Submitted:
24 August 2023
Posted:
29 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Energy Model for the Confined Electron
3. Calculation of Partition Function and Thermodynamic Functions
3.1. Entropy of the System and Caloric Response
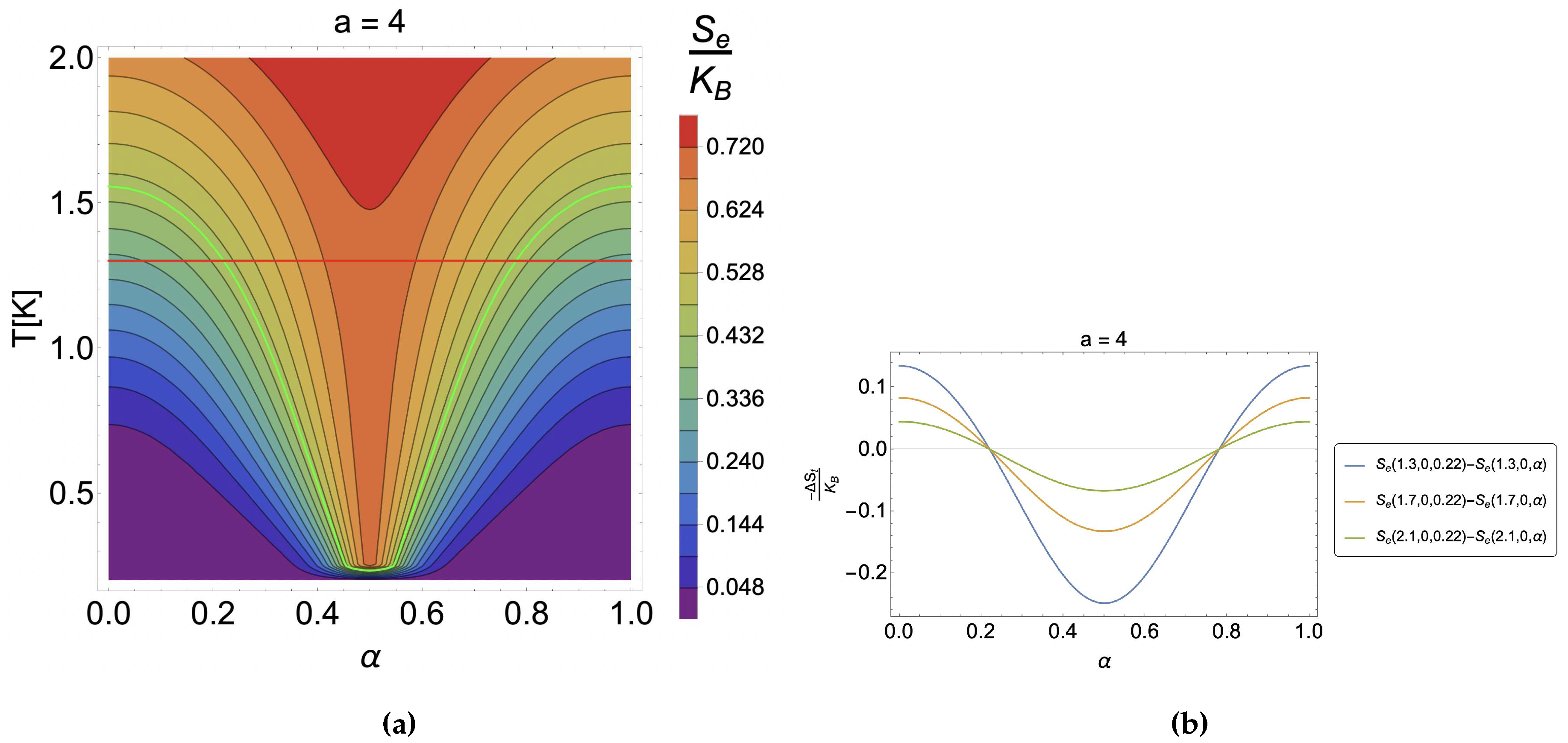
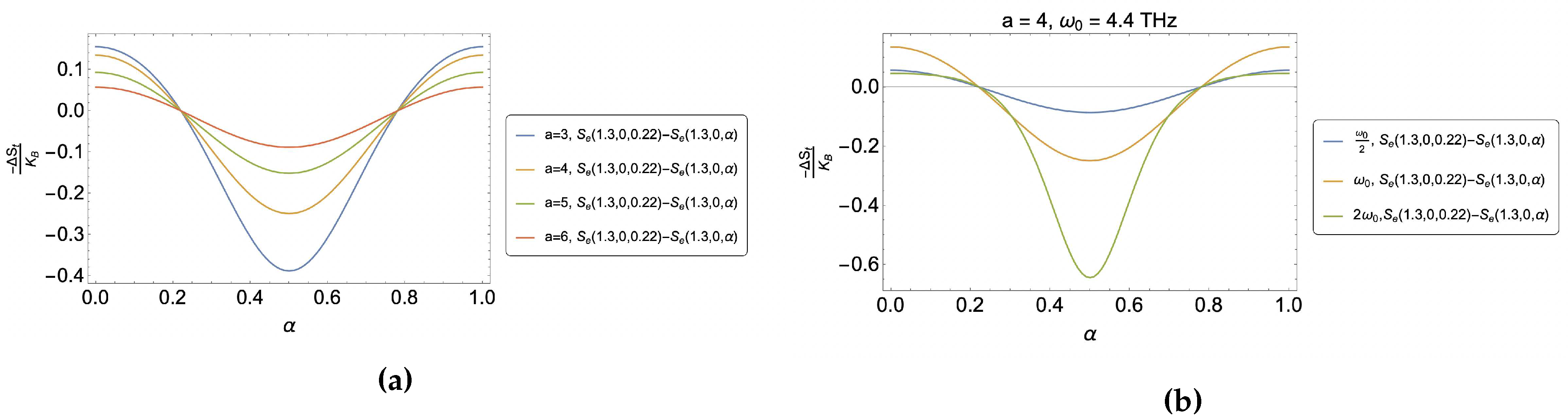
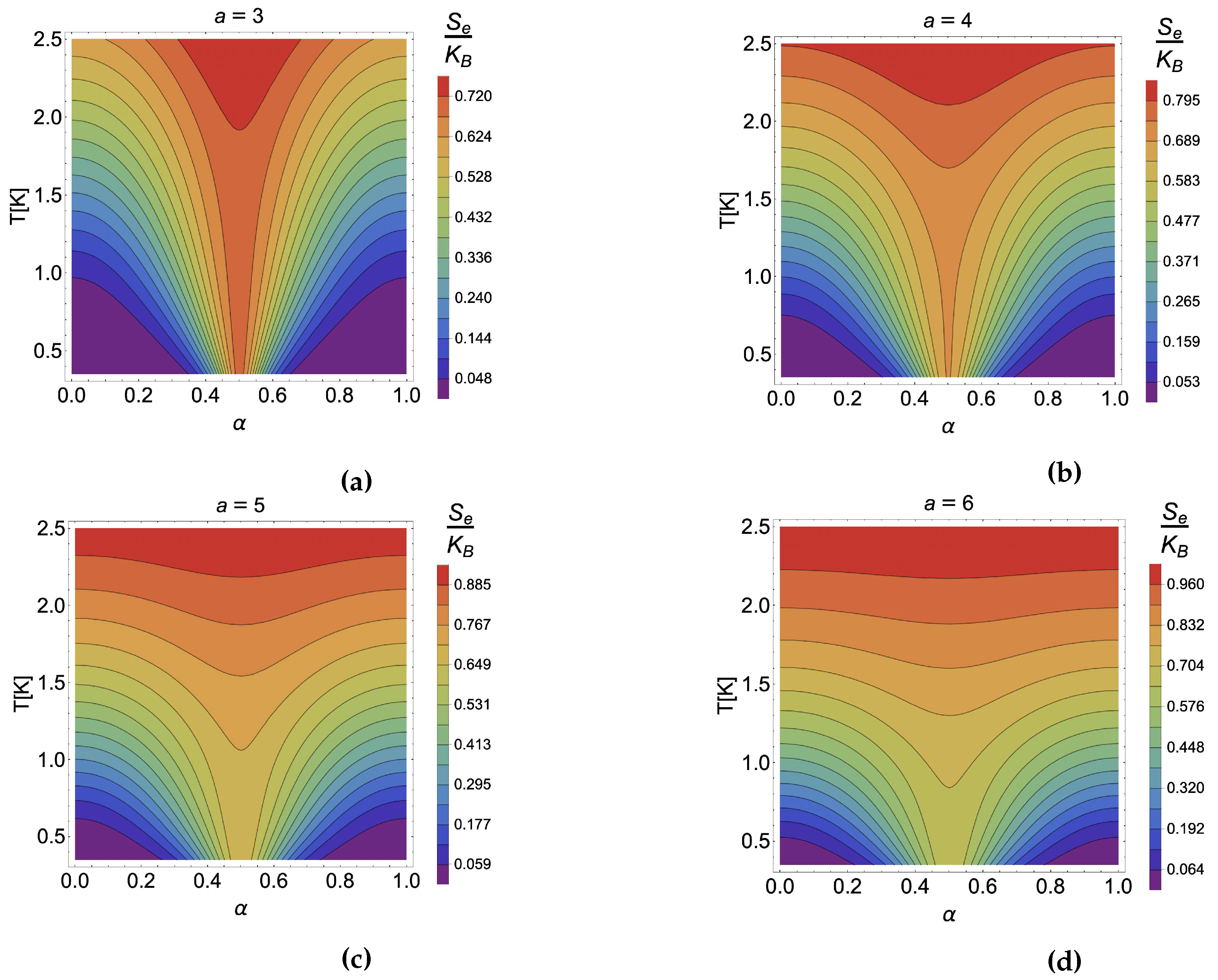
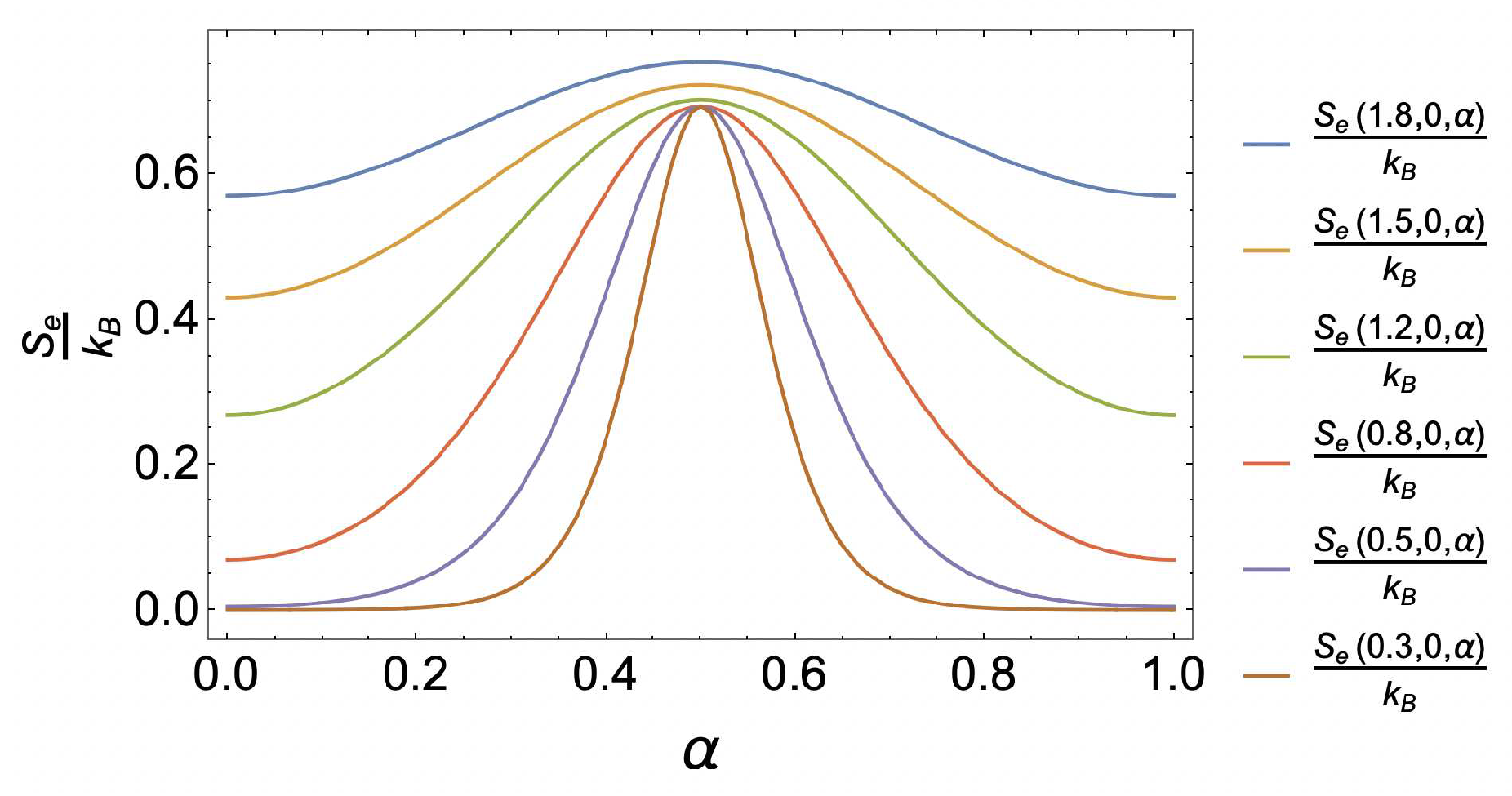
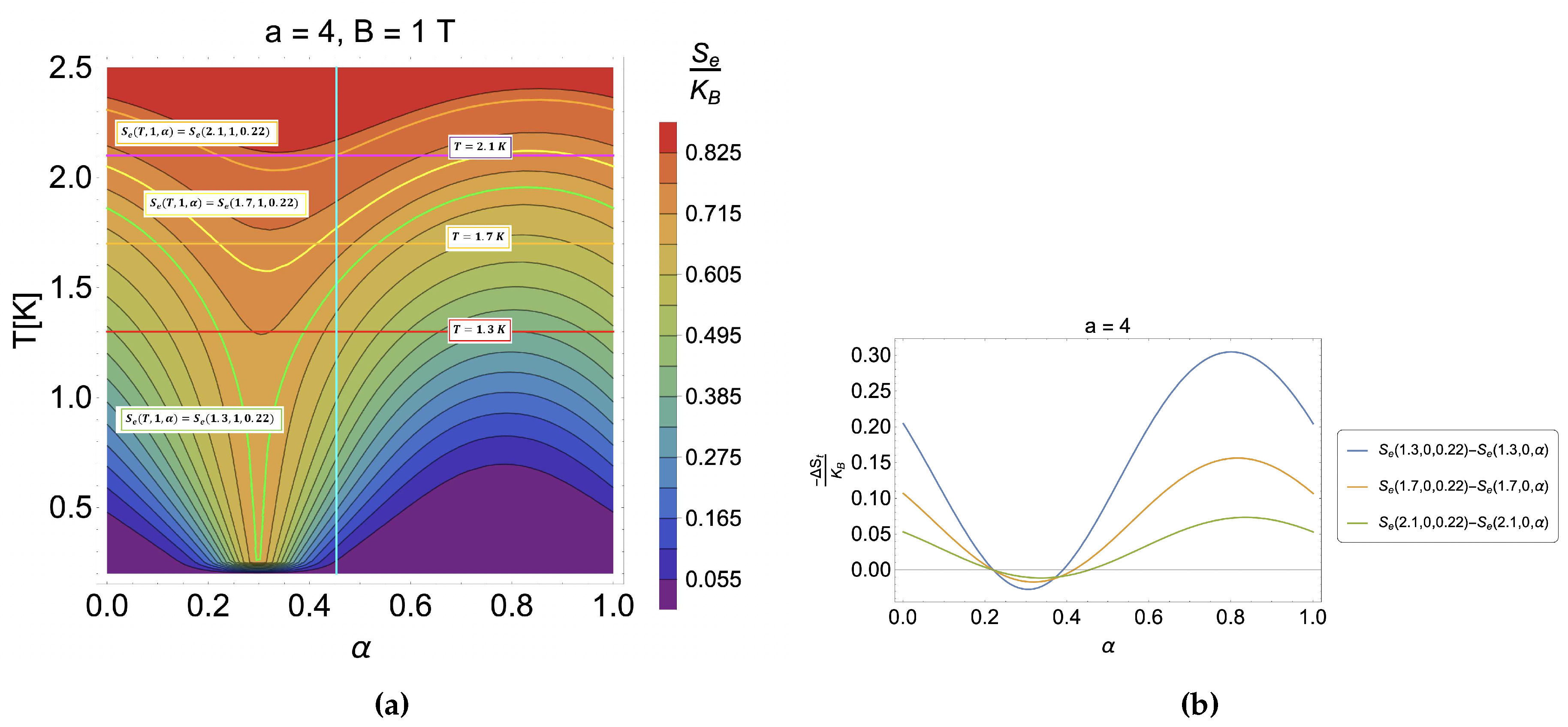
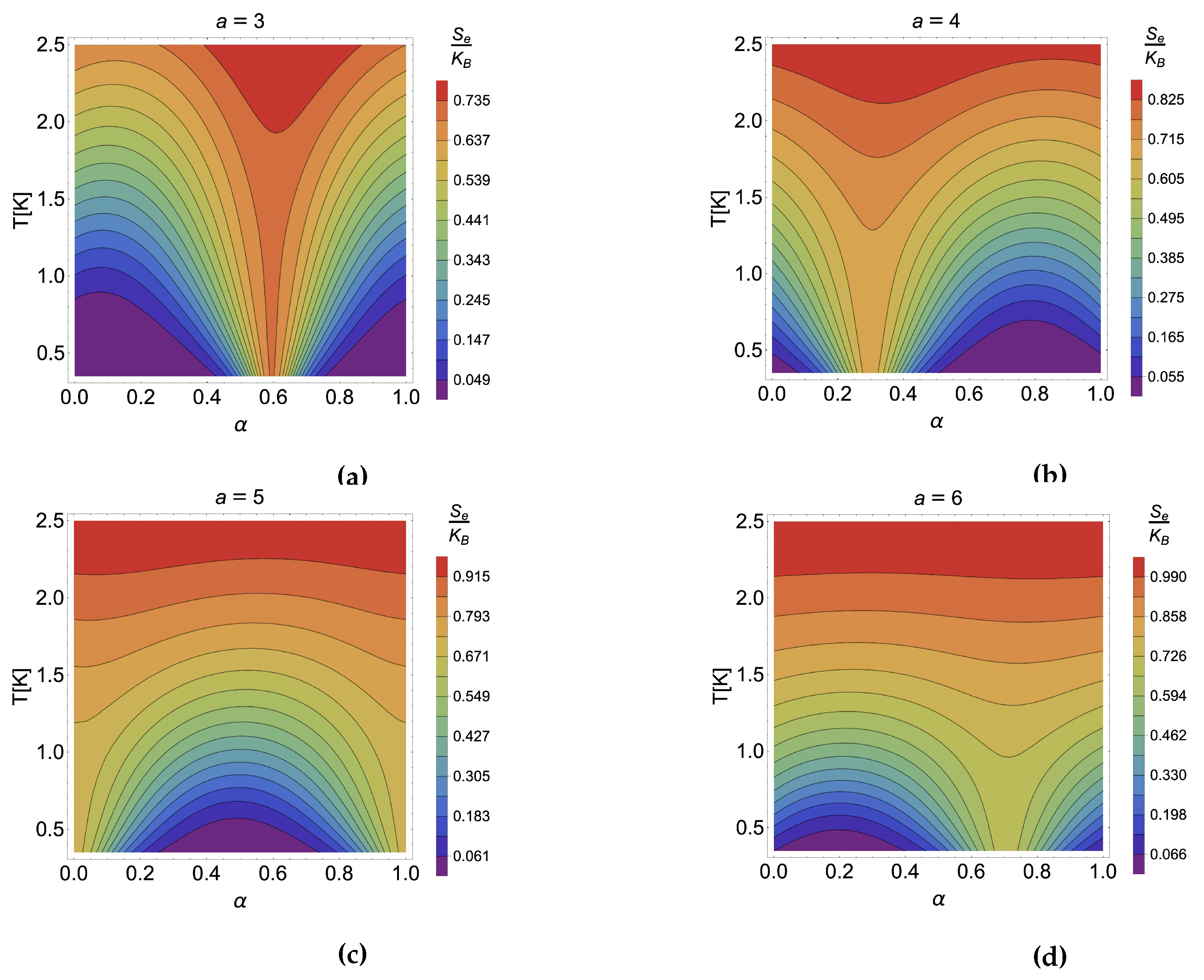
4. Results and discussion
4.1. Caloric effect without external magnetic field
4.2. Caloric effect in the presence of external magnetic field
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reis, M.S. Magnetocaloric and barocaloric effects of metal complexes for solid state cooling: Review, trends and perspectives. Coordination Chemistry Reviews 2020, 417, 213357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschneidner, K. A., Jr.; Pecharsky, V. K. Magnetocaloric materials. Annual review of materials science 2020, 30, 387–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, V.; Blázquez, J. S.; Ipus, J. J.; Law, J. Y.; Moreno-Ramírez, L. M.; Conde, A. Magnetocaloric effect: From materials research to refrigeration devices. Progress in Materials Science 2020, 93, 112–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishin, A. M.; Spichkin, Y. I. The magnetocaloric effect and its applications. PCRC Press.
- Warburg, E. Magnetische Untersuchungen. Ueber einige Wirkungen der Coërcitivkraft. Ann. Phys. (Leipzig) 1881, 249, 141–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, P.; Piccard, A. Le pheénoméne magnétocalorique. J. Phys. (Paris) 1917, 7, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, P.; Piccard, A. Sur un nouveau phénoméne magnétocalorique. Comptes Rendus 1918, 166, 352–354. [Google Scholar]
- Debye, P. Einige Bemerkungen zur Magnetisierung bei tiefer Temperatur. Annals of Physics 1926, 81, 1154–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giauque, W. F.; Macdougall, D. P. The Production of Temperatures below One Degree Absolute by Adiabatic Demagnetization of Gadolinium Sulfate. Journal of the American Chemical Society 1935, 57, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G. V. Magnetic heat pumping near room temperature. Journal of Applied Physics 1976, 47, 3673–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecharsky, V. K.; Gschneidner, K. A. Jr. Giant Magnetocaloric Effect in Gd5(Si2Ge2). Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 4494–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M. S. Oscillating magnetocaloric effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 052511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, R.; Tkáč, V.; Orendáčová, A.; Orendáč, M.; Valentab, V.; Sechovský, V.; Feher, A. Experimental study of magnetocaloric effect in the two-level quantum system KTm(MoO4)2. Physica B: Condensed Matter 2018, 536, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Amirov, A. A.; Huang, H. A review on different theoretical models of electrocaloric effect for refrigeration. Frontiers in Energy 2023, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J. F. Electrocaloric materials. Annual Review of Materials Research 2011, 41, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Sungtaek Ju, Y. A solid-state refrigerator based on the electrocaloric effect. Applied Physics Letters 2012, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Sungtaek Ju, Y.; Qian, S.; Geng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ling, J.; Hwang, Y.; Radermacher, R.; Cui, J. A review of elastocaloric cooling: Materials, cycles and system integrations. International journal of refrigeration 2016, 64, 101380. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lei, L.; Fang, G. Elastocaloric cooling of shape memory alloys: A review. Materials Today Communications 2021, 28, 102706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloveras, P.; Tamarit, J. L. Advances and obstacles in pressure-driven solid-state cooling: A review of barocaloric materials. MRS Energy Sustainability 2021, 8, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, L.; Greco, A.; Masselli, C. Cooling through barocaloric effect: A review of the state of the art up to 2022. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress 2022, 33, 101380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloveras, P.; Stern-Taulats, E.; Barrio, M.; Tamarit, J. L.; Crossley, S.; Li, W.; Moya, X. Giant barocaloric effects at low pressure in ferrielectric ammonium sulphate. Nature communications 2015, 6, 8801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloveras, P.; Aznar, A.; Barrio, M.; Negrier, P.; Popescu, C.; Planes, A.; Tamarit, J. L. Colossal barocaloric effects near room temperature in plastic crystals of neopentylglycol. Nature communications 2019, 10, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, A.; K., *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Gschneidner, K. A.; Pecharsky, V. K. Negative to positive magnetoresistance and magnetocaloric effect in Pr0.6Er0.4Al2. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2015, 621, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florez, J. M.; Vargas, P.; Garcia, C.; Ross, C. A. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2013, 25, 226004. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudl, M.; Campanini, D.; Caron, L.; Hoglin, V.; Sahlberg, M.; Nordblad, P.; Rydh, A. Thermodynamics around the first-order ferromagnetic phase transition of Fe2P single crystals. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 144432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X. F.; Caron, L.; Roy, P.; Dung, N. H.; Zhang, L.; Kockelmann, W. A.; et al. Tuning the phase transition in transition-metal-based magnetocaloric compounds. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 89, 174429–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosin, S.; Prozorova, L.; Smirnov, A.; Golov, A.; Berkutov, I.; Petrenko, O.; et al. Magnetocaloric effect in pyrochlore antiferromagnet Gd2Ti2O7. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 2005094413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yuan, F.-Y.; Wang, J.-Z.; Feng, T.-F.; Hu, G.-Q. Conventional and inverse magnetocaloric effect in Pr2CuSi3 and Gd2CuSi3 compounds. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2014, 592, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Chen, G.; Yang, W.; Wei, J.; Hua, M.; Du, H.; et al. Magnetic frustration and magnetocaloric effect in AlFe2-x Mn x B2 (x = 0-0.5) ribbons. Journal of Physics D-Applied Physics 2015, 48, 335001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balli, M.; Fruchart, D.; Zach, R. Negative and conventional magneto- caloric effects of a MnRhAs single crystal. Journal of Applied Physics 2014, 115, 203909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolat, V. S.; Izgi, T.; Kaya, A. O.; Bayri, N.; Gencer, H.; Atalay, S. Metamagnetic transition and magnetocaloric effect in charge-ordered Pr0.68Ca0.32- xSrxMnO3 (x=0, 0.1, 0.18, 0.26 and 0.32) compounds. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 2010, 322, 427433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, M. H.; Morales, M. B.; Bingham, N. S.; Srikanth, H.; Zhang, C. L.; Cheong, S.-W. Phase coexistence and magnetocaloric effect in La5/8-y Pry Ca3/8MnO3(y= 0.275). Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 094413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, M.; Majumdar, S.; Giri, S.; Iles, G. N.; Chatterji, T. Anomalous magnetic field dependence of magnetocaloric effect at low temperature in Pr0.52Sr0.48MnO3 single crystal. Journal of Applied Physics 2010, 107, 076101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalowski, K.; Balcerzak, T. Normal and inverse magnetocaloric effect in magnetic multilayers with antiferromagnetic interlayer coupling. Journal of Physics Condensed Matter 2014, 26(38), 386003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midya, A.; Khan, N.; Bhoi, D.; Mandal, P. Giant magnetocaloric effect in magnetically frustrated EuHo2O4 and EuDy2O4 compounds. Applied Physics Letters 2012, 101, 132415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, X.; Kar-Narayan, S.; Mathur, N. D. Caloric materials near ferroic phase transitions. Nature Materials 2014, 13, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, F.; Porcari, G.; Yibole, H.; van Dijk, N.; Bruck, E. Taming the First-Order Transition in Giant Magnetocaloric Materials. Advanced Materials 2014, 26, 2671–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.-Y.; Wang, D.-H.; Cao, Q.-Q.; Liu, E.-K.; Liu, J.; Du, Y.-W. Electric Field Control of the Magnetocaloric Effect. Advanced Materials 2014, 27, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbandyan, V. B.; Zvereva, E. A.; Nikulin, A. Y.; Shukaev, I. L.; Whangbo, M.- H.; Koo, H.-J.; et al. New Phase of MnSb2O6 Prepared by Ion Exchange: Structural, Magnetic, and Thermodynamic Properties. Inorganic Chemistry 2015, 54, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkac, V.; Orendacova, A.; Cizmar, E.; Orendac, M.; Feher, A.; Anders, A. G. Giant reversible rotating cryomagnetocaloric effect in KEr(MoO4)2 induced by a crystal-field anisotropy. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 024406–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, R.; Ohno, T.; Kitazawa, H. A generalized magnetic refrigeration scheme. Applied Physics Letters 2014, 104, 052415–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, R.; Tanaka, S.; Ohno, T.; Kitazawa, H. Magnetic ordered structure dependence of magnetic refrigeration efficiency. Journal of Applied Physics 2014, 116, 053908-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Ren, Q.; Fang, C.; Dou, S. Large entropy change accompanying two successive magnetic phase transitions in TbMn2Si2 for magnetic refrigeration. Applied Physics Letters 2015, 106, 182405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szałowski, K.; Balcerzak, T. Normal and inverse magnetocaloric effect in magnetic multilayers with antiferromagnetic interlayer coupling. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 2014, 26, 386003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Ranke, J. P.; Alho, B. P.; Nóbrega, B.P.; de Oliveira, N. A. Understanding the inverse magnetocaloric effect through a simple theoretical model. Physica B 2009, 404, 056004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Ranke, J. P.; de Oliveira, N. A.; Alho, B. P.; Plaza, E. J. R.; de Sousa, V.S. R.; Caron, L.; Reis, M. S. Understanding the inverse magnetocaloric effect in antiferro- and ferrimagnetic arrangements. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 3045–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zverev, V. I.; Tishin, A. M.; Min, Z.; Mudryk, Y.; Gschneidner Jr, K. A.; Pecharsky, V.K. Magnetic and magnetothermal properties, and the magnetic phase diagram of single-crystal holmium along the easy magnetization direction. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 2015, 27, 146002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zverev, V. I.; Saletsky, A. M.; Gimaev, R. R.; Tishin, A. M.; Miyanaga, T.; and Staunton, J. B. Influence of structural defects on the magnetocaloric effect in the vicinity of the first order magnetic transition in Fe50.4 Rh49.6. Applied Physics Letters 2016, 108, 192405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M. S. Oscillating adiabatic temperature change of diamagnetic materials. Solid State Communications 2012, 152, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M. S. Oscillating magnetocaloric effect on graphenes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 222405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M. S. Step-like features on caloric effects of graphenes. Physics Letters A 2014, 378, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M. S. Magnetocaloric cycle with six stages: Possible application of graphene at low temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 102401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alisultanov, Z.Z.; Reis, M. S. Oscillating magneto - and electrocaloric effects on bilayer graphenes. Solid State Communications 2015, 206, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Reis, M.S. Barocaloric effect on graphene. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 13257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedehi, H. R.; Khordad, R. Magnetocaloric effect, magnetic susceptibility and specific heat of tuned quantum dot/ring systems. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures 2021, 134, 114886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegar-Sedehi, H. R. Magnetocaloric effect in Rashba spin-orbit coupling and Zeeman splitting of a narrow nanowire quantum dot. The European Physical Journal Plus 2021, 136, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrete, O.A.; Peña, F. J.; Florez, J. M.; Vargas, P. Magnetocaloric Effect in Non-Interactive Electron Systems: “The Landau Problem” and Its Extension to Quantum Dots Entropy 2018, 20, 557. [PubMed]
- Kato, M.; Endo, A.; Katsumoto, S.; and Iye, Y. Aharonov-Bohm-type oscillations in antidot lattices in the quantum Hall regime. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 155318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräfe, J.; Weigand, M.; Stahl, C.; Träger, N.; Kopp, M.; Schütz, G.; Goering, E.; Haering, F.; Ziemann, P.; Wiedwald, U. Combined first-order reversal curve and x-ray microscopy investigation of magnetization reversal mechanisms in hexagonal antidot lattices. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 014406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräfe, J.; Weigand, M.; Stahl, C.; Träger, N.; Schütz, G.; Goering, E.; Skripnik, M.; Nowak, U.; Haering, F.; Ziemann, P.; Wiedwald, U. Geometric control of the magnetization reversal in antidot lattices with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 104421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, D.; Richter, K.; Menschig, A.; Bergmann, R.; Schweizer, H.; von Klitzing, K.; Weimann, G. Quantized Periodic Orbits in Large Antidot Arrays. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 70, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukmirović, N.; Stojanović, V.; and Vanević, M. Electron-phonon coupling in graphene antidot lattices: An indication of polaronic behavior. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 041408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornow, M.; Weiss, D.; Klitzing, K.; Eberl, K.; Bergman, E.; and Strelniker, Y. Anisotropic Magnetoresistance of a Classical Antidot Array. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prance, J. R.; Smith, C. G.; Griffiths, J. P.; Chorley, S. J.; Anderson, D.; Jones, G. A. C.; Farrer, I.; Ritchie, D. A. Electronic Refrigeration of a Two-Dimensional Electron Gas. PRL 2009, 102, 146602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hübel, A.; Held, K.; Weis, J.; Klitzing, K. v. Correlated Electron Tunneling through Two Separate Quantum Dot Systems with Strong Capacitive Interdot Coupling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 186804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hübel, A.; Weis, J.; Dietsche, W.; Klitzing, K. v. Two laterally arranged quantum dot systems with strong capacitive interdot coupling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 102101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donsa, S.; Andergassen, S.; Held, K. Double quantum dot as a minimal thermoelectric generator. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 89, 125103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogachek, E.N.; Landman, U. Edge states, Aharonov-Bohm oscillations, and thermodynamic and spectral properties in a two-dimensional electron gas with an antidot Phys. Rev. B 1995, 52, 14067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrete, O. A.; Peña, F. J.; Vargas, P. Magnetocaloric effect in an antidot: The effect of the Aharonov-Bohm flux and antidot radius. Entropy 2018, 20, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yu, H.; Sadrzadeh, A.; Yakobson, B. Riemann Surfaces of Carbon as Graphene Nanosolenoids. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacak, L.; Hawrylak, P.; Wójs, A. Quantum Dots; Springer-Verlag, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, E.; Barticevic, Z.; Pacheco, M. Electronic spectrum of a two-dimensional quantum dot array in the presence of electric and magnetic fields in the Hall configuration. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 2005 71, 165301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




