1. Introduction
Official data indicate a global problem regarding the discharge of untreated wastewater in the Republic of Serbia because only 5-10% of wastewater is treated. The consequence of the high degree of untreated wastewater discharged into watercourses from municipal and industrial sewage systems results in a high content of potentially toxic elements (cadmium and nickel) according to the level of maximum permissible concentration and frequency of its occurrence. The analysis based on the data of the system monitoring shows that in some localities the concentrations exceeded the allowed ones (Veljković et al., 2010). Bioaccumulation and biodegradability characterize cadmium and thus classify it as a metal of great toxicological importance (Jafaryan et al., 2019). The UK Department of the Environment and the European Economic Community Hazardous Substances Directive classifies cadmium as a priority pollutant, while in the United States it is listed as a carcinogen B1 (Jie et al., 2016). PVC-based products, in addition to paints, nickel-cadmium batteries, are some examples of the use of this metal. Phosphorous fertilizers also have high cadmium content and their use contributes to the increased uptake of this toxic metal into the soil and water. By detecting elevated concentrations of nickel, due to its wide application in various types of industries, nickel has reached this list as a priority substance. (Ebrahimi et al., 2018; Abdelwaheb et al., 2019). In Serbia, agricultural land accounts for 57.6% of the total area, in addition to providing food and other various products, which also leads to negative environmental consequences. Phosphorus is the main nutrient for the development of living organisms and these reasons are used for the production of fertilizers, as well as in the production of food, chemical products, and detergents (Krüger and Adam, 2017). According to the EPA regulation, 0.1 mgL-1 of phosphate is allowed to be released (Nguyen et al., 2017; Afridi et al., 2019). Increased phosphate concentrations in industrial wastewater, as well as leaching from agricultural land, result in eutrophication, so the removal of phosphate is necessary due to its adverse effects on the environment and aquatic organisms (Nguyen et al., 2017). Among the many applied physico-chemical treatments for the removal of selected metals, adsorption has emerged as an effective method due to its high selectivity, low cost, and ease of performance in a wide range of experimental conditions (Bai et al., 2019). Nano-zero valence iron (nZVI) has attracted a lot of attention in the removal of both inorganic and organic pollutants, as well as the possibility of applying different methods for its production. Solid (powdery) nZVI has limited practical application (Tang et al., 2021) due to easy aggregation, rapid corrosion, reduced nanoparticle reactivity, thus blocking the purification of the medium, reducing the adsorption efficiency, and ultimately creating secondary pollution (Yu et al., 2021). In the last few years, plant extracts and other natural products have been used for the synthesis of nanomaterials (Wang et al., 2014). The importance of polyphenols present in plant extracts is reflected in their dual function in synthesis, because they represent a reducing agent of Fe(III) salts, and they also represent a stabilizer of nanoparticles. In addition to the above, the characteristic of green materials is the high volume of antioxidants, which is associated with the appearance of the composition and dimensions of nano Fe0 particles (Borja et al., 2015). Li and colleagues, in 2021, noticed some of the advantages of nZVI synthesized from plants, compared to traditional methods: polyphenolic matrix can expand which prolongs the reactivity of nZVI, resulting in reduced agglomeration, plant extracts are waste, less toxic have a high-rate production and low price. In this paper oak leaves were utilized for nZVI forming.
The spherical core-shell structure contributes to the dual role of nZVI in metal removal: (1) adsorption - independent on nZVI surface oxide layers and synergistic effect between the porous material and nZVI, including electrostatic adsorption, surface compensation (2) reduction - strong reduction components Fe0 and Fe2+ represent an electron donor in the reduction process (Li et al., 2021). Adsorption of cadmium and nickel with nZVI as adsorbent is contingent on the metal contaminant's standard redox potential (E0). Iron hydro(oxide) as a coating has a significant role in the removal of Cd, because the similarity of E0, between this metal and Fe0, indicates the process of adsorption on the coating. A positive E0 relative to Fe0, with Ni, indicates reduction and adsorption (O’Carroll et al., 2013). Geochemical shapes like pH, matrix, inceptive concentrations, etc. can influence the metal removal mechanism with nZVI.
The dependence on operative parameters and the efficiency of the applied treatment is proportional, which requires an optimization trial. With the progress of chemical treatments, researchers are facing the problem of a limited number of operational parameters, because their increase increases the number of experiments. A set of empirical statistical methods is used to determine the optimal conditions, based on the application of quantitative data from appropriately designed experiments. Definitive screening design (DSD) is an innovative statistical method for designing an experiment based on a numerical algorithm (Jones and Nachtsheim, 2011; Mohamed et al., 2017). The analysis thus conceived is used to determine the significant factors and to predict their two-factor interactions, additionally, the total count of operation is described through the predicted coefficient of the example of the equation itself. This statistical method allows the application of a significantly reduced number of experiments performed with maximum precision (Jones and Nachtsheim, 2011; Fidaledo et al., 2013).
The exploration was monitored in four sections:
(1) synthesis of nZVI using oak leaves polyphenols; (2) application of DSD to optimize the cadmium and phosphate and nickel and phosphate removal processes, as well as to test the effect of operating parameters, inceptive metal concentration, inceptive ion concentration, quantity oak-nZVI doses, and pH; (3) examination of the efficacy of simultaneous removal of Cd(II) and phosphate ions or Ni(II) and phosphate ions by oak-nZVI adsorbent (4) resolution of kinetic adsorption parameters for Cd(II) and Ni(II) in the presence of phosphate on oak- nZVI (5) proposed mechanism of simultaneous removal of Cd(II) and phosphate or Ni(II) and phosphate.
2. Methods and materials
2.1. Chemicals
Necessary chemicals were procured from the following manufacturers: Centrohem Serbia - iron (III) chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3 • 6H2O), POCH - sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and nitric acid (HNO3), Sigma Aldrich - NiSO4 • 6H2O and KH2PO4, JT Baker - Cd(CH3COO)2 • 2H2O. Stock solutions were prepared by dissolving in predetermined masses in deionized water.
2.2. Synthesis of oak-nZVI
Due to the high volume of antioxidants, oak leaves were collected for the formation of nZVI in the territory of Vojvodina, Serbia. The leaves were dried at 50°C for 48 h, after which they were ground using a kitchen chopper and sieved through a 2 mm sieve (Machado et al., 2013; Jokić Govedarica et. al., 2022). In this way, the prepared leaves are used in the further preparation of the extract for the production of iron nanoparticles. 3.7 g leaves were weighed in 100 ml of deionized water and stirred for 20 minutes at 80°C. The created extract was filtered through a Buchner funnel and mixed with 0.1 M Fe3+ solution whose volume ratio was 1: 3, concentration in the forming nanomaterial was 1.395 gL-1.
2.3. Experimental procedure
Each experimental sample contained a mixture of metals and ions, and its final volume was 100 ml. Basic solutions (100 mgL-1) of metals (Cd2+ and Ni2+) and ions (PO43-) were prepared by dissolving the substances listed in section 2.1, then diluted to the desired concentration (1 mgL-1, 5 mgL-1, and 9 mgL- 1). By adding oak-nZVI in doses of 2 ml, 9 ml, and 16 ml, the efficiency of removal of selected pollutants were monitored. In Chapter 2.2. it is stated that the concentration of oak-nZVI is 1,395 gL-1, ie at the above doses, its concentration in the experimental mixture of 100 ml would be 0.0279 gL-1, 0.125 gL-1, and 0.223 gL-1, respectively. The pH value (2, 6, and 10) in the samples was corrected with 0.1 M HNO3 and 0.1 M NaOH solution, respectively. The sample shaker was set at 180 rpm for 60 min, at a constant temperature of 23°C. Centrifugation (4000 rpm) and filtering of samples (0.22 mm filter) was necessary. Residual metal concentrations in the samples were analyzed by inductively coupled plasma with mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, Agilent Technologies 7700 Series), and phosphates by the SRPS EN ISO 6878: 2008 method. Adsorption kinetics are described by first- and second-order models.
2.4. Definitive screening design (DSD)
During this study, the influence of four operational parameters was examined, using the DSD model: inceptive metal concentration (1 - 9 mgL
-1), inceptive ion concentration (1 - 9 mgL
-1) quantity oak-nZVI (2 - 16 ml), and pH (2-10). The deadline values of investigated parameters were selected according to literature data (S
leiman et al., 2017; Rana et al., 2018; Gasemloo et al., 2019). Selected concentrations of metals and ions in aqueous solutions are high so that they can represent groundwater pollution or wastewater. The study by
Poguberović et al., 2016 was the guide for the selection of quantity nanomaterials. Suppositionally, DSD is becoming a minimum 2k + 1 experiment for k numerical factors. Which represents thirteen experiments that were obtained for this paperwork. Performing levels of selected variables and the corresponding code (-1, 0, + 1) are shown in the supplementary material (
Table S1). The form of the experiment (Supplementary material
Table S2) is presented through a combination of 13 series in duplicate, with an additional 2 central points, representing a total of 28 series.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Statistical analysis for the simultaneous cadmium and phosphate removal
The assessment of active linear effects (cadmium/nickel concentration, phosphate concentration, pH value, and nZVI dosage), two-factor interaction effects, and quadratic effects with a minimal number of required experiments was conducted using a DSD model.
3.1.1. DSD model evaluation - cadmium/phosphate
Supplementary material (
Table S3) presents the results obtained for the adsorption process efficiency in the removal of cadmium and phosphate from synthetic aqueous solution. Adsorption removal efficiencies range from 15.44% to 99.01% and 29.00% to 97.00% for cadmium and phosphate, respectively. Maximum and minimum removal efficiencies are achieved under a different set of process conditions, confirming the assumption that the adsorption process largely depends on the conducted experimental conditions.
The selection of the regression model that best fit the obtained experimental results was made using a JMP (SAS) stepwise regression analysis. In that way, a beneficiary selects a pair of candidate models from a large number of models, while the final selection is based on the standard selection criteria: Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC), Akaike Information Criterion, (AIC), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), coefficient of determination / adjusted coefficient of determination (R2 / R2adj) (Kecić et al., 2018).
A lower coefficient of determination for the phosphate removal (R
2 = 0.737) was obtained in comparison to cadmium removal (R
2 = 0.823). However, the approximate values of the AIC and BIC parameters imply a good approximation of the experimental data (Supplementary material
Table S5). The outcome of the analysis of variance (ANOVA) test (F <0.0001), as well as the "Lack of fit" test (F> 0.05), indicated that the regression model is highly significant (Supplementary material
Table S5).
The adequate approximation is confirmed using diagnostic plots in Supplementary material
Figure S1 which includes the normal allocation diagram and the deviation diagram of the standardized residuals relative to the zero lines. The experimental predicted values versus actual values are in good correlation for both cadmium and phosphate removal (Fig S1a and S1c), where points follow the regressed diagonal line. The deviation diagram of the standardized residuals relative to the zero lines (Fig S1b and S1d) does not show a value that tends to be scattered, rather point dots are randomized in space, meaning that the variance is homogenous across the range of predicted removal efficiency values.
Table 1 shows the estimated model parameters. The factors with statistical significance (bolded values) contribute the most to the removal efficiency of cadmium and phosphate from the synthetic solution by the adsorption process. Cadmium and phosphate concentration are statistically significant parameters, positively influencing the cadmium removal process. Two-factor interactions of importance have not been identified for this process. The Pareto diagram (Supplementary material
Figure S2) presents the uttermost validity, comparing the relative dimensions and statistical significance of the effects.
Phosphate removal efficiency is affected by the amount of oak-nZVI and cadmium concentration. Although not statistically significant, pH is part of three statistically significant interactions with oak-nZVI dosage, cadmium concentration, and phosphate concentration (
Table 1).
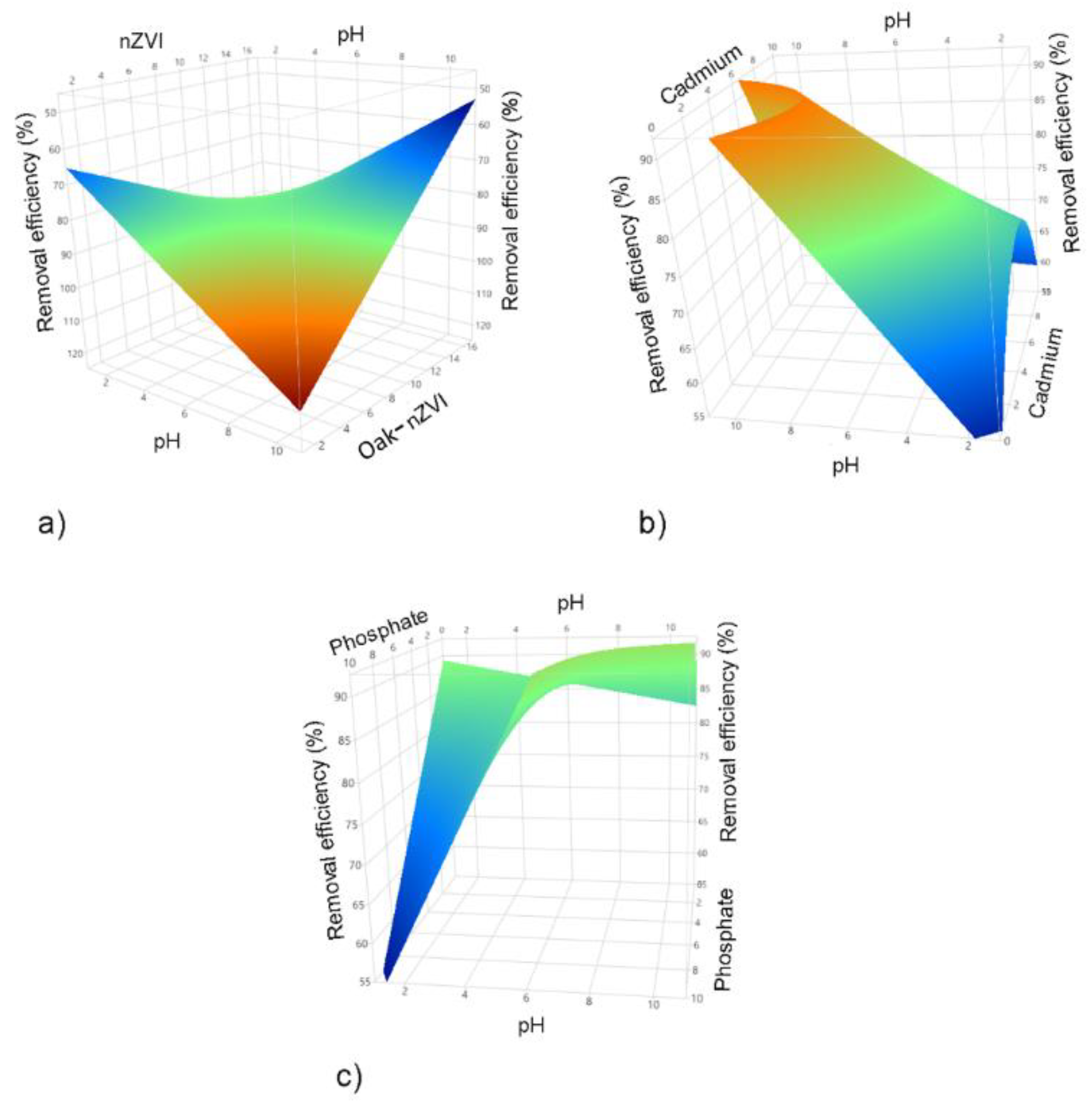
Relevant two-factor interactions are given via 3D response surface diagrams (Picture 1) The synergistic effect of pH and oak-nZVI doses is shown in
Figure 1a. Maximum phosphate removal efficiency is achieved by increasing the pH from 2 to 10 while keeping the oak-nZVI dosage at its low level (4 ml). The most expressive effect on phosphate removal is at high pH values (9). The sorption capacity that decreases with an increasing dose of adsorbent can be attributed to the aggregation of oak-nZVI particles and the equilibrium achieved under the given conditions. The appearance of aggregates reduces the surface area, which increases the length of the diffusion path. (
Moharami et al., 2013).
The highest phosphate removal efficiency is obtained at low cadmium concentration level and high pH level (
Figure 1b). The prominent dependence of adsorption efficiency on the pH value is indicated in
Figure 1c. The amount of phosphate ion on the oak-nZVI surface increased rapidly with the pH increase in the pH range from 2 to 6.
Kong et al. (2018) concluded that almost complete phosphate removal can be achieved with phosphate concentrations below 100 mgL
-1, over a large range pH of 3 to 11, which is favorable for the treatment of extremely acidic and alkaline effluents, even at low phosphate concentrations, which is also concluded by this research.
3.1.2. Process optimization of cadmium and phosphate adsorption
Since this experimental design aims to maximize the removal efficiency of two metal ions and phosphate concerning process conditions, important optimization progress was determined based on the capability of JMP software. Process parameters are optimized based on the tested parameters: 1 ≤ X1 ≤ 9, 1 ≤ X2 ≤ 9, 2 ≤ X3 ≤ 10, 2 ≤ X4 ≤ 16, to select the best input parameter solution for best adsorption performance. The optimization plot shown in
Figure 2 graphically depicts how the removal efficiency changes as a function of one of the variables, while all other variables remain constant.
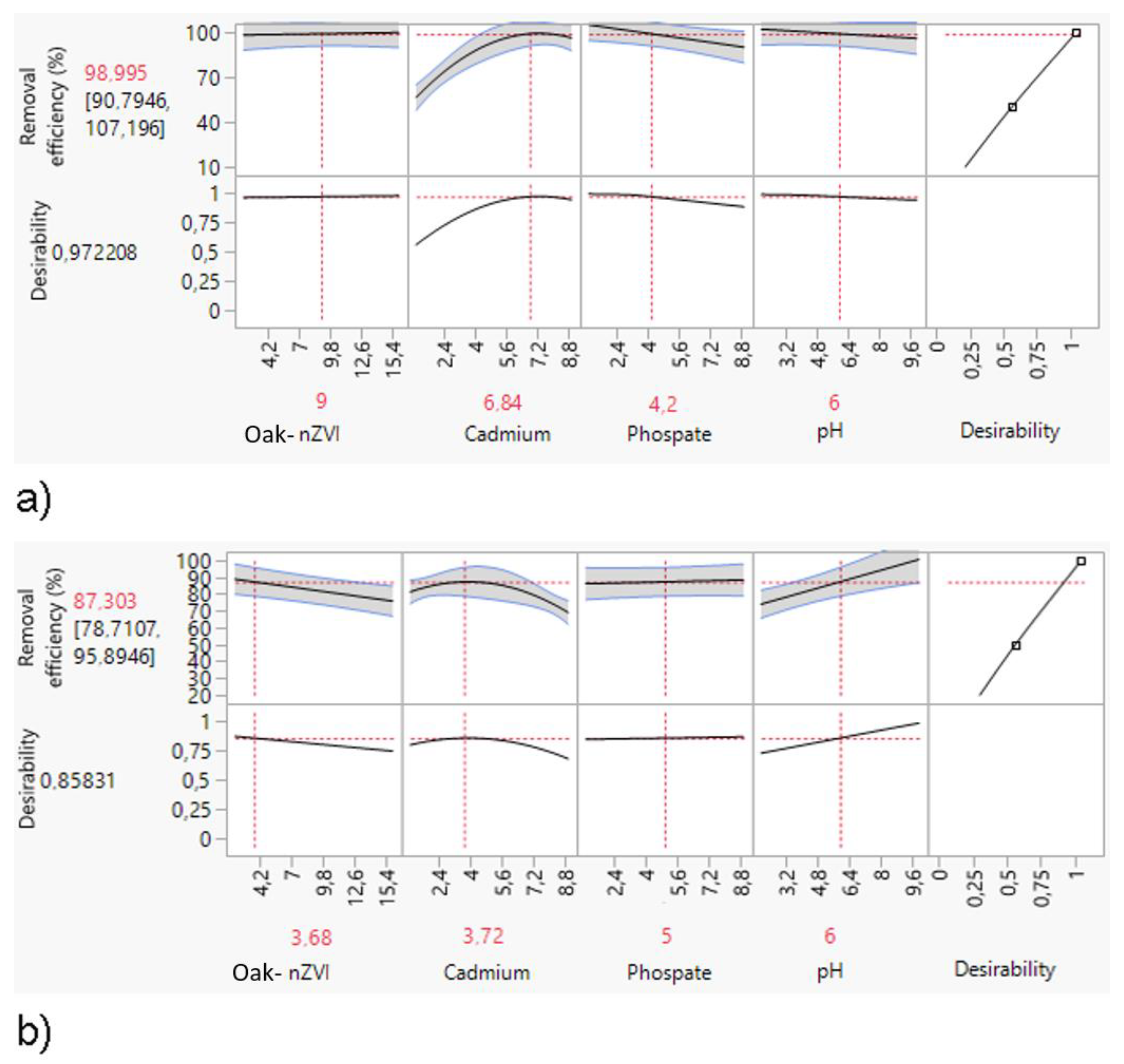
The statistical model suggests 98.99% performance elevation of cadmium under the following excellent conditions: 9 ml of oak-nZVI dosage, 6.84 mgL
-1 of cadmium concentration, 4.2 mgL
-1 of phosphate concentration, and pH 6 (
Figure 2a). Medium dose oak-nZVI and neutral pH contribute to cadmium elimination Reporting
Tu et al. (2012) also confirm our claims that the removal of cadmium from aqueous solution using green nanoparticles is most desirable at pH 5 to 6.
Alimohammadi et al. (2013) pointed out that nanomaterials increment accelerates the removal efficiency of cadmium to the point when adsorption equilibrium is reached, after that, the addition of the adsorbent does not affect the elimination performance.
Based on the prediction profiler (
Figure 2b) 87.30% of phosphate removal was proposed under the following conditions: 3.68 ml of nZVI dosage, 3.72 mgL
-1 of cadmium concentration, 5 mgL
-1 of phosphate concentration, and pH 6.
Afridi et al., (2019) indicate the effect of cadmium concentration on phosphate removal efficiency and their mutual competition. In this paper, high removal efficiencies for both pollutants indicated their simultaneous removal (
Figure 2b).
Confirmation of effectiveness suggested excellent conditions and received regression model, eight confirmation tests were performed under the determined optimal process conditions (Supplementary material
Table S6) and the 95% confidence interval was calculated. It can be concluded that the optimal removal efficiencies suggested by the JMP software (
Figure 2) fit into the confidence intervals (
Table S6), which confirms the assumption that the adopted regression model describes well the cadmium and phosphate removal process using oak-nZVI, but also that the model in this research chapter met the needs necessary for the validation test.
Different forms of cadmium can be found in water: Cd
2+, Cd(OH)
2(s), and Cd(OH)
+. Adsorption Cd
2+ is lower, at lower pH ranges, it is assumed that there are competition H
+ ions and Cd
2+ for adsorption sites at oak-nZVI and low dissociation of carboxyl groups. In general, the adsorbed amounts of Cd
2+ on oak-nZVI were higher in the more alkaline range. Increasing the pH value also increases the negative charge of the nanoparticle surface and therefore, the adsorption capacity is increased through electrostatic interactions. The higher adsorption capacity of Cd
2+ at pH 7.0 is possible through ionization of acidic functional groups (carboxyl groups). However, Cd
2+ ions tend to deposition in Cd(OH)
2 at higher pH values (
Ihsanullah et al., 2015). This effect weakens electrostatic interactions and increases adsorption. It is expected that the mechanism of Cd sorption on oak- nZVI will be realized through surface complexation:
The mechanisms of elimination of cadmium and phosphate are adsorption and precipitation, in both cases, phosphate plays an important role, because in the first case it causes adsorption, while in the second it is deposited in metallic or hydroxide form. The dominant factor for the adsorption of cadmium ions is the pH of the treated water. Iron oxides tend to enhance the negatively charged surface, as shown in previous studies (
Stietiia and Wang, 2014; Baohong et al., 2020). In this experiment the increase in negative electrification is a consequent reaction of FeOOH and HPO
42− (Eq 5):
On top of that metal phosphate deposition and hydroxide deposition is the primary cadmium immobilization system. These new metal phosphate compounds have extremely low solubility, high chemical stability, and thermodynamic stability over a wide pH range (Wang and Xing, 2004; Husson et al., 2015). An important factor affecting Cd immobilization is pH.
The formation of Cd-phosphate precipitates is a consequence of phosphoric acid disintegration. The precipitate formed is also responsible for the immobilization of Cd. Cd
5H
2(PO
4)
4•4H
2Cd phosphate crystallization can be formed under acidic conditions. Cd formations in the base medium are Cd
3(PO
4)
2, Cd
5H
2(PO
4) • 4H
2O, and Cd(H
2PO
4)
2 (
Husson et al., 2015).
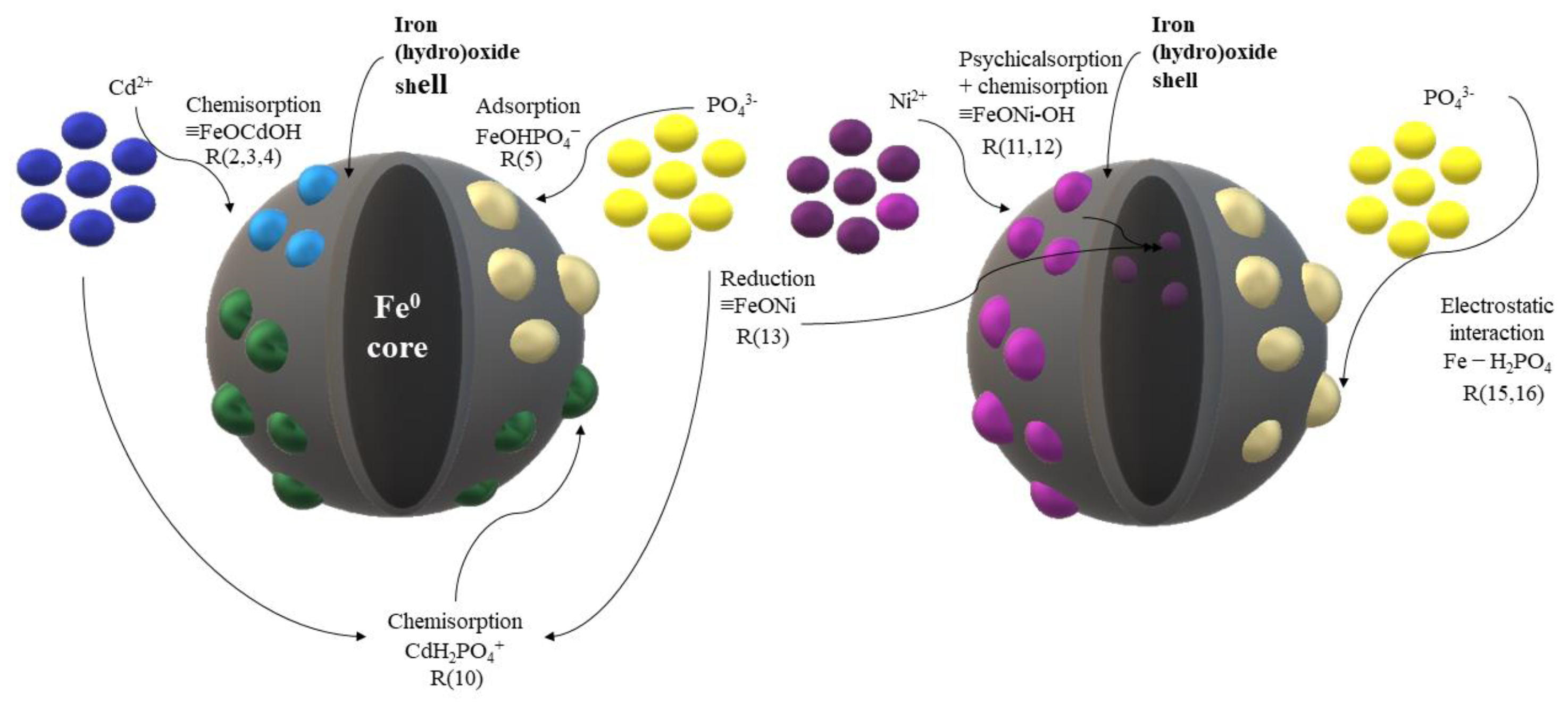
One can postulate that simultaneous removal of cadmium and phosphate ions could be attributed to electrostatic interaction and specific surface bonding. Further on, the cadmium and phosphate can react and precipitate, but obtained precipitate can also be adsorbed onto the FeOOH shell through chemisorption processes (inner-sphere complexation).
Based on the obtained results, it is not possible to explain multiple increases in the capacity and affinity for cadmium and phosphate adsorption under the tested conditions, so it is necessary to perform additional tests.
3.2. Statistical analysis for the simultaneous removal of nickel and phosphate
3.2.1. DSD model evaluation - nickel/phosphate
Adsorption experiment by using oak-nZVI as an adsorbent resulted in maximum removal efficiency of 97.38% for nickel and 97.70% for phosphate from the synthetic aqueous matrix (Supplementary material
Table S7). The results obtained by adsorption efficiency measurements for the 28 treatment combinations, were statistically analyzed using JMP software.
Descriptive factors of the selected statistical models (Supplementary material
Table S8), as well as the results of the ANOVA test and the "Lack of fit" test (Supplementary material
Table S9), imply a positive approximation of preliminary data and the significance of the selected model.
The adopted regression model explains approximately 71.5% and 91% of the variance for nickel and phosphate removal, respectively in the observed adsorption efficiency values.
Additional model adequacy is investigated in the same way as in the experiment for cadmium and phosphate removal (Chapter 3.2.1) and it is an interpretation by diagnostic plots (Supplementary material in
Figure S3).
The statistical important linear aspect, two-factor interactions, and quadratic effects that have the most pronounced effects on nickel and phosphate removal are shown in
Table 2 and using the Pareto illustration (additional material in
Figure S4).
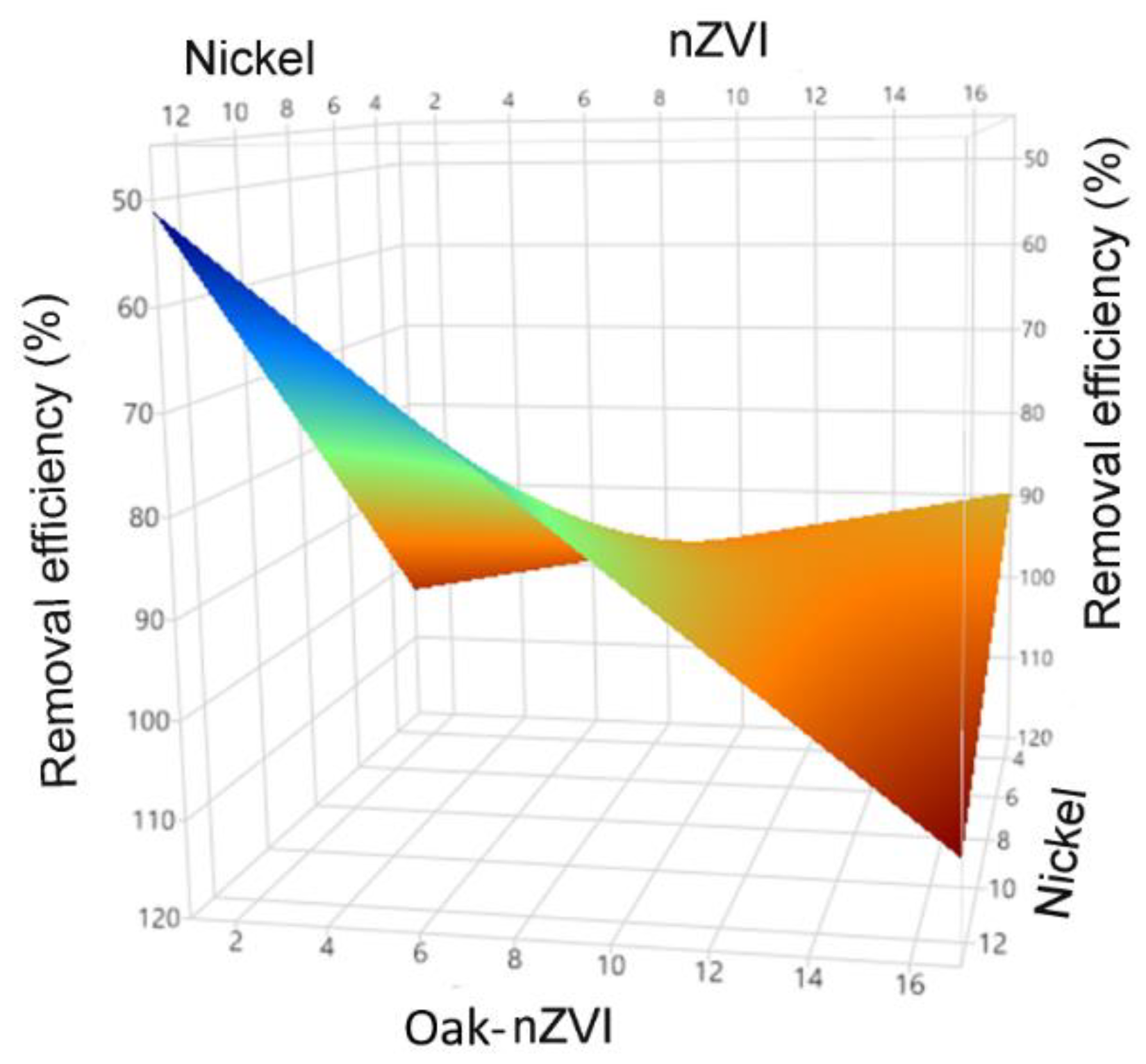
Considering the nickel concentration during the nickel adsorption on oak-nZVI, both the linear and quadratic terms are statistically important. The main role is played by the positive sign in front of the linear term, while the quadratic term is negative, which suggests that the increase of the nickel concentrations contributes to the removal process of metal ions up to a certain point, after which further increase has the opposite effect. This is confirmed by the prediction profiler (
Figure 3) which shows that the optimal nickel concentrations lie between the center and high level, equaling approximately 6 mgL
-1.
The efficiency of phosphate abolition is determined by three linear components: nickel concentration, phosphate concentration, and pH. In this process, one two-factor interaction between the oak-nZVI dosage and nickel concentration, as well as one quadratic interaction of phosphate concentration were observed.
The two-factor interaction of nickel concentration and oak-nZVI dosage within the phosphate removal process is shown by the response surface plot in
Figure 3. If the oak-nZVI dose is maintained at its intermediate level (9 ml), the efficiency of the phosphate removal process will decrease with nickel concentration increment. The scientific explanation is yes the same oak-nZVI dosage, higher concentrations of nickel in the aqueous solution have a greater tendency to adsorb on the nanomaterial surface than phosphate ion (
Lee and Kim, 2017). In this paper, we have concluded that the removal of nickel and phosphate is simultaneous, which is explained in the next chapter.
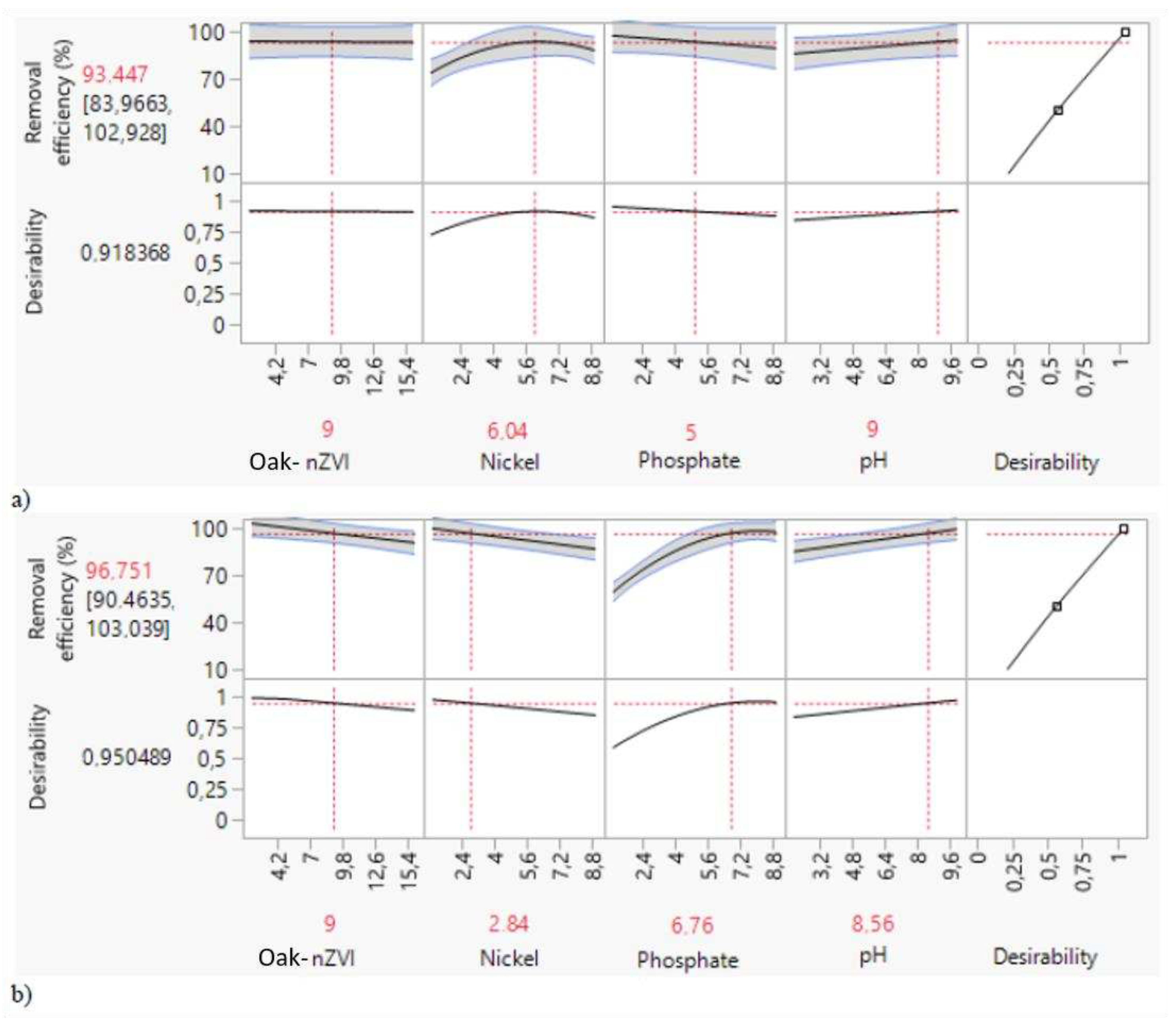
3.2.2. Process optimization of nickel and phosphate adsorption
The prediction profilers (
Figure 4a and 4b) illustrate the efficiency of nickel and phosphate removal as a function of four independent variables.
The highest nickel removal efficiency of 93.44% was proposed in appointed circumstances: 9 ml of oak-nZVI dosage, 6.04 mgL
-1 of nickel concentration, 5.0 mgL
-1 of phosphate concentration, and pH 9. The results (
Li and Zhang, 2007; Efecan et al., 2009; O’Carroll et al., 2013) suggest that different iron nanoparticles remove nickel by sorption followed by reduction. The order of nickel elimination is physical sorption - chemisorption - reduction to elemental form, which is also represented by reactions:
A complex is formed on the surface of nanoparticles (reactions 11 and 12), and (13) defines the reduction of nickel on the surface (
Figure 5). Research conducted by
Efecan et al. (2009) of Ni(II) adsorption on oak-nZVI indicates that Ni exists in the divalent state up to pH 8.5, while at higher pH values different hydroxyl forms of an ion such as Ni(OH)
+, Ni(OH)
2 and Ni(OH)
3- can be found depending on the pH.
The obtained optimal conditions for effective phosphate removal from 96.75%: 9 ml of oak-nZVI dosage, 2.84 mgL-1 of nickel concentration, 6.76 mgL-1 of phosphate concentration, and pH 8.56
Iron ion on the adsorbent surface occurs as a protonated hydrated iron oxide which, in addition to ligand exchange, has been absorbed by H
2PO
4− by electrostatic interactions (Equations 14 – 16, Figure 7):
If we observe this system, the removal of nickel was pronouncedly improved coexisting H2PO4-, meanwhile, nickel had a significant effect on the adoption of H2PO4- in the entire range of analyzed concentrations. According to previous studies (Zhang et al., 2017), anions increased the adsorption sits for metal ions condensing the double electric layer, heightening elimination of nickel can be attributed to the chelating ligand of adsorbed H2PO4− as well as electric binary compression layer. Synchronized, amino chelated adsorbed nickel has the properties of an action bridge thereby promoting the adsorption of H2PO4−.
As described in chapter 2.4, experimental verification of the proposed optimum was performed with eight additional experiments (Supplementary material in
Table S10). The proposed maximum removal efficiency of nickel and phosphate fit into a 95% confidence interval, which confirms the assumption that the adopted regression model describes the nickel and phosphate removal process well using oak-nZVI adsorbent.
3.3. Adsorption kinetics
The adsorption kinetic parameters for Cd and Ni, shown in Supplementary material
Figure S5a, indicate that the reaction equilibrium is reached after 60 min and 45 min, after which the adsorption is constant. In Chapter 2.3. the kinetic models used in the adsorption estimation for this study are listed and are shown in Figures S5b and S5c. The obtained values for the parameter of determination (R
2) are shown in (Supplementary material in
Table S11) and suggest the matching of the pseudo-second model with the mathematical model and its ideal description adsorption rate of Cd and Ni. The suitability of this model is further confirmed by the agreement of experimentally and theoretically determined values of QE. Previous research by the authors also confirms that the pseudo-II-order model best describes the rate of adsorption of divalent metal ions (
Poguberović et al., 2016). The pseudo-II-order model assumes that chemisorption occurs, whereby metal ions tend to reach the maximum value of the coordination number. Based on the above, it can be concluded that the driving force of adsorption is directly proportional to the number of accessible, potentially integrating sites on the oak-nZVI surface.
3.4. Interaction mechanisms summary
Nano-valent iron has a variety of uses for the treatment of potentially toxic metal ions, presenting a certain capacity and practical application for their remediation. There is still controversy about the system of interactions between pollutants and nZVI. In water, the surface of the oak-nZVI shell is composed of Fe
2O
3, Fe
3O
4, FeOOH, etc., providing productive sites for a different reaction for contaminant removal. Phosphate is polyacid and the prevailing phosphate species are largely depending on pH. When the pH is in the range 2.12 ≤ pH ≤7.21 phosphate is in the form of H
2PO
4-, and in the range of pH from 7.21 ≤ pH ≤ 12.67 the phosphate is in the form HPO
42-. As mentioned earlier, phosphate reacts with oak-nZVI via electrostatic adsorption.
Nagoya et al. (2019) concluded that the flow and extent of the interaction of nZVI and phosphate seriously oscillate with the pH value of the medium. The process of phosphate adsorption on the exterior of the oak-nZVI can be created by possible reactions:
Based on the findings from this publication, it can be said that the trend of phosphate adsorption efficiency is primarily influenced by the pH of the solution. The electrostatic adsorption of monovalent and divalent anionic phosphate is by correlation with the interaction of oak-nZVI surface that is positively or negatively charged. Synchronous elimination of cadmium and phosphate ions can be described by the following mechanism: electrostatic interaction and specific surface bonding, enabling two forms of Cd depending on the pH conditions: CdH
2PO
4+ and CdHPO
4 are the processes that are realized first. Secondly, obtained precipitate CdHPO
4 is adsorbed onto the FeOOH shell through chemisorption processes (inner-sphere complexation) (
Figure 5). At low pH values, more than half of the dissolved cadmium in the presence of phosphate occurs in the form of CdH
2PO
4+, while at higher pH values it precipitates cadmium in the form of CdHPO
4, which significantly affects their removal (
Ayati et al., 2001). In terms of pH, both models propose a lightly acidic to neutral medium under pH 6, which presents an environmental benefit and confirms the fact that effluent can be released into the recipient from this aspect. Therefore, it is not necessary to modify the optimal conditions suggested by the model.
During the process of removing nickel and phosphate, it is suggested that Ni(II) initially binds by surface complexation to the outer shell of the oak-nZVI and is gradually reduced to metallic Ni on the surface of nanoparticles. Oak-nZVI has a good capacity for Ni(II) absorption in terms of efficient and fast kinetics and strong uptake capacity. Based on the obtained results, efficient synchronized removal of nickel and phosphate can be observed. This is explained by the phenomenon that anions increase the sites for the adsorption of heavy metals by the condensation of a double electric layer.
3.5. Consideration for environmental applicability
The merged wastewater represents the bulk of industrial and domestic wastewater, so the urgent need for simultaneous removal of coexisting different kinds of heavy metals (in our case, Cd and Ni) and anions (e.g. PO43-) is indispensable. Many scientific results gathered (Boparai et al., 2011; Tosco et al., 2014) are becoming clear that the application of nZVI is one of the most important materials for water purification and environmental remediation. The structural composition of the nucleus-shell of the nanoparticle provides two roles, the nucleus acts as an electron transporter, and the shell has a role in surface complexation. Surface precipitation and adsorption are the primary mechanisms of metal and ion elimination using nZVI (Pasinszki and Krebsz, 2020).
The green synthesis of nZVI makes this research favorable from both economic and environmental points of view. Cheap and green starting materials and the use of water as a green reaction medium is a promising option for large-scale synthesis.
Obtained high removal efficiencies of investigated pollutants (> 98% for Cd, > 93% for Ni, and > 87% for PO43-) makes this material a promising candidate for the implementation of a new generation of adsorbent used in a full-scale system.
4. Conclusion
In short, it is assumed that the green nZVI with oak leaves used in this experiment are acceptable for preparation because they are ecological, non-toxic, and low-cost adsorbents to simultaneously remove cadmium and nickel with the presence of phosphate. By observing two separate processes: simultaneous removal of Cd(II) and phosphate and simultaneous removal of Ni(II) and phosphate, the difference in the mechanism of their removal is dependent on E0 and pH environment, so cadmium is removed by adsorption and precipitation, nickel is removed by surface by complexation and reduction, and phosphate removal is attributed to electrostatic adsorption. Also, the proposed model for Cd(II) has an advantage in terms of pH, because no additional neutralization treatment is required, which reduces operating costs and the cost of using chemicals. The definitive screening design is functional, effective, and has high accuracy. The experiment conceived in this way is convenient because a large number of operating parameters are included. In the simultaneous removal of cadmium and phosphate, for cadmium removal statistically significant parameters are cadmium concentration and phosphate concentration. For phosphate removal in addition to individual cadmium concentration and oak-nZVI dose, the pH value yielded three statistically significant two-factor interactions with oak-nZVI dose, cadmium, and phosphate concentration. For simultaneous removal of nickel and phosphate, the single and quadratic nickel concentrations have the greatest influence on nickel removal, while in phosphate removal, nickel concentration, phosphate concentration, and pH occur as single statistically significant parameters. The oak-nZVI dose and nickel concentration occur as a two-factor significant interaction and occur in one quadratic interaction of phosphate concentration. All optimized conditions were verified within the statistical model, and it was found that the proposed optimized removal efficiencies fit into the 95% confidence interval thus confirming the selection of the appropriate model. Examination of the adsorption kinetics of Cd (II) and Ni (II) on oak-nZVI showed a rapid response and better agreement of the obtained data with the kinetic model of the pseudo-second-order. The conducted research has contributed to the application of a significantly reduced number of performed experiments with maximum precision and to defining the factors with the most pronounced influence on the process, thus this work promotes economy and speed. The shortcomings of nZVI and its possible modifications to achieve better characteristics which are being discussed. Corrosion is considered to be the leading problem, but it also has its positive sides, which have been proven in this paper. The generated FeOOH on the surface proved to be very good and important for the removal of pollutants of interest. Finally, the good performance of oak-nZVI is reflected in their durability, sustainability, and above all a simple method of synthesis, and as their most important feature is the high potential for decontamination of wastewater, and special reference to phosphate-continuous water. The cost-effectiveness of this treatment is also reflected in the fact that tertiary treatment would be avoided on a full-scale application due to the good simultaneous removal of both, metal ions and phosphorus. There are many publications on the application of nZVI, their modification, removal of various pollutants from all environmental media, but it must be taken into account that everything is still at the level of laboratory research. To achieve practical application, it is necessary to focus on the following challenges:
(1) The use of large-scale with a guarantee of efficiency, safety, and economy.
(2) Monitoring terrain data due to the presence of numerous environmental influences.
(3) Long-term effects on biological cycles and their fate in the environment.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (Grant No. 451-03-9/2021-14/200125 and 451-03-9/2021-14/200156). The content of this document is the sole liability of the University of Novi Sad, Faculty of Sciences. Also, the authors gratefully acknowledge the Science Fund of the Republic of Serbia for the Program for excellent projects of young researchers (PROMIS) – Waste Water Force project (6066881). Project no. 2019-2.1.11-TÉT-2020-00152 has been implemented with the support provided by the Ministry of Innovation and Technology of Hungary from the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund.
References
- Abdelwaheb, M. , Jebali, K., Dhaouadi, H., Dridi-Dhaouadi, S., 2019. Adsorption of nitrate, phosphate, nickel, and lead on soils: Risk of groundwater contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 179,182-187. [CrossRef]
- Afridi, M.N. , Lee, W.H., Kim, J.O., 2019. Effect of phosphate concentration, anions, heavy metals, and organic matter on phosphate adsorption from wastewater using anodized iron oxide nanoflakes. Environ. Res. 171, 428–436. [CrossRef]
- Alimohammadi, N. , Shadizadeh, S.R., Kazeminezhad, I., 2013. Removal of cadmium from drilling fluid using nano-adsorbent. Fuel. 111, 505-509. [CrossRef]
- Ayati, M. , Madsen, H.E.L., 2001 Solubility Product of the Cadmium Phosphate Cd5H2(PO4)4·4H2O at 37 °C. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 46,113-116. [CrossRef]
- Bai, L. , Hu, C., Liu H., Qu, J., 2019. Selective adsorption of fluoride from drinking water using NiAl-layered metal oxide film electrode. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 539, 146-151. [CrossRef]
- Baohong, H. , Lei, S., Li, H., Hongwei, S., 2020. Immobilization of Cd and phosphorus utilization in eutrophic river sediments by biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron, Environ. Technol. [CrossRef]
- Boparai, H.K. , Joseph, M., O'Carroll, D.M., 2011. Kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium ion removal by adsorption onto nano zerovalent iron particles. J. Hazard. Mater. 186, 458–465. [CrossRef]
- Borja, J.Q. , Ngo, M.A.S., Saranglao, C.C., Tiongco, R.P.M., Roque, E.C., Dugos, N.P., 2015. Synthesis of green zero-valent iron using polyphenols from dried green tea extract, School of Engineering, Taylor’s University.
- Ebrahimi, R. , Hayati, B., Shahmoradi, B., Rezaee, R., Safari, M., Maleki, A., Yetilmezsoy, K., 2018. Adsorptive removal of nickel and lead ions from aqueous solutions by poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers (G4). Environ. Technol. & Inn. 12, 261–272. [CrossRef]
- Efecan, N. , Shahwan, T., Eroğlu, A.E., Lieberwirth, I., 2009. Characterization of the uptake of aqueous Ni2+ ions on nanoparticles of zero-valent iron (nZVI). Desalination. 249, 1048-1054. [CrossRef]
- Fidaledo, M. , Lavecchia, R., Petrucci, E., Zuorro, A., 2016. Application of a novel definitive screening design to decolorization of an azo dye on boron-doped diamond electrodes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13, 835-842. [CrossRef]
- Gasemloo, S. , Khosravi, M., Sohrabi, M.R., Dastmalchi, S., Gharbani, P., 2019. Response surface methodology (RSM) modeling to improve removal of Cr(VI) ions from tannery wastewater using sulfated carboxymethyl cellulose nanofiller. J. Clean. Prod. 208, 736-742. [CrossRef]
- Husson, J.S. , Graber, E.O., Zwieten, L., Taherymoosavi, S., Thomas, T., Nielsen, S., Ye, J., Pan, G., Chia, C., Munroe, P., Allen, J., Lin, Y., Fan, X., Donne, S., 2015. The Electrochemical Properties of Biochars and How They Affect Soil Redox Properties and Processes. Agronomy. 5, 322-340. [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, F.A. , Al-Khaldi, B., Abusharkh, B., Khaledet, M., Atieh, M.A., Nasser, M.S., Tahar, I., Tawfik A.S., Agarwal, S., Vinod, T., Gupta, K., 2015. Adsorptive removal of cadmium(II) ions from liquid phase using acid modified carbon-based adsorbents. J. Mol. Liq. 204, 255–263. [CrossRef]
- Jafaryan, A. , Sadjadi, S., Gharib, A., Ahmadi, S.J., 2019. Optimization of cadmium adsorption from aqueous solutions by functionalized graphene and the reversible magnetic recovery of the adsorbent using response surface methodology, Appl. Organomet. Chem. 33, e5085. [CrossRef]
- Jie, L. , Changlun, C., Kairuo, Z., Xiangke, W., 2016. Nanoscale zero-valent iron particles modified on reduced graphene oxides using a plasma technique for Cd(II) removal. J. Taiwan Inst. of Chem. Eng. 59, 384-394. [CrossRef]
- Jokić Govedarica, J. , Tomašević Pilipović, D., Gvojić, V., Kerkez, Đ., Leovac Maćerak, A., Slijepčević, N., Bečelić-Tomin, M., 2022. The application of „green„ synthesized nulavalant iron for removal of Cd (II) from water. Water and sanitary technology L XII(2) 13-20. UDK: 502.51:504.5:546.48 546.72:502.174.
- Jones, B. , Nachtsheim, C.J., 2013. Definitive screening designs with added two-level categorical factors. J. Qual. Technol. 45,121-129. [CrossRef]
- Kong, L. , Tian, Y., Li, N., Liu, Y., Zhang, J., Zuo, W., 2018. Highly-effective phosphate removal from aqueous solutions by calcined nano-porous palygorskite matrix with embedded lanthanum hydroxide. App. Clay Sci. 162, 507–517. [CrossRef]
- Kecić, V. , Kerkez, Đ., Prica, M., Lužanin, O., Bečelić-Tomin, M., Tomašević Pilipović, D., Dalmacija, B., 2018. Optimization of azo printing dye removal with oak leaves-nZVI/H2O2 system using statistically designed experiment. J. Clean. Prod. 202, 65-80. [CrossRef]
- Krüger, O. , Adam, C., 2015. Phosphorus in recycling fertilizers-analytical challenges. Environ. Res. 155, 353–358. [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H. , Kim, J.O., 2017. Effect of coexisting components on phosphate adsorption using magnetite particles in water, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26, 1054–1060. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q. , Zhang, W.X., 2007. Sequestration of metal cations with zero-valent iron nanoparticles – a study with high-resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HR-XPS). J. Phys. Chem. C. 111, 6939–6946. [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. , Chen, Z., Wang, H., Yang, H., Wen, T., Wang, S., Hu, B., Wang X. (2021) Removal of organic compounds by nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites. Science of the Total Environment 792,148546. [CrossRef]
- Machado, S. , Pinto, S., Grosso, J., Nouws, H., Albergaria, J., Deleruee Matos, C., 2013. Green production of zero-valent iron nanoparticles using tree leaf extracts. Sci. Total Environ. 445, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, O.A. , Masood, S.H., Bhowmik, J.L., 2017. Investigation on the flexural creep stiffness behavior of PC-ABS material processed by fused deposition modeling using response surface definitive screening design. J. Min. Met. Mat. Soc. 69, 498-505. [CrossRef]
- Moharami, S. , Jalal, M., 2013. Removal of phosphorus from aqueous solution by Iranian natural adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 223, 328–339. [CrossRef]
- Nagoya, S. , Nakamichi, S., Kawase, Y., 2019. Mechanisms of phosphate removal from aqueous solution by zero-valent iron: A novel kinetic model for electrostatic adsorption, surface complexation and precipitation of phosphate under oxic conditions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 218, 120–129. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T. , Ngo, H.H., Guo, W.S., 2015. Adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solutions and sewage using zirconium loaded okara (ZLO): fixed-bed column study. Sci. Total Environ. 523, 40–49. [CrossRef]
- O’Carroll, D. , Sleep, B., Krol, M., Boparai, H., Kocur, C. 2013. Nanoscale zero valent iron and bimetallic particles for contaminated site remediation. Adv. Water Resour. 51, 104-122. [CrossRef]
- Pasinszki, T. , Krebsz, M., 2020. Synthesis and Application of Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles in Water Treatment, Environmental Remediation, Catalysis, and Their Biological Effects. A review, Nanomaterials. 10. [CrossRef]
- Poguberović, S. , Krčmar, D., Maletić, S., Dalmacija, B., Tomašević Pilipović, D., Kerkez, Ð., Rončević, S, 2016. Removal of Ni(II) and Cu(II) from aqueous solutions using ‘green’ zero-valent iron nanoparticles produced by oak and mulberry leaf extracts. Water Sci. Technol. 74, 2115-2123. [CrossRef]
- Rana, A. , Kumari, N., Tyagi, M., Jagadevan, S., 2018. Leaf-extract mediated zero-valent iron for oxidation of Arsenic (III): Preparation, characterization and kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 347, 91–100. [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, N. , Deluchat, V., Wazne, M., Mallet, M., Courtin-Nomade, A., Kazpard, V., Baudu, M., 2017. Phosphate removal from aqueous solutions using zero valent iron(ZVI): Influence of solution composition and ZVI aging, Colloid. Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 514, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Stietiya, M.H. , Wang, J.J., 2014. Zinc and cadmium adsorption to aluminum oxide nanoparticles is affected by naturally occurring ligands. J. Environ. Qual. 43, 498-506. [CrossRef]
- Tang, H. , Zhang, S, Pang, H., Wang, J., Wang, X, Song, G., Yu, S. (2021) Insights into enhanced removal of U(VI) by melamine sponge supported sulfurized nanoscale zero-valent iron. Journal of Cleaner Production 329,129662. [CrossRef]
- Tosco, T. , Papini, P.M., Cruz. C.V., Sethi, R., 2014. Nanoscale zerovalent iron particles for groundwater remediation: a review. J. Clean. Prod. 77, 10–21. [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.J. , You, C.F., Chang, C.K., 2012. Kinetics and thermodynamics of adsorption for Cd on green manufactured nano-particles. J. Hazard. Mater. 235, 116-122. [CrossRef]
- Veljković, N. , Vidojević, D., Jovičić, M., 2010. Environmental and health impact of pollutants from urban wastewater. “Wastewater, municipal solid waste and hazardous waste, Association for Water Technology and Sanitary Engineering, 29. March - 1. April 2010, Subotica, Serbia.
- Wang, K. , Xing, B., 2004. Mutual effects of cadmium and phosphate on their adsorption and desorption by goethite, Environ. Pollut. 127, 13-20. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. , Luo, H., Zhang, Z., Wu, Y., Zhang, J., Chen, S., 2014. Removal of As(III) and As(V) from aqueous solutions using nanoscale zero-valent iron-reduced graphite oxide modified composites. J. Hazard. Mater. 268, 124–131. [CrossRef]
- Yu, S., Pang H., Huang, S., Tang, H., Wang S., Qiu, M., Chen Z., Yang, H., Song, G., Fu D., Hu B., Wang X. (2021) Recent advances in metal-organic framework membranes for water treatment: A review. Science of the Total Environment 800 149662. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H. , Liu, F.Q., Zhu, C.Q., Zhang, X.P., Wei, M.M., Wang, F.H., Ling, C., Li, A.M., 2017 Multifold enhanced synergistic removal of nickel and phosphate by a(N.Fe)-dual-functional bio-sorbent: Mechanism and application. J. Hazard. Mater. 329, 290–298. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).