Submitted:
15 September 2023
Posted:
19 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Observations and Data Analysis
2.1. Instrumentation
2.2. Data Analysis
2.2.1. Enhancement of fine structures in dynamic spectra
- Suppression of the continuum background: It was performed by means of high-pass filtering in time, using either Gaussian filters or time derivatives (differential spectra), which enhanced fast time-varying spectral structures, such as pulsations, fibers and zebras.
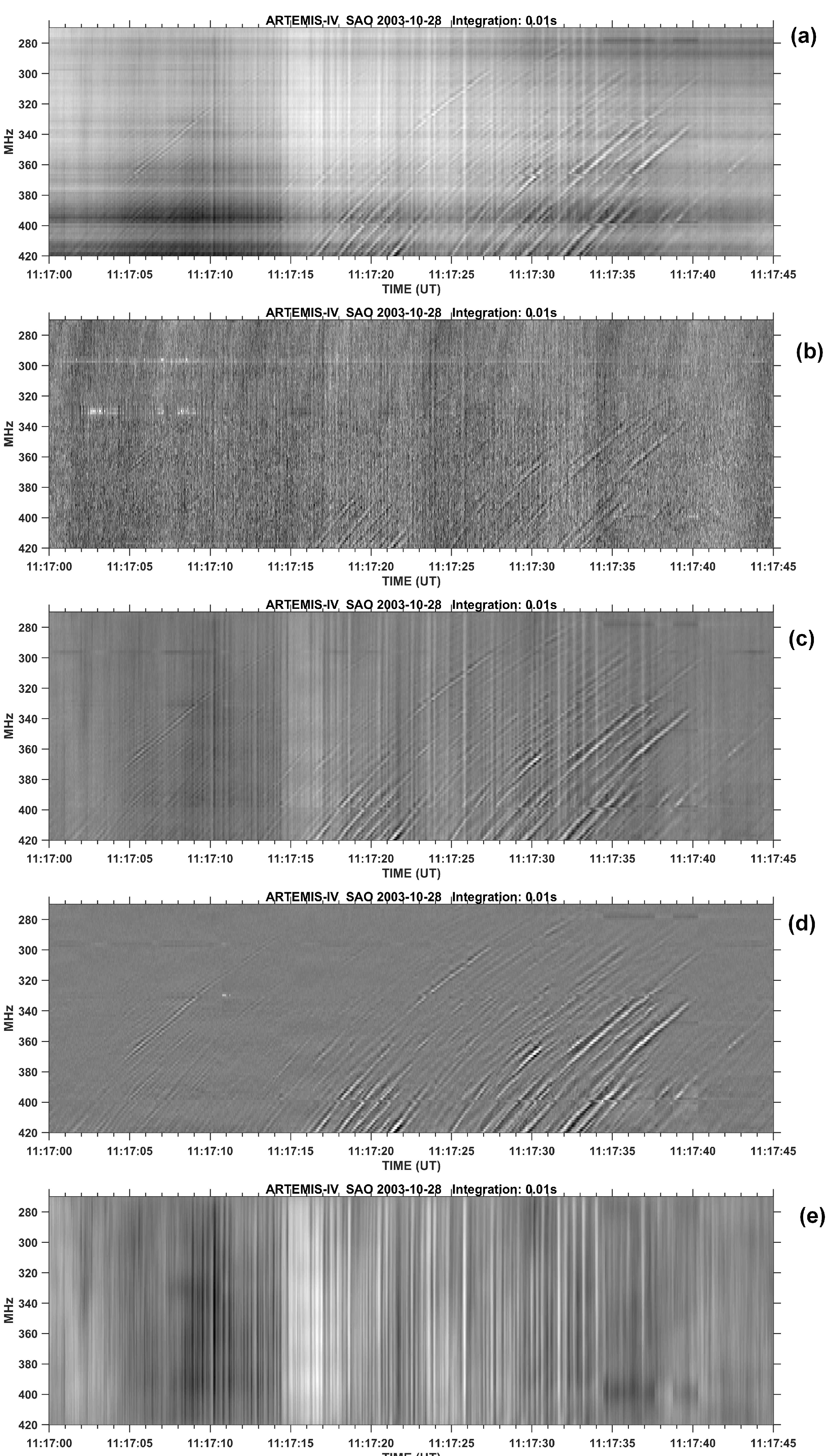
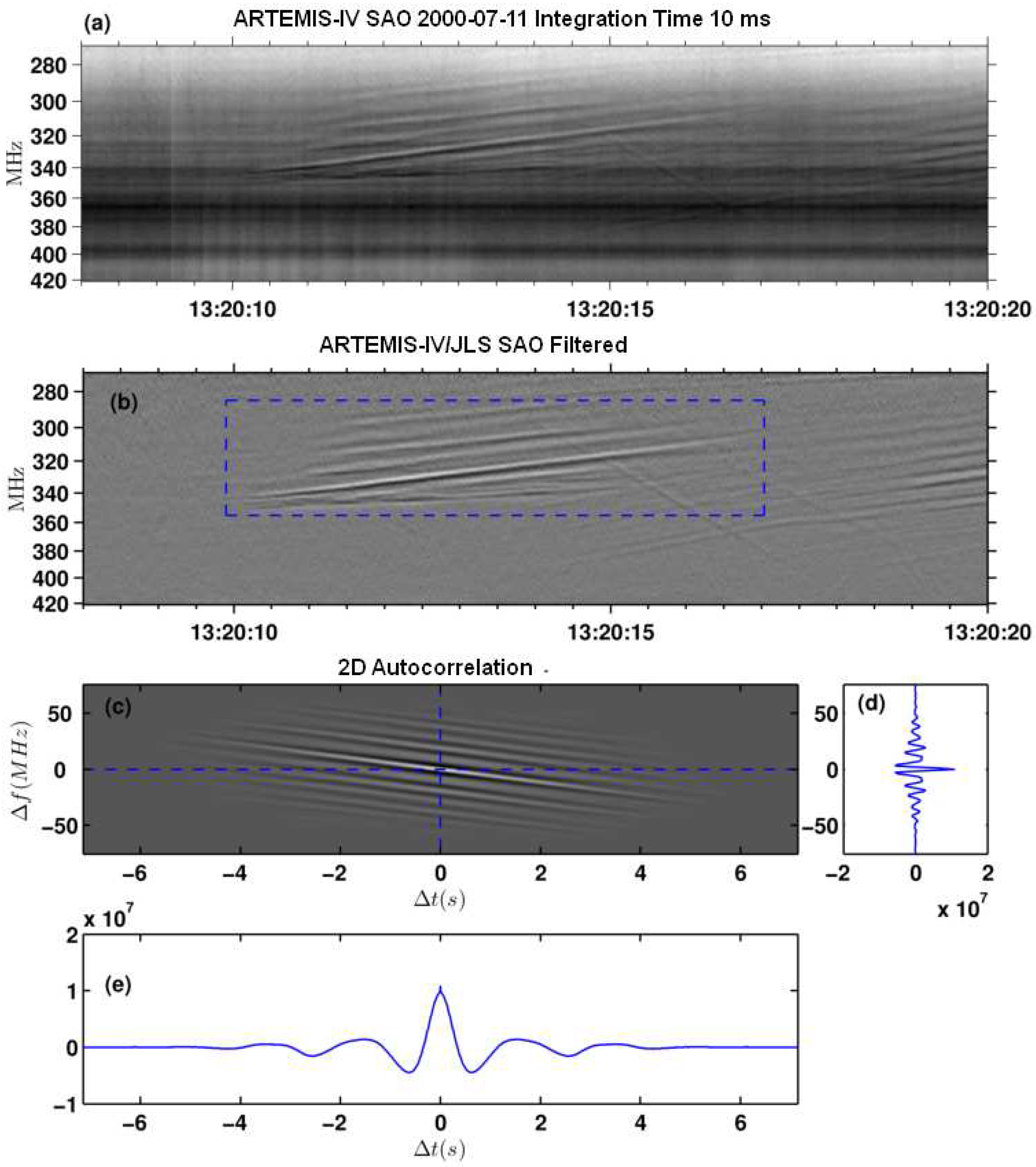
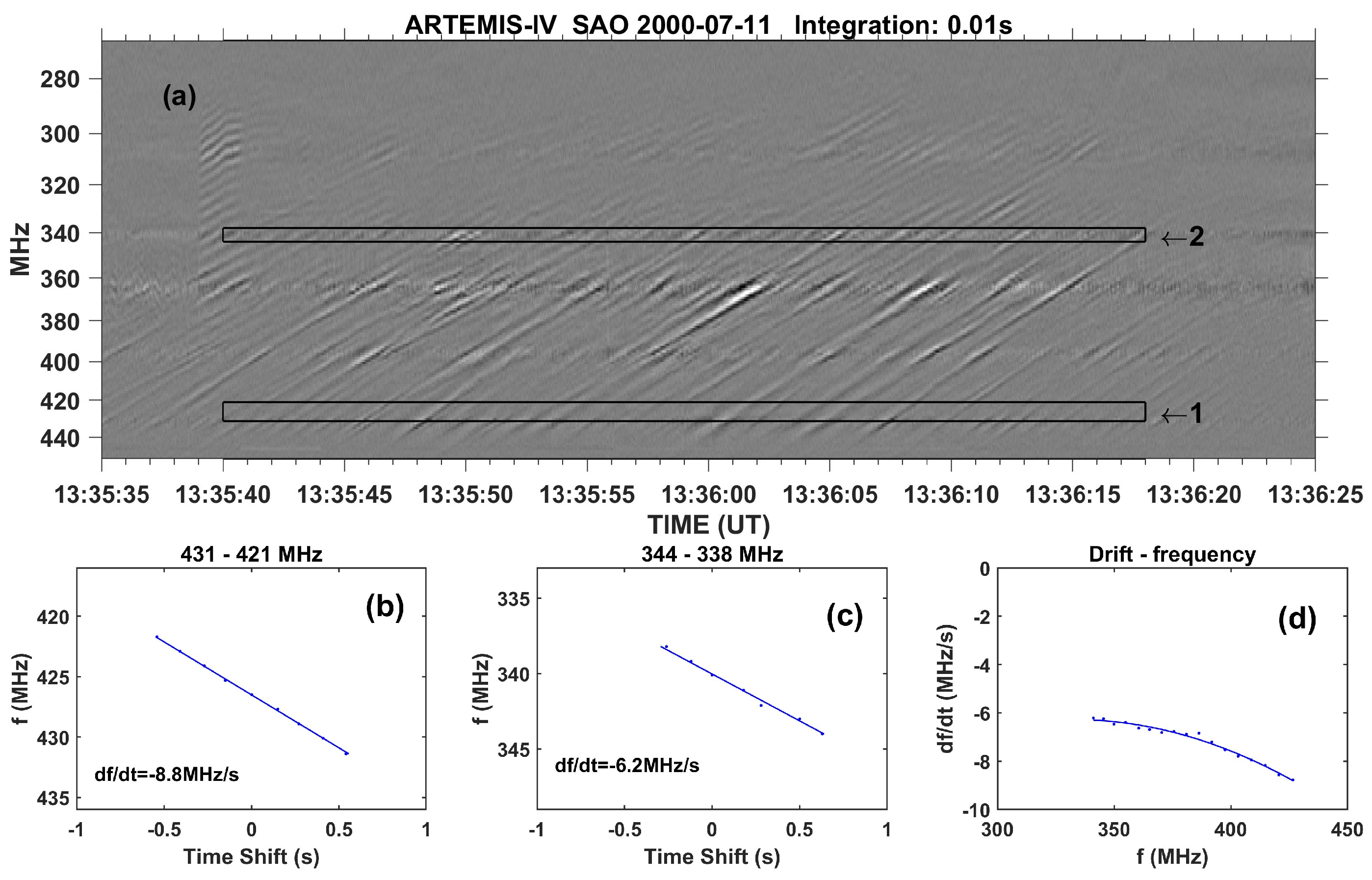
- Separation of overlapping fine structures: It was used mostly in the case of the type-IV data set. We used both high-pass and low-pass filters on dynamic spectra along the frequency axis. In this case the high-pass filtering, provides pulsation suppression and facilitates detecting fibers and similar structures while the complementary low-pass filtering provides suppression of drifting structures, such as fibers. (see [30,32] for a detailed description of this method).
2.2.2. Measurement of bulk parameters
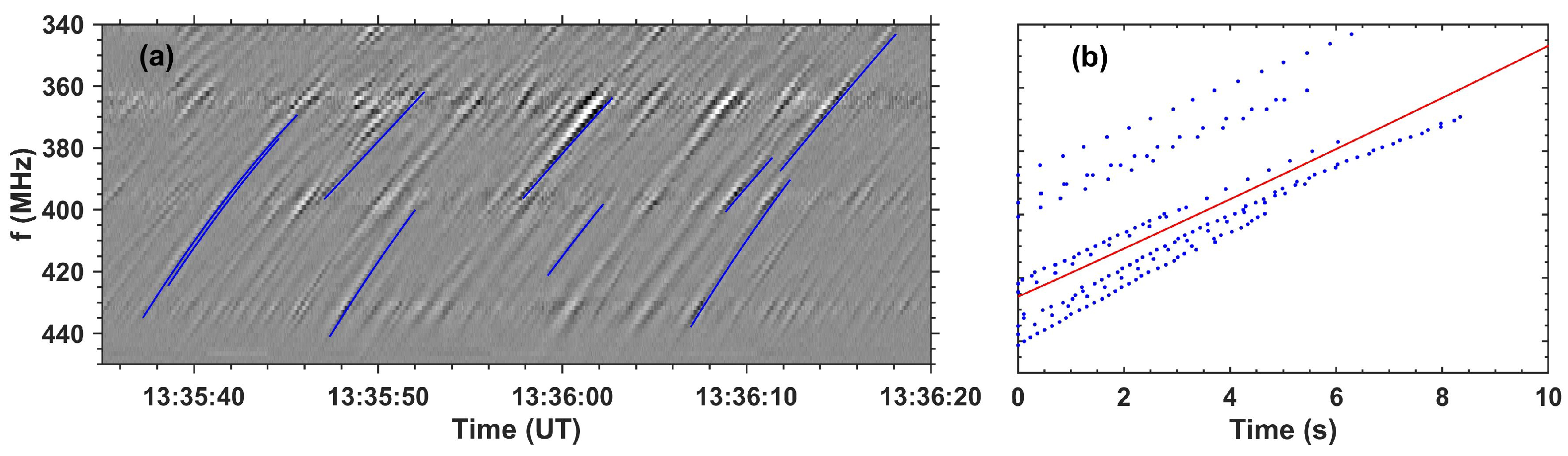
2.2.3. Drift rate and exciter speed
3. Fine Structure Classification in the Metric Wavelength Range
3.1. Featureless Broadband, or Diffuse, Continuum
3.2. Pulsating Structures
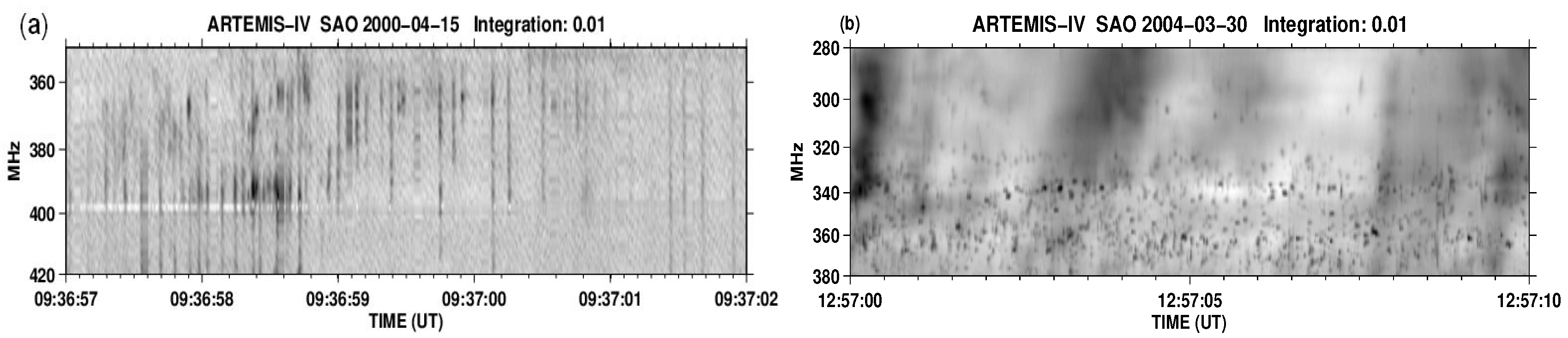
3.3. Narrow-Band Bursts
3.4. Intermediate-Drift Bursts
3.5. Emission Bands
- A single-emission band, designated as evolving emission line (EEL), first reported by Chernov et al. [104] in the 350-450 MHz frequency range, at the low-frequency cutoff of a pulsating structure, and by Fu et al. [25] and Ning et al. [105] in the GHz range is included in this class, although the emission mechanism appears to be somewhat different from the zebras. After Chernov et al. [104], the observed EEL was the result of electrostatic maser at double plasma resonance.
- A structure detected at about 1416–1420 MHz by Oberoi et al. [107]. It consists of a group of short 2-4 ms parallel stripes with a relative delay with decreasing frequency. The total duration of the group is about 16 ms. Due to the band structure, this burst may be considered as a group of emission bands; the short time scale and frequency bandwidth of these bands, however, show some similarity of this burst to narrow-band burst chain.
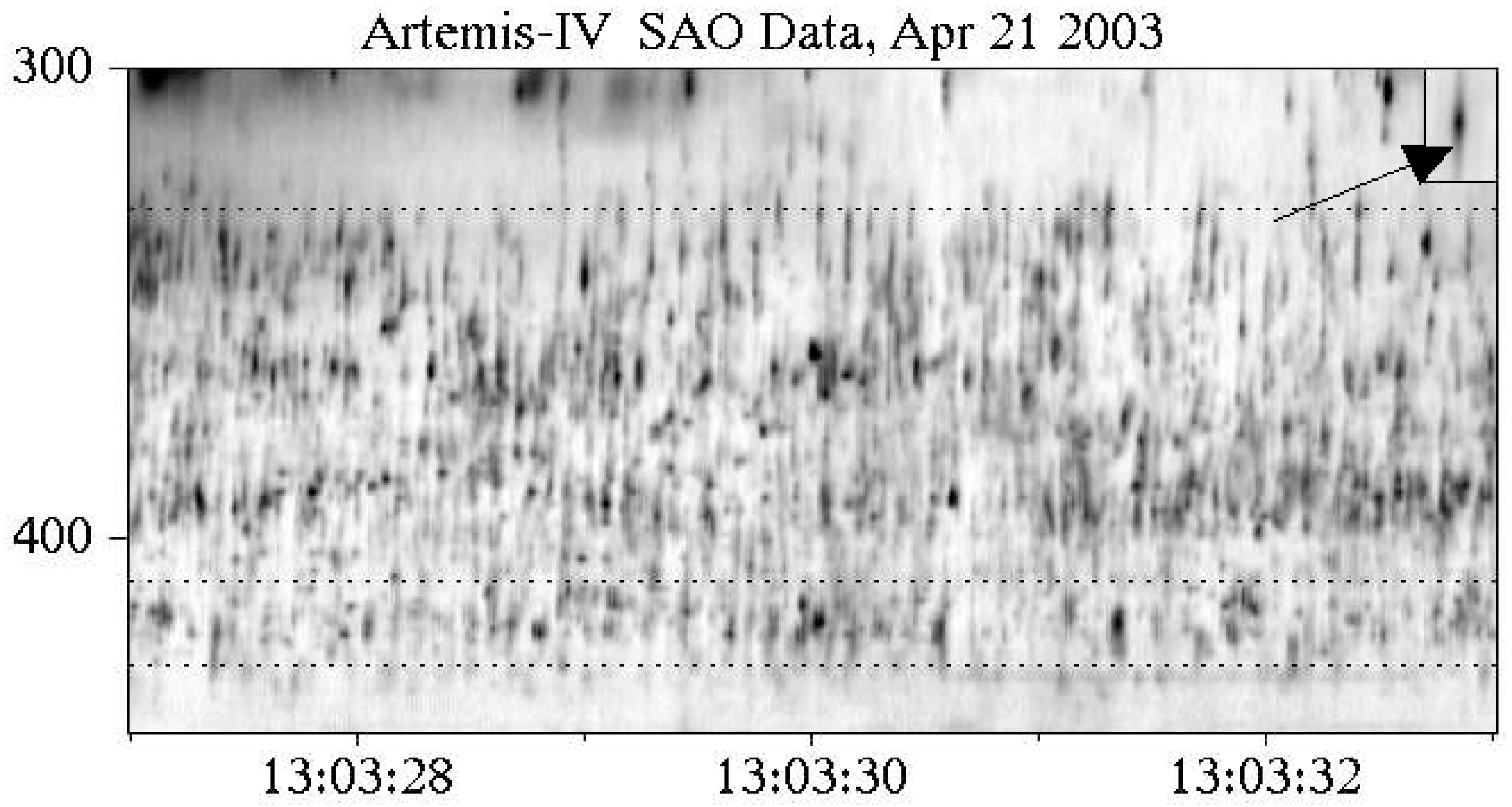
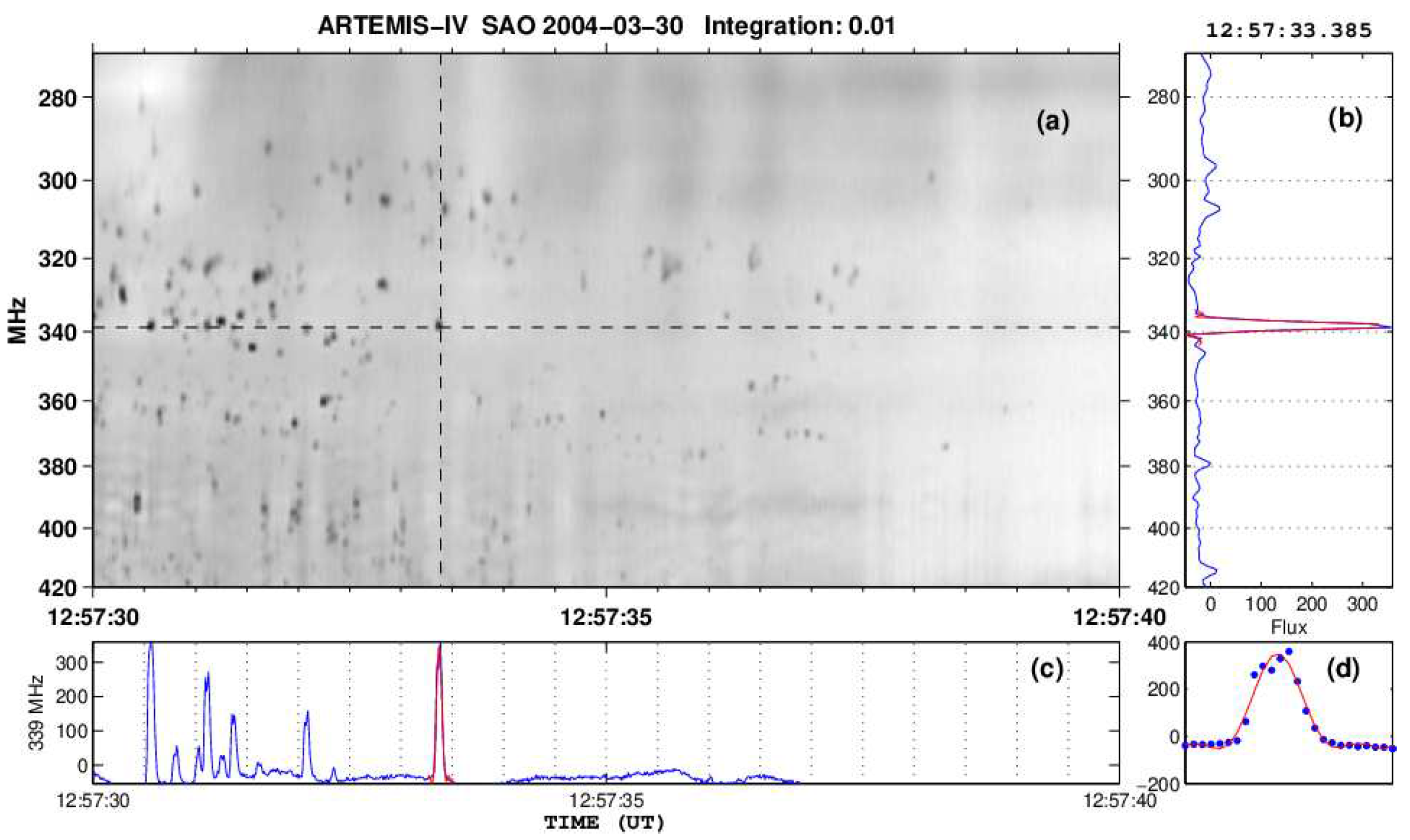
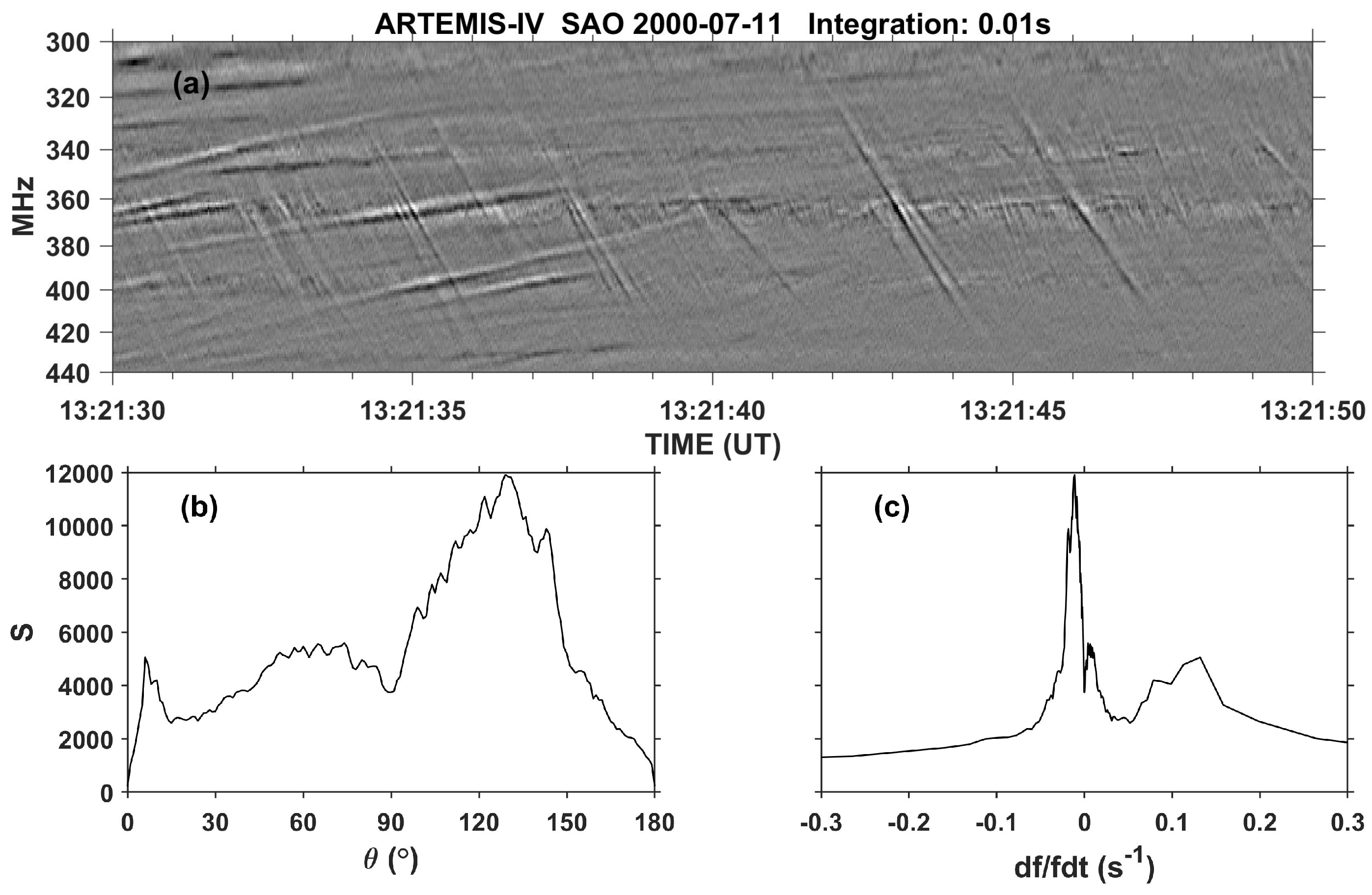
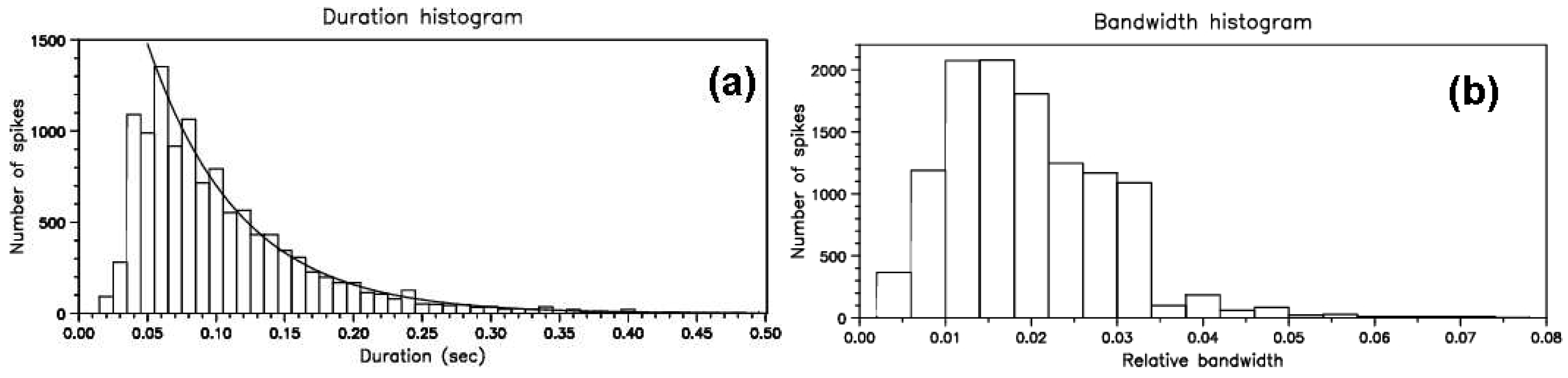
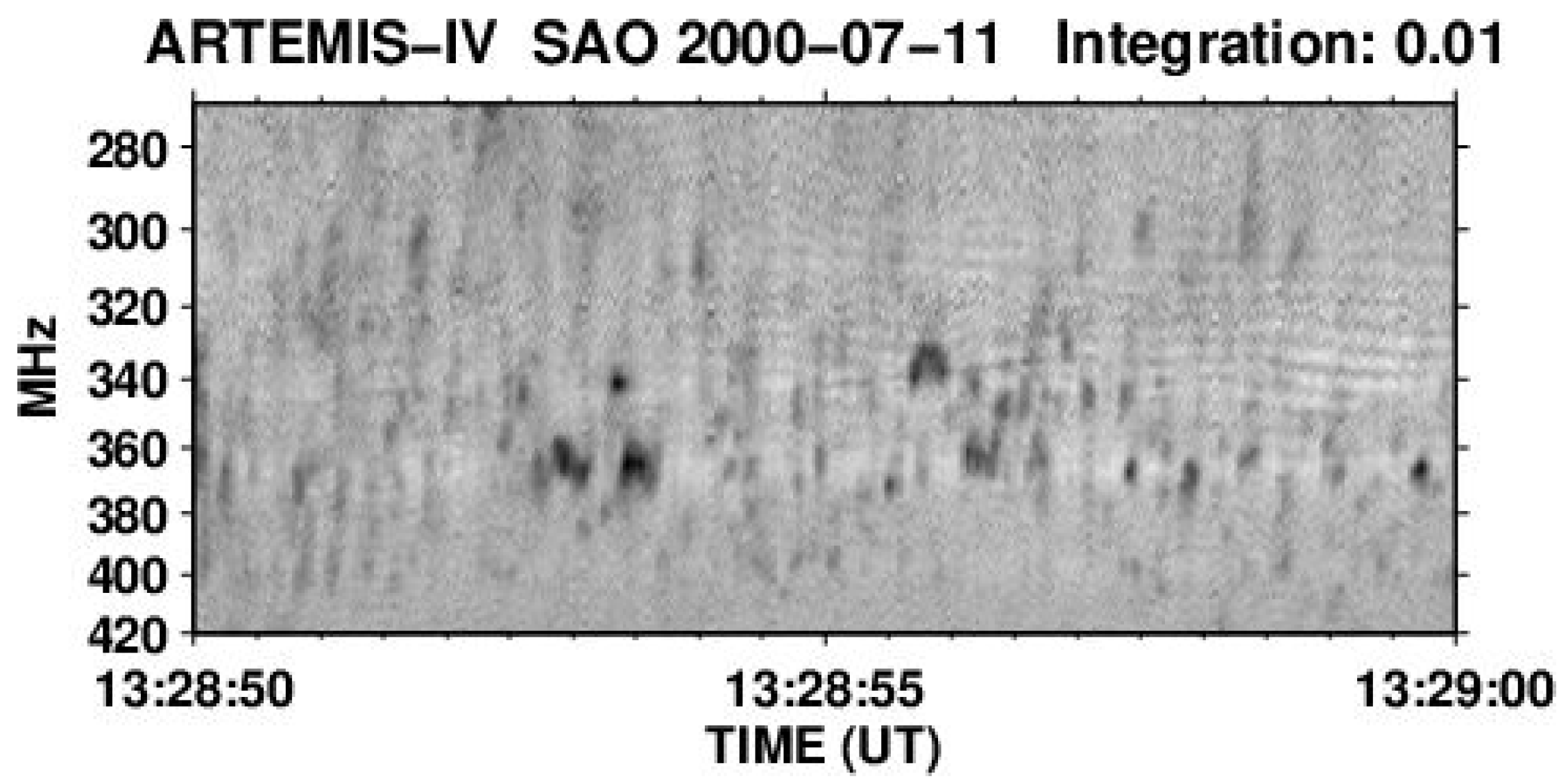
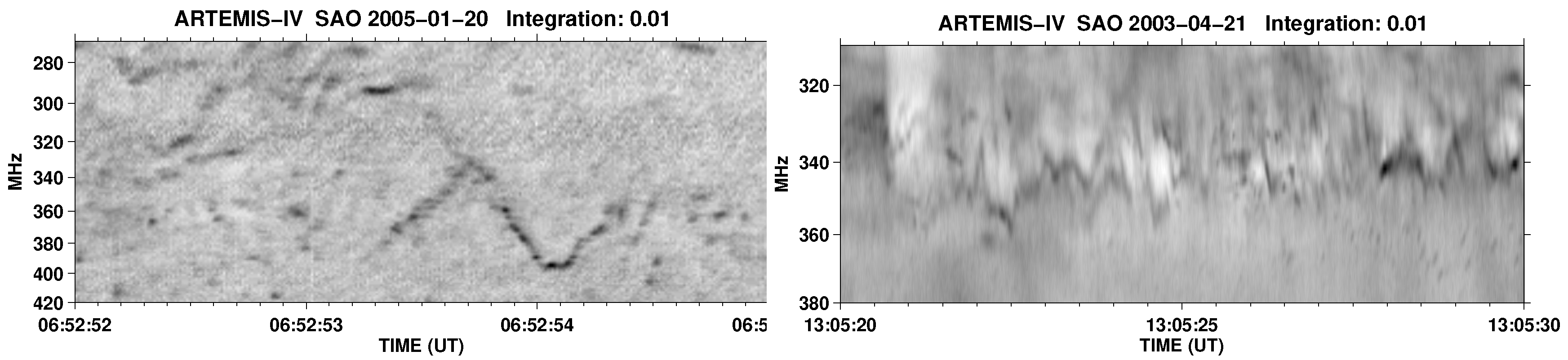
4. Type IV-associated narrow-band bursts (spikes)
4.1. Characteristics of Individual Bursts and Chains
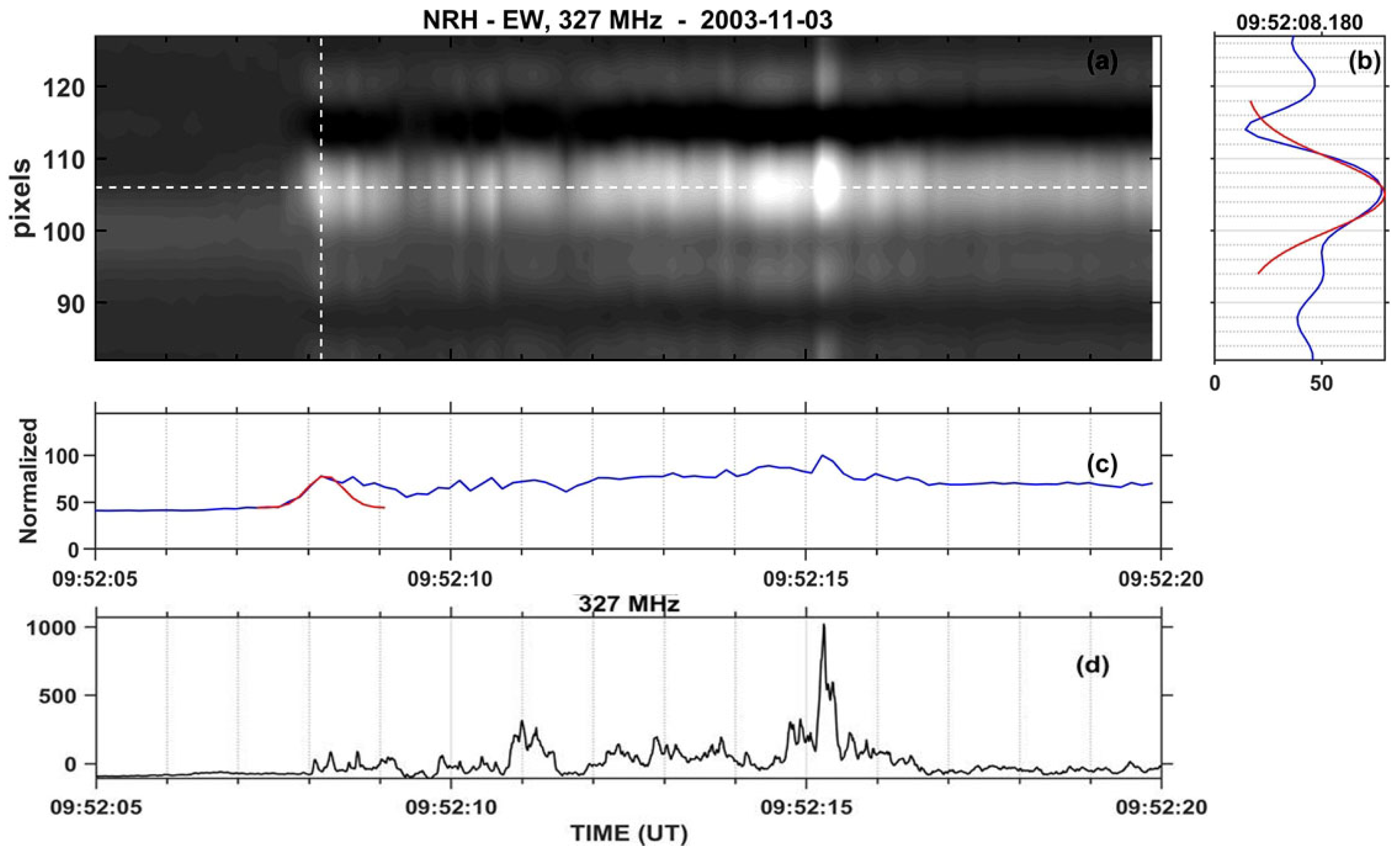
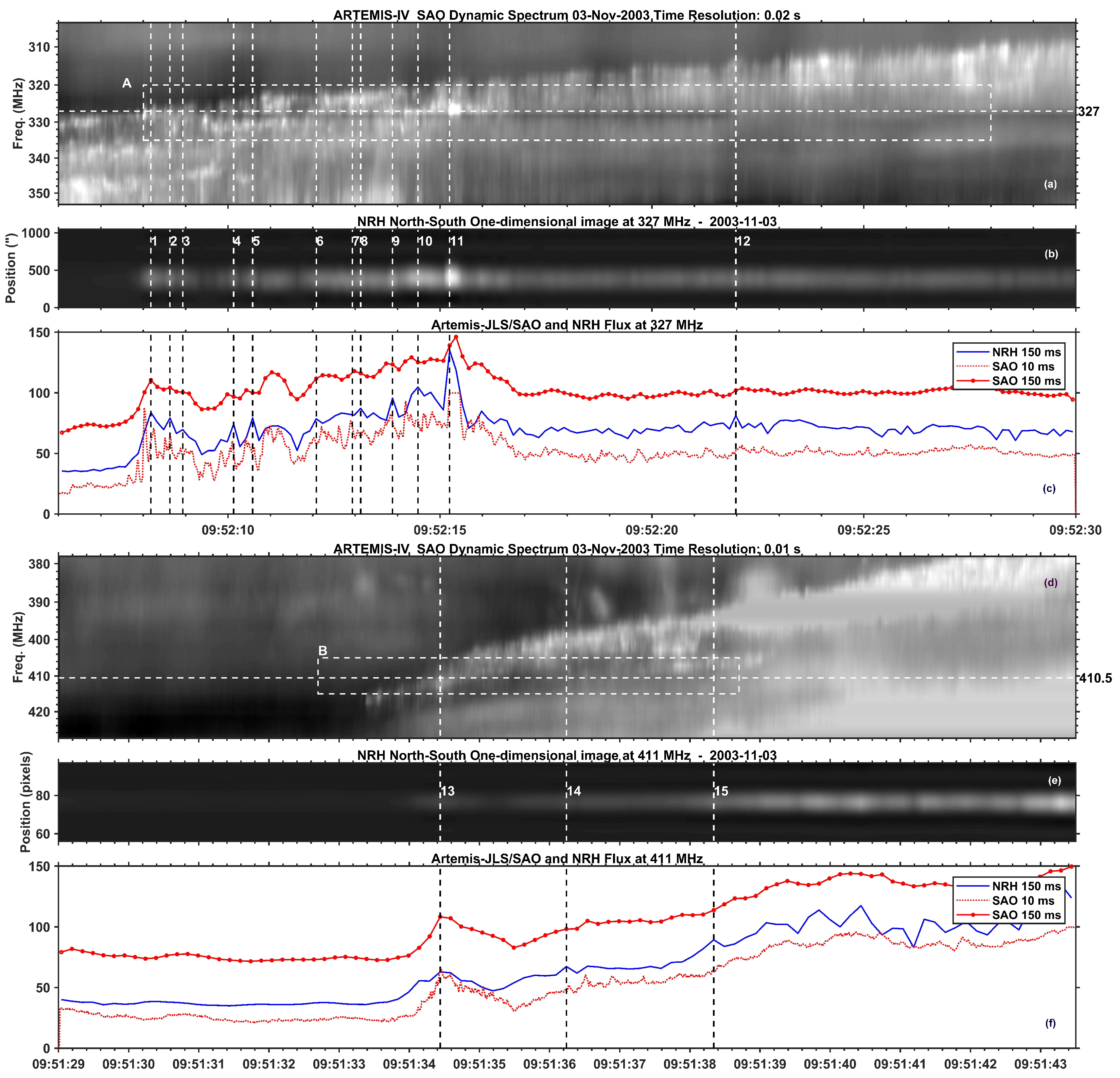
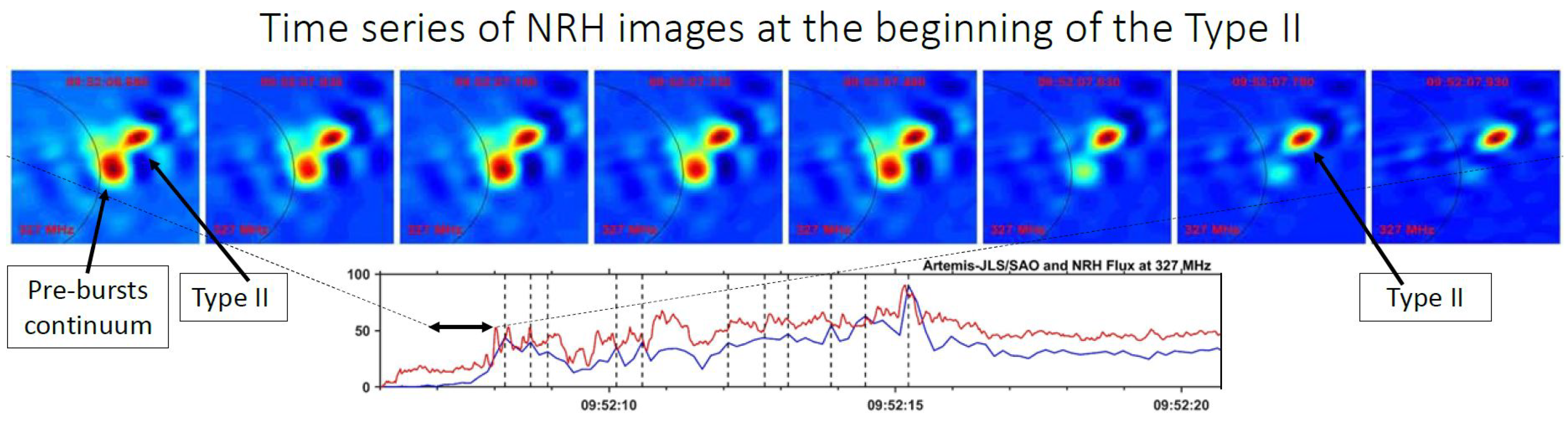
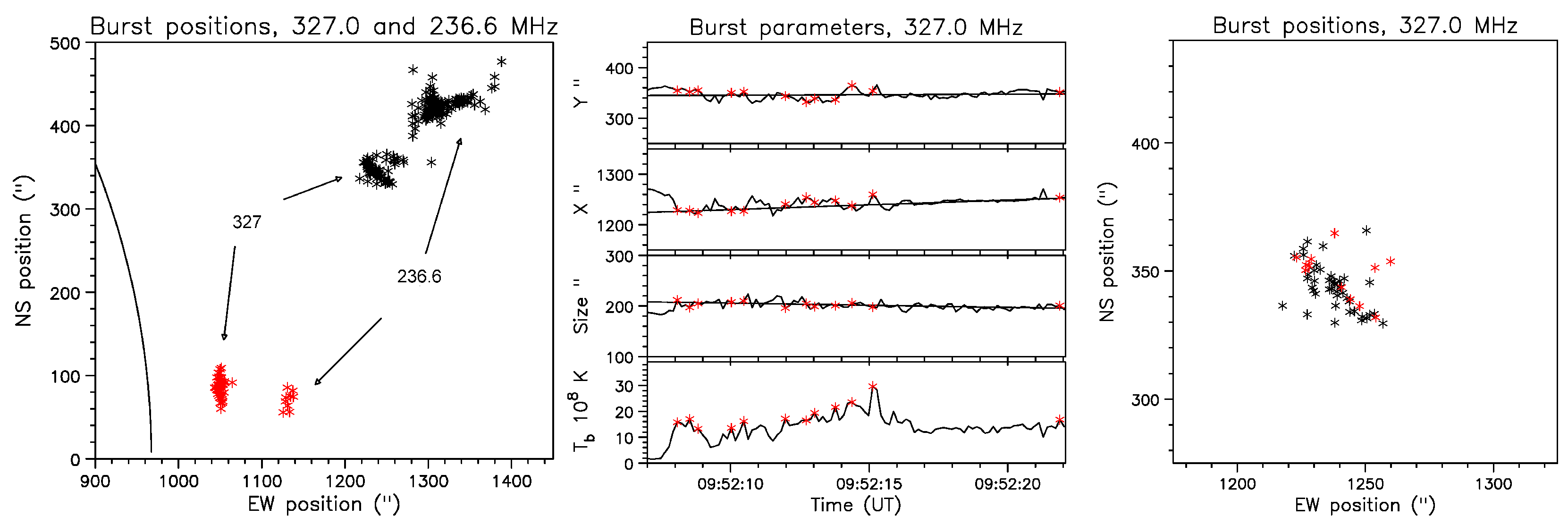
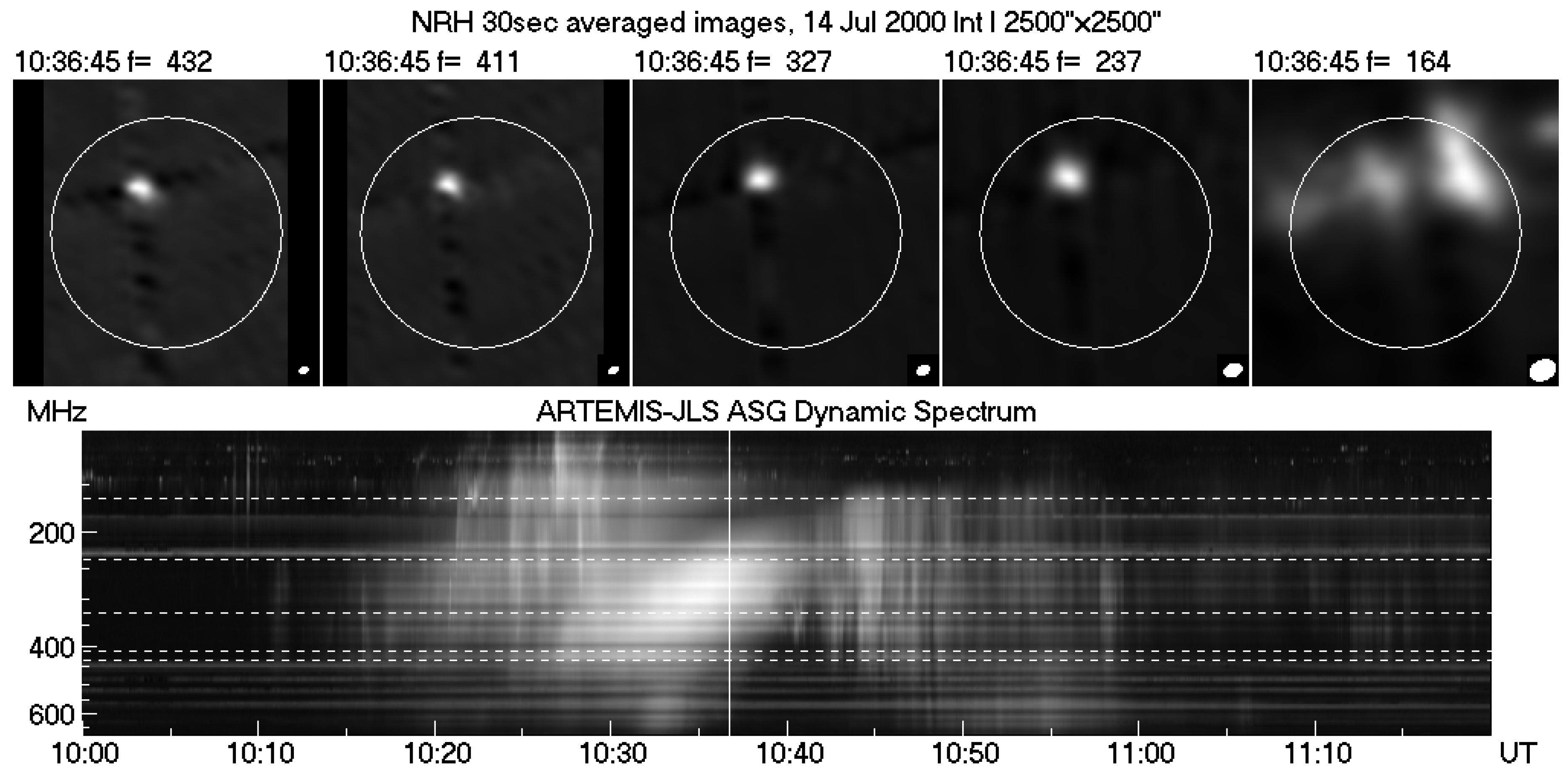
4.2. Spectral Imaging of Spikes with ARTEMIS-IV/JLS & NRH
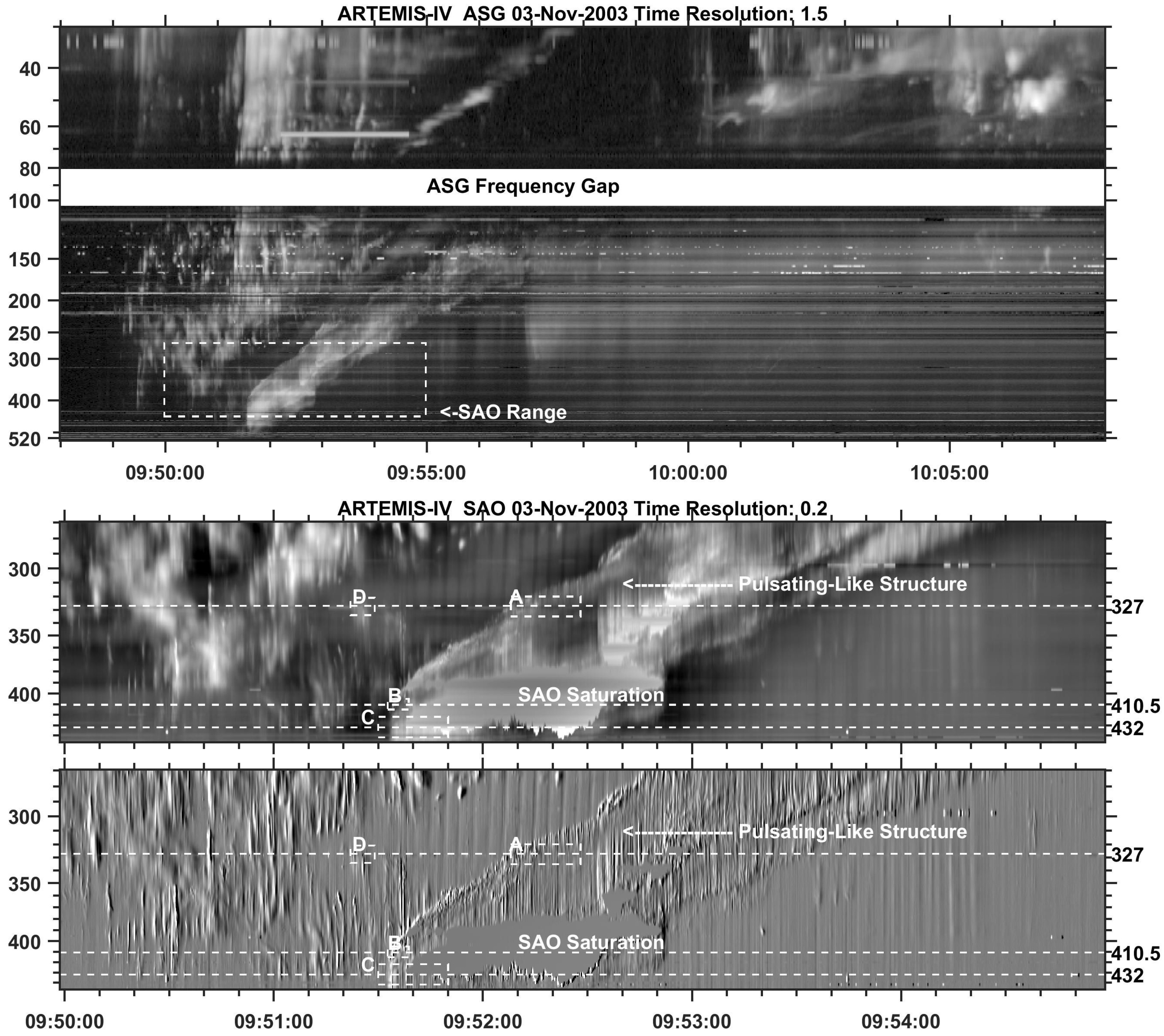
5. Type II associated fine structure
5.1. Overview of the November 3, 2003 Event (SOL2003-11-03T09:43:20)
5.2. Comparison of Spectral and Imaging Data
5.3. Type II & Type IV, associated narrow-band bursts: Similarities & Differences
6. Type IV–Associated Intermediate–Drift Bursts (Fibers)
6.1. Information from Dynamic Spectra
6.1.1. Fiber Burst Classes
- Fibers with an emission ridge and a lower frequency (LF) absorption ridge: They are the majority of our data set, with the remaining five classes represented by a few cases only [see [57]]. The three-wave coupling process, , implies that the emission is enhanced at and reduced at , being the whistler frequency.
- Fibers with emission ridges only: It is possible for the whistler-Langmuir wave coupling () to produce an emission ridge without absorption if the background is suppressed (e.g. by induced scattering) [see [156]]
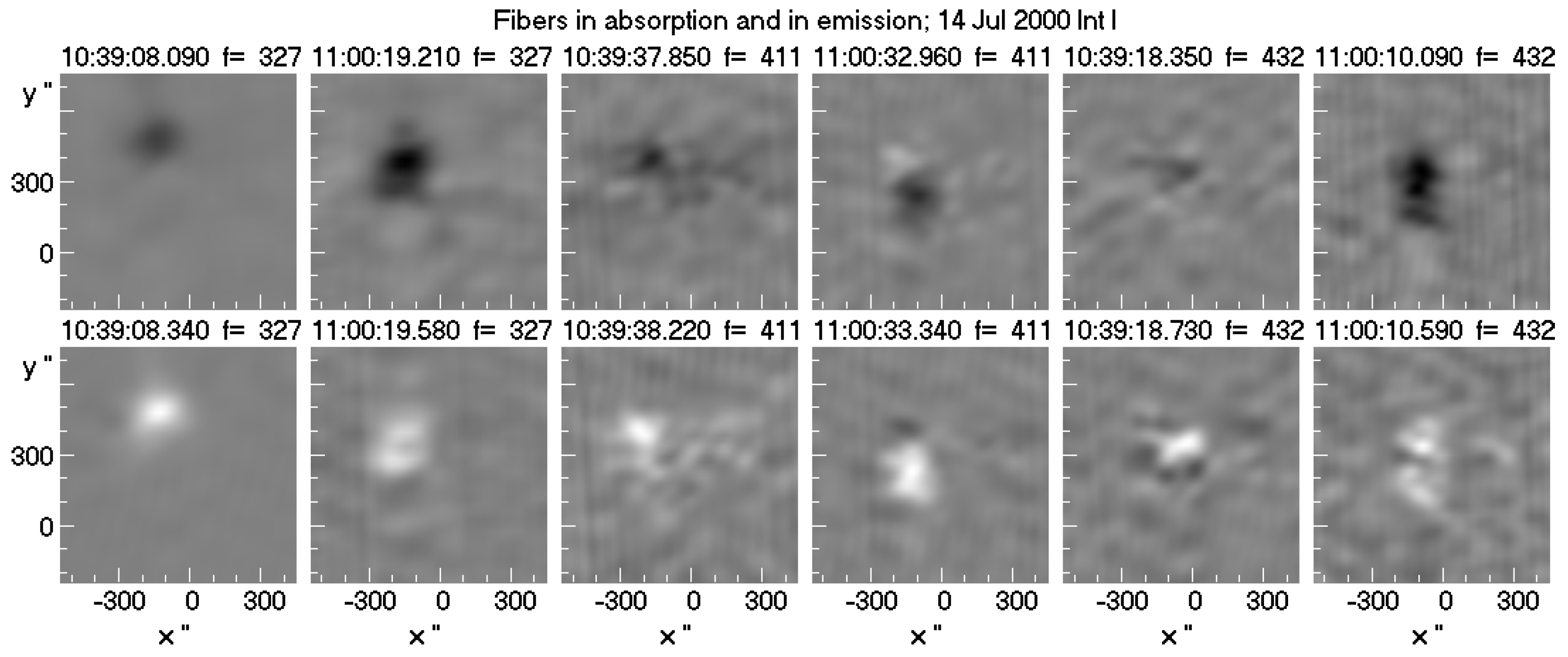
- Fibers appearing in absorption on the Type IV continuum: They may appear when the emission is suppressed or scattered [see [81]]
- Fibers with an emission ridge between two absorption ridges [110,157]: This type of fiber probably results from a combination of coalescence () and decay (). This implies energy flow from the Langmuir wave background toward higher and lower frequencies which is expected to create an absorption ridge between two emission ridges.
- Two emission ridges separated by an absorption ridge: This might be interpreted by the same as above combination of coalescence and decay, but in this case we have two absorption ridges transfering their energy to an emission ridge sandwiched between them. The question on the conditions that favor either direction of energy flow is, to the best knowledge of the authors, open.
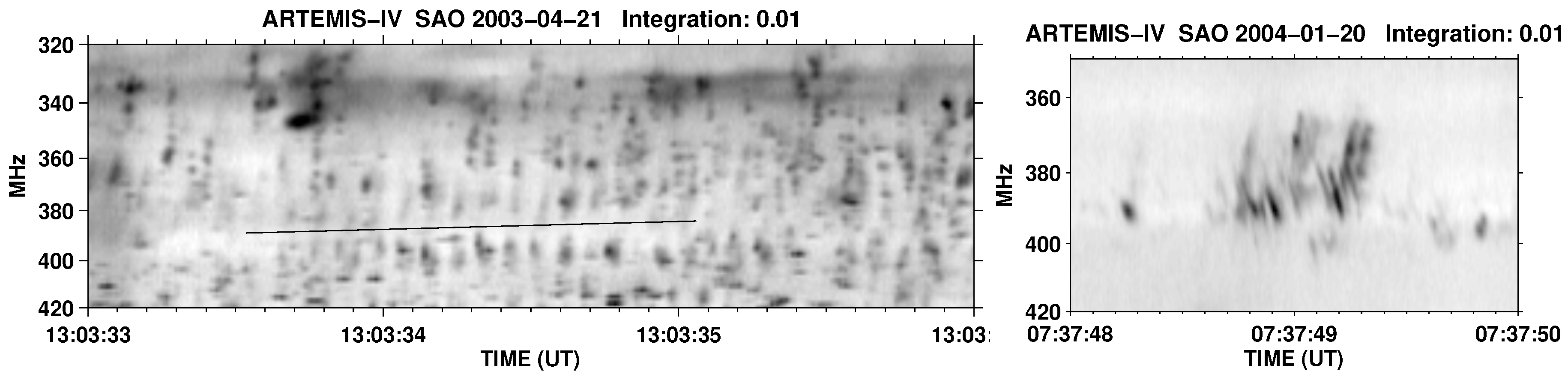
- Narrowband intermediate drift bursts (also narrowband stripes or small fibers in the decimetric wave band after Chernov et al. [159]): In the Bouratzis et al. [57] spectra, there are few recordings of IDBs of narrow frequency extent ( MHz on average, corresponding to 3% relative bandwidth). Their frequency drift rate was about equal or somewhat lower than the typical fiber drift; they had either an LF absorption–HF emission or an HF emission–absorption–LF emission ridge structure.
- Fast drift fiber bursts (FDBs): They are similar in form to the "typical" fibers exhibiting the characteristic emission-absorption pattern but their drift rate is comparable to the drift rate of the type-III bursts.
- Rope-like fiber bursts: They consist of recuring chains of narrowband fibers with negative frequency drift, relative bandwidth and repetition rates exceeding that of the typical fibers; the group drift rate of the chains is comparable to the type–II drift. These characteristics are thought to result from whistler generation within localized magnetic traps [87,160] possibly guided by MHD disturbances such as, fast shock fronts in reconnection or shocks overcoming the leading edge of a CME [88,89,161,162,163]. The relatively high repetition rate has been interpreted in terms of a smaller than a coronal loop size of the magnetic trap; this corresponds to a higher bounce frequency of the trapped electrons.
- Isolated slow-drifting fibres, [158]: They appear mainly in the decimetric range, with very few in the metric and the microwave ranges. Contrary to the "typical" fibers who tend to appear in groups, they are isolated. The main difference from the "typical" fibers is their frequency drift rate; sometimes it is near zero, in others the drift rate varies sharply with time giving a sawtooth-like appearance on the dynamic spectra.
6.1.2. Fiber Statistics
- The frequency difference between the absorption and emission peaks () was in the range 3.0-9.5 MHz with average of about 5.6 MHz.
- The fiber instantaneous bandwidth () of the emission ridge measured at FWHM had a mean value equal to 2.4 MHz; the relative instantaneous bandwidth () was which is about half the mean of the .
- The average repetition time was ≈0.90 s, with few values above 1.5 s (see also Bernold and Treumann [91], Figure 5]).
- The average value and the dispersion of the IDB frequency range for the regular (negative ) and reverse drift (positive ) bursts were 16.4 MHz and 33.8±21.3 MHz respectively.
- The average value of the total duration of fiber emission was 3.7 s with few fibers lasting more than 10 s.
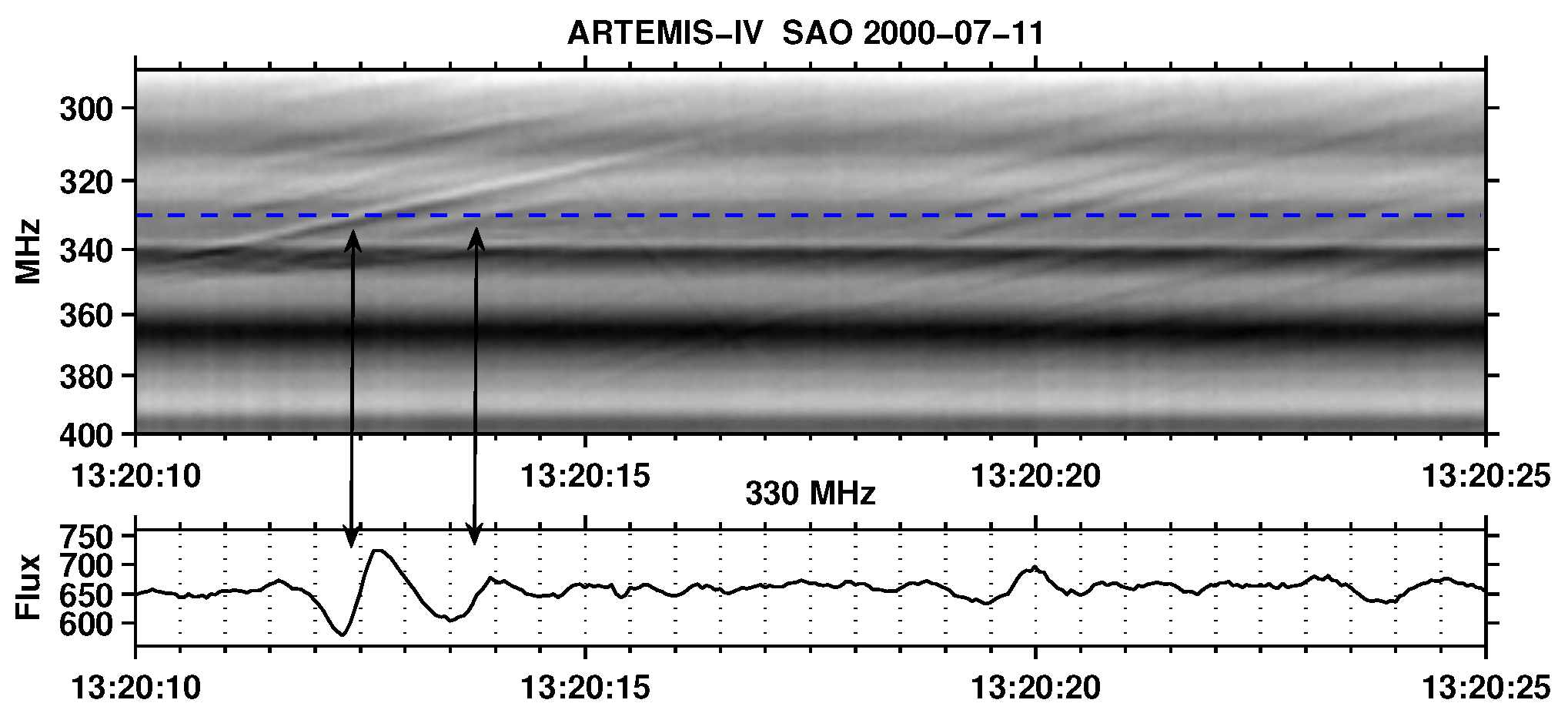
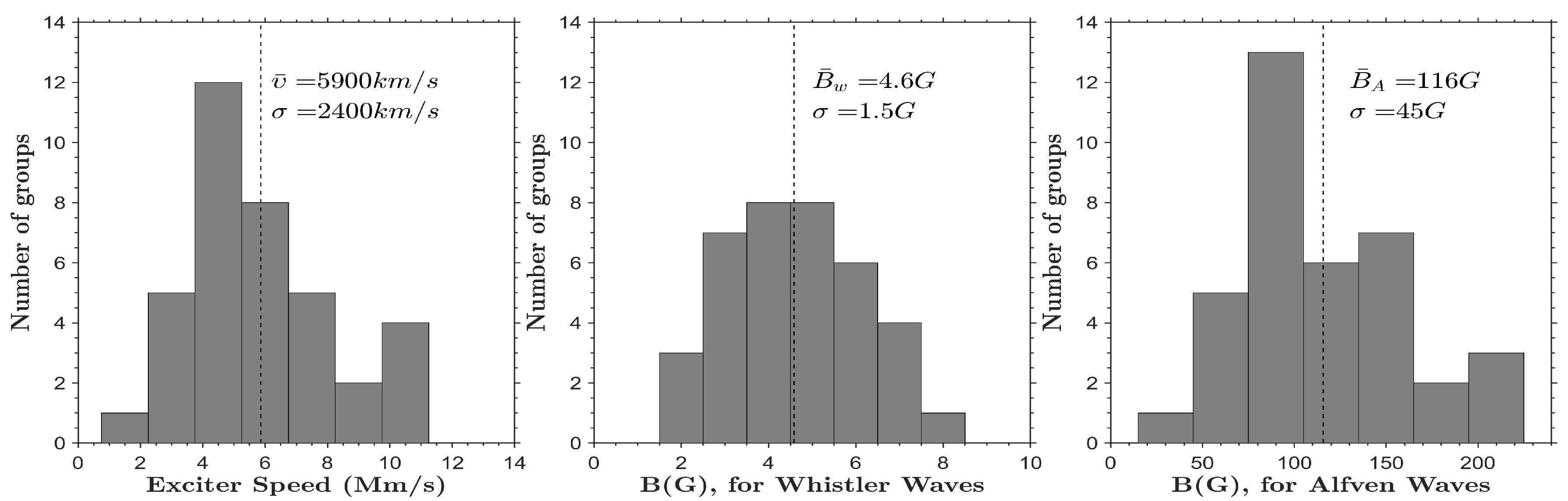
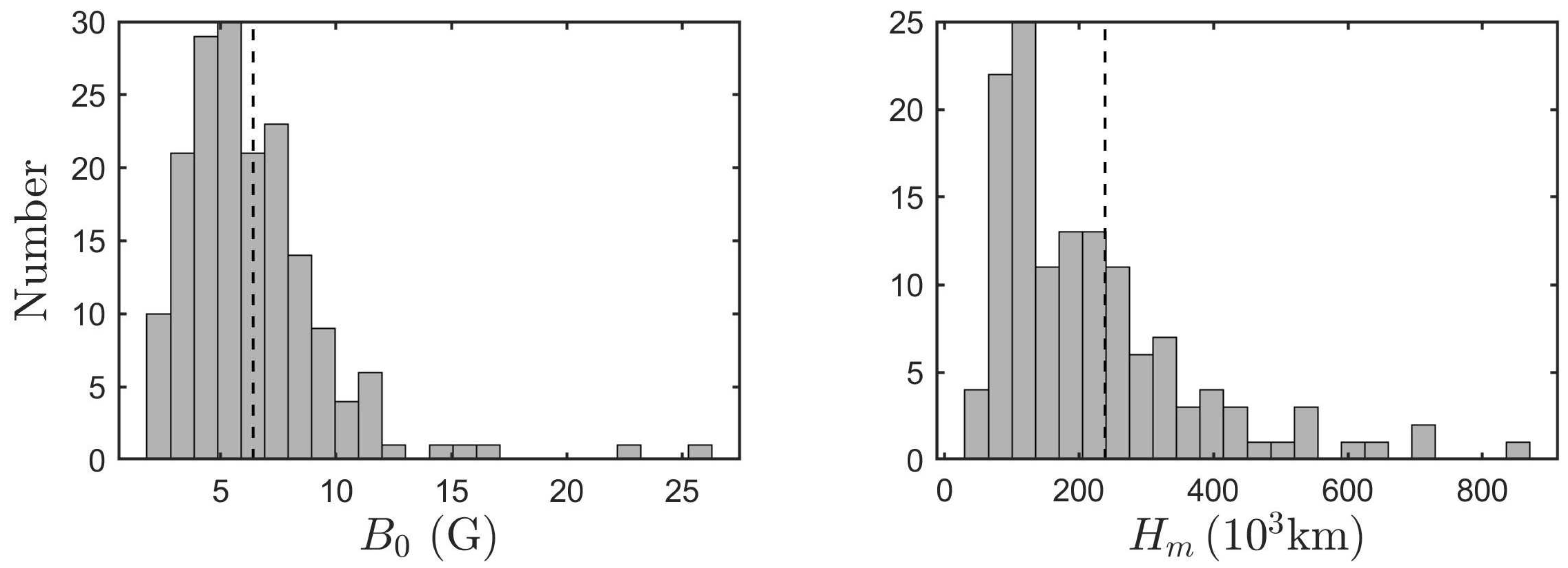
6.1.3. Computation of the exciter speed and the magnetic field
6.1.4. Relations between observed parameters
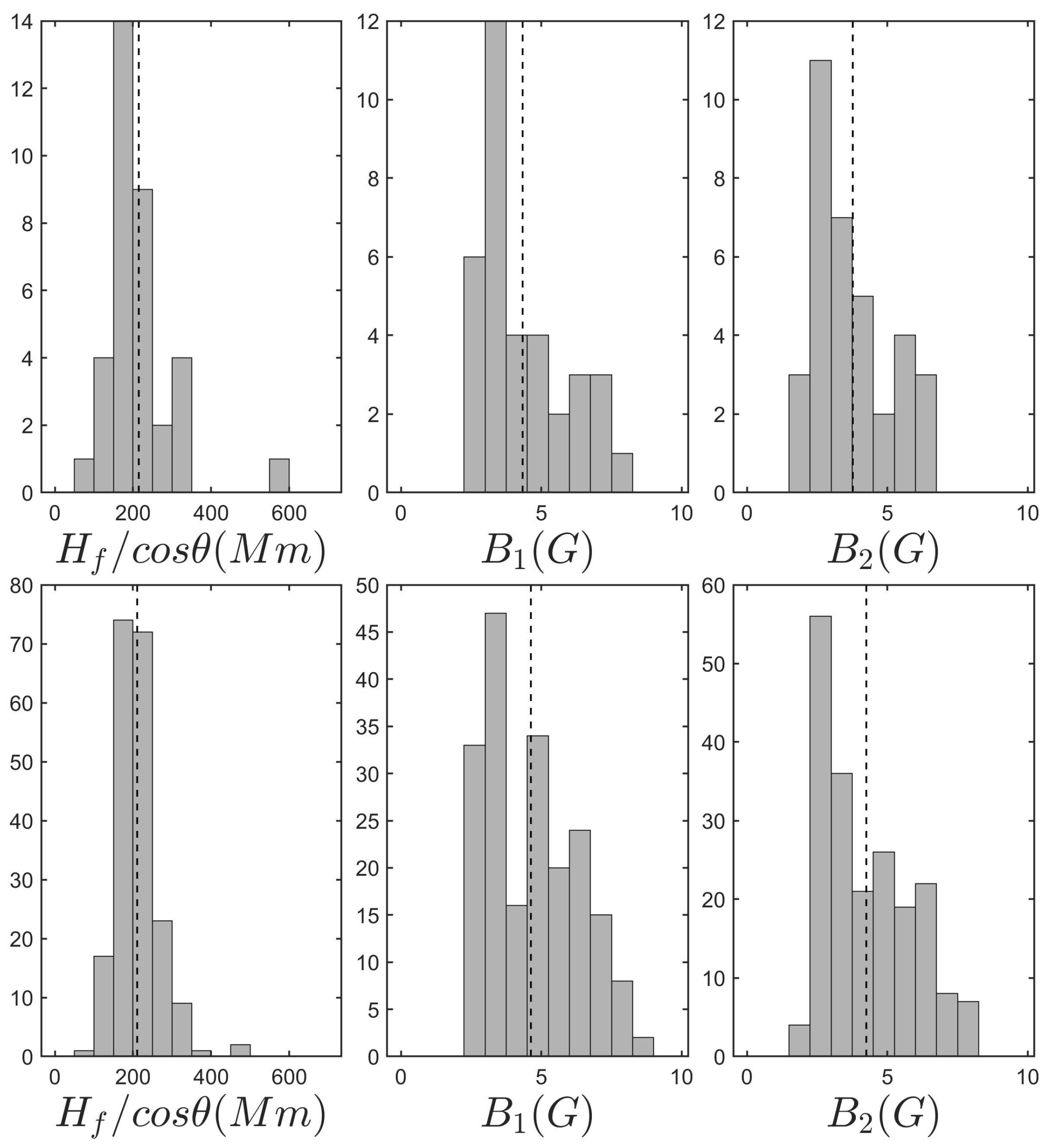
- Fiber repetition time, T, versus frequency drift rate, : Based on the discussion in Kuijpers [[83], Sect. 4.2] and their measurements of fiber parameters, Bouratzis et al. [[57], Sect. 6.2] showed that, the product, , is almost constant; they also provided a theoretical interpretation. The left panel of Figure 27 shows a scatter-plot of the the repetition time T, versus frequency drift rate bounded by the .
- Relative drift rate () versus relative instantaneous bandwidth (): Elgaroy and Soldal [169] were the first to obtain a linear relation between and (See their Eq. 2). In [[57], Sect. 6.2] upper and lower bounds of the slope C of the linear equation were estimated; the results are shown in the middle panel panel of Figure 27
- Repetition time, T, and duration at fixed frequency, : In [[57], Sect. 6.3] an empirical relationship was presented and duly justified theoretically. The right panel of Figure 27 presents the scatter plot of measured duration at fixed frequency versus the repetition time, which is consistent with the linear relationship
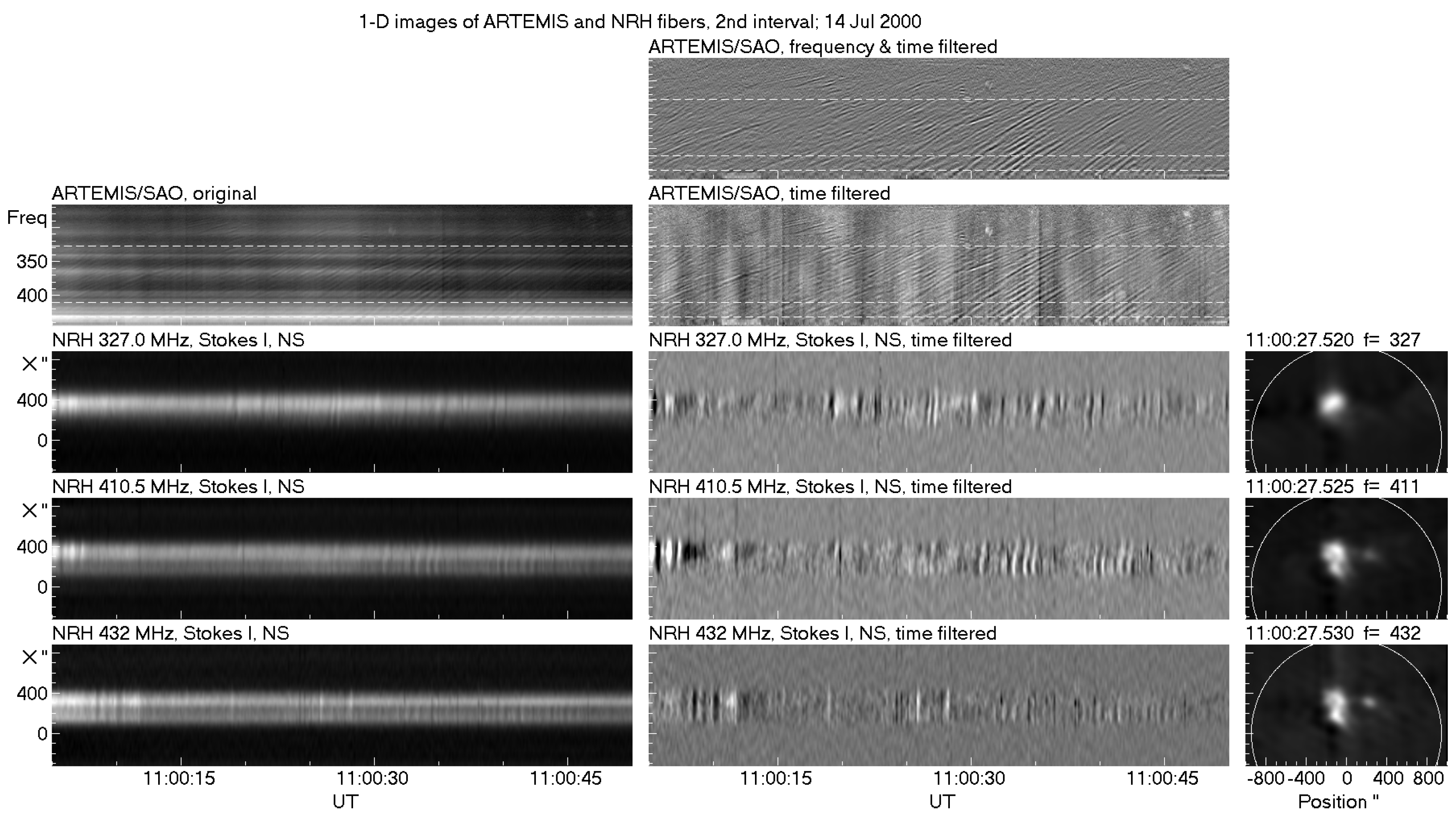
6.2. Spectral Imaging of Fibers
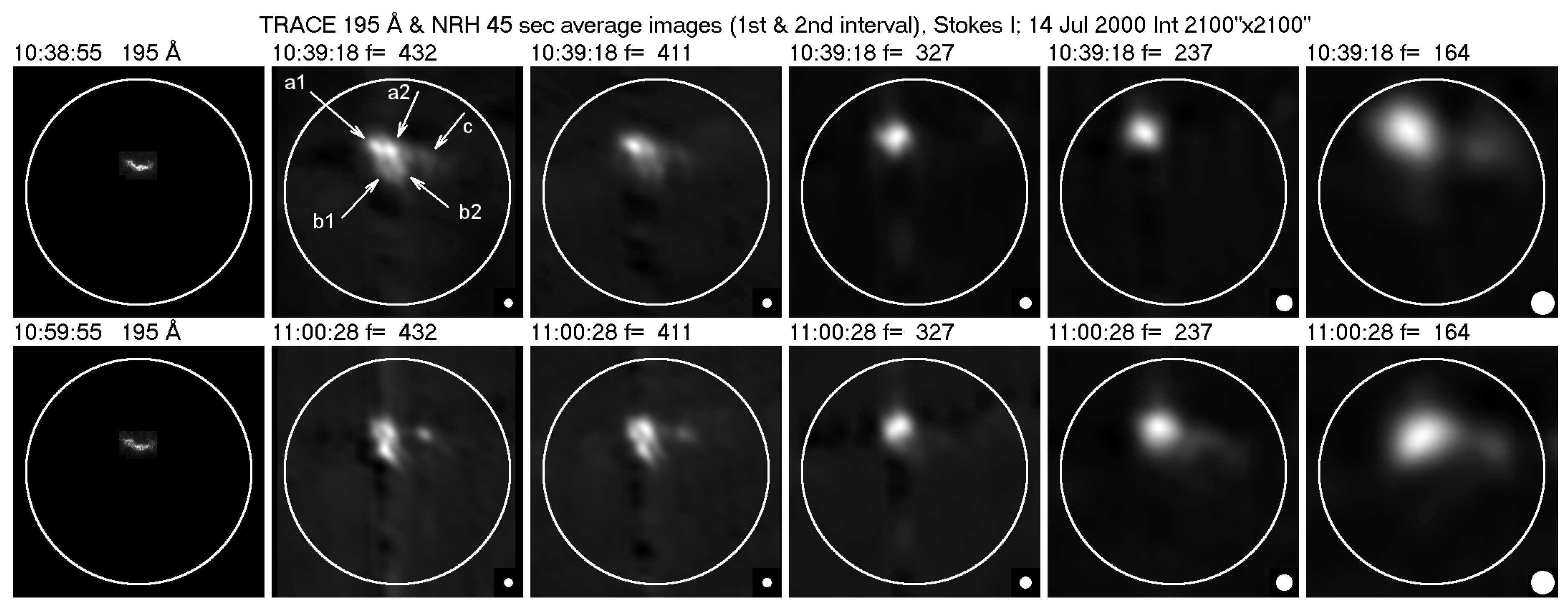
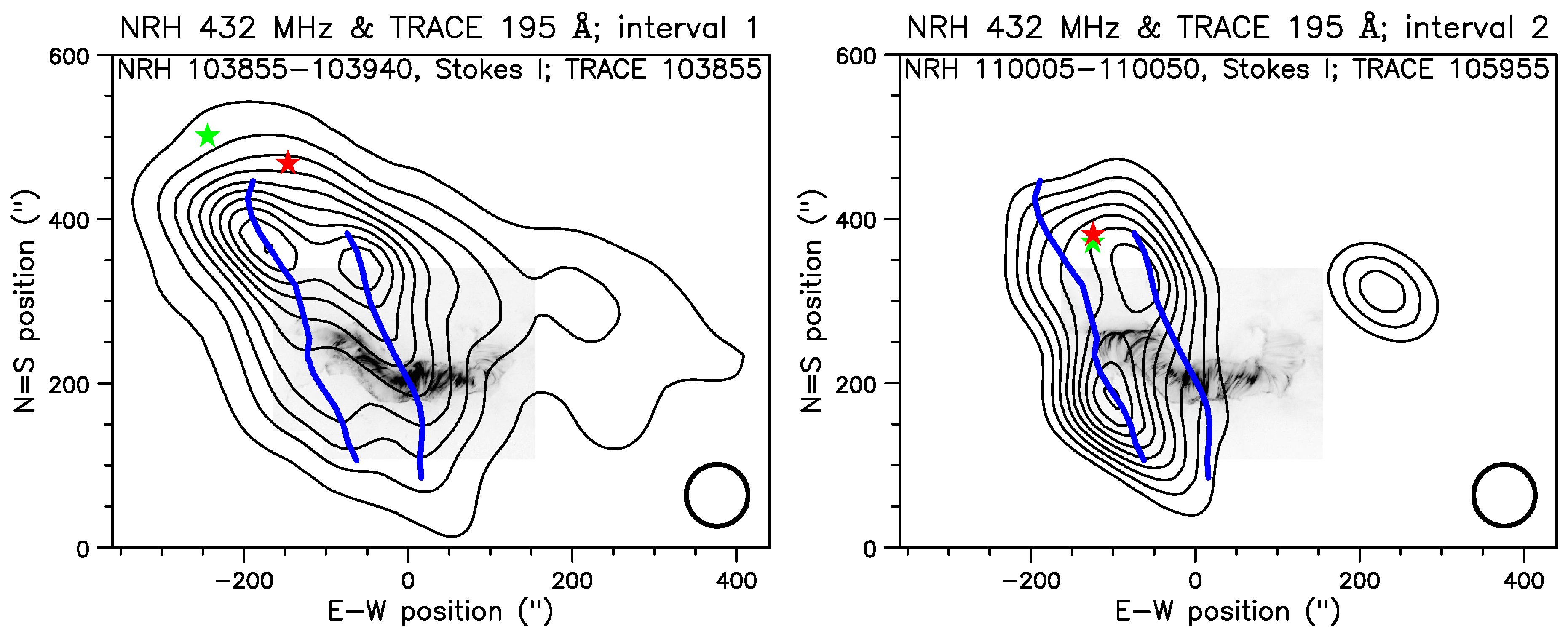
6.2.1. The event of July 14, 2000–Evolution of the Type-IV Continuum
6.2.2. Structure of the fiber-emitting sources
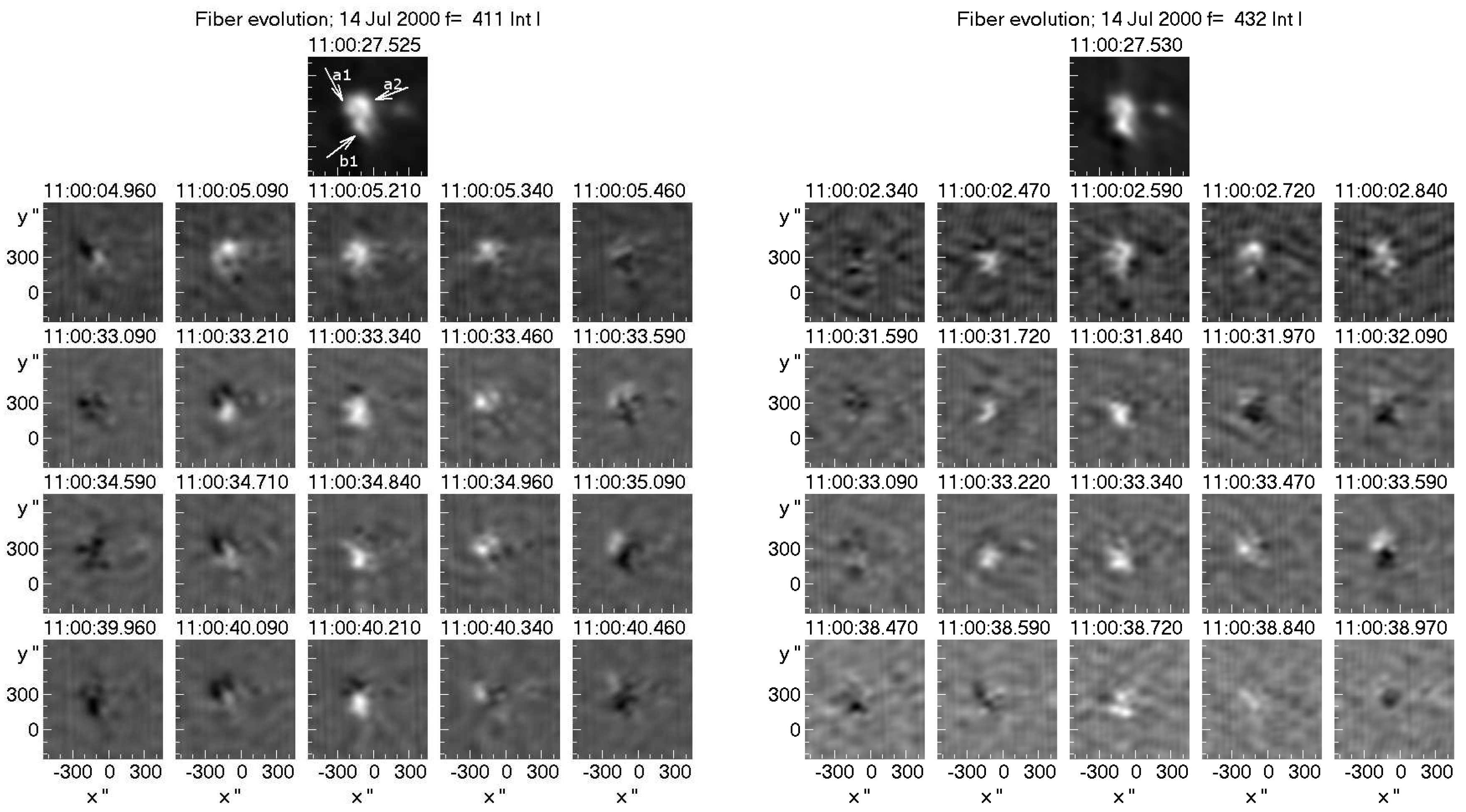
6.2.3. Imaging of individual fibers
6.2.4. Apparent motions in individual fibers
6.2.5. Exciter speed and frequency scale length
6.2.6. Fibers in emission and absorption
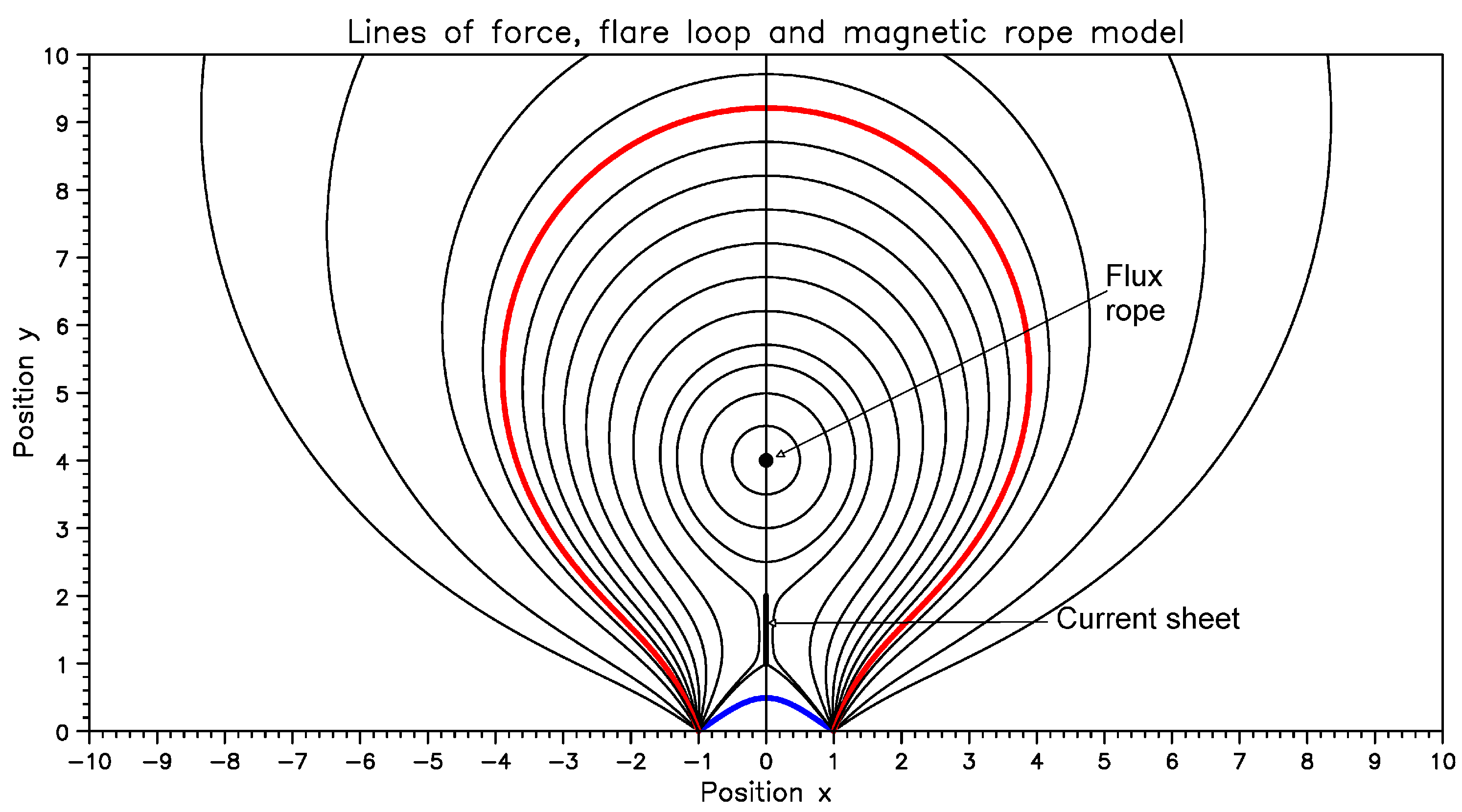
7. Summary & Discussion
7.1. Classification of Fine Structure Radio Bursts
7.2. Narrow-Band Burst (Spike) Source Structure
7.3. Intermediate Drift Bursts (Fibers)
8. Future Prospects and the New Generation of Spectroscopic Imaging Systems
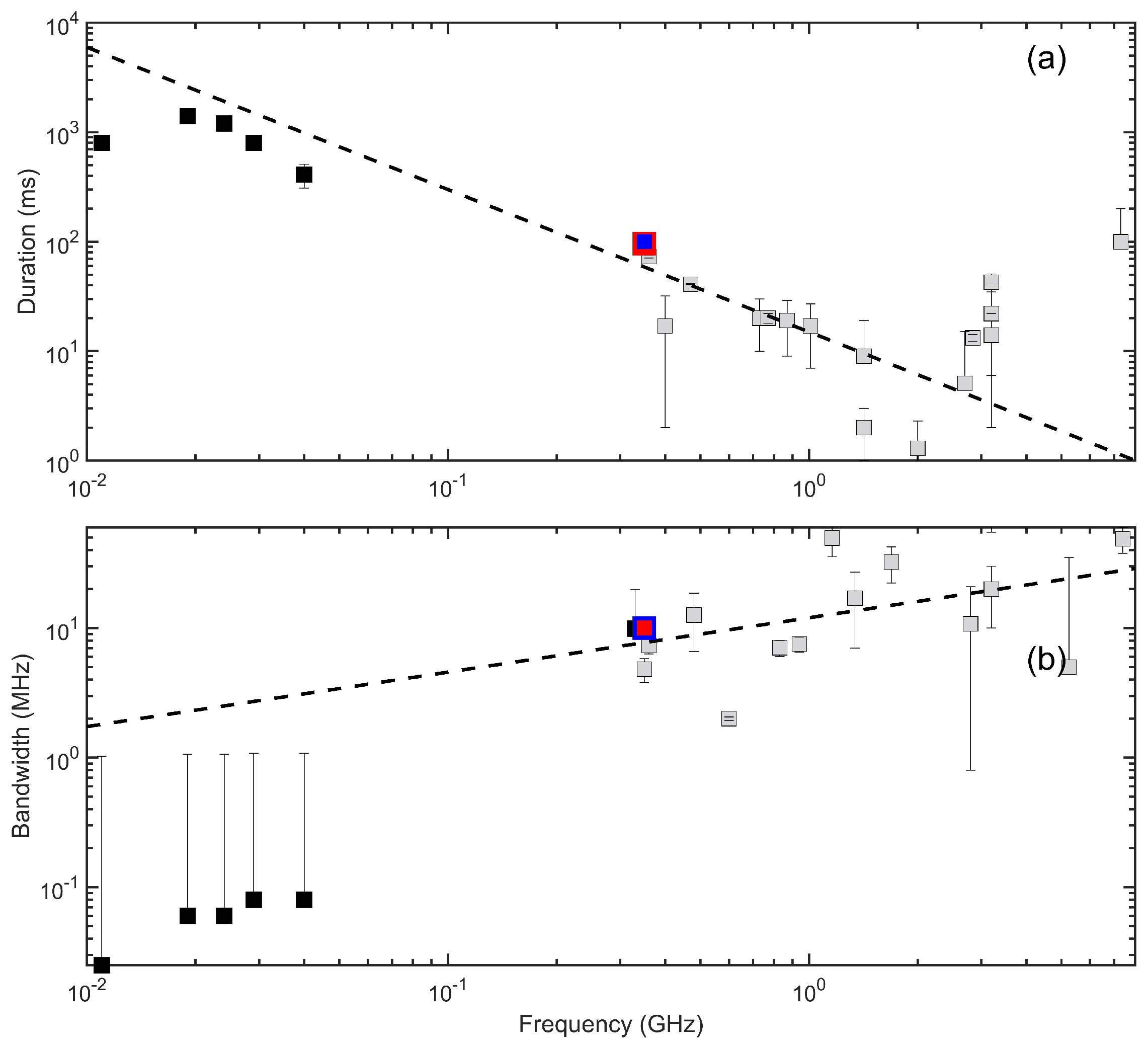
- The time and frequency resolution of a radiospectrograph should be consistent with the duration and the frequency extend of the smallest fine structure (e.g. spikes); in the case of radioheliographs, similar time resolution is highly desirable. The angular resolution should also be consistent with the bandwidth of the FS as the latter corresponds to its spatial extend. The duration and the frequency extent of the spikes depend on the observation frequency (see Sect. 5.3 and [149,150,151,152,195] for the applicable scaling laws) so that the corresponding resolution may be selected accordingly.
- At least two data points need be recorded per isolated spike burst. This corresponds to a sampling interval less than half of the averaged spike duration. Furthermore, the two data-points are the minimum resolution required for spike frequency drift rate calculations. By the same argument, the frequency resolution should be less than half the averaged bandwidth.
- For radioheliographs, the same requirements as regards time and frequency resolution appear reasonable; however the number of available frequency channels, the sensitivity requirement, and the computational power in the data processing pipeline may impose trade-offs [see [195]].
- The constraints presented above are applicable also to the members of the the intermediate drift burst family; although the frequency extend of a considerable part of these exceeds significantly that of the spikes, their possible hyperfine structure of spike-like constituents should be considered.
- A combined radioheliograph-radiospectrograph capability with high time, frequency and angular resolution, as exemplified by the LOFAR, is highly desirable. The latter, depending on the observation frequency, is bound to require a rather large baseline.
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARTEMIS | Appareil de Routine pour le Traitement et l’Enregistrement Magnetique de l’ |
| Information Spectral | |
| CME | Coronal Mass Ejection |
| EOVSA | Expanded Owens Valley Solar Array |
| EUV | Extreme Ultra-Violet |
| FDB | Fast Drift Fiber Burst |
| FS | Fine Structure |
| FT | Fourier Transform |
| FWHM | Full Width at Half Maximum |
| GOES | Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite |
| HF | Higher-Frequency |
| HXR | Hard X-Rays |
| IDB | Intermediate Drift Burst |
| JLS | Jean Louis Steinberg [see JLS obituary in [197] |
| LF | Lower-Frequency |
| LOFAR | Low Frequency Array |
| MHD | Magnetohydrodynamic |
| MUSER | Mingantu Ultrawide Spectral Radioheliograph |
| MWA | Murchison Widefield Array |
| NRH | Nançay Radio-Heliograph |
| QPP | Quasi-Periodic Pulsation |
| SKA | Square Kilometre Array |
| SOHO | Solar and Heliospheric Observatory |
| SSS | Super Short Structure |
| SRH | The Siberian Radiohelograph |
| SXR | Soft X-Rays |
| TRACE | Transition Region and Coronal Explorer |
Appendix A. Spike Durations and Spectral Widths in a Wide Observation Frequency Range (10 MHz–7.40 GHz).
| Freq. | Duration | Time | Width | Freq. res. | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [GHz] | [ms] | res.[ms] | [MHz] | [MHz] | |
| 0.011 | 800.0 | 100 | 0.025 | 1 | Shevchuk et al. [200] |
| 0.019 | 1400.0 | 100 | 0.060 | 1 | Melnik et al. [199] |
| 0.024 | 1000.0 | 100 | 0.060 | 1 | Melnik et al. [199] |
| 0.029 | 800.0 | 100 | 0.080 | 1 | Melnik et al. [199] |
| 0.040 | 410.0 | 100 | 0.080 | 1 | Shevchuk et al. [200] |
| 0.330 | – | – | 9.900 | 1-10 | Benz et al. [201] |
| 0.350 | 100.0 | 10 | 10.00 | 1.6 | Bouratzis et al. [54] |
| 0.350 | 96.0 | 10 | 10.00 | 1.4 | Armatas et al. [62] |
| 0.350 | – | – | 4.800 | 1 | Messmer and Benz [202] |
| 0.360 | – | – | 7.320 | 1 | Csillaghy and Benz [152] |
| 0.360 | 73.0 | 2 | – | 1 | Guedel and Benz [149] |
| 0.400 | 4–30 | 1 & 10 | ∼20 | – | Magdalenić et al. [73] |
| 0.470 | 41.0 | 0.5 | – | 3 | Guedel and Benz [149] |
| 0.480 | – | – | 12.600 | 6 | Csillaghy and Benz [152] |
| 0.600 | – | 100 | ∼2 | 0.061 | Benz et al. [67] |
| 0.730 | 20.0 | 10 | – | 10 | Guedel and Benz [149] |
| 0.770 | 20.0 | 2 | – | 10 | Guedel and Benz [149] |
| 0.830 | – | – | 7.040 | 1 | Csillaghy and Benz [152] |
| 0.870 | 19.0 | 10 | – | 10 | Guedel and Benz [149] |
| 0.940 | – | – | 7.500 | 1 | Messmer and Benz [202] |
| 1.010 | 17.0 | 10 | – | 10 | Guedel and Benz [149] |
| 1.160 | – | – | 49.500 | 14 | Csillaghy and Benz [152] |
| 1.340 | – | – | 17.000 | 10 | Csillaghy and Benz [152] |
| 1.420 | 2.0 | 1 | – | – | Wang and Xie [203] |
| 1.420 | 9.0 | 1 & 10 | – | – | Mészárosová et al. [150] |
| 1.690 | – | – | 32.300 | 10 | Csillaghy and Benz [152] |
| 2.000 | 1.3 | 1 | – | – | Wang and Xie [203] |
| 2.700 | 5.1 | 1 & 10 | – | – | Mészárosová et al. [150] |
| 2.800 | – | – | 10.800 | 10 | Csillaghy and Benz [152] |
| 2.840 | 13.2 | 1 | – | – | Wang and Xie [203] |
| 3.200 | 14.0 | 8 | – | 10 | Chernov et al. [204] |
| 3.200 | 42.7 | 8 | 117.300 | 10 | Wang and Xie [203] |
| 3.200 | 8–36 | 8 | 20–110 | 10 | Wang et al. [205] |
| 5.250 | – | 5 | ∼30 | 10 | Rozhansky et al. [151] |
| 7.300 | ∼100 | 100 | 120.000 | 10 | Benz et al. [206] |
| 7.400 | – | – | 48.700 | 11 | Csillaghy and Benz [152] |
Appendix B. Average Values of Characteristic Parameters for Individual Fibers & Groups.
| Normal (<0) Drift | Typical Fibers | Fast Drift Bursts | Rope-like | Narrow Band IDFs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Groups | 38 | One | One | One |
| (MHz s) | -8.43 ± 3.29 | -142.8 | -45.3 | -5.86 |
| (s) | (20±8)·10 | -0.36 | -0.10 | -0.014 |
| (s) | 0.30 ± 0.20 | 6·10 | 0.21 | 0.30 |
| T (s) | 0.98 ± 0.74 | 0.24 | 0.43 | 0.80 |
| (MHz) | 2.4 ± 0.8 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 2.0 |
| (10) | 9.0 ± 4 | 13.2 | 25.1 | 9.4 |
| (MHz) | 5.5 ± 2.2 | 7.5 | 6.90 | 3.18 |
| (10) | 15 ± 6 | 25 | 20 | 9 |
| Individual Fibers | 441 | 11 | 13 | 19 |
| (s) | 4.26 ± 2.61 | 0.55 ± 0.17 | 0.49 ± 0.11 | 2.66 ± 1.10 |
| (MHz) | -37.9 ± 16.4 | -44.3 ± 19.1 | 16.8 ± 2.9 | 7.9 ± 4.3 |
| () | -103±44 | -138 ± 66 | -60 ± 10 | -23 ± 13 |
| Reverse (>0) Drift | Typical Fibers | Fast Drift Bursts | Rope-like | Narrow Band IDFs |
| Fiber Groups | One | Three | Two | |
| (MHz s) | 8.15 | 73.4 ± 31.0 | – | 3.71 ± 2.6 |
| (s) | – | 0.009 ± 0.006 | ||
| (s) | – | 0.58 ± 0.39 | ||
| T (s) | 0.60 | – | 0.80 | |
| (MHz) | 2.4 | 4.3 ± 1.2 | – | 3.0 ± 1.4 |
| (10) | 8.2 | 12.7 ± 2.2 | – | 9.1 ± 4.8 |
| (MHz) | 6.4 | 5.9 ± 1.4 | – | 3.33 ± 1.65 |
| (10) | 18 | 17 ± 5 | – | 9 ± 5 |
| Individual Fibers | 13 | 61 | – | 31 |
| (s) | 3.73 ± 2.29 | 1.04 ± 0.47 | – | 2.0 ± 0.80 |
| (MHz) | 33.8 ± 21.3 | 67.4 ± 14.0 | – | 8.4 ± 6.0 |
| (10) | 92±58 | 198 ± 42 | – | 23 ± 16 |
References
- Simnett, G.M.; Benz, A.O. The role of metric and decimetric radio emission in the understanding of solar flares. Astron & Astrophys. 1986, 165, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, K.L. Energetic electrons in impulsive solar flares: Radio diagnostics. Advances in Space Research 2005, 35, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yan, Y.H.; Liu, Y.Y. A Study of Solar Radio Bursts with Fine Structures during Flare/CME Events. Sol. Phys. 2008, 253, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morosan, D.E.; Kumari, A.; Kilpua, E.K.J.; Hamini, A. Moving solar radio bursts and their association with coronal mass ejections. Astron & Astrophys. 2021, 647, L12, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/2103.05942]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morosan, D.E.; Pomoell, J.; Kumari, A.; Vainio, R.; Kilpua, E.K.J. Shock-accelerated electrons during the fast expansion of a coronal mass ejection. Astron & Astrophys. 2022, arXiv:astro-ph.SR/2211.06049]668, A15, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/2211.06049]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárta, M.; Karlický, M. Radio Diagnostics of Solar Flare Reconnection. Hvar Observatory Bulletin 2005, 29, 205–214. [Google Scholar]
- Aurass, H. Signatures of magnetic reconnection in solar radio observations? Advances in Space Research 2007, 39, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pick, M. Overview of Solar Radio Physics and Interplanetary Disturbances. In Proceedings of the Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Gary, D.E.; Keller, C.U., Eds., 2004, Vol. 314, Astrophysics and Space Science Library, p. 17. [CrossRef]
- Pick, M.; Vilmer, N. Sixty-five years of solar radioastronomy: flares, coronal mass ejections and Sun Earth connection. Astron.& Astrophys. Rev. 2008, 16, 1–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nindos, A.; Aurass, H.; Klein, K.L.; Trottet, G. Radio Emission of Flares and Coronal Mass Ejections. Invited Review. Sol. Phys. 2008, 253, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouloumvakos, A.; Nindos, A.; Valtonen, E.; Alissandrakis, C.E.; Malandraki, O.; Tsitsipis, P.; Kontogeorgos, A.; Moussas, X.; Hillaris, A. Properties of solar energetic particle events inferred from their associated radio emission. Astron & Astrophys. 2015, 580, A80, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1507.03776]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaivani, P.P.; Prakash, O.; Shanmugaraju, A.; Feng, L.; Lu, L.; Gan, W.; Michalek, G. Analysis of Type II and Type III Radio Bursts Associated with SEPs from Non-Interacting/Interacting Radio-Loud CMEs. Astrophysics 2021, 64, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaivani, P.P.; Shanmugaraju, A.; Prakash, O.; Kim, R.S. Statistical Characteristics on SEPs, Radio-Loud CMEs, Low Frequency Type II and Type III Radio Bursts Associated with Impulsive and Gradual Flares. Earth Moon and Planets 2020, 123, 61–85, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/2007.05726]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miteva, R.; Samwel, S.W.; Zabunov, S. Solar Radio Bursts Associated with In Situ Detected Energetic Electrons in Solar Cycles 23 and 24. Universe 2022, 8, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, K.L.; Musset, S.; Vilmer, N.; Briand, C.; Krucker, S.; Francesco Battaglia, A.; Dresing, N.; Palmroos, C.; Gary, D.E. The relativistic solar particle event on 28 October 2021: Evidence of particle acceleration within and escape from the solar corona. Astron & Astrophys. 2022, 663, A173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, A.O. Radio Diagnostics of Flare Energy Release. In Proceedings of the Energy Conversion and Particle Acceleration in the Solar Corona, Berlin Springer Verlag; Klein, L., Ed., 2003, Vol. 612, Lecture Notes in Physics, pp. 80–95. [CrossRef]
- Nindos, A.; Aurass, H. Pulsating Solar Radio Emission. In Proceedings of the The High Energy Solar Corona: Waves, Eruptions,Particles, Berlin Springer Verlag; K.-L. Klein & A. L. MacKinnon., Ed., 2007, Vol. 725, Lecture Notes in Physics, pp. 251–277. [CrossRef]
- Bernold, T. A catalogue of fine structures in type IV solar radio bursts. Astron.& Astrophys.S 1980, 42, 43–58. [Google Scholar]
- Slottje, C. Atlas of fine structures of dynamic spectra of solar type IV-dm and some type II radio bursts. Dissertation, Utrecht Observatory 1981.
- Guedel, M.; Benz, A.O. A catalogue of decimetric solar flare radio emission. Astron.& Astrophys.S 1988, 75, 243–259. [Google Scholar]
- Isliker, H.; Benz, A.O. Catalogue of 1-3 GHz solar flare radio emission. Astron.& Astrophys.S 1994, 104, 145–160. [Google Scholar]
- Allaart, M.A.F.; van Nieuwkoop, J.; Slottje, C.; Sondaar, L.H. Fine structure in solar microwave bursts. Sol. Phys. 1990, 130, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiřička, K.; Karlický, M.; Mészárosová, H.; Snížek, V. Global statistics of 0.8-2.0 GHz radio bursts and fine structures observed during 1992-2000 by the Ondřejov radiospectrograph. Astron & Astrophys. 2001, 375, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiřička, K.; Karlický, M.; Mészárosová, H. Occurrences of different types of 0.8-2.0 GHz solar radio bursts and fine structures during the solar cycle. In Proceedings of the Solspa 2001, Proceedings of the Second Solar Cycle and Space Weather Euroconference; Sawaya-Lacoste, H., Ed., 2002, Vol. 477, ESA Special Publication, pp. 351–354.
- Fu, Q.J.; Yan, Y.H.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.J. A New Catalogue of Fine Structures Superimposed on Solar Microwave Bursts. Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics 2004, 4, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mészárosová, H.; Karlický, M.; Jiřička, K. Ten Types of Solar Radio Bursts and Fine Structures Observed by the Ondřejov 0.8-2.0 GHz Radio-Spectrograph. Hvar Observatory Bulletin 2005, 29, 309–318. [Google Scholar]
- Bouratzis, C.; Hillaris, A.; Alissandrakis, C.E.; Preka-Papadema, P.; Moussas, X.; Caroubalos, C.; Tsitsipis, P.; Kontogeorgos, A. Fine Structure of Metric Type IV Radio Bursts Observed with the ARTEMIS-IV Radio-Spectrograph: Association with Flares and Coronal Mass Ejections. Sol. Phys. 2015, 290, 219–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroubalos, C.; Maroulis, D.; Patavalis, N.; Bougeret, J.L.; Dumas, G.; Perche, C.; Alissandrakis, C.; Hillaris, A.; Moussas, X.; Preka-Papadema, P.; et al. The New Multichannel Radiospectrograph ARTEMIS-IV/HECATE, of the University of Athens. Experimental Astronomy 2001, 11, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroubalos, C.; Alissandrakis, C.E.; Hillaris, A.; Preka-Papadema, P.; Polygiannakis, J.; Moussas, X.; Tsitsipis, P.; Kontogeorgos, A.; Petoussis, V.; Bouratzis, C.; et al. Ten Years of the Solar Radiospectrograph ARTEMIS-IV. In Proceedings of the Recent Advances in Astronomy and Astrophysics; Solomos, N., Ed., 2006, Vol. 848, American Institute of Physics Conference Series, pp. 864–873. [CrossRef]
- Kontogeorgos, A.; Tsitsipis, P.; Moussas, X.; Preka-Papadema, G.; Hillaris, A.; Caroubalos, C.; Alissandrakis, C.; Bougeret, J.L.; Dumas, G. Observing the Sun at 20–650 MHz at Thermopylae with Artemis. Space Sci. Rev. 2006, 122, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogeorgos, A.; Tsitsipis, P.; Caroubalos, C.; Moussas, X.; Preka-Papadema, P.; Hilaris, A.; Petoussis, V.; Bouratzis, C.; Bougeret, J.L.; Alissandrakis, C.E.; et al. The improved ARTEMIS IV multichannel solar radio spectrograph of the University of Athens. Experimental Astronomy 2006, 21, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogeorgos, A.; Tsitsipis, P.; Caroubalos, C.; Moussas, X.; Preka-Papadema, P.; Hilaris, A.; Petoussis, V.; Bougeret, J.L.; Alissandrakis, C.E.; Dumas, G. Measuring solar radio bursts in 20-650 MHz. Measurement 2008, 41, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdraon, A.; Delouis, J.M. The Nançay Radioheliograph. In Proceedings of the Coronal Physics from Radio and Space Observations, Berlin Springer Verlag; Trottet, G., Ed., 1997, Vol. 483, Lecture Notes in Physics, pp. 192–201. [CrossRef]
- Klein, K.L.; Kerdraon, A. Solar physics at Nançay radio observatory: Recent developments. In Proceedings of the 2011 XXXth URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium. IEEE, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Vasanth, V.; Chen, Y.; Feng, S.; Ma, S.; Du, G.; Song, H.; Kong, X.; Wang, B. An Eruptive Hot-channel Structure Observed at Metric Wavelength as a Moving Type-IV Solar Radio Burst. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 830, L2, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1609.06546]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanth, V.; Chen, Y.; Lv, M.; Ning, H.; Li, C.; Feng, S.; Wu, Z.; Du, G. Source Imaging of a Moving Type IV Solar Radio Burst and Its Role in Tracking Coronal Mass Ejection from the Inner to the Outer Corona. Astrophys. J. 2019, 870, 30, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1810.11815]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alissandrakis, C.E.; Nindos, A.; Patsourakos, S.; Hillaris, A. Multiwavelength observations of a metric type-II event. Astron & Astrophys. 2021, 654, A112, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/2108.02855]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alissandrakis, C.E.; Patsourakos, S.; Nindos, A.; Bouratzis, C.; Hillaris, A. First detection of metric emission from a solar surge. Astron & Astrophys. 2022, 662, A14, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/2203.01043]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brueckner, G.E.; Howard, R.A.; Koomen, M.J.; Korendyke, C.M.; Michels, D.J.; Moses, J.D.; et al. . The Large Angle Spectroscopic Coronagraph (LASCO). Sol. Phys. 1995, 162, 357–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashiro, S.; Gopalswamy, N.; Michalek, G.; St. Cyr, O.C.; Plunkett, S.P.; Rich, N.B.; Howard, R.A. A catalog of white light coronal mass ejections observed by the SOHO spacecraft. Journal of Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, 7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalswamy, N.; Yashiro, S.; Michalek, G.; Stenborg, G.; Vourlidas, A.; Freeland, S.; Howard, R. The SOHO/LASCO CME Catalog. Earth Moon and Planets 2009, 104, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashiro, S.; Gopalswamy, N.; St. Cyr, O.C.; Lawrence, G.; Michalek, G.; Young, C.A.; Plunkett, S.P.; Howard, R.A. Development of SOHO/LASCO CME Catalog and Study of CME Trajectories. AGU Spring Meeting Abstracts 2001, p. 31.
- Handy, B.N.; Acton, L.W.; Kankelborg, C.C.; Wolfson, C.J.; Akin, D.J.; Bruner, M.E.; Caravalho, R.; Catura, R.C.; Chevalier, R.; Duncan, D.W.; et al. The transition region and coronal explorer. Sol. Phys. 1999, 187, 229–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahler, S.W.; Kreplin, R.W. The NRL SOLRAD X-ray detectors: A summary of the observations and a comparison with the SMS/GOES detectors. Sol. Phys. 1991, 133, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemen, J.R.; Duncan, D.W.; Edwards, C.G.; Friedlaender, F.M.; Jurcevich, B.K.; Morrison, M.D.; Springer, L.A.; Stern, R.A.; Wuelser, J.P.; Bruner, M.E.; et al. The solar x-ray imager for GOES. In Proceedings of the Telescopes and Instrumentation for Solar Astrophysics; Fineschi, S.; Gummin, M.A., Eds., 2004, Vol. 5171, Proc. SPIE, pp. 65–76. [CrossRef]
- Delaboudinière, J.P.; Artzner, G.E.; Brunaud, J.; Gabriel, A.H.; Hochedez, J.F.; Millier, F.; et al. . EIT: Extreme-Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope for the SOHO Mission. Sol. Phys. 1995, 162, 291–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.P.; Hurford, G.J.; Madden, N.W.; Dennis, B.R.; Crannell, C.J.; Holman, G.D.; Ramaty, R.; von Rosenvinge, T.T.; Zehnder, A.; van Beek, H.F.; et al. High-Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (HESSI) Small Explorer mission for the next (2000) solar maximum. In Proceedings of the Missions to the Sun II; Korendyke, C.M., Ed., 1998, Vol. 3442, Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, pp. 2–12. [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.P.; Dennis, B.R.; Hurford, G.J.; Smith, D.M.; Zehnder, A.; Harvey, P.R.; Curtis, D.W.; Pankow, D.; Turin, P.; Bester, M.; et al. The Reuven Ramaty High-Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (RHESSI). Sol. Phys. 2002, 210, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fárník, F.; Garcia, H.; Karlický, M. New Solar Broad-Band Hard X-Ray Spectrometer: First Results. Sol. Phys. 2001, 201, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, G.J.; Meegan, C.A.; Parnell, T.A.; Wilson, R.B. The Burst and Transient Source Experiment for the Gamma-Ray Observatory. In Proceedings of the Gamma Ray Transients and Related Astrophysical Phenomena; Lingenfelter, R.E.; Hudson, H.S.; Worrall, D.M., Eds., 1982, Vol. 77, American Institute of Physics Conference Series, pp. 443–451. [CrossRef]
- Fishman, G.J.; Meegan, C.A.; Parnell, T.A.; Wilson, R.B.; Paciesas, W. BATSE/GRO observational capabilities. In Proceedings of the American Institute of Physics Conference Series; Woosley, S.E., Ed., 1984, Vol. 115, American Institute of Physics Conference Series, pp. 651–66. [CrossRef]
- Guidice, D.A.; Cliver, E.W.; Barron, W.R.; Kahler, S. The Air Force RSTN System. In Proceedings of the Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society, 1981, Vol. 13, pp. 553–+.
- Messerotti, M.; Zlobec, P.; Padovan, S. The Trieste near-real-time coronal radio surveillance program: a tool for solar activity monitoring and forecasting. Mem. Societa Astronomica Italiana 2001, 72, 633–636. [Google Scholar]
- Bouratzis, C.; Hillaris, A.; Alissandrakis, C.E.; Preka-Papadema, P.; Moussas, X.; Caroubalos, C.; Tsitsipis, P.; Kontogeorgos, A. High resolution observations with Artemis-IV and the NRH. I. Type IV associated narrow-band bursts. Astron & Astrophys. 2016, 586, A29, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1512.02481]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armatas, S.; Bouratzis, C.; Hillaris, A.; Alissandrakis, C.E.; Preka-Papadema, P.; Kontogeorgos, A.; Tsitsipis, P.; Moussas, X. High-resolution observations with ARTEMIS/JLS and the NRH. IV. Imaging spectroscopy of spike-like structures near the front of type-II bursts. Astron & Astrophys. 2022, 659, A198, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/2201.07832]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Gary, D.E. Dynamic Spectral Imaging of Decimetric Fiber Bursts in an Eruptive Solar Flare. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, 77, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1709.08137]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouratzis, C.; Hillaris, A.; Alissandrakis, C.E.; Preka-Papadema, P.; Moussas, X.; Caroubalos, C.; Tsitsipis, P.; Kontogeorgos, A. High resolution observations with Artemis-JLS. II. Type IV associated intermediate drift bursts. Astron & Astrophys. 2019, 625, A58, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1904.02262]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsipis, P.; Kontogeorgos, A.; Moussas, X.; Preka-Papadema, P.; Hillaris, A.; Petoussis, V.; Caroubalos, C.; Alissandrakis, C.E.; Bougeret, J.L.; Dumas, G. Detection of slopes of linear and quasi-linear structures in noisy background, using 2D-FFT. In Proceedings of the Recent Advances in Astronomy and Astrophysics; Solomos, N., Ed., 2006, Vol. 848, American Institute of Physics Conference Series, pp. 874–882. [CrossRef]
- Tsitsipis, P.; Kontogeorgos, A.; Hillaris, A.; Moussas, X.; Caroubalos, C.; Preka-Papadema, P. Fast estimation of slopes of linear and quasi-linear structures in noisy background, using Fourier methods. Pattern Recogn. 2007, 40, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohjolainen, S.; van Driel-Gesztelyi, L.; Culhane, J.L.; Manoharan, P.K.; Elliott, H.A. CME Propagation Characteristics from Radio Observations. Sol. Phys. 2007, 244, 167–188, [0711.3168]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohjolainen, S.; Hori, K.; Sakurai, T. Radio Bursts Associated with Flare and Ejecta in the 13 July 2004 Event. Sol. Phys. 2008, 253, 291–303, [0809.3896]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armatas, S.; Bouratzis, C.; Hillaris, A.; Alissandrakis, C.E.; Preka-Papadema, P.; Moussas, X.; Mitsakou, E.; Tsitsipis, P.; Kontogeorgos, A. Detection of spike-like structures near the front of type-II bursts. Astron & Astrophys. 2019, 624, A76, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1902.10617]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newkirk, G.J. The Solar Corona in Active Regions and the Thermal Origin of the Slowly Varying Component of Solar Radio Radiation. Astrophys. J. 1961, 133, 983–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vršnak, B.; Magdalenić, J.; Zlobec, P. Band-splitting of coronal and interplanetary type II bursts. III. Physical conditions in the upper corona and interplanetary space. Astron & Astrophys. 2004, 413, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poquerusse, M. Relativistic type III solar radio bursts. Astron & Astrophys. 1994, 286, 611–625. [Google Scholar]
- Klassen, A.; Karlický, M.; Mann, G. Superluminal apparent velocities of relativistic electron beams in the solar corona. Astron & Astrophys. 2003, 410, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, A.O.; Monstein, C.; Beverland, M.; Meyer, H.; Stuber, B. High Spectral Resolution Observation of Decimetric Radio Spikes Emitted by Solar Flares - First Results of the Phoenix-3 Spectrometer. Sol. Phys. 2009, 260, 375–388, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/0909.4137]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alissandrakis, C.E.; Bouratzis, C.; Hillaris, A. High-resolution observations with ARTEMIS-JLS and the NRH. III. Spectroscopy and imaging of fiber bursts. Astron & Astrophys. 2019, 627, A133,[arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1906.03434]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, A.O. Decimeter Burst Emission and Particle Acceleration. In Proceedings of the Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Gary, D.E.; Keller, C.U., Eds., 2004, Vol. 314, Astrophysics and Space Science Library, p. 203. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, B.; Karlický, M.; Mészárosová, H.; Huang, J.; Tan, C.; Simões, P.J.A. Solar Radio Bursts with Spectral Fine Structures in Preflares. Astrophys. J. 2015, 799, 30, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1411.4766]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Tan, B. Microwave Bursts with Fine Structures in the Decay Phase of a Solar Flare. Astrophys. J. 2012, 745, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouratzis, C.; Preka-Papadema, P.; Hillaris, A.; Tsitsipis, P.; Kontogeorgos, A.; Kurt, V.G.; Moussas, X. Radio Observations of the 20 January 2005 X-class Flare. Sol. Phys. 2010, 267, 343–359, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/0912.3782]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalenić, J.; Vršnak, B.; Zlobec, P.; Hillaris, A.; Messerotti, M. Classification and Properties of Supershort Solar Radio Bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2006, 642, L77–L80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalenić, J.; Hillaris, A.; Zlobec, P.; Vršnak, B. Millisecond solar radio bursts in the metric wavelength range. In Proceedings of the Recent Advances in Astronomy and Astrophysics; Solomos, N., Ed., 2006, Vol. 848, American Institute of Physics Conference Series, pp. 224–228, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1009.4477]. [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Tan, B.; Yan, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Dou, Y. Fine structure events in microwave emission during solar minimum. Solar-Terrestrial Physics 2019, 5, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Tan, C. Microwave Quasi-periodic Pulsation with Millisecond Bursts in a Solar Flare on 2011 August 9. Astrophys. J. 2012, 749, 28, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1202.1578]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgaroy, E.O. Solar noise storms. Oxford Pergamon Press International Series on Natural Philosophy 1977, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, A.O. Millisecond radio spikes. Sol. Phys. 1986, 104, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, A.O. 4.1.2.8 Radio bursts of the non-thermal Sun. Solar System, Landolt Börnstein- Group VI Astronomy and Astrophysics, Volume 4B. 2009, p. 189. [CrossRef]
- Iwai, K.; Miyoshi, Y.; Masuda, S.; Tsuchiya, F.; Morioka, A.; Misawa, H. Spectral Structures and Their Generation Mechanisms for Solar Radio Type-I Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2014, 789, 4, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1405.0708]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgarøy, . Intermediate drift bursts. In Proceedings of the CESRA-3, Committee of European Solar Radio Astronomers; Delannoy, J.; Poumeyrol, F., Eds., 1972, Vol. 3, p. 174.
- Kuijpers, J. A possible generating mechanism for intermediate drift bursts. In Proceedings of the CESRA-3, Committee of European Solar Radio Astronomers; Delannoy, J.; Poumeyrol, F., Eds., 1972, Vol. 3, p. 130.
- Kuijpers, J. Generation of intermediate drift bursts in solar type IV radio continua through coupling of whistlers and Langmuir waves. Sol. Phys. 1975, 44, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijpers, J. Theory of type IV DM bursts. In Proceedings of the Radio Physics of the Sun; M. R. Kundu & T. E. Gergely., Ed., 1980, Vol. 86, IAU Symposium, pp. 341–360.
- Elgarøy. Intermediate drift bursts. Institute of Theoretical Astrophysics, Blindern-Oslo 1982, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Aurass, H.; Rausche, G.; Mann, G.; Hofmann, A. Fiber bursts as 3D coronal magnetic field probe in postflare loops. Astron & Astrophys. 2005, 435, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, G.; Baumgaertel, K.; Chernov, G.P.; Karlicky, M. Interpretation of a special fine structure in type-IV solar radio bursts. Sol. Phys. 1989, 120, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, G.P. Whistlers in the solar corona and their relevance to fine structures of type IV radio emission. Sol. Phys. 1990, 130, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, G.P. Solar Radio Bursts with Drifting Stripes in Emission and Absorption. Space Sci. Rev. 2006, 127, 195–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, G.P. Unusual stripes in emission and absorption in solar radio bursts: Ropes of fibers in the meter wave band. Astronomy Letters 2008, 34, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernold, T.E.X.; Treumann, R.A. The fiber fine structure during solar type IV radio bursts - Observations and theory of radiation in presence of localized whistler turbulence. Astrophys. J. 1983, 264, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alissandrakis, C.E.; Gary, D.E. Radio Measurements of the Magnetic field in the Solar Chromosphere and the Corona. Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences 2021, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B. Diagnostic Functions of Solar Coronal Magnetic Fields from Radio Observations. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics 2022, 22, 072001, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/2205.00136]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ning, H.; Kong, X.; Wang, B.; Hosseinpour, M. Plasma Emission Induced by Electron Cyclotron Maser Instability in Solar Plasmas with a Large Ratio of Plasma Frequency to Gyrofrequency. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 891, L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, J.; Ning, H.; Zhang, Z. An alternative form of the fundamental plasma emission through the coalescence of Z-mode waves with whistlers. Physics of Plasmas 2021, 28, 040701, [arXiv:physics.plasm-ph/2104.04267]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, G.P. Manifestation of quasilinear diffusion on whistlers in the fine-structure radio sources of solar radio bursts. Plasma Physics Reports 2005, 31, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnik, E.Y.; Zaitsev, V.V.; Aurass, H.; Mann, G. A Special Radio Spectral Fine Structure Used for Plasma Diagnostics in Coronal Magnetic Traps. Sol. Phys. 2009, 255, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnik, E.Y.; Zaitsev, V.V.; Aurass, H.; Mann, G.; Hofmann, A. Solar type IV burst spectral fine structures. II. Source model. Astron & Astrophys. 2003, 410, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurass, H.; Klein, K.L.; Zlotnik, E.Y.; Zaitsev, V.V. Solar type IV burst spectral fine structures . I. Observations. Astron & Astrophys. 2003, 410, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlický, M.; Bárta, M.; Jiřička, K.; Mészárosová, H.; Sawant, H.S.; Fernandes, F.C.R.; Cecatto, J.R. Radio bursts with rapid frequency variations - Lace bursts. Astron & Astrophys. 2001, 375, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.C.R.; Sawant, H.S.; Cecatto, J.R.; Krishan, V.; Karlický, M.; Rosa, R.R. Evidence of Plasma Resonance Instability from Observations of Solar Decimetric Fine Structures. Brazilian Journal of Physics 2003, 33, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.C.R.; Krishan, V.; Andrade, M.C.; Cecatto, J.R.; Freitas, D.C.; Sawant, H.S. High resolution studies of intermediate drift bursts. Advances in Space Research 2003, 32, 2545–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Bastian, T.S.; Gary, D.E.; Jing, J. Spatially and Spectrally Resolved Observations of a Zebra Pattern in a Solar Decimetric Radio Burst. Astrophys. J. 2011, 736, 64, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1105.0715]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, G.P.; Markeev, A.K.; Poquerusse, M.; Bougeret, J.L.; Klein, K.L.; Mann, G.; Aurass, H.; Aschwanden, M.J. New features in type IV solar radio emission: combined effects of plasma wave resonances and MHD waves. Astron & Astrophys. 1998, 334, 314–324. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Z.; Wu, H.; Xu, F.; Meng, X. High-Frequency Evolving Emission Lines for the 25 August 1999 Solar Flare. Sol. Phys. 2008, 250, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.Y.; Yao, Q.J.; Meng, X.; Wu, H.A. Some Observed Results of Solar Radio Spectrometer at 4.5-7.5 GHz. Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics 2001, 1, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberoi, D.; Evarts, E.R.; Rogers, A.E.E. High Temporal and Spectral Resolution Interferometric Observations of Unusual Solar Radio Bursts. Sol. Phys. 2009, 260, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melrose, D.B.; Dulk, G.A. Electron-cyclotron masers as the source of certain solar and stellar radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 1982, 259, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleishman, G.D.; Mel’Nikov, V.F. Millisecond solar radio spikes. Soviet Physics Uspekhi 1998, 41, 1157–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, G.P. Fine Structure of Solar Radio Bursts; Vol. 375, Springer Science & Business Media, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Bakunin, L.M.; Chernov, G.P. Broadband Solar Bursts of the Spike Type. Sov. Astron. 1985, 29, 564–568. [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowski, B.P.; Kus, A.J. Millisecond solar radio spikes observed at 1420 MHz. Mem. Societa Astronomica Italiana 2007, 78, 264. [Google Scholar]
- Sawant, H.S.; Fernandes, F.C.R.; Cecatto, J.R.; Vats, H.O.; Neri, J.A.C.F.; Portezani, V.A.; Martinon, A.R.F.; Karlický, M.; Jiřička, K.; Mészárosová, H. Decimetric dot-like structures. Advances in Space Research 2002, 29, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroubalos, C.; Poquerusse, M.; Bougeret, J.; Crepel, R. Radio evidence for a magnetic mirror effect on beams of subrelativistic electrons in the solar corona. Astrophys. J. 1987, 319, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, A.A. On the superfine structure of solar microwave bursts. Astronomy Letters 2007, 33, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, G.P.; Sych, R.A.; Meshalkina, N.S.; Yan, Y.; Tan, C. Spectral and spatial observations of microwave spikes and zebra structure in the short radio burst of May 29, 2003. Astron & Astrophys. 2012, 538, A53, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1111.5405]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Yan, Y.; Tan, C.; Sych, R.; Gao, G. Microwave Zebra Pattern Structures in the X2.2 Solar Flare on 2011 February 15. Astrophys. J. 2012, 744, 166, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1109.5765]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárta, M.; Karlický, M. Turbulent plasma model of the narrowband dm-spikes. Astron & Astrophys. 2001, 379, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárta, M.; Karlický, M. Radio Signatures of Solar Flare Reconnection. Astrophys. J. 2005, 631, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárta, M.; Büchner, J.; Karlický, M.; Skála, J. Spontaneous Current-layer Fragmentation and Cascading Reconnection in Solar Flares. I. Model and Analysis. Astrophys. J. 2011, 737, 24, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1011.4035]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da̧browski, B.P.; Rudawy, P.; Falewicz, R.; Siarkowski, M.; Kus, A.J. Millisecond radio spikes in the decimetre band and their related active solar phenomena. Astron & Astrophys. 2005, 434, 1139–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantos, P.; Alissandrakis, C.E.; Rigaud, D. Quiet-Sun Emission and Local Sources at Meter and Decimeter Wavelengths and Their Relationship with the Coronal Neutral Sheet. Sol. Phys. 1992, 137, 225–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantos, P. Low Frequency Observations of the Quiet Sun: a Review. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Nobeyama Symposium; Bastian, T.S.; Gopalswamy, N.; Shibasaki, K., Eds., 1999, pp. 11–24.
- Payne-Scott, R.; Yabsley, D.E.; Bolton, J.G. Relative Times of Arrival of Bursts of Solar Noise on Different Radio Frequencies. Nature 1947, 160, 256–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, J.P.; McCready, L.L. Observations of the Spectrum of High-Intensity Solar Radiation at Metre Wavelengths. I. The Apparatus and Spectral Types of Solar Burst Observed. Australian Journal of Scientific Research A Physical Sciences 1950, 3, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, J.P.; Smerd, S.F. Radio Bursts from the Solar Corona. Annual Reviews Astron.& Astrophys. 1972, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, Y. On the Exciters of Type II and Type III Solar Radio Bursts. PPubl. ASJ 1960, 12, 376. [Google Scholar]
- Aurass, H.; Mann, G. Radio Observation of Electron Acceleration at Solar Flare Reconnection Outflow Termination Shocks. Astrophys. J. 2004, 615, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, G.; Warmuth, A.; Aurass, H. Generation of highly energetic electrons at reconnection outflow shocks during solar flares. Astron & Astrophys. 2009, 494, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmuth, A.; Mann, G.; Aurass, H. Modelling shock drift acceleration of electrons at the reconnection outflow termination shock in solar flares. Observational constraints and parametric study. Astron & Astrophys. 2009, 494, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysaphi, N.; Reid, H.A.S.; Kontar, E.P. First Observation of a Type II Solar Radio Burst Transitioning between a Stationary and Drifting State. Astrophys. J. 2020, 893, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smerd, S.F.; Sheridan, K.V.; Stewart, R.T. Split-band structure in type II radio bursts from the sun. Astrophysics Letters 1975, 16, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Du, G.; Chen, Y.; Lv, M.; Kong, X.; Feng, S.; Guo, F.; Li, G. Temporal Spectral Shift and Polarization of a Band-splitting Solar Type II Radio Burst. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2014, 793, L39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Kong, X.; Chen, Y.; Feng, S.; Wang, B.; Li, G. An Observational Revisit of Band-split Solar Type-II Radio Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2015, 812, 52, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1509.03832]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginzburg, V.L.; Zhelezniakov, V.V. On the mechanisms of sporadic solar radio emission. In Proceedings of the URSI Symp. 1: Paris Symposium on Radio Astronomy; Bracewell, R.N., Ed., 1959, Vol. 9, IAU Symposium, p. 574.
- Gopalswamy, N. Recent advances in the long-wavelength radio physics of the Sun. Planet. Space Sci. 2004, 52, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.A. Solar Radio Bursts of Spectral Type II. Australian Journal of Physics 1959, 12, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, V.V.; Stepanov, A.V. Origin of electron streams generating the “herringbone” structure of type II bursts. Radiophysics and Quantum Electronics 1974, 17, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, I.H.; Robinson, R.D. Herringbone bursts associated with type II solar radio emission. Sol. Phys. 1987, 111, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandas, M.; Karlický, M. On a Herringbone Structure of Solar Type II Bursts. In Proceedings of the Magnetic Fields and Solar Processes; A. Wilson & et al.., Ed., 1999, Vol. 448, ESA Special Publication, pp. 1071–+.
- Carley, E.P.; Long, D.M.; Byrne, J.P.; Zucca, P.; Bloomfield, D.S.; McCauley, J.; Gallagher, P.T. Quasiperiodic acceleration of electrons by a plasmoid-driven shock in the solar atmosphere. Nature Physics 2013, 9, 811–816, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1406.0743]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorovskyy, V.V.; Melnik, V.N.; Konovalenko, A.A.; Brazhenko, A.I.; Panchenko, M.; Poedts, S.; Mykhaylov, V.A. Fine and Superfine Structure of the Decameter-Hectometer Type II Burst on 7 June 2011. Sol. Phys. 2015, 290, 2031–2042, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1508.06801]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, G.P. The relationship between fine structure of the solar radio emission at meter wavelengths and coronal transients. Astronomy Letters 1997, 23, 827–837. [Google Scholar]
- Chernov, G.P.; Stanislavsky, A.A.; Konovalenko, A.A.; Abranin, E.P.; Dorovsky, V.V.; Rucker, G.O. Fine structure of decametric type II radio bursts. Astronomy Letters 2007, 33, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Bastian, T.S.; Shen, C.; Gary, D.E.; Krucker, S.; Glesener, L. Particle acceleration by a solar flare termination shock. Science 2015, 350, 1238–1242, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1512.02237]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomichev, V.V.; Chernov, G.P. Solar Radio Bursts Associated with Standing Shock Waves. Geomagnetism and Aeronomy 2020, 60, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomichev, V.; Chernov, G. Termination Shock as a Source of Unusual Solar Radio Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2020, 901, 65, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/2008.06105]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauphin, C.; Vilmer, N.; Krucker, S. Observations of a soft X-ray rising loop associated with a type II burst and a coronal mass ejection in the 03 November 2003 X-ray flare. Astron & Astrophys. 2006, 455, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedel, M.; Benz, A.O. Time profiles of solar radio spikes. Astron & Astrophys. 1990, 231, 202–212. [Google Scholar]
- Mészárosová, H.; Veronig, A.; Zlobec, P.; Karlický, M. Analysis of solar narrow band dm-spikes observed at 1420 and 2695 MHz. Astron & Astrophys. 2003, 407, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozhansky, I.V.; Fleishman, G.D.; Huang, G.L. Millisecond Microwave Spikes: Statistical Study and Application for Plasma Diagnostics. Astrophys. J. 2008, 681, 1688–1697, [0803.2380]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csillaghy, A.; Benz, A.O. The bandwidth of millisecond radio spikes in solar flares. Astron & Astrophys. 1993, 274, 487. [Google Scholar]
- Young, C.W.; Spencer, C.L.; Moreton, G.E.; Roberts, J.A. A Preliminary Study of the Dynamic Spectra of Solar Radio Bursts in the Frequency Range 500-950 Mc/s. Astrophys. J. 1961, 133, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiricka, K.; Karlický, M.; Mészárosová, H. High-frequency Intermediate Drift Bursts and Zebra Patterns. In Proceedings of the Magnetic Fields and Solar Processes; Wilson, A.; et al.., Eds., 1999, Vol. 448, ESA Special Publication, p. 829.
- Chernov, G.P. Some Features of the Formation of Filaments in Type IV Radio Bursts. Sov. Astron. 1990, 34, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Kuijpers, J.; Slottje, C. Fiber bursts concurrent with a weak noise storm. Sol. Phys. 1976, 46, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messmer, P.; Chernov, G.P.; Zlobec, P.; Gorgutsa, R. Unusual behaviour of zebra-pattern in the event July 28, 1999. In Proceedings of the Solar Variability: From Core to Outer Frontiers; Wilson, A., Ed., 2002, Vol. 2, ESA Special Publication, pp. 701–704.
- Chernov, G.P.; Fomichev, V.V. Slowly drifting radio fibres. MNRAS 2023, 522, 1930–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, G.P.; Yan, Y.; Fu, Q.; Tan, C.; Wang, S. Unusual Zebra Patterns in the Decimeter Wave Band. Sol. Phys. 2008, 250, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, G. Fiber bursts and related phenomena. Astronomische Nachrichten 1990, 311, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, G.P. Behaviour of Whistlers in Coronal Magnetic Traps and its Relevance to a New Fine Structure in Solar Type–IV Radio Bursts. In Proceedings of the Basic Plasma Processes on the Sun; Priest, E.R.; Krishan, V., Eds., 1990, Vol. 142, IAU Symposium, p. 515.
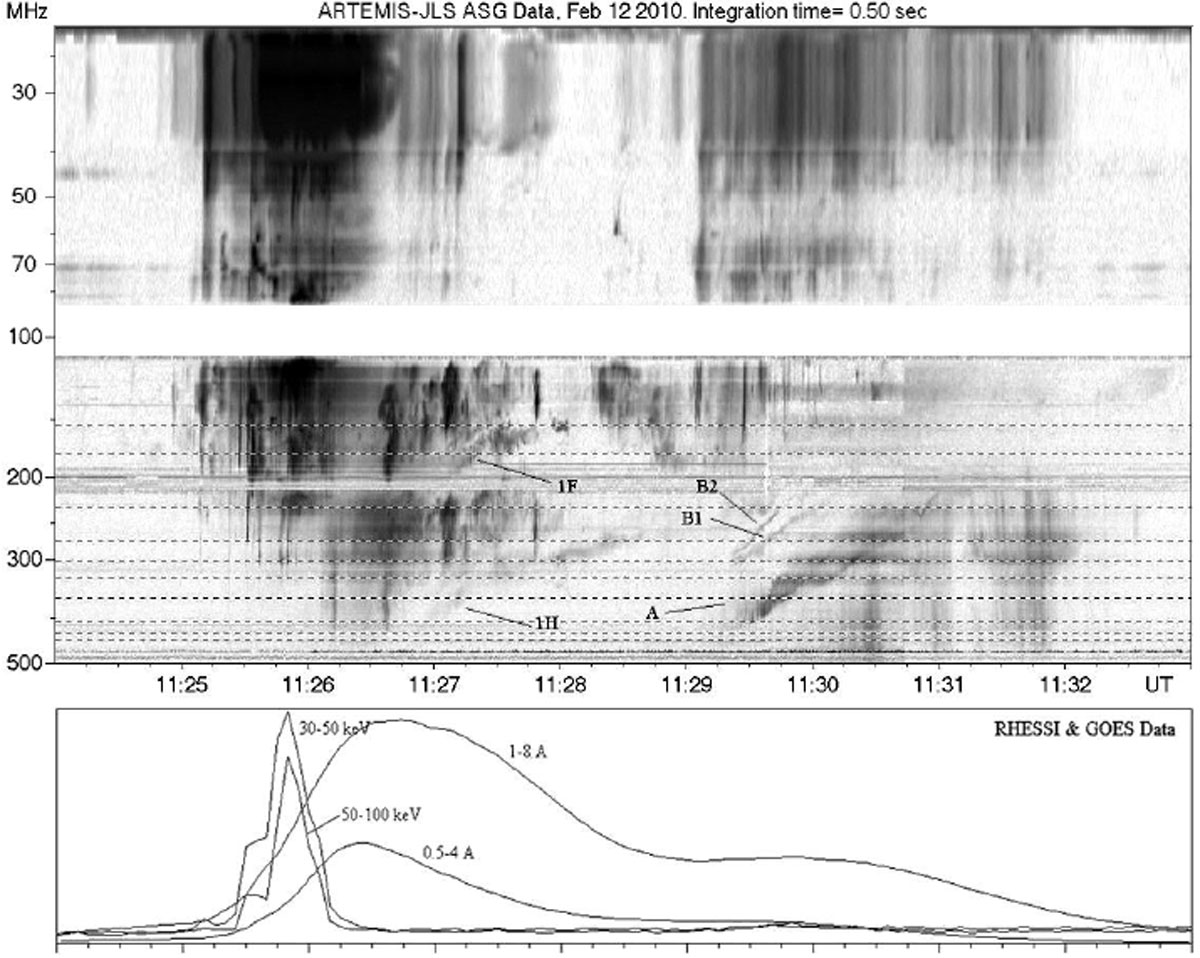
- Chernov, G.P.; Fomichev, V.V.; Gorgutsa, R.V.; Markeev, A.K.; Sobolev, D.E.; Hillaris, A.; Alissandrakis, K. Fine structural features of radio-frequency radiation of the solar flare of February 12, 2010. Geomagnetism and Aeronomy 2014, 54, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, G. In Solar Flares: Investigations and Selected Research; Nova Science Publishers, Inc., 2016; chapter 5: Latest news on zebra patterns in the solar radio emission, pp. 101–150. ISBN: 978-1-53610-204-8.
- Benz, A.O.; Mann, G. Intermediate drift bursts and the coronal magnetic field. Astron & Astrophys. 1998, 333, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, Y.; Ono, T.; Tsuchiya, F.; Misawa, H.; Kumamoto, A.; Katoh, Y.; Masuda, S.; Miyoshi, Y. Narrowband frequency-drift structures in solar type IV bursts. Earth, Planets, and Space 2013, 65, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, V.N.; Konovalenko, A.A.; Brazhenko, A.I.; Rucker, H.O.; Dorovskyy, V.V.; Abranin, E.P.; Lecacheux, A.; Lonskaya, A.S. Bursts in emission and absorption as a fine structure of Type IV bursts. In Proceedings of the American Institute of Physics Conference Series; Chakrabarti, S.K.; Zhuk, A.I.; Bisnovatyi-Kogan, G.S., Eds., 2010, Vol. 1206, American Institute of Physics Conference Series, pp. 450–454. [CrossRef]
- Slottje, C. Peculiar absorption and emission microstructures in the type IV solar radio outburst of March 2, 1970. Sol. Phys. 1972, 25, 210–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausche, G.; Aurass, H.; Mann, G. Fiber Bursts and the Coronal Magnetic Field. Central European Astrophysical Bulletin 2008, 32, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Elgaroy, O.; Soldal, O. Correlation between bandwidth and frequency drift velocity of intermediate drift bursts. Astron & Astrophys. 1981, 104, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, K.L.; Trottet, G.; Lantos, P.; Delaboudinière, J.P. Coronal electron acceleration and relativistic proton production during the 14 July 2000 flare and CME. Astron & Astrophys. 2001, 373, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, S.; Kosugi, T.; Hudson, H.S. A Hard X-ray Two-Ribbon Flare Observed with Yohkoh/HXT. Sol. Phys. 2001, 204, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, R.; Fu, Q.; Tan, C.; Xu, L.; Wang, S.; Lin, H. Broadband Radio Bursts and Fine Structures during the Great Solar Event on 14 July 2000. Sol. Phys. 2001, 204, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroubalos, C.; Alissandrakis, C.E.; Hillaris, A.; Nindos, A.; Tsitsipis, P.; Moussas, X.; Bougeret, J.L.; Bouratzis, K.; Dumas, G.; Kanellakis, G.; et al. ARTEMIS IV Radio Observations of the 14 July 2000 Large Solar Event. Sol. Phys. 2001, 204, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, K.K.; Forbes, T.G. Predicted Light Curves for a Model of Solar Eruptions. Astrophys. J. 2005, 630, 1133–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgaroy, O. Discussion on the classification of fine structures in continua. Sol. Phys. 1986, 104, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.W.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, B.; Wu, Z.; Kong, X.L.; Du, Q.F.; Zhang, J.R.; Zhao, G.Q. Harmonics of Solar Radio Spikes at Metric Wavelengths. Sol. Phys. 2018, 293, 39, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1802.03541]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.W. The properties of solar radio spikes with harmonics and the associated EUV brightenings. Astrophys. &Space Sci. 2019, 364, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalenić, J.; Marqué, C.; Fallows, R.A.; Mann, G.; Vocks, C.; Zucca, P.; Dabrowski, B.P.; Krankowski, A.; Melnik, V. Fine Structure of a Solar Type II Radio Burst Observed by LOFAR. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 897, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausche, G.; Aurass, H.; Mann, G.; Karlický, M.; Vocks, C. On Solar Intermediate Drift Radio Bursts at Decimeter and Meter Wavelength. Sol. Phys. 2007, 245, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carley, E.P.; Vilmer, N.; Simões, P.J.A.; Ó Fearraigh, B. Estimation of a coronal mass ejection magnetic field strength using radio observations of gyrosynchrotron radiation. Astron & Astrophys. 2017, 608, A137, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1709.05184]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gary, D.E. New Insights from Imaging Spectroscopy of Solar Radio Emission. Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics 2023, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gary, D.E.; Hurford, G.J.; Nita, G.M.; White, S.M.; McTiernan, J.; Fleishman, G.D. The Expanded Owens Valley Solar Array (EOVSA). In Proceedings of the American Astronomical Society Meeting Abstracts #224, 2014, Vol. 224, American Astronomical Society Meeting Abstracts, p. 123.60.
- Gary, D.E. Early Observations with the Expanded Owens Valley Solar Array. In Proceedings of the AAS/Solar Physics Division Abstracts #47, 2016, Vol. 47, AAS/Solar Physics Division Meeting, p. 301.01.
- Altyntsev, A.; Lesovoi, S.; Globa, M.; Gubin, A.; Kochanov, A.; Grechnev, V.; Ivanov, E.; Kobets, V.; Meshalkina, N.; Muratov, A.; et al. Multiwave Siberian Radioheliograph. Solar-Terrestrial Physics 2020, 6, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogod, V.M.; Lebedev, M.K.; Ovchinnikova, N.E.; Ripak, A.M.; Storozhenko, A.A. Spectroradiometry of the Solar Corona on the RATAN-600. Cosmic Research 2023, 61, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, F.; Geng, L.; Chen, L.; Tan, C.; Chen, X.; Su, C.; Tan, B. Mingantu Spectral Radioheliograph for Solar and Space Weather Studies. Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences 2021, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, M.; Gunst, A.W.; Nijboer, R. The LOFAR Telescope: System Architecture and Signal Processing. IEEE Proceedings 2009, 97, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Haarlem, M.P.; Wise, M.W.; Gunst, A.W.; Heald, G.; McKean, J.P.; Hessels, J.W.T.; de Bruyn, A.G.; Nijboer, R.; Swinbank, J.; Fallows, R.; et al. LOFAR: The LOw-Frequency ARray. Astron & Astrophys. 2013, 556, A2, [arXiv:astro-ph.IM/1305.3550]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowski, B.P.; Krankowski, A.; Rothkaehl, H.; Błaszkiewicz, L. Solar Studies with the LOFAR Telescope. In Proceedings of the 37th Meeting of the Polish Astronomical Society; Różańska, A.; Bejger, M., Eds., 2016, Vol. 3, pp. 116–119.
- Morosan, D.E.; Gallagher, P.T.; Zucca, P.; Fallows, R.; Carley, E.P.; Mann, G.; Bisi, M.M.; Kerdraon, A.; Konovalenko, A.A.; MacKinnon, A.L.; et al. LOFAR tied-array imaging of Type III solar radio bursts. Astron & Astrophys. 2014, 568, A67, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1407.4385]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carley, E.P.; Baldovin, C.; Benthem, P.; Bisi, M.M.; Fallows, R.A.; Gallagher, P.T.; Olberg, M.; Rothkaehl, H.; Vermeulen, R.; Vilmer, N.; et al. Radio observatories and instrumentation used in space weather science and operations. Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate 2020, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zucca, P.; Kozarev, K.; Carley, E.; Wang, C.; Franzen, T.; Dabrowski, B.; Krankowski, A.; Magdalenic, J.; Vocks, C. Imaging of the Quiet Sun in the Frequency Range of 20-80 MHz. Astrophys. J. 2022, 932, 17, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/2205.00065]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nindos, A.; Kontar, E.P.; Oberoi, D. Solar physics with the Square Kilometre Array. Advances in Space Research 2019, 63, 1404–1424, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1810.04951]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, S.; Carley, E.P.; Oberoi, D.; Gallagher, P.T. Imaging-spectroscopy of a band-split type II solar radio burst with the Murchison Widefield Array. Astron & Astrophys. 2023, 670, A169, [arXiv:astro-ph.SR/2212.07698]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.l.; Cheng, J.; Tan, C.m.; Kou, H.x. Scaling-laws of Radio Spike Bursts and Their Constraints on New Solar Radio Telescopes. Chinese Astronomy and Astrophysics 2019, 43, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, T.S.; Gary, D.E.; White, S.M.; Hurford, G.J. Toward a Frequency-Agile Solar Radiotelescope. In Proceedings of the Synoptic Solar Physics; Balasubramaniam, K.S.; Harvey, J.; Rabin, D., Eds., 1998, Vol. 140, Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series, p. 563.
- Lequeux, J.; Bertout, C.; Aghanim, N.; Forveille, T. Jean-Louis Steinberg (1922-2016). Astron & Astrophys. 2016, 586, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da̧browski, B.P.; Rudawy, P.; Karlický, M. Millisecond Radio Spikes in the Decimetric Band. Sol. Phys. 2011, 273, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, V.N.; Shevchuk, N.V.; Konovalenko, A.A.; Rucker, H.O.; Dorovskyy, V.V.; Poedts, S.; Lecacheux, A. Solar Decameter Spikes. Sol. Phys. 2014, 289, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchuk, N.V.; Melnik, V.N.; Poedts, S.; Dorovskyy, V.V.; Magdalenic, J.; Konovalenko, A.A.; Brazhenko, A.I.; Briand, C.; Frantsuzenko, A.V.; Rucker, H.O.; et al. The Storm of Decameter Spikes During the Event of 14 June 2012. Sol. Phys. 2016, 291, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, A.O.; Csillaghy, A.; Aschwanden, M.J. Metric spikes and electron acceleration in the solar corona. Astron & Astrophys. 1996, 309, 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Messmer, P.; Benz, A.O. The Minimum bandwidth of narrowband spikes in solar flare decimetric radio waves. Astron & Astrophys. 2000, 354, 287–295, [arXiv:astro-ph/9912502]. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Xie, R.X. Millisecond spikes in a short decimetric solar radio burst. Sol. Phys. 1999, 185, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, G.P.; Fu, Q.J.; Lao, D.B.; Hanaoka, Y. Ion-Sound Model of Microwave Spikes with Fast Shocks in the Reconnection Region. Sol. Phys. 2001, 201, 153–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Yan, Y.H.; Liu, Y.Y.; Fu, Q.J.; Tan, B.L.; Zhang, Y. Solar Radio Spikes in 2.6 - 3.8 GHz during the 13 December 2006 Event. Sol. Phys. 2008, 253, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, A.O.; Su, H.; Magun, A.; Stehling, W. Millisecond microwave spikes at 8 GHz during solar flares. Astron.& Astrophys.S 1992, 93, 539–544. [Google Scholar]
| 1 | see also technical description at http://artemis-iv.phys.uoa.gr/ARTEMIS%20PRESENTATION%20FOR%20LOIS.htm
|
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 |


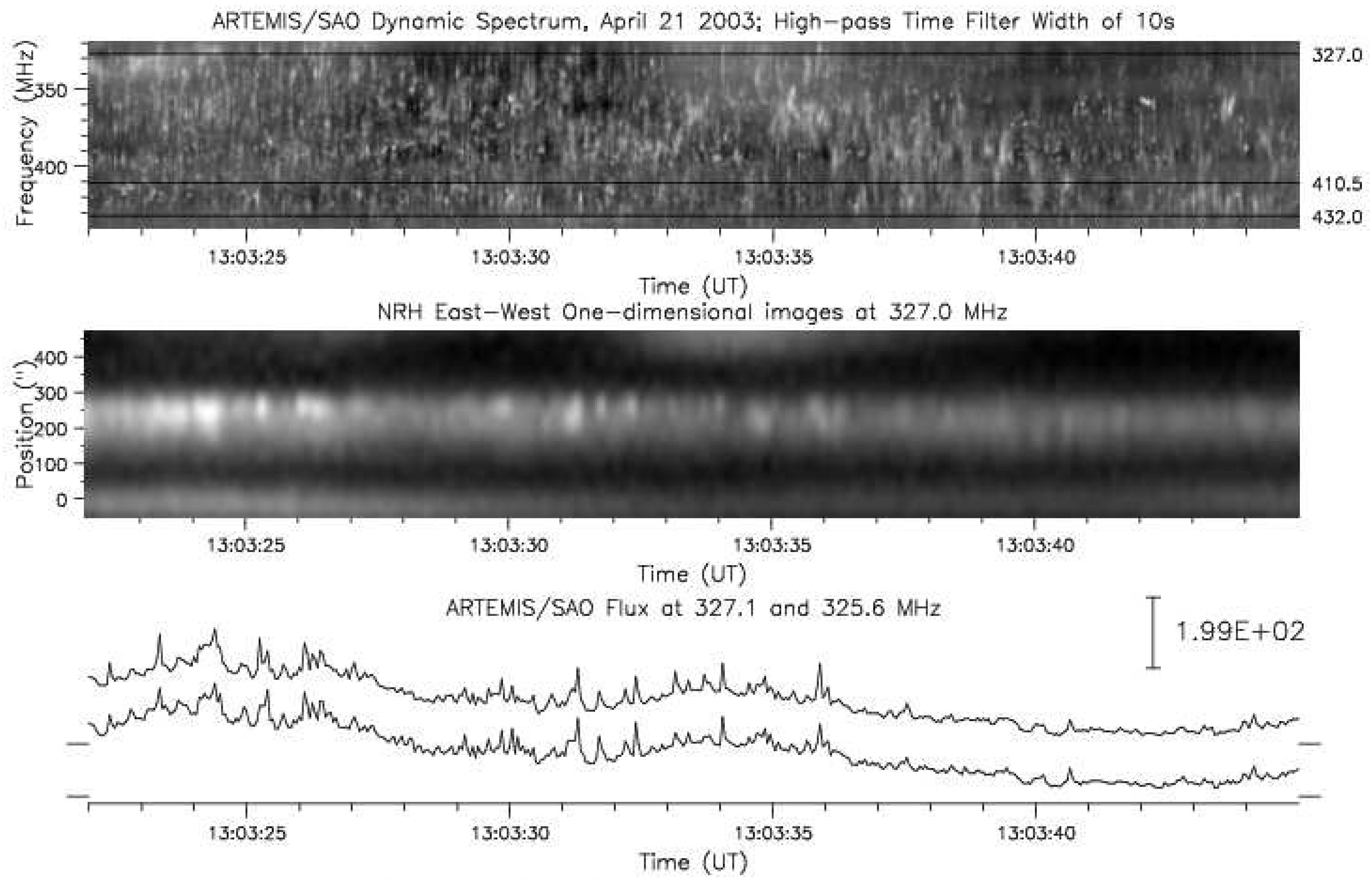
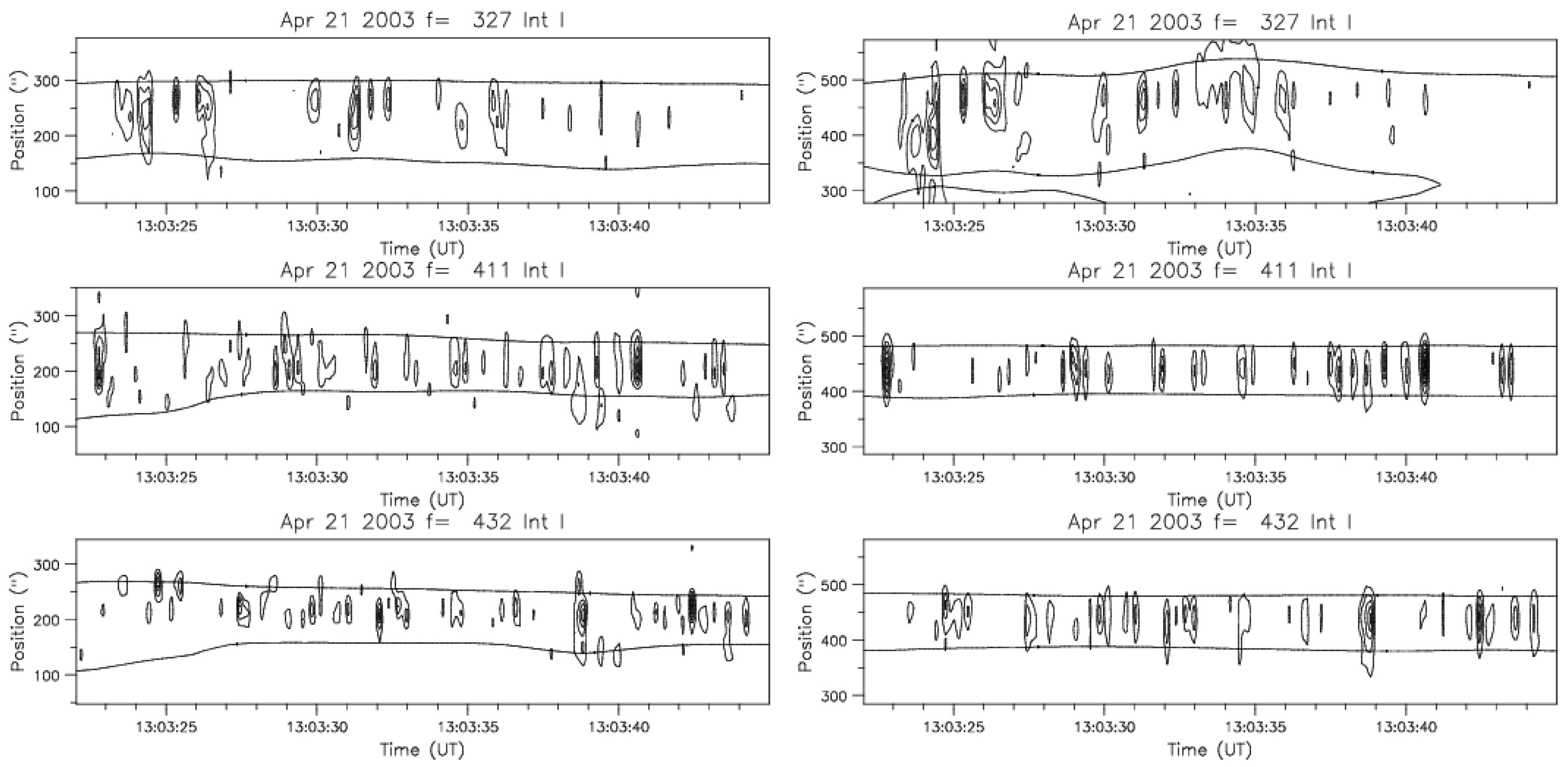


| Parameter | 327 | 411 | 432 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MHz | MHz | MHz | |
| Number of spikes | 8 | 15 | 13 |
| Shift, | 35 | 11 | 18 |
| Spike , 10 K | 1.2 | 1.9 | 1.6 |
| ratio, spikes/background | 0.57 | 0.85 | 0.66 |
| Area ratio from 2D | 0.86 | 0.81 | 0.83 |
| Area ratio from 1D | 0.32 | 0.50 | 0.41 |
| Size from 1D, in | 86 | 82 | 72 |
| Parameter | Type II spike-like | Type IV |
|---|---|---|
| bursts | spikes | |
| Number of spikes | 642 | 11579 |
| Number of spikes/event | 160 | 330 |
| Duration (ms) | ||
| Average | 96 | 100 |
| Standard deviation | 54 | 66 |
| Relative bandwidth | ||
| Average | 1.7% | 2.0% |
| Standard deviation | 0.5% | 1.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





