Submitted:
28 August 2023
Posted:
29 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
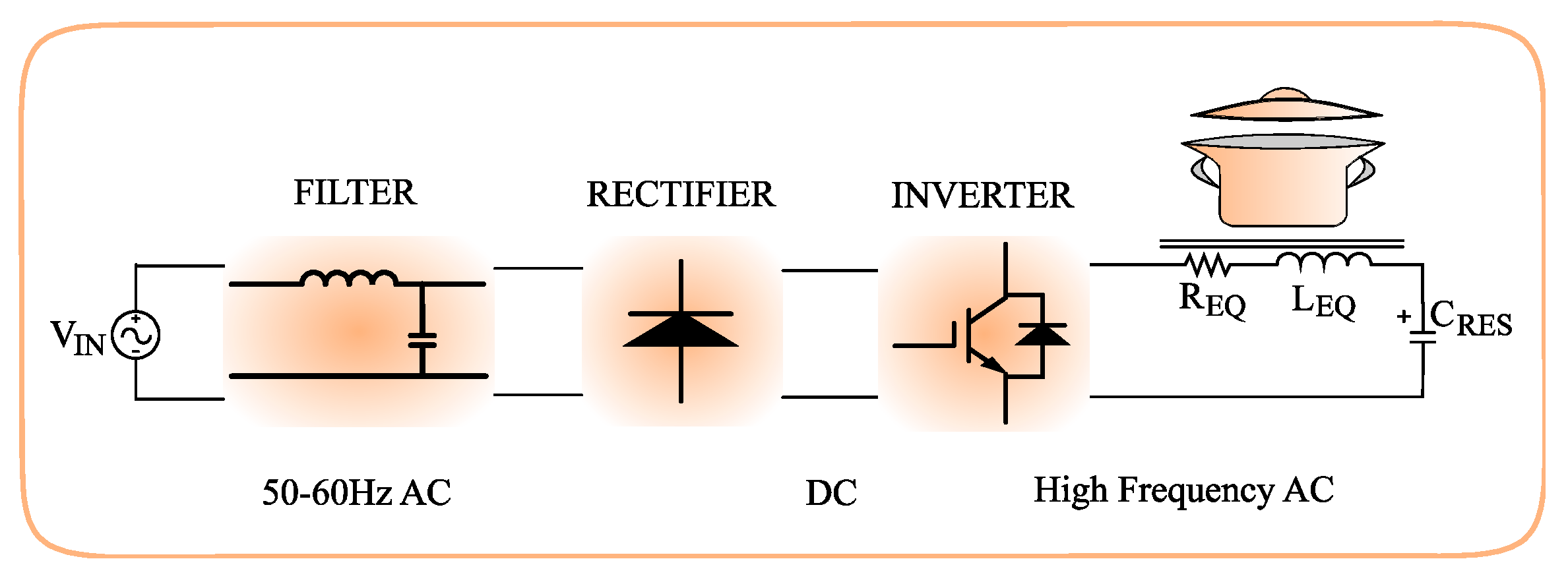
1. Introduction
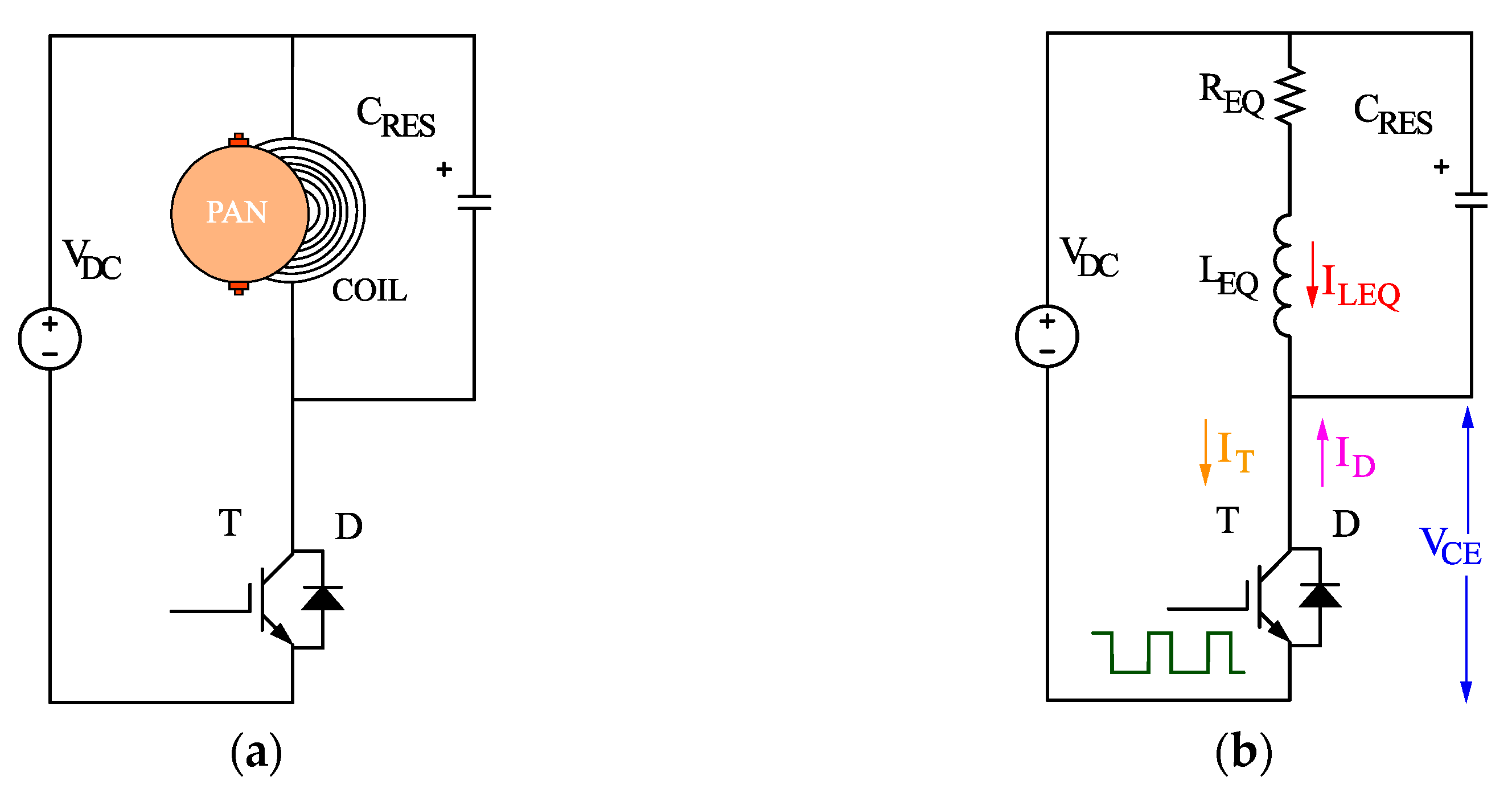
2. Circuit Description
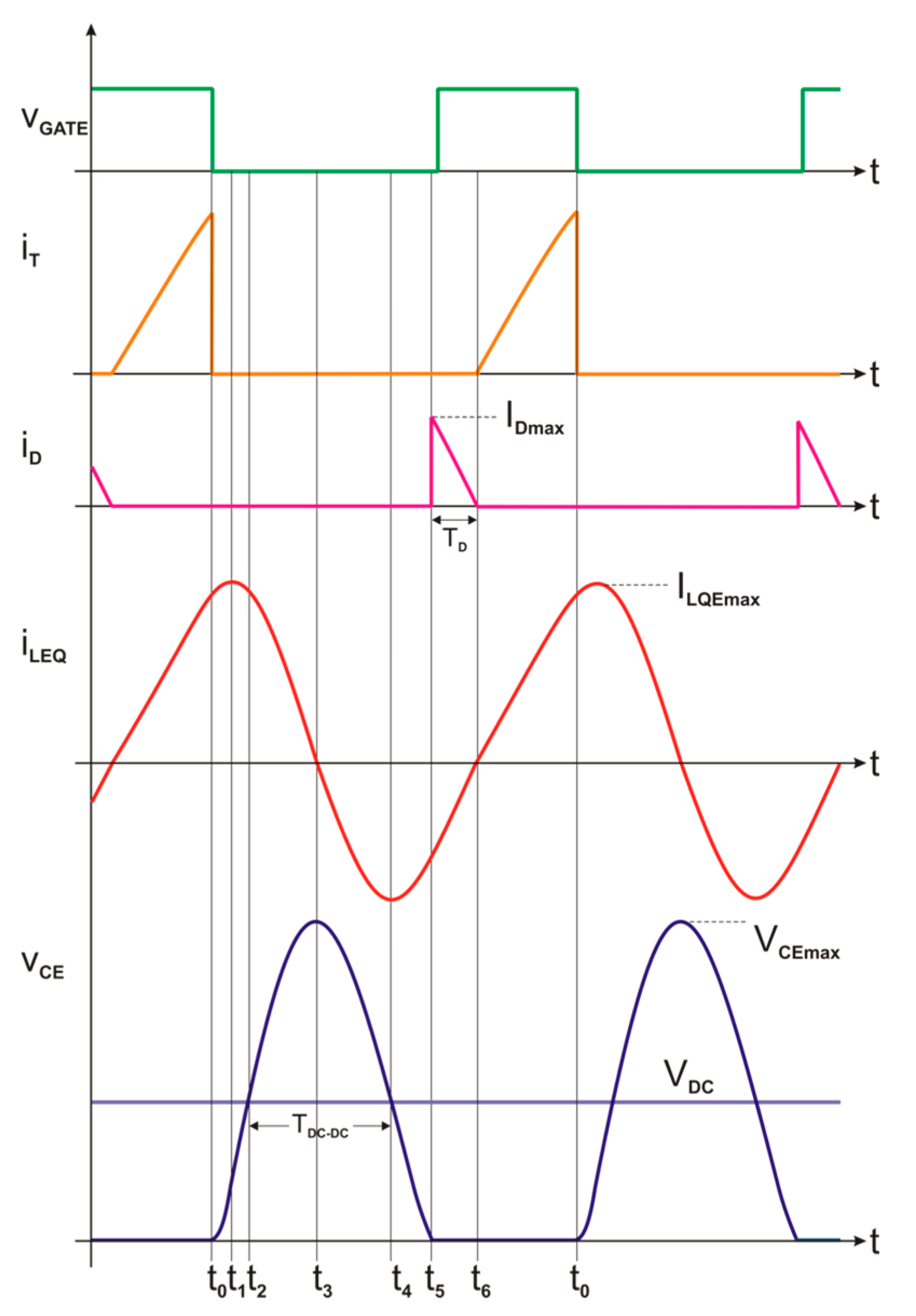
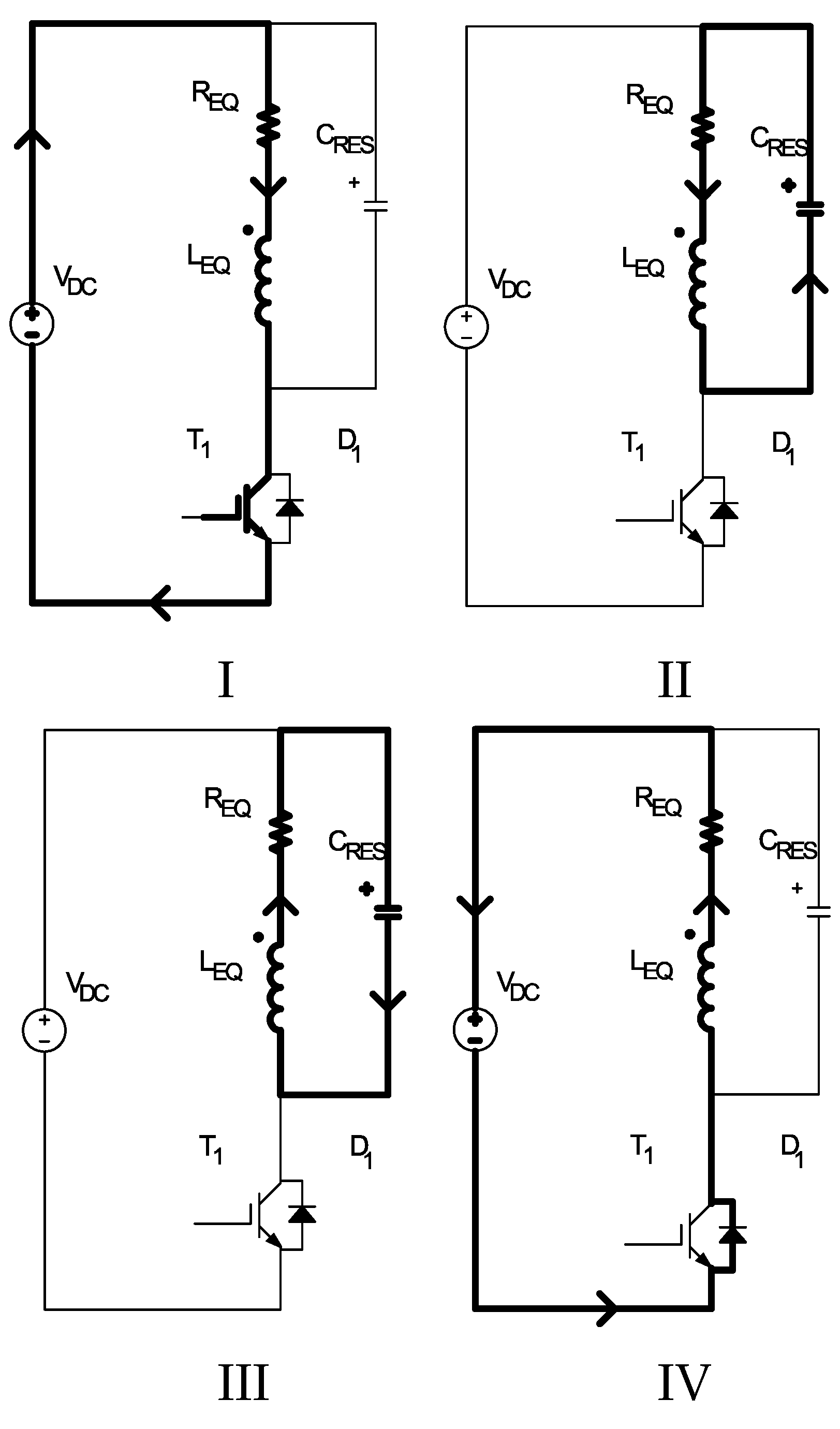
2.1. Circuit Operating Modes – Waveform Equations
2.2. Safe Operating Area for Quasi Resonant Inverter
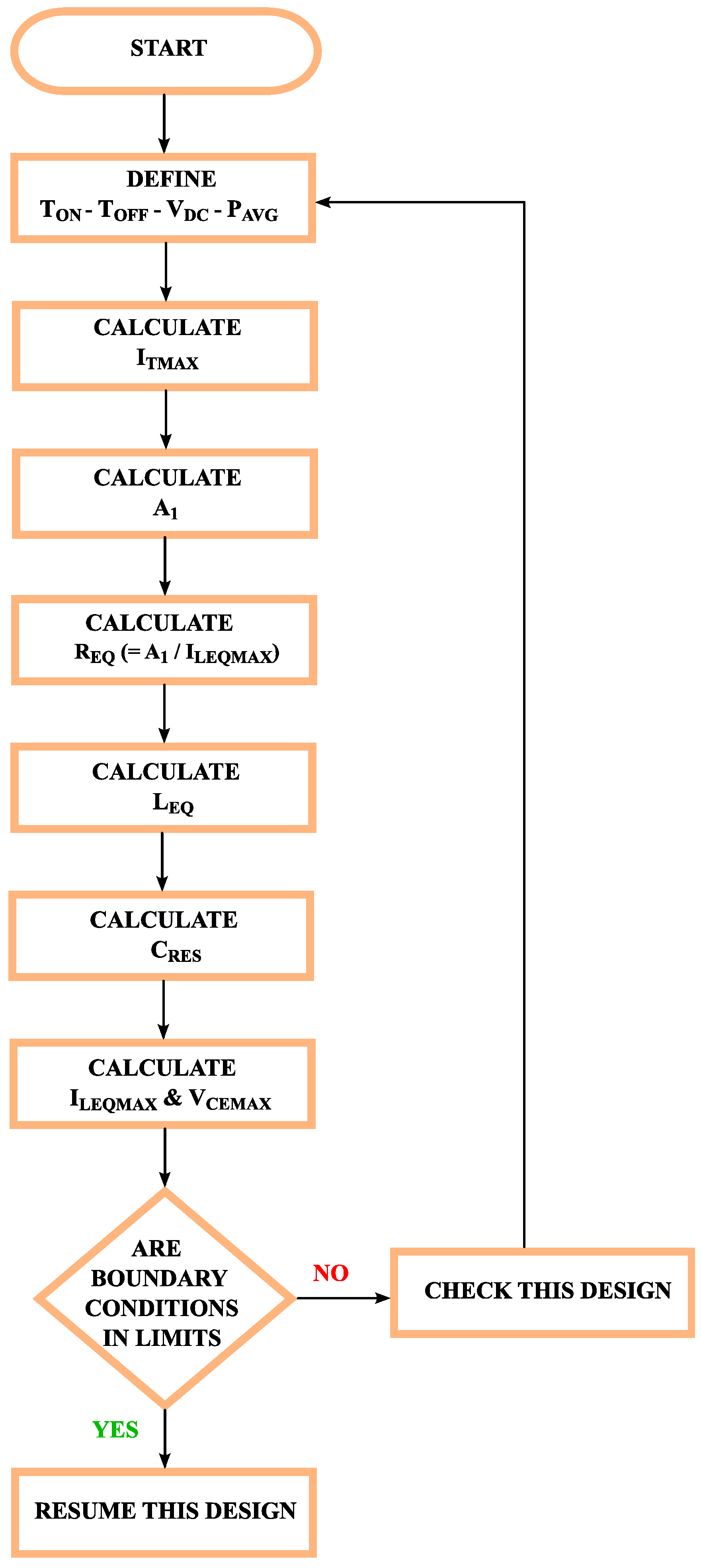
3. Proposed Design Method For Quasi Resonant Inverter
- The dc source voltage , the average input power , the switch turns on time and the switch turn off time variables are defined.
- The maximum value of the coil current is calculated with the help of the relevant circuit equations.
- By detecting the 1st harmonic component of the voltage applied to the resonant circuit, the load resistance is calculated.
- After calculating the load resistance , the equivalent inductance value is calculated with the help of the circuit equations.
- It is determined the of the series circuit with the help of calculated variables.
- The resonant capacitor value is calculated with the help of resonant frequency and inductance value .
- The design is verified by calculating the coil current and capacitor voltage boundary conditions.
3.1. Defining of the Time Intervals and , the Source Voltage and the Input Power :
3.2. Calculation of the Maximum Coil Current :
3.3. Calculation of Value by Determining the 1st Harmonic Component of The DC Voltage:
3.4. Calculation of the Equivalent Inductance Value :
3.4.1. calculation using series circuit switch current value:
3.4.2. calculation using inductor voltage value:
3.4.3. calculation using inductor energy value:
3.5. Determination The Series RLC Circuit Parameters:
3.6. Calculation of the Resonant Circuit Capacitor Value Inductance Value :
3.7. Calculation of Current and Voltage Boundary Conditions of Semiconductor Switch:
3.8. The Flowchart of the Proposed Design Method
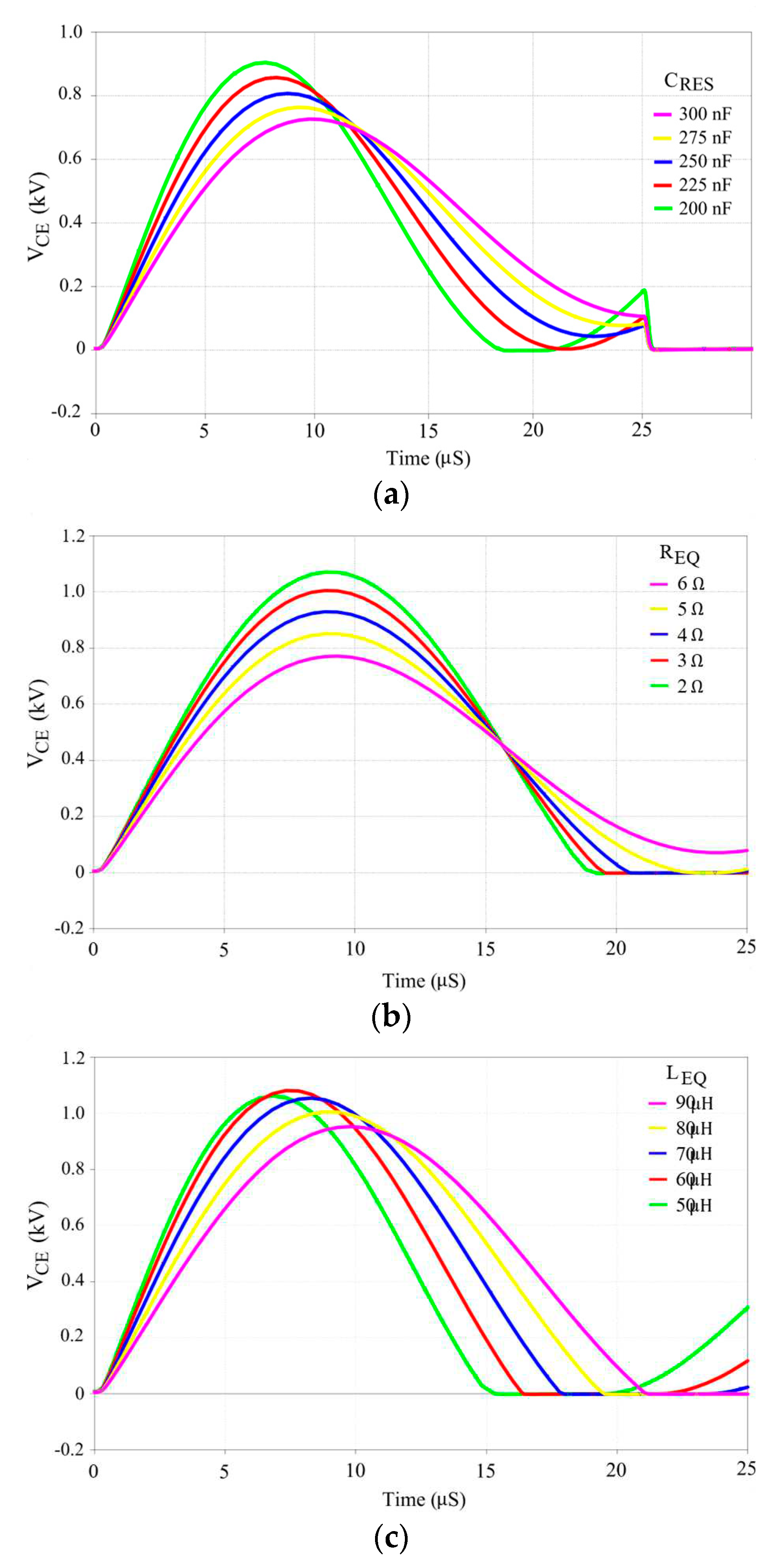
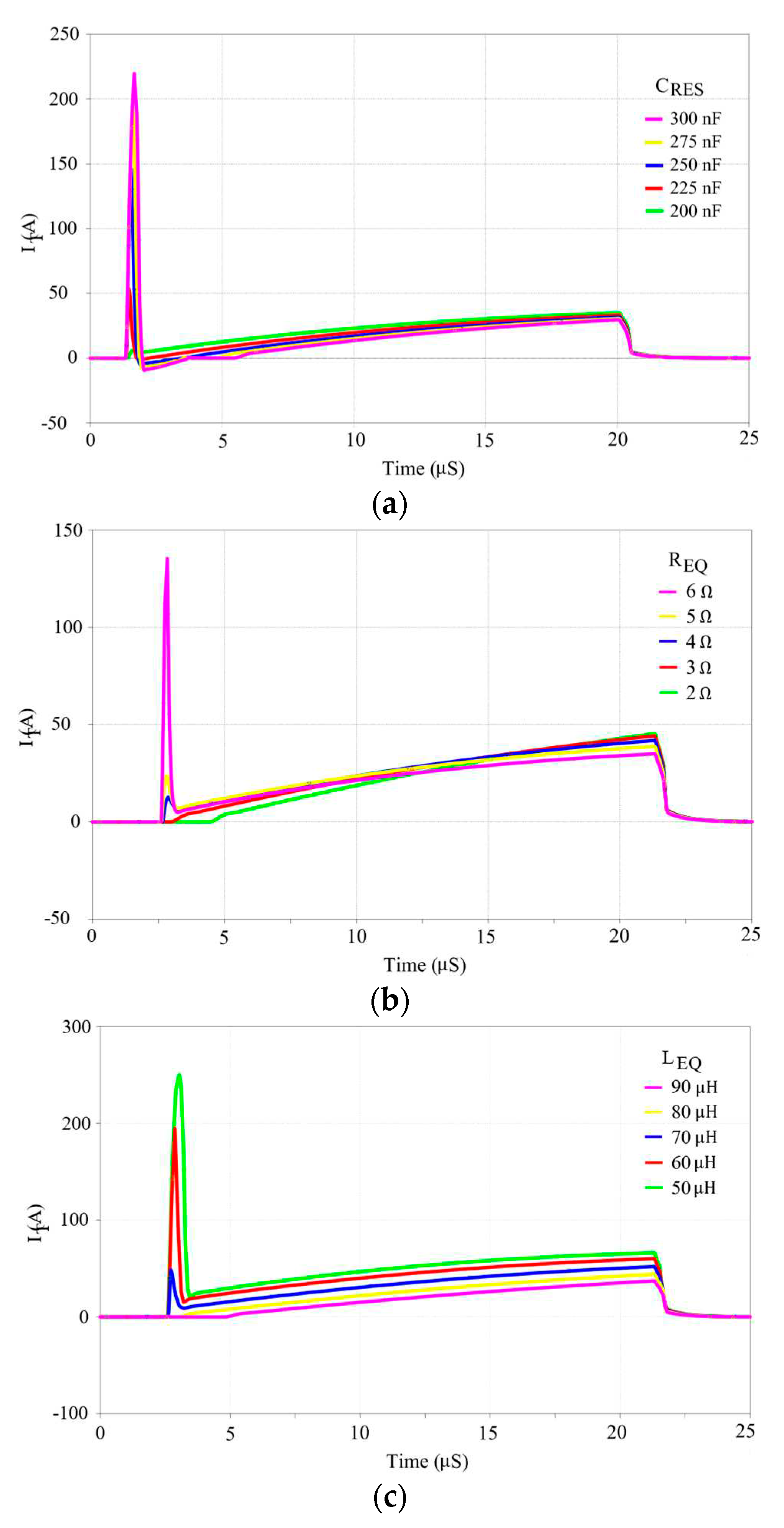
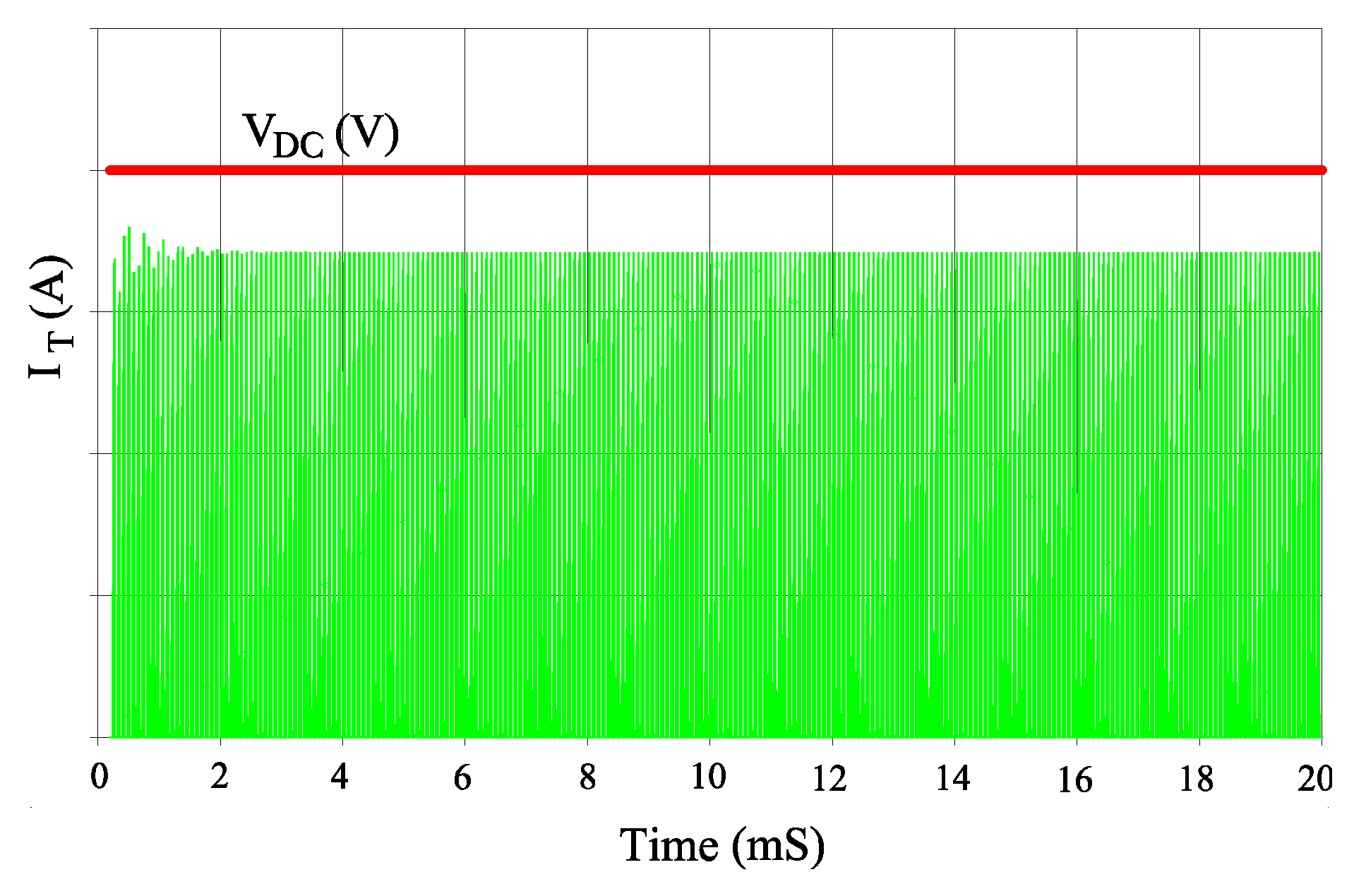
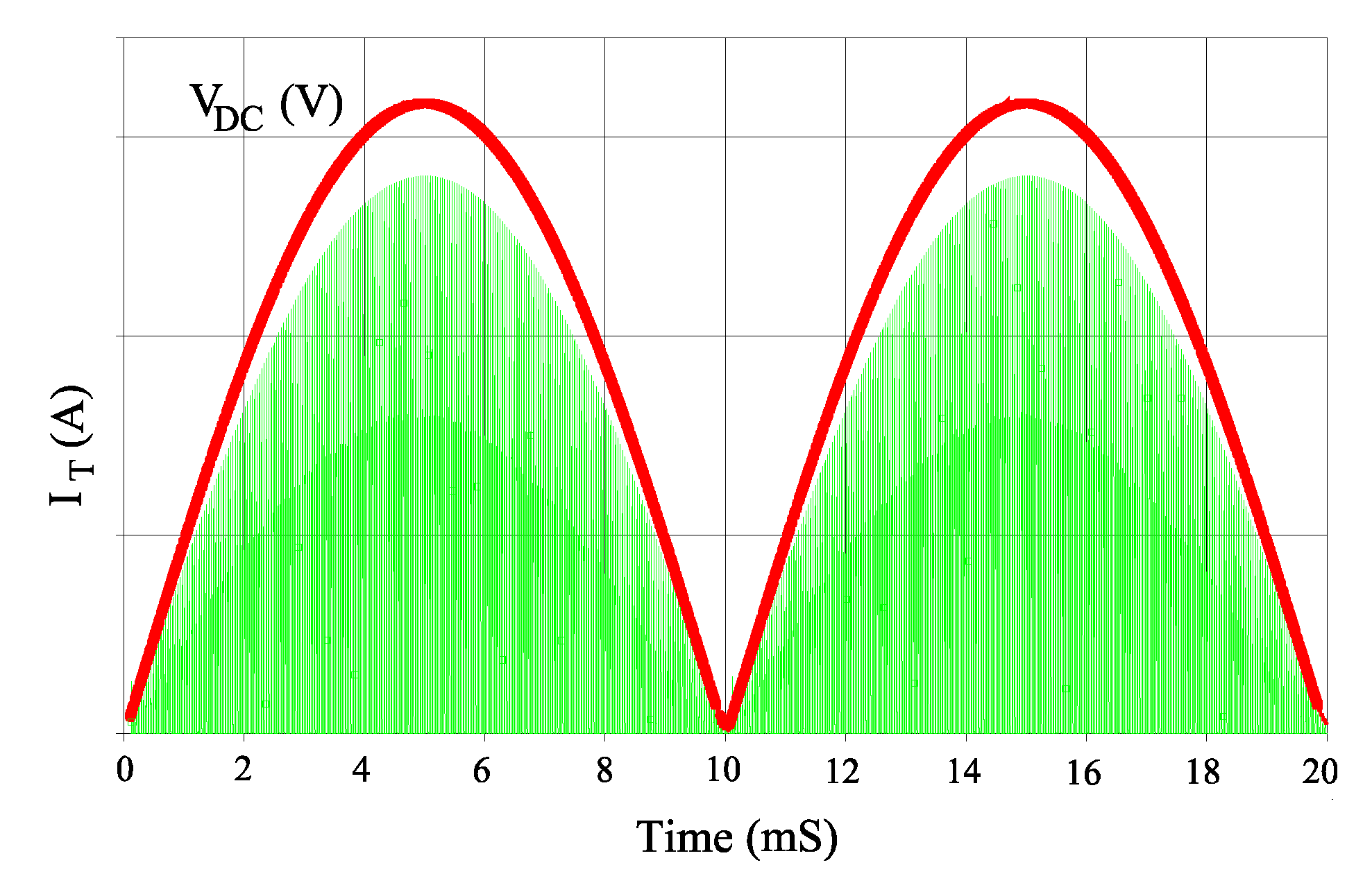
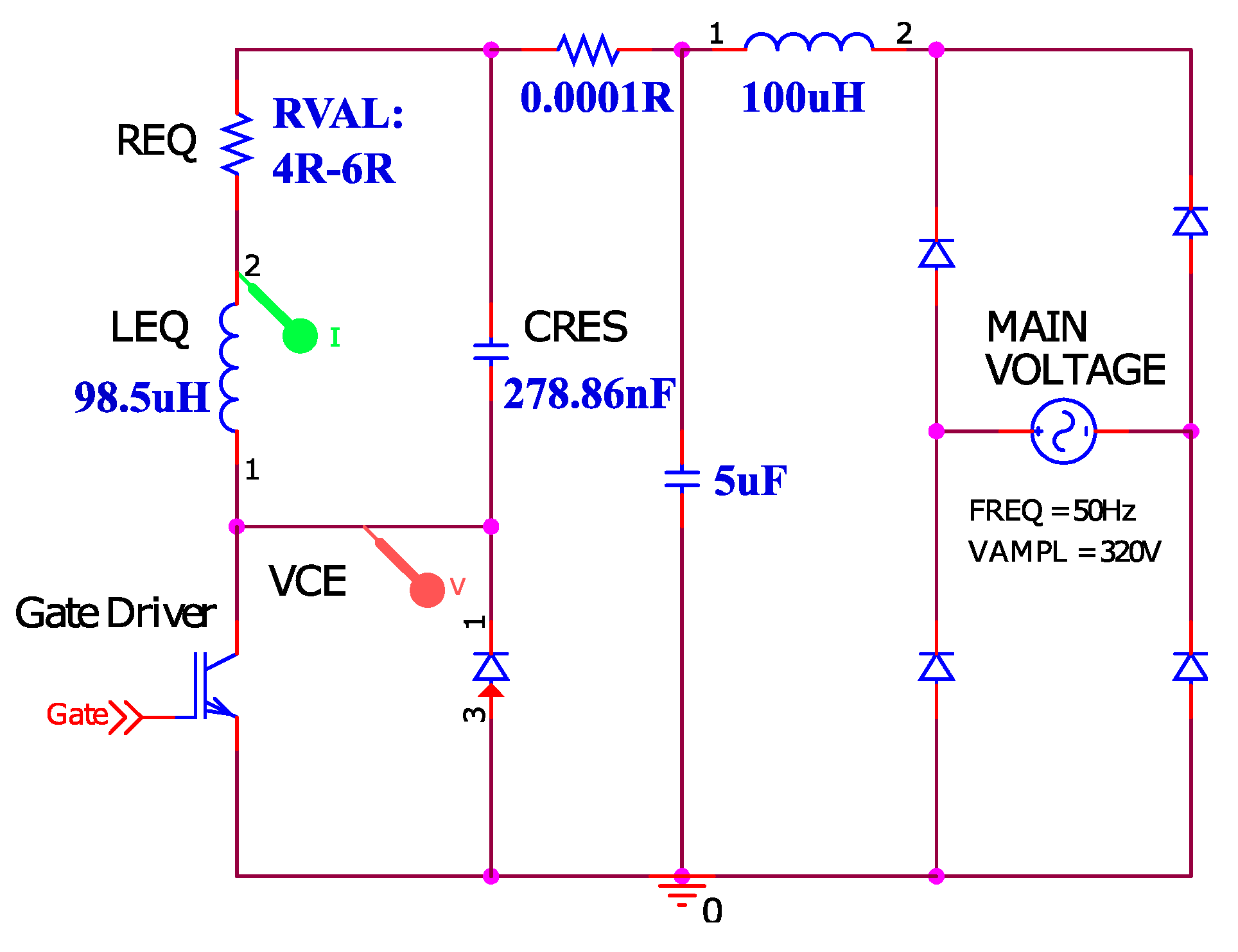
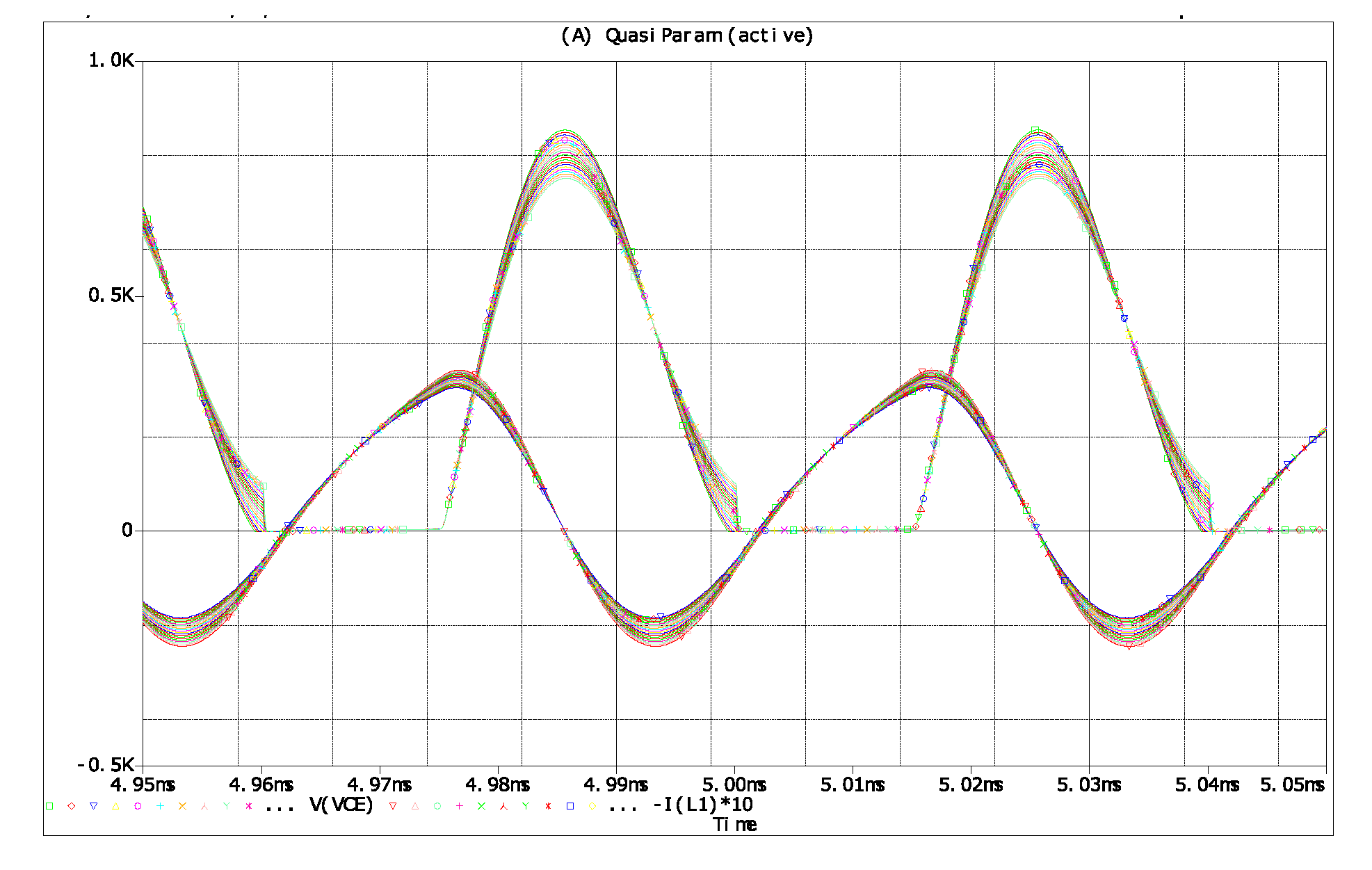
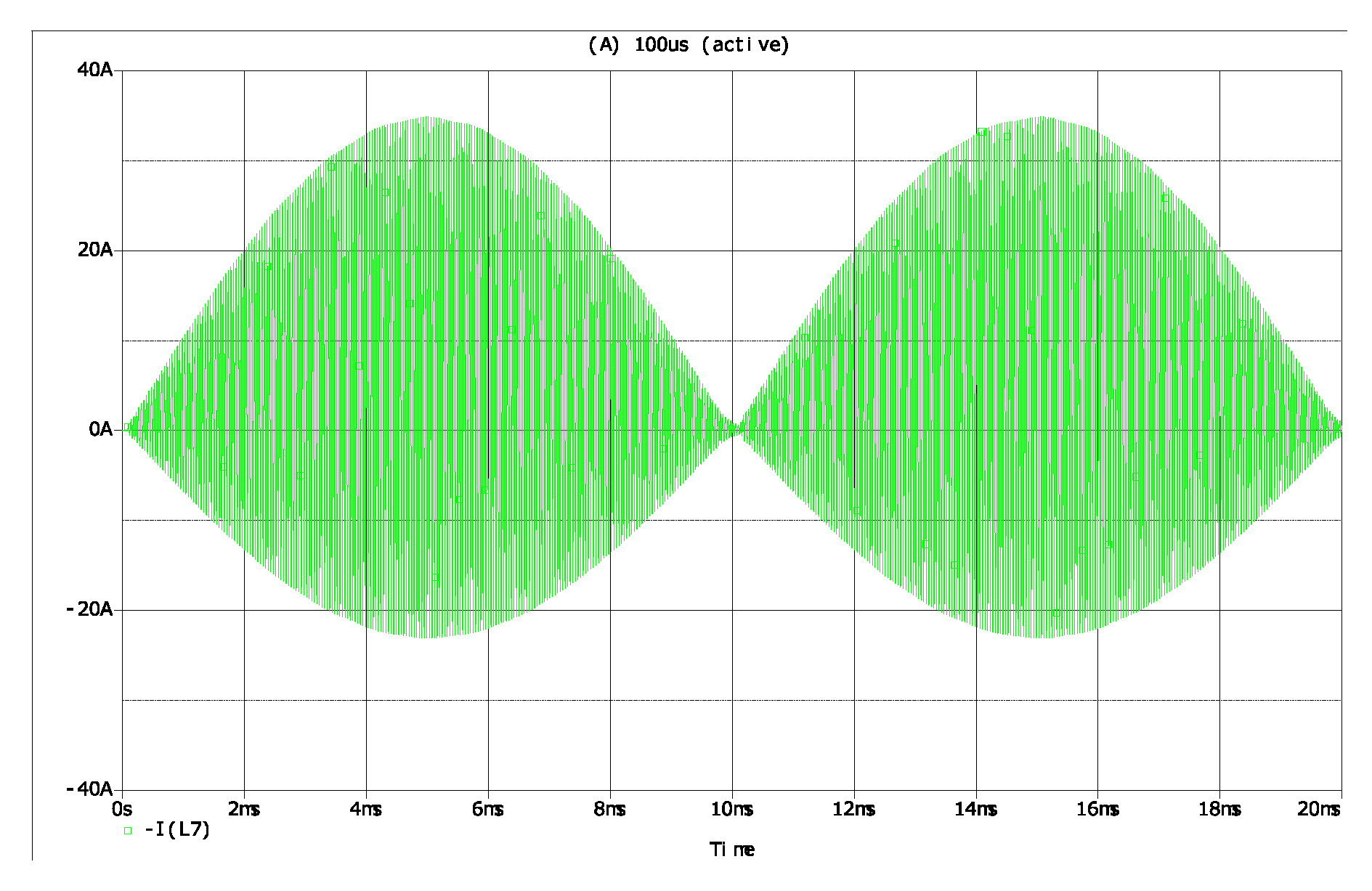
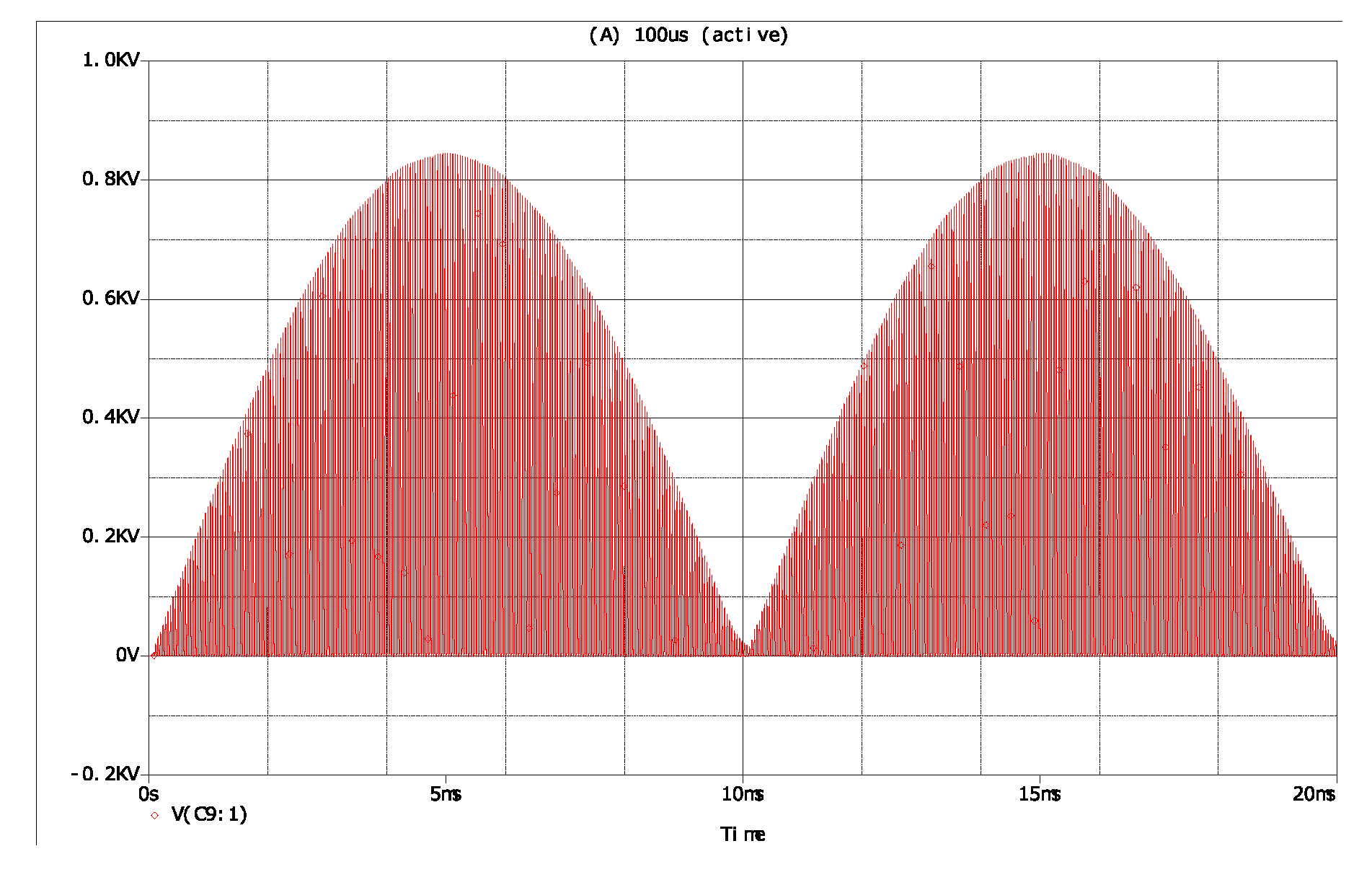
4. Verification of Proposed Analysis Method
4.1. Calculation Results
4.2. Simulation Results
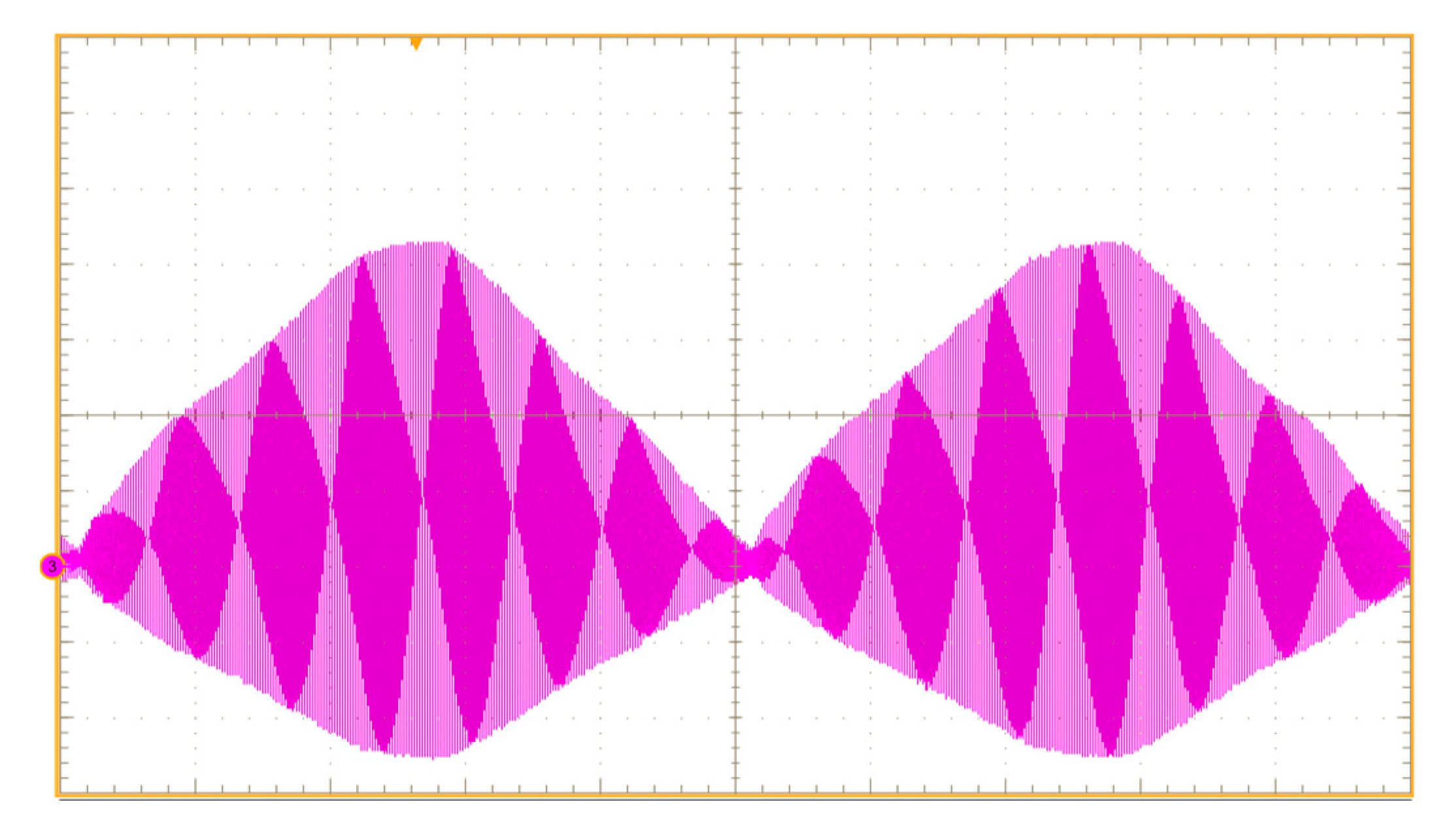
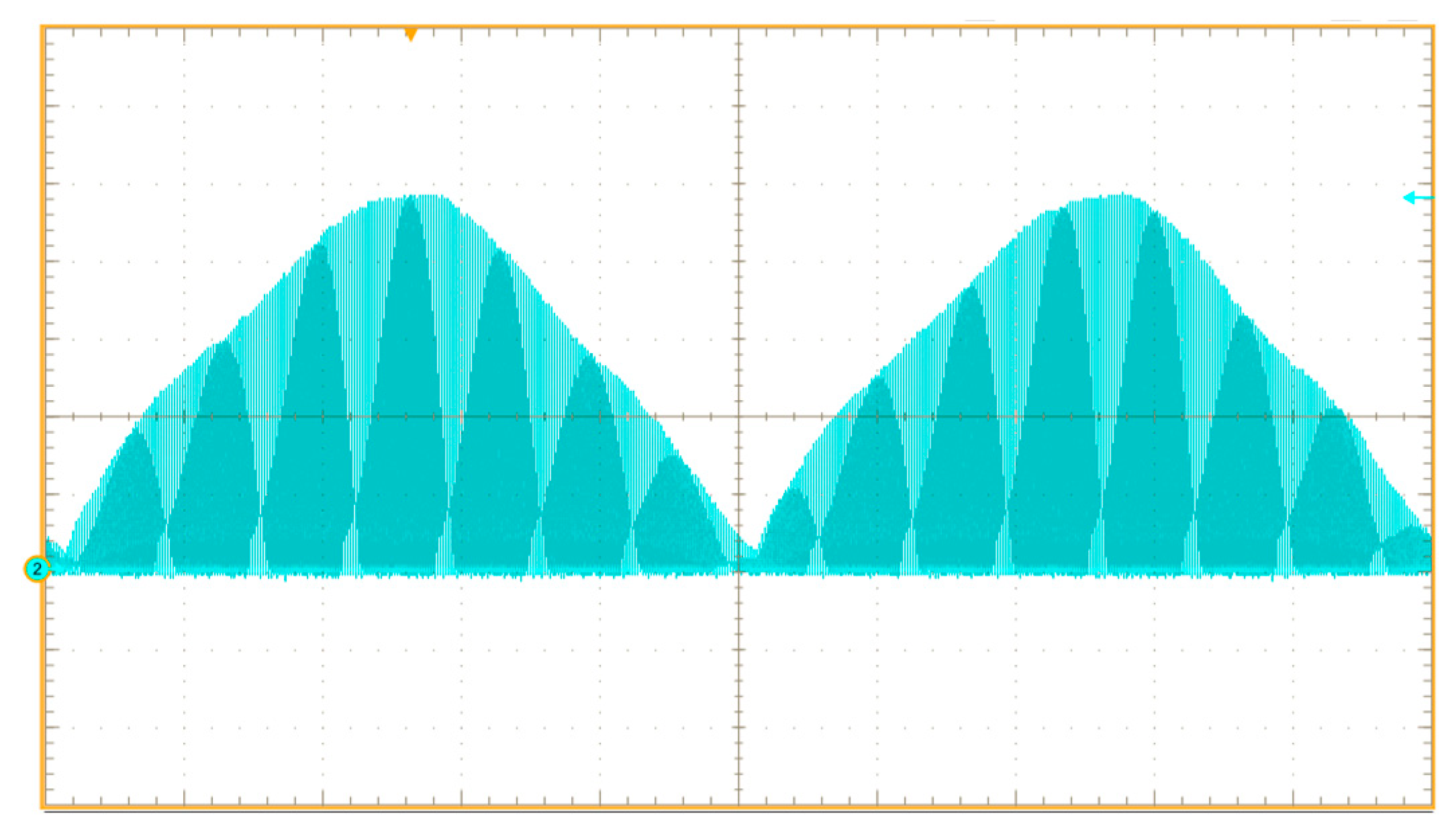
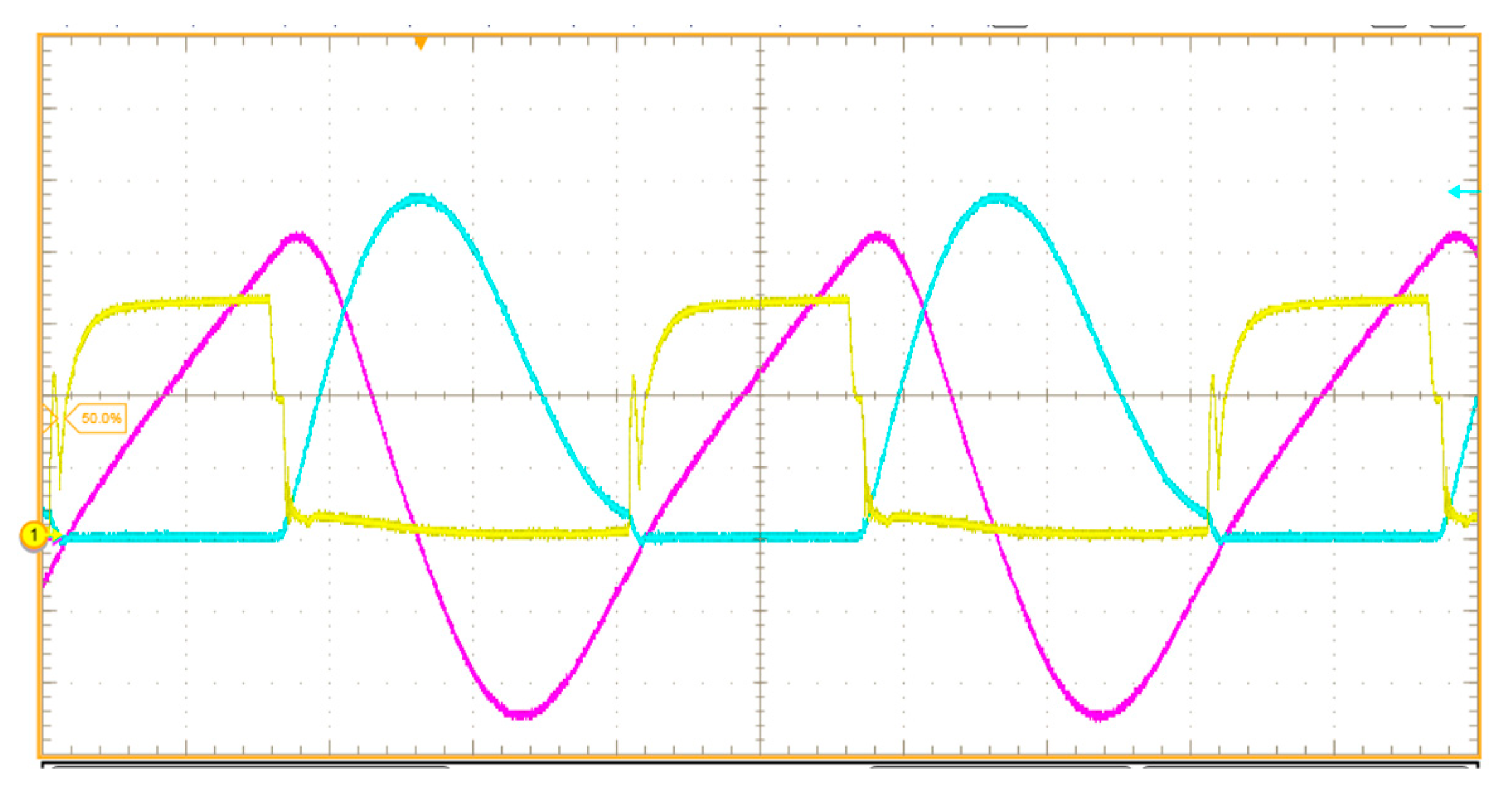
4.3. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- W. P. W. KOMATSU, “A simple and reliable class E inverter for induction heating applications,” Int. J. Electron., vol. 84, no. 2, pp. 157–165, Feb. 1998. [CrossRef]
- H. OMORI and M. NAKAOKA, “New single-ended resonant inverter circuit and system for induction-heating cooking apparatus,” Int. J. Electron., vol. 67, no. 2, pp. 277–296, Aug. 1989. [CrossRef]
- T. Tanaka, “A new induction cooking range for heating any kind of metal vessels,” IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron., vol. 35, no. 3, pp. 635–641, 1989. [CrossRef]
- Lucía, P. Maussion, E. Dede, and J. M. Burdío, “Induction heating technology and its applications: Past Developments, current Technology, and future challenges,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 61, no. 05, pp. 2509–2520, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Lucia, D. Navarro, P. Guillen, H. Sarnago, and S. Lucia, “Deep Learning-Based Magnetic Coupling Detection for Advanced Induction Heating Appliances,” IEEE Access, vol. 7. pp. 181668–181677, 2019. [CrossRef]
- U. Has and D. Wassilew, “Temperature control for food in pots on cooking hobs,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 46, no. 5, pp. 1030–1034, 1999. [CrossRef]
- C. Ekkaravarodome, P. Charoenwiangnuea, and K. Jirasereeamornkul, “The simple temperature control for induction cooker based on class-E resonant inverter,” in 2013 10th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology, May 2013, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- M. K. Kazimierczuk and S. Wang, “Frequency-domain analysis of series resonant converter for continuous conduction mode,” IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 270–279, Apr. 1992. [CrossRef]
- Lucia, H. Sarnago, and J. M. Burdio, “Soft-stop optimal trajectory control for improved operation of the series resonant multi-inverter,” IECON Proc. (Industrial Electron. Conf., pp. 3283–3288, 2014. [CrossRef]
- D. Paesa, C. Franco, S. Llorente, G. Lopez-Nicolas, and C. Sagues, “Adaptive Simmering Control for Domestic Induction Cookers,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., vol. 47, no. 5, pp. 2257–2267, Sep. 2011. [CrossRef]
- M. Ozturk, F. Zungor, B. Emre, and B. Oz, “Quasi Resonant Inverter Load Recognition Method,” IEEE Access, vol. 10, no. August, pp. 89376–89386, 2022. [CrossRef]
- V. Crisafulli and C. V. Pastore, “New control method to increase power regulation in a AC/AC quasi resonant converter for high efficiency induction cooker,” in Proceedings - 2012 3rd IEEE International Symposium on Power Electronics for Distributed Generation Systems, PEDG 2012, 2012, pp. 628–635. [CrossRef]
- H. Sarnago, O. Lucia, A. Mediano, and J. M. Burdio, “A Class-E Direct AC–AC Converter With Multicycle Modulation for Induction Heating Systems,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 61, no. 5, pp. 2521–2530, May 2014. [CrossRef]
- H. Sarnago, O. Lucia, A. Mediano, and J. M. Burdio, “Direct AC–AC Resonant Boost Converter for Efficient Domestic Induction Heating Applications,” IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 1128–1139, Mar. 2014. [CrossRef]
- P. Vishnuram and G. Ramachandiran, “Capacitor-less induction heating system with self-resonant bifilar coil,” International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, vol. 48, no. 9. pp. 1411–1425, 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. P. Park, M. Kim, J. H. Jung, and H. S. Kim, “Load adaptive modulation method for all-metal induction heating application,” Conf. Proc. - IEEE Appl. Power Electron. Conf. Expo. - APEC, vol. 2018-March, pp. 3486–3490, 2018. [CrossRef]
- H. Sarnago, O. Lucia, and J. M. Burdio, “Multiple-output ZCS resonant inverter for multi-coil induction heating appliances,” Conf. Proc. - IEEE Appl. Power Electron. Conf. Expo. - APEC, pp. 2234–2238, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Lucia, C. Carretero, D. Palacios, D. Valeau, and J. M. Burdío, “Configurable snubber network for efficiency optimisation of resonant converters applied to multi-load induction heating,” Electron. Lett., vol. 47, no. 17, pp. 989–991, 2011. [CrossRef]
- M. S. Huang, C. C. Liao, Z. F. Li, Z. R. Shih, and H. W. Hsueh, “Quantitative Design and Implementation of an Induction Cooker for a Copper Pan,” IEEE Access, vol. 9. pp. 5105–5118, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. H. Jeong, J. Il Jin, H. P. Park, and J. H. Jung, “Enhanced load adaptive modulation of induction heating series resonant inverters to heat various-material vessels,” J. Power Electron., vol. 22, no. 6, pp. 1020–1032, 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. Han, K. T. Chau, W. Liu, X. Tian, and H. Wang, “A Dual-Resonant Topology-Reconfigurable Inverter for All-Metal Induction Heating,” IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron., vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 3818–3829, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. R. Ramalingam, C. S. Boopthi, S. Ramasamy, M. Ahsan, and J. Haider, “Induction heating for variably sized ferrous and non-ferrous materials through load modulation,” Energies, vol. 14, no. 24, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Jin, M. Kim, J. Han, K. Kang, and J. H. Jung, “Input voltage selection method of half-bridge series resonant inverters for all-metal induction heating applications using high turn-numbered coils,” J. Power Electron., vol. 20, no. 6, pp. 1629–1637, 2020. [CrossRef]
- E. Jang, S. M. Park, D. Joo, H. M. Ahn, and B. K. Lee, “Analysis and Comparison of Topological Configurations for All-Metal Induction Cookers,” J. Electr. Eng. Technol., vol. 14, no. 6, pp. 2399–2408, 2019. [CrossRef]
- H. Sarnago, Ó. Lucía, A. Mediano, and J. M. Burdío, “Analytical Model of the Half-Bridge Series Resonant Inverter for Improved Power Conversion Efficiency and Performance,” IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 30, no. 8, pp. 4128–4143, 2015. [CrossRef]
- H. I. Hsieh, C. C. Kuo, and W. Te Chang, “Study of half-bridge series-resonant induction cooker powered by line rectified DC with less filtering,” IET Power Electron., 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. Sarnago, P. Guillén, J. M. Burdío, and O. Lucia, “Multiple-Output ZVS Resonant Inverter Architecture for Flexible Induction Heating Appliances,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 157046–157056, 2019. [CrossRef]
- H. W. Koertzen, J. D. van Wyk, and J. A. Ferreira, “Design of the half-bridge, series resonant converter for induction cooking,” PESC Rec. - IEEE Annu. Power Electron. Spec. Conf., vol. 2, pp. 729–735, 1995. [CrossRef]
- N. Altintas, M. Ozturk, and U. Oktay, “Performance evaluation of pan position methods in domestic induction cooktops,” Electr. Eng., 2023. [CrossRef]
- Hirota, H. Omori, K. A. Chandra, and M. Nakaoka, “Practical evaluations of single-ended load-resonant inverter using application-specific IGBT and driver IC for induction-heating appliance,” in Proceedings of 1995 International Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems. PEDS 95, pp. 531–537. [CrossRef]
- Sheikhian, N. Kaminski, S. Voß, W. Scholz, and E. Herweg, “Optimisation of Quasi-resonant Induction Cookers,” 2013 15th Eur. Conf. Power Electron. Appl. EPE 2013, 2013. [CrossRef]
- M. Ozturk and N. Altintas, “Multi-output AC–AC converter for domestic induction heating,” Electr. Eng., vol. 105, no. 1, pp. 297–316, Feb. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Villa, D. Navarro, A. Dominguez, J. I. Artigas, and L. A. Barragan, “Vessel Recognition in Induction Heating Appliances - A Deep-Learning Approach,” IEEE Access, vol. 9. pp. 16053–16061, 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. Spateri, F. Ruiz, and G. Gruosso, “Modelling and Simulation of Quasi-Resonant Inverter for Induction Heating under Variable Load,” Electron., vol. 12, no. 3, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Zheng-Feng Li, Jhih-Cheng Hu, Ming-Shi Huang, Yi-Liang Lin, Chun-Wei Lin, and Yu-Min Meng, “Load Estimation for Induction Heating Cookers Based on Series RLC Natural Resonant Current.” doi: 10.3390/en15041294.
- H. Sarnago, O. Lucía, and J. M. Burdio, “A Versatile Resonant Tank Identification Methodology for Induction Heating Systems,” IEEE Trans. Power Electron., vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 1897–1901, Mar. 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. Acero, J. M. Burdío, L. A. Barragán, and R. Alonso, “A model of the equivalent impedance of the coupled winding-load system for a domestic induction heating application,” IEEE Int. Symp. Ind. Electron., no. 1, pp. 491–496, 2007. [CrossRef]
- J. Acero, O. Lucia, C. Carretero, I. Lope, and C. Diez, “Efficiency improvement of domestic induction appliances using variable inductor-load distance,” in 2012 Twenty-Seventh Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Feb. 2012, pp. 2153–2158. [CrossRef]
- H. Okuno, H. Yonemori, and M. Kobayashi, “Relation of gap length and resonant frequency about a double-coil drive type IH cooker,” in 2008 15th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems, Aug. 2008, pp. 65–68. [CrossRef]
- P. Charoenwiangnuea, C. Ekkaravarodome, I. Boonyaroonate, P. Thounthong, and K. Jirasereeamornkul, “Design of domestic induction cooker based on optimal operation class-E inverter with parallel load network under large-signal excitation,” J. Power Electron., vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 892–904, 2017. [CrossRef]
- P. Charoenwiangnuea, S. Wangnipparnto, and S. Tunyasrirut, “Design of A Class-E Direct AC-AC Converter with Only One Capacitor and One Inductor for Domestic Induction Cooker,” in 2021 18th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology (ECTI-CON), May 2021, pp. 679–682. [CrossRef]
- S. Yilmaz, B. S. Sazak, and S. Cetin, “Design and implementation of web-based training tool for a single switch induction cooking system using PHP,” Elektron. ir Elektrotechnika, no. 3, pp. 89–92, 2010, [Online]. Available: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Design-and-Implementation-of-Web-Based-Training-for-Yilmaz-Sazak/d44d3831c3d6722cf80422afd7a4eabaf1f091f9.
- B. S. Sazak, “Design of a 500W Resonant Induction Heater,” Pamukkale Univ. J. Eng. …, pp. 1–12, 2011, [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/267858491_DESIGN_OF_A_500W_RESONANT_INDUCTION_HEATER.
- H. Zeroug, T. M. Leulmi, M. M. Lograda, and N. Tadrist, “Design and development of IGBT resonant inverters for domestic induction heating applications,” in 6th IET International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives (PEMD 2012), 2012, pp. F22–F22. [CrossRef]
- L. Meng, K. Wai, E. Cheng, S. Member, and K. W. Chan, “Systematic Approach to High-Power and Energy-Efficient Industrial Induction Cooker System : Circuit Design , Control Strategy , and Prototype Evaluation,” vol. 26, no. 12, pp. 3754–3765, 2011.
- H. Terai et al., “Comparative Performance Evaluations of IGBTs and MCT in Single-Ended Quasi-Resonant Zero Voltage Soft Switching Inverter,” no. 1, pp. 2178–2182.
- H. Omori, H. Yamashita, M. Nakaoka, and T. Maruhashi, “A novel type induction-heating single-ended resonant inverter using new bipolar Darlington-Transistor,” in 1985 IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Jun. 1985, pp. 590–599. [CrossRef]
- Millán, D. Puyal, J. M. Burdío, O. Lucía, and C. M. De Luna, “IGBT Selection Method for the Design of Resonant Inverters for Domestic Induction Heating Keywords Method to measure the power losses,” vol. 1.
- J. Acero et al., “The domestic induction heating appliance: An overview of recent research,” in 2008 Twenty-Third Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, Feb. 2008, pp. 651–657. [CrossRef]
- T. Nishida, S. Moisseev, E. Hiraki, and M. Nakaoka, “Duty Cycle Controlled Soft Combutation High Frequency Inverter for Consumer Induction Cooker and Steaimer,” pp. 1846–1851, 1846.
- V. Crisafulli and M. Antretter, “Design considerations to increase power density in induction cooking applications using the new Field stop II technology IGBTs,” PCIM Eur. 2015; Int. Exhib. Conf. Power Electron. Intell. Motion, Renew. Energy Energy Manag. Proc., no. May, pp. 19–21, 2015.
- M. N. O. S. Charles K. Alexander, Fundamentals of Electric Circuits, 7th Editio. McGraw-Hill Education,.
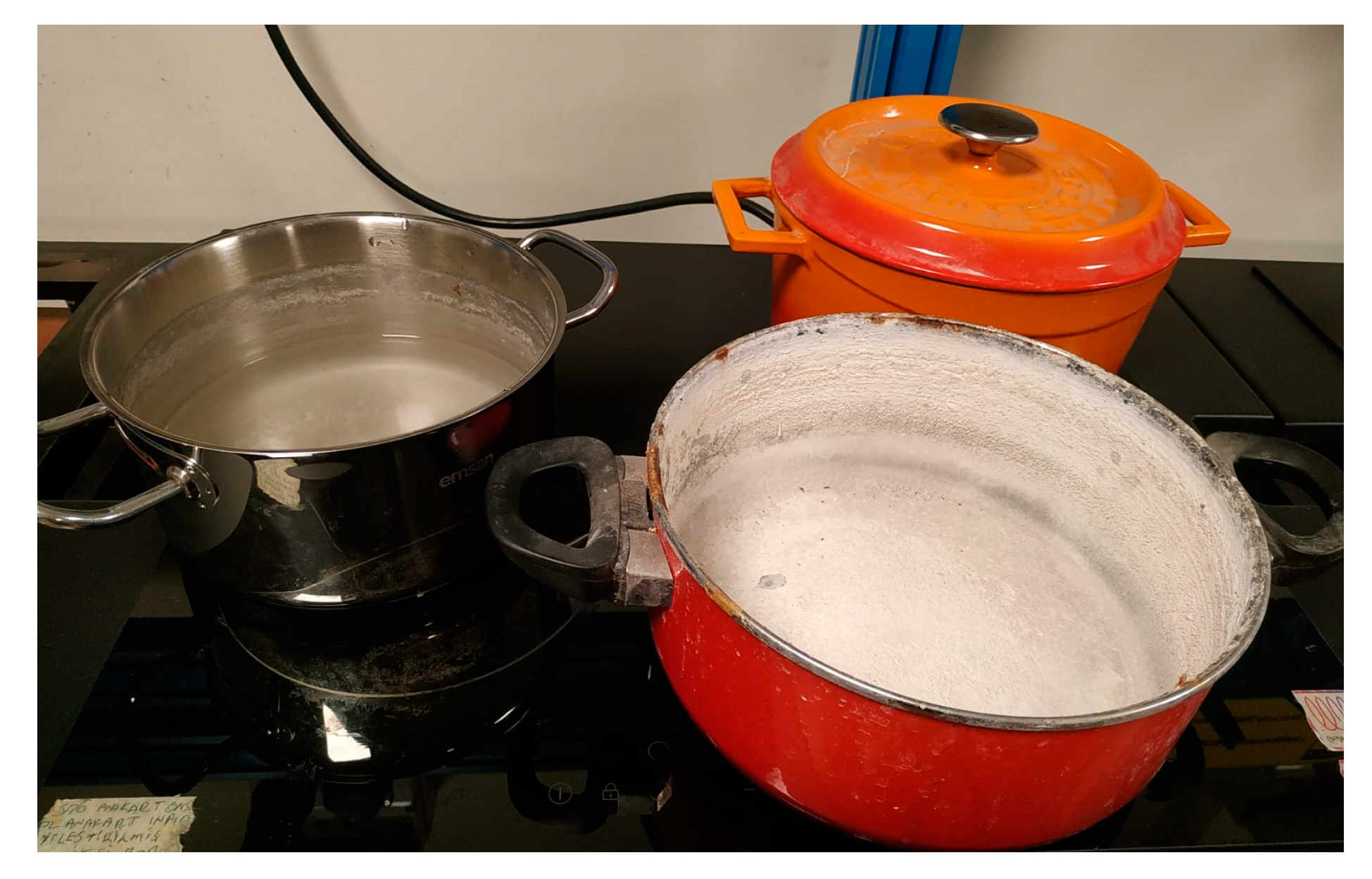
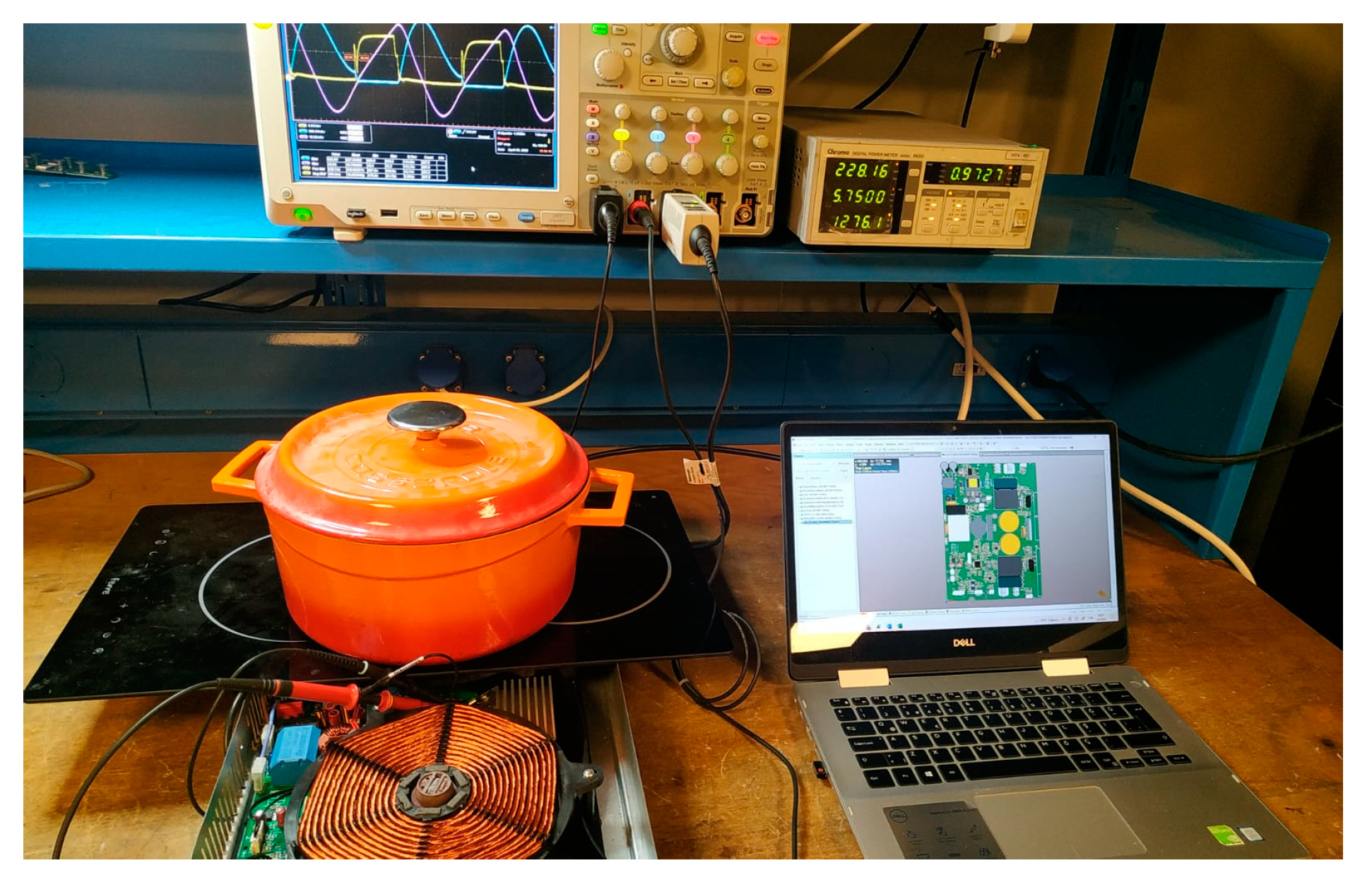
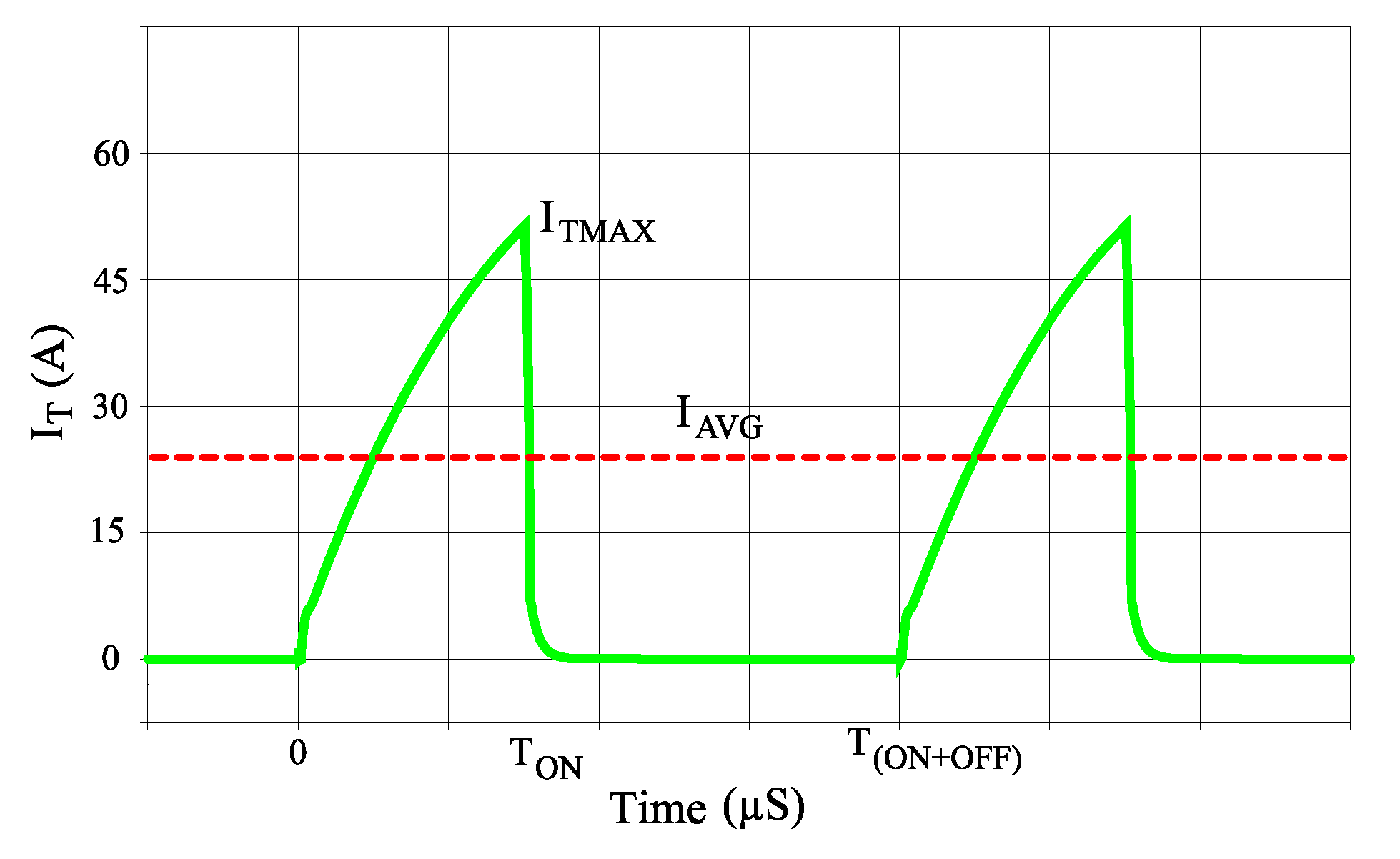
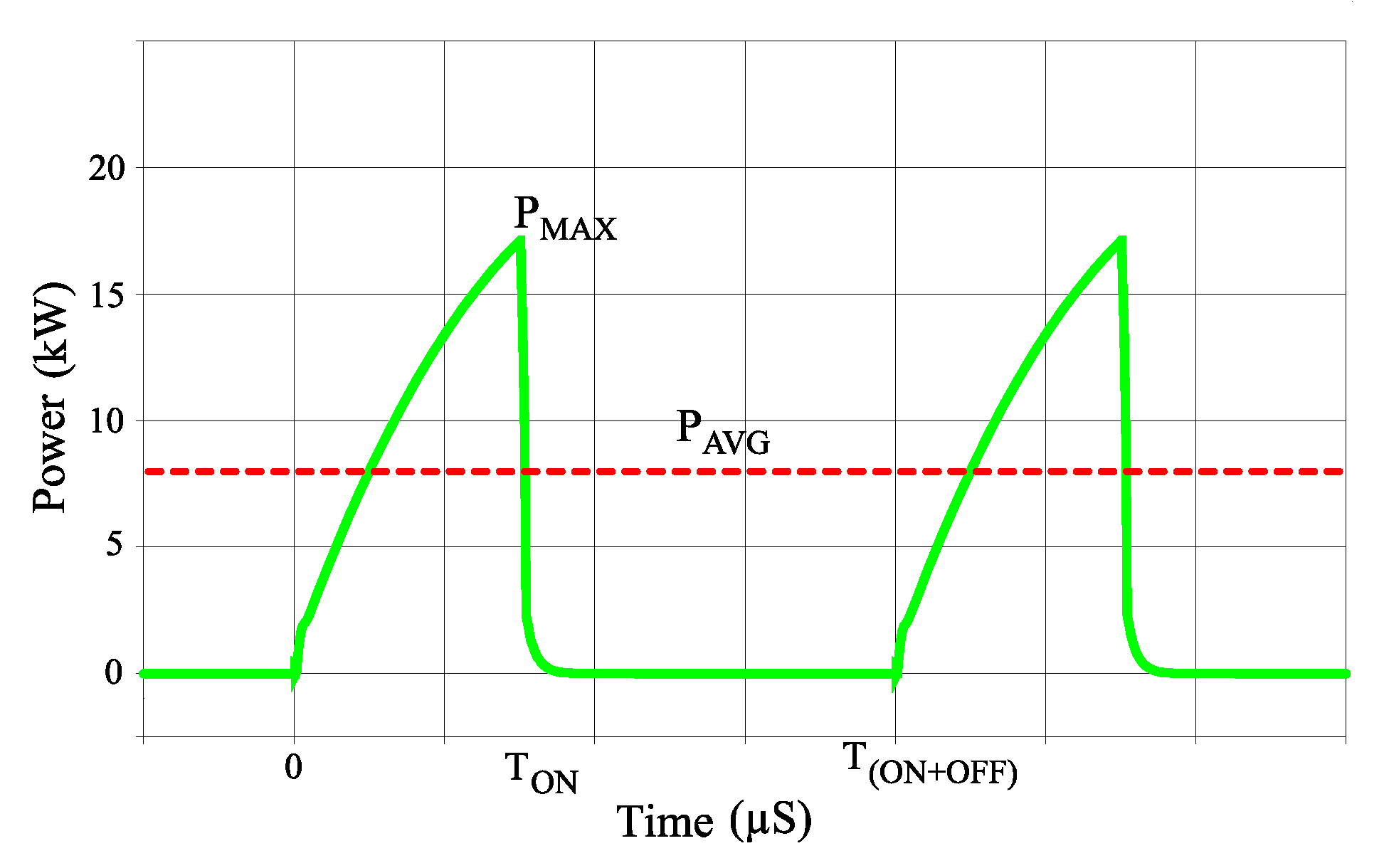
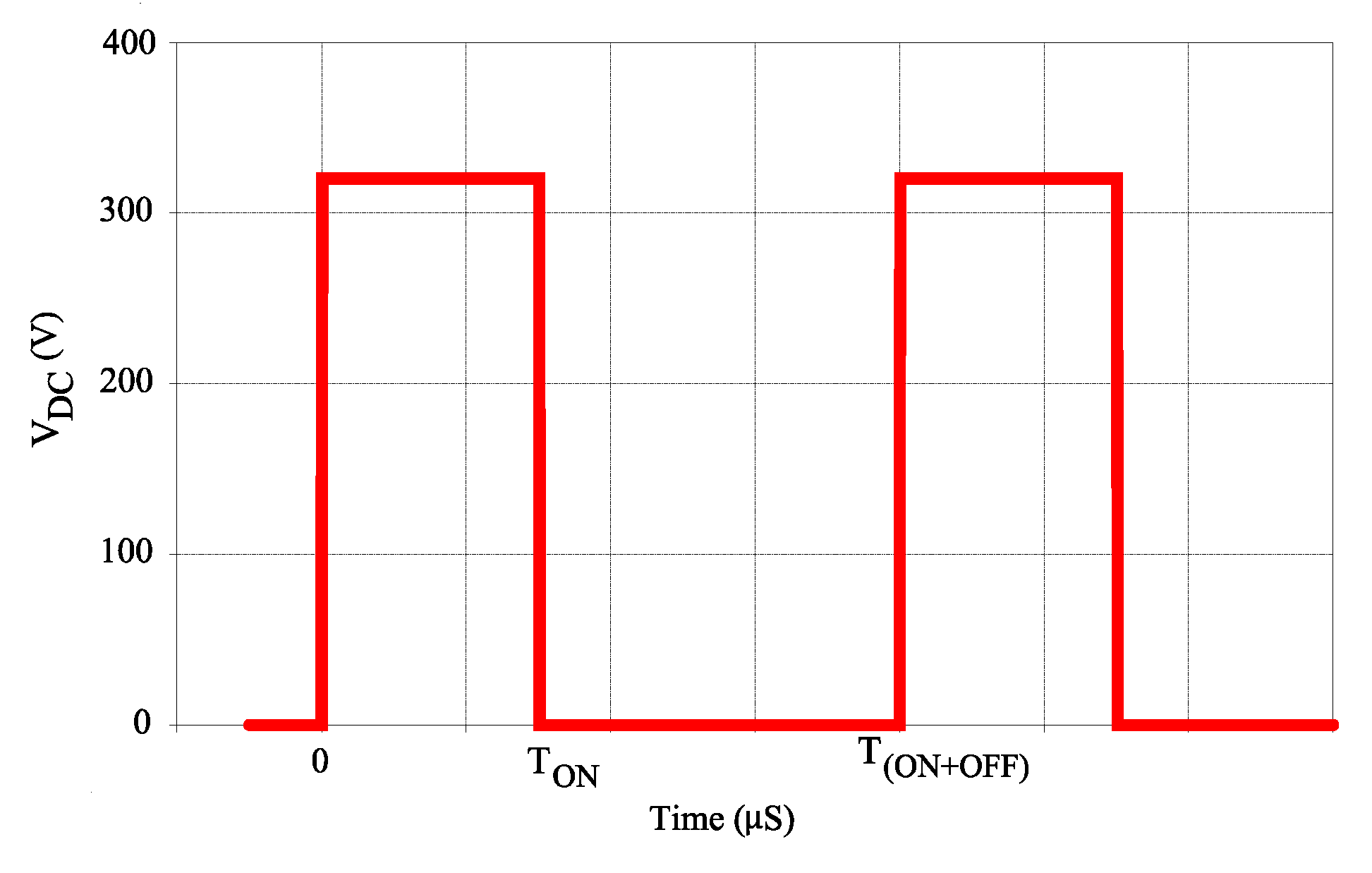


| Pre-Defined Circuit Parameters | |
| Calculated Circuit Parameters | |
| Calculated Boundary Conditions | |
| Input Circuit Parameters | Output Boundary Parameters | Output Power | |||
| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Unit |
| Number of turns | 28 | ||
| External diameter of the coil | 180 | mm | |
| Inner diameter of the coil | 30 | mm | |
| Distance between coil winding and ferrite bars | 4 | mm | |
| Distance between coil winding and pan | 4 | mm | |
| Strand amount of a litz wire | 66 | ||
| Wire diameter of single strand | 0,27 | ||
| Ferrite permeability | 800 | ||
| Equivalent inductance with no load | 110 | µH | |
| Equivalent resistance with no load | 0,12 | ||
| Equivalent inductance with cast iron pan | 89,76 | µH | |
| Equivalent resistance with cast iron pan | 4,21 | ||
| Equivalent inductance with stainless steel pan | 81,81 | µH | |
| Equivalent resistance with stainless steel pan | 3,36 | ||
| Equivalent inductance with silit silargan pan | 69,07 | µH | |
| Equivalent resistance with silit silargan pan | 2,48 |
| Input Circuit Parameters | Output BoundaryParameters | Output Power | |||
| Input Circuit Parameters | Output BoundaryParameters | Output Power | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




