Submitted:
06 May 2025
Posted:
08 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Adsorbent Preparation
2.2. Characteriation of the Cationic Adsorbent
2.3. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.4. Experimental Design
3. Results
3.1. Design of Statistical Experiments
| Sorption parameters | Factors | 24 FFD | CCD | |||
| Levels | Levels | |||||
| -1 | +1 | -1 | 0 | +1 | ||
| Initial nitrate concentration, Co (mg/L) | A | 10 | 50 | 10 | 30 | 50 |
| pH value | B | 4 | 8 | 4 | 6 | 8 |
| Temperature, T (0C) | C | 20 | 40 | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| Contact time, t (min) | D | 5 | 35 | 5 | 20 | 35 |
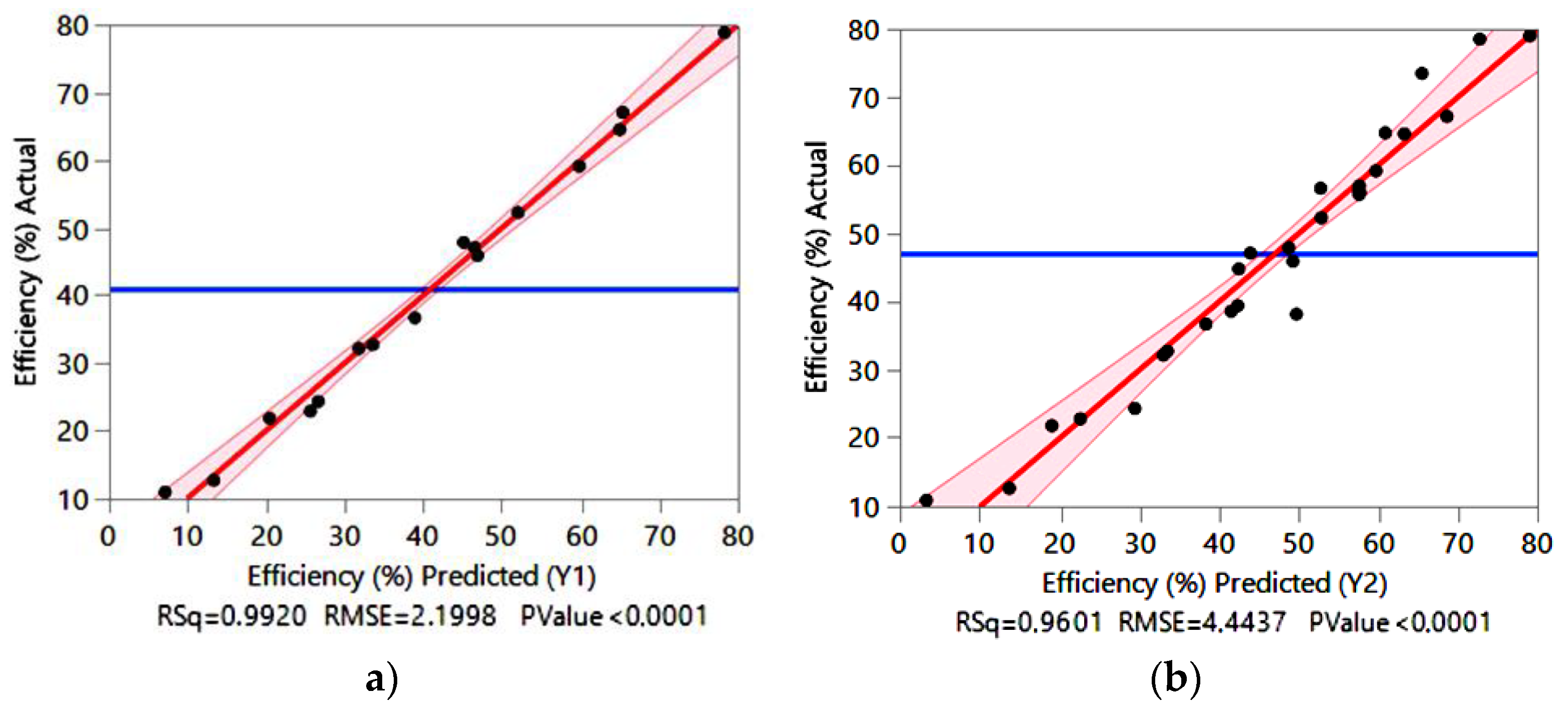
3.2. Regression Models and Analytical Validation
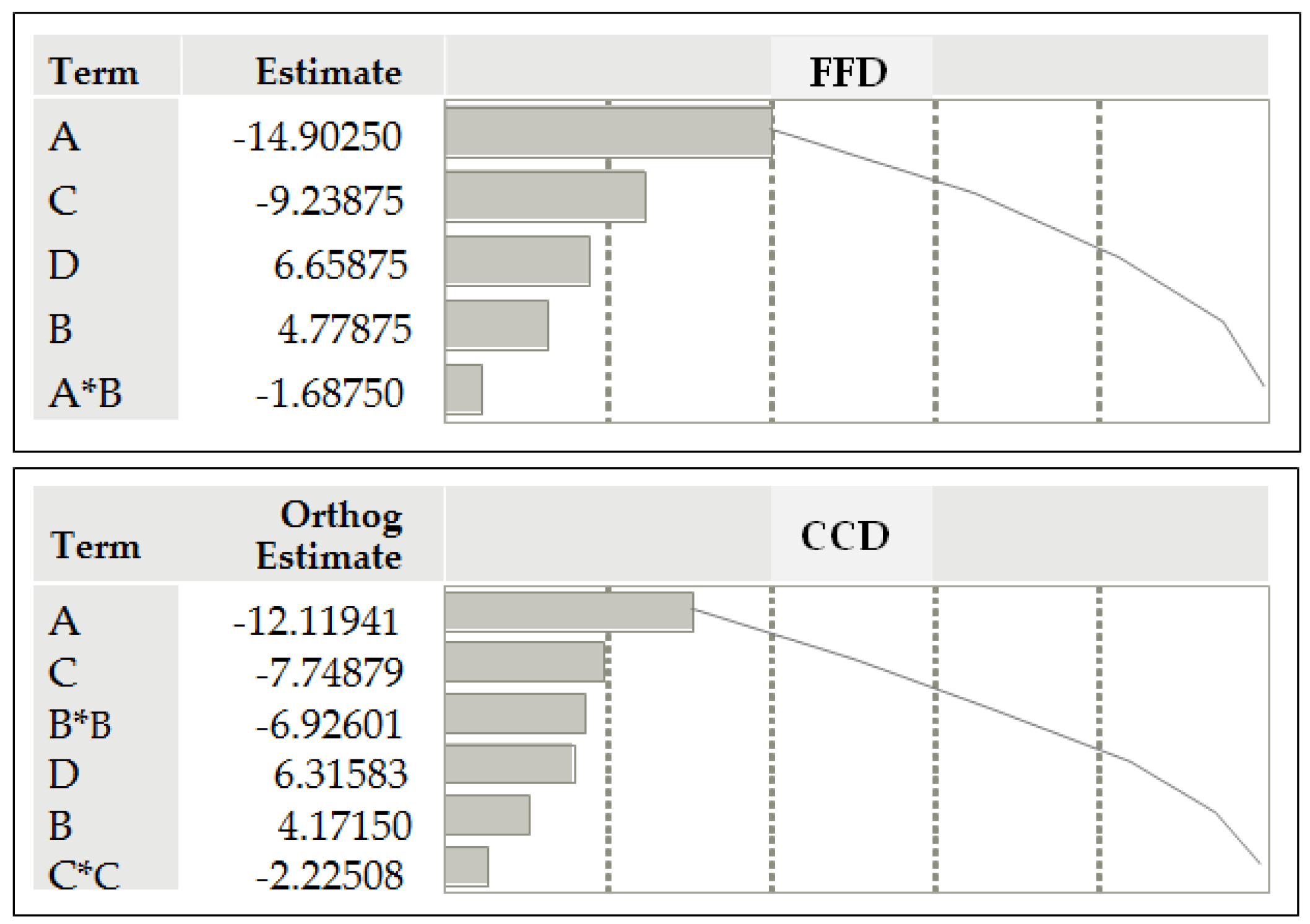
- a linear polynomial model by FFD:Y1 = 41.08 – 14.90×A + 4.78×B – 9.24×C + 6.65×D – 1.69×AB
- a nonlinear polynomial model by CCD:Y2 = 57.59 – 15.12×A + 5.20×B – 9.67×C + 7.88×D – 10.04×B2 – 6.40×C2
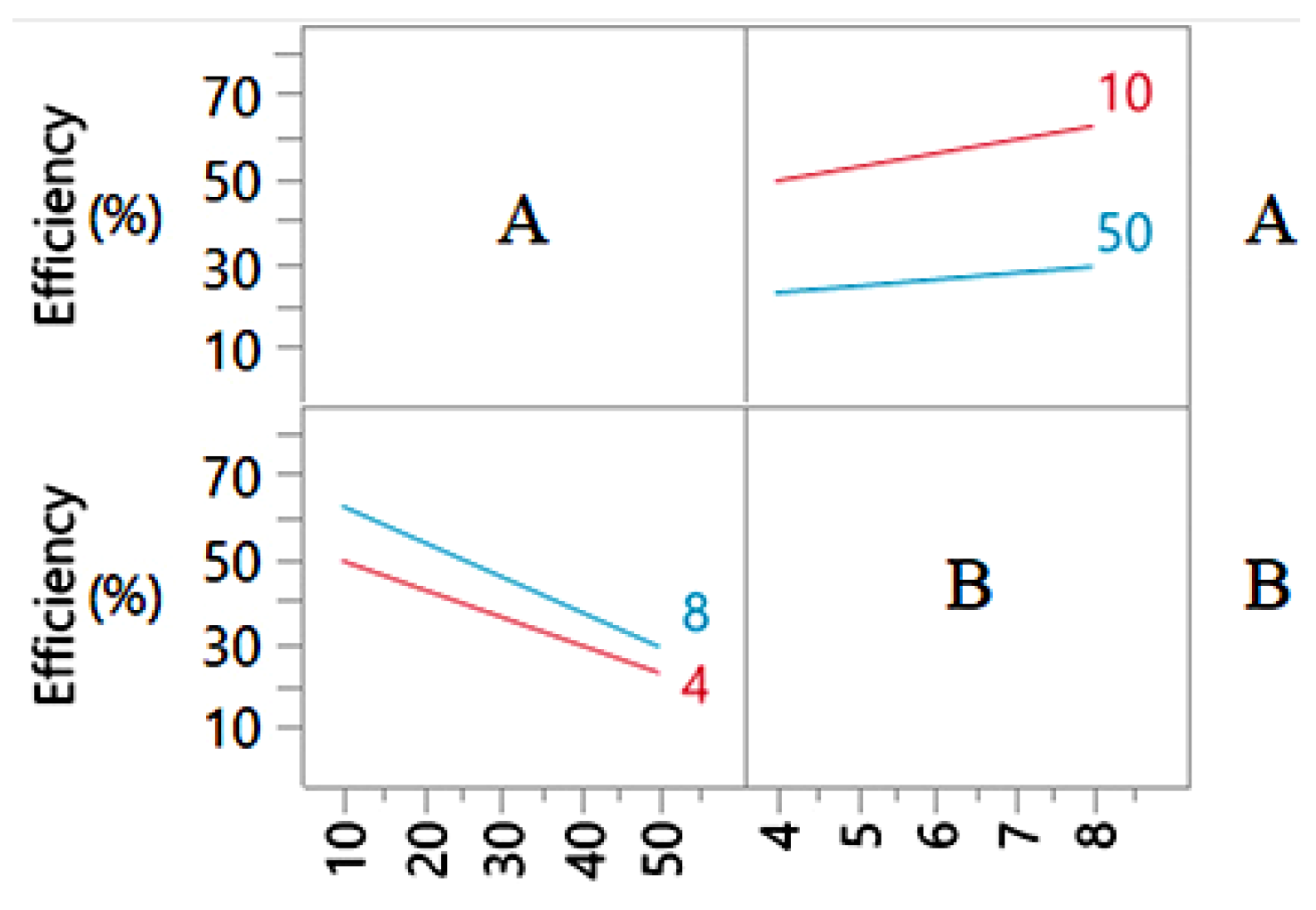
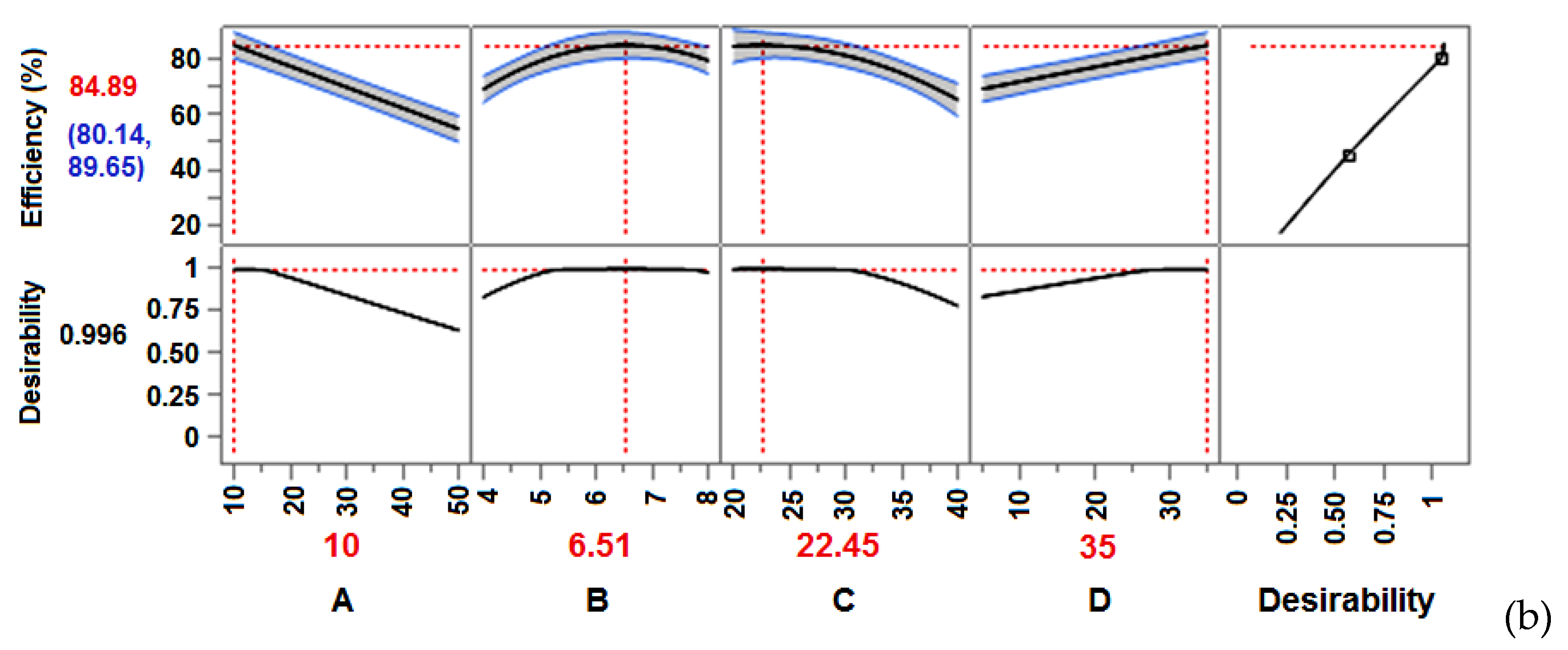
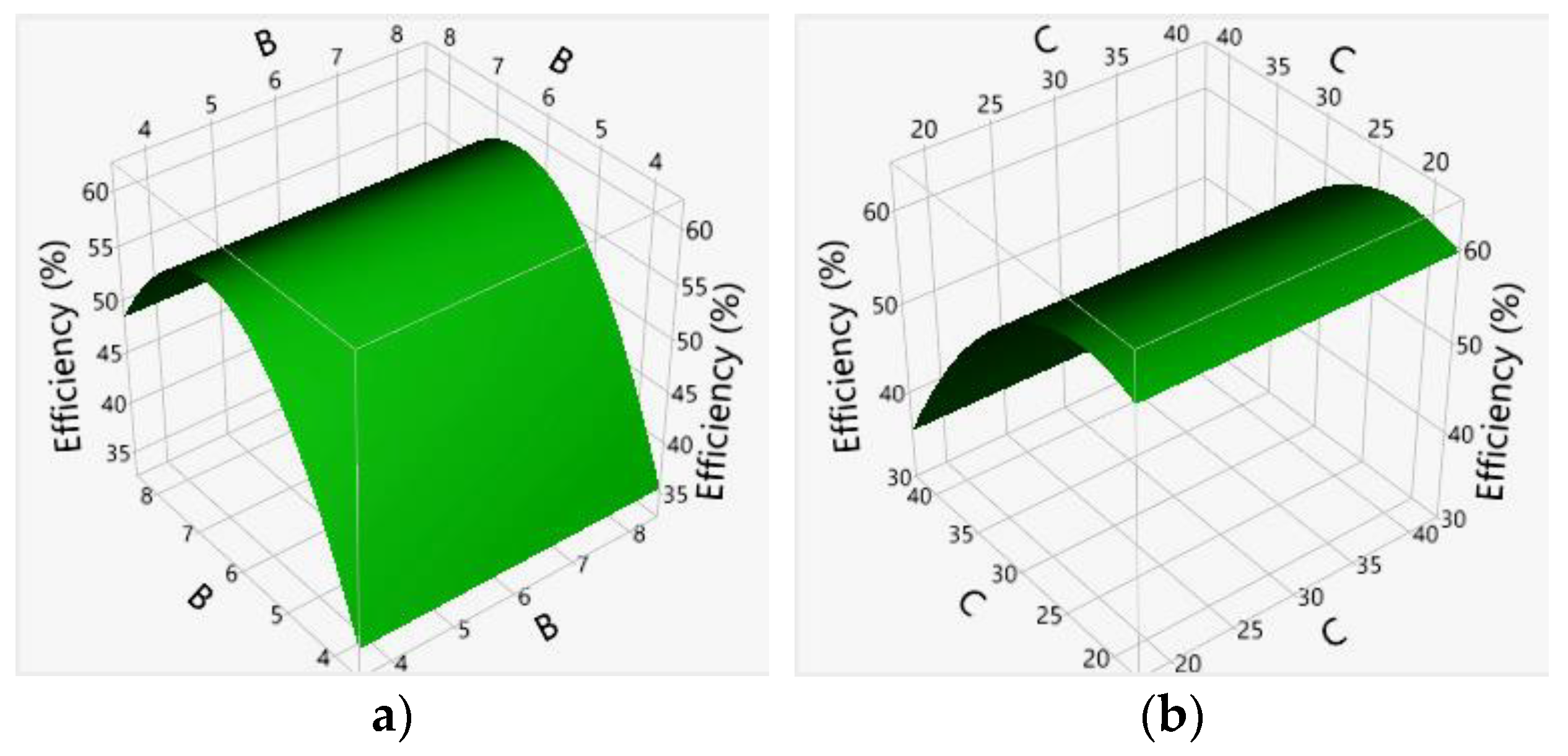
3.3. Effects of Main Factors and Their Interactions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance test |
| CCD | Central Composite Design |
| CGS | Calabash gourd shell |
| CHTAC | N-(3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl) trimethylammonium chloride |
| DF | Degrees of freedom |
| DoE | Design of Experiments |
| FFD | Full Factorial Design |
| pHpzc | pH value at the point of zero charge |
| RSM | Response Surface Methodology |
References
- Valiente, N.; Gil-Márquez, J.M.; Gómez-Alday, J.J.; Andreo, B. Unraveling groundwater functioning and nitrate attenuation in evaporitic karst systems from southern Spain: an isotopic approach. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 123, 104820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Xue, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhu, Y. Study on the influence of surface potential on the nitrate adsorption capacity of metal modified biochar. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhu, Z. Removal of nitrate from aqueous solution using cetylpyridinium bromide (CPB) modified zeolite as adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.I.M. Biological denitrification of groundwater. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2000, 123, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeman, J.J.; Steyn, A. Nitrate removal with reverse osmosis in a rural area in South Africa. Desalination 2003, 155, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shady, A.; Peng, C.; Bi, J.; Xu, H.; Juan Almeria, O. Recovery of Pb(II) and removal of NO₃⁻ from aqueous solutions using integrated electrodialysis, electrolysis, and adsorption process. Desalination 2012, 286, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. A review of emerging adsorbents for nitrate removal from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieillard, J.; Bouazizi, N.; Nkuigue Fotsing, P.; Samir, B.; Raguillet, K.; Cosme, J.; Abou Serhal, C.; Mignot, M.; Sophie Bette, M.; Auger, P.; Luiz Dotto, G.; Le Derf, F. Herbs carbonization and activation for fast sorption of nitrate ions: a new challenge for a full treatment of groundwater pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 82637–82646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Carrott, P.J.M.; Ribeiro Carrott, M.M.L.; Suhas, D. Low-cost adsorbents: Growing approach to wastewater treatment—a review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 783–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keränen, A.; Leiviskä, T.; Hormi, O.; Tanskanen, J. Removal of nitrate by modified pine sawdust: Effects of temperature and co-existing anions. J. Environ. Manage. 2015, 147, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliedeh, M.A.; Aljbour, S.H.; Al-Harahsheh, A.M.; Al-Zboon, K.; Al-Harahsheh, S. Implementing 24-1 fractional factorial design for filing the gaps in ovat sorption studies of nitrate ions onto Jordanian zeolitic tuff. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2021, 56, 331–341. [Google Scholar]
- Karić, N.; Maia, A.S.; Teodorović, A.; Atanasova, N.; Langergraber, G.; Crini, G.; Ribeiro, A.R.L.; Đolić, M. Bio-waste valorisation: Agricultural wastes as biosorbents for removal of (in)organic pollutants in wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 9, 100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, R.P.; Kalariya, M.; Parmar, S.K.; Sheth, N.R. Phytochemical and pharmacological review of Lagenaria sicereria. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2010, 1, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, D.L.; Smith, B.D.; Clarke, A.C.; Sandweiss, D.H.; Tuross, N. An Asian origin for a 10,000-year-old domesticated plant in the Americas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18315–18320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolić, G.; Marković Nikolić, D.; Bojić, A.; Bojić, D.; Nikolić, Lj.; Stanojević, Lj.; Durmišević, M.; Simonović, N.; Kostić, M. Bottle gourd (Lagenaria vulgaris) shell as a natural, biodegradable, highly available, cheap, agricultural by-product, miscellaneous biomass, ion exchanger, biosorbent and fertilizer. Chapter In: Sorption - New Perspectives and Applications; Margeta, K., Farkaš, A., Eds.; Publisher: InTechOpen, London, UK, 2024; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, E.; Kumar, S.; Verma, C.; Sarkar, S.; Maji, P.K. A comprehensive review on technological advances of adsorption for removing nitrate and phosphate from waste water. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaruban, M.; Loganathan, P.; Shim, W.G.; Kandasamy, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Vigneswaran, S. Enhanced removal of nitrate from water using amine-grafted agricultural wastes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maculewicz, J.; O’Sullivan, A.D.; Barker, D.; Tat Wai, K.; Basharat, S.; Bello-Mendoza, R. Novel quaternary ammonium functionalized cellulosic materials for nitrate adsorption from polluted waters. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025, 236, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković Nikolić, D.Z.; Bojić, A.; Bojić, D.; Cvetković, D.; Cakić, M.; Nikolić, G.S. Preconcentration and immobilization of phosphate from aqueous solutions in environmental cleanup by a new bio-based anion exchanger. Waste Biomass Valor. 2020, 11, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, G.S.; Simonović, N.; Nikolić, Lj.; Durmišević, M.; Marković Nikolić, D.; Ristić, N.; Bojić, A. An integrated OVAT-RSM design to gaps-filling in the study of phosphate sorption process onto cationic modified bottle gourd shell. Adv. Technol. 2023, 12, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-C.; Kang, J.-K.; Jang, H.-Y.; Park, J.-A.; Kim, S.-B. Multi-parameter experiments and modeling for nitrate sorption to quaternary ammonium-functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimers in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 11023–11036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafshejani, L.D.; Naserib, A.A.; Moradzadehc, M.; Daneshvard, E.; Bhatnagard, A. Applications of soft computing techniques for prediction of pollutant removal by environmentally friendly adsorbents (case study: the nitrate adsorption on modified hydrochar). Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, J. Design of experiments for engineers and scientists, Book chapter, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Ltd., 2014; ISBN 978-0-08-099417-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, M.; Asaithambi, P.; Befekadu, A.; Alemayehu, E. Optimization of indigenous natural coagulants process for nitrate and phosphate removal from wet coffee processing wastewater using response surface methodology: In the case of Jimma Zone Mana district. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baei, M.S.; Esfandian, H.; Nesheli, A.A. Removal of nitrate from aqueous solutions in batch systems using activated perlite: an application of response surface methodology. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 11, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, G.S.; Marković Nikolić, D.; Nikolić, T.; Stojadinović, D.; Andjelković, T.; Kostić, M.; Bojić, A. Nitrate removal by sorbent derived from waste lignocellulosic biomass of Lagenaria vulgaris: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2021, 15, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković Nikolić, D.Z.; Bojić, A.Lj.; Savić, S.R.; Petrović, S.M.; Cvetković, D.J.; Cakić, M.D.; Nikolić, G.S. Synthesis and physicochemical characterization of anion exchanger based on green modified bottle gurd shell. J. Spectrosc 2018, 1856109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, J. 6 - Full factorial designs. In Design of Experiments for Engineers and Scientists, Book chapter, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Ltd., 2023; pp. 65–87. ISBN 9780443151736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 8th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2012; pp. 233–292. ISBN 1118214714. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, A.T.; Makwana, A.R.; Ahammed, M.M. The use of response surface methodology for modelling and analysis of water and wastewater treatment processes: a review. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Mallavarapu, M.; Naidu, R. Preparation, characterization of surfactants modified clay minerals and nitrate adsorption. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.C.; Patel, R.K. Use of agricultural waste for the removal of nitrate-nitrogen from aqueous medium. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nujić, M.; Milinković, D.; Habuda-Stanić, M. Nitrate removal from water by ion exchange. Croat. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 9, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasivayam, C.; Höll, W.H. Quaternized biomass as an anion exchanger for the removal of nitrate and other anions from water. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, G.; Zhang, P.; Shen, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Y. Development of iron-based biochar for enhancing nitrate adsorption: Effects of specific surface area, electrostatic force, and functional groups. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristek Janković, A.; Habuda-Stanić, M.; Dong, H.; Tutić, A.; Romić, Ž.; Ergović Ravančić, M.; Landeka Dragičević, T.; Šiljeg, M. Utilization of modified sunflower seed as novel adsorbent for nitrates removal from wastewater. Water 2024, 16, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabani, M.; Amrane, A.; Bensmaili, A. Kinetic modelling of the adsorption of nitrates by ion exchange resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 125, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, N.; Ren, B.; Xu, B.; Li, D.; Xia, Y.; Xu, C.; Hua, E. Bamboo chopstick biochar electrodes and enhanced nitrate removal from groundwater. Processes 2022, 10, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, A.; Godini, H.; Dehestani, S.; Khavanin, A. Application of impregnated almond shell activated carbon by zinc and zinc sulfate for nitrate removal from water. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2008, 5, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Orlando, U.S.; Baes, A.U.; Nishijima, W.; Okada, M. Preparation of agricultural residue anion exchangers and its nitrate maximum adsorption capacity. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, U.S.; Baes, A.U.; Nishijima, W.; Okada, M. A new procedure to produce lignocellulosic anion exchangers from agricultural waste materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stjepanović, M.; Velić, N.; Habuda-Stanić, M. Modified hazelnut shells as a novel adsorbent for the removal of nitrate from wastewater. Water 2022, 14, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, B.-Y.; Yue, W.-W.; Yue, Q.-Y. Adsorption kinetics of nitrate from aqueous solutions onto modified wheat residue. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2007, 308, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoudi, S.; Saad, R.; Belkacemi, K. Adsorptive removal of phosphate and nitrate anions from aqueous solutions using ammonium-functionalized mesoporous silica. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 8806–8812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Runs | Pattern | A | B | C | D | Efficiency Y (%) |
Predicted Y1 (%) FFD |
Predicted Y2 (%) CCD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −−−− | 10 | 4 | 20 | 5 | 52.29 | 52.09 | 50.15 |
| 2 | +−−− | 10 | 4 | 20 | 5 | 22.86 | 25.67 | 22.56 |
| 3 | −+−− | 10 | 8 | 20 | 5 | 64.58 | 65.03 | 65.39 |
| 4 | −−+− | 50 | 4 | 40 | 5 | 32.74 | 33.62 | 32.76 |
| 5 | −−−+ | 50 | 4 | 20 | 35 | 67.12 | 65.41 | 67.42 |
| 6 | ++−− | 50 | 8 | 20 | 5 | 32.17 | 31.85 | 31.05 |
| 7 | +−+− | 10 | 4 | 40 | 5 | 10.93 | 7.19 | 7.20 |
| 8 | +−−+ | 50 | 4 | 20 | 35 | 36.71 | 38.98 | 39.27 |
| 9 | −++− | 30 | 8 | 40 | 5 | 47.12 | 46.55 | 44.83 |
| 10 | −+−+ | 30 | 8 | 20 | 35 | 78.93 | 78.35 | 82.92 |
| 11 | −−++ | 30 | 4 | 40 | 35 | 45.91 | 46.94 | 47.29 |
| 12 | +++− | 30 | 8 | 40 | 5 | 12.67 | 13.37 | 12.52 |
| 13 | ++−+ | 30 | 8 | 20 | 35 | 47.88 | 45.17 | 48.02 |
| 14 | +−++ | 30 | 4 | 40 | 35 | 21.84 | 20.51 | 21.18 |
| 15 | −+++ | 30 | 8 | 40 | 35 | 59.16 | 59.86 | 59.62 |
| 16 | ++++ | 30 | 8 | 40 | 35 | 24.35 | 26.69 | 26.75 |
| 17 | 0a00 | 30 | 4 | 30 | 20 | 39.42 | 41.96 | |
| 18 | 0A00 | 30 | 8 | 30 | 20 | 56.61 | 52.36 | |
| 19 | 00a0 | 10 | 6 | 20 | 20 | 64.72 | 60.46 | |
| 20 | 00A0 | 50 | 6 | 40 | 20 | 38.58 | 41.13 | |
| 21 | 000a | 10 | 6 | 30 | 5 | 38.17 | 47.06 | |
| 22 | 000A | 10 | 6 | 30 | 35 | 73.42 | 62.82 | |
| 23 | 0000 | 10 | 6 | 30 | 20 | 56.24 | 57.49 | |
| 24 | 0000 | 50 | 6 | 30 | 20 | 55.71 | 57.49 | |
| 25 | 0000 | 50 | 6 | 30 | 20 | 56.98 | 57.49 | |
| 26 | 0000 | 50 | 6 | 30 | 20 | 55.96 | 57.49 | |
| 27 | a000 | 10 | 6 | 30 | 20 | 78.45 | 75.89 | |
| 28 | A000 | 50 | 6 | 30 | 20 | 44.81 | 45.66 |
| Source of variation | DF | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F Ratio | |||||
| Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | ||
| Model | 5 | 6 | 6039.3931 | 8879.7938 | 1207.88 | 1479.97 | 249.6024 | 74.9481 | |
| Error | 10 | 21 | 48.3921 | 414.6776 | 4.84 | 19.75 | Prob.> F | ||
| Corrected Total | 15 | 27 | 6087.7852 | 9294.4714 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| Determination coefficients | |||||||||
| Y1 (using FFD) | Y2 (using CCD) | ||||||||
| R2 | 0.992 | 0.960 | |||||||
| R2 adjusted | 0.988 | 0.943 | |||||||
| R2 predicted | 0.979 | 0.925 | |||||||
| DF – Degrees of Freedom; Prob. – probability (p-value) | |||||||||
| Full Factorial Design | |||||
| Source | Nparm | DF | Sum of Squares | F Ratio | Prob. > F |
| A | 1 | 1 | 3553.3521 | 675.7728 | <0.0001* |
| B | 1 | 1 | 365.3832 | 69.4882 | <0.0004* |
| C | 1 | 1 | 1365.6720 | 259.7221 | <0.0001* |
| D | 1 | 1 | 709.4232 | 134.9174 | <0.0001* |
| A*B | 1 | 1 | 45.5625 | 8.6650 | <0.0321* |
| A*C | 1 | 1 | 4.1616 | 0.7914 | 0.4144 |
| B*C | 1 | 1 | 10.0806 | 1.9171 | 0.2248 |
| A*D | 1 | 1 | 0.3136 | 0.0596 | 0.8168 |
| B*D | 1 | 1 | 0.0650 | 0.0124 | 0.9158 |
| C*D | 1 | 1 | 7.4802 | 1.4226 | 0.2865 |
| Central Composite Design | |||||
| Source | Nparm | DF | Sum of Squares | F Ratio | Prob. > F |
| A | 1 | 1 | 4112.6404 | 171.3500 | <0.0001* |
| B | 1 | 1 | 487.2401 | 20.3005 | <0.0006* |
| C | 1 | 1 | 1681.2268 | 70.0470 | <0.0001* |
| D | 1 | 1 | 1116.9113 | 46.5353 | <0.0001* |
| B*B | 1 | 1 | 275.5755 | 11.4816 | 0.0048* |
| C*C | 1 | 1 | 115.8299 | 4.8260 | 0.0468* |
| A*B | 1 | 1 | 45.5625 | 1.8983 | 0.1915 |
| A*C | 1 | 1 | 4.1616 | 0.1734 | 0.6839 |
| B*C | 1 | 1 | 10.0806 | 0.4200 | 0.5282 |
| A*D | 1 | 1 | 0.3136 | 0.0131 | 0.9107 |
| B*D | 1 | 1 | 0.0650 | 0.0027 | 0.9593 |
| C*D | 1 | 1 | 7.4802 | 0.3117 | 0.5862 |
| A*A | 1 | 1 | 27.7316 | 1.1554 | 0.3020 |
| D*D | 1 | 1 | 16.8535 | 0.7022 | 0.4172 |
| * statistical significant factors and interactions; DF – Degrees of Freedom; Prob. – probability (p-value); Nparm - Nonparametric analysis of multivariate data | |||||
| Full Factorial Design | ||||
| Term | Estimate | Std. Error | t Ratio | Prob. > |t| |
| Intercept | 41.0787 | 0.549955 | 74.69 | <0.0001* |
| A | -14.9025 | 0.549955 | -27.10 | <0.0001* |
| B | 4.7787 | 0.549955 | 8.69 | <0.0001* |
| C | -9.2387 | 0.549955 | -16.80 | <0.0001* |
| D | 6.6587 | 0.549955 | 12.11 | <0.0001* |
| A*B | -1.6875 | 0.549955 | -3.07 | 0.0119* |
| Central Composite Design | ||||
| Term | Estimate | Std. Error | t Ratio | Prob>|t| |
| Intercept | 57.5852 | 1.486101 | 38.75 | <0.0001* |
| A | -15.1155 | 1.047392 | -14.43 | <0.0001* |
| B | 5.2027 | 1.047392 | 4.97 | <0.0001* |
| C | -9.6644 | 1.047392 | -9.23 | <0.0001* |
| D | 7.8772 | 1.047392 | 7.52 | <0.0001* |
| B*B | -10.0413 | 2.417854 | -4.15 | 0.0005* |
| C*C | -6.4063 | 2.417854 | -2.65 | 0.0150* |
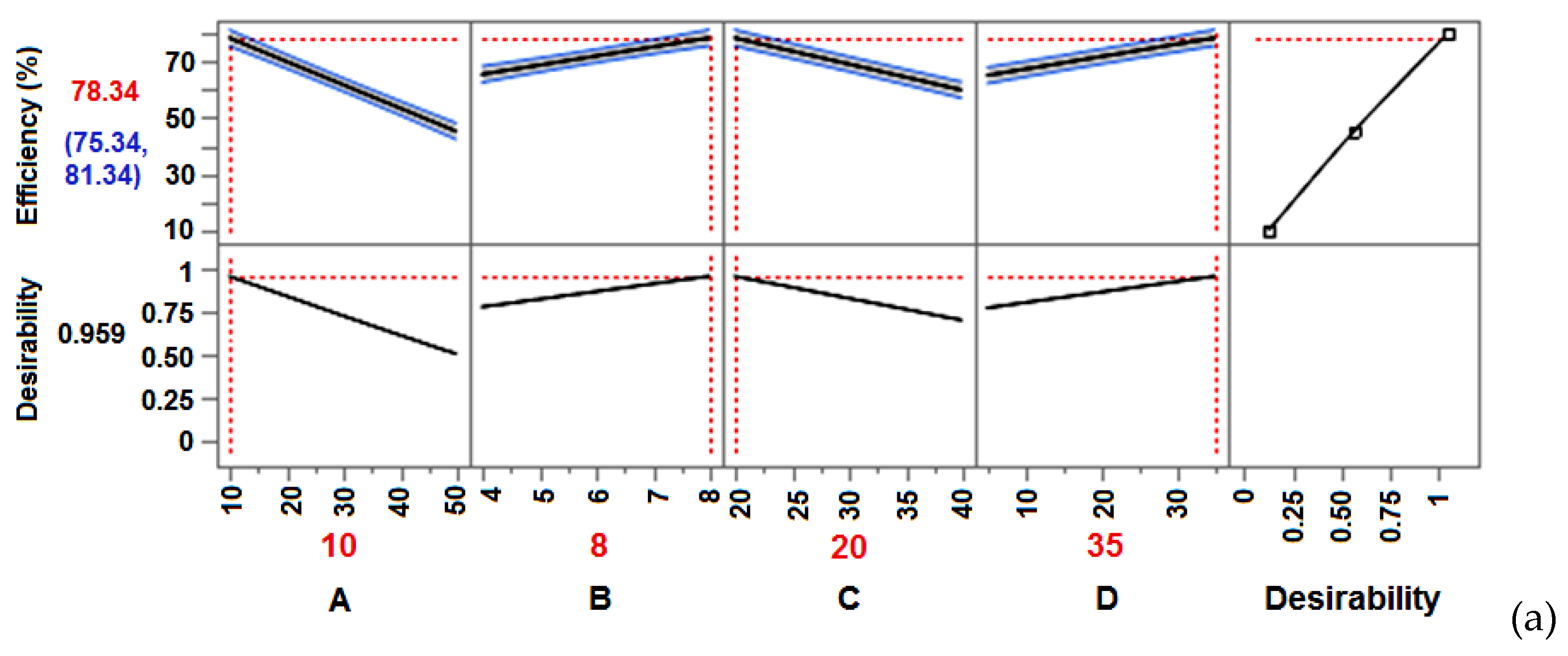
| DoE | A (C0) |
B (pH) |
C (T) |
D (t) |
Efficiency (%) |
Efficiency (%) Lower CI |
Efficiency (%) Upper CI | Desirability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FFD | 10 | 8 | 20 | 35 | 78.345 | 75.343 | 81.347 | 0.9591 |
| CCD | 10 | 6.52 | 22.46 | 35 | 84.897 | 80.144 | 89.650 | 0.9962 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorpt. capacity (mg/g) |
Nitrate solution (mg/L) |
Contact time (min, h) |
Temp. (0C) |
pH | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Halloysite | 0.54 | 100 | 17 h | Room | 5.4 | [31] |
| Wheat straw charcoal | 1.10 | 25 | 10 min | 15 | - | [32] |
| Commercial activated carbon | 1.22 | 25 | 10 min | 15 | - | [32] |
| Weak base anion exchanger Duolite A7 | 6.51 | 100 | 360 min | 25 | 5.4 | [33] |
| Cross-linked and quaternized chinese reed | 7.55 | 40 | 10 min | 25 | 5.8 | [34] |
| Modified corn-cob | 9.35 | - | - | - | - | [35] |
| Modified sunflower seed shells | 12.98 | 300 | 120 min | 25 | 7.5 | [36] |
| Strong base anion exchange resin Relite A490 | 13.02 | 100 | 360 min | 25 | 5.4 | [33] |
| Modified QLD-bentonite | 14.76 | 100 | 17 h | Room | 5.4 | [31] |
| Commercial anion exchanger Amberlite IRA-400 | 14.80 | - | - | - | - | [37] |
| Modified bambo chopstick | 16.39 | - | - | - | - | [38] |
| Impregnated almond shell activated carbon | 16-17 | 50 | 120 min | 20 | 6.2 | [39] |
| * Modified CGS | 16.53 | 50 | 40 min | 23 | 6.5 | * |
| Commercial anion exchanger Amberlite IRA-900 | 16.80 | - | - | - | - | [40] |
| Modified rice hull | 18.48 | 30 | 48 h | 30 | - | [41] |
| Modified sugarcane bagasse | 19.74 | 30 | 48 h | 30 | - | [41] |
| Modified hazelnut shells | 25.79 | - | - | - | - | [42] |
| Modified wheat residue | 29.12 | 500 | 150 min | 23 | 6.8 | [43] |
| Ammonium-functionalized mesoporous silica | 46.00 | 700 | 60 min | 5 | 8.0 | [44] |
| * CGS - modified calabash gourd shell (in this article) | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





