Submitted:
01 September 2023
Posted:
05 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study site and treatment
2.2. Shoot growth
2.3. Leaf traits
2.4. Chlorophyll SPAD values
2.5. Leaf biomass
2.6. Fruit traits
2.7. Data analysis
3. Results
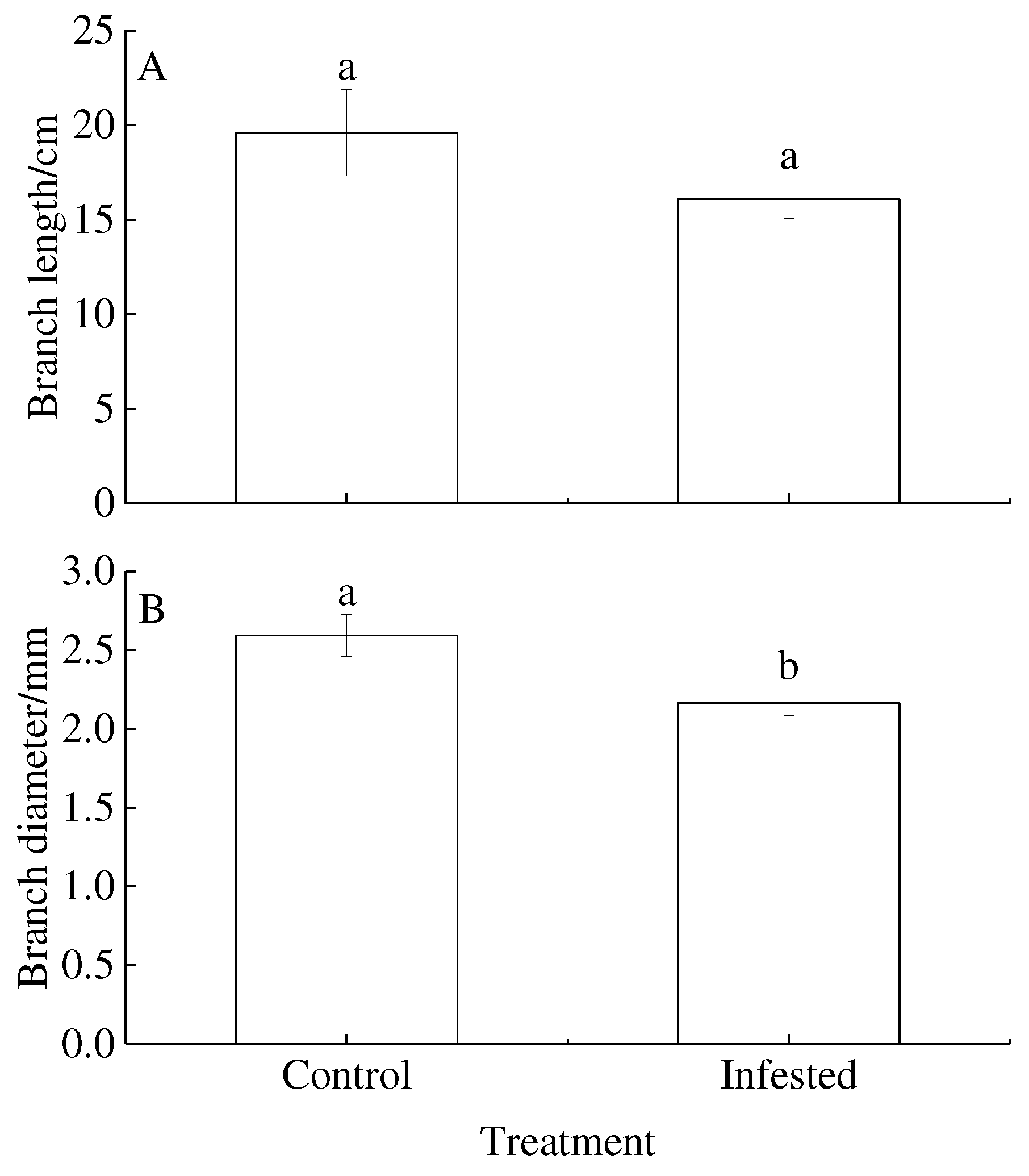
3.1. Shoot growth
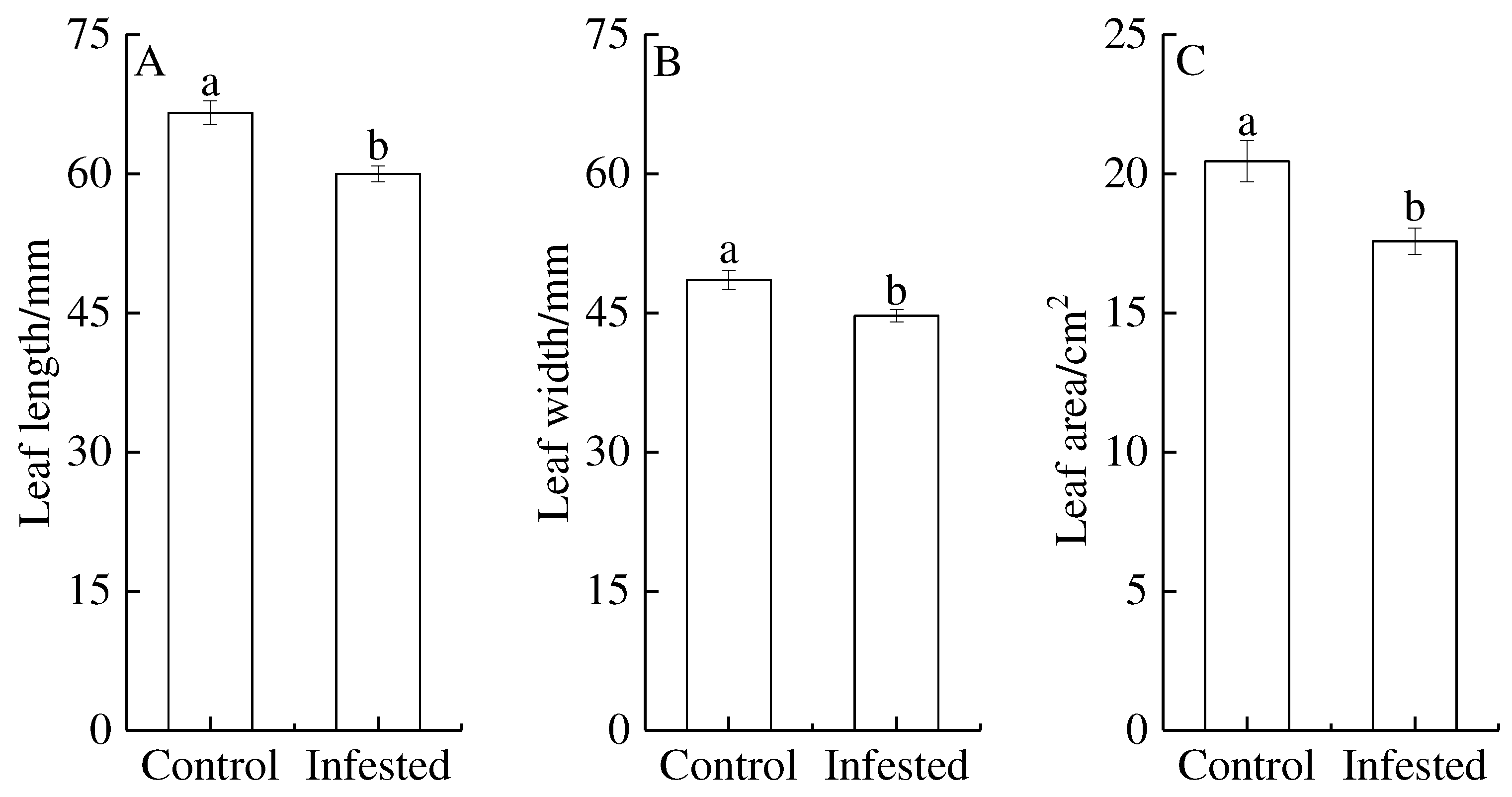
3.2. Leaf traits
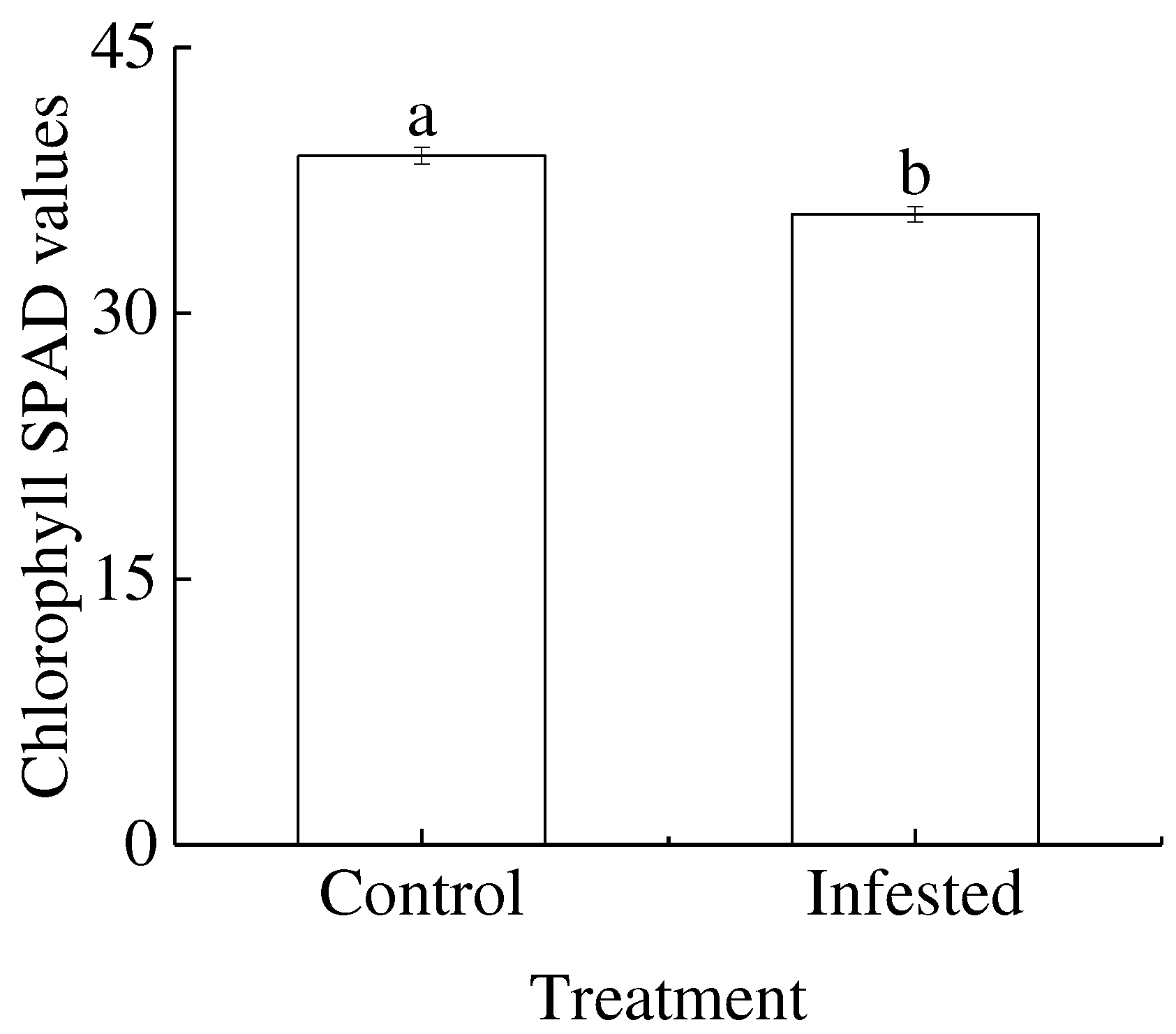
3.3. Chlorophyll SPAD values
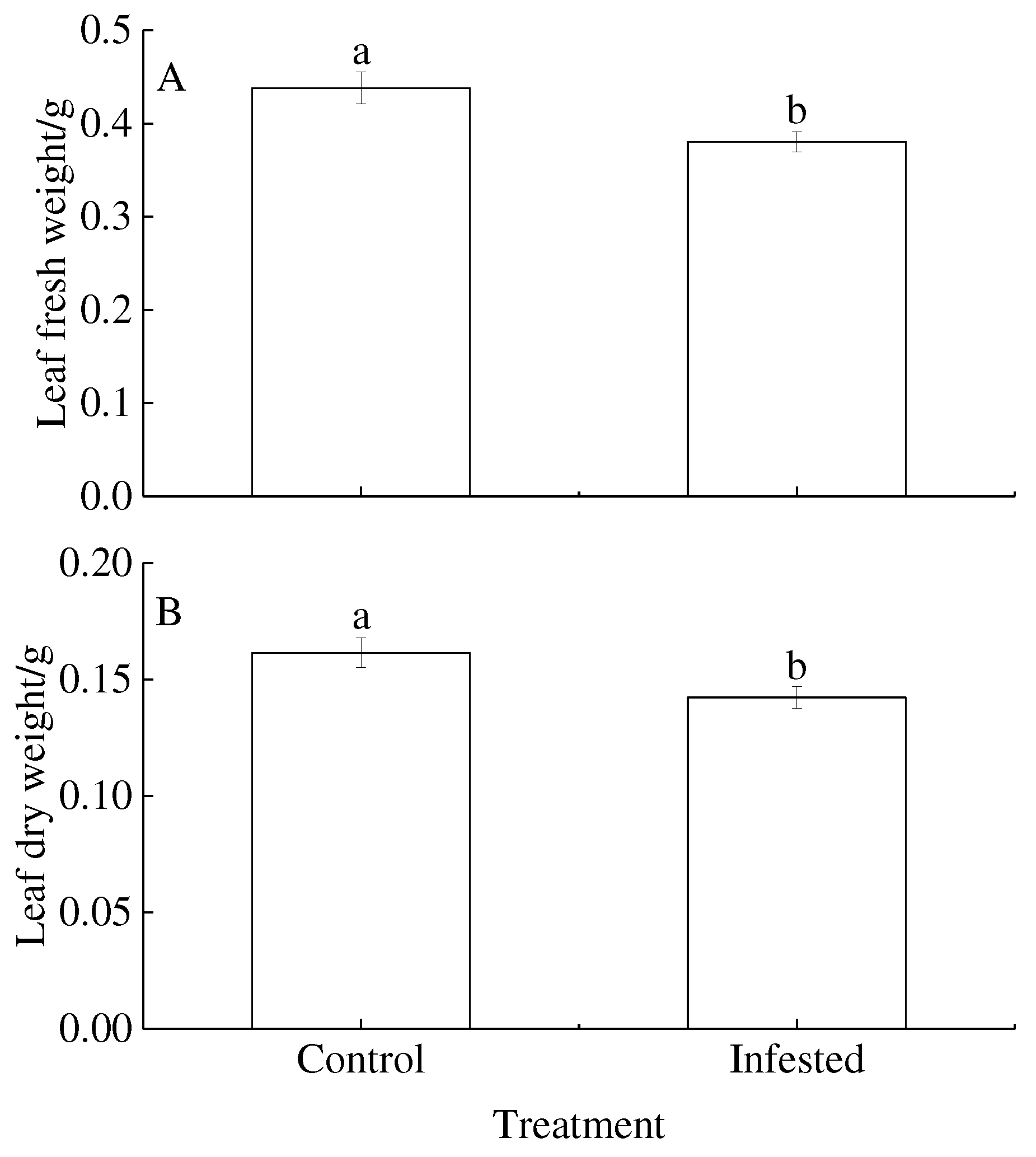
3.4. Leaf biomass
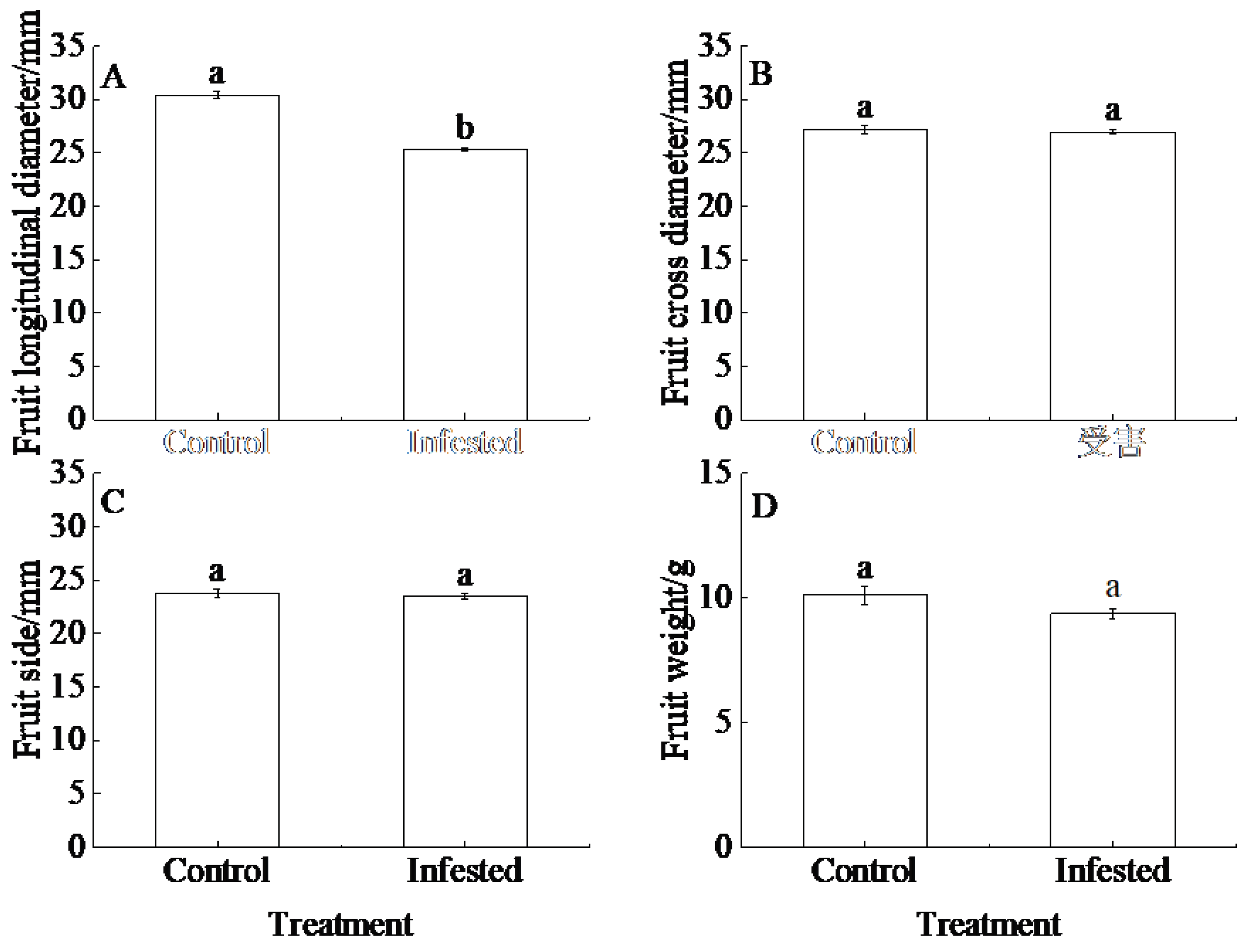
3.5. Fruit traits
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of the GS infection on growth of wild apricot
4.2. Effect of GS infestation leaf traits of wild apricot
4.3. Effect of GS infection on Photosynthetic products of wild apricot
4.4. Effect of GS infection on wild fruit forest
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, J.J. ; Crowther, T.W.; Picard, N.; Wiser, S.K.; Zhou, M.; Alberti, G.; Schulze, E.D.; McGuire, A.D.; Bozzato, F.; Pretzsch, H.; de-Miguel, S.; Paquette, A.; Hérault, B.; et al. Positive biodiversity-productivity relationship predominant in global forests. Science 2016, 354(6309), aaf8957. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Ou, X.H. Using insect for indicator to monitor and assess forest ecosystm health. World Forestry Res. 2006, 19(4), 22-25.
- Lu, W. Z.; Xiao, J. F.; Cui, X.W.; Xu, F.H.; Lin, G.X.; Lin, G.H. Insect occurs have transient effects on carbon fluxes and vegetative growth but longer-term impacts on reproductive growth in a mangrove forest. Agr. Forest Meteorol. 2019, 279(4), 107747. [CrossRef]
- Michael, A. Are changes in plants due to enhanced CO2 contributing to insect population declines? Environ. Entomol. 2019, 48(2), 274-275. [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.P.; Schowalter, T.D. Aphid-induced reduction of shoot and root growth in Douglas-fir seedlings. Ecol. Entomol. 2010, 26(4), 411-416. [CrossRef]
- Rubino, L.; Charles, S.; Sirulnik, A.G.; Tuininga, A.R.; Lewis, J.D. Invasive insect effects on nitrogen cycling and host physiology are not tightly linked. Tree Physiol. 2015, 35(2), 124–133. [CrossRef]
- Watson, G.W.; Adalla, C.B.; Shepard, B.M.; Carner, G.R. Aspidiotus rigidus Reyne (Hemiptera: Diaspididae): A devastating pest of coconut in the Philippines. Agr. Forest Ento. 2015, 17(1), 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Becker, C.; Bot, J.L.; Larbat, R.; Lavoir, A.V.; Desneux, N. Plant nutrient supply alters the magnitude of indirect interactions between insect herbivores: From foliar chemistry to community dynamics. J. Ecol. 2019, 108(4), 1497-1510. [CrossRef]
- You, Y.R.; An, C.P.; Li, C.Y. Insect feeding assays with Spodoptera exigua on Arabidopsis thaliana. Bio-protocol 2020, 10(5), e3538. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.W.; Liu, L.Q.; Wang, Y.N.; Zhang, Q.P.; Fan, G.Q.; Zhang, S.K.; Wang, Y.T.; Liao, K. Genetic diversity, population structure, and relationships of apricot (Prunus) based on restriction site-associated DNA sequencing. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7(1), 69-82. [CrossRef]
- Zeven, A.C.; Zhukovsky, P.M. Dictionary of cultivated plants and their centres of diversity: Excluding ornamentals, forest trees and lower plants. Wageningen: Centre for Agricultural Publishing and Documentation, 1975, 36.
- Zhebentyayeva, T.; Reighard, G.; Gorina, V.; Abbott, A. Simple sequence repeat (SSR) analysis for assessment of genetic variability in apricot germplasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106(3), 435-444. [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.K.; Chaudhury, R.; Dhariwal, O.P.; Mir, S. Genetic diversity and traditional uses of wild apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) in high-altitude north-western Himalayas of India. Plant Genet. Resour. 2010, 8(3), 249-257. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.S. On the eco-geographical characters and the problems of classification of the wild fruit-tree forest in the Ili Valley of Sinkiang. Acta Bot. Sin. 1973, 15(2), 239-253.
- Khadivi-Khub, A.; Khalili, Z. A breeding project: The selection of promising apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) genotypes with late blooming time and high fruit quality. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 216, 93-102. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, X.S.; Liu, G.J.; Liang, Q.; He, T.M.; Feng, J.R. Interspecific hybridization of Prunus persica with P. armeniaca and P. salicina using embryo rescue. Plant Cell Tis. Org. 2007, 88(3), 289-299. [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Xu, Z. Relation ship of the occurences and evolutions of wild-fruit forests with climatic factors in the Tinshan Mountain. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occidentalia Sin. 2005, 25(11), 2266-2271.
- Fang, Z.Y.; Li, L.Y.; Maola, A.; Zhou, L.; Lu, B. Effects of human disturbance on plant diversity of wild fruit forests in western Tianshan Mountain. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 39(2), 267-274.
- Wang, Z.Q. Zootaxa of China. Insecta XXII. Beijing: Science Press, 2001, 237-243.
- Malumphy, C.; Anderson, H. Plant pest factsheet: Globose scale, Sphaerolecanium prunastri[EB/OL]. https://planthealthportal.defra.gov.uk/assets/factsheets/Plant-Pest-Factsheet-S.-prunastri-June-2016v3.pdf, 2016-09-28/2021.04.03.
- Wang, C. Investigation on the species of Coccaidea from Shaanxi garden (Hemiptera: Coccoidea)[M]. Yang Ling: Northwest A & F University, 2010, 21.
- Karaca, I.; Japoshvili, G.; Demirozer, O. The chalcid parasitoid complex (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea) associated with the globose scale (Sphaerolecanium prunastri Fonscolombe) (Hemiptera: Coccoidea) in Isparta Province, Turkey and some east European countries. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2003, 110(5), 505-511. [CrossRef]
- Aksit, T.; Apak, F.K. Effects of some insecticides with infestation rate and some biological characteristics of Sphaerolecanium prunastri (Fonscolombe, 1834) (Hemiptera: Coccidae) on plum. Turk. J. Entom. 2013, 37(1), 133-144.
- Yiğit, T.; Tunaz, H. Determination of Sphaerolecanium prunastri Fonscolombe, 1834 ( Hemiptera: Coccidae ), and its parasitoids and predators in apricot areas of Malatya province, Turkey. Acta Hortic. 2018, 1214, 67-71. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Chen, Y.N.; Li, W.H.; Chen, Y.P. Distribution of soil organic carbon under different vegetation zones in the Ili River Valley, Xinjiang. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20(5), 729-740. [CrossRef]
- Coleman, T.W.; Seybold, S. J. Previously unrecorded damage to oak, Quercus spp., in southern California by the goldspotted oak borer, Agrilus coxalis Waterhouse (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). The Pan-Pac. Entomol. 2008, 84(4), 288-300. [CrossRef]
- Moussa S, Salman A, Bakry M. The negative effects of Parlatoria blanchardii (Targ.) infestation on the morphological and chemical characters of certain varieties leaflets of date palm trees at Luxor governorate. Egypt. Acad. J. Biolog. Sci., 2012, 5(1), 169-181.
- Simbiken, N.A.; Cooper, P.D.; Powell, K.S. Development and feeding effect of frosted scale Parthenolecanium pruinosum Cocquillet (Hemiptera: Coccidae) on selected Vitis vinifera L. cultivars. Aust. J. Grape Wine R. 2015, 21(3), 451-457. [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Ye, W.F.; Pan, Z.P.; Lu, Y.Y. Effect on population density of Phenacoccus solenopsis Tinsley on the growth of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis. J. Environ. Entomol. 2021, 43(1), 60-65.
- Cockfield, S.D.; Potter, D.A. Interaction of Euonymus scale (Homoptera: Diaspididae) feeding damage and severe water stress on leaf abscission and growth of Euonymus fortunei. Oecologia, 1986, 71(1), 41-46. [CrossRef]
- Cockfield, S.D.; Potter, D.A. Euonymus scale (Homoptera: Diaspididae) effects on plant growth and leaf abscission and implications for differential site selection by male and female scales. J. Econ. Entomol. 1990, 83(3), 995-1001. [CrossRef]
- Cockfield, S.D.; Potter, D.A.; Houtz, R.L. Chlorosis and reduced photosynthetic CO2 assimilation of Euonymus fortunei infested with Euonynlus scale (Homoptera: Diaspididae). Environ. Entomol. 1987, 16(3), 1314-1318. [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, B.; Mason, L.J. Effects of scale insect herbivory and shading on net gas exchange and growth of a subtropical tree species (Guaiacum sanctum L.). Oecologia, 1990, 84(4), 468-473. [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.I.; Reed, D.A.; Perring, T.M.; Palumbo, J.C. Feeding damage by Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) and impact on growth and chlorophyll content of Brassicaceous plant species. Arthropod-Plant Inte. 2014, 8(2), 89-100. [CrossRef]
- Canelo, T.; Gaytán, Á.; González-Bornay, G.; Bonal, R. Seed loss before seed predation: Experimental evidence of the negative effects of leaf feeding insects on acorn production. Integr. Zool. 2018, 13(3), 238-250. [CrossRef]
- Proietti, P. Effect of fruiting on leaf gas Exchange in Olive (Olea Europaea L.). Photosynthetica, 2000, 38(3), 397-402. [CrossRef]
- Hura, T.; Hura, K.; Grzesiak, M.; Rzepka, A. Effect of long-term drought stress on leaf gas exchange and fluorescence parameters in C3 and C4 plants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2007, 29(2), 103-113. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kumar, H.; Prasad, F.M.; Singh, K. Chlorophyll and carotenoid loss in Psidium guajva caused by Abgrallaspis cyanophylli. Ann. Plant Protect. Sci. 2009, 17(1), 245-246.
- Goławska, S.; Krzyżanowski, R.; Łukasik, I. Relationship between aphid infestation and chlorophyll content in fabaceae species. Acta Biol. Cracov. Bot. 2010, 52(2), 76-80. [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, P.J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.B.; Huang, F.; Li, M.J. Chlorophyll content and chlorophyll fluorescence in tomato leafs tnfested with an invasive mealybug, Phenacoccus solenopsis (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae). Environ. Entomol. 2013, 42(5): 973-979. [CrossRef]
- Nabil, H.A. Relationship Between Kilifia acuminata (Signoret) and Chlorophyll Percentage Loss on Mango leafs. J. Entomol. 2013, 10(2): 110-114. [CrossRef]
- Golan, K.; Rubinowska, K.; Kmiec, K.; Kot, I.; Gorska-Drabik, E.; Lagowska, B.; Michalek, W. Impact of scale insect infestation on the content of photosynthetic pigments and chlorophyll fluorescence in two host plant species. Arthropod-Plant Inte. 2015, 9(1), 55-65. [CrossRef]
- Walstad, J.D.; Nielsen, D.G.; Johnson, N.E. Effect of the pine needle scale on photosynthesis of Scots pine. Forest Sci. 1973, 19(2), 109-111.
- Moore, G.W.; Watts, D.A.; Goolsby, J.A. Ecophysiological responses of giant reed (Arundo donax) to herbivory. Invas. Plant Sci. Mana. 2010, 3(4), 521-529. [CrossRef]
- Retuerto, R.; Fernandez-Lema, B.; Rodriguez-Roiloa, Obeso, J.R. Increased photosynthetic performance in holly trees infested by scale insects. Funct. Ecol. 2004, 18(5), 664-669. [CrossRef]
- Vranjic, J.O.; Ash, J.E. Scale insects consistently affect roots more than shoots: The impact of infestation size on growth of eucalypt seedlings. J. Ecol. 1997, 85(2), 143-149. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.C.; Eubanks, M.D. Overcompensation for insect herbivory: A review and meta-analysis of the evidence. Ecology, 2019, 100(3), 2585-2625. [CrossRef]
- Nordkvist, M.; Klapwijk, M.J.; Edenius, L.R.; Björkman, C. Interacting effects of insect and ungulate herbivory on Scots pine growth. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10(1): 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Kerchev, P.I.; Fenton, B.; Foyer, C.H.; Hancock, R.D. Plant responses to insect herbivory: Interactions between photosynthesis, reactive oxygen species and hormonal signalling pathways. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35(2), 441-453. [CrossRef]
- Velikova, V.; Salerno, G.; Frati, F.; Peri, E.; Conti, E.; Colazza, S.; Loreto, F. Influence of feeding and oviposition by phytophagous pentatomids on photosynthesis of herbaceous plants. J. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 36(6), 629-641. [CrossRef]
- Delaney, K.J.; Haile, F.J.; Peterson, R.K.D.; Higley, L.G. Seasonal patterns of leaf photosynthesis after insect herbivory on Common Milkweed, Asclepias syriaca: Reflection of a physiological cost of reproduction, not defense? Am. Midl. Nat. 2009, 162(2), 224-238. [CrossRef]
- Dungan, R.J.; Kelly, D.; Turnbull, M. Separating host-tree and environmental determinants of honeydew production by Ultracoelostoma scale insects in a Nothofagus forest. Ecol. Entomol. 2007a, 32(4), 338-348. [CrossRef]
- Dungan, R.J.; Turnbull, M.H.; Kelly, D. The carbon costs for host trees of a phloem-feeding herbivore. J. Ecol. 2007b, 95(4), 603-613. [CrossRef]
- Miezite, O.; Okmanis, M.; Indriksons, A.; Indriksons, A.; Ruba, J.; Polmanis, L.; Freimane, L. Assessment of sanitary conditions in stands of Norway spruce (Picea abies Karst.) damaged by spruce bud scale (Physokermes piceae Schrnk.). iForest. 2013, 6(2), 73-78. [CrossRef]
- Martins, D.S.; Fornazier, M.J.; Culik, M.P.; Ventura, J.A.; Ferreira, P.S.F.; Zanuncio, J.C. Scale insect (Hemiptera: Coccoidea) pests of Papaya (Carica papaya) in Brazil. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2014, 107(8), 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Dimetry, N.; Abdel-Moniem, A. Physical and chemical variability in sugarcane fields infested with the red-striped soft scale insect, Pulvinaria Tenuivalvata(Newstead). Arch.Phytopathol. Plant Protect. 2004, 37(4), 327-337. [CrossRef]
- Salman, A.M.A.; Bakry, M.M.S. Relationship between the rate of infestation with the Mealybug, Icerya Seychellarum (Westwood) (Margarodidae: Homoptera) and the yield loss of seedy Balady Mango trees at Luxor governorate. World Rural Observ. 2012, 4(4), 50-56.
- Bakry, M.M.S.; Mohamed, G.H. Relationship between the rates of infestation with the California red scale insect, Aonidiella aurantii (Mask.) (Hemiptera: Diaspidae) and the yield loss of mango trees at Luxor governorate, Egypt. Egypt. J. Agric. Res., 2015, 93(3), 41-60.
- Hussain, A.; Razaq, M.; Zaka, S.M.; Shahzad, W.; Mahmood, K. Effect of aphid infestation on photosynthesis, growth and yield of Brassica carinata A. Braun. Pak. J. Zool. 2015, 47(5), 1335-1340.
- May, B.M.; Carlyle, J.C. Effect of defoliation associated with Essigella californica on growth of mid-rotation Pinus radiata. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2003, 183(1), 297-312. [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, F. Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) yield and photosynthetic response to simulated insect defoliation and Grasshopper (Orthoptera: Acrididae) feeding. Nebraska: The University of Nebraska - Lincoln, 2013, 85-98.
- Lu, Q.H.; Ge, Z.H. Observation on the stylet and the parasitical site segment of Japanese pine bast scale. Forest Res. 1988, 1(2), 191-194.
- Miller-Pierce M.R.; Orwig, D.A.; Preisser, E. Effects of hemlock woolly adelgid and elongate hemlock scale on eastern hemlock growth and foliar chemistry. Environ. Entomol. 2010, 39(2), 513-519. [CrossRef]
- Orwig, D.A.; Thompson, J.R.; Povak, N.A.; Manner, M.; Niebyl, D, Forter, D.R. A foundation tree at the precipice: Tsuga canadensis health after the arrival of Adelges tsugae in central New England. Ecosphere, 2012, 3(1), 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Maclean, D.A. Impacts of insect occurs on tree mortality, productivity, and stand development. Can. Entomol. 2015, 148(1). 1-22.
- Zhang, P,; Cui, Z.J.; Xu, H.; Ali, A; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.X.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhou, X.B.; Lu, Z.Z. Thirst or malnutrition: The impacts of invasive insect Agrilus mali on the physiological status of wild apple trees. Forests, 2020, 11(440), 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Radville, L.; Chaves, A.; Preisser, E.L. Variation in plant defense against invasive herbivores: Evidence for a hypersensitive response in eastern hemlocks (Tsuga canadensis). J. Chem. Ecol. 2011, 37(6), 592-597. [CrossRef]
- Visakorpi, K.; Gripenberg, S.; Malhi, Y.; Bolas, C.; Oliveras, I.; Harris, N.; Rifai, S.; Riutta, T. Small-scale indirect plant responses to insect herbivory could have major impacts on canopy photosynthesis and isoprene emission. New Phytol. 2018, 220(3), 799-810. [CrossRef]
- Zvereva, E.L.; Lanta, V.; Kozlov, M.V. Effects of sap-feeding insect herbivores on growth and reproduction of woody plants: A meta-analysis of experimental studies. Oecologia, 2010, 163(4), 949-960. [CrossRef]
- Stephens, A.E.A.; Westoby, M. Effects of insect attack to stems on plant survival, growth, reproduction and photosynthesis. OIKOS, 2014, 124(3), 266-273. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Huntly, N. Herbivorous insects reduce growth and reproduction of big sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata). Arthropod-Plant Inte. 2010, 4(4), 257-266. [CrossRef]
- Halitschke, R.; Hamilton, J.G.; Kessler, A. Herbivore-specific elicitation of photosynthesis by mirid bug salivary secretions in the wild tobacco Nicotiana attenuata. New Phytologist, 2011, 191(2), 528-535. [CrossRef]
- DeLucia, E.H.; Nabity, P.D.; Zavala, J.A.; Berenbaum, M.R. Climate change: Resetting plant-insect interactions. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160(4), 1677-1685. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G.; Cai, Y.L.; Fang, Y.; Jing, J.; Li, K. Induced response in Schima superba: Effects of early-season herbivory on leaf traits and subsequent insect attack. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9(51), 8731-8738.
- Ancheta, J.; Heard, S.B. Impacts of insect herbivores on rare plant populations. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144(10), 2395-2402. [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.H.; Sarfraz, R.M. Impacts of insect herbivores on plant populations. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 62(1), 207-230. [CrossRef]
- Domec, J.C.; Rivera, L.N.; King, J.S.; Peszlen, I.; Hain, F.; Smith, B.; Frampton, J. Hemlock woolly adelgid (Adelges tsugae) infestation affects water and carbon relations of eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis) and Carolina hemlock (Tsuga caroliniana). New Phytol. 2013, 199(2), 452-463.
- Haavik, L.J.; Billings, S.A.; Guldin, J.M.; Stephen, F.M. Emergent insects, pathogens and drought shape changing patterns in oak decline in North America and Europe. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2015, 354, 190-205. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



