1. Introduction
Balance and related falls may be a combination of neurologic conditions but also detraining from inactivity and aging. Sarcopenia, weakness in postural muscles due to a lifestyle of prolonged sitting, and low back pain result in reduced compensatory muscle activation [
1,
2,
3,
4]. These changes in activation timing and recruitment pattern can result in a loss of postural control and increased risk of falls or injury [
5] Balance improvements can be achieved by disrupting the neuromuscular system, so that it is forced to adjust in postural stability and muscle activation, otherwise known as compensatory adjustments. Stable posture is achieved by making multiple minor adjustments as opposed to large rapid motions [
2].
A large body of literature has examined the effects of instability training on the changes in muscle activation and strength [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12]. Typically, the percent maximal voluntary contraction was assessed with varied types of instability challenges. These challenges have been grouped according to the location of the instability. Unstable surfaces, such as Swiss ball [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18], Bosu ball [
7], TRX bands, wobble boards and surfaces that may vary are termed “bottom up” instability devices, while loads that are carried and affect the stability of the upper body are termed “Top down” devices. Other devices are specific to a single limb, such as Bodyblade trainers [
19,
20]. A common theme among the studies suggests that when the instability is bottom up, there is a redistribution of muscle activation to the core and supporting muscles. Marshall and Murphy [
17] had subjects perform bench press exercise at 60% 1RM on a stable bench and a Swiss ball bench. They found increased deltoid and abdominal activity on the less stable Swiss ball, suggesting greater core and limb stability activation. Other studies have shown similar results using plank exercise [
21] balance boards [
22] and Bosu or Swiss ball exercise (12,13,14). However, just activating core musculature may not result in improvements in postural control. In fact, research has suggested that lifting stable loads, allows one to lift heavier loads, and actually activate more core musculature than with unstable loads [
6,
8,
9,
11,
18]. Anderson and Behm [
11] showed reductions in peak force when subjects lifted on an unstable surface, and Hamlyn et al. [
10] showed that core muscle activation was significantly greater with 80% 1RM squat and deadlift compared to body weight instability exercises.
Stability during movement is not solely related to the amount of strength that can be deployed by a given muscle. Specificity of training would dictate that to train for stability, there must be perturbations that train the neuromuscular system to adapt. While there are several methods of creating unstable surfaces (bottom down) for instability, there are limited methods and investigations of upper body perturbations that would force postural muscle compensation. Nairn et al. has shown that the location of the instability will influence the location of compensatory muscle activation [
23,
24] and studies are also suggesting that another way to examine stability is examining the variability of activation, sometimes called “force steadiness”. Force steadiness can be obtained by reducing the latency between destabilization and muscle reactivity [
25], improving joint proprioception [
26]. Perturbation balance training consists of destabilizing forces that force repeated muscular contractions to maintain stability [
27]. Perturbations may be manually applied, as in a sudden bump, or lifting a load that induces destabilizing forces [
28,
29,
30,
31,
32]. While there is substantial research regarding the effect of perturbation balance training using the bottom-up training method [
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38], there are limited studies examining and upper body perturbation training program on improvements in force steadiness.
One training tool used to induce upper body perturbation is a water-filled training tube known as a “slosh tube”. Most training tubes are simple cylinders partially filled with water. During a lift the water creates inertial movements in a variety of directions, forcing support muscles to rapidly compensate. Novel water-filled training tube studies by Glass et al. [
31,
32] used a tube that was fitted with a central valve that could be manipulated, creating different flow variations. In one study (2016) subjects completed a bicep curls with different valve settings (open flow, 45-degree angle obstruction to flow, and no flow control) and found significant variability in muscle activation in the paraspinal and deltoid muscles during both concentric and eccentric contractions. Rather than examining the amount of muscle activated, the exercise was performed with an 11.4 kg tube and the log of the coefficient of variation was determined as a marker of force steadiness. A similar study was performed using an overhead squat, and showed that as the valve setting was changed, the muscles that showed the most reactivity and instability also changed. These studies showed that water-filled tubes create perturbations due to turbulance and can induce the variability of muscle contraction that may serve as a neuromuscular training tool.
Water-filled tubes can induce compensatory muscle activation, however, to date little research is available on whether training with these tubes can reduce the variability in muscle contractions using instability training. The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of two weeks of instability training using a water-filled training tube on force steadiness during an instability challenge.
2. Materials and Methods
Subjects were recruited from a university population. They were healthy, active, and free of any skeletomuscular condition or injury that might impair their ability to complete the study.
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Grand Valley State University (protocol code 20-015, approved July 29, 2019). Based on most recent published studies using the same device [
31,
32] with a power of .80 and effect size of .40, given a control and experimental group- a target size of 30 (15 control, 15 experimental) subjects was projected to have adequate power for analysis. Subjects’ characteristics are shown in
Table 1.
2.1. Day 1 Assessment
After providing signed informed consent subjects completed a health history questionnaire as part of initial assessment. Height, body mass and resting seated blood pressure was recorded. Subjects with resting blood pressure over 130/90 were excluded for participation. Following initial screenings, subjects were randomly assigned to either the Control (CON) or Experimental (EXP) group. Randomization was completed using a random number generator (
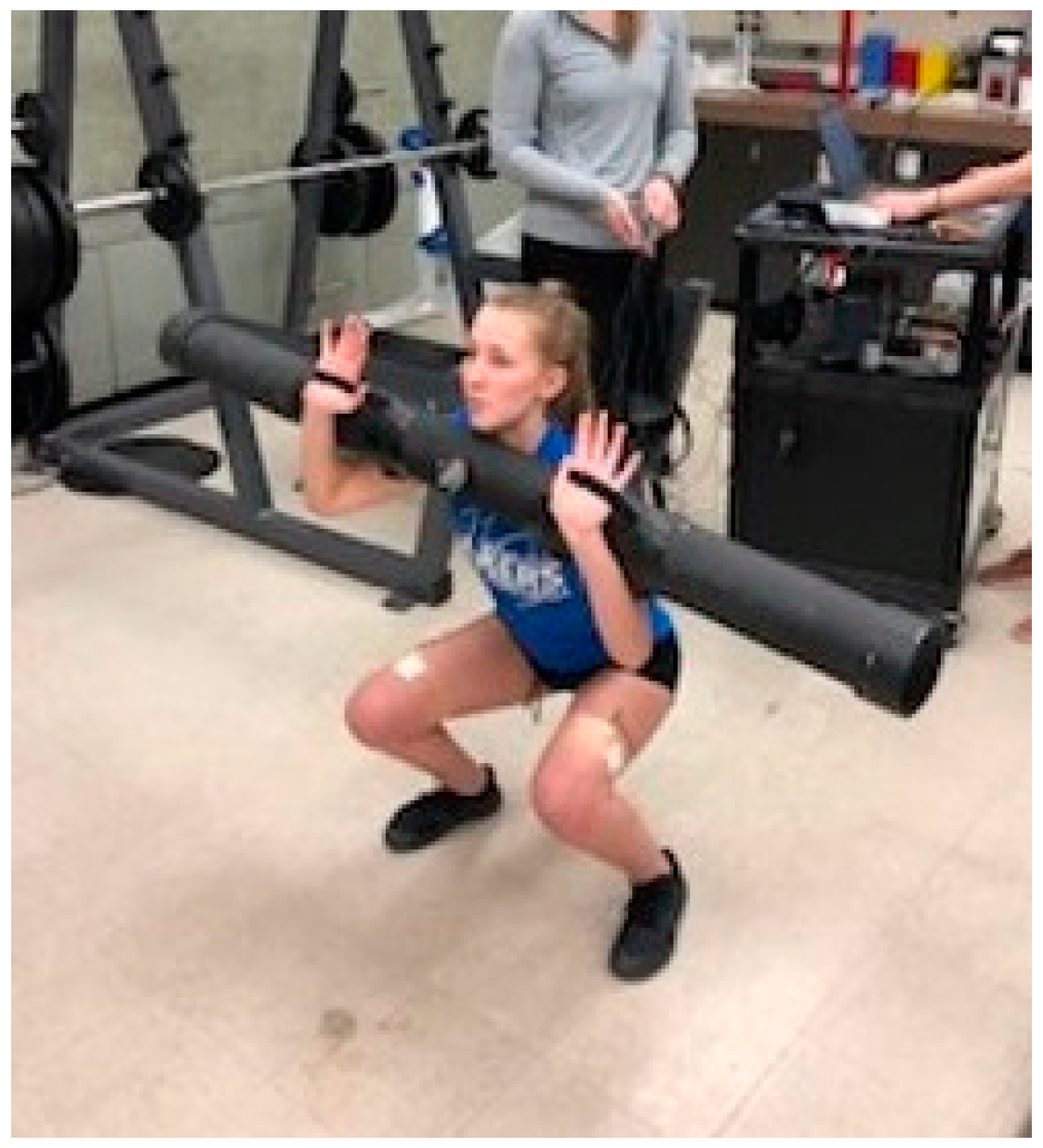
https://www.graphpad.com/quickcalcs/randomize2/). Subjects were then provided a familiarization period with the water -filled instability tube. Two spotters were used to place the tube into the hands of the subjects in the front squat position (
Figure 1) and a metronome timer was set to pace a 17 repetition per minute pace. Subjects practiced with 5 to 10 repetitions with a stable tube as well as the unstable tube.
Following the familiarization period subjects were prepared for electromyographic (EMG) electrode placement. Subjects’ skin were shaved and cleaned with alcohol, after which 6 pre-amplified surface electrodes (Biopac systems TSD 150B 20mm interelectrode distance) were placed bilaterally over the muscles of the anterior deltoid, paraspinal and vastus lateralis muscles in locations established by Cram [
39]. Flexible tape was used to secure electrodes to the skin and still allow freedom of movement. Following subject preparation all subjects completed the initial testing for EMG steadiness by completing one set of 10 repetitions with the stable tube, followed by the unstable tube. EMG data were recorded at 2,000 samples per second using a Biopac MP160 system (Goleta CA, USA) and Acknowledge software (Biopac version 5.0). Subjects were paced on each contraction using a metronome set at a 17 rep/min cadence. Due to the unstable nature of the squat when partially filled with water, a manual (visual) marking system was used to determine the transition between concentric and eccentric contractions.
2.2. Training tube specifications
The instability tube was constructed of high-density plastic material, with screw caps on each end to allow for water addition. The tube dimensions (Length- 159.4 cm, Diameter 11.4cm, circumference 36.2cm) necessitated straps be attached as support for securing the tube during the squat maneuver (
Figure 1). Dry weight of the tube was 5.0kg and for the study 6.0L of water was added for a maximum weight of 16.0kg. A volume was chosen that maximized both water movement and adequate load stimulus. The tube was also fitted with an adjustable central valve, which could be set at a 45-degree position to provide water turbulence in line with the spinal column during the squat (unstable EXP setting). The valve could also be closed to prevent movement of water across the tube (stable CON setting).
2.3. Training Days
Both CON and EXP subjects completed six exercise sessions with their respective tube. Training days were set a minimum of 48h apart. If a day was missed, it was rescheduled within a week to ensure all subjects completed 6 sessions of training. Subjects reported to the training lab having not done any other exercise that day. Subjects warmed up on a cycle ergometer at 25-30 watts for 5 minutes. Following the cycling, subjects completed 2 sets of 10 body weight squats with 3 minutes of rest between each set. Following this warmup subjects complete 4 sets of 15 repetitions with their respective tube condition (CON Stable, EXP unstable).
2.4. Post testing
On the last test day, subjects repeated the initial 10 repetition test for both the stable and unstable tube, with EMG data collected bilaterally on the anterior deltoid, paraspinal and vastus lateralis muscles. There was no familiarization trial on the posttest day.
2.5. Data processing
All raw EMG data were filtered using a filter suggested by the manufacturer (Biopac systems) to remove ECG waveforms observed in the core (paraspinal) muscles. This was a high pass filter, Blackman -67db, with a 30 Hz cutoff frequency and 255 coefficients. The pre-amplified electrodes also had a 58-61Hx band stop filter to remove background noise from electrical lighting. Data were then rectified, and each concentric and eccentric contraction were individually integrated (IEMG) for all repetitions and all muscles. The means and SD of the IEMG for concentric and eccentric contractions were computed across all muscles for pre and post training trials, for stable and unstable squat settings. Force steadiness was measured using the natural log of the percent coefficient of variation (Ln (SD/mean)). To complete an analysis of variance (ANOVA analysis, 3 assumptions needed to be met: the CV values must be approximately normally distributed, the variances of the population must be equal, and the observations must be independent. Two assumptions were not me: the equal variance assumption and the normality assumption. This necessitated the use of the natural LogCV.
2.6. Statistical analysis
A three-way analysis of variance was used to detect differenced by group (CON vs EXP) contraction type (Concentric vs Eccentric) and condition (pre vs post). This was performed for each muscle. Post hoc Tukey tests were used for paired comparisons in the presence of main effects.
3. Results
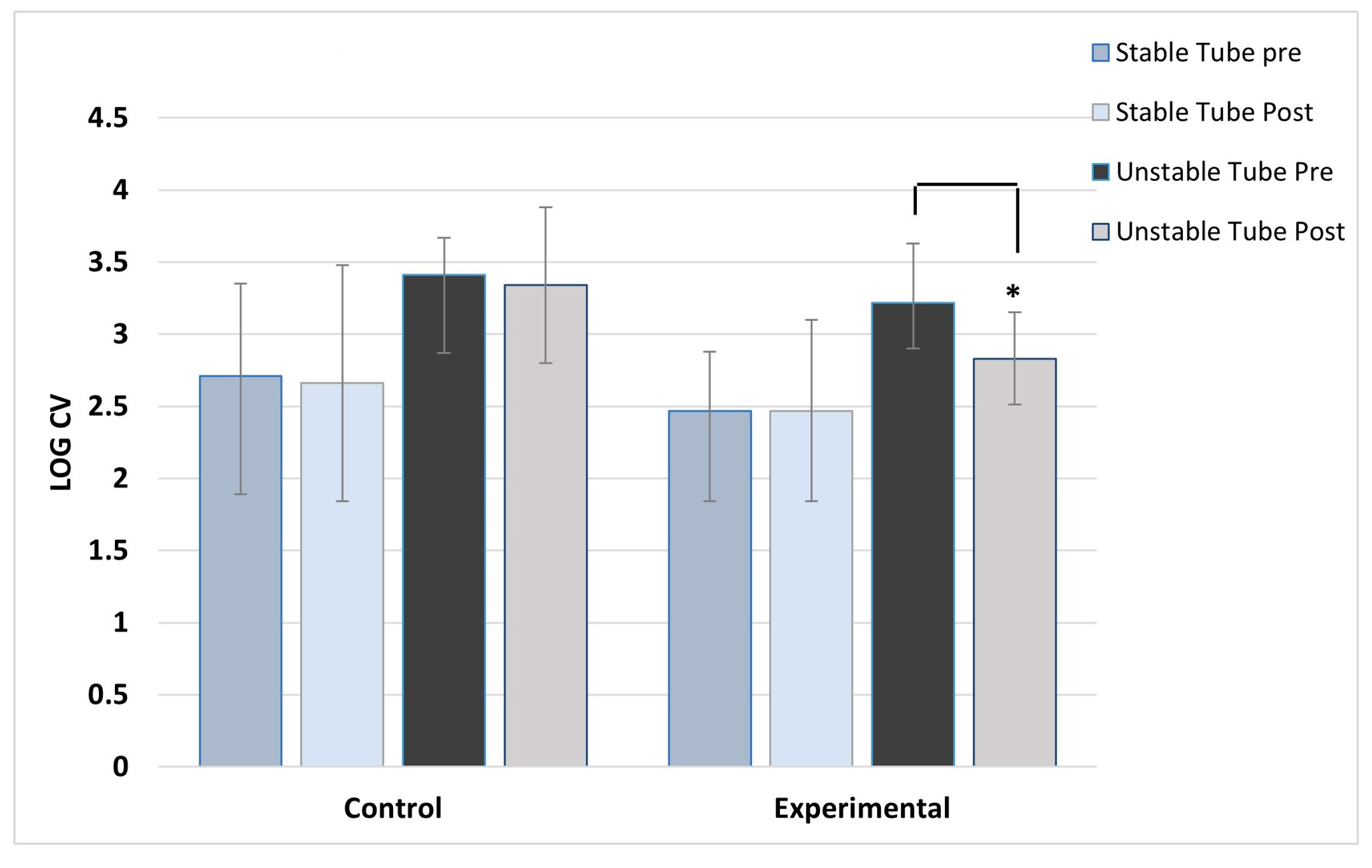
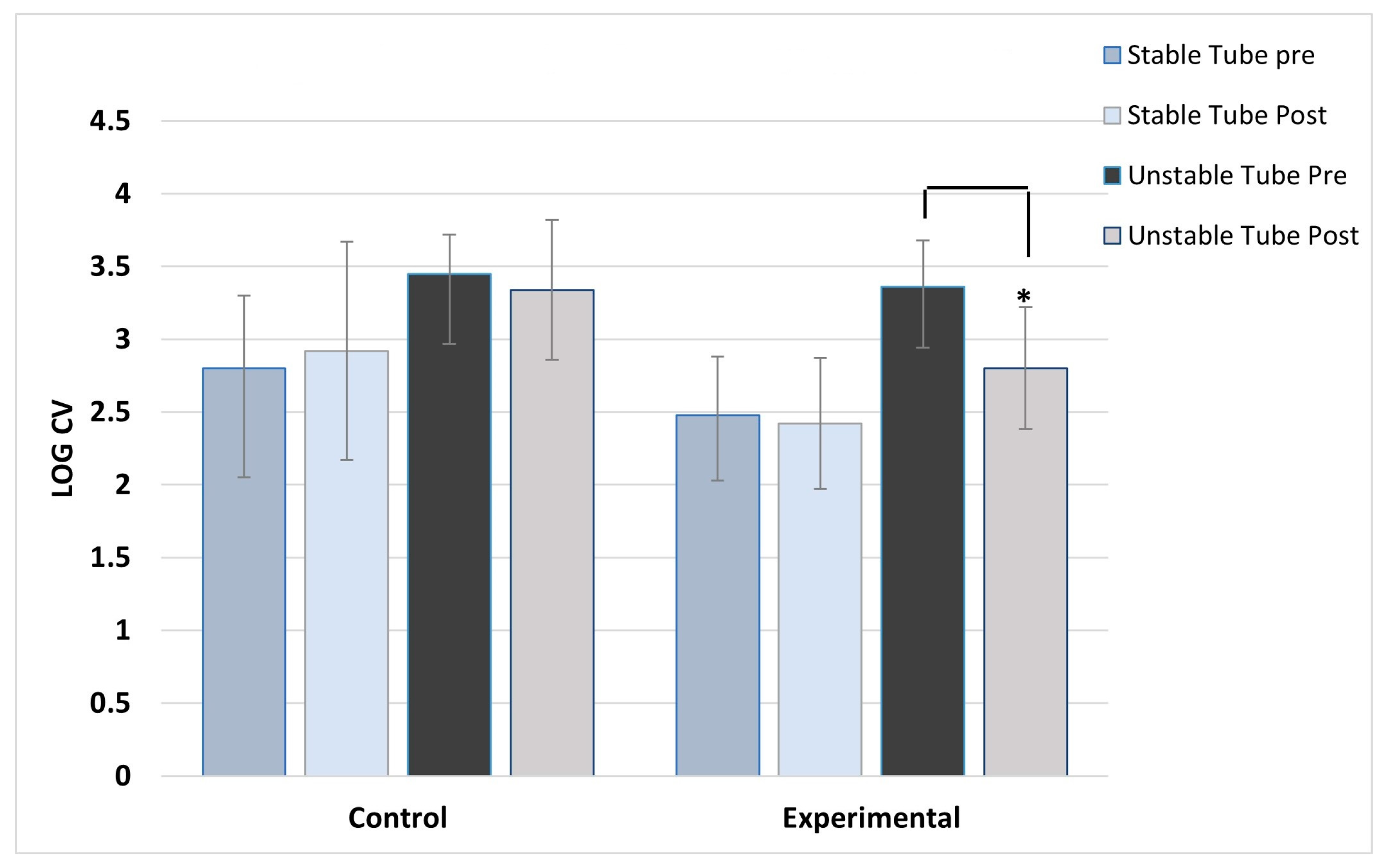
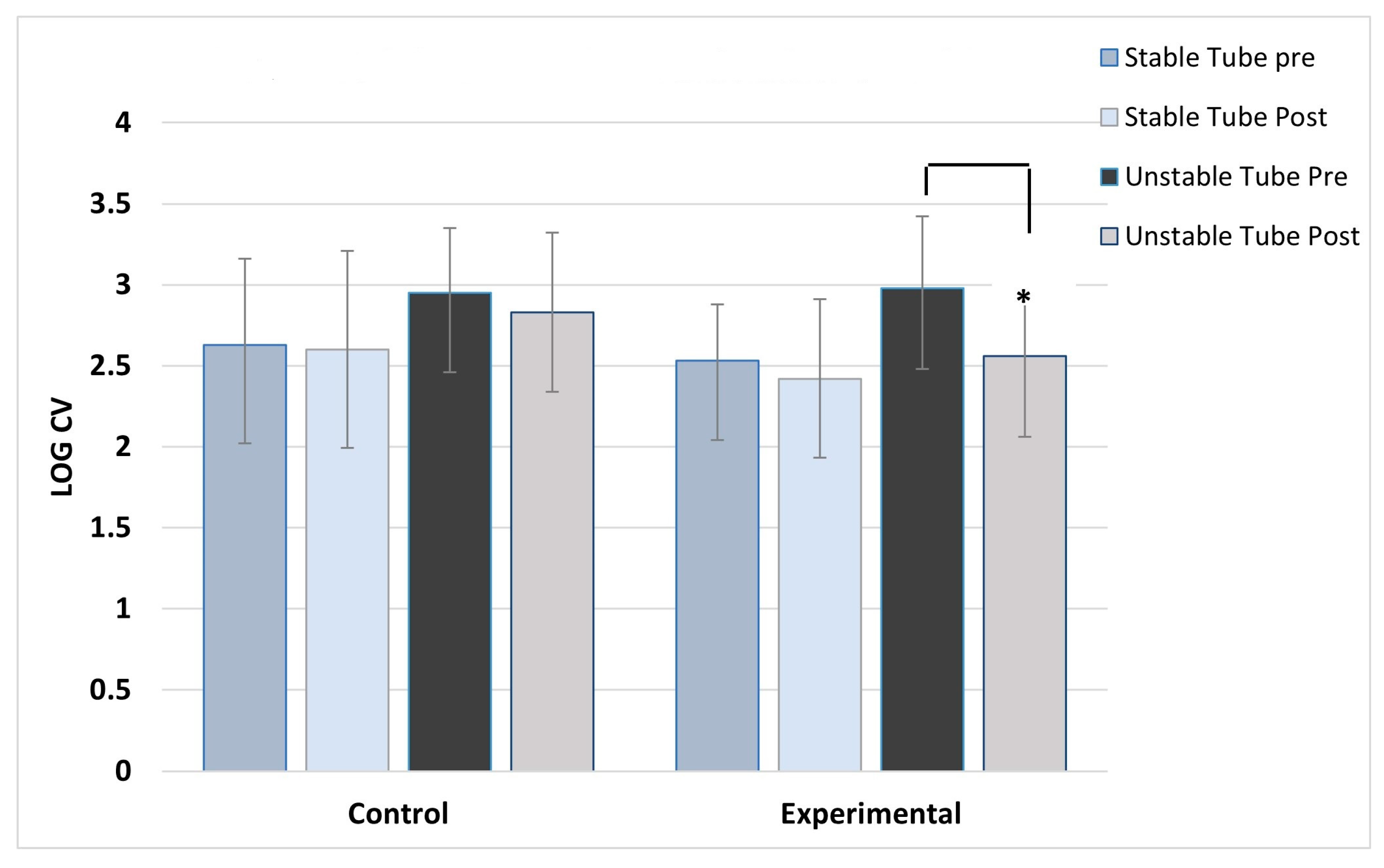
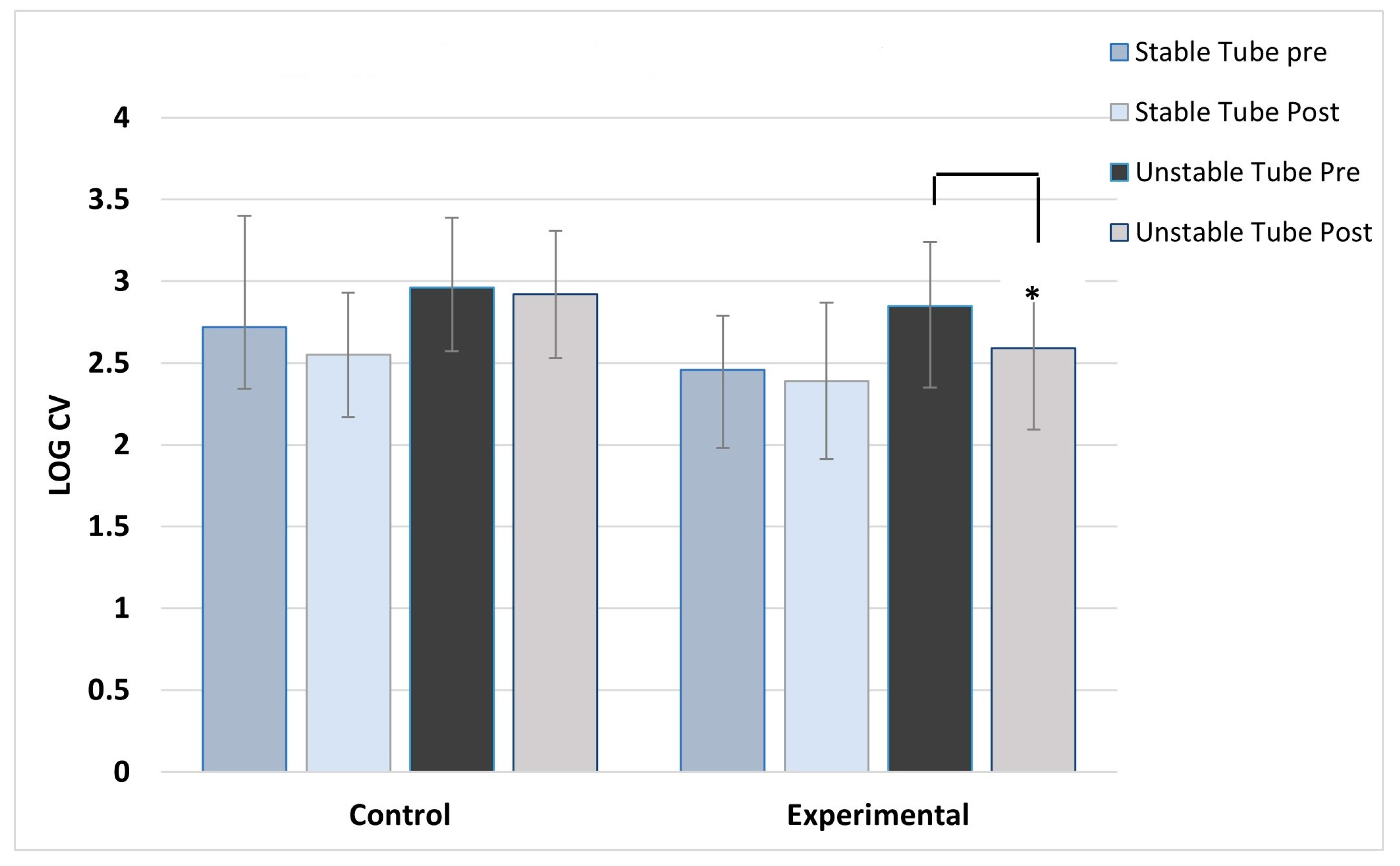
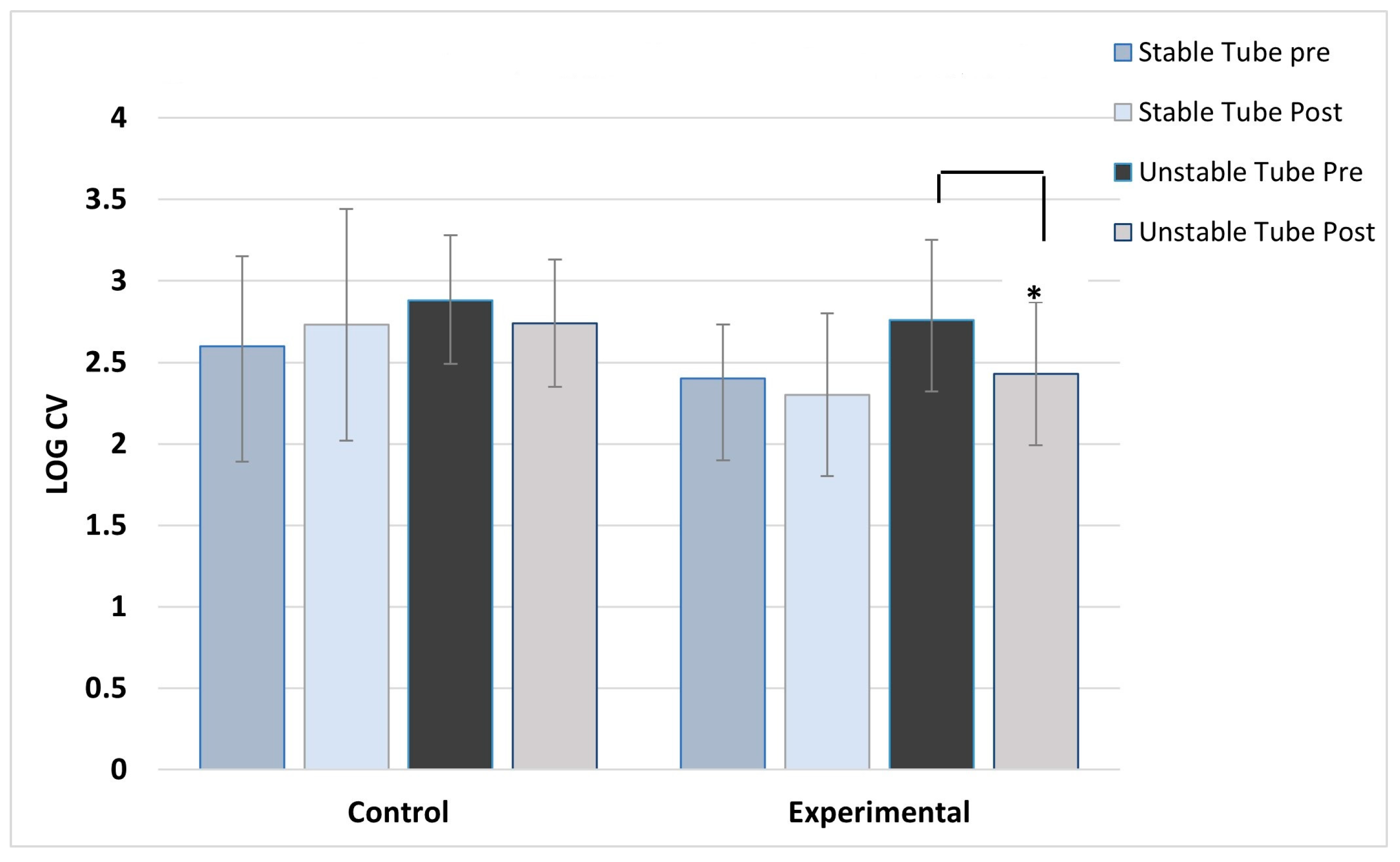
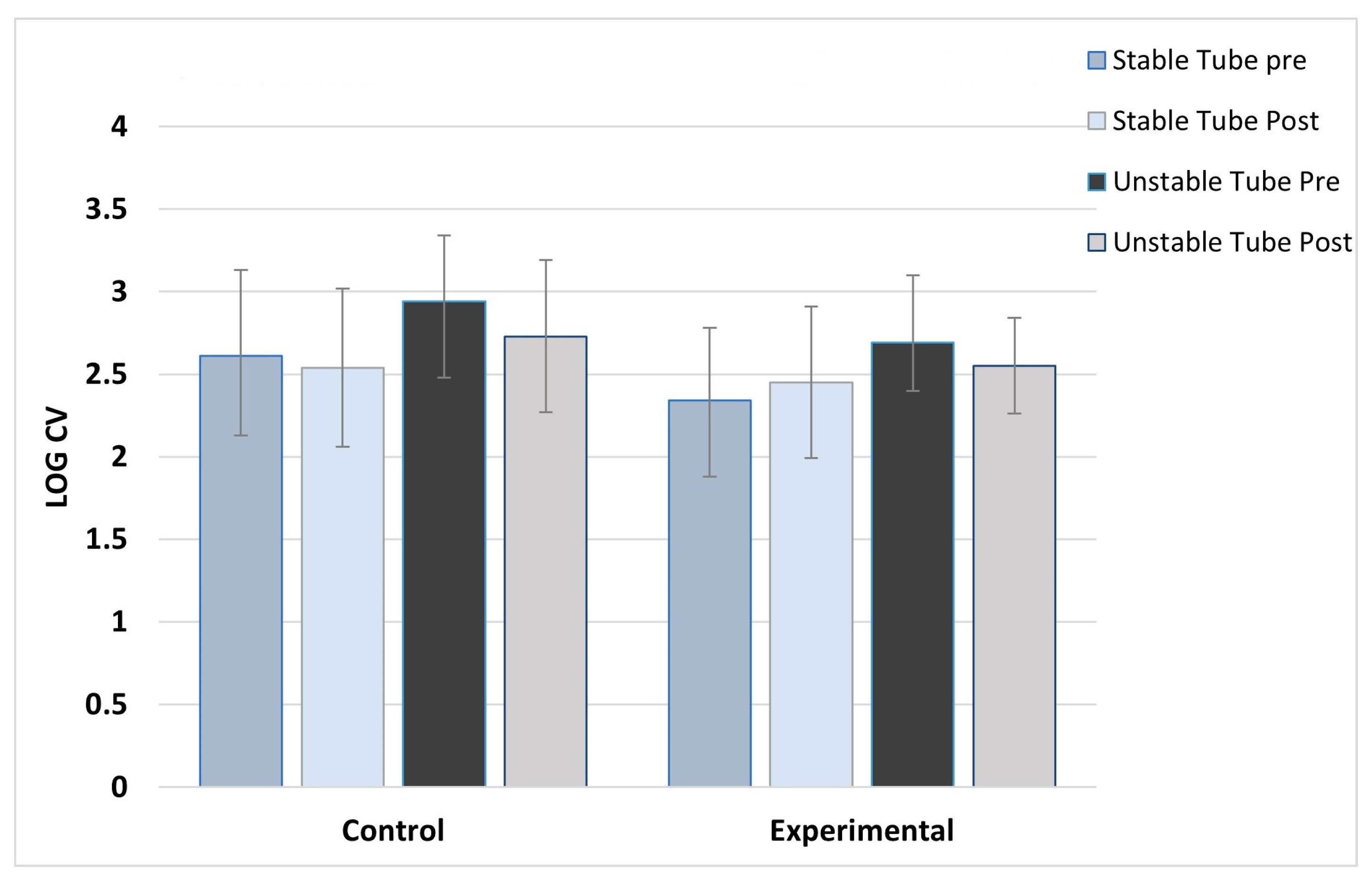
ANOVA results showed no main effect differences between concentric and eccentric contractions, so the results for contraction type were collapsed and data combined for analysis. As expected, the control group showed no post training changes in activation variability for any muscles, across both stable and unstable tube tests. For the experimental group, significant post-training reductions in activation variability during unstable tube testing were seen in five of the six muscles studied. The experimental group showed no pre-post changes in activation variability for the stable tube test. The magnitude of reduction ranged between 9-17% in activation variability.
Table 2 and
Table 3 show the mean (SD) data for the control and experimental groups pre-post training.
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5,
Figure 6 and
Figure 7 show the activation variability results comparisons between the control and experimental groups. A significant training effect was seen for the experimental group for all muscles except the left vastus lateralis muscle. Instability training resulted in significant reductions in activation variability when presented with the unstable tube test. The control group did not show any changes in EMG activation variability pre-post training.
4. Discussion
The results of this study show significant reductions in the variability of muscle activation (improved force steadiness) during a destabilizing weight training challenge following 2 weeks of instability training. Healthy active subjects trained across six sessions with a water-filled instability tube showed significant improvements in force steadiness measured by EMG in the deltoids, paraspinal and vastus lateralis muscles. Control subjects training with a stable tube showed no improvement in force steadiness. Balance and postural stability are not simply the result of muscle strength, but rather the ability of the muscles to initiate small, rapid contractions of postural support muscles to maintain stability. Research is plentiful with studies examining the effect of instability training on improvements in muscle activation [
6,
7,
9,
10,
12,
13,
14,
15,
17,
20,
21,
23,
24,
29,
30], however few have examined improvements in the compensatory activation of muscles to maintain force steadiness. This study demonstrated that even in healthy active individuals force steadiness can be improved with only two weeks of training.
Training for improvements in the neuromuscular system may come in many forms. For muscle tissue growth overload in the form of weight and fatigue of the myofibrils is essential for tissue hypertrophy. However, stability is also dependent upon the degree of compensatory adjustment [
29], onset of firing [
25] and coordination of firing [
25,
26,
33,
34] of various postural muscles. Often these force adjustments are small, yet rapid. Standard forms of strength training will not provide the stimulus for adaptation in this case. Instead, training specificity dictates that the load challenge be random, unpredictable, and involve a wide range of muscles for balance control. In fact, studies suggest that as instability increases the training load that can be used is reduced (11,13). Therefore, training loads needed to produce minor balance perturbations should be small, rapid, and random.
Imbalance can be initiated in the upper body as result of postural deficiencies, mass redistribution due to obesity and physical perturbation by means of a bump or sudden change in direction. The present study examined muscles challenged by an upper body perturbation requiring a “top down” adjustment in muscle activation to maintain stability. Utilizing the water-filled tube, random and unstable loads were given during training, resulting in a degree of muscle activation variation. Significant adaptations to these perturbations were seen in deltoid, paraspinal and vastus lateralis muscles, indicating a whole-body adaptation and improvement in force steadiness. Upper body instability has previously been induced using water-filled tubes. In a series of studies Glass et al [
31,
32] found that water filled tubes with a central valve redirecting water flow in different planes created significant perturbation to upper body support musculature. Ditroilo et al. [
29] used the squat exercise to induce instability and increased postural sway using a water-filled device along with associated activation of core musculature. As per the concept of specificity of training, adaptations to instability challenges can only be trained by giving the subjects unexpected perturbation.
Perturbation training is a relatively new concept, and studies have been examining different means of providing instability challenges. However, interest is increasing among clinicians [
27,
35,
38]. Safely providing random instability challenges force patients to use proprioceptive, tactile and visual cues to regulate balance. If the patients themselves are initiating movement that results in the random instability, as is the case with water-filled tube training, then the device can serve as effective biofeedback to help coordinate movement. Training with a water-filled tube means that the movement of the exercising individual is partially responsible for the degree of instability created. Unstable movement would exacerbate the forces of water and resulting instability. With the biofeedback linking movement to instability, the user begins to adopt more stable movement practices to reduce the amount of instability. Coupling the smoother movement with improved compensatory activation of posture support muscles thus results in improved force steadiness. Biofeedback is often visually linked, where the exercise monitors their movement by following a visual tracking of changes in center of pressure [
40] . This can sometimes be disorienting and is not utilizing any internal feedback sensations. Water tube training provides this immediate proprioceptive feedback, which may translate into a more manageable feedback system. In the present study we utilized young healthy individuals with no balance problem, yet still saw significant improvements in force steadiness. This is likely due to the effective biofeedback training that resulted in subjects executing smoother movements that resulted in less water movement and therefore less instability.
Functional training involves a mix of training techniques to cause a range of neuromuscular adaptations. The advantage of a water-filled training tube is that the load is light, and the perturbations relatively minor. This allows more selective training of postural muscles during a function movement, such as walking, squatting or other movements that involve posture stabilization. Our study demonstrated that 2 weeks of instability training resulted in improved force steadiness in muscles in the deltoid, back and legs compared to control subjects. Future studies should examine training in balance limited populations with equipment suited to their present condition. Used in concert with muscle strengthening exercises and heavier loads, instability training may help the patient develop a wider range of functional performance.
Author Contributions
Stephen C. Glass was the lead author for project conception and methodology design, IRB approval, assisted with data collection, EMG data processing, statistical analysis. Primary on writing drafts. Kamryn A. Wisneski asssisted with subject recruitment and scheduling, data collection and EMG data processing. She was the lead on statistical analysis. Assisted with editing and review of manuscript draft.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board for human research at Grand Valley State University (protocol code 20-015, approved July 29, 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent (signed) was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written consent has been obtained for the image used (
Figure 1).
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
This research has been supported by numerous undergraduate student research assistants from the Grand Valley State University Exercise Science Program who volunteered their time to contribute to the data collection and data processing for this study. Over 30 students across 3 years that included COVID related pauses in data collection and subject recruitment. We would also like to acknowledge our subjects, who showed amazing reliability and adherance to the testing and training timeline.
Conflicts of Interest
No conflicts on interest exist with this study. The study is not funded by any agency or industry.
References
- Thelen, D.G.; Muriuki, M.; James, J.; schultz, A.B.; Ashton-Miller, J.A.; Alexander, N.B. Muscle activities used by young and old adults when stepping to regain balance duyring a forward fall. J. Electromyography Kines. 2000, 10, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudino, R.; dos Santos, M.J.; Mazo, G.Z. Delayed compensatory postural adjustments after lateral perturbations contribute to the reduced ability of older adults to control body balance. Motor Control. 2017, 21, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, R.; Kahrizi, S.; Parnianpour, M.; Bahrami, F.; Kazemnejad, A.; Mobini, B. The study of the variability of anticipatory adjustments in patients with recurrent non-specific low back pain. J. Back & Musculoskel Rehab. 2014, 27, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Oddsson, L.I.E.; De Luca, C.J. Activation imbalances in lumbar spine muscles in the presence of chronic low back pain. J. Appl Phys. 2003, 94, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, N.P.; Cholwecki, J.; Van Dieen, J.H.; Kawchuk, G.; Hodges, P.W. Are stability and instability relevant concept for back pain? J. Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2019, 49, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemkova, E. Instability resistance training for health and performance. J. Trad Compl Med. 2017, 7, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mate-Munoz, J.L.; Anton, A.J.M.; Jimenez, P.J.; Garnacho-Castano, M.V. Effects of instability versus traditional resistance training on strength, power and velocity in untrained men. J. Sports Sci & Med. 2014, 13, 460–468. [Google Scholar]
- Drinkwater, E.J.; Pritchett, E.J.; Behm, D. Effect of instability and resistance on unintentional squat-lifting kinetics. Int J. Sports Phys Perform. 2007, 2, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeterbakken, A.H.; Van Den Tiller, R.; Fimland, M.S. A comparison of muscle activity and 1-RM strength of three chest-press exercises with different stability requirements. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlyn, N.; Behm, D.G.; Young, W.B. Trunk muscle activation during dynamic weight-training exercises and isometric instability activities. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, K.G.; Behm, D.G. Maintenance of EMG activity and loss of force output with instability. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2004, 18, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Norwood, J.T.; Anderson, G.S.; Gaetz, M.B.; Twist, P.W. Electromyographic activity of the trunk stabilizers during stable and unstable bench press. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 343–347. [Google Scholar]
- Kohler, J.M.; Flanagan, S.P.; Whiting, W.C. Muscle activation patterns while lifting stable and unstable loads on stable and unstable surfaces. J. Strength and Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.M.; Kutz, M.R.; Morgan, A.L.; Fullenkamp, A.M.; Ballenger, R. An evaluation of upper-body muscle activation during coupled and uncoupled instability resistance training. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 1833–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekendiz, B.; Cug, M.; Korkusuz, F. Effects of swiss-ball core strength training on strength, endurance, flexibility, and balance in sedentary women. J. Strength Cond Res. 2010, 24, 3032–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, P.W.; Dip Sci, P.G.; Murphey, B.A. Core stability exercises on and off a swiss ball. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005, 86, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, P.W.M.; Murphey, B.A. Increased deltoid and abdominal muscle activity during swiss ball bench press. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2006, 20, 745–750. [Google Scholar]
- Nuzzo, J.L.; McCaulley, G.O.; Cormie, P.; Cavill, M.J.; McBride, J.M. Trunk muscle activity during stability ball and free weight exercises. J. Strength Cond Res. 2008, 22, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, V.; Alvar, B.; Behm, D. Bodyblade™ training in athletes with traumatic anterior shoulder instability. Int J. Sports Phys Ther. 2023, 18, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, G.D.; Sola, M.; Dougherty, C.; Huddleson, S. Quantitative examination of upper and lower extremity muscle activation during common shoulder rehabilitation exercises using the bodyblade. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 2509–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snarr, R.L.; Esco, M.R. Electromyographical comparison of plank variations performed with and without instability devices. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 3298–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbalaeimahdi, M.; Alizadeh, M.H.; Minoonejad, H.; Behm, D.G.; Alizadeh, S. Higher leg and trunk muscle activation during balance control in copers versus people with chronic ankle instability and healthy female athletes. Sports 2022, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nairn, B.C.; Sutherland, C.A.; Drake, J.D.M. Location of instability during a bench press alters movement patterns and electromyographic activity. J. Strength Cond Res. 2015, 29, 3162–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nairn, B.C.; Sutherland, C.A.; Drake, J.D.M. Motion and muscle activity are affected by instability location during a squat exercise. J. Strength Cond Res. 2017, 31, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, J.; Pizzari, T.; Buttifant, D. Muscle onset can be improved by therapeutic exercise: A systematic review. Phys Ther Sport. 2011, 12, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cug, M.; Ak, E.; Ozdemir, R.A.; Korkusuz, F.; Behm, D.G. The effect of instability training on knee joint proprioception and core strength. J. Sport Sci and Med. 2012, 11, 468–474. [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield, A.; Danells, C.J.; Innes, E.L.; Musselman, K.; Salbach, N.M. A survey of Canadian healthcare professionals’ practices regarding reactive balance training. Physiother Theory & Practice. 2021, 37, 787–800. [Google Scholar]
- Behm, D.G.; Sanchez, J.C.C. Instability resistance training across the exercise continuum. Sports Phys Ther. 2013, 5, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditroilo, M.; O’Sullivan, R.; Harnan, B.; Crossey, A.; Gillmor, B.; Dardis, W.; Grainger, A. Water-filled training tubes increase core muscle activation and somatosensory control of balance during squat. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 2002–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, G.A.; McCurdy, K.W.; Ernest, J.M.; Doscher, M.W.; Walters, S.D. Specificity of machine, barbell and water-filled log bench press resistance training on measures of strength. J. Strength Cond Res. 2007, 21, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, S.C.; Blanchette, T.W.; Karwan, L.A.; Pearson, S.S.; OʼNeil, A.P.; Karlik, D.A. Core Muscle Activation During Unstable Bicep Curl Using a Water-Filled Instability Training Tube. J. Strength Cond Res 2016, 30, 3212–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, S.C.; Albert, R.W. Compensatory muscle activation during unstable overhead squat using a water-filled training tube. J. Strength Cond Res. 2018, 32, 32,1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santuz, A.; Ekizos, A.; Eckardt, N.; Kibele, A.; Arampatzis, A. Challenging human locomotion: Stability and modular organization in unsteady conditions. Sci Reports. 2018, 8, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smania, N.; Corato, E.; Tinazzi, M.; Stanzani, C.; Fiaschi, A.; Girardi, P.; Gandolfi, M. Effect of balance training on postural instability in patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease. Neurorehab Neural Repair. 2010, 24, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviles, J.; Porter, G.C.; Estabrooks, P.A.; Alexander, N.B.; Madigan, M.L. Potentiation of reactive balance training within continuing care retirement communities. Translational J. ACSM. 2020, 5, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalambous, L.H.; Champion, R.B.; Smith, L.R.; Mitchell, A.C.S.; Bailey, D.P. Effects of interrupting sitting with use of a treadmill desk versus prolonged sitting on postural stability. Int. J. Sports Med. 2019, 40, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.A.; Allen, S.P.; Hamilton, L.D.; Grabowski, A.M.; Enoka, R.M. Differences in postural sway among healthy adults are associated with the ability to perform steady contractions with leg muscles. Exp Brain Res. 2020, 238, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, A.; Wong, J.S.; Bryce, B.; Knorr, S.; Patterson, K.K. Does perturbation-based balance training prevent falls? Systematic review and meta-analysis of preliminary randomized controlled trials. Phys.Ther. 2015, 95, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criswell, E. (Ed.) Cram’s Introduction to Surface Electromyography, 3rd ed.; Jones & Bartlett: Burlington, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bechly, K.E.; Carender, W.J.; Myles, J.D.; Sienko, K.H. Determining the preferred modality for real-time biofeedback during balance training. Gait& Posture 2013, 37, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).