1. Introduction
Geopolymers, a pioneering class of inorganic polymers, have gained prominence due to their exceptional properties and eco-friendly nature. J. Davidovich [
1] initially introduced geopolymers as novel entities synthesized via the polycondensation of aluminosilicate materials in a highly alkaline milieu. In contrast to crystalline zeolites featuring (Si-O-Al) polymer frameworks, geopolymers establish amorphous networks characterized by covalent bonds among inorganic crystals. These networks consist of SiO4 and AlO4 tetrahedral frameworks interconnected via oxygen atoms, culminating in a semi-crystalline 3D aluminosilicate microstructure [
2].
Geopolymers stand out for their superior mechanical traits, reduced permeability, resilience against chemical aggression, and prolonged fire resistance compared to conventional Portland cement. Their environmental sustainability is underscored by minimal carbon dioxide emissions during production, coupled with cost-effectiveness and durability [
3]. Geopolymers have found application in diverse realms including heat and sound absorption [
4], fire protection [
5], and construction materials serving as catalysts, adsorbents, and fillers [
6,
7].
Advancements in optimizing GC attributes and refining fabrication processes have led to the emergence of highly porous geopolymer foam composites [
8,
9,
10,
11]. These lightweight foams demonstrate remarkable resistance to acidic environments, reduced thermal conductivity, and lower sintering temperatures. Fortified with aluminum-based metal powder, inorganic basalt fibers, and glass fibers, geopolymer foam achieves a delicate equilibrium between low density and strength. Diverse foaming agents contribute to synthesizing low-density geopolymers conducive to surface application. Notably, potassium-based geopolymers incorporating coarse fly ash, quartz sand, and silica fume as fillers have exhibited structural integrity even after fire tests, with negligible macroscopic damage [
12].
While geopolymer foaming may impact mechanical properties, it significantly amplifies insulation capabilities, presenting a compelling alternative to traditional insulation materials. Geopolymers hold promise for crafting fire-resistant coatings and efficient thermal and acoustic insulators. Comprehensive studies have delved into the repercussions of elevated temperatures on geopolymers, influencing physical and mechanical attributes encompassing apparent density, water absorption, weight loss, drying shrinkage, and compressive and flexural strengths [
13,
14,
15]. This study specifically examines the fire resistance capacity of geopolymer coatings, a crucial determinant for their practical implementation.
Numerous investigations have probed the influence of high temperatures on geopolymer materials [
16,
17,
18,
19]. These endeavors have unveiled diverse outcomes, ranging from diminished compressive strength and augmented mass loss at 1000 °C [
17], to reduced compressive strength and Young’s modulus with increasing temperatures[
18]. While coarse fly ash-based geopolymer mortars may sustain strength at 1000 °C[
19], geopolymer foams (GFs) have demonstrated robust strength retention and minimal thermal shrinkage under elevated temperatures [
20,
21,
22]. Alkali-activated fly ash GC foam exhibit improved durability at 1100°C [
21], and sintering enhances the mechanical properties of acid-based geopolymers [
23].
Sprayed concrete, commonly known as shotcrete, is a technique employed in subterranean constructions like tunnels, eliminating the need for formwork and sometimes even reinforcement [
24]. The process involves projecting a concrete mix onto a prepared surface using specialized equipment. Tailoring the mix composition with modified compounds and fibers can optimize its physical and mechanical properties [
25]. Careful consideration of concrete rheology and deformability during application ensures uniformity and load-bearing capacity [
26]. The procedure entails surface prep, concrete mixing, initial application, reinforcement mat placement, reapplication, and upkeep [
27]. Advanced methods like wet spraying and accelerant additives enhance quality and efficiency [
28]. A versatile nozzle can improve mixing and diminish dust hazards. This technique revolutionizes underground construction with its versatility and adaptability.
This study significantly contributes to unraveling the fire resistance of steel-reinforced fly ash geopolymers, drawing comparisons with OPC concrete [
15]. It elucidates the protective application of foamed geopolymer coatings on steel plates, spotlighting both thermal stability and the spraying procedure. Substantial emphasis is laid on harnessing GCs to enhance fire protection and insulation attributes. By advancing our comprehension of geopolymer coatings’ behavior at elevated temperatures, this research fosters opportunities for optimizing their practical deployment across diverse industries.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The research utilized the "Baucis lk" binder from Ceské Lupkové Závody, a.s., an aluminosilicate binder activated by metakaolin, and potassium hydroxide. Metakaolin results from calcining kaolinite at 500-800 °C, correlating reactivity with physical strength. Metakaolin’s uniformity makes it a geopolymer formation benchmark. Mechanical enhancements in geopolymers came from chopped basalt fibers from Basaltex, a.s. These fibers are 3.2 mm long, 13 μm in diameter, with a density of 2.67 g/cm
3 and thermal conductivity of 0.031-0.038 W/mK. Coarse silica sand from Sklopisek Strelec, a.s., with 0.3-0.8 mm size and density of 2.65 g/cm
3, contributed to structural coherence and mechanical strength. Fire resistance improved with fire-retardant additives: silica fume and aluminum powders. Silica fume, from Kema Morava—sanacní centrum a.s., had 90 wt.% SiO
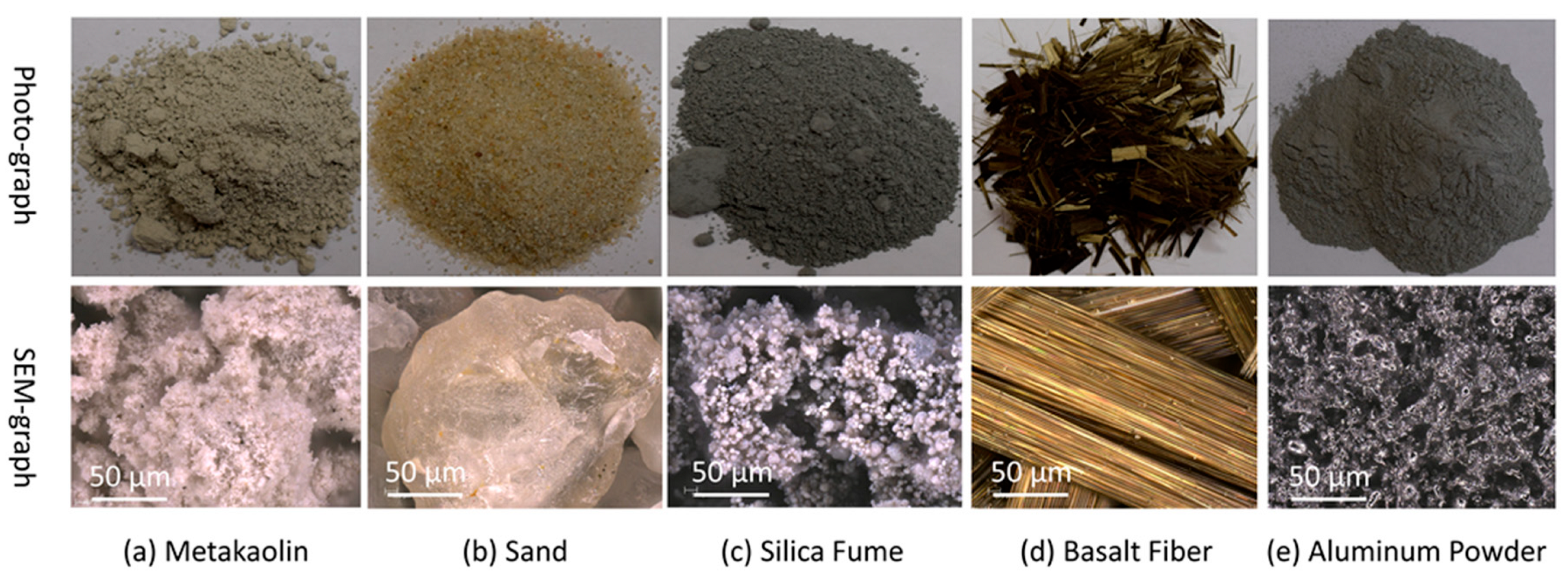
2 and average grain size 1 mm. Aluminum powder from Pkchemie, Inc., had an average particle size of 51.47 μm. Interaction of Aluminum powder with the alkaline solution led to entrapped hydrogen-rich gas mixtures due to separate gas and polymer phases. These components collectively form the basis of this comprehensive investigation. Photo-graph and SEM-graph of raw materials are presented in
Figure 1.
2.2. Samples preparation
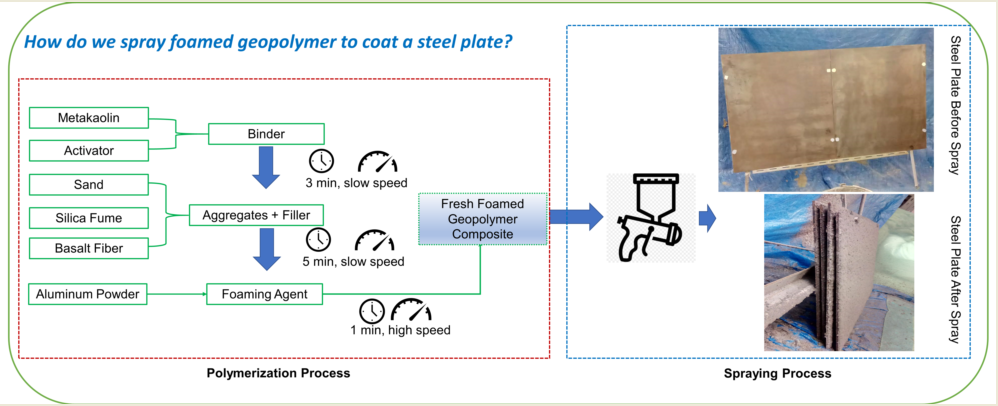
Geopolymer coatings were applied to a carbon steel plate by spraying. The steps involved in preparing the geopolymer mix were as follows: First, cement-based metakaolin and an alkaline potassium activator (in a 5:4 ratio according to the manufacturer) were thoroughly mixed for three minutes. Second, silica fume, sand, and fibers were added to the geopolymer mortar and mixed for five minutes. The aluminum powder was added at the final stage and mixed at high speed for one minute resulting in a foaming effect on the geomortar (Note: If the geopolymer does not foam, then do not add this step). The proportions of the foamed and non-foam geopolymer composition compared to metakaolin are presented in
Table 1.
The mixture was then sprayed onto the steel plate and cured at room temperature for 28 days. The preparation procedure of GC for application spray is shown in
Figure 2.
2.3. Methods
The apparent density of GC materials was measured according to standard CSN EN 1936 and was estimated by dividing the mass of the sample by its apparent volume. It was determined on a series of samples dedicated before the bending strength test. The samples have dimensions of 30 by 30 by 150 mm3.
The mechanical properties of the GCs were evaluated utilizing the Instron model 4202 testing machine in accordance with the ˇCSN EN 1015-11 standard. To assess the flexural strengths, the three-point bending tests were employed. The specimens, measuring 30 by 30 by 150 mm3 for flexural strength tests and 30 by 30 by 30 mm3 for compressive strength tests, were subjected to compression and bending assessments. The tests were conducted under ambient conditions at a temperature of 22 ± 3 °C, utilizing a 10 kN load cell and a crosshead speed of 2.5 mm. For each experimental series, the average compressive and flexural strengths were derived from measurements taken on three individual samples.
Simulated weathering aging experiments have carried ISO 4892-2 with a Test Chamber (Q-SUN Xe-1-S, Q-Lab Corporation, Westlake, USA). The intensity was set at 0.51 W/m2, and the wavelength was 340 nm. The chamber’s inside temperature stayed at 50 ± 5 °C. The samples 30 by 30 by 15 mm3 underwent 102 min radiation treatment. The samples had been eliminated from the chamber after 1000 cycles (1000 h) for further observation and appearance evaluation. The process of weathering aging testing was examed using microstructural analysis using image analysis tools.
The JEOL JSM-IT200 scanning electron microscope (SEM) was used for microstructural research. Using test samples with dimensions of 100 by 100 by 15 mm3, the thermal conductivity was investigated using the NETZSCH HFM 446 instrument.
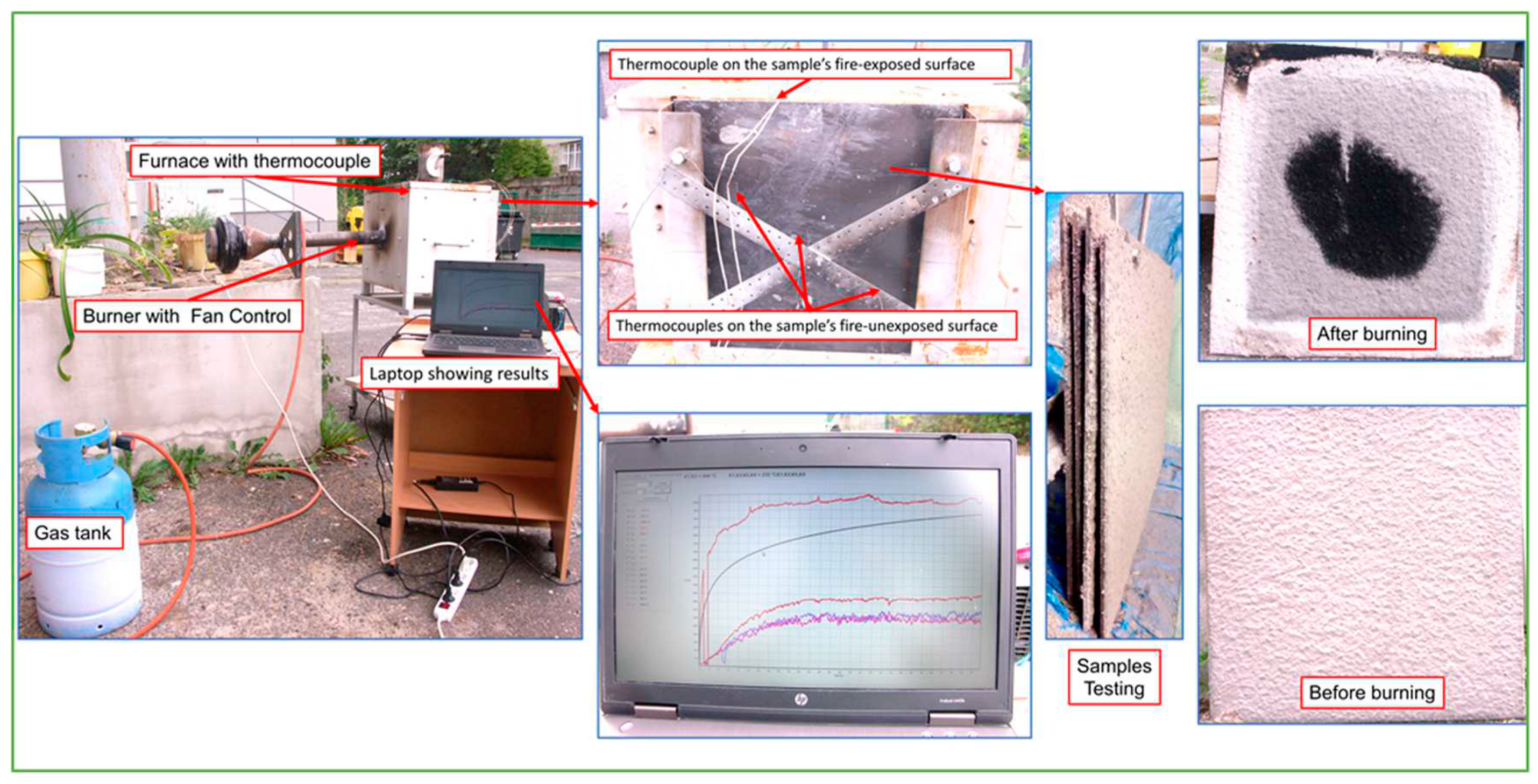
The fire resistance tests were carried out on a 500 by 500 by 5 mm
3 steel plate, covered with a 6 mm thick layer of foam geopolymer. A thermocouple was attached both to the outside and inside of the natural gas furnace. The experimental setup is shown in
Figure 3. For more details on the experimental setup, the readers are referred to [
10,
29].
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Physical, mechanical, and thermal properties
The results from experimental investigations of compressive strength, flexural strength, density, and porosity are presented in
Table 2. Both types of research belong to the category of lightweight construction materials [
30]. Compare with a concrete density of 2400 kg/m
3 [
12]. foam geopolymer and non-foam geopolymer lighter 72.08 %, and 36.67 %, respectively. The lightness of GC materials is highly dependent on aggregates and fillers, and they also greatly affect their properties.
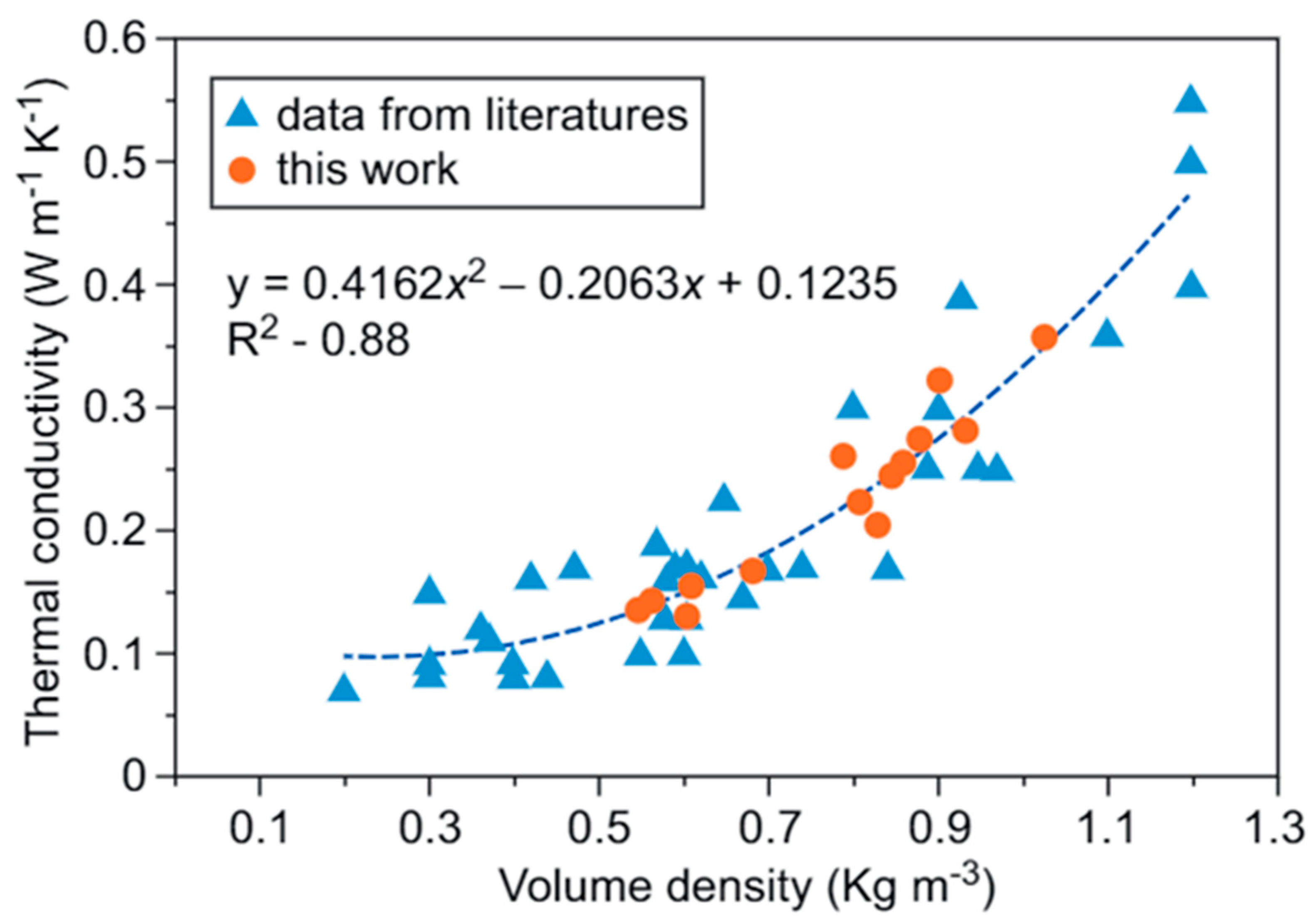
The results in
Table 2 only show a clear distinction: when the geopolymer has a higher density, it has better mechanical properties. In contrast, thermodynamic properties when the GC materials are lighter, the thermal conductivity coefficient is lower and the thermal resistance is higher. On the other hand, The relationship of the thermal conductivity with the volume density is shown in
Figure 4.
The comparison between the foam geopolymer material and its non-foam counterpart reveals discernible differences in their mechanical properties. Specifically, the foam geopolymer exhibits compressive strength and bending strength values lower than 10.85 and 13.5, respectively. Furthermore, a differential in density, thermal conductivity, and production cost are evident, with values lower than 2.27, 5.49, and 1.8, respectively. This points towards a notable variation in the material characteristics between the two forms of GCs.
Moreover, the thermal resistance of the lightweight geopolymer material stands prominently higher, with a value of 4.7 times greater than that of the non-foam geopolymer counterpart. This particular attribute of enhanced thermal resistance holds significant significance as it signifies the material’s capacity to endure high temperatures, thus aligning with the essential quality of refractory materials [
13]. The use of metakaolin, a key constituent, contributes to the material’s commendable physical attributes, as corroborated by the congruence of its values with those presented in Table 3. In this context, geopolymer cement formulated with metakaolin material showcases favorable thermal properties.
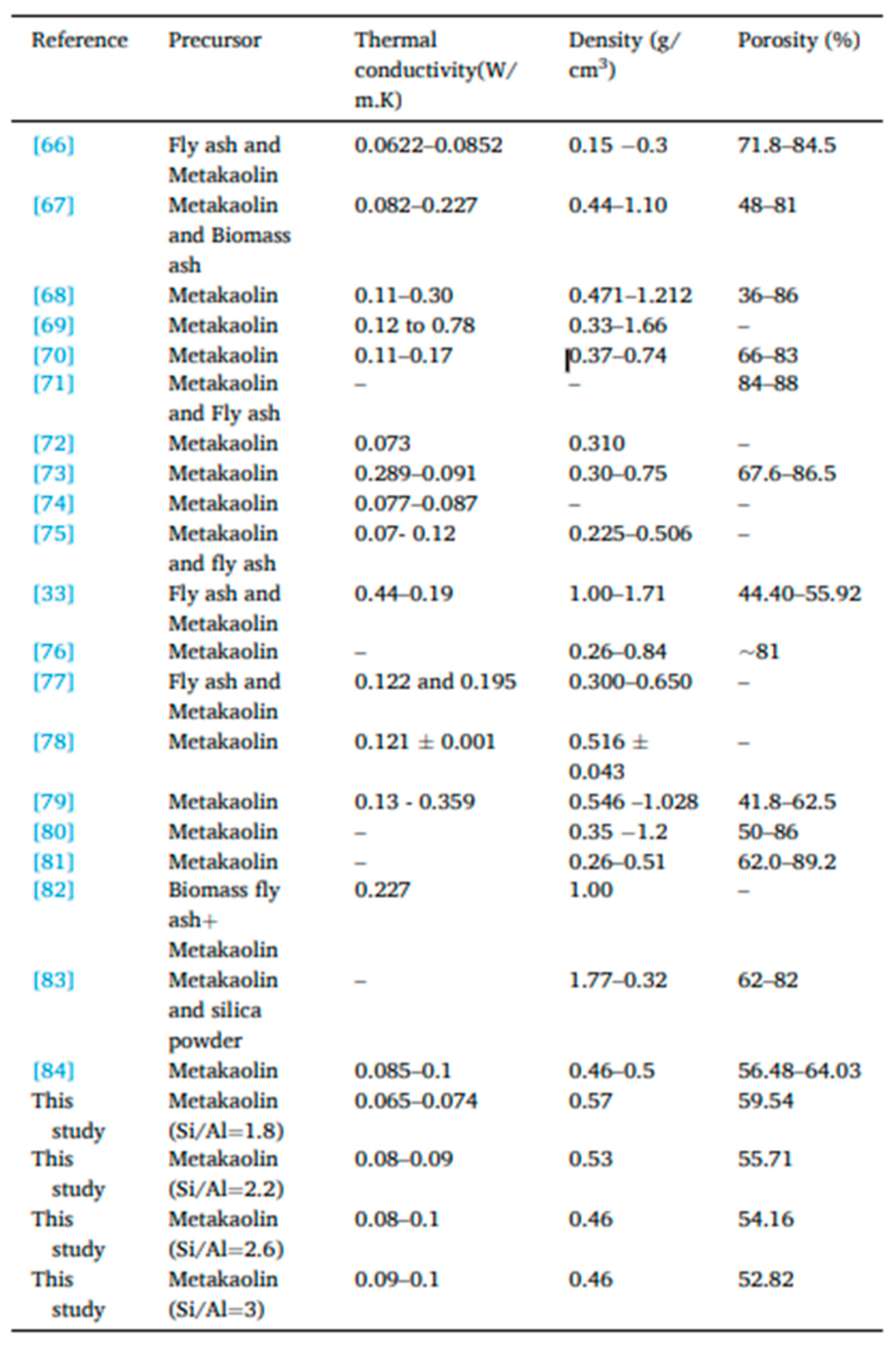
Empirical evidence substantiates the favorable attributes of metakaolin-based geopolymer cement, evident in its specific density ranging between 0.07-0.2 W/(m·K), density spanning from 370-740 Kg/m3, and porosity falling within the range of 55 %-80 % (Table 3). These quantifiable parameters collectively validate the material’s thermal prowess, as denoted by its efficient thermal conductivity values. In summation, the discourse underscores the notable distinctions in mechanical and thermal attributes between foam and non-foam geopolymer materials. It also underscores the pivotal role of metakaolin in imparting commendable thermal characteristics to geopolymer cement, substantiated by quantifiable values presented in Table 3.
Table 3. Comparing thermal physical properties of aerated geopolymers based on metakaolin [
7].
The thermal conductivity of a material is subject to multifarious influences, with porosity holding particular sway as a determining factor. The intricate interplay between porosity and thermal conductivity is pivotal, wherein heightened porosity within the GC corresponds to diminished thermal conductivity albeit at the cost of reduced structural strength. Schematic elucidations of the techniques employed to instigate porosity are delineated in
Figure 5. The morphological characteristics attributed to chemical methodologies predominantly manifest when chemical reactions yield hydrogen or oxygen gases entrapped within the crystalline matrix of GCs.
The methodological approach employed within this journal entails the utilization of aluminum foam, a choice rooted in its propensity to engage in reactions even at ambient temperatures, coupled with its expeditious curing kinetics. This rationale underscores the researcher’s deliberate emphasis on the fusion of theoretical inquiry and practical implementation. A comparative analysis of foaming methodologies reveals distinctive attributes: while the application of H
2O
2 necessitates a curing span of up to 48 hours contingent upon composition and curing temperature [
11] the utilization of silica powder mandates reaction initiation at temperatures surpassing 60 °C [
32]. This comparative assessment underscores the expediency of the selected aluminum foam route in expediting the foaming process.
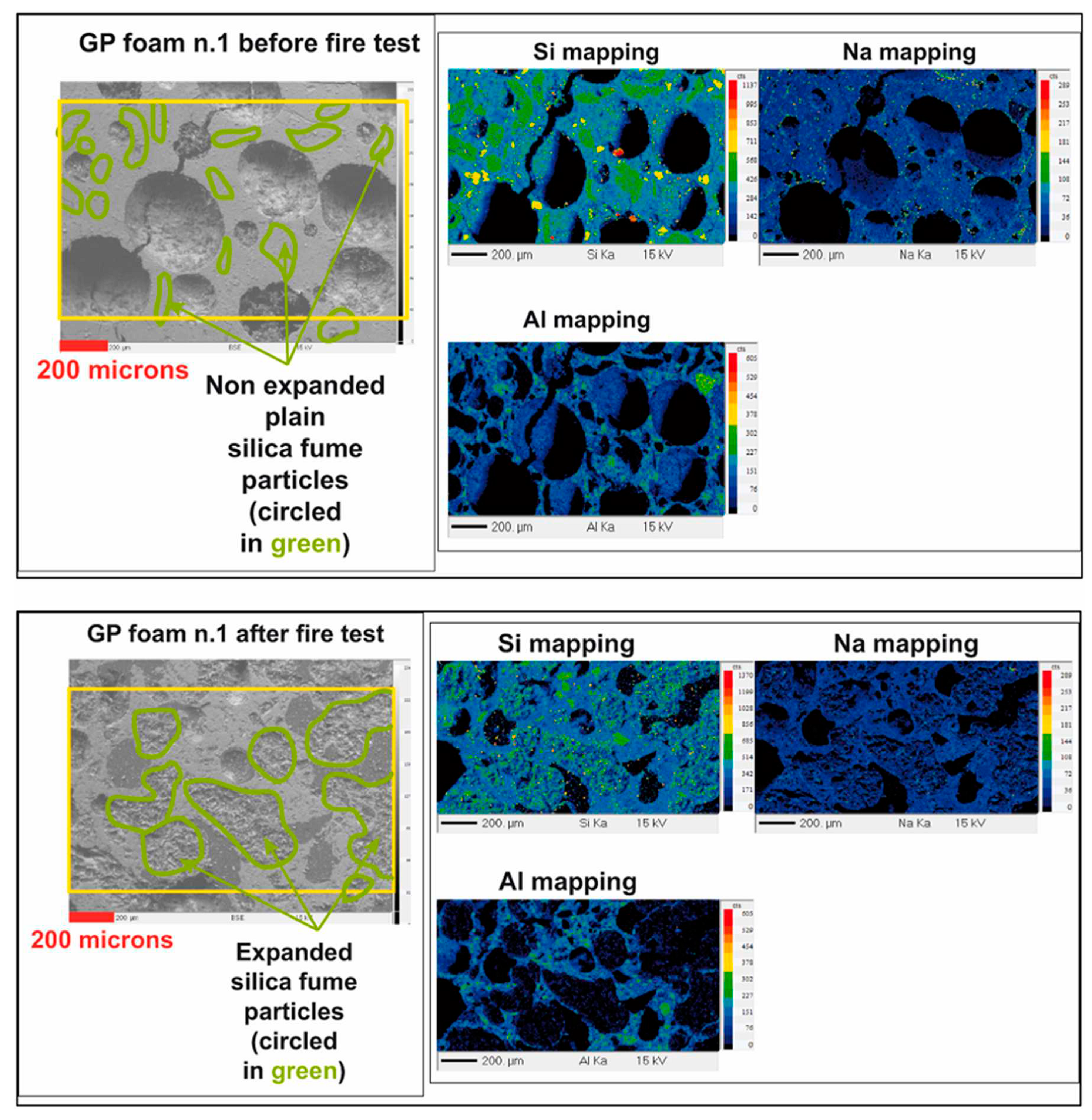
The porosity of the studied foamed geopolymer is 68 % after the end of fire testing is 58 %.
Figure 6 shows that after the fire, silica fume expands and creates small pores, and pore sizes decreased ( than those existing before the fire).
The production cost of foam and non-foam geopolymer is represented value of 250 and 450 USD/m
3. The global cost product of fresh concrete is decried by 200-300 USD/m
3. The product cost of fresh concrete for each company is different [
6]. The production cost has a positive linear relationship with the strength grade and the density of the GCs.
3.2. Fire resistance properties
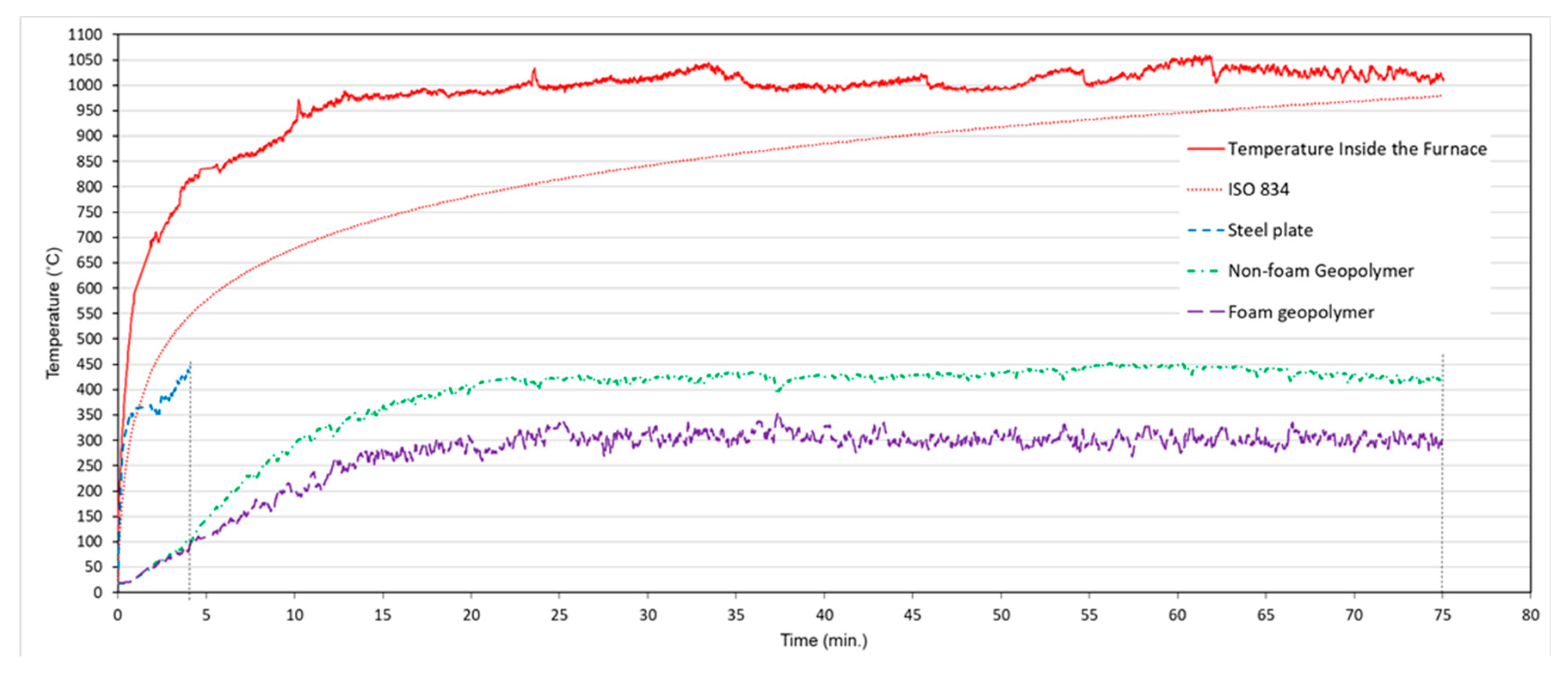
The temperature-time curve of the sample test is shown in
Figure 7. Initially, the surface temperature of the samples exposed to the flame of a gas burner rapidly increased up to 20 minutes, and then saturation occurred. The sample (with a coating thickness of 6 mm) withstood the fire for a period of 75 minutes, while the steel plate without the coating layer withstood only 3.78 minutes. The fire resistance of samples is also affected by the thermal conductivity of the coatings as well as their thickness. On the Temperature-Time Curve from the 20th to the 75th minute, the temperature inside the furnace and the temperature outside the test sample were almost constant. Results show that geopolymer foams provide excellent thermal barriers, reducing the temperature of the steel plate by up to 150°C. As the heat outside the plate is exposed to the environment, it is lost. In the next study, the author will investigate the behavior of the Temperature-Time curve as a function of the test conditions. On the outside, the test sample is covered with an insulating material. Geopolymers composites have been studied due to their unique properties such as good fire resistance.
The constitution of the geopolymer material undergoes transformations during processes of degradation, combustion, diffusion, and thermal conduction. This intricate interplay is further exacerbated by evolving conditions of temperature. With escalating temperatures, a proliferation of microcracks emerges, both in number and size, along the material’s surface. This phenomenon significantly diminishes the thermal conductivity of the GCs [
5].
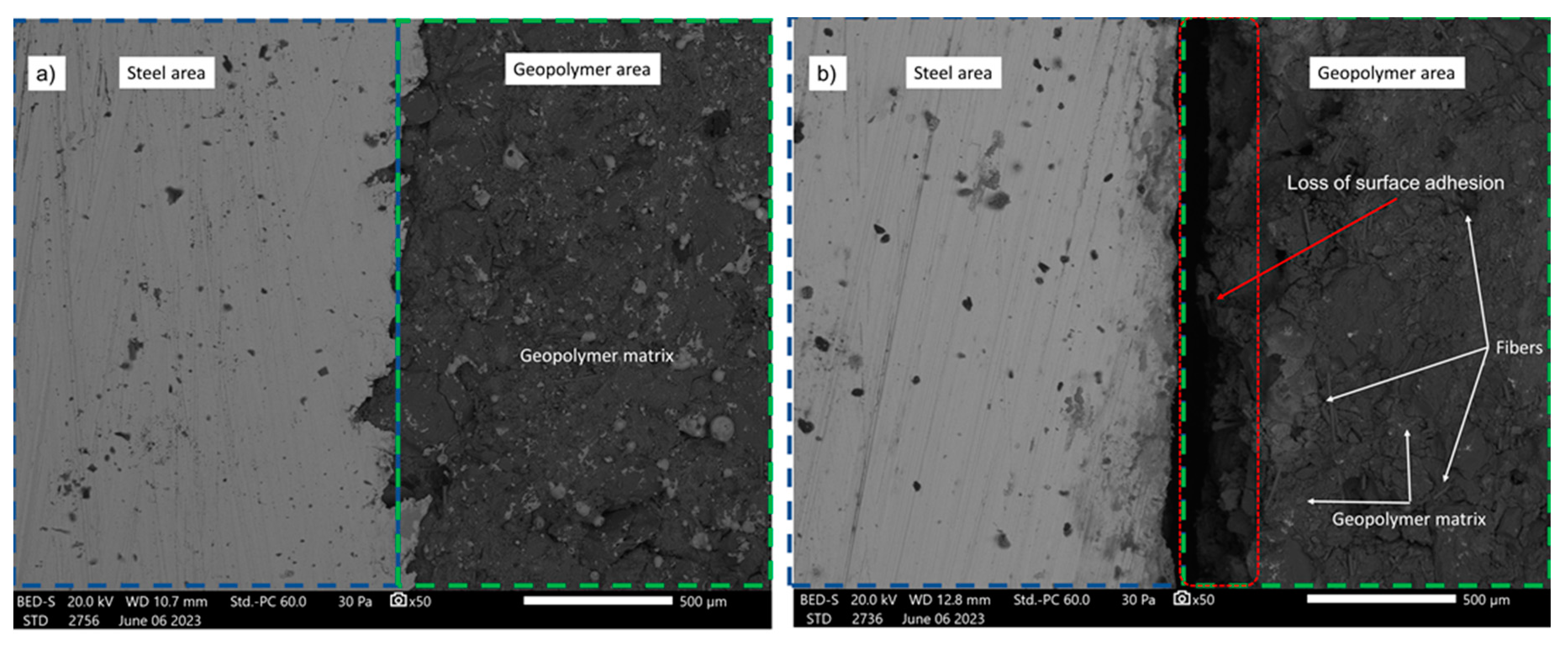
The investigation extends to SEM micrographs, offering insights into the interfacial zone connecting the GCs and steel substrates. These micrographs, encompassing pre- and post-1000-hour aging test, find represented in
Figure 8 and
Figure 9. The robust structural integrity characterizing the foamed geopolymer is conspicuously resilient when subjected to the rigors of the durability assessment, an observation lucidly depicted in
Figure 8. In stark contrast, the non-foamed geopolymer material is shown to undergo detachment from the steel substrate, a phenomenon well-evidenced in
Figure 9.
4. Conclusions
The study has demonstrated the fire resistance and properties of GCs formulated using alkali-activated metakaolin and aluminum powder. With the presented method, a substrate of any configuration and shape can be coated effectively. Geopolymers can also be sprayed on different surfaces from different angles, allowing different operations to be performed.
The GC foams provide excellent thermal insulation and up to 75 minutes of fire resistance with a 6 mm coating, significantly reducing temperatures compared to uncoated steel.
The GC foam also exhibits a density of 670 kg/m³, thermal conductivity of 0.166 W/m·K, 68% porosity, and a production cost of 250 US Dollars per cubic meter.
The research underscores the potential of foamed geopolymer coatings for effective and economical surface protection.
Author Contributions
Van Su Le: Methodology, Investigation, Writing the draft manuscript, Editing Kinga Plawecka: Investigation, Formal Analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
This publication was written at the Technical University of Liberec, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering with the support of the Institutional Endowment for the Long-Term Conceptual Development of Research Institutes, as provided by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic in the year 2023.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript: “Geopolymer Composites: Manufacturing of sandwich steel and geopolymer structures with spray technology without Formwork’’.
References
- Davidovits:, J. Geopolymers and Geopolymeric Materials. Journal of thermal analysis 1989, 35, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Years of Successes and Failures in Geopolymer Applications. Market Trends and Potential Breakthroughs. In Proceedings of the Geopolymer 2002 conference; Geopolymer Institute Saint-Quentin, France; Melbourne, Australia. 2002; Vol. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Ishwarya, G.; Gupta, M.; Bhattacharyya, S.K. Geopolymer Concrete: A Review of Some Recent Developments. Constr Build Mater 2015, 85, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.V.; Le, V.S.; Louda, P.; Szczypiński, M.M.; Ercoli, R.; Růek, V.; Łoś, P.; Prałat, K.; Plaskota, P.; Pacyniak, T.; et al. Low-Density Geopolymer Composites for the Construction Industry. Polymers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarazin, J.; Davy, C.A.; Bourbigot, S.; Tricot, G.; Hosdez, J.; Lambertin, D.; Fontaine, G. Flame Resistance of Geopolymer Foam Coatings for the Fire Protection of Steel. Composites Part B-engineering 2021, 222, 109045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanun, Y.; Alisjahbana, S.W.; Ma’Soem, D.M.; Setiawan, M.I.; Ahmar, A.S. Designing Cost Production of Concrete. J Phys Conf Ser 2018, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degefu, D.M.; Liao, Z.; Berardi, U.; Labbé, G. The Dependence of Thermophysical and Hygroscopic Properties of Macro-Porous Geopolymers on Si/Al. J Non Cryst Solids 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazan, P.; Kozub, B.; Łach, M.; Korniejenko, K. Evaluation of Hybrid Melamine and Steel Fiber Reinforced Geopolymers Composites. Materials 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabba, L. Cement-Free Building Materials: Mix Design and Properties in View of Their Application in Civil Engineering.; 2018.
- Le, V.S.; Louda, P. Research of Curing Time and Temperature-Dependent Strengths and Fire Resistance of Geopolymer Foam Coated on an Aluminum Plate. Coatings 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, M.N.G.; dos Santos, C.M.; de Souza, M.T.G.; de Vasconcelos, E.A.; Nobrega, A.C.V.; Marinho, É.P. Use of Sodium Metasilicate as Silica Source and Stabilizing Agent in Two–Part Metakaolin–H2o2 Geopolymer Foams. SSRN Electronic Journal 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, D.H. ‘Concrete’ Manipulatives, Concrete Ideas. Contemporary Issues in Early Childhood 2000, 1, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prałat, K.; Ciemnicka, J.; Koper, A.; Szczypiński, M.M.; Łoś, P.; Nguyen, V.V.; Le, V.S.; Rapiejko, C.; Ercoli, R.; Buczkowska, K.E. Determination of the Thermal Parameters of Geopolymers Modified with Iron Powder. Polymers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, V.S.; Louda, P.; Tran, H.N.; Nguyen, P.D.; Bakalova, T.; Buczkowska, K.E.; Dufková, I. Study on Temperature-Dependent Properties and Fire Resistance of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Foams. Polymers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Li, H.; Shuai, Q.; Wang, L. Fire Resistance of Alkali Activated Geopolymer Foams Produced from Metakaolin and Na2O2. Materials 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhang, W.; Shi, D. Effect of Elevated Temperature on the Properties of Geopolymer Synthesized from Calcined Ore-Dressing Tailing of Bauxite and Ground-Granulated Blast Furnace Slag. Constr Build Mater 2014, 69, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithambaram, S.; Kumar, S.; Prasad, M.M. Thermo-Mechanical Characteristics of Geopolymer Mortar. Constr Build Mater 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Mocadlo, R.; Zhao, M.; Sisson, R.D.; Tao, M.; Liang, J. Preparation of a Geopolymer from Red Mud Slurry and Class F Fly Ash and Its Behavior at Elevated Temperatures. Constr Build Mater 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kürklü, G. The Effect of High Temperature on the Design of Blast Furnace Slag and Coarse Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Mortar. Composites Part B-engineering 2016, 92, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- František, Š.; Rostislav, Š.; Zdeněk, T.; Petr, S.; Vít, Š.; Zuzana, Z.C. Preparation and Properties of Fly Ashbased Geopolymer Foams. Ceramics-Silikáty 2014, 58, 188–197. [Google Scholar]
- Hlaváek, P.; milauer, V.; kvára, F.; Kopecký, L.; ulc, R. Inorganic Foams Made from Alkali-Activated Fly Ash: Mechanical, Chemical and Physical Properties. J Eur Ceram Soc 2015, 35, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilla, M.S.; de Mello Innocentini, M.D.; Morelli, M.R.; Colombo, P. Geopolymer Foams Obtained by the Saponification/Peroxide/Gelcasting Combined Route Using Different Soap Foam Precursors. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 2017, 100, 3440–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cui, X.; He, Y.; Liu, S.; Gong, S. The Phase Evolution of Phosphoric Acid-Based Geopolymers at Elevated Temperatures. Mater Lett 2012, 66, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprayed Concrete Multipurpose Nozzle (2020) | Tong Youdan. Available online: https://typeset.io/papers/sprayed-concrete-multipurpose-nozzle-2zn9lf93qi (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Concrete Spraying Construction Method (2019) | Wang Mingchen. Available online: https://typeset.io/papers/concrete-spraying-construction-method-4ix4w13ma1 (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Concrete Spraying Construction Technology (2019) | Xiao Fulei. Available online: https://typeset.io/papers/concrete-spraying-construction-technology-4x1lmjzcsq (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Alekseev, V.; Bazhenova, S. Optimization of Concrete Compositions for Sprayed Concrete in the Consruction of Underground Structures. Bulletin of Belgorod State Technological University named after. V. G. Shukhov 2020, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melbye, T.A.; Dimmock, R.H. Modern Advances and Applications of Sprayed Concrete. Shotcrete: Engineering Developments 2020, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.S.; Louda, P.; Tran, H.N.; Nguyen, P.D.; Bakalova, T.; Buczkowska, K.E.; Dufková, I. Study on Temperature-Dependent Properties and Fire Resistance of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Foams. Polymers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.S. Influence of Foam Densities in Cellular Lightweight Concrete. Int J Res Appl Sci Eng Technol 2017, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.S. Thermal Conductivity Of Reinforced Geopolymer Foams. Ceramics - Silikaty 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdolotti, L.; Liguori, B.; Capasso, I.; Errico, A.; Caputo, D.; Lavorgna, M.; Iannace, S. Synergistic Effect of Vegetable Protein and Silicon Addition on Geopolymeric Foams Properties. J Mater Sci 2015, 50, 2459–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Pullar, R.C.; Labrincha, J.A. Geopolymer Foams: An Overview of Recent Advancements. Prog Mater Sci 2020, 109, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).