Submitted:
23 August 2023
Posted:
24 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. NPAS and the Molecular Clockwork
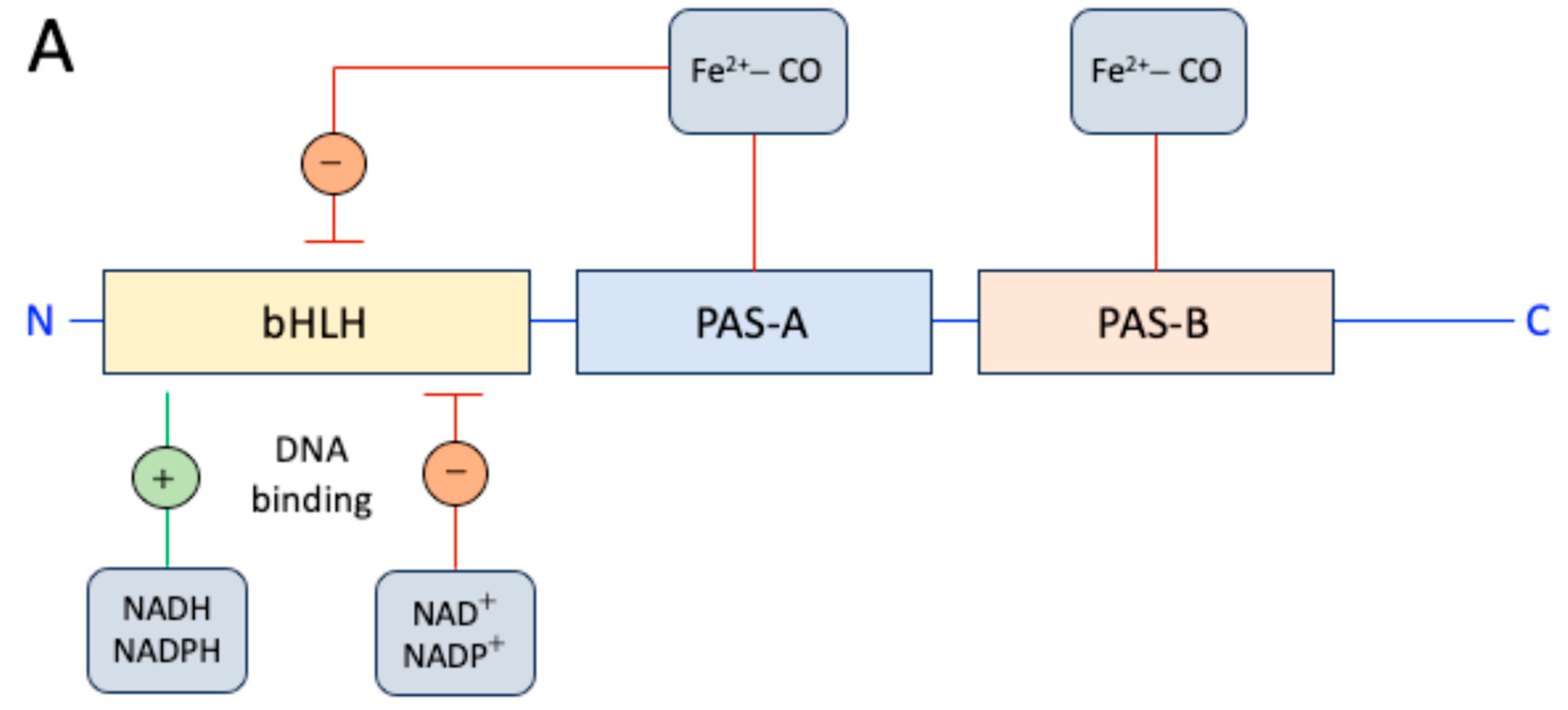
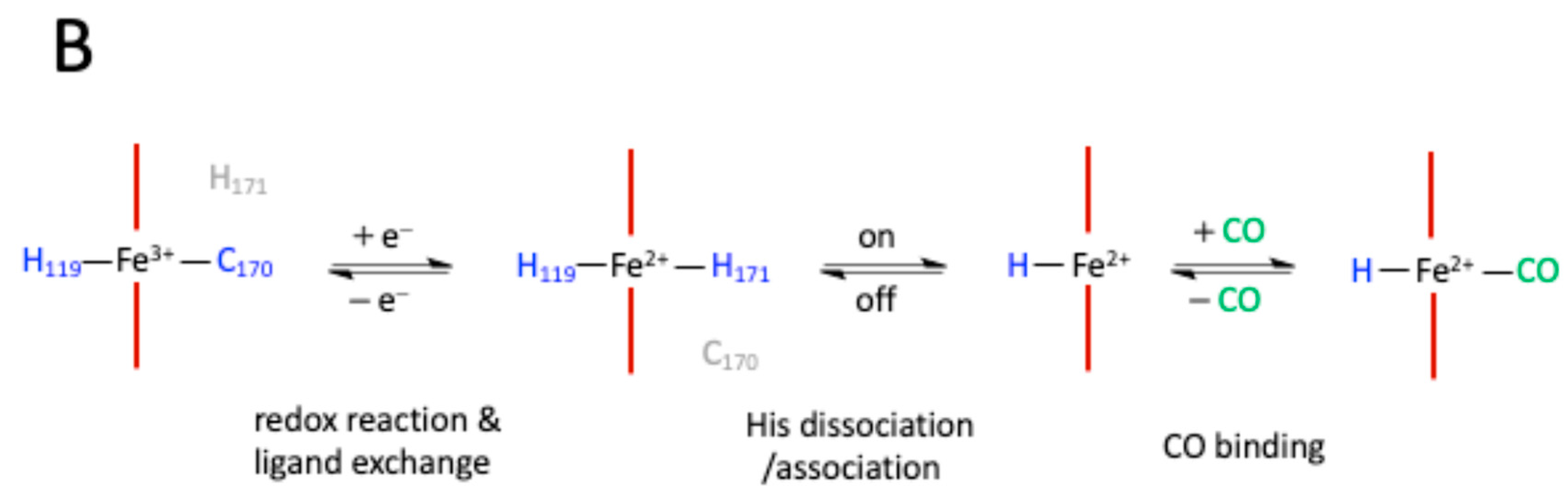
3. NPAS2, hemeprotein and gas-responsive transcription factor
4. NPAS2 and Metabolic Pathways
5. NPAS2 and the Central Nervous System in Mammals
6. NPAS2 in Cancer Onset and Progression
7. NPAS2 and the Cardiovascular System
8. NPAS2 and the Process of Wound Healing
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaix A, Zarrinpar A, Panda S. The circadian coordination of cell biology. J Cell Biol. 2016 Oct 10;215(1):15-25. [CrossRef]
- Hastings MH, Reddy AB, Maywood ES. A clockwork web: circadian timing in brain and periphery, in health and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003 Aug;4(8):649-61. [CrossRef]
- Partch, C.L.; Green, C.B.; Takahashi, J.S. Molecular architecture of the mammalian circadian clock. Trends Cell Boil. 2014, 24, 90–99.
- Maywood ES, O'Neill JS, Reddy AB, Chesham JE, Prosser HM, Kyriacou CP, Godinho SI, Nolan PM, Hastings MH. Genetic and molecular analysis of the central and peripheral circadian clockwork of mice. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007;72:85-94. [CrossRef]
- Ray S, Reddy AB. Cross-talk between circadian clocks, sleep-wake cycles, and metabolic networks: Dispelling the darkness. Bioessays. 2016 Apr;38(4):394-405. [CrossRef]
- Bass J, Takahashi JS. Circadian integration of metabolism and energetics. Science. 2010 Dec 3;330(6009):1349-54. [CrossRef]
- Hastings MH, Maywood ES, Brancaccio M. Generation of circadian rhythms in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018;19(8):453-469. [CrossRef]
- Varadarajan S, Tajiri M, Jain R, et al. Connectome of the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus: New Evidence of the Core-Shell Relationship. eNeuro. 2018;5(5):ENEURO.0205-18.2018. Published 2018 Oct 2. [CrossRef]
- Brancaccio M, Patton AP, Chesham JE, Maywood ES, Hastings MH. Astrocytes Control Circadian Timekeeping in the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus via Glutamatergic Signaling. Neuron. 2017;93(6):1420-1435.e5. [CrossRef]
- Reick, M., Garcia, J. A., Dudley, C., & McKnight, S. L. (2001). NPAS2: an analog of clock operative in the mammalian forebrain. Science (New York, N.Y.), 293(5529), 506–509. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, J.S. Transcriptional architecture of the mammalian circadian clock. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 164–179.
- Milev NB, Rhee SG, Reddy AB. Cellular Timekeeping: It's Redox o'Clock. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018 May 1;10(5):a027698. [CrossRef]
- Robinson I, Reddy AB. Molecular mechanisms of the circadian clockwork in mammals. FEBS Lett. 2014 Aug 1;588(15):2477-83. [CrossRef]
- Reddy AB. Genome-wide analyses of circadian systems. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2013;(217):379-88. [CrossRef]
- Cardone, L.; Hirayama, J.; Giordano, F.; Tamaru, T.; Palvimo, J.J.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Circadian clock control by SUMOylation of BMAL1. Science 2005, 309, 1390–1394.
- Lee, J.; Lee, Y.; Lee, M.J.; Park, E.; Kang, S.H.; Chung, C.H.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, K. Dual modification of BMAL1 by SUMO2/3 and ubiquitin promotes circadian activation of the CLOCK/BMAL1 complex. Mol. Cell. Boil. 2008, 28, 6056–6065.
- Sahar, S.; Zocchi, L.; Kinoshita, C.; Borrelli, E.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Regulation of BMAL1 protein stability and circadian function by GSK3beta-mediated phosphorylation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8561.
- Duez H, Staels B. Rev-erb-alpha: an integrator of circadian rhythms and metabolism. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009 Dec;107(6):1972-80. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.E.; DiTacchio, L.; Hayes, K.R.; Vollmers, C.; Pulivarthy, S.; Baggs, J.E.; Panda, S.; Hogenesch, J.B. Harmonics of circadian gene transcription in mammals. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000442.
- Bozek, K.; Relogio, A.; Kielbasa, S.M.; Heine, M.; Dame, C.; Kramer, A.; Herzel, H. Regulation of clock-controlled genes in mammals. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4882.
- Noshiro, M., Furukawa, M., Honma, S., Kawamoto, T., Hamada, T., Honma, K., & Kato, Y. (2005). Tissue-specific disruption of rhythmic expression of Dec1 and Dec2 in clock mutant mice. Journal of biological rhythms, 20(5), 404–418. [CrossRef]
- Doi M, Hirayama J, Sassone-Corsi P. Circadian regulator CLOCK is a histone acetyltransferase. Cell. 2006 May 5;125(3):497-508. [CrossRef]
- Nakahata, Y.; Kaluzova, M.; Grimaldi, B.; Sahar, S.; Hirayama, J.; Chen, D.; Guarente, L.P.; Sassone-Corsi, P. The NAD+-dependent deacetylase SIRT1 modulates CLOCK-mediated chromatin remodeling and circadian control. Cell 2008, 134, 329–340.
- Asher, G.; Gatfield, D.; Stratmann, M.; Reinke, H.; Dibner, C.; Kreppel, F.; Mostoslavsky, R.; Alt, F.W.; Schibler, U. SIRT1 regulates circadian clock gene expression through PER2 deacetylation. Cell 2008, 134, 317–328.
- Nakahata, Y.; Sahar, S.; Astarita, G.; Kaluzova, M.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Circadian control of the NAD+ salvage pathway by CLOCK-SIRT1. Science 2009, 324, 654–657.
- Ramsey, K.M.; Yoshino, J.; Brace, C.S.; Abrassart, D.; Kobayashi, Y.; Marcheva, B.; Hong, H.K.; Chong, J.L.; Buhr, E.D.; Lee, C.; et al. Circadian clock feedback cycle through NAMPT-mediated NAD+ biosynthesis. Science 2009, 324, 651–654.
- Rutter, J., Reick, M., Wu, L. C., & McKnight, S. L. (2001). Regulation of clock and NPAS2 DNA binding by the redox state of NAD cofactors. Science (New York, N.Y.), 293(5529), 510–514. [CrossRef]
- Dioum, E. M., Rutter, J., Tuckerman, J. R., Gonzalez, G., Gilles-Gonzalez, M. A., & McKnight, S. L. (2002). NPAS2: a gas-responsive transcription factor. Science (New York, N.Y.), 298(5602), 2385–2387. [CrossRef]
- Kaasik, K., & Lee, C. C. (2004). Reciprocal regulation of haem biosynthesis and the circadian clock in mammals. Nature, 430(6998), 467–471. [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T., Sato, E., Sato, A., Sagami, I., Shimizu, T., & Kitagawa, T. (2005). CO-dependent activity-controlling mechanism of heme-containing CO-sensor protein, neuronal PAS domain protein 2. The Journal of biological chemistry, 280(22), 21358–21368. [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T., Sagami, I., Shimizu, T., Ishimori, K., & Kitagawa, T. (2012). Effects of the bHLH domain on axial coordination of heme in the PAS-A domain of neuronal PAS domain protein 2 (NPAS2): conversion from His119/Cys170 coordination to His119/His171 coordination. Journal of inorganic biochemistry, 108, 188–195. [CrossRef]
- Mukaiyama, Y., Uchida, T., Sato, E., Sasaki, A., Sato, Y., Igarashi, J., Kurokawa, H., Sagami, I., Kitagawa, T., & Shimizu, T. (2006). Spectroscopic and DNA-binding characterization of the isolated heme-bound basic helix-loop-helix-PAS-A domain of neuronal PAS protein 2 (NPAS2), a transcription activator protein associated with circadian rhythms. The FEBS journal, 273(11), 2528–2539. [CrossRef]
- Koudo, R., Kurokawa, H., Sato, E., Igarashi, J., Uchida, T., Sagami, I., Kitagawa, T., & Shimizu, T. (2005). Spectroscopic characterization of the isolated heme-bound PAS-B domain of neuronal PAS domain protein 2 associated with circadian rhythms. The FEBS journal, 272(16), 4153–4162. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y. D., Barnard, M., Tian, H., Li, X., Ring, H. Z., Francke, U., Shelton, J., Richardson, J., Russell, D. W., & McKnight, S. L. (1997). Molecular characterization of two mammalian bHLH-PAS domain proteins selectively expressed in the central nervous system. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 94(2), 713–718. [CrossRef]
- Crumbley, C., Wang, Y., Kojetin, D. J., & Burris, T. P. (2010). Characterization of the core mammalian clock component, NPAS2, as a REV-ERBalpha/RORalpha target gene. The Journal of biological chemistry, 285(46), 35386–35392. [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, R., Matsubara, C., Node, K., Takumi, T., & Akashi, M. (2013). Nuclear receptor-mediated cell-autonomous oscillatory expression of the circadian transcription factor, neuronal PAS domain protein 2 (NPAS2). The Journal of biological chemistry, 288(51), 36548–36553. [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y., Kang, H. S., Angers, M., & Jetten, A. M. (2011). Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor γ directly regulates neuronal PAS domain protein 2 transcription in vivo. Nucleic acids research, 39(11), 4769–4782. [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, K., Tajima, F., Ishijima, S., & Sagami, I. (2015). Changes in pH and NADPH regulate the DNA binding activity of neuronal PAS domain protein 2, a mammalian circadian transcription factor. Biochemistry, 54(2), 250–259. [CrossRef]
- DeBruyne, J. P., Weaver, D. R., & Reppert, S. M. (2007). CLOCK and NPAS2 have overlapping roles in the suprachiasmatic circadian clock. Nature neuroscience, 10(5), 543–545. [CrossRef]
- Bertolucci, C., Cavallari, N., Colognesi, I., Aguzzi, J., Chen, Z., Caruso, P., Foá, A., Tosini, G., Bernardi, F., & Pinotti, M. (2008). Evidence for an overlapping role of CLOCK and NPAS2 transcription factors in liver circadian oscillators. Molecular and cellular biology, 28(9), 3070–3075. [CrossRef]
- Landgraf, D., Wang, L. L., Diemer, T., & Welsh, D. K. (2016). NPAS2 Compensates for Loss of CLOCK in Peripheral Circadian Oscillators. PLoS genetics, 12(2), e1005882. [CrossRef]
- Itoh, R., Fujita, K., Mu, A., Kim, D. H., Tai, T. T., Sagami, I., & Taketani, S. (2013). Imaging of heme/hemeproteins in nucleus of the living cells expressing heme-binding nuclear receptors. FEBS letters, 587(14), 2131–2136. [CrossRef]
- Ascenzi, P., Bocedi, A., Leoni, L., Visca, P., Zennaro, E., Milani, M., & Bolognesi, M. (2004). CO sniffing through heme-based sensor proteins. IUBMB life, 56(6), 309–315. [CrossRef]
- Gilun, P., Stefanczyk-Krzymowska, S., Romerowicz-Misielak, M., Tabecka-Lonczynska, A., Przekop, F., & Koziorowski, M. (2013). Carbon monoxide-mediated humoral pathway for the transmission of light signal to the hypothalamus. Journal of physiology and pharmacology: an official journal of the Polish Physiological Society, 64(6), 761–772.
- Minegishi, S., Sagami, I., Negi, S., Kano, K., & Kitagishi, H. (2018). Circadian clock disruption by selective removal of endogenous carbon monoxide. Scientific reports, 8(1), 11996. [CrossRef]
- Mazzoccoli, G., De Cosmo, S., & Mazza, T. (2018). The Biological Clock: A Pivotal Hub in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Pathogenesis. Frontiers in physiology, 9, 193. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. M., Zhang, Y., Tsuchiya, H., Smalling, R., Jetten, A. M., & Wang, L. (2015). Small heterodimer partner/neuronal PAS domain protein 2 axis regulates the oscillation of liver lipid metabolism. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.), 61(2), 497–505. [CrossRef]
- He, Y., Cen, H., Guo, L., Zhang, T., Yang, Y., Dong, D., & Wu, B. (2022). Circadian oscillator NPAS2 regulates diurnal expression and activity of CYP1A2 in mouse liver. Biochemical pharmacology, 206, 115345. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z., Lin, Y., Gao, L., Yang, Z., Wang, S., & Wu, B. (2019). Cyp3a11 metabolism-based chronotoxicity of brucine in mice. Toxicology letters, 313, 188–195. [CrossRef]
- Musiek, E. S., Lim, M. M., Yang, G., Bauer, A. Q., Qi, L., Lee, Y., Roh, J. H., Ortiz-Gonzalez, X., Dearborn, J. T., Culver, J. P., Herzog, E. D., Hogenesch, J. B., Wozniak, D. F., Dikranian, K., Giasson, B. I., Weaver, D. R., Holtzman, D. M., & Fitzgerald, G. A. (2013). Circadian clock proteins regulate neuronal redox homeostasis and neurodegeneration. The Journal of clinical investigation, 123(12), 5389–5400. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J. A., Zhang, D., Estill, S. J., Michnoff, C., Rutter, J., Reick, M., Scott, K., Diaz-Arrastia, R., & McKnight, S. L. (2000). Impaired cued and contextual memory in NPAS2-deficient mice. Science (New York, N.Y.), 288(5474), 2226–2230. [CrossRef]
- Ozburn, A. R., Kern, J., Parekh, P. K., Logan, R. W., Liu, Z., Falcon, E., Becker-Krail, D., Purohit, K., Edgar, N. M., Huang, Y., & McClung, C. A. (2017). NPAS2 Regulation of Anxiety-Like Behavior and GABAA Receptors. Frontiers in molecular neuroscience, 10, 360. [CrossRef]
- Ozburn, A. R., Falcon, E., Twaddle, A., Nugent, A. L., Gillman, A. G., Spencer, S. M., Arey, R. N., Mukherjee, S., Lyons-Weiler, J., Self, D. W., & McClung, C. A. (2015). Direct regulation of diurnal Drd3 expression and cocaine reward by NPAS2. Biological psychiatry, 77(5), 425–433. [CrossRef]
- DePoy, L. M., Becker-Krail, D. D., Zong, W., Petersen, K., Shah, N. M., Brandon, J. H., Miguelino, A. M., Tseng, G. C., Logan, R. W., & McClung, C. A. (2021). Circadian-Dependent and Sex-Dependent Increases in Intravenous Cocaine Self-Administration in Npas2 Mutant Mice. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 41(5), 1046–1058. [CrossRef]
- Puig, S., Shelton, M. A., Barko, K., Seney, M. L., & Logan, R. W. (2022). Sex-specific role of the circadian transcription factor NPAS2 in opioid tolerance, withdrawal and analgesia. Genes, brain, and behavior, 21(7), e12829. [CrossRef]
- Becker-Krail, D. D., Parekh, P. K., Ketchesin, K. D., Yamaguchi, S., Yoshino, J., Hildebrand, M. A., Dunham, B., Ganapathiraju, M. K., Logan, R. W., & McClung, C. A. (2022). Circadian transcription factor NPAS2 and the NAD+-dependent deacetylase SIRT1 interact in the mouse nucleus accumbens and regulate reward. The European journal of neuroscience, 55(3), 675–693. [CrossRef]
- Gamble, M. C., Chuan, B., Gallego-Martin, T., Shelton, M. A., Puig, S., O'Donnell, C. P., & Logan, R. W. (2022). A role for the circadian transcription factor NPAS2 in the progressive loss of non-rapid eye movement sleep and increased arousal during fentanyl withdrawal in male mice. Psychopharmacology, 239(10), 3185–3200. [CrossRef]
- Parekh, P. K., Logan, R. W., Ketchesin, K. D., Becker-Krail, D., Shelton, M. A., Hildebrand, M. A., Barko, K., Huang, Y. H., & McClung, C. A. (2019). Cell-Type-Specific Regulation of Nucleus Accumbens Synaptic Plasticity and Cocaine Reward Sensitivity by the Circadian Protein, NPAS2. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 39(24), 4657–4667. [CrossRef]
- Herichová, I., Hasáková, K., Lukáčová, D., Mravec, B., Horváthová, Ľ., & Kavická, D. (2017). Prefrontal cortex and dorsomedial hypothalamus mediate food reward-induced effects via npas2 and egr1 expression in rat. Physiological research, 66(Suppl 4), S501–S510. [CrossRef]
- Franken, P., Dudley, C. A., Estill, S. J., Barakat, M., Thomason, R., O'Hara, B. F., & McKnight, S. L. (2006). NPAS2 as a transcriptional regulator of non-rapid eye movement sleep: genotype and sex interactions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(18), 7118–7123. [CrossRef]
- Evans, D. S., Parimi, N., Nievergelt, C. M., Blackwell, T., Redline, S., Ancoli-Israel, S., Orwoll, E. S., Cummings, S. R., Stone, K. L., Tranah, G. J., Study of Osteoporotic Fractures (SOF), & Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) Study Group (2013). Common genetic variants in ARNTL and NPAS2 and at chromosome 12p13 are associated with objectively measured sleep traits in the elderly. Sleep, 36(3), 431–446. [CrossRef]
- Dall'Ara, I., Ghirotto, S., Ingusci, S., Bagarolo, G., Bertolucci, C., & Barbujani, G. (2016). Demographic history and adaptation account for clock gene diversity in humans. Heredity, 117(3), 165–172. [CrossRef]
- Yeim, S., Boudebesse, C., Etain, B., & Belliviera, F. (2015). Biomarqueurs et gènes circadiens dans le trouble bipolaire [Circadian markers and genes in bipolar disorder]. L'Encephale, 41(4 Suppl 1), S38–S44. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. I., Lee, H. J., Cho, C. H., Kang, S. G., Yoon, H. K., Park, Y. M., Lee, S. H., Moon, J. H., Song, H. M., Lee, E., & Kim, L. (2015). Association of CLOCK, ARNTL, and NPAS2 gene polymorphisms and seasonal variations in mood and behavior. Chronobiology international, 32(6), 785–791. [CrossRef]
- Milhiet, V., Boudebesse, C., Bellivier, F., Drouot, X., Henry, C., Leboyer, M., & Etain, B. (2014). Circadian abnormalities as markers of susceptibility in bipolar disorders. Frontiers in bioscience (Scholar edition), 6(1), 120–137. [CrossRef]
- Partonen T. (2012). Clock gene variants in mood and anxiety disorders. Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996), 119(10), 1133–1145. [CrossRef]
- Soria, V., Martínez-Amorós, E., Escaramís, G., Valero, J., Pérez-Egea, R., García, C., Gutiérrez-Zotes, A., Puigdemont, D., Bayés, M., Crespo, J. M., Martorell, L., Vilella, E., Labad, A., Vallejo, J., Pérez, V., Menchón, J. M., Estivill, X., Gratacòs, M., & Urretavizcaya, M. (2010). Differential association of circadian genes with mood disorders: CRY1 and NPAS2 are associated with unipolar major depression and CLOCK and VIP with bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology : official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 35(6), 1279–1289. [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C., Willeit, M., Smedh, C., Ekholm, J., Paunio, T., Kieseppä, T., Lichtermann, D., Praschak-Rieder, N., Neumeister, A., Nilsson, L. G., Kasper, S., Peltonen, L., Adolfsson, R., Schalling, M., & Partonen, T. (2003). Circadian clock-related polymorphisms in seasonal affective disorder and their relevance to diurnal preference. Neuropsychopharmacology : official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 28(4), 734–739. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y., Lindsey-Boltz, L. A., Vaughn, C. M., Selby, C. P., Cao, X., Liu, Z., Hsu, D. S., & Sancar, A. (2021). Circadian clock, carcinogenesis, chronochemotherapy connections. The Journal of biological chemistry, 297(3), 101068. [CrossRef]
- Sancar, A., & Van Gelder, R. N. (2021). Clocks, cancer, and chronochemotherapy. Science (New York, N.Y.), 371(6524), eabb0738. [CrossRef]
- Mocellin, S., Tropea, S., Benna, C., & Rossi, C. R. (2018). Circadian pathway genetic variation and cancer risk: evidence from genome-wide association studies. BMC medicine, 16(1), 20. [CrossRef]
- Rao, X., & Lin, L. (2022). Circadian clock as a possible control point in colorectal cancer progression (Review). International journal of oncology, 61(6), 149. [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Arnal L., Hakim O., Patel V.R., Baldi P., Hager G.L., and Sassone-Corsi P.. 2013. Cycles in spatial and temporal chromosomal organization driven by the circadian clock. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 20:1206–1213. [CrossRef]
- Shu, X. S., Li, L., & Tao, Q. (2012). Chromatin regulators with tumor suppressor properties and their alterations in human cancers. Epigenomics, 4(5), 537–549. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q., Han, S., Liu, X., Wang, S., & Ma, H. (2022). Integrated single-cell and transcriptome sequencing analyses determines a chromatin regulator-based signature for evaluating prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Frontiers in oncology, 12, 1031728. [CrossRef]
- Tang, X., Qi, C., Zhou, H., & Liu, Y. (2022). A novel metabolic-immune related signature predicts prognosis and immunotherapy response in lung adenocarcinoma. Heliyon, 8(8), e10164. [CrossRef]
- Chai, R., Liao, M., Ou, L., Tang, Q., Liang, Y., Li, N., Huang, W., Wang, X., Zheng, K., & Wang, S. (2022). Circadian Clock Genes Act as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers of Glioma: Clinic Implications for Chronotherapy. BioMed research international, 2022, 9774879. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z., Liang, Z., Gao, W., Yu, S., Hou, Z., Li, K., & Zeng, P. (2022). Identification of circadian clock genes as regulators of immune infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Journal of Cancer, 13(11), 3199–3208. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H., Gao, Y., Hu, S., Fan, Z., Wang, X., & Li, S. (2021). Bioinformatics Analysis of Differentially Expressed Rhythm Genes in Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Frontiers in genetics, 12, 680528. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P., Yang, T., Mu, J., Zhao, J., Yang, Y., Yan, Z., Hou, Y., Chen, C., Xing, J., Zhang, H., & Li, J. (2020). Circadian clock gene NPAS2 promotes reprogramming of glucose metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer letters, 469, 498–509. [CrossRef]
- Yang, T., Yuan, P., Yang, Y., Liang, N., Wang, Q., Li, J., Lu, R., Zhang, H., Mu, J., Yan, Z., & Chang, H. (2019). NPAS2 Contributes to Liver Fibrosis by Direct Transcriptional Activation of Hes1 in Hepatic Stellate Cells. Molecular therapy. Nucleic acids, 18, 1009–1022. [CrossRef]
- Xu, T., Jin, T., Lu, X., Pan, Z., Tan, Z., Zheng, C., Liu, Y., Hu, X., Ba, L., Ren, H., Chen, J., Zhu, C., Ge, M., & Huang, P. (2022). A signature of circadian rhythm genes in driving anaplastic thyroid carcinoma malignant progression. Cellular signalling, 95, 110332. [CrossRef]
- Lesicka, M., Jabłońska, E., Wieczorek, E., Seroczyńska, B., Siekierzycka, A., Skokowski, J., Kalinowski, L., Wąsowicz, W., & Reszka, E. (2018). Altered circadian genes expression in breast cancer tissue according to the clinical characteristics. PloS one, 13(6), e0199622. [CrossRef]
- Yi, C., Mu, L., de la Longrais, I. A., Sochirca, O., Arisio, R., Yu, H., Hoffman, A. E., Zhu, Y., & Katsaro, D. (2010). The circadian gene NPAS2 is a novel prognostic biomarker for breast cancer. Breast cancer research and treatment, 120(3), 663–669. [CrossRef]
- Monsees, G. M., Kraft, P., Hankinson, S. E., Hunter, D. J., & Schernhammer, E. S. (2012). Circadian genes and breast cancer susceptibility in rotating shift workers. International journal of cancer, 131(11), 2547–2552. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B., Dai, Z. M., Zhao, Y., Wang, X. J., Kang, H. F., Ma, X. B., Lin, S., Wang, M., Yang, P. T., & Dai, Z. J. (2015). Current evidence on the relationship between two common polymorphisms in NPAS2 gene and cancer risk. International journal of clinical and experimental medicine, 8(5), 7176–7183.
- Zhu, Y., Leaderer, D., Guss, C., Brown, H. N., Zhang, Y., Boyle, P., Stevens, R. G., Hoffman, A., Qin, Q., Han, X., & Zheng, T. (2007). Ala394Thr polymorphism in the clock gene NPAS2: a circadian modifier for the risk of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. International journal of cancer, 120(2), 432–435. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X., Lv, X., Zhu, L., Xu, K., Shi, C., Cui, L., & Ding, H. (2021). The Circadian Gene NPAS2 Act as a Putative Tumor Stimulative Factor for Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma. Cancer management and research, 13, 9329–9343. [CrossRef]
- Feng, D., Xiong, Q., Zhang, F., Shi, X., Xu, H., Wei, W., Ai, J., & Yang, L. (2022). Identification of a Novel Nomogram to Predict Progression Based on the Circadian Clock and Insights Into the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Prostate Cancer. Frontiers in immunology, 13, 777724. [CrossRef]
- Ma, S., Chen, Y., Quan, P., Zhang, J., Han, S., Wang, G., Qi, R., Zhang, X., Wang, F., Yuan, J., Yang, X., Jia, W., & Qin, W. (2023). NPAS2 promotes aerobic glycolysis and tumor growth in prostate cancer through HIF-1A signaling. BMC cancer, 23(1), 280. [CrossRef]
- Wendeu-Foyet, M. G., Koudou, Y., Cénée, S., Trétarre, B., Rébillard, X., Cancel-Tassin, G., Cussenot, O., Boland, A., Bacq, D., Deleuze, J. F., Lamy, P. J., Mulot, C., Laurent-Puig, P., Truong, T., & Menegaux, F. (2019). Circadian genes and risk of prostate cancer: Findings from the EPICAP study. International journal of cancer, 145(7), 1745–1753. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y., Stevens, R. G., Hoffman, A. E., Fitzgerald, L. M., Kwon, E. M., Ostrander, E. A., Davis, S., Zheng, T., & Stanford, J. L. (2009). Testing the circadian gene hypothesis in prostate cancer: a population-based case-control study. Cancer research, 69(24), 9315–9322. [CrossRef]
- Yu, C. C., Chen, L. C., Chiou, C. Y., Chang, Y. J., Lin, V. C., Huang, C. Y., Lin, I. L., Chang, T. Y., Lu, T. L., Lee, C. H., Huang, S. P., & Bao, B. Y. (2019). Genetic variants in the circadian rhythm pathway as indicators of prostate cancer progression. Cancer cell international, 19, 87. [CrossRef]
- Benna, C., Rajendran, S., Spiro, G., Tropea, S., Del Fiore, P., Rossi, C. R., & Mocellin, S. (2018). Associations of clock genes polymorphisms with soft tissue sarcoma susceptibility and prognosis. Journal of translational medicine, 16(1), 338. [CrossRef]
- Iyyanki, T., Zhang, B., Wang, Q., Hou, Y., Jin, Q., Xu, J., Yang, H., Liu, T., Wang, X., Song, F., Luan, Y., Yamashita, H., Chien, R., Lyu, H., Zhang, L., Wang, L., Warrick, J., Raman, J. D., Meeks, J. J., DeGraff, D. J., … Yue, F. (2021). Subtype-associated epigenomic landscape and 3D genome structure in bladder cancer. Genome biology, 22(1), 105. [CrossRef]
- Song, B., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Wan, C., Zhang, L., & Zhang, W. (2019). NPAS2 regulates proliferation of acute myeloid leukemia cells via CDC25A-mediated cell cycle progression and apoptosis. Journal of cellular biochemistry, 120(5), 8731–8741. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P., Li, J., Zhou, F., Huang, Q., Zhang, J., Guo, X., Lyu, Z., Zhang, H., & Xing, J. (2017). NPAS2 promotes cell survival of hepatocellular carcinoma by transactivating CDC25A. Cell death & disease, 8(3), e2704. [CrossRef]
- Chen, R., D'Alessandro, M., & Lee, C. (2013). miRNAs are required for generating a time delay critical for the circadian oscillator. Current biology : CB, 23(20), 1959–1968. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F., Pu, Y., Qian, L., Zang, C., Tao, Z., & Gao, J. (2017). MiR-20a-5p promotes radio-resistance by targeting NPAS2 in nasopharyngeal cancer cells. Oncotarget, 8(62), 105873–105881. [CrossRef]
- Franzoni, A., Markova-Car, E., Dević-Pavlić, S., Jurišić, D., Puppin, C., Mio, C., De Luca, M., Petruz, G., Damante, G., & Pavelić, S. K. (2017). A polymorphic GGC repeat in the NPAS2 gene and its association with melanoma. Experimental biology and medicine (Maywood, N.J.), 242(15), 1553–1558. [CrossRef]
- Anea, C. B., Merloiu, A. M., Fulton, D. J. R., Patel, V., & Rudic, R. D. (2018). Immunohistochemistry of the circadian clock in mouse and human vascular tissues. Vessel plus, 2, 16. [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A. M., Cheng, Y., Kapoor, S., Reilly, D., Price, T. S., & Fitzgerald, G. A. (2007). Circadian variation of blood pressure and the vascular response to asynchronous stress. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(9), 3450–3455. [CrossRef]
- Leu, H. B., Chung, C. M., Lin, S. J., Chiang, K. M., Yang, H. C., Ho, H. Y., Ting, C. T., Lin, T. H., Sheu, S. H., Tsai, W. C., Chen, J. H., Yin, W. H., Chiu, T. Y., Chen, C. I., Fann, C. S., Chen, Y. T., Pan, W. H., & Chen, J. W. (2015). Association of circadian genes with diurnal blood pressure changes and non-dipper essential hypertension: a genetic association with young-onset hypertension. Hypertension research: official journal of the Japanese Society of Hypertension, 38(2), 155–162. [CrossRef]
- Bray, M. S., Shaw, C. A., Moore, M. W., Garcia, R. A., Zanquetta, M. M., Durgan, D. J., Jeong, W. J., Tsai, J. Y., Bugger, H., Zhang, D., Rohrwasser, A., Rennison, J. H., Dyck, J. R., Litwin, S. E., Hardin, P. E., Chow, C. W., Chandler, M. P., Abel, E. D., & Young, M. E. (2008). Disruption of the circadian clock within the cardiomyocyte influences myocardial contractile function, metabolism, and gene expression. American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology, 294(2), H1036–H1047. [CrossRef]
- Westgate, E. J., Cheng, Y., Reilly, D. F., Price, T. S., Walisser, J. A., Bradfield, C. A., & FitzGerald, G. A. (2008). Genetic components of the circadian clock regulate thrombogenesis in vivo. Circulation, 117(16), 2087–2095. [CrossRef]
- Takeda, N., & Maemura, K. (2015). The role of clock genes and circadian rhythm in the development of cardiovascular diseases. Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, 72(17), 3225–3234. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q., Zhao, J., Liu, L., Wang, X., & Gu, X. (2023). Identification of the potential biomarkers associated with circadian rhythms in heart failure. PeerJ, 11, e14734. [CrossRef]
- Chavva, H., Brazeau, D. A., Denvir, J., Primerano, D. A., Fan, J., Seeley, S. L., & Rorabaugh, B. R. (2021). Methamphetamine-induced changes in myocardial gene transcription are sex-dependent. BMC genomics, 22(1), 259. [CrossRef]
- Cantone, L., Tobaldini, E., Favero, C., Albetti, B., Sacco, R. M., Torgano, G., Ferrari, L., Montano, N., & Bollati, V. (2020). Particulate Air Pollution, Clock Gene Methylation, and Stroke: Effects on Stroke Severity and Disability. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(9), 3090. [CrossRef]
- Schallner, N., Lieberum, J. L., Gallo, D., LeBlanc, R. H., 3rd, Fuller, P. M., Hanafy, K. A., & Otterbein, L. E. (2017). Carbon Monoxide Preserves Circadian Rhythm to Reduce the Severity of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Mice. Stroke, 48(9), 2565–2573. [CrossRef]
- Clements, A., Shibuya, Y., Hokugo, A., Brooks, Z., Roca, Y., Kondo, T., Nishimura, I., & Jarrahy, R. (2023). In vitro assessment of Neuronal PAS domain 2 mitigating compounds for scarless wound healing. Frontiers in medicine, 9, 1014763. [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, Y., Hokugo, A., Okawa, H., Kondo, T., Khalil, D., Wang, L., Roca, Y., Clements, A., Sasaki, H., Berry, E., Nishimura, I., & Jarrahy, R. (2022). Therapeutic downregulation of neuronal PAS domain 2 (Npas2) promotes surgical skin wound healing. eLife, 11, e71074. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




