius r as was assumed at the beginning of the 20th century, but for practical purposes in order to perform the calculations we are going to re-do this assumption and use the radius atomic number provided in the periodic table of the chemical elements.
Calculation of the scale factor of the Boltzmann´s constant when we work at the level of the atomic nucleus.
| Dc12= 1.5 10ˉ⁸ cm = 1.5 10ˉ¹⁰ m |
Where Dc12 is diameter of the C12 atom
Where Rc12 is radius of the C12 atom
Where Dn is diameter of the neutron
Where Rn is radius of the neutron
| VaC12 = (4/3) ᴨ R³ = (4/3) x 3.14 x (0.75 10ˉ¹⁰) ³ |
| VaC12 = 1.76 10ˉ³⁰ m³ |
Where VaC12 is volume of the C12 atom
| Vn = (4/3) ᴨ R³ = (4/3) x 3.14 x (0.4 10ˉ¹⁵) ³ |
| Vn = 0.267 10ˉ⁴⁵ m³ |
Where Vn is volume of the neutron
| Dn = VaC12 / Vn = 1.76 10ˉ³⁰ / 0.267 10ˉ⁴⁵ = 6.591 10¹⁵ |
| Dn = 6.59 10¹⁵ |
Where Dn is scale factor of Boltzmann's constant for neutron stars.
If we consider that at first N were formed by carbon 12 atoms (point particles); In a neutron star, the point particles correspond to neutrons and the number of point particles will be equal to the scale correction factor of the Boltzmann´s constant multiplied by N, that is, N´ = Dn x N
With this, the equation of state becomes:
| P x V = N´x Kʙ x T (9) |
| P x V = Dn x N x Kʙ x T (10) |
Now, if we consider that (P x V) / T = constant, and in addition to fulfilling that,
N increases by a factor Dn, then:
Equation (10) remains:
| P x V = Dn x N x (Kʙ /Dn) x T (11) |
| P x V = N´x Kʙn x T (12) |
| (P x V) / T = constant (13) |
If we consider the other option, Kʙ = constant, equation (11) becomes:
| P x V = (Dn N) x Kʙ x (T/ Dn) (14) |
We see, for KB = constant, the temperature of the neutron star becomes zero.
| Kʙn = Kʙ / Dn = 1.38 10ˉ²³ / 6.59 10¹⁵ |
| Kʙn = 2.0 10ˉ³⁹ J/K |
Where, Kʙn is approximate effective Boltzmann´s constant for a neutron star.
- ii)
ii) Equation of state of ideal gases and the plasma of quarks and gluons
Idealizing, we are going to suppose that in a plasma of quarks and gluons the punctual particles are the quarks.
Where Rc12 is radius of the C12 atom.
Where Rq is quark radius.
| Vc12 = (4/3) ᴨ R³ = (4/3) x 3.14 x (0.75 10⁻¹⁰) ³ |
| Vc12 = 1.76 10⁻³⁰ mᶾ |
Where Vc12 is volume of the C12 atom
| Vq = (4/3) ᴨ R³ = (4/3) x 3.14 x (0.43 10⁻¹⁸) ³ = 0.33 10⁻⁵⁴ mᶾ |
Where Vq is volume of the quark
| Dq = Vc12 / Vq = 1,76 10⁻³⁰ / 0,33 10⁻⁵⁴ = 5,33 10²⁴ |
| Dq = 5,33 10²⁴ |
Where, Dq is scale factor of Boltzmann's constant for the plasma of quarks and gluons
If we consider that at first N were formed by carbon 12 atoms (point particles), in a plasma of quarks and gluons, the point particles correspond to quarks and the amount of point particles will be equal to the scale correction factor of the Boltzmann constant multiplied by N, that is, N´ = Dq x N
With this, the equation of state becomes:
| P x V = N´x Kʙ x T (15) |
| P x V = Dq x N x Kʙ x T (16) |
if we consider that (P x V) / T = constant, and in addition to fulfilling that,
N increases by a factor Dq, then:
Equation (10) remains:
| P x V = Dq x N x (Kʙ /Dq) x T (17) |
| P x V = N´x Kʙq x T (18) |
| (P x V) / T = constant (19) |
If we consider the other option, Kʙ = constant, equation (17) becomes:
| P x V = Dq x N x Kʙ x (T/Dq) |
We see, for KB = constant, the temperature of the plasma of quarks and gluons is zero.
| Kʙq = Kʙ / Dq = 1.38 10⁻²³ / 5.33 10²⁴ = 0.25 10⁻⁴⁷ J/K |
| Kʙq = 0.25 10⁻⁴⁷ J/K |
Where, Kʙq is effective Boltzmann´s constant, at quark level scale.
3. Application of the model and results
For our calculations we are going to consider the Hawking´s equation of the temperature of a black hole as true:
T = hc³ / (8ᴨKʙGM)
Where h is Planck´s constant, c is speed light, Kʙ is Boltzmann´s constant, G is Newton´s gravitational constant and M es a mass.
3.1. Calculation of the effective Boltzmann´s constant for white dwarf stars
The masses of white dwarf stars vary from 0.5 Mϴ to 1.40 Mϴ.
Where Mϴ is solar mass
The temperature of the core of the star varies from 5 10⁶ K to 20 10⁶ K.
We are going to use the following equation, T = hc³ / (8ᴨKʙGM)
- i)
For M = 0.5 Mϴ = 0.5 x 2 10³⁰ = 10³⁰ kg
| T = 5 10⁶ K |
| Kʙ = hc³ / (8ᴨTGM) |
| Kʙe = 6.63 10⁻³⁴ x 27 10²⁴ / 8 x 3.14 x 5 10⁶ x 6.67 10⁻¹¹ x 10³⁰ |
| Kʙe = 179.01 10⁻¹⁰ / 837.75 10²⁵ = 0.2136 10⁻³⁵ |
| Kʙe = 2.136 10⁻³⁶ J/K |
| D = Kʙ / Kʙe, D = 1.38 10⁻²³ / 2.136 10⁻³⁶ = 0.646 10¹³ |
| D = 6.46 10¹² |
Where D, scale contraction factor for a white dwarf star
| D = Vc12 / Ve, Ve = Vc12 / D = 1.33 x 3.13 x 0.4218 10⁻³⁰ / 6.46 10¹² |
| Ve = 1.76 10⁻³⁰ / 6.46 10¹² = 0.272 10⁻⁴² |
| Ve = 2,727 10⁻⁴³ mᶾ |
Where Mϴ is solar mass, T is temperature, Kʙe is Boltzmann´s constant for white dwarf stars, D is scale factor of Boltzmann´s constant and Ve is volume.
- ii)
For M = 1.4 Mϴ = 1.4 x 2 10³⁰ = 2.8 10³⁰ kg
| T = 20 10⁶ K |
| Kʙ = hc³ / (8ᴨTGM) |
| Kʙe = 6.63 10⁻³⁴ x 27 10²⁴ / 8 x 3.14 x 20 10⁶ x 6.67 10⁻¹¹ x 2.8 10³⁰ |
| Kʙe = 179.01 10⁻¹⁰ / 9382.82 10²⁵ = 0.01907 10⁻³⁵ |
| Kʙe = 1.907 10⁻³⁷ J/K |
| D = Kʙ / Kʙe, D = 1.38 10⁻²³ / 1.907 10⁻³⁷ = 0.7236 10¹⁴ |
| D = 7.236 10¹³ |
Where D, scale contraction factor for a white dwarf star
| D = Vc12 / Ve, Ve = (Vc12 / D) = 1.33 x 3.13 x 0.4218 10⁻³⁰ / 7.236 10¹³ |
| Ve = 1.76 10⁻³⁰ / 7.236 10¹³ = 0.2432 10⁻⁴³ |
| Ve = 2.432 10⁻⁴⁴ mᶾ |
Where Mϴ is solar mass, T is temperature, Kʙe is Boltzmann´s constant for white dwarf stars, D is scale factor of Boltzmann´s constant and Ve is volume.
3.2. Calculation of the effective Boltzmann´s constant for neutron stars
The masses of neutron stars vary from 1.4 Mϴ to 2.2 Mϴ
Where Mϴ is solar mass.
The temperature of the core of the neutron stars varies from 10¹¹ K to 10¹² K.
We are going to use the following equation, T = hc³ / (8ᴨKʙGM)
- i)
For M = 1.4 Mϴ = 1.4 x 2 10³⁰ = 2.8 10³⁰ kg
| T = 10¹¹ K |
| Kʙ = hc³ / (8ᴨTGM) |
| Kʙn = 6.63 10⁻³⁴ x 27 10²⁴ / 8 x 3.14 x 10¹¹ x 6.67 10⁻¹¹ x 2.8 10³⁰ |
| Kʙn = 179.01 10⁻¹⁰ / 469.14 10³⁰ = 0.3815 10⁻⁴⁰ |
| KBn = 3.815 10⁻⁴¹ J/K |
| D = Kʙ / Kʙn, D = 1.38 10⁻²³ / 3.815 10⁻⁴¹ = 0.361 10¹⁸ |
| D = 3.61 10¹⁷ |
Where D, Scale contraction factor for a neutron star
| D = Vc12 / Vn, Vn = (Vc12 / D) = 1.33 x 3.13 x 0.4218 10⁻³⁰ / 3.61 10¹⁷ |
| Vn = 1.76 10⁻³⁰ / 3.61 10¹⁷ = 0.4875 10⁻⁴⁷ |
| Vn = 4.875 10⁻⁴⁸ mᶾ |
Where Mϴ is solar mass, T is temperature, Kʙn is Boltzmann´s constant for neutron stars, D is scale factor of Boltzmann´s constant and Vn is neutron volume.
- ii)
For M = 2.2 Mϴ = 2.2 x 2 10³⁰ = 4.4 10³⁰ kg
| T = 10¹² K |
| Kʙ = hc³ / (8ᴨTGM) |
| Kʙn = 6.63 10⁻³⁴ x 27 10²⁴ / 8 x 3.14 x 10¹² x 6.67 10⁻¹¹ x 4.4 10³⁰ |
| Kʙn = 179.01 10⁻¹⁰ / 737.22 10³¹ = 0.2428 10⁻⁴¹ |
| Kʙn = 2.42 10⁻⁴² J/K |
| D = Kʙ / Kʙn, D = 1.38 10⁻²³ / 2.42 10⁻⁴² = 0.5702 10¹⁹ |
| D = 5.702 10¹⁸ |
Where D, Scale contraction factor for a neutron star
| D = Vc12 / Vn, Vn = (Vc12 /D) = 1.33 x 3.13 x 0.4218 10⁻³⁰ / 5.702 10¹⁸ |
| Vn = 1.76 10⁻³⁰ / 5.702 10¹⁸ |
| Vn = 3.086 10⁻⁴⁹ mᶾ |
Where Mϴ is solar mass, T is temperature, Kʙn is Boltzmann´s constant for white dwarf stars, D is scale factor of Boltzmann´s constant and Vn is neutron volume.
3.3. Calculation of the effective Boltzmann´s constant for a black hole of three solar masses
The mass of the black hole is 3.0 Mϴ
Where Mϴ is solar mass
The temperature of a black hole at its formation is 10¹³ K.
Here it is important to clarify that the temperature of a black hole is chosen when it is formed, T = 10¹³ K, equal to the temperature at which, in particle collisions, matter forms the soup of quarks and gluons.
| M = 3Mϴ = 3 x 2 10³⁰ = 6.0 10³⁰ kg |
| T = 10¹³ K |
| Kʙ = hc³ / (8ᴨTGM) |
| Kʙq = 6.63 10⁻³⁴ x 27 10²⁴ / (8 x 3.14 x 10¹³ x 6.67 10⁻¹¹ x 6.0 10³⁰) |
| Kʙq = 179.01 10⁻¹⁰ / 1005.30 10³² = 0.1780 10⁻⁴² = 1.78 10⁻⁴³ J/k |
| Kʙq = 1.78 10⁻⁴³ J/K |
| D = Kʙ / Kʙq, D = 1.38 10⁻²³ / 1.780 10⁻⁴³ = 0.7752 10²⁰ = 7.752 10¹⁹ |
| D = 7.752 10¹⁹ |
Where D, Scale contraction factor for a black hole of three solar masses
| D = Vc12 / Vq, Vq = (Vc12 / D) = 1.33 x 3.13 x 0.4218 10⁻³⁰ / 7.752 10¹⁹ |
| Vq = 1.76 10⁻³⁰ / 7.752 10¹⁹ = 0.2270 10⁻⁴⁹ = 2.270 10⁻⁵⁰ mᶾ |
| Vq = 2,270 10⁻⁵⁰ mᶾ, volume of the quark. |
Where Mϴ is solar mass, T is temperature, Kʙq is Boltzmann´s constant for black hole, D is scale factor of Boltzmann´s constant and Vq is quark volume.
| V = (4/3) x π x R³, R = ᶾ √ (V / 1.33 x π) = ᶾ √ (2.270 10⁻⁵⁰ / 4.17) |
| V = ᶾ √ 0.5435 10⁻⁵⁰ |
| R = ᶾ √ 5.435 10⁻⁵¹ = 1.758 10⁻¹⁷ m |
| R = 1.758 10⁻¹⁷ m |
Where R, corresponds to the radius of the quark when a black hole is formed.
3.4. Determination of the curvature of space-time
Calculation of the curvature of space-time of our planet earth
curved spacetime:
| Kʙ = hc³ / (8ᴨTGM) |
| M = 5.97 10²⁴ kg |
Where T is temperature
| Kʙt = (6.62 10ˉ³⁴ x 27 10²⁴) / (8 x 3.14 x 6 10³ x 6.67 10ˉ¹¹ x 5.97 10²⁴) |
| Kʙt = 178.74 10ˉ¹⁰ / 6000.65 10¹⁶ = 0.0297 10ˉ²⁶ = 2.97 10ˉ²⁸ J/K |
| Kʙt = 2.97 10ˉ²⁸ J/K |
Where Kʙt is Boltzmann’s constant of earth
| Et = Kʙt x Tt |
| Et = 2.97 10ˉ²⁸ J/K x 6 10³ K |
| Et = 17.82 10ˉ²⁵ J |
| Et = h x ft |
Where Et is energy
| ft = Et / h = 17.82 10ˉ²⁵ / 6.62 10ˉ³⁴ = 2.69 10⁹ |
| ft = 2.69 10⁹ Hz |
Where ft is frequency
| c = λt x ft; λt = c / ft |
| λt = 3 10⁸ / 2.69 10⁹ = 1.11 10ˉ¹ = 0.11 m |
| λt = 0.11 m |
Where λt is wavelength
| Degree = λt / 360 = 0.11 / 360 = 0.00030 m |
| second of arc = degree / 3600 |
| second of arc = 0.00030 / 3600 = 0.0000000849 m |
| second of arc = 0.0000000849 m |
| second of arc = 8.49 10ˉ⁸ m |
We are going to carry out the same calculations but for Kʙ = 1.38 10ˉ²³ J/K
Flat espace-time:
| E = Kʙ x Tt |
| E = 1.38 10ˉ²³ J/K x 6 10³ K |
| E = 8.28 10ˉ²⁰ J |
| E = h x ft |
Where E is energy
Where ft is frequency
| c = λt x ft; λt = c / ft |
| λt = 3 10⁸ / 1.25 10¹⁴ = 2.4 10ˉ⁶ |
| λt = 2.4 10ˉ⁶ m |
Where λt is wavelength
| Degree = λt / 360 = 2.4 10ˉ⁶ / 360 = 0.00666 10ˉ⁶ m |
| second of arc = degree / 3600 |
| second of arc = 0.00666 10ˉ⁶ / 3600 = 1.85 10ˉ¹² |
| second of arc = 1.85 10ˉ¹² m |
| Cv = curved space time / flat space time |
| Cv = 8.49 10ˉ⁸ m / 1.85 10ˉ¹² m |
| Cv = 4.58 10⁴ times |
| 1/Cv = 21.83 microsecond |
1/Cv, time correction in GPS for the curvature of space-time in a cycle /dia.
Calculation of the force and acceleration of the earth
| F = - (G Mm) / r² |
| m = 1 kg |
| F = - 6.67 x 5.97 10²⁴ / (6.37 10⁶) ² |
| F = - 9.81 N |
| g = - 9.81 m/s² |
Calculation of the space-time curvature for the sun
curved spacetime:
| Kʙ = hc³ / (8ᴨTGM) |
| M = 1.98 10³⁰ kg |
| T = 1.5 10⁷ K |
| Kʙs = (6.62 10ˉ³⁴ x 27 10²⁴) / (8 x 3.14 x 1.5 10⁷ x 6.67 10ˉ¹¹ x 1.98 10³⁰) |
| Kʙs = 178.74 10ˉ¹⁰ / 497.62 10²⁶ = 0.3591 10ˉ³⁶ |
| Kʙs = 3.59 10ˉ³⁷ J/K |
| Es = Kʙs x Ts |
| Es = 3.59 10ˉ³⁷ x 1.5 10⁷ |
| Es = 5.38 10ˉ³⁰ J/K |
| Es = h x fs |
| fs = Es / h = 5.38 10ˉ³⁰ / 6.62 10ˉ³⁴ = 0.81 10⁴ = 8.1 10³ Hz |
| fs = 8.1 10³ Hz |
| c = λs x fs; λs = c / fs |
| λs = 3 10⁸ / 8.1 10³ = 0.37 10⁵ = 3.7 10⁴ =37,000 m |
| λs = 3.7 10⁴ m |
Where M is earth mass, T is temperature, Kʙs is Boltzmann’s constant of sun, fs is frequency and λs is wavelength.
| Degree = λs / 360 = 37000 / 360 = 102.77 m |
| second of arc = degree / 3600 |
| second of arc = 102.77 / 3600 = 0.0285 m |
| second of arc = 0.0285 m |
We are going to carry out the same calculations but for Kʙ = 1.38 10ˉ²³ J/K
Flat space-time:
| E = Kʙ x Ts |
| E = 1.38 10ˉ²³ x 1.5 10⁷ |
| E = 2.07 10ˉ¹⁶ J/K |
| E = h x f |
| f = E / h = 2.07 10ˉ¹⁶ / 6.62 10ˉ³⁴ = 0.3126 10¹⁸ |
| f = 3.12 10¹⁷ Hz |
| c = λ x f; λ = c / f |
| λ = 3 10⁸ / 0.312 10¹⁸ |
| λ = 9.61 10ˉ¹⁰ m |
| Degree = λ / 360 = 9.61 10ˉ¹⁰ / 360 = 0.02669 10ˉ¹⁰ m |
| Segundo de arco = Degree / 3600 |
| Segundo de arco = 0.02669 10ˉ¹⁰ / 3600 |
| Segundo de arco = 0.02669 10ˉ¹⁰ / 3600 = 0.00000741 10ˉ¹⁰ |
| Segundo de arco = 7.41 10ˉ¹⁶ m |
| Cv = curved space time / flat space time |
| Cv = 28.5 10ˉ³ m / 7.41 10ˉ¹⁶ m |
| Cv = 3.84 10¹³ times |
Calculation of the force and acceleration of the sun
| F = - (G Mm) / r² |
| m = 1 kg |
| Fs = - 6.67 10ˉ¹¹ x 1.98 10³⁰ / (6.95 10⁸) ² = - 13.20 10¹⁹ / 48.30 10¹⁶ = 0.273 10³ |
| Fs = - 2,73 10² N |
| gs = - 2.73 10² m/s² |
Calculation of the space-time curvature for a white dwarf star
Curved Space-time:
| Kʙ = hc³ / (8ᴨTGM) |
| Kʙe = 1.97 10ˉ³⁷ J/K |
| Ee = Kʙe x Te |
| Ee = 1.9 10ˉ³⁷ x 2 10⁷ |
| Ee = 3.8 10ˉ³⁰ J/K |
| Ee = h x fe |
| fe = Ee / h = 3.8 10ˉ³⁰ / 6.62 10ˉ³⁴ = 0.5740 10⁴ = 5.74 10³ |
| fe= 5740 Hz |
| c = λe x fe; λe = c / fe |
| λe = 3 10⁸ / 5.740 10³ |
| λe = 0.5226 10⁵ m = 52264 m = 5.224 10³ m |
Where Kʙe is Boltzmann´s constant for a white dwarf star, Ee is energy, fe is frequency and λe is wavelength.
| Degree = λe / 360 = 52264 / 360 = 145.17 m |
| second of arc = degrees / 3600 |
| second of arc = 145.17 / 3600 |
| second of arc = 0.0403 m |
We are going to carry out the same calculations but for Kʙ = 1.38 10ˉ²³ J/K
Flat space-time:
| Kʙ = 1.38 10ˉ²³ J/K |
| E = Kʙ x Te |
| E = 1.38 10ˉ²³ x 2 10⁷ |
| E = 2.76 10ˉ¹⁶ J/K |
| E = h x fe |
| fe = Ee / h = 2.76 10ˉ¹⁶ / 6,62 10ˉ³⁴ = 0.4123 10¹⁸ |
| fe= 4.12 10¹⁷ Hz |
| c = λe x fe; λe = c / fe |
| λe = 3 10⁸ / 4.12 10¹⁷ = 0.72 10ˉ⁹ m |
| Degree = λe / 360 |
| Degree = 0.72 10ˉ⁹ / 360 = 0.002 10ˉ⁹ m |
| Degree = 0.002 10ˉ⁹ m |
| second of arc = degrees / 3600 |
| second of arc = 0.002 10ˉ⁹ / 3600 = 5.55 10ˉ⁷ x 10ˉ⁹ |
| second of arc = 5.55 10ˉ¹⁶ m |
| Cv = curved space time / flat space time |
| Cv = 0.0403 m / 5.55 10ˉ¹⁶ m |
| Cv = 0.007.2 10¹⁶ |
| Cv = 7.2 10¹³ times |
Calculation of the force and acceleration of gravity for a white dwarf star
| F = - (G M m) / r² |
| m = 1 kg |
| Fe = - 6,67 10ˉ¹¹ x 2.8 10³⁰ / (6.3 10⁶) ² = - 18.67 10¹⁹ / 39.69 10¹² = - 0,47 10⁷ |
| Fe = - 4.7 10⁶ N |
| ge = - 4.7 10⁶ m/s² |
Calculation of the curvature of space-time for a neutron star
Curved space-time:
| Kʙ = hc³ / (8ᴨTGM) |
| Kʙn = 2.42 10ˉ⁴² J/K |
| En = Kʙn x Tn |
| En = 2.42 10ˉ⁴² x 10¹² |
| En = 2.42 10ˉ³⁰ J/K |
| En = h x fn |
| fn= En / h = 2.42 10ˉ³⁰ / 6.62 10ˉ³⁴ = 0.3655 10⁴ |
| fn = 3.655 10³ Hz |
| c = λn x fn; λn = c / fn |
| λn = 3 10⁸ / 3.655 10³ |
| λn = 8.207 10⁴ m |
Where Kʙn is Boltzmann´s constant for neutron star, En is energy, fn is frequency and λn is wavelength.
| Degree = λn / 360 = 82070 / 360 = 227.99 m |
| Degree = 227.99 m |
| second of arc = degrees / 3600 |
| second of arc = 227.99 / 3600 |
| second of arc = 0.0633 m |
We are going to carry out the same calculations but for Kʙ = 1.38 10ˉ²³ J/K
Flat space-time:
| Kʙ = 1.38 10ˉ²³ J/K |
| E = Kʙ x Tn |
| E = 1.38 10ˉ²³ x 10¹² |
| E = 1.38 10ˉ¹¹ J/K |
| E = h x fn |
| Fn = En / h = 1.38 10ˉ¹¹ / 6.62 10ˉ³⁴ = 0.2084 10²³ |
| Fn = 2.084 10²² Hz |
| c = λn x fn; λn = c / fn |
| λn = 3 10⁸ / 2.084 10²² |
| λn = 1.43 10ˉ¹⁴ m |
| Degree = λn / 360 = 1.43 10ˉ¹⁴ / 360 = 0.00397 10ˉ¹⁴ = 3.97 10ˉ¹⁷ m |
| Degree = 3.97 10ˉ¹⁷ m |
| second of arc = degrees / 3600 |
| second of arc = 3.97 10ˉ¹⁷ m / 3600 |
| second of arc = 3.97 10ˉ¹⁷ m / 3600 = 1.1 10ˉ²⁰ m |
| second of arc = 1.1 10ˉ²⁰ m |
| Cv = curved space time / flat space time |
| Cv = 0.0633 m / 1.1 10ˉ²⁰ m = 6.33 10ˉ² / 1.1 10ˉ²⁰ = 5.75 10¹⁸ |
| Cv = 5.75 10¹⁸ m |
Calculation of the force and acceleration of gravity for a neutron star
| F = - (G M m) / r² |
| m = 1 kg |
| Fn = - 6,67 10ˉ¹¹ x 4.4 10³⁰ / (12 10³) ² = - 29.34 10¹⁹ / 144 10⁶ = - 0,20 10¹³ |
| Fn = - 2.0 10¹² N |
| gn = - 2.0 10¹² m/s² |
Calculation of the curvature of space-time for a black hole of three solar masses
Curved space-time:
| Kʙ = hc³ / (8ᴨTGM) |
| Kʙʜ = 1.78 10ˉ⁴³ J/K |
| Eʙʜ = Kʙʜ x Tʙʜ |
| Eʙʜ = 1.78 10ˉ⁴³ x 10¹³ |
| Eʙʜ = 1.78 10ˉ³⁰ J |
| Eʙʜ = h x fʙʜ |
| fʙʜ = Eʙʜ / h = 1.78 10ˉ³⁰ / 6.62 10ˉ³⁴ = 0.2688 10⁴ |
| fʙʜ = 2.688 10³ |
| c = λ ʙʜ x fʙʜ; λʙʜ = c / fʙʜ |
| λʙʜ = 3 10⁸ / 2.688 10³ |
| λʙʜ = 1.11 10⁵ m |
Where Kʙʜ is Boltzmann´s constant for a Black Hole, Eʙʜ is energy, fʙʜ is frequency and λʙʜ is wavelength.
| Degree = λ / 360 = 111000 / 360 = 308.33 m |
| Degree = 308.33 m |
| second of arc = degree / 3600 |
| second of arc = 308.33 / 3600 |
| second of arc = 0.0856 m |
We are going to carry out the same calculations but for Kʙ = 1.38 10ˉ²³ J/K
Flat space-time:
| Kʙ = 1.38 10ˉ²³ J/K |
| E = Kʙ x Tʙʜ |
| E = 1.38 10ˉ²³ x 10¹³ |
| E = 1.38 10ˉ¹⁰ J |
| E = h x fʙʜ |
| fʙʜ = E / h = 1.38 10ˉ¹⁰ / 6.62 10ˉ³⁴ = 0.2084 10²⁴ |
| fʙʜ = 2.084 10²³ |
| c = λ ʙʜ x fʙʜ; λʙʜ = c / fʙʜ |
| λʙʜ = 3 10⁸ / 2.084 10²³ |
| λʙʜ = 1.439 10ˉ¹⁵ m |
| Degree = λ / 360 = 1.439 10ˉ¹⁵ / 360 = 0.00399 10ˉ¹⁵ = 3.9910ˉ¹⁸ m |
| Degree = 3.9910ˉ¹⁸ m |
| second of arc = degree / 3600 |
| second of arc = 3.99 10ˉ¹⁸ / 3600 = 1.108 10ˉ²¹ m |
| second of arc = 1.108 10ˉ²¹ m |
| Cv = curved space time / flat space time |
| Cv = 0.0856 m / 1.108 10ˉ²¹ m = 0.0772 10²¹ |
| Cv = 7.72 10¹⁹ |
Calculation of the force and acceleration of gravity of a black hole
| F = - (G M m) / r² |
| m = 1 kg |
| Fʙʜ = - 6,67 10ˉ¹¹ x 6 10³⁰ / (9 10³) ² = - 40.02 10¹⁹ / 81 10⁶ = - 0.5 10¹³ |
| Fʙʜ = - 5.0 10¹² N |
| gʙʜ = - 5.0 10¹² m/s² |
We must emphasize that the two methods used to calculate the characteristics of curved space-time (Kʙ, E, f, λ,Cv, g, etc), are equivalent and give us the same result.
The first method consists of taking the volume of the carbon 12 atom as a reference for a flat space-time and comparing it with the volume of a neutron or a quark, in order to calculate some fundamental characteristics of a curved space-time (Kʙ, E, f, λ,Cv, g, etc). see 2. i) and 2. ii).
The second method consists of applying the Hawking temperature equation of a black hole, T = hc³ / (8ᴨKʙGM), in order to calculate some fundamental characteristics of curved space-time (Kʙ, E, f, λ,Cv, g, etc). see 3.).
When we talk about the effective Boltzmann´s constant, we refer to a value between (1.38 10⁻²³ > Kв effective > 1.78 10⁻⁴³) J/K, for curved space-time.
When we talk about Boltzmann´s constant for flat space-time, Kв =1.38 10⁻²³ J/K.
We can also say that Newton's theory of gravity and Einstein's theory of general relativity are two sides of the same coin and as such we can use them in future calculations together with the theory of the generalization of Boltzmann's constant in curved space-time.
Elegantly, using the theory of the generalization of the Boltzmann´s constant in curved spacetime, we have shown how to quantize the curvature of space-time.
It is also important to note that the scale contraction factor of the Boltzmann´s constant D, for a white dwarf star, neutron star and a black hole, is equivalent to the curvature Cv, calculated for a curved space-time. In general, this relationship is always fulfilled, for any state of matter.
Generally, we say in the presence of mass, space-time curves; however, we saw in our calculations that in the presence of mass, space-time curves and contracts. The curvature of space time is interpreted by Einstein's theory of general relativity, in the case of the earth we quantify it by Cv = 4.58 10⁴ times. The contraction of the space-time of the mass of the earth with respect to flat space-time, we can interpret it through Newton's theory of gravity, in the case of the earth we can quantify it through a gravitational force that exerts an acceleration on the bodies of g = 9.81 m/s²
To finish with these comments, in
Table 1, we observe that to form a black hole of three solar masses, space-time is reduced or contracted by a factor of 7.72 10¹⁹ times. This is the maximum curvature of space-time that it can support. As the black hole of three solar masses grows, a phenomenon occurs that we are going to explain below, the Planck´s length begins to decrease, according to the theory of the RLC electrical model of the universe, as the black hole grows, the Planck´s length decreases until a moment comes when the black hole disintegrates producing the Big Bang.
we can intuitively say that the Big Bang is the process by which space-time recovers its original size, that is, during the Big Bang, all the space-time that was compressed to form a black hole, or primordial atom, is recovered.
4. Shannon-Bgibbs entropy ratio and the effective boltzmann´s constant
Information Theory applied to atomic systems
As mentioned, the entropy concept can be interpreted in two ways: as a measure of the system's irreversibility, within the scope of thermodynamics; and the measure of the degree of disorder of the system, in Statistical Mechanics. In these two developments, both thermodynamic entropy and statistical entropy appear not as an initial concept of a theory, but after a whole treatment and physical predictions. Within the scope of Information Theory, Shannon's entropy appears as the starting point of a theory, as a measure of uncertainty of any probability distribution, without physical predictions. The a priori detachment of physical ideas for the construction of Shannon's entropy, contrary to seeming a disadvantage in its application in Physics, allows its applicability to more diverse situations, where statistical entropy cannot be applied directly, due to restrictions of the point of view of Physics.
Being constructed based on a probability distribution, it is reasonable to analyze the probability density
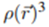
provided by Quantum Mechanics from the point of view of Information Theory. It is at this point that Information Theory comes into contact with Quantum Theory. For a continuous probability density distribution
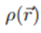
provided by the wave function of the system in position space, that is,
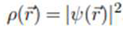
, the Shannon entropy for continuous systems, given by Eq. (2.7), takes the form:

The Shannon entropy in position space, Sr, measures the uncertainty in the particle's location in space. For atomic systems, the case treated in the present work, where the movement of electrons under the action of an atomic nucleus is studied, the quantity, multiplied by the electronic charge of the system, q, represents the electronic probability density of the system. Thus, in particular, Sr is a measure of uncertainty in the location of the electron.
By applying a Fourier Transform to the wave function in position space,, we can determine its representation in the space of moments,, and their respective probability distribution,, In this case the Shannon entropy for continuous systems takes the form:
The Shannon entropy in momentum space, Sp, measures the uncertainty in predicting the momentum of the particle, in particular the electron.
(3.11) and (3.12) respectively give the Shannon entropies of the system in position space and in momentum space. Because it treats distributions other than the Gaussian well, the Shannon entropy is thought to be a more satisfactory measure of the uncertainty or spread of a probability distribution than the measure provided by the standard deviation.
Iwo Bialynicki-Birula and Jerzy Mycielsh provide a proof for an important uncertainty relation based on Information Theory:
where n is the dimension in position space. The entropy relation thus derived came to be known as the BBM relation or entropy sum St. Such an uncertainty relation involving the Shannon entropies Sr and Sp is more general than the Heisenberg uncertainty relation, in the sense that we can derive Eq. (3.10) of Eq. (3.13), but the opposite is not possible.
The entropic uncertainty relation has the clear meaning of presenting a minimum threshold value for the sum St, which is reached by Gaussian wave functions. The conjugate Shannon entropy in position space and Shannon entropy in momentum space have an inverse relationship. In this way, the more a probability distribution is wide in the space of positions, the narrower it will be in the space of moments and vice versa, obeying Eq. (3.13).
The Shannon entropies referring to Eqs. (3.11), (3.12) and (3.13) are for probability densities for a particle. A generalization for a number N of particles is given by:
where Sr(N ) and Sp(N ) are Shannon entropies where the probability densities and , are normalized to a number N of particles. An interesting feature of the sum St(N ) is the fundamental role given the densities and, in the formalism used for Information Theory.
Using the first functional model given by the Thomas-Fermi theory for neutral atoms, Eqs. (3.14) and (3.15), respectively, take the form:
where N means the number of electrons in the atom. Comparing the relations (3.20) and (3.17) we have a very great similarity.
Initially, it is conjectured that the sum St, involving the distribution of electrons in atoms using the quantities Sr(N ) and Sp(N ), where N is the number of electrons, can take the following form:
Later works showed that the previous property is much more general, it is valid regardless of the types of constituent particles of the system (fermions or bosons), with α and β values close to depend on the type of particle in question. Thus, the form given by Eq. (3.21) is conjectured to be universal.
5. Application of the model and results
The equation (3.21) is the equation we are going to work with.
Shannon-Gibbs Entropy Relationship
Within the scope of Information Theory, Shannon's entropy appears as the starting point of a theory, as a measure of uncertainty of any probability distribution, without physical predictions.
In 1902 Gibbs presents a formalization of Statistical Mechanics with a method based on the concept of ensembles, we will understand by ensemble the set of microstates accessible to the system.
Sɢ entropy from a statistical mechanics point of view.
Kʙ, Boltzmann´s constant
5.1. For a Carbon 12 atom
A) We will calculate the Shannon-BGibbs entropy relation considering Boltzmann's constant for a white dwarf star.
a) Kвe = hc³/ (8ᴨTGM)
| Kвe = 1.90 10⁻³⁷ J/K, curved space-time. |
| For M = 1.4 Mϴ = 1.4 x 2 10³⁰ = 2.8 10³⁰ kg |
| T = 20 10⁶ K |
| Kвe = 6.63 10⁻³⁴ x 27 10²⁴ / (8 x 3.14 x 20 10⁶ x 6.67 10⁻¹¹ x 2.8 10³⁰) |
| Kвe = 1.90 10⁻³⁷ J/K |
| D = Kв / Kвe, D = 1.38 10⁻²³ / 1.90 10⁻³⁷ = 0.7236 10¹⁴ |
| D = 7,23 10¹³ |
For a carbon 12 atom, the approximate BGibbs´s entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ = 7.23 10¹³ x 1.90 10⁻³⁷ |
| Sɢ = 13.73 10⁻²⁴ |
For N = 1 carbon 12 atom, we have:
Shannon´s entropy
N = D = 7.23 10¹³, N number of particles.
St(ɴ) = 7.23 10¹³, α e β <<< N
In the volume of a carbon 12 atom under normal conditions of pressure, volume and temperature we have the amount of D = 7.23 10¹³ carbon 12 atoms in a white dwarf star.
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / BGibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 7.23 10¹³ / 13.73 10⁻²⁴ = 0.52 10³⁷ |
| R = 0,52 10³⁷ |
b) Kв = 1.38 10⁻²³ J/K, flat space-time.
For a carbon 12 atom, the approximate BGibbs´s entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ = 7.23 10¹³ x 1.38 10⁻²³ = 9.97 10⁻¹⁰ |
For N = 1 carbon 12 atom, we have:
Shannon´s entropy
N = D = 7.23 10¹³, N number of particles.
St(ɴ) = 7.23 10¹³, α e β <<< N
n the volume of a carbon 12 atom under normal conditions of pressure, volume and temperature we have the amount of D = 7.23 10¹³ carbon 12 atoms in a white dwarf star.
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / BGibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 7,23 10¹³ / 9,97 10⁻¹⁰ = 0,72 10²³ |
| R = 0,72 10²³ |
B) We will calculate the Shannon-BGibbs entropy relation considering Boltzmann's constant for a neutron star.
a) Kвn = hc³/ (8ᴨTGM)
| Kвn = 2.42 10⁻⁴² J/K, for curved space-time. |
For M = 2.2 Mϴ = 2.2 x 2 10³⁰ = 4.4 10³⁰ kg
| T = 10¹² K |
| Kвn = 6.63 10⁻³⁴ x 27 10²⁴ / 8 x 3.14 x 10¹² x 6.67 10⁻¹¹ x 4.4 10³⁰ |
| Kвn = 179.01 10⁻¹⁰ / 737.22 10³¹ = 0.2428 10⁻⁴¹ |
| Kвn = 2.42 10⁻⁴² J/K |
| D = Kв / Kвn; D = 1.38 10⁻²³ / 2.42 10⁻⁴² = 0.5702 10¹⁹ |
| D = 5.702 10¹⁸ |
For a carbon 12 atom, the approximate Gibbs entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ |
For N = 1 carbon 12 atom, we have:
| Sɢ = 5.70 10¹⁸ x 2.42 10⁻⁴² = 13.79 10⁻²⁴ |
| Sɢ = 13.79 10⁻²⁴ J/K |
Shannon´s entropy
N = D = 5.702 10¹⁸, N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 5,702 10¹⁸, α and β <<< N
In the volume of a carbon 12 atom under normal conditions of pressure, volume and temperature we have the amount D = 5,702 10¹⁸ neutrons, in an ideal neutron star.
Shannon–Gibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon entropy / Gibbs entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 5.70 10¹⁸ / 13.79 10⁻²⁴ = 0.41 10⁴² |
| R = 0.41 10⁴² |
b) Kв = 1.38 10⁻²³ J/K, flat space-time
For a carbon 12 atom, the approximate Gibbs entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ |
For N = 1 carbon 12 atom, we have:
| Sɢ = 5.70 10¹⁸ x 1.38 10⁻²³ = 7.86 10⁻⁵ |
| Sɢ = 7.89 10⁻⁵ J/K |
Shannon´s entropy
N = D = 5.702 10¹⁸; N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 5,702 10¹⁸, α and β <<< N
In the volume of a carbon 12 atom under normal conditions of pressure, volume and temperature we have the amount of D = 5.702 10¹⁸ neutrons, in an ideal neutron star.
Shannon-BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 5.70 10¹⁸ / 7.89 10⁻⁵ = 0.72 10²³ |
| R = 0.72 10²³ |
C) We will calculate the Shannon-BGibbs entropy relation considering Boltzmann's constant for a Black Hole of 3 solar masses.
a) Kвq = 1.78 10ˉ⁴³ J/K
| Kвq = hc³/ (8ᴨTGM) |
| M = 3Mϴ = 3 x 2 10³⁰ = 6.0 10³⁰ kg |
| T = 10¹³ K |
| Kвq = 6.63 10⁻³⁴ x 27 10²⁴ / (8 x 3.14 x 10¹³ x 6.67 10⁻¹¹ x 6.0 10³⁰) |
| Kвq = 1.78 10⁻⁴³ J/K; Boltzmann´s constant of a black hole. |
| D = Kв / Kвq; D = 1.38 10⁻²³ / 1.780 10⁻⁴³ = 0.7752 10²⁰ = 7.752 10¹⁹ |
| D = 7.75 10¹⁹ |
For a carbon 12 atom, the approximate Gibbs entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ |
For N = 1 carbon 12 atom, we have:
| Sɢ = 7.75 10¹⁹ x 1.78 10⁻⁴³ |
| Sɢ = 13.79 10⁻²⁴ |
Shannon´s entropy
N = D = 7.75 10¹⁹, N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 7.75 10¹⁹, α and β <<< N
In the volume of a carbon 12 atom under normal conditions of pressure, volume and temperature we have the amount of D = 7.75 10¹⁹ quarks, in a Black Hole.
Shannon-BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 7.75 10¹⁹ / 13.79 10⁻²⁴ = 0.56 10⁴³ |
| R = 0,56 10⁴³ |
b) Kв = 1.38 10⁻²³ J/K, for flat space-time
For a carbon 12 atom, the approximate Gibbs entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ |
For N = 1 carbon 12 atom, we have:
| Sɢ = 7.75 10¹⁹ x 1.38 10⁻²³ |
| Sɢ = 10.69 10⁻⁴ |
Shannon´s entropy
N = D = 7.75 10¹⁹, N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 7.75 10¹⁹, α and β <<< N
In the volume of a carbon 12 atom under normal conditions of pressure, volume and temperature we have the amount of D = 7.75 10¹⁹ quarks, in a Black Hole.
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 7.75 10¹⁹ / 10.69 10⁻⁴ = 0.72 10²³ |
| R = 0,72 10²³ |
D) We will calculate the Shannon-BGibbs entropy relation considering Boltzmann's constant under normal conditions of pressure, volume and temperature.
To carry out our calculations, we are going to use the calculations made in the Master's Thesis, written by Wallas Santos Nascimento entitled, on some characteristics of Shannon´s entropy for confined atomic systems.
From the Paper, we take the following values of St(ɴ)
Atoms with one electron:
For confined hydrogen atoms, St(ɴ) = 6.5
For confined ionized helium atom, St(ɴ) = 6.5
For doubly ionized confined lithium atom, St(ɴ) = 6.5
Atom with two electrons:
For confined helium atom, St(ɴ) = 13.0
For confined ionized lithium atom, St(ɴ) = 13.0
Confined harmonic oscillator:
For confined harmonic oscillator, St(ɴ) = 2.00
For a carbon 12 atom, the approximate Gibbs entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ |
For N = 1 carbon 12 atom, we have:
If we look at the values of St(ɴ) calculated in the examples in the paper, we see that St(ɴ) takes values between 2, 6 and 13.
St(ɴ) = α = 6
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 6 10⁰ / 1.38 10⁻²³ = 4.34 10²³ |
| R = 4.34 10²³ |
St(ɴ) = α = 13
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 1.3 10¹ / 1.38 10⁻²³ = 0.94 10²⁴ = 0.94 10²⁴ |
| R = 0.94 10²⁴ |
St(ɴ) = α = 2
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 2 10⁰ / 1.38 10⁻²³ = 1.44 10²⁴ = 1.44 10²⁴ |
| R = 1.44 10²⁴ |
5.2. For N = 6.02 10²³ particles
A) We will calculate the Shannon-BGibbs entropy relation considering Boltzmann's constant for a white dwarf star.
a) Kвe = 1.90 10⁻³⁷ J/K, curved space-time.
| Kвe = hc³/ (8ᴨTGM) |
| For M = 1.4 Mϴ = 1.4 x 2 10³⁰ = 2.8 10³⁰ kg |
| T = 20 10⁶ K |
| Kвe = 6.63 10⁻³⁴ x 27 10²⁴ / (8 x 3.14 x 20 10⁶ x 6.67 10⁻¹¹ x 2.8 10³⁰) |
| Kвe = 1.90 10⁻³⁷ J/K |
| D = Kв / Kвe; D = 1.38 10⁻²³ / 1.90 10⁻³⁷ = 0.7236 10¹⁴ |
| D = 7.23 10¹³ |
For N = 6.02 10²³ particles, the approximate Gibbs´s entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ = 6.02 10²³ x 1.9 10⁻³⁷ = 8.3 10⁻¹⁴ |
Shannon´s entropy
N = 6.02 10²³; N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 6.02 10²³; α and β <<< N
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 6.02 10²³ / 8.3 10⁻¹⁴ = 0.72 10³⁷ |
| R = 0.72 10³⁷ |
b) Kв = 1.38 10⁻²³ J/K, for flat spacetime
For N = 6.02 10²³ particles, the approximate BGibbs´s entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ = 6.02 10²³ x 1.38 10⁻²³ = 8.3 |
| Para N = 6.02 10²³: |
| Sɢ = 8.3 J/K |
Shannon´s entropy
N = 6.02 10²³; N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 6.02 10²³, α and β <<< N
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon entropy / Gibbs entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 6.02 10²³ / 8.3 = 0.72 10²³ |
| R = 0.72 10²³ |
B) We will calculate the Shannon-BGibbs entropy relation considering Boltzmann's constant for a neutron star
a) Kвn = 2.42 10⁻⁴² J/K, for curved spacetime
| Kвn = hc³/ (8ᴨTGM) |
| For M = 2.2 Mϴ = 2.2 x 2 10³⁰ = 4.4 10³⁰ kg |
| T = 10¹² K |
| Kвn = 6.63 10⁻³⁴ x 27 10²⁴ / (8 x 3.14 x 10¹² x 6.67 10⁻¹¹ x 4.4 10³⁰) |
| Kвn = 2.42 10⁻⁴² J/K |
| D = Kв / Kвn; D = 1.38 10⁻²³ / 2.42 10⁻⁴² = 0.5702 10¹⁹ |
| D = 5.702 10¹⁸ |
For N = 6.02 10²³ particles, the approximate Gibbs entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ |
| Sɢ = 6.02 10²³ x 2.42 10⁻⁴² = 14.56 10⁻¹⁹ |
| Sɢ = 1.45 10⁻¹⁸ J/K |
Shannon´s entropy
N = 6.02 10²³; N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 6.02 10²³; α and β <<< N
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 6.02 10²³ / 1.45 10⁻¹⁸ = 4.15 10⁴¹ |
| R = 4.15 10⁴¹ |
b) Kв = 1.38 10⁻²³ J/K, for flat space-time
For N = 6.02 10²³ particles, the approximate Gibbs entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ |
For N = 6.02 10²³ particles, we have:
| Sɢ = 6.02 10²³ x 1.38 10⁻²³ = 8.31 |
| Sɢ = 8.31 J/K |
Shannon´s entropy
N = 6.02 10²³, N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 6.02 10²³, α and β <<< N
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 6.02 10²³ / 8.31 = 0.72 10²³ |
| R = 0.72 10²³ |
C) We will calculate the Shannon-BGibbs entropy relation considering the Boltzmann´s constant for a Black Hole of 3 solar masses.
a) Kвq = 1.78 10⁻⁴³ J/K, for curved space-time
| Kвq = hc³/ (8ᴨTGM) |
| M = 3Mϴ = 3 x 2 10³⁰ = 6.0 10³⁰ kg |
| T = 10¹³ K |
| Kвq = 6.63 10⁻³⁴ x 27 10²⁴ / (8 x 3.14 x 10¹³ x 6.67 10⁻¹¹ x 6.0 10³⁰) |
| Kвq = 1.78 10⁻⁴³ J/K, Boltzmann constant of a black hole |
| D = Kв / Kвq, D = 1.38 10⁻²³ / 1.780 10⁻⁴³ = 0.7752 10²⁰ = 7.752 10¹⁹ |
| D = 7.75 10¹⁹ |
For N = 6.02 10²³ particles, the approximate Gibbs´s entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ |
For N = 6.02 10²³, we have:
| Sɢ = 6.02 10²³ x 1.78 10⁻⁴³ |
| Sɢ = 1.07 10⁻¹⁹ |
Shannon´s entropy
N = 6.02 10²³, N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 6.02 10²³, α and β <<< N
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 6.02 10²³ / 1.07 10⁻¹⁹ = 5.6 10⁴² |
| R = 5.6 10⁴² |
b) Kв = 1.38 10⁻²³ J/K, for flat spacetime
For N = 6.02 10²³ particles, the approximate Gibbs entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ |
For N = 6.02 10²³, we have:
| Sɢ = 6.02 10²³ x 1.38 10⁻²³ = 8.31 |
| Sɢ = 8.31 J/K |
Shannon´s entropy
N = 6.02 10²³, N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 6.02 10²³, α and β <<< N
Shannon-BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 6.02 10²³ / 8.31 = 0.72 10²³ |
| R = 0.72 10²³ |
5.3. For N = 10¹⁵ 6.02 10²³ particles
A) We will calculate the Shannon-BGibbs entropy relation considering Boltzmann's constant for a white dwarf star.
a) Kвe = 1.907 10⁻³⁷ J/K, for curved space-time
| Kвe = hc³/ (8ᴨTGM) |
| For M = 1.4 Mϴ = 1.4 x 2 10³⁰ = 2.8 10³⁰ kg |
| T = 20 10⁶ K |
| Kвe = 6.63 10⁻³⁴ x 27 10²⁴ / (8 x 3.14 x 20 10⁶ x 6.67 10⁻¹¹ x 2.8 10³⁰) |
| Kвe = 1.907 10⁻³⁷ J/K |
| D = Kв / Kвe, D = 1.38 10⁻²³ / 1.907 10⁻³⁷ = 0.7236 10¹⁴ |
| D = 7.236 10¹³ |
For N = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, the approximate Gibbs entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ = 10¹⁵ 6.02 10²³ x 1.9 10⁻³⁷ = 8.3 10¹ |
For N = 10¹⁵ 6.02 10²³, we have:
Shannon´s entropy
N = 10¹⁵ 6.02 10²³, N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 10¹⁵ 6.02 10²³, α and β <<< N
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 10¹⁵ 6.02 10²³ / 8.3 10¹ = 0.72 10³⁷ |
| R = 0.72 10³⁷ |
b) Kв = 1.38 10⁻²³ J/K, for flat space-time
For N = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³ particles, the approximate Gibbs entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³ x 1.38 10⁻²³ = 8.3 10¹⁵ |
For N = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, we have:
Shannon´s entropy
N = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, α and β <<< N
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³ / 8.3 10¹⁵ = 0.72 10²³ |
| R = 0.72 10²³ |
B) We will calculate the Shannon-Gibbs entropy relation considering Boltzmann's constant for a neutron star.
a) Kвn = 2.42 10⁻⁴² J/K, for curved space-time
For M = 2.2 Mϴ = 2.2 x 2 10³⁰ = 4.4 10³⁰ kg
| T = 10¹² K |
| Kвn = 6.63 10⁻³⁴ x 27 10²⁴ / (8 x 3.14 x 10¹² x 6.67 10⁻¹¹ x 4.4 10³⁰) |
| Kвn = 2.42 10⁻⁴² J/K |
| D = Kв / Kвn, D = 1.38 10⁻²³ / 2.42 10⁻⁴² = 0.5702 10¹⁹ |
| D = 5,702 10¹⁸ |
For N = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³ particles, the approximate Gibbs`s entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ |
For N = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, we have:
| Sɢ = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³ x 2.42 10⁻⁴² = 14.56 10⁻⁴ |
| Sɢ = 1.45 10⁻³ J/K |
Shannon´s entropy
N = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, α and β <<< N
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³ / 1.45 10⁻³ = 4.15 10⁴¹ |
| R = 4,15 10⁴¹ |
b) Kв = 1.38 10⁻²³ J/K, for flat space-time
For N = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, the approximate Gibbs´s entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ |
For N = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, we have:
| Sɢ = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³ x 1.38 10⁻²³ = 8.31 10¹⁵ |
| Sɢ = 8.31 10¹⁵ J/K |
Shannon´s entropy
N = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, α and β <<< N
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³ / 8.31 10¹⁵ = 0.72 10²³ |
| R = 0.72 10²³ |
C) We will calculate the Shannon-Gibbs entropy relation considering the Boltzmann´s constant for a Black Hole of 3 solar masses.
a) Kвq = 1.78 10⁻⁴³ J/K, for a curved space-time
| Kвq = hc³/ (8ᴨTGM) |
| M = 3Mϴ = 3 x 2 10³⁰ = 6.0 10³⁰ kg |
| T = 10¹³ K |
| Kвq = 6.63 10⁻³⁴ x 27 10²⁴ / (8 x 3.14 x 10¹³ x 6.67 10⁻¹¹ x 6.0 10³⁰) |
| Kвq = 1.78 10⁻⁴³ J/K Boltzmann´s constant of a black hole |
| D = Kв / Kвq, D = 1.38 10⁻²³ / 1.780 10⁻⁴³ = 0.7752 10²⁰ = 7.752 10¹⁹ |
| D = 7.75 10¹⁹ |
For N = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³ particles, the approximate Gibbs´s entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ |
For N = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, we have:
| Sɢ = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³ x 1.78 10⁻⁴³ |
| Sɢ = 1,07 10⁻⁴ J/K |
Shannon´s entropy
N = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, α and β <<< N
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³ / 1.07 10⁻⁴ = 5.6 10⁴² |
| R = 5.6 10⁴² |
b) Kв = 1.38 10⁻²³ J/K, for flat space-time
For N = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³ particles, the approximate Gibbs entropy will be:
| Sɢ = ΔE /T = PV/T = nR = N Kʙ |
For N = 10¹⁵x 6.02 10²³, we have:
| Sɢ = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³ x 1.38 10⁻²³ = 8.31 10¹⁵ |
| Sɢ = 8.31 10¹⁵ J/K |
Shannon´s entropy
N = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, N number of particles
St(ɴ) = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³, α and β <<< N
Shannon–BGibbs entropy relation
| R = Shannon´s entropy / Gibbs´s entropy |
| R = St(ɴ) / Sɢ |
| R = 10¹⁵ x 6.02 10²³ / 8.31 10¹⁵ = 0.72 10²³ |
| R = 0.72 10²³ |
5.4. We will calculate the approximate Shannon-Gibbs relationship for white dwarf stars, neutron stars and black holes.
A) Calculation of the Shannon-Gibbs relationship for white dwarf stars.
a) Curve space-time:
| M = 0.76 solar masses |
| R = 0.01 Radius of the sun |
| M = 2 10³⁰ x 0.76 |
| M = 1.52 10³⁰ kg |
Where M is mass
| R = 0.01 x 6.96 10⁸ m |
| R = 6.96 10⁶ m |
Where R is radius
| Vt = (4/3) x π x R³ |
| Vt = 337.15 10²⁷ m³ |
Where Vt is Volume
| N = 337.15 10²⁷ / 2.43 10⁻⁴⁴ |
| N = 138.74 10⁷¹ |
Where N is particles numbers
| Sɢ = N Kʙe = 138.74 10⁷¹ x 1.90 10⁻³⁷ |
| Sɢ = 263.60 10³⁴ |
| Sɢ = 2.63 10³⁶ J/K |
Where Sɢ is Gibbs´s entropy
| St(N) = N = 138.74 10⁷¹ |
| St(N) = 138.74 10⁷¹ = 1.38 10⁷³ |
Where St(N) Shannon´s entropy
| R = St(N) / Sɢ |
| R = 138.74 10⁷¹ / 2.63 10³⁶ |
| R = 5.27 10³⁶ |
Where R is Shannon-Gibbs entropy relation
b) Flat space-time:
| Sɢ = N Kʙ = 138.74 10⁷¹ x 1.38 10⁻²³ |
| Sɢ = 191.46 10⁴⁸ J/K |
Where Sɢ is Gibbs´s entropy
Where St(N) Shannon´s entropy
| R = St(N) / Sɢ |
| R = 138.74 10⁷¹ / 191.46 10⁴⁸ |
| R = 0.72 10²³ |
Where R is Shannon-Gibbs entropy relation
B) Calculation of the Shannon-Gibbs relation for neutron stars
Where R is radius
| Vt = (4/3) x π x R³ |
| Vt = 3580.56 10⁹ m |
Where Vt is volume
| N = Vt / Vn = 3580.56 10⁹ / 4.87 10⁻⁴⁸ |
| N = 735.22 10⁵⁷ = 73.52 10⁵⁸ |
Where N is particles number
| Sɢ = N Kʙe = 7.3510⁵⁹ x 3.81 10⁻⁴¹ |
| Sɢ = 28,00 10¹⁸ J/K |
Where Sɢ is Gibbs´s entropy
| St(N) = N = 73.52 10⁵⁸ |
| St(N) = 73.52 10⁵⁸ |
Where St(N) is Shannon´s entropy
| R = St(N) / Sɢ |
| R = 73.52 10⁵⁸ / 28.00 10¹⁸ |
| R = 2.62 10⁴⁰ |
Where R is Shannon-Gibbs entropy relation
b) Flat space-time:
| Sɢ = N Kʙn = 7.3510⁵⁹ x 1.38 10⁻²³ |
| Sɢ = 10.14 10³⁶ J/K |
Where Sɢ is Gibbs´s entropy
Where St(N) is Shannon´s entropy
| R = St(N) / Sɢ |
| R = 7.35 10⁵⁹ / 10.14 10³⁶ |
| R = 0.72 10²³ |
Where R is Shannon-Gibbs entropy relation
C) Calculation of the Shannon-BGibbs relation for black holes
a) Curved space-time:
| M = 3 solar masses = 6 10³⁰ kg |
Where R is radius
| Vt = (4/3) x π x R³ |
| Vt = 2934,17 10³ m³ |
Where Vt is volume
| N = Vt / Vq = 2934,17 10⁹ / 2,27 10⁻⁵⁰ |
| N = 1292.17 10⁵⁹ = 12.92 10⁶¹ |
Where N is particles numbers
| Sɢ = N Kʙq = 12.92 10⁶¹ x 1.78 10⁻⁴³ |
| Sɢ = 2.29 10¹⁹ J/K |
Where Sɢ is Gibbs´s entropy
| St(N) = N = 12.92 10⁶¹ |
| St(N) = 12.92 10⁶¹ |
Where St(N) is Shannon´s entropy
| R = St(N) / Sɢ |
| R = 12.92 10⁶¹ / 2.29 10¹⁹ |
| R = 5.64 10⁴² |
Where R is Shannon-Gibbs entropy relation
b) Flat space-time:
| Sɢ = N Kʙ = 12.92 10⁶¹ x 1.38 10⁻²³ |
| Sɢ = 17.82 10³⁸ J/K |
Where Sɢ is Gibbs´s entropy
| St(N) = N = 12.92 10⁶¹ |
| St(N) = 12.92 10⁶¹ |
Where St(N) is Shannon´s entropy
| R = St(N) / Sɢ |
| R = 12.92 10⁶¹ / 17.82 10³⁸ |
| R = 0.72 10²³ |
Where R is Shannon-Gibbs entropy relation
5.5. Analysis and example
If we look at
Table 2, we see that the Shannon-Gibbs entropy relation depends on the effective Boltzmann´s constant. We see that for Kʙ = 1.38 10ˉ²³ J/K, the entropy relationship is the same for the different states of matter, if we change the effective Boltzmann´s constant, we see that it depends on the number of fundamental particles.
In conclusion, we define that the effective Boltzmann´s constant determines the Shannon-Gibbs entropy relation and this remains constant, that is, there is no loss of information, as long as the effective Boltzmann´s constant is the same.
We can see that the information is encoded in the number of fundamental particles (neutrons, quarks, etc.); which we represent by the effective Boltzmann´s constant. Through this mechanism the information is always preserved.
In the article, RLC electrical modelling of black hole and early universe. Generalization of Boltzmann's constant in curved space-time, there are many examples related to the effective Boltzmann´s constant.
Next, we will present an extremely important example that will help us understand how the effective Boltzmann´s constant is related to the origin of elementary particles; In addition to helping us understand how the theory of the generalization of Boltzmann's constant allows us to unite the theory of general relativity and quantum mechanics.
Example:
Origin of the electron, the down quark and the top quark
To determine the origin of the fundamental particles, it is important to use the generalization theory of Boltzmann's constant for curved space-time and also to understand the concept of symmetry breaking of the electroweak unification theory.
The concept of symmetry breaking in electroweak unification theory basically explains how the Higgs field gives mass to fundamental particles. In a simple, didactic and non-technical way we are going to demonstrate how fundamental particles really acquire mass.
The theory of the generalization of the Boltzmann´s constant for curved space-time teaches us that there is an electromagnetic energy and a gravitational energy, in other words, there is an electromagnetic temperature and a gravitational temperature, an electromagnetic frequency and a gravitational frequency and also a length electromagnetic wave and a gravitational wavelength.
The generalization theory of Boltzmann's constant for curved spacetime associates electromagnetic energy to the field of strong and weak electromagnetic interactions; it also associates gravitational energy to space-time, that is, to the field of gravitational interactions.
The theory of the generalization of the Boltzmann constant for curved space-time, allows us to unite the theory of general relativity and the theory of quantum mechanics, allowing us to define a spectrum of gravitational waves, gravitons, analogous to the spectrum of electromagnetic waves, photons; In this way, we are able to quantify the curvature of space-time in the presence of mass or energy.
Spectrum of electromagnetic waves:
| Eε = h x fε |
| Cε = λε x fε |
| Eε = h x Cε / λε |
| Eε = Kʙε x Tε |
| Kʙɛ = 1.38 10⁻²³ J/K |
Gravitational wave spectrum:
| Eɢ = h x fɢ |
| Cɢ = λɢ x fɢ |
| Eɢ = h x Cɢ / λɢ |
| Eɢ = Kʙɢ x Tɢ |
| Kʙɢ = 1.38 10⁻²³ J/K to 1.78 10⁻⁴³ J/K |
Einstein's equation of general relativity and the correspondence of Maldacena ADS = CFT, tells us that both matter (energy) and space-time have to be quantized and through the generalization theory of Boltzmann's constant we achieve that goal.
We consider T = 10¹⁰ K and a contraction of space-time in a dimension of 10⁵ times, with respect to flat space-time for Kʙ = 1.38 10⁻²³ J/K.
In the analysis we performed on the item: 3.3. Calculation of the effective Boltzmann´s constant for a black hole of three solar masses; we see that the contraction factor of Boltzmann's constant, D, is equal to D = 7.52 10¹⁹, in three dimensions. In one dimension it would be approximately 10⁶.
For the electron and down quark, we are going to consider a contraction factor in a dimension of the order of 10⁵, for a temperature of 10¹⁰ K.
Let's calculate the wavelength of the electron:
| C = λ x f |
| λ = C / f |
| λ = 3 10⁸ / 1.23 10²⁰ = 2.44 10⁻¹² m |
| λ / 2 = 1.22 10⁻¹² m |
Where C is speed light, f is frequency and λ is wavelength for flat space-time.
Calculation of the diameter of the electron:
To calculate the diameter of the electron, we are going to consider the scale contraction factor of Boltzmann's constant for the electron, D = 10⁵.
| De = (λ/2) / 10⁵ = 1.22 10⁻¹² / 10⁵ = 1.22 10⁻¹⁷ m |
| De = 1.22 10⁻¹⁷ m |
Re, electron radius
See reference article (2), the diameter of the electron must be less than < 10ˉ¹⁷ m, a value very close to the calculated De = 1.22 10⁻¹⁷ m, Rtq = 6.1 10ˉ¹⁸ m.
In this example, intuitively, using the theory of the generalization of Boltzmann's constant in curved space-time, we have calculated the diameter and radius of the electron.
The conceptual idea of the origin of the fundamental particles is simple and compatible with the theory of the Higgs´s field.
It also gives us to understand the difference between Fermions and Bosons.
Fermions are bosons that, upon reaching certain physical characteristics, get space-time to surround them, forming the fundamental particles, that condition, makes them move at a speed less than light. Bosons are energetic entities that cannot be enveloped or covered by space-time and therefore move at the speed of light. Temperature plays a fundamental role in this entire process.
In the next article we will generalize for the rest of the fundamental particles.
Above 10¹⁶ k, temperature at which the symmetry break occurs.
Calculation of the diameter of the down quark
| C = λ x f |
| λ = C / f |
| λ = 3 10⁸ / 11.60 10²⁰ = 2.58 10⁻¹³ m |
| λ / 2 = 1.29 10⁻¹³ m |
Where C is speed light, f is frequency and λ is wavelength for flat space-time.
To calculate the diameter of the down quark, we are going to consider the scale contraction factor of Boltzmann's constant for down quark, D = 10⁵.
| Ddq = (λ/2) / D |
| Ddq = (λ/2) / 10⁵ = 1.29 10⁻¹³ / 10⁵ = 1.29 10⁻¹⁸ m |
| Ddq = 1.29 10⁻¹⁸ m |
Rdq, down quark radius
See reference article (1), the radius of the quark is given by Rq = 0.43 10ˉ¹⁸ m, a value very close to the calculated Rdq = 0.64 10⁻¹⁸ m.
Calculation of the diameter of the top quark
For top quark, we are going to consider a contraction factor in a dimension of the order of 10⁶, for a temperature of 10¹⁵ K.
| E = Kʙ x T |
| E = 1.38 10ˉ²³ x 2 10¹⁵ = 2.76 10ˉ⁸ J |
| E = h x f |
| f = E / h = 2.76 10ˉ⁸ / 6.62 10ˉ³⁴ = 0.41 10²⁶ = 4.1 10²⁵ Hz |
| c = λ x f |
| λ = c/f = 3 10⁸ / 4.1 10²⁵ = 0.73 10ˉ¹⁷m |
| λ = 7.3 10ˉ¹⁸ m |
Where C is speed light, f is frequency, λ is wavelength for flat space-time.
To calculate the diameter of the top quark, we are going to consider the scale contraction factor of Boltzmann's constant for top quark, D = 10⁶.
| Dtq = (λ/2) / D |
| Dtq = (λ/2) / 10⁶ = 3.65 10⁻¹⁸ / 10⁶ = 3.65 10⁻²⁴ m |
| Dtq = 3.65 10⁻²⁴ m |
Dtq, diameter of the top quark
| Rtq = 1.82 10⁻²⁴ m |
| Rtq = radius of the top quark |
In the examples given, in the calculation of the diameter of the electron, of the down quark and the top quark, by means of a simple conceptual idea, given by the theory of the generalization of the Boltzmann´s constant in curved space-time, we can perceive how the theory Quantum joins the theory of gravity to explain the origin of elementary particles.
It is important to clarify that temperature is a very important parameter in determining the scale factor of Boltzmann's constant in curved space-time.
Above the temperature 10¹⁶ K, symmetry break, it is understood that the force of disintegration or repulsion is much greater than the force of compression of space-time, in this situation, it is not possible to form particles of matter.
6. Conclusions
We have shown that the theory of the generalization of the Boltzmann´s constant in curved space-time allows us to quantify or measure the curvature and contraction of space-time, that is: in the presence of a mass in the structure of space-time, we can quantify the curvature and contraction of space-time by means of the following parameters, Cv (curvature of space-time), D (space-time compression or expansion factor of space-time) and g (gravitational acceleration). This simple conceptual idea is what we use to determine the origin of fundamental particles, specifically, we use the contraction factor of Boltzmann's constant D, to quantify the radius of the fundamental particles.
In order to quantify the curvature and contraction of space-time, we have developed the concept of effective Boltzmann´s constant, which is nothing more than considering the variable Boltzmann´s constant, which depends on the state of matter. In other words, there is a Boltzmann´s constant for flat space-time (Kʙ = 1.38 10⁻²³ J/K) and an effective Boltzmann´s constant (Kʙ = 1.38 10⁻²³ J/K to 1.78 10⁻⁴³ J/K), for curved space-time.
We have also shown by means of the Shannon-Boltzmann-Gibbs entropy relation that there is no loss of information, the information is encoded in the number of particles and depends on the state of matter, in other words, depends of the effective Boltzmann´s constant.
Finally, we must remember that in the presence of mass, space-time is curved and contracted, precisely the concept of curvature and contraction of space-time is what allows us to quantify it, using this simple conceptual idea, through the theory of generalization of the Boltzmann´s constant in curved space-time, we managed to unite the theory of gravity with the theory of quantum mechanics, which we try to demonstrate through simple examples in which we calculate the radius of the electron, down quark and top quark.
About the authors
HECTOR GERARDO FLORES (ARGENTINA, 1971). I studied Electrical Engineering with an electronic orientation at UNT (Argentina); I worked and continue to work in oil companies looking for gas and oil for more than 25 years, as a maintenance engineer for seismic equipment in companies such as Western Atlas, Baker Hughes, Schlumberger, Geokinetics, etc.
Since 2010, I study theoretical physics in a self-taught way.
In the years 2020 and 2021, during the pandemic, I participated in the course and watched all the online videos of Cosmology I and Cosmology II taught by the Federal University of Santa Catarina, UFSC.
MARIA ISABEL GONÇALVEZ DE SOUZA (Brazil, 1983). I studied professor of Portuguese language at the Federal University of Campina Grande and professor of pedagogy at UNOPAR University, later I did postgraduate, specialization. I am currently a qualified teacher and I work for the São Joao do Rio do Peixe Prefecture, Paraiba. I am Hector's wife and my studies served to collaborate in the formatting of his articles, corrections, etc; basically, help in the administrative part with a small emphasis in the technical part analysing and sharing ideas.
Conflicts of Interests
The authors declares that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- ZEUS Collaboration, 2016. Limits on the effective quark radius from inclusive ep scattering at HERA. Accepted for publication in Physics Letters B. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1604.01280.pdf.
- Reinaldo Augusto da Costa Bianchi. UNIVERSIDADE DE SÃO PAULO, INSTITUTO DE FÍSICA PARTÍCULAS ELEMENTARES: A PROCURA DAS PARTÍCULAS W E Z. https://fei.edu.br/~rbianchi/publications/particulas-elementares.pdf.
- Flores, H. G; Preprints 2023, 2023052246. Rlc Electrical Modelling of Black Hole and Early Universe. Generalization of Boltzmann’s Constant in Curved Space-Time. [CrossRef]
- Laurent Pitre ∗, Mark D. Plimmer, Fernando Sparasci, Marc E. Himbert; 2019. Determinations of the Boltzmann constant. https://hal.science/hal-02166573/file/1-s2.0-S1631070518301348-main.pdf.
- Eisberg Resnick, Física Cuántica.
- Eyvind, H. Wichmann. Física cuántica.
- Sears – Zemansky. Física Universitaria con Física Moderna Vol II.
- Dissertação de Mestrado, Wallas Santos Nascimento, Universidade Federal da Bahia, Instituto de Física, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Física, Junho de 2013. Dissertação intitulada: Sobre algumas características da entropia de Shannon para sistemas atômicos confinados. https://repositorio.ufba.br/bitstream/ri/28664/1/disserta%C3%A7%C3%A3o_wallas_final.pdf.
- La Constante de Boltzmann y la temperature https://cuentoscuanticos.com/2011/10/08/constante-de-boltzmann-temperatura/. 2011.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
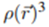 provided by Quantum Mechanics from the point of view of Information Theory. It is at this point that Information Theory comes into contact with Quantum Theory. For a continuous probability density distribution
provided by Quantum Mechanics from the point of view of Information Theory. It is at this point that Information Theory comes into contact with Quantum Theory. For a continuous probability density distribution 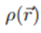 provided by the wave function of the system in position space, that is,
provided by the wave function of the system in position space, that is, 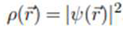 , the Shannon entropy for continuous systems, given by Eq. (2.7), takes the form:
, the Shannon entropy for continuous systems, given by Eq. (2.7), takes the form: