Submitted:
22 August 2023
Posted:
23 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant materials
2.2. Genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) analysis
2.3. Basic statistical analysis
2.4. Population structure and linkage disequilibrium (LD) analyses
2.5. Genome-wide association analysis
2.6. Candidate Gene Identification
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic evaluation of grain traits
3.2. Structure of durum population and SNP density on the genomes
3.3. Linkage disequilibrium analysis
3.4. Genome-wide association analysis
3.5. Putative candidate genes underlying grain size and shape-related traits in durum wheat
4. Discussion
4.1. Phenotypic evaluation
4.2. MTAs identified for grain size and shape traits
4.3. Candidate gene prediction
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harlan, J.R. Crops and man; American Society of Agronomy, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Zohary, D.; Hopf, M. Domestication of plants in the Old World: The origin and spread of cultivated plants in West Asia, Europe and the Nile Valley; Oxford University Press, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Heun, M.; Schäfer-Pregl, R.; Klawan, D.; Castagna, R.; Accerbi, M.; Borghi, B.; Salamini, F. Site of Einkorn Wheat Domestication Identified by DNA Fingerprinting. Science 1997, 278, 1312–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, H.; Brandolini, A.; Schäfer-Pregl, R.; Salamini, F. AFLP analysis of a collection of tetraploid wheats indicates the origin of emmer and hard wheat domestication in southeast Turkey. Mol Biol Evol 2002, 19, 1797–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nihikiwa, K. Species relationship of wheat and its putative ancestors as viewed from isozyme variation. In Proceedings of the Proc. 6th Int. Wheat Genet. Symp. 1983; pp. 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Dvorák, J.; Terlizzi, P.; Zhang, H.B.; Resta, P. The evolution of polyploid wheats: identification of the A genome donor species. Genome 1993, 36, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorák, J.; Zhang, H.B. Variation in repeated nucleotide sequences sheds light on the phylogeny of the wheat B and G genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1990, 87, 9640–9644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.; Stebbins, G.L. Morphological evidence concerning the origin of the B genome in wheat. American Journal of Botany 1956, 43, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royo, C.; Soriano, J.M.; Alvaro, F. Wheat: A Crop in the Bottom of the Mediterranean Diet Pyramid. In Mediterranean Identities, Borna, F.-B., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, 2017; p. Ch. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Chris, G. World Durum Outlook. Available online: http://www.internationalpasta.org/resources/IPO%20BOARD%202013/2%20Chris%20Gillen.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2017).
- Statistic-Canada. Canada: Outlook for Principal Field Crops. Available online: http: //www.agr.gc.ca/eng/industry-markets-and-trade/statistics-and-market-information/by-product-sector/ crops-industry/outlook-for-principal-field-crops-in-canada/canada-outlook-for-principal-field-cropsfebruary-16-2016/?id=1455720699951 (accessed on 7 April 2017).
- USDA Foreign Agricultural Service, A. , Turkey. USDA Foreign Agricultural Service. Grain and Feed Annual; GAIN Report No: TR5016; USDA Foreign Agricultural Service: Ankara, Turkey, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- International Grains Council. World Grain Statistics 2016. Available online: https://www.igc.int/en/subscriptions/subscription.aspx 2020 (accessed on 21 May 2020).
- Food-Price-Index. Food Price Index (FPI). Available online: http://www.fao.org/worldfoodsituation/foodpricesindex/en/ (accessed on 22 December 2016).
- Breseghello, F.; Sorrells, M.E. Association mapping of kernel size and milling quality in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Genetics 2006, 172, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gegas, V.C.; Nazari, A.; Griffiths, S.; Simmonds, J.; Fish, L.; Orford, S.; Sayers, L.; Doonan, J.H.; Snape, J.W. A genetic framework for grain size and shape variation in wheat. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botwright, T.L.; Condon, A.G.; Rebetzke, G.J.; Richards, R.A. Field evaluation of early vigour for genetic improvement of grain yield in wheat. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research 2002, 53, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, H.A.; Moaveni, P.; Maroufi, K. Effect of seed size on seedling production in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Advances in Environmental Biology 2011, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Desiderio, F.; Zarei, L.; Licciardello, S.; Cheghamirza, K.; Farshadfar, E.; Virzi, N.; Sciacca, F.; Bagnaresi, P.; Battaglia, R.; Guerra, D.; et al. Genomic Regions From an Iranian Landrace Increase Kernel Size in Durum Wheat. Frontiers in Plant Science 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.M.; Tamhankar, S.A.; Oak, M.D.; Raut, A.L.; Honrao, B.K.; Rao, V.S.; Misra, S.C. Mapping of QTL for agronomic traits and kernel characters in durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.). Euphytica 2013, 190, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.A.; Ficco, D.B.M.; Laidò, G.; Marone, D.; Papa, R.; Blanco, A.; Gadaleta, A.; Vita, P.D.; Mastrangelo, A.M. A dense durum wheat × T. dicoccum linkage map based on SNP markers for the study of seed morphology. Molecular breeding 2014, 34, 1579–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Xu, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, L.; Yu, Q.; Liao, S.; Jiang, C.; Feng, B.; Wang, T. Identification and validation of major QTL for grain size and weight in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). The Crop Journal 2023, 11, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Jaiswal, V.; Mishra, V.K.; Paliwal, R.; Balyan, H.S.; Gupta, P.K. QTL mapping for some grain traits in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 2018, 24, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, Y.; Nguyen, A.T.; Yoshioka, M.; Iehisa, J.C.; Takumi, S. Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling grain size and shape in the D genome of synthetic hexaploid wheat lines. Breed Sci 2013, 63, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Liang, F.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, H.; Sun, Q.; Ni, Z. Identification of QTL for Grain Size and Shape on the D Genome of Natural and Synthetic Allohexaploid Wheats with Near-Identical AABB Genomes. Frontiers in Plant Science 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Liu, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, W.; Yang, W.; Yin, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, S.; Sun, J.; et al. Unraveling the genetic architecture of grain size in einkorn wheat through linkage and homology mapping and transcriptomic profiling. J Exp Bot 2019, 70, 4671–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesiz, U.; Balyan, H.S.; Özkan, H. QTL detection for grain size and shape traits using an improved genetic map in einkorn wheat (Triticum monococcum L.). Euphytica 2023, 219, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Schwartz, C.; Singh, A.; Warthmann, N.; Kim, M.C.; Maloof, J.N.; Loudet, O.; Trainer, G.T.; Dabi, T.; Borevitz, J.O.; et al. QTL Mapping in New Arabidopsis thaliana Advanced Intercross-Recombinant Inbred Lines. PLOS ONE 2009, 4, e4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, A.; Farlow, A. The advantages and limitations of trait analysis with GWAS: a review. Plant Methods 2013, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuberosa, R.; Salvi, S.; Sanguineti, M.C.; Landi, P.; Maccaferri, M.; Conti, S. Mapping QTLs regulating morpho-physiological traits and yield: case studies, shortcomings and perspectives in drought-stressed maize. Ann Bot 2002, 89 Spec No, 941–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, A.; Feyissa, T.; Tuberosa, R.; Maccaferri, M.; Sciara, G.; Letta, T.; Abeyo, B. Genome-wide association mapping for grain shape and color traits in Ethiopian durum wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum). The Crop Journal 2020, 8, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ullah, Z.; Alam, N.; Naqvi, S.; Jamil, M.; Bux, H.; Sher, H. Genetic analysis of wheat grains using digital imaging and their relationship to enhance grain weight. Scientia Agricola 2020, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Yang, J.; Song, S.-j.; Xu, K.; Liu, H.-d.; Zhang, S.-h.; Yang, X.-j.; Zhao, Y. Genome–wide association study of grain morphology in wheat. Euphytica 2021, 217, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Jin, J.; Duan, S.; Zhen, W.; Xie, C.; Ma, J. Dissecting the genetic basis of grain morphology traits in Chinese wheat by genome wide association study. Euphytica 2021, 217, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wen, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, S.; He, Z.; Rasheed, A.; Jin, H.; Zhang, C.; Yan, J.; et al. Genetic architecture of grain yield in bread wheat based on genome-wide association studies. BMC Plant Biol 2019, 19, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, P.; Kumar, J.; Sharma, S.; Meher, P.K.; Balyan, H.S.; Gupta, P.K.; Sharma, S. GWAS for main effects and epistatic interactions for grain morphology traits in wheat. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 2022, 28, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Hu, W.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Xie, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. Appraising the Genetic Architecture of Kernel Traits in Hexaploid Wheat Using GWAS. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, A.; Xia, X.; Ogbonnaya, F.; Mahmood, T.; Zhang, Z.; Mujeeb-Kazi, A.; He, Z. Genome-wide association for grain morphology in synthetic hexaploid wheats using digital imaging analysis. BMC Plant Biol 2014, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekeu, H.; Ngonkeu, E.L.M.; Bélanger, S.; Djocgoué, P.F.; Abed, A.; Torkamaneh, D.; Boyle, B.; Tsimi, P.M.; Tadesse, W.; Jean, M.; et al. GWAS identifies an ortholog of the rice D11 gene as a candidate gene for grain size in an international collection of hexaploid wheat. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 19483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, L.; Ren, Y.; Dong, Z.; Cui, D.; Chen, F. Genome-wide association study revealed that the TaGW8 gene was associated with kernel size in Chinese bread wheat. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanke, C.D.; Ling, J.; Plieske, J.; Kollers, S.; Ebmeyer, E.; Korzun, V.; Argillier, O.; Stiewe, G.; Hinze, M.; Neumann, F.; et al. Analysis of main effect QTL for thousand grain weight in European winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by genome-wide association mapping. Front Plant Sci 2015, 6, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xu, S.; Chao, S.; Sun, Q.; Liu, S.; Xia, G. A Genome-Wide Association Study of Highly Heritable Agronomic Traits in Durum Wheat. Frontiers in Plant Science 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volante, A.; Barabaschi, D.; Marino, R.; Brandolini, A. Genome-wide association study for morphological, phenological, quality, and yield traits in einkorn (Triticum monococcum L. subsp. monococcum). G3 Genes|Genomes|Genetics 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talini, R.F.; Brandolini, A.; Miculan, M.; Brunazzi, A.; Vaccino, P.; Pè, M.E.; Dell’Acqua, M. Genome-wide association study of agronomic and quality traits in a world collection of the wild wheat relative Triticum urartu. The Plant Journal 2020, 102, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Singh, N.; Kaur, S.; Bains, N.S.; Uauy, C.; Poland, J.; Chhuneja, P. Genome-Wide Association Study of Grain Architecture in Wild Wheat Aegilops tauschii. Front Plant Sci 2017, 8, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Lv, L.; Li, J.; Ma, F.; Bai, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Song, C.-p. Genome-wide association study of grain shapes in Aegilops tauschii. Euphytica 2021, 217, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, A.; Wenzl, P.; Huttner, E.; Carling, J.; Xia, L.; Blois, H.; Caig, V.; Heller-Uszynska, K.; Jaccoud, D.; Hopper, C.; et al. Diversity arrays technology: a generic genome profiling technology on open platforms. Methods Mol Biol 2012, 888, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furbank, R.T.; Tester, M. Phenomics – technologies to relieve the phenotyping bottleneck. Trends in Plant Science 2011, 16, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 49. Tanabata, T.; Shibaya, T.; Hori, K.; Ebana, K.; Yano, M. SmartGrain: High-Throughput Phenotyping Software for Measuring Seed Shape through Image Analysis Plant Physiology 2012, 160, 1871–1880. [CrossRef]
- Zadoks, J.C.; Chang, T.T.; Konzak, C.F. A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed research 1974, 14, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivoto, T.; Lúcio, A.D.C. metan: An R package for multi-environment trial analysis. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 2020, 11, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, J. JASP (Version 0.11.1)[Computer software]. 2019. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- SAS Institute Inc. JMP®, Version 9.0. SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, 2021; pp. 1989–2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Summers, R.M.; Zhang, Z. BLINK: a package for the next level of genome-wide association studies with both individuals and markers in the millions. GigaScience 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradbury, P.J.; Zhang, Z.; Kroon, D.E.; Casstevens, T.M.; Ramdoss, Y.; Buckler, E.S. TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Huang, M.; Fan, B.; Buckler, E.S.; Zhang, Z. Iterative Usage of Fixed and Random Effect Models for Powerful and Efficient Genome-Wide Association Studies. PLOS Genetics 2016, 12, e1005767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Z.; Xu, J.; Yin, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, S.; Li, X.; et al. rMVP: A Memory-efficient, Visualization-enhanced, and Parallel-accelerated Tool for Genome-wide Association Study. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 2021, 19, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabieyan, E.; Bihamta, M.R.; Moghaddam, M.E.; Mohammadi, V.; Alipour, H. Genome-wide association mapping for wheat morphometric seed traits in Iranian landraces and cultivars under rain-fed and well-watered conditions. Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 17839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Li, J.; Hu, W.; Yu, J.; Khan, S.U.; Khan, M.H.U.; Xie, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. Uncovering genomic regions controlling plant architectural traits in hexaploid wheat using different GWAS models. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 6767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schierenbeck, M.; Alqudah, A.M.; Lohwasser, U.; Tarawneh, R.A.; Simón, M.R.; Börner, A. Genetic dissection of grain architecture-related traits in a winter wheat population. BMC Plant Biology 2021, 21, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.Q.; Sun, Y.; Guo, T.; Shi, C.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Kan, Y.; Xiang, Y.H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.B.; Li, Y.C.; et al. UDP-glucosyltransferase regulates grain size and abiotic stress tolerance associated with metabolic flux redirection in rice. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergès, V.; Dutilleul, C.; Godin, B.; Collet, B.; Lecureuil, A.; Rajjou, L.; Guimaraes, C.; Pinault, M.; Chevalier, S.; Giglioli-Guivarc’h, N.; et al. Protein Farnesylation Takes Part in Arabidopsis Seed Development. Front Plant Sci 2021, 12, 620325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.-J.; Huang, W.; Shi, M.; Zhu, M.-Z.; Lin, H.-X. A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nature Genetics 2007, 39, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Li, N.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Y. The Ubiquitin Receptor DA1 Regulates Seed and Organ Size by Modulating the Stability of the Ubiquitin-Specific Protease UBP15/SOD2 in Arabidopsis The Plant Cell 2014, 26, 665–677. The Plant Cell 2014, 26, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Corke, F.; Smith, C.; Bevan, M.W. Control of final seed and organ size by the DA1 gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes Dev 2008, 22, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiao, X.; Kong, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Fang, R.; Yan, Y. The histone deacetylase HDA703 interacts with OsBZR1 to regulate rice brassinosteroid signaling, growth and heading date through repression of Ghd7 expression. The Plant Journal 2020, 104, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.B.; Huang, H.Y.; Hu, Y.W.; Zhu, S.W.; Wang, Z.Y.; Lin, W.H. Brassinosteroid regulates seed size and shape in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 2013, 162, 1965–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, C.; Zhou, G.; Li, C. Harnessing Transcription Factors as Potential Tools to Enhance Grain Size Under Stressful Abiotic Conditions in Cereal Crops. Frontiers in Plant Science 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Wang, D.; Duan, P.; Zhang, B.; Xu, R.; Li, N.; Li, Y. WIDE AND THICK GRAIN 1, which encodes an otubain-like protease with deubiquitination activity, influences grain size and shape in rice. The Plant Journal 2017, 91, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, J.; Liu, J.; Mu, Y.; Tang, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, G.; Wei, Y.; et al. Molecular characterization of the TaWTG1 in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Gene 2018, 678, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong-Bo, S.; Zong-Suo, L.; Ming-An, S. LEA proteins in higher plants: Structure, function, gene expression and regulation. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2005, 45, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, D.R.; Hattori, T.; Carson, C.B.; Vasil, V.; Lazar, M.; Vasil, I.K. The Viviparous-1 developmental gene of maize encodes a novel transcriptional activator. Cell 1991, 66, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Guo, L.; Ji, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, Q.; Wu, Y. The B3 domain-containing transcription factor ZmABI19 coordinates expression of key factors required for maize seed development and grain filling. The Plant Cell 2020, 33, 104–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamski, N.M.; Anastasiou, E.; Eriksson, S.; O’Neill, C.M.; Lenhard, M. Local maternal control of seed size by KLUH/CYP78A5-dependent growth signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106, 20115–20120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, M.; Zhang, N.; Sauvage, C.; Muños, S.; Blanca, J.; Cañizares, J.; Diez, M.J.; Schneider, R.; Mazourek, M.; McClead, J.; et al. A cytochrome P450 regulates a domestication trait in cultivated tomato. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2013, 110, 17125–17130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Liu, C.; Song, L.; Li, Y.; Li, M. PaCYP78A9, a Cytochrome P450, Regulates Fruit Size in Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.). Frontiers in Plant Science 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Dai, A.; Wei, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, B.; Jiang, N.; Feng, X. Arabidopsis KLU homologue GmCYP78A72 regulates seed size in soybean. Plant Molecular Biology 2016, 90, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Cheng, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Song, W.; Appels, R.; Zhao, H. Expression of TaCYP78A3, a gene encoding cytochrome P450 CYP78A3 protein in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), affects seed size. The Plant Journal 2015, 83, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Cerny, R.E.; Bhat, D.S.; Brown, S.M. Cloning of an Arabidopsis Patatin-Like Gene, STURDY, by Activation T-DNA Tagging. Plant Physiology 2001, 125, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, K.; Ai, J.; Deng, X.; Hong, Y.; wang, X. Patatin-related phospholipase A, pPLAIIIα, modulates the longitudinal growth of vegetative tissues and seeds in rice. Journal of Experimental Botany 2015, 66, 6945–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Huang, D.; Yin, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, D.; Gong, C.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y. The phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C1 modulates flowering time and grain size in rice. Planta 2022, 256, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.Z.; Ding, S.; Wang, H.C.; Sun, F.; Huang, W.L.; Song, S.; Xu, C.; Tan, B.C. The pentatricopeptide repeat protein EMP9 is required for mitochondrial ccmB and rps4 transcript editing, mitochondrial complex biogenesis and seed development in maize. New Phytologist 2017, 214, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Tan, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, Z.; et al. Analysis of the genetic architecture of maize kernel size traits by combined linkage and association mapping. Plant Biotechnol J 2020, 18, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chang, X.; Jing, R.; Hao, C.; Zhang, X. TEF-7A, a transcript elongation factor gene, influences yield-related traits in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Journal of Experimental Botany 2014, 65, 5351–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giancaspro, A.; Giove, S.L.; Zacheo, S.A.; Blanco, A.; Gadaleta, A. Genetic Variation for Protein Content and Yield-Related Traits in a Durum Population Derived From an Inter-Specific Cross Between Hexaploid and Tetraploid Wheat Cultivars. Front Plant Sci 2019, 10, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.H.T.; Martinoia, E.; Lee, Y. Functions of ABC transporters in plant growth and development. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 2018, 41, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
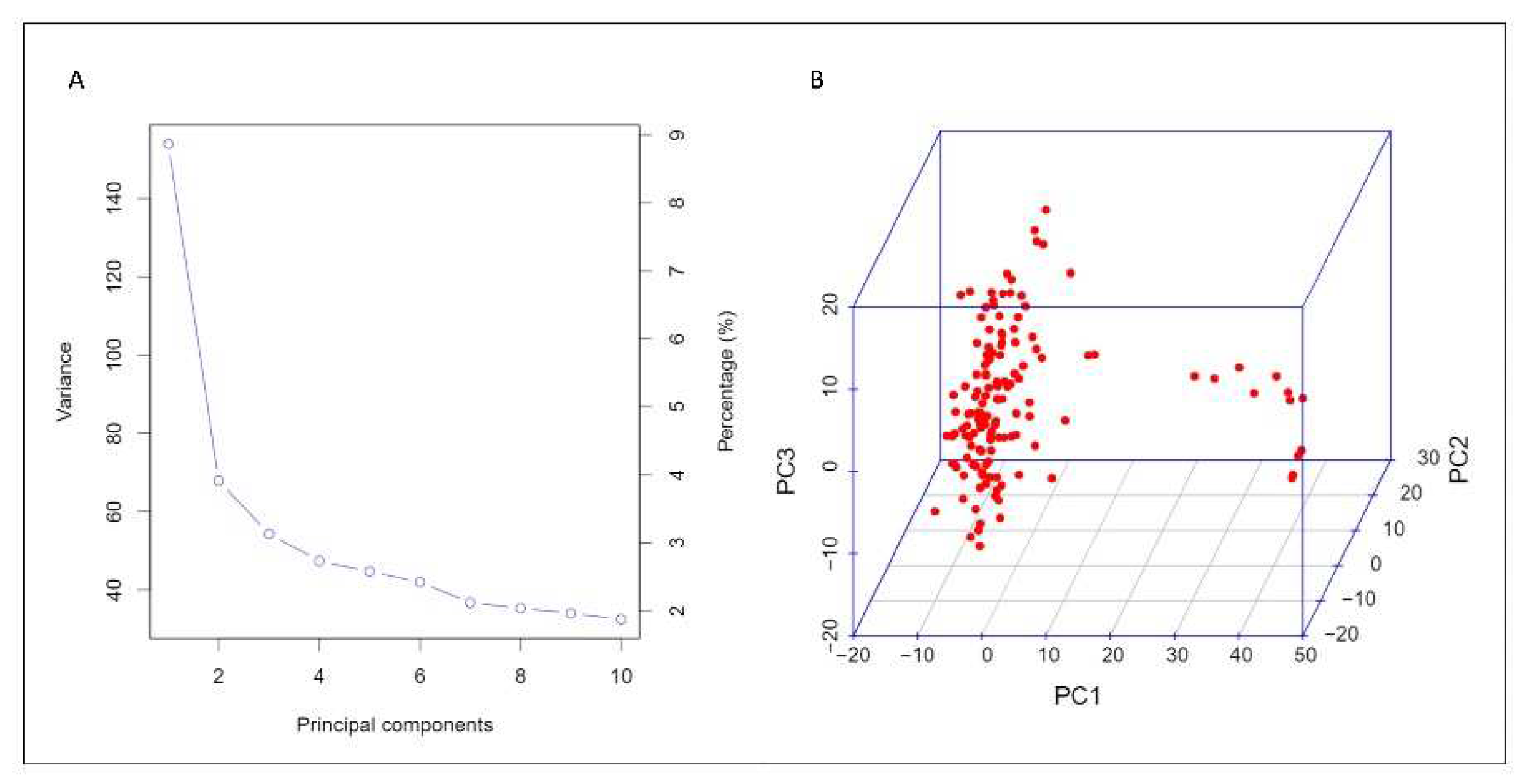
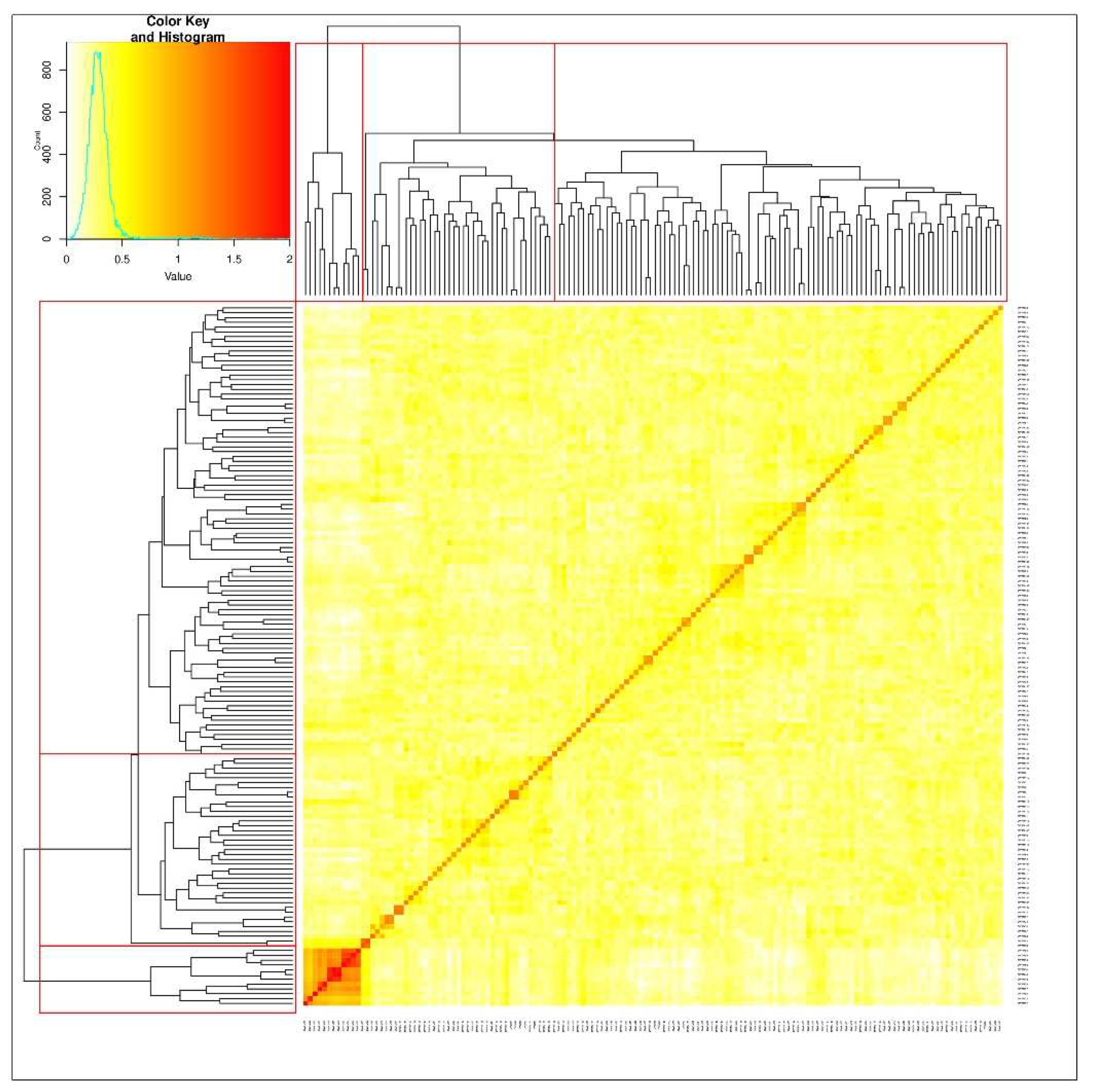
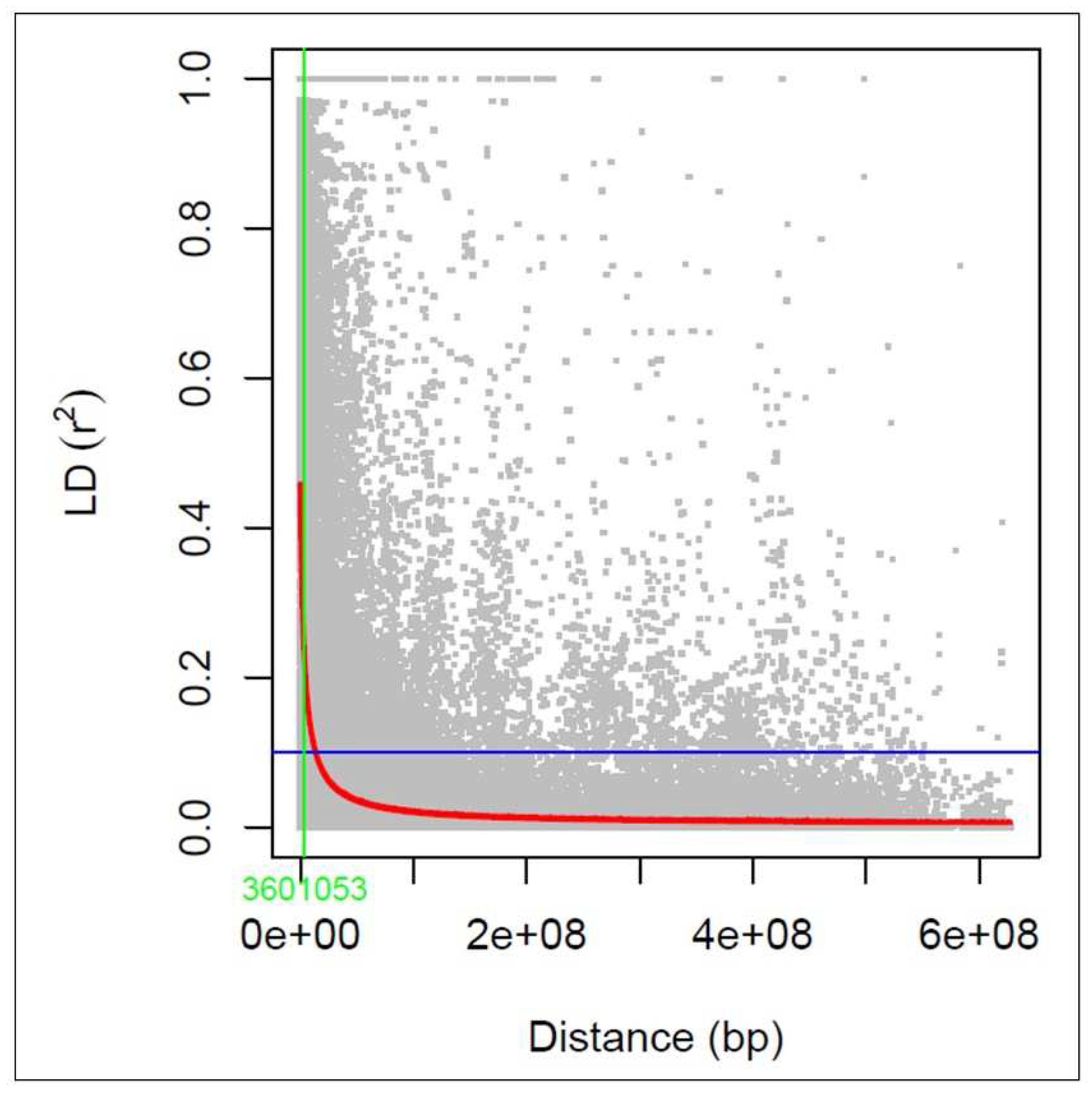
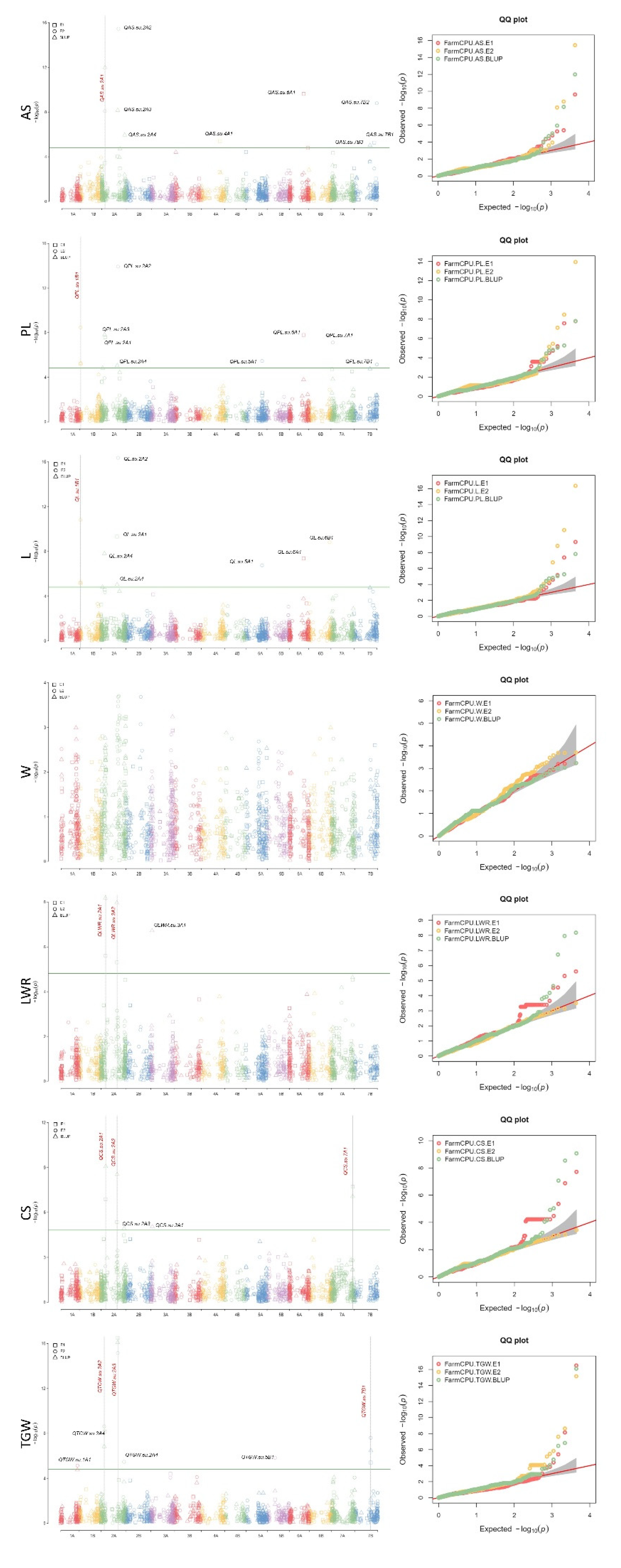
| Mean Square | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Df | AS | PL | L | W | LWR | CS | TGW |
| Environment | 1 | 11.40933*** | 2.61750*** | 0.02955 | 0.58264*** | 0.25699*** | 0.00012 | 735.42254*** |
| Genotype | 145 | 14.15645*** | 4.99604*** | 1.06796*** | 0.11702*** | 0.13180*** | 0.00373*** | 156.41942*** |
| Gen×Env | 145 | 4.39758*** | 0.74099*** | 0.12123*** | 0.05957*** | 0.02099*** | 0.00071*** | 75.01062*** |
| Residuals | 580 | 0.48459 | 0.12962 | 0.02207 | 0.00558 | 0.00220 | 0.00007 | 3.89443 |
| Variable | Max | Mean | Min | Range | Skewness | Kurtosis | CV(%) | h2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS | 26.55 | 20.61 | 14.33 | 12.22 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 3.37 | 0.97 |
| PL | 23.59 | 19.48 | 16.88 | 6.71 | 0.49 | 0.70 | 1.84 | 0.97 |
| L | 9.74 | 7.88 | 6.79 | 2.95 | 0.59 | 1.00 | 1.88 | 0.98 |
| W | 3.93 | 3.44 | 2.66 | 1.26 | -0.35 | 0.91 | 2.16 | 0.96 |
| LWR | 3.12 | 2.29 | 1.92 | 1.20 | 1.06 | 2.03 | 2.04 | 0.98 |
| CS | 0.74 | 0.68 | 0.56 | 0.18 | -0.73 | 0.82 | 1.23 | 0.98 |
| TGW | 73.80 | 52.19 | 23.84 | 49.96 | -0.16 | 0.82 | 3.77 | 0.98 |
| Environment | AS | PL | L | W | LWR | CS | TGW | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | vs | E2 | 0.535*** | 0.746*** | 0.798*** | 0.337*** | 0.744*** | 0.690*** | 0.364*** |
| E1 | vs | Mean | 0.868*** | 0.931*** | 0.946*** | 0.858*** | 0.948*** | 0.929*** | 0.804*** |
| E1 | vs | BLUP | 0.868*** | 0.931*** | 0.946*** | 0.856*** | 0.948*** | 0.920*** | -0.013 |
| E2 | vs | Mean | 0.884*** | 0.938*** | 0.950*** | 0.772*** | 0.918*** | 0.890*** | 0.846*** |
| E2 | vs | BLUP | 0.884*** | 0.938*** | 0.951*** | 0.773*** | 0.917*** | 0.891*** | 0.267** |
| Mean | vs | BLUP | 1.000*** | 1.000*** | 1.000*** | 0.999*** | 0.999*** | 0.982*** | 0.163* |
| Trait | Environment | MTA | SNP-ID | Chr. | Position | P value1 | MAF | Add. Eff.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS | E2/BLUP | QAS.su.2A1 | SNP-1095449 | 2A | 104,655,222 | 1.02E-12 | 0.33 | -0.76 |
| PL | E1/E2/BLUP | QPL.su.1B1 | SNP-100083695 | 1B | 29,327,461 | 3.37E-09 | 0.20 | 0.40 |
| L | E1/E2/BLUP | QL.su.1B1 | SNP-100083695 | 1B | 29,327,461 | 1.53E-11 | 0.20 | 0.22 |
| LWR | E1/BLUP | QLWR.su.2A1 | SNP-1150369 | 2A | 148,130,749 | 6.62E-09 | 0.28 | 0.05 |
| E1/BLUP | QLWR.su.2A2 | SNP-991737 | 2A | 505,958,255 | 1.09E-08 | 0.36 | -0.05 | |
| CS | E1/BLUP | QCS.su.2A1 | SNP-1150369 | 2A | 148,130,749 | 8.48E-10 | 0.28 | -0.01 |
| E1/BLUP | QCS.su.2A2 | SNP-991737 | 2A | 505,958,255 | 2.88E-09 | 0.36 | -0.01 | |
| E1/BLUP | QCS.su.7A1 | SNP-1059714 | 7A | 673,131,697 | 1.94E-08 | 0.41 | -0.01 | |
| TGW | E2/BLUP | QTGW.su.2A2 | SNP-3025548 | 2A | 106,204,569 | 2.35E-09 | 0.33 | -2.90 |
| E1/E2/BLUP | QTGW.su.2A3 | SNP-991434 | 2A | 531,237,720 | 3.17E-17 | 0.40 | -4.24 | |
| E1/E2/BLUP | QTGW.su.7B1 | SNP-5369680 | 7B | 500,369,002 | 2.48E-08 | 0.45 | -2.12 |
| Chr.a | Border markersb | Start-end position bp | Interval (kb) | MTA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1B | SNP-1115814/SNP-2280550 | 24,863,377-36,112,065 | 11,248 |
QPL.su.1B1 QL.su.1B1 |
| 2A | SNP-979718/SNP-1042666 | 101,167,973-122,694,915 | 21,526 |
QAS.su.2A1 QTGW.su.2A2 |
| 2A | SNP-2276567/SNP-100097879 | 143,150,820-152,458,413 | 9,307 |
QLWR.su.2A1 QCS.su.2A1 |
| 2A | SNP-1127014/SNP-4002509 | 501,916,772-557,449,430 | 55,532 |
QLWR.su.2A2 QCS.su.2A2 QTGW.su.2A3 |
| 7B | SNP-1127813/SNP-100112890 | 500,368,572-515,733,522 | 15,364* | QTGW.su.7B1 |
| MTA | Gene stable ID | Start (bp) | End (bp) | Gene description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QAS.su.2A1 | TRITD2Av1G047210 | 103,948,645 | 103,949,427 | UDP-glycosyltransferase |
| TRITD2Av1G047390 | 104,433,296 | 104,434,726 | Glycosyltransferase | |
| *QCS.su.2A1&QLWR.su.2A1 | TRITD2Av1G065030 | 148,285,931 | 148,287,017 | BES1/BZR1 homolog 1 |
| QCS.su.7A1 | TRITD7Av1G256220 | 673,119,977 | 673,122,833 | B3 domain-containing protein |
| *QL.su.1B1&QPL.su.1B1 | TRITD1Bv1G011760 | 28,778,557 | 28,780,832 | Protoheme IX farnesyltransferase |
| TRITD1Bv1G012100 | 29,705,090 | 29,707,420 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 2 | |
| TRITD1Bv1G012160 | 29,874,848 | 29,875,394 | Histone deacetylase 2 G | |
| TRITD1Bv1G012200 | 29,884,927 | 29,885,280 | Histone deacetylase 2 G | |
| TRITD1Bv1G012290 | 29,918,548 | 29,918,919 | Histone deacetylase 2 G | |
| *QLWR.su.2A2&QCS.su.2A2 | TRITD2Av1G180930 | 505,163,820 | 505,168,048 | Transcription factor |
| TRITD2Av1G181270 | 505,956,404 | 505,957,413 | Late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) hydroxyproline | |
| QTGW.su.2A2 | TRITD2Av1G048230 | 106,205,594 | 106,206,602 | Cytochrome P450 |
| TRITD2Av1G048320 | 106,340,477 | 106,344,484 | Patatin | |
| TRITD2Av1G048480 | 107,026,668 | 107,032,955 | B3 domain-containing protein G | |
| QTGW.su.2A3 | TRITD2Av1G191770 | 532,722,987 | 532,723,607 | Phospholipase C 2 G |
| TRITD2Av1G191850 | 532,838,099 | 532,841,739 | Pentatricopeptide repeat-containing protein | |
| QTGW.su.7B1 | TRITD7Bv1G159220 | 500,914,944 | 500,920,059 | Elongation factor like protein |
| TRITD7Bv1G159310 | 501,013,722 | 501,029,428 | ABC transporter B family protein |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




