Submitted:
28 August 2023
Posted:
30 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
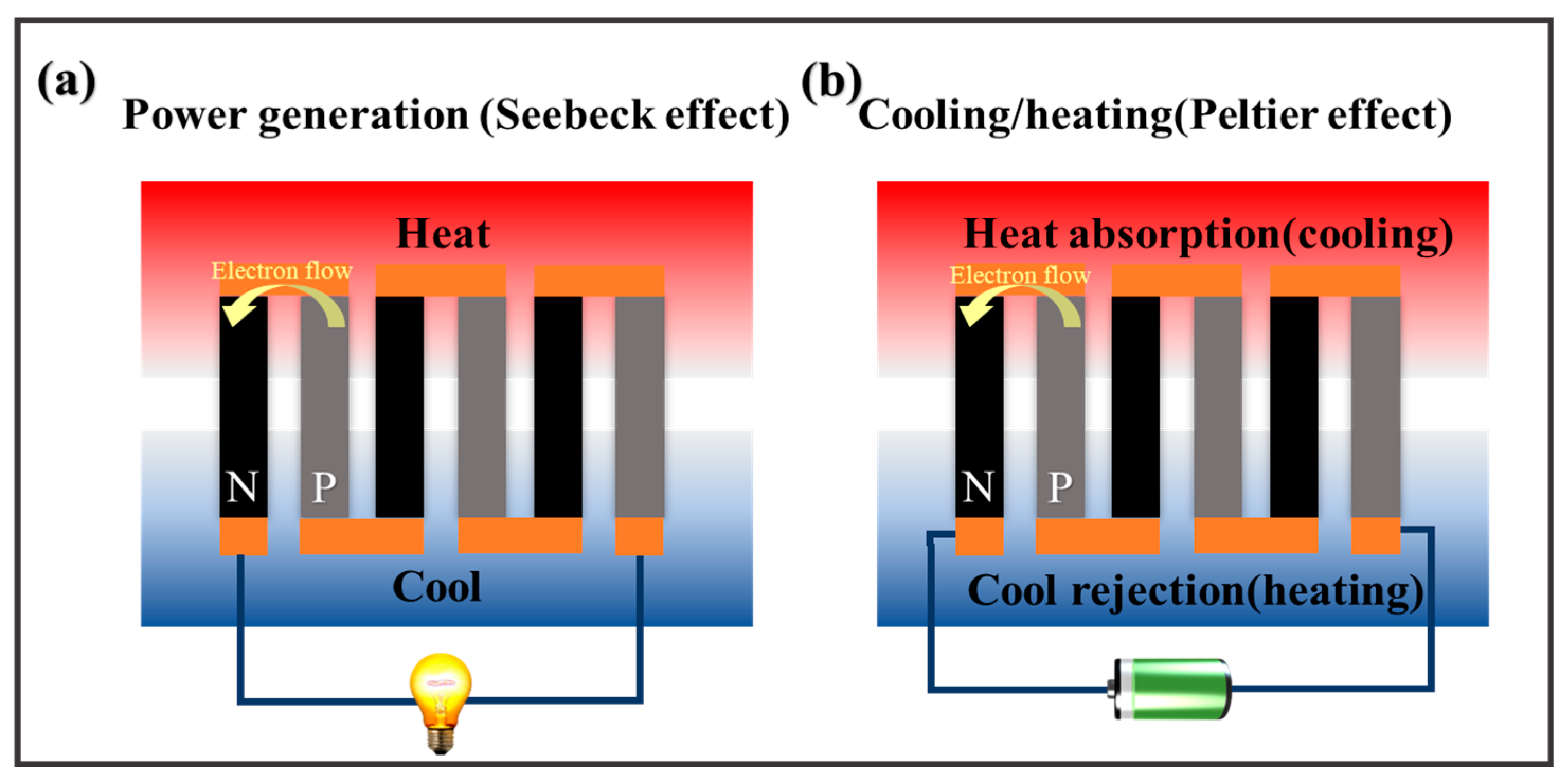
2. Wearable Thermo-Electrochemical Cells
2.1. Thermo-Electrochemical Cells
2.1.1. The Seebeck Coefficient of TECs
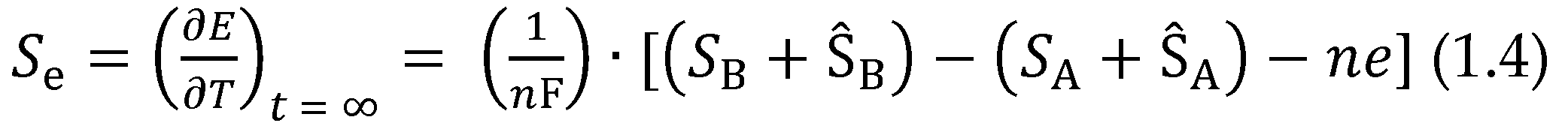
2.1.2. Performance Index of TECs
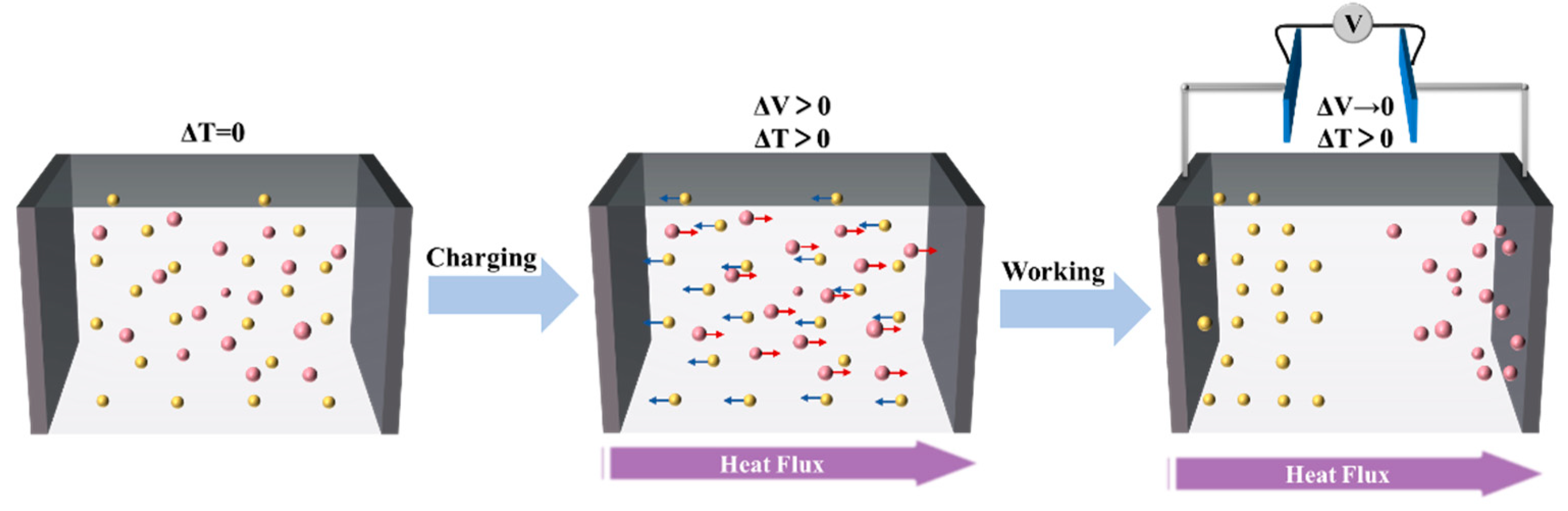
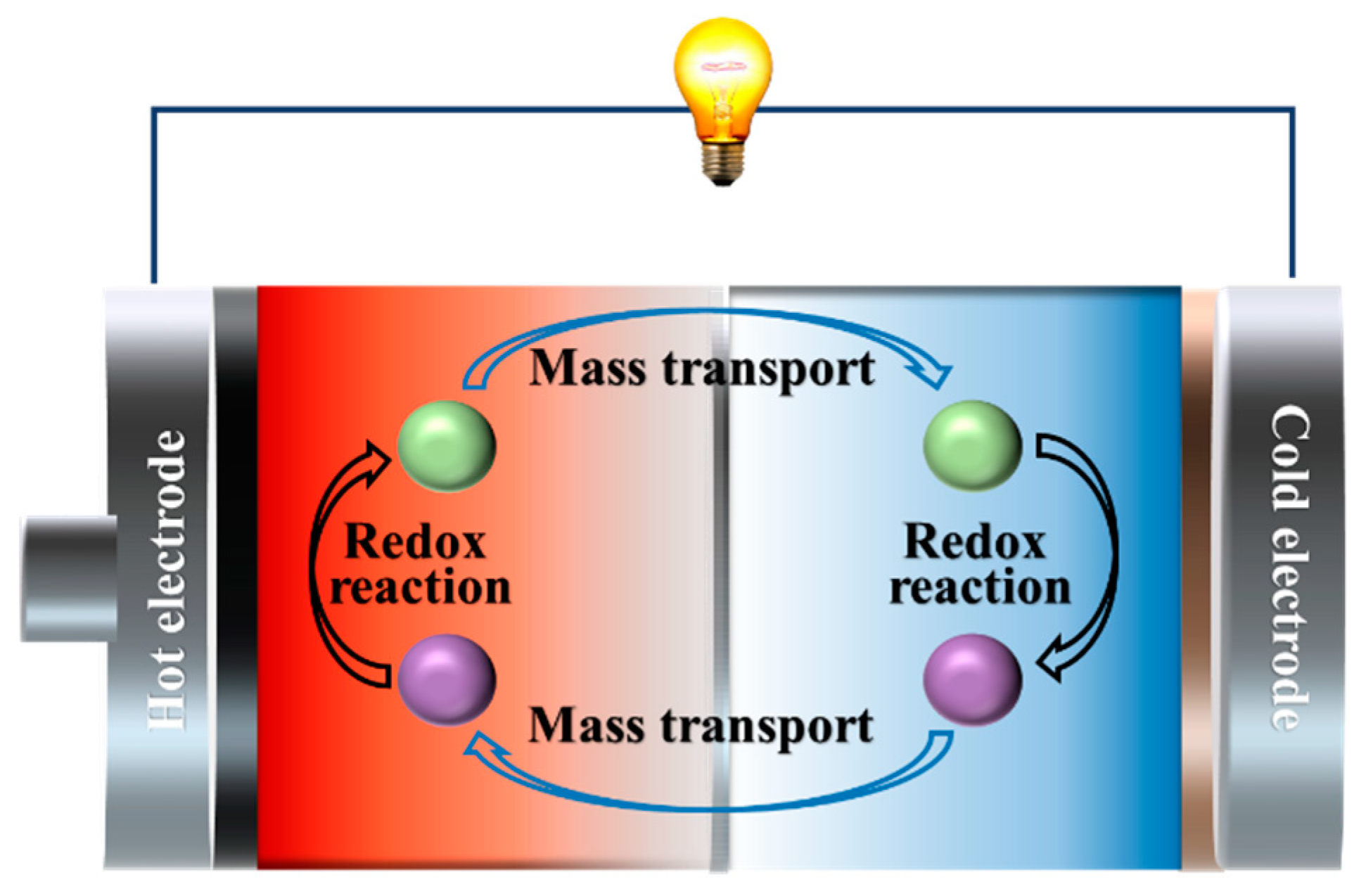
2.2. Electrochemical Thermogalvanic Effect
2.3. Quasi-Solid-State Electrolyte
2.3. Electrode
3. Device Integration and Applications
4. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burmistrov, I.; Khanna, R.; Gorshkov, N.; Kiselev, N.; Artyukhov, D.; Boychenko, E.; Yudin, A.; Konyukhov, Y.; Kravchenko, M.; Gorokhovsky, A.; Kuznetsov, D. Advances in thermo-electrochemical (TEC) cell performances for harvesting low-grade heat energy: A review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, B.; Guo, C.-Y. Advances in thermoelectric composites consisting of conductive polymers and fillers with different architectures. Molecules 2022, 27, 6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Luo, Q.; Yin, S.; Lu, W.; He, H.; Guo, C.-Y. Organic/inorganic thermoelectric composites electrochemical synthesis, properties, and applications. Journal of Materials Science 2021, 56, 19311–19328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Dai, K.; Li, C.; Fan, Y.; Chen, G.; Zheng, Q. Soft organic thermoelectric materials: Principles, current state of the art and applications. Small 2022, 18, 2104922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sootsman, J. R.; Chung, D. Y.; Kanatzidis, M. G. New and old concepts in thermoelectric materials. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2009, 48, 8616–8639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; He, J. Thermopower and harvesting heat. Science 2021, 371, 343–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, H.; Hao, F.; Liu, R.; Wang, T.; Qiu, P.; Burkhardt, U.; Grin, Y.; Chen, L. Room-temperature ductile inorganic semiconductor. Nature Materials 2018, 17, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, X.; Lacey, S. D.; Mi, R.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, F.; Song, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, G.; Dai, J.; Yao, Y.; Das, S.; Yang, R.; Briber, R. M.; Hu, L. Cellulose ionic conductors with high differential thermal voltage for low-grade heat harvesting. Nature Materials 2019, 18, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Cheng, H.; Yue, S.; Ouyang, J. Quasi-solid state nanoparticle/(ionic liquid) gels with significantly high ionic thermoelectric properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2020, 8, 10813–10821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Gao, N.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y. Thermoelectric converters based on ionic conductors. Chemistry – An Asian Journal 2021, 16, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Qian, X.; Han, C.-G.; Li, Q.; Chen, G. Ionic thermoelectric materials for near ambient temperature energy harvesting. Applied Physics Letters 2021, 118, 020501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.; Liu, G.; An, M.; Zhang, Y.; Song, D.; Qi, X.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Du, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lu, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Lin, C.; Ma, W.; Huang, B.; Du, X.; Zhang, X. Reversible bipolar thermopower of ionic thermoelectric polymer composite for cyclic energy generation. Nature Communications 2023, 14, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.; Gao, T.; Wang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, H.; Xiao, D. A novel gel thermoelectric chemical cell for harvesting low-grade heat energy. ChemSusChem 2023, 16, e202201815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Huang, Y.-T.; Liu, C.; Mu, K.; Li, K. H.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Su, C.-H.; Feng, S.-P. Direct thermal charging cell for converting low-grade heat to electricity. Nature Communications 2019, 10, 4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quickenden, T. I.; Vernon, C. F. Thermogalvanic conversion of heat to electricity. Solar Energy 1986, 36, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, M. F.; MacFarlane, D. R.; Pringle, J. M. Thermo-electrochemical cells for waste heat harvesting – progress and perspectives. Chemical Communications 2017, 53, 6288–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Qiu, L.; Lian, Y.; Dai, Y.; Yin, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, W.; Tao, X. (Early view) Gigantic and continuous output power in ionic thermo-electrochemical cells by using electrodes with redox couples. Advanced Science 2023, 2303407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, M.; Ling, W.; Cheng, L.; Lei, H.; Li, W.; Huang, Y. Thermo-electrochemical cells for heat to electricity conversion: From mechanisms, materials, strategies to applications. Energy & Environmental Science 2022, 15, 3670–3687. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Sherrell, P. C.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Potentially wearable thermo-electrochemical cells for body heat harvesting: From mechanism, materials, strategies to applications. Advanced Science 2021, 8, 2100669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wei, S.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, M.; Chen, G.; Huang, Y. Mxene and carbon-based electrodes of thermocells for continuous thermal energy harvest. Small Methods 2023, 7, 2300190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Shi, Z.; Wei, Q.; Ma, G.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.; Wu, P.; Hu, Z. Double hydrogen-bonding reinforced high-performance supramolecular hydrogel thermocell for self-powered sensing remote-controlled by light. Advanced Functional Materials 2023, 33, 2211720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Inoue, H.; Ujita, M.; Yamada, T. Advancement of electrochemical thermoelectric conversion with molecular technology. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2023, 62, e202213449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Sun, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Niu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wang, C. Redox-induced thermocells for low-grade heat harvesting: Mechanism, progress, and their applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2022, 10, 20730–20755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, A.; Lin, C.-H.; Buttry, D. A.; Mujica, V.; Taylor, R. A.; Prasher, R. S.; Phelan, P. E. Liquid thermoelectrics: Review of recent and limited new data of thermogalvanic cell experiments. Nanoscale and Microscale Thermophysical Engineering 2013, 17, 304–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hong, M.; Dargusch, M.; Zou, J.; Chen, Z.-G. High-efficiency thermocells driven by thermo-electrochemical processes. Trends in Chemistry 2021, 3, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quickenden, T. I.; Mua, Y. A review of power generation in aqueous thermogalvanic cells. Journal of The Electrochemical Society 1995, 142, 3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Yu, B.; Huang, L.; Hu, B.; Xu, M.; Feng, G.; Zhou, J. Liquid-state thermocells: Opportunities and challenges for low-grade heat harvesting. Joule 2021, 5, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Cola, B. A.; Haram, N.; Barisci, J. N.; Lee, S.; Stoughton, S.; Wallace, G.; Too, C.; Thomas, M.; Gestos, A.; Cruz, M. E. d.; Ferraris, J. P.; Zakhidov, A. A.; Baughman, R. H. Harvesting waste thermal energy using a carbon-nanotube-based thermo-electrochemical cell. Nano Letters 2010, 10, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, G. J.; Toberer, E. S. Complex thermoelectric materials. Nature Materials 2008, 7, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
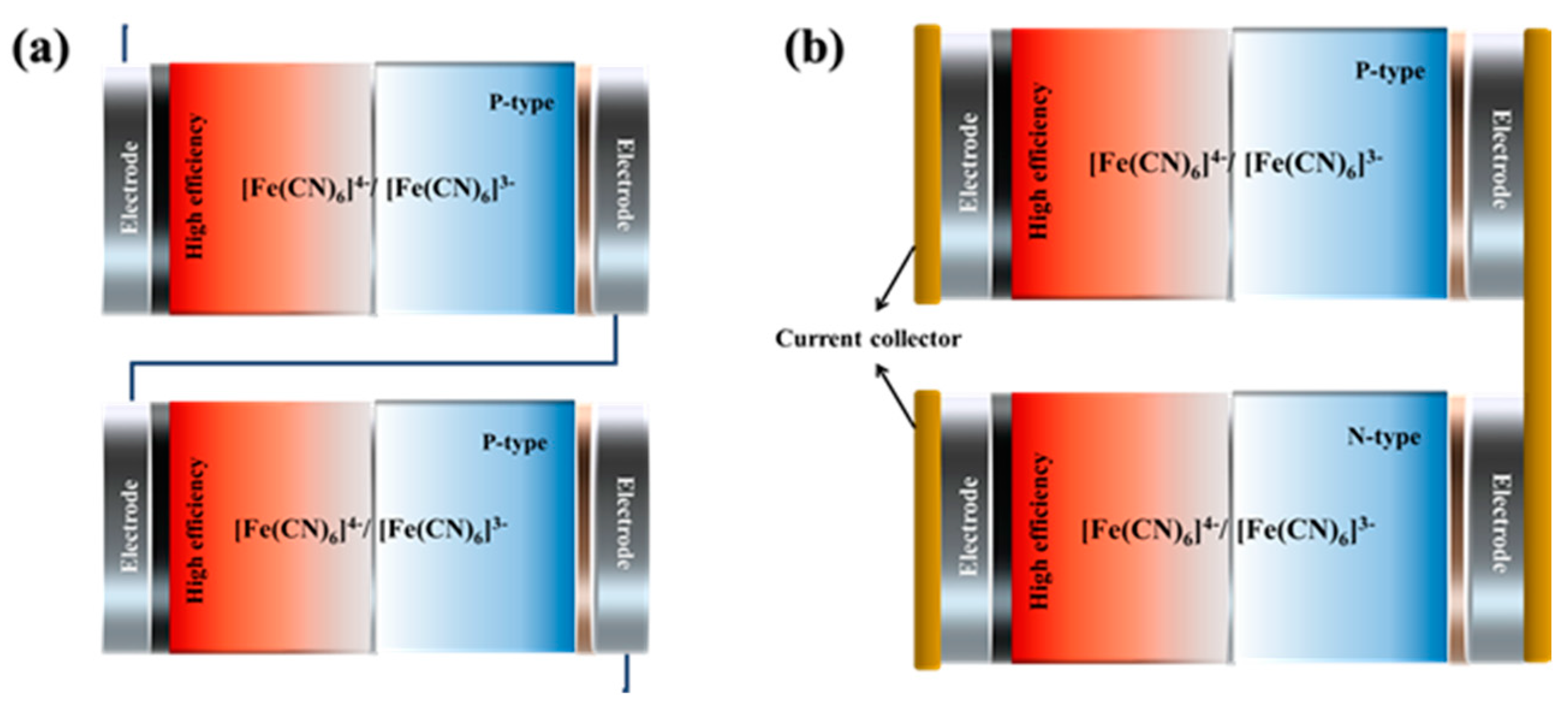
- Zhang, L.; Kim, T.; Li, N.; Kang, T. J.; Chen, J.; Pringle, J. M.; Zhang, M.; Kazim, A. H.; Fang, S.; Haines, C.; Al-Masri, D.; Cola, B. A.; Razal, J. M.; Di, J.; Beirne, S.; MacFarlane, D. R.; Gonzalez-Martin, A.; Mathew, S.; Kim, Y. H.; Wallace, G.; Baughman, R. H. High power density electrochemical thermocells for inexpensively harvesting low-grade thermal energy. Advanced Materials 2017, 29, 1605652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-M.; Kang, S.-Y.; Lee, B.-J.; Lee, J.; Kwon, J.; Lee, D.; Kim, Y.-T. (Early view) Fe─N─C electrocatalyst for enhancing Fe(ii)/Fe(iii) redox kinetics in thermo-electrochemical cells. Advanced Functional Materials 2023, 2304067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, T. J.; Tachikawa, N.; MacFarlane, D. R.; Pringle, J. M. Investigation of the kinetic and mass transport limitations in thermoelectrochemical cells with different electrode materials. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2014, 16, 2527–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
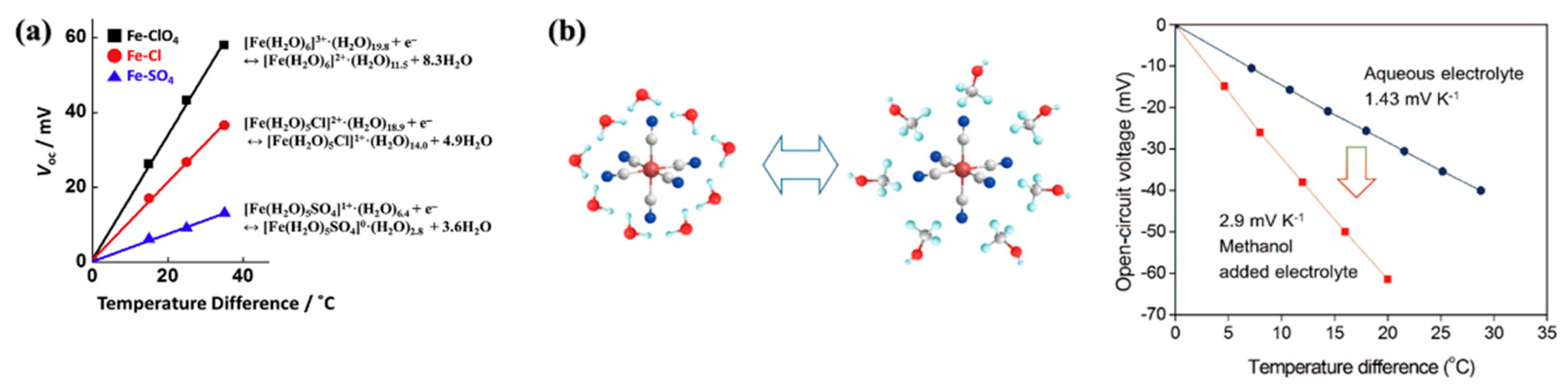
- Kim, K.; Hwang, S.; Lee, H. Unravelling ionic speciation and hydration structure of Fe(iii/ii) redox couples for thermoelectrochemical cells. Electrochimica Acta 2020, 335, 135651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Lee, J. S.; Lee, G.; Yoon, H.; Yoon, J.; Kang, T. J.; Kim, Y. H. High thermopower of ferri/ferrocyanide redox couple in organic-water solutions. Nano Energy 2017, 31, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liu, T.-H.; Qian, X.; Yang, R. (Early view) Effect of solvation shell structure on thermopower of liquid redox pairs. EcoMat 2023, e12385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
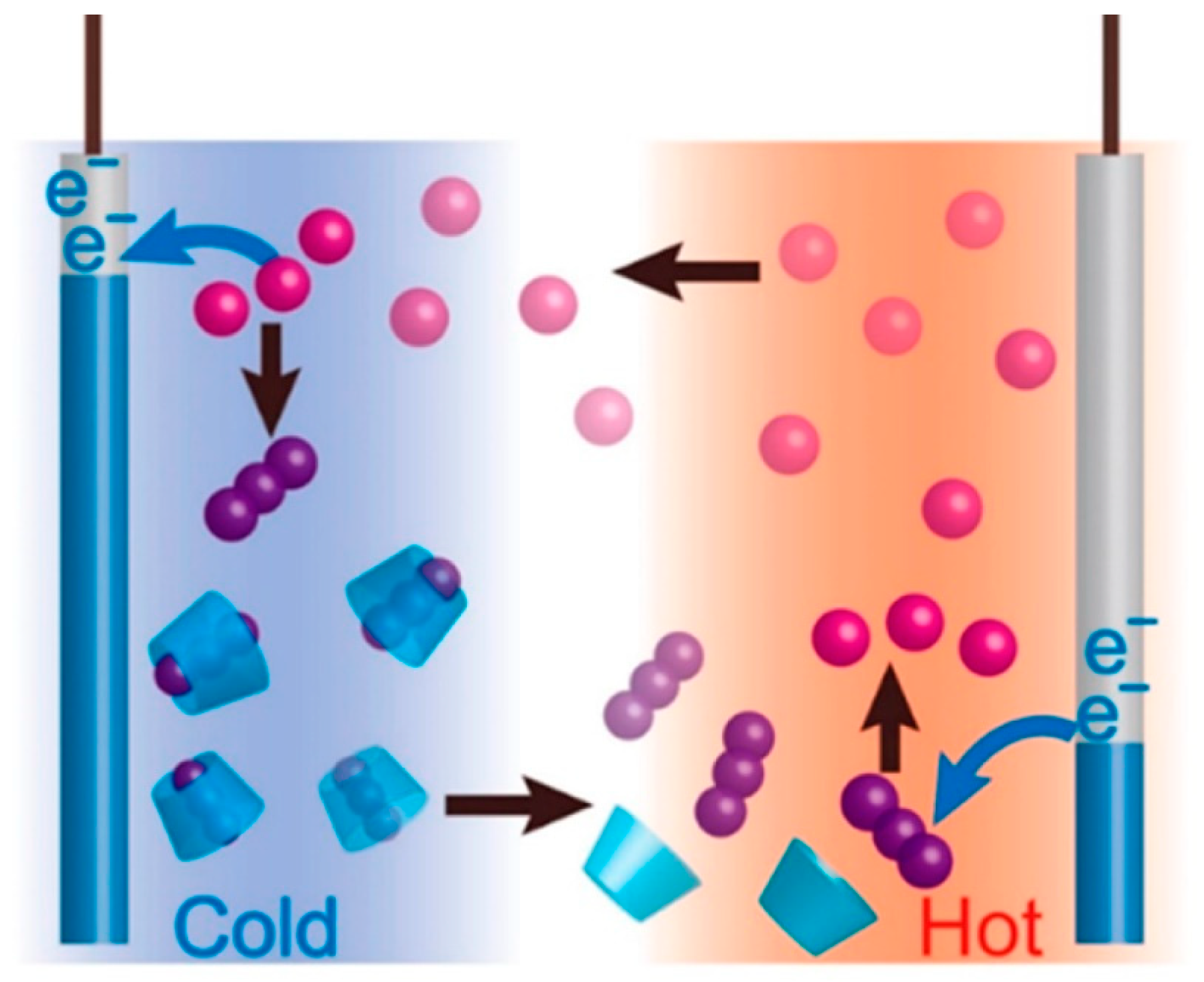
- Duan, J.; Feng, G.; Yu, B.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Yang, P.; Feng, J.; Liu, K.; Zhou, J. Aqueous thermogalvanic cells with a high seebeck coefficient for low-grade heat harvest. Nature Communications 2018, 9, 5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahami, S.; Weaver, M. J. Entropic and enthalpic contributions to the solvent dependence of the thermodynamics of transition-metal redox couples: Part ii. Couples containing ammine and ethylenediamine ligands. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Electrochemistry 1981, 122, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yamada, T.; Kimizuka, N. Supramolecular thermo-electrochemical cells: Enhanced thermoelectric performance by host–guest complexation and salt-induced crystallization. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2016, 138, 10502–10507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B. Y.; Duan, J. J.; Cong, H. J.; Xie, W. K.; Liu, R.; Zhuang, X. Y.; Wang, H.; Qi, B.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z. L.; Zhou, J. Thermosensitive crystallization-boosted liquid thermocells for low-grade heat harvesting. Science 2020, 370, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Yu, B.; Liu, K.; Li, J.; Yang, P.; Xie, W.; Xue, G.; Liu, R.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J. P-N conversion in thermogalvanic cells induced by thermo-sensitive nanogels for body heat harvesting. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Li, M.; Shi, X.-L.; Chen, Z.-G. Advances in ionic thermoelectrics: From materials to devices. Advanced Energy Materials 2023, 13, 2203692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Zhao, X.; Yang, J.; Ke, K.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Yang, W. (Early view) Enhanced ion-selective diffusion achieved by supramolecular interaction for high thermovoltage and thermal stability. Energy & Environmental Materials 2022, e12562. [Google Scholar]
- Tabaie, Z.; Omidvar, A. Human body heat-driven thermoelectric generators as a sustainable power supply for wearable electronic devices: Recent advances, challenges, and future perspectives. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Greene, G. W.; MacFarlane, D. R.; Pringle, J. M. Redox-active quasi-solid-state electrolytes for thermal energy harvesting. ACS Energy Letters 2016, 1, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Liu, K.; Chen, Q.; Mo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Feng, G.; Zhou, J. Wearable thermocells based on gel electrolytes for the utilization of body heat. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2016, 55, 12050–12053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Black, J. J.; Aldous, L. Thermoelectrochemistry using conventional and novel gelled electrolytes in heat-to-current thermocells. Electrochimica Acta 2017, 225, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, Z.; Hu, R.; Luo, X. Gel-based thermocells for low-grade heat harvesting. Europhysics Letters 2021, 135, 26001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wallace, G. G.; Beirne, S.; Chen, J. All-polymer wearable thermoelectrochemical cells harvesting body heat. iScience 2021, 24, 103466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Buckingham, M. A.; Zhang, S.; Aldous, L.; Beirne, S.; Wallace, G.; Chen, J. The significance of supporting electrolyte on poly (vinyl alcohol)–iron(ii)/iron(iii) solid-state electrolytes for wearable thermo-electrochemical cells. Electrochemistry Communications 2021, 124, 106938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
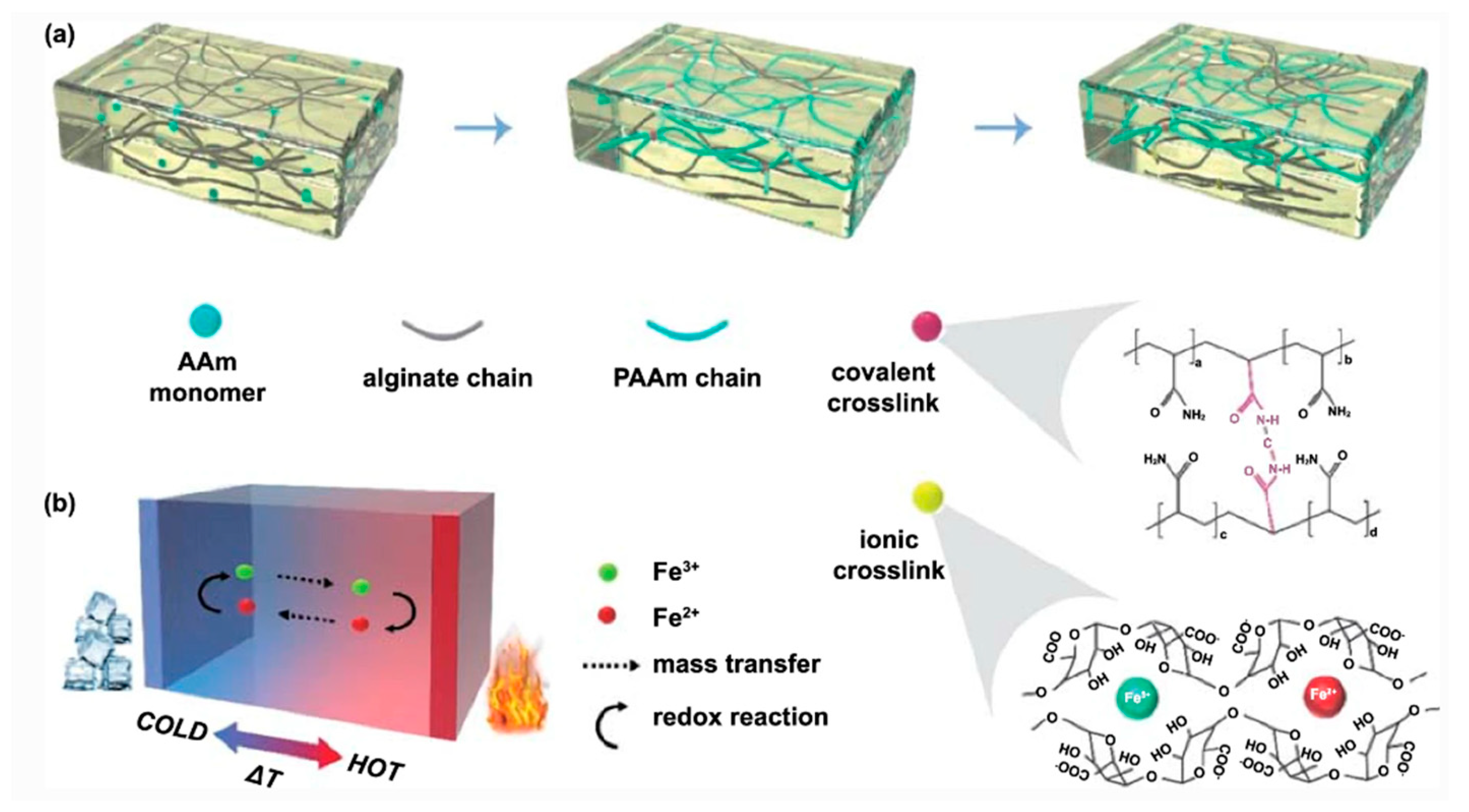
- Liu, L.; Zhang, D.; Bai, P.; Mao, Y.; Li, Q.; Guo, J.; Fang, Y.; Ma, R. Strong tough thermogalvanic hydrogel thermocell with extraordinarily high thermoelectric performance. Advanced Materials 2023, 35, 2300696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Lei, Z.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y. Hierarchically anisotropic networks to decouple mechanical and ionic properties for high-performance quasi-solid thermocells. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 8347–8357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.; Zhou, J.; Liang, L.; Huang, X.; Lv, H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, G. Regulating thermogalvanic effect and mechanical robustness via redox ions for flexible quasi-solid-state thermocells. Nano-Micro Letters 2022, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Lv, H.; Shi, X.-l.; Liu, Z.; Chen, G.; Chen, Z.G.; Sun, G. A flexible quasi-solid-state thermoelectrochemical cell with high stretchability as an energy-autonomous strain sensor. Materials Horizons, 2021, 8, 2750–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Li, Z.; Xie, D.; Zhu, K.; Du, C.; Liang, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, G. Aqueous eutectic hydrogel electrolytes enable flexible thermocells with a wide operating temperature range. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2023, 11, 6986–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-M.; Kwon, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, B.-J.; Kim, K.-S.; Yu, D.-S.; Kim, Y.-T. Hybrid thermo-electrochemical energy harvesters for conversion of low-grade thermal energy into electricity via tungsten electrodes. Applied Energy 2021, 299, 117334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-M.; Kwon, J.; Lee, J.; Han, I. K.; Kim, K.-S.; Kim, Y. S.; Kim, Y.-T. Cost-efficient nickel-based thermo-electrochemical cells for utilizing low-grade thermal energy. Journal of Power Sources 2021, 494, 229705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.; Kysar, J. W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Song, J.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Men, D.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.-E. Chemical nature of electrochemical activation of carbon electrodes. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2019, 144, 111534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, H.; Kim, T.; Song, H.; Choi, J.; Park, J. S.; Ovalle-Robles, R.; Yang, H. D.; Kihm, K. D.; Baughman, R. H.; Lee, H. H.; Kang, T. J.; Kim, Y. H. High-efficiency electrochemical thermal energy harvester using carbon nanotube aerogel sheet electrodes. Nature Communications 2016, 7, 10600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Guo, H.; Li, G.; Yan, L.; Zhang, X.; Song, W. Assembling hollow carbon sphere-graphene polylithic aerogels for thermoelectric cells. Nano Energy 2017, 39, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Ma, J.; Wu, D.; Chen, B.; Du, C.; Liang, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Rao, F.; Chen, G.; Liu, Z. Constructing flexible film electrode with porous layered structure by MXene/SWCNTS/PANI ternary composite for efficient low-grade thermal energy harvest. Advanced Functional Materials 2023, 33, 2209806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liang, G.; Li, M.; Yang, Q.; Ma, J.; Li, N.; Dong, B.; Huang, Q.; Chen, F.; Fan, J.; Zhi, C. Intrinsic voltage plateau of a NB2CTX MXene cathode in an aqueous electrolyte induced by high-voltage scanning. Joule 2021, 5, 2993–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, B.; Zhu, M.; Schmidt, O. G. Flexible MXene films for batteries and beyond. Carbon Energy 2022, 4, 598–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Xie, L.; Han, F.; Wei, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, M.; Schmidt, O. G.; Wang, L. Nanoscale parallel circuitry based on interpenetrating conductive assembly for flexible and high-power zinc ion battery. Advanced Functional Materials 2019, 29, 1901336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Peng, J.; Lai, W.; Wu, D.; Zuo, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Chou, S. In-situ electrochemically activated surface vanadium valence in v2c mxene to achieve high capacity and superior rate performance for Zn-ion batteries. Advanced Functional Materials 2021, 31, 2008033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. H.; Lee, J. H.; Palem, R. R.; Suh, M.-S.; Lee, H. H.; Kang, T. J. Iron (ii/iii) perchlorate electrolytes for electrochemically harvesting low-grade thermal energy. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Buckingham, M. A.; Aldous, L.; Sherrell, P. C.; Wallace, G. G.; Ryder, G.; Faisal, S.; Officer, D. L.; Beirne, S.; Chen, J. Advanced wearable thermocells for body heat harvesting. Advanced Energy Materials 2020, 10, 2002539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W.; Tian, H. Adaptable and wearable thermocell based on stretchable hydrogel for body heat harvesting. Advanced Energy Materials 2022, 12, 2201542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




