Submitted:
18 August 2023
Posted:
25 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials/Constituent materials
2.1.1. Aggregates
2.1.1.1. The granularity of the aggregates, according to SR EN 933-1: 2012 [45]
2.1.1.2. Real density and water absorption coefficient for (RCA)
- ρw - volumetric mass of water at the test temperature (0,9973 la T=240 C), Mg/m3
- M1 - mass in air of saturated and superficially dried aggregates, g;
- M2 - mass of the pycnometer containing the sample of saturated aggregates, g;
- M3 - pycnometer mass filled with water only, g;
- M4 - mass in air of the test sample dried in the oven, g.
2.1.1.3. The resistance to fragmentation of the coarse aggregate (Los Angeles coefficient) for (RCA) according to SR EN 1097-2: 2010 [47] and [38]
2.1.1.4. Abrasion testing of coarse aggregate (MicroDeval coefficient) for (RCA)
2.1.1.5. Flattening coefficient for (RCA) according to SR EN 933-3: 2012 [49]
2.1.2. Cement
2.1.3. WGP-Waste Glass Powder
2.1.4. The water used is in accordance with SR EN 1008: 2003) [71]
2.1.5. Additives used in the composition of the concrete mixtures, in accordance with SR EN 934-2+A1 [72]
2.2. Methods for designing and determining the properties of mixtures/Mixes/Mixing procedure/Sampling and methodology/
2.2.1. Design and preparation of road concrete recipes for BcR4 class
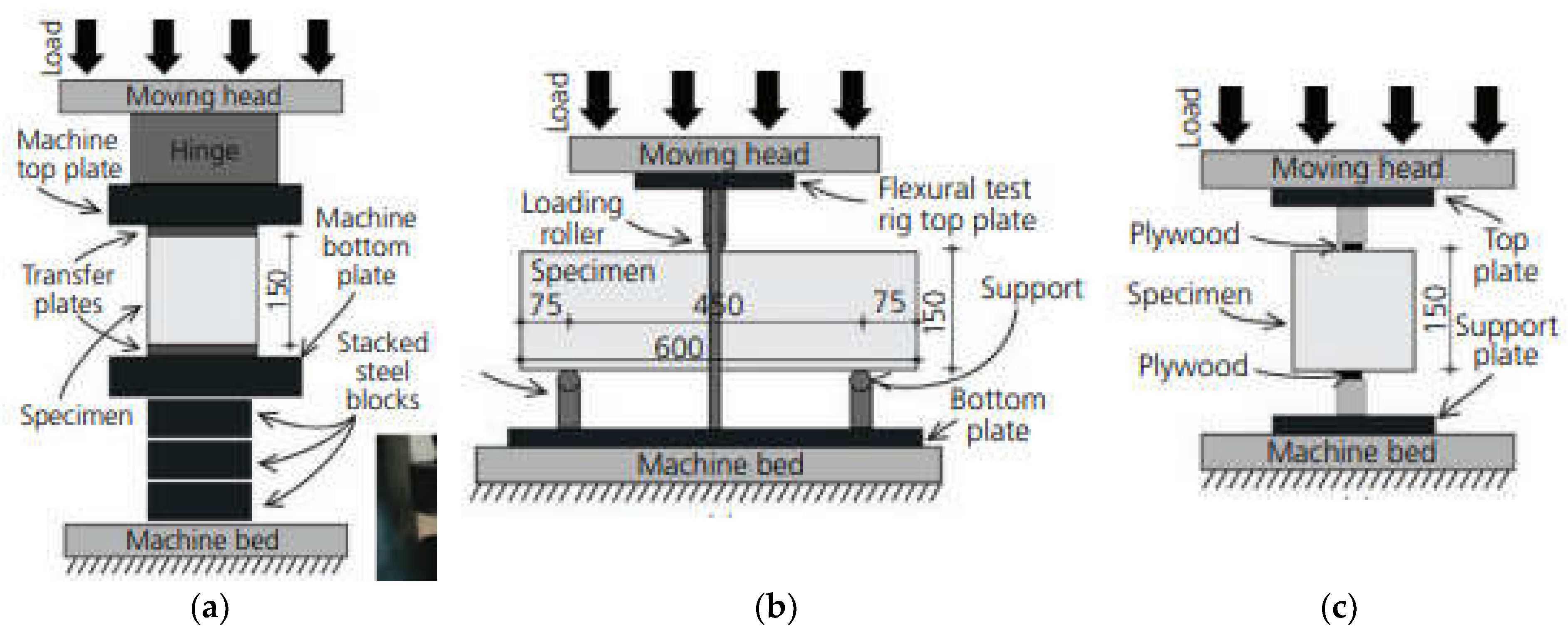
2.2.2. Determinations in the Fresh and Hardened State of BcR Concrete
2.2.2.1. Determinations in the Fresh State of BcR Concrete
2.2.2.3. Determinations of Mechanical Strength and Durability of BcR Concrete
- Flexural strength (fct,fl) in accordance with SR EN 12390-5 [80]
- Compressive strength (fcm) in accordance with SR EN 12390-3 [81]
- Splitting tensile strength (fct,sp) in accordance with SR EN 12390-6 [82]
- Hardened concrete density (ρa) in accordance with SR EN 12390-7 [83]
- Loss of strength after 100 freeze-thaw cycles in accordance with SR 3518 [84]
- Carbonation depth determination according to SR CR 12793 [88]
2.2.2.6. Abrasion Resistance–Volume Loss
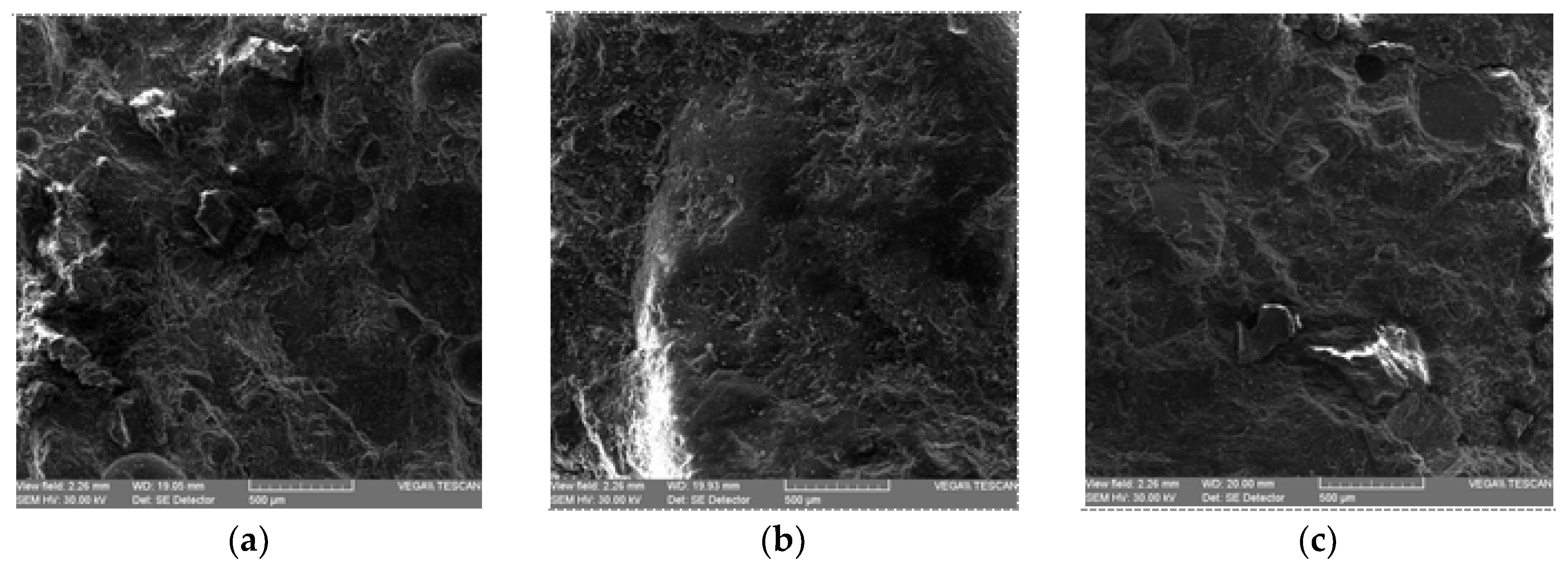
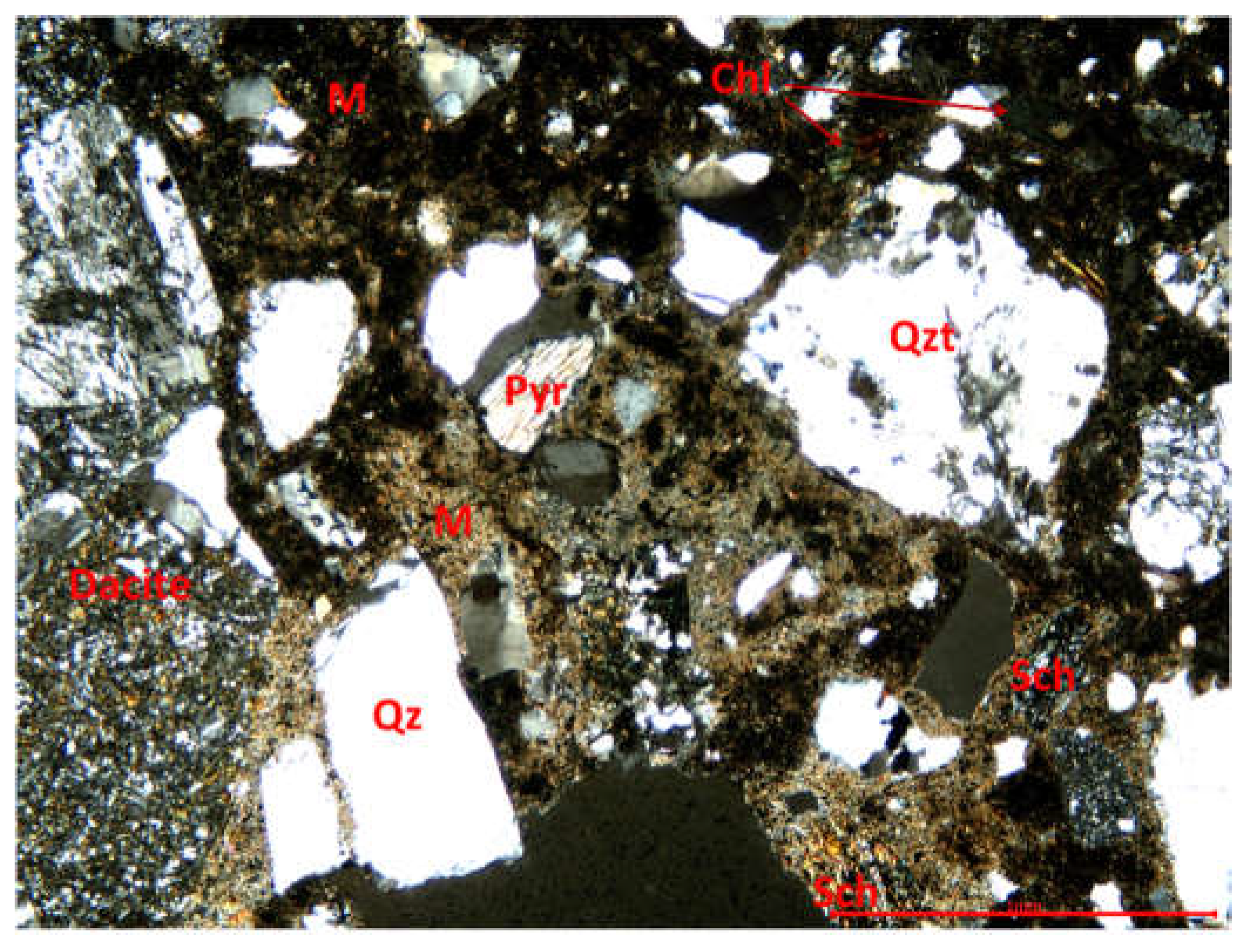
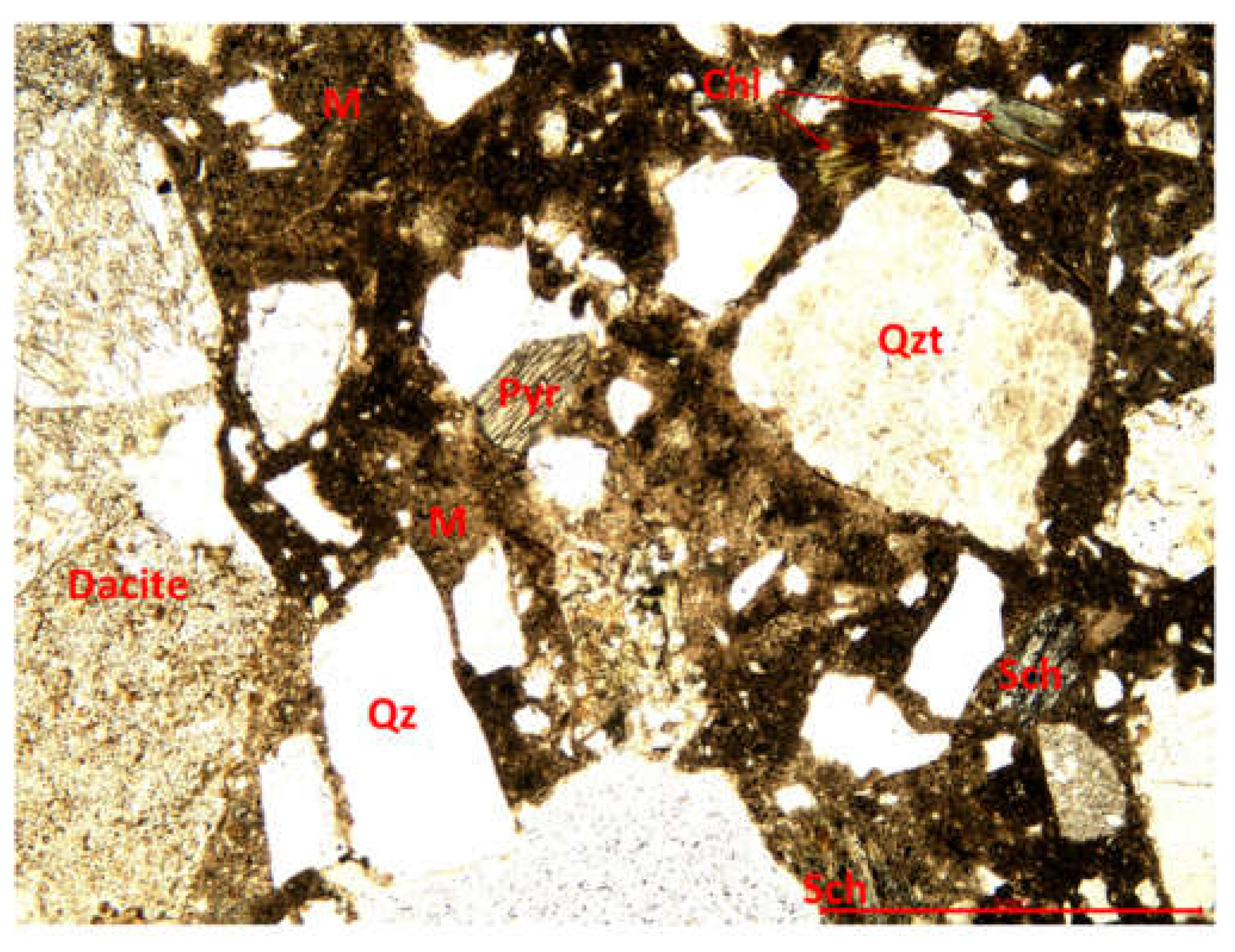
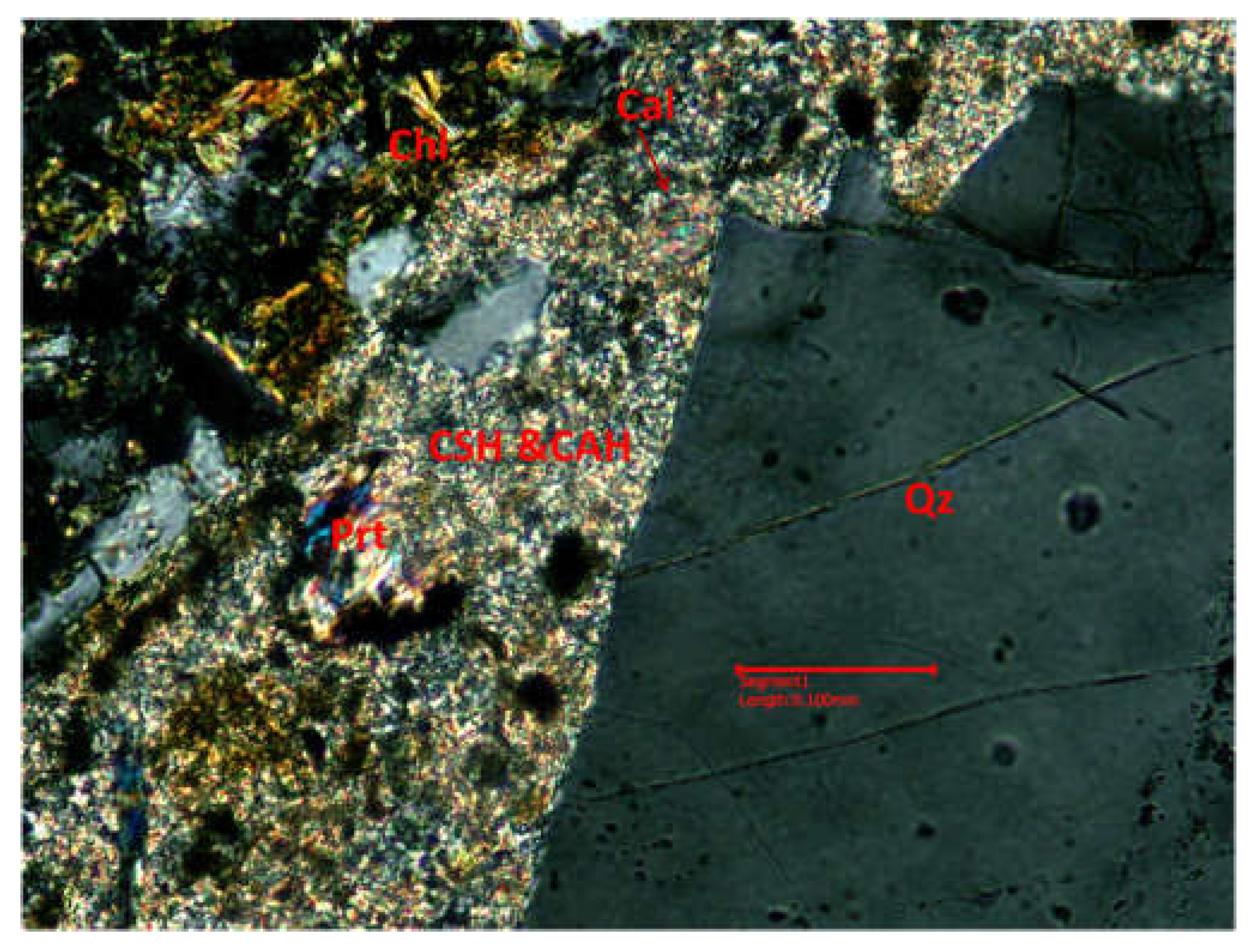
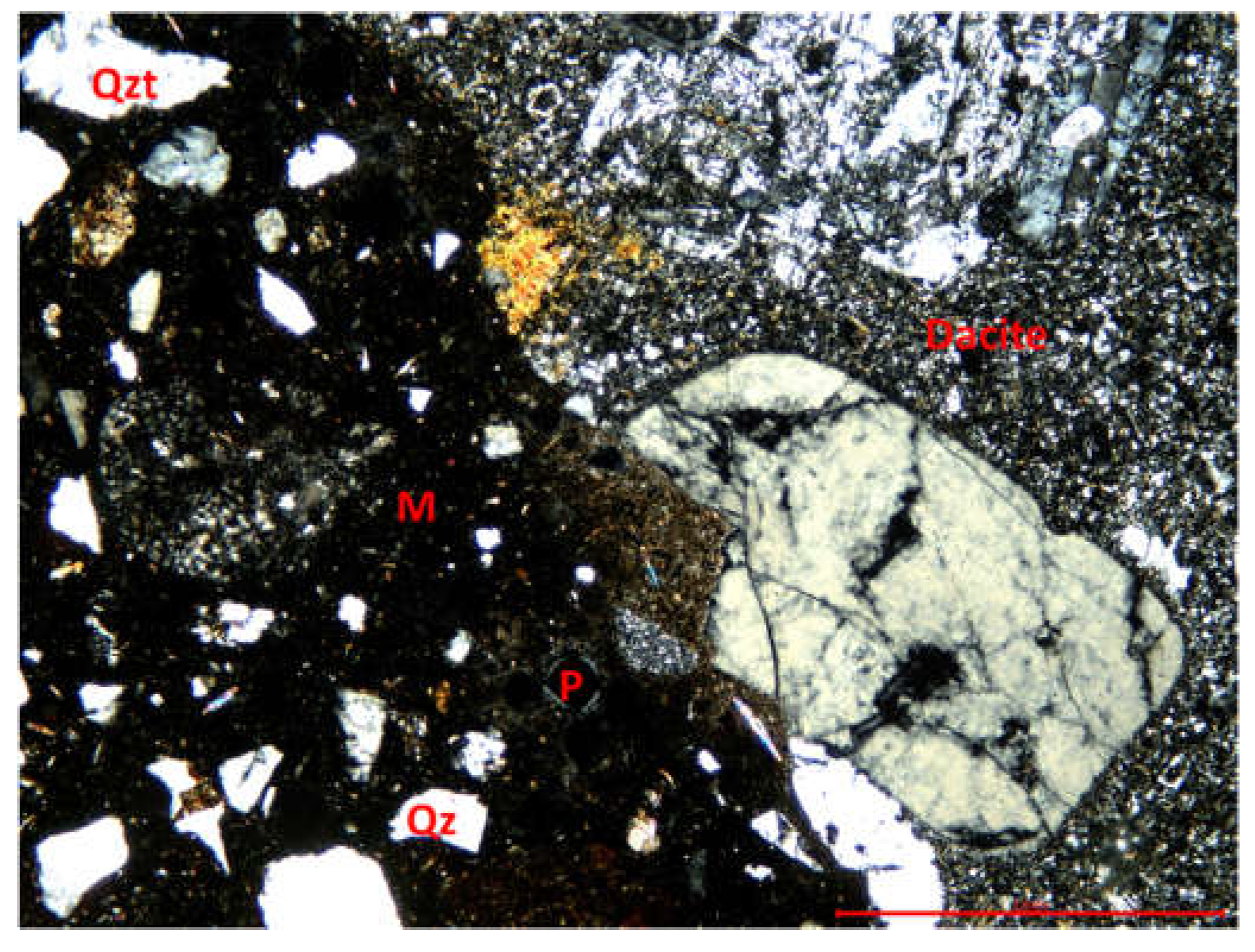
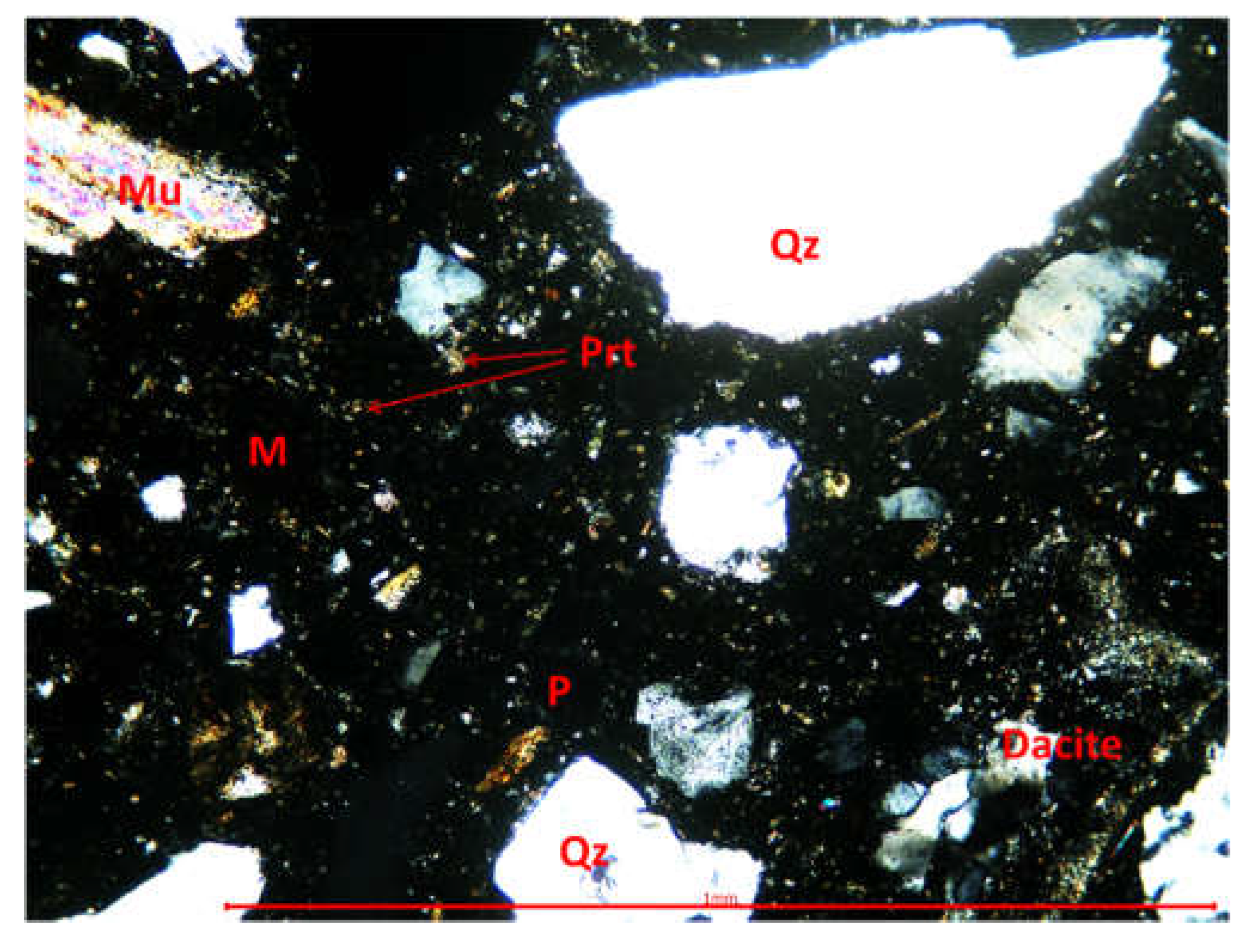
2.2.3. Microstructural determinations
3. Results
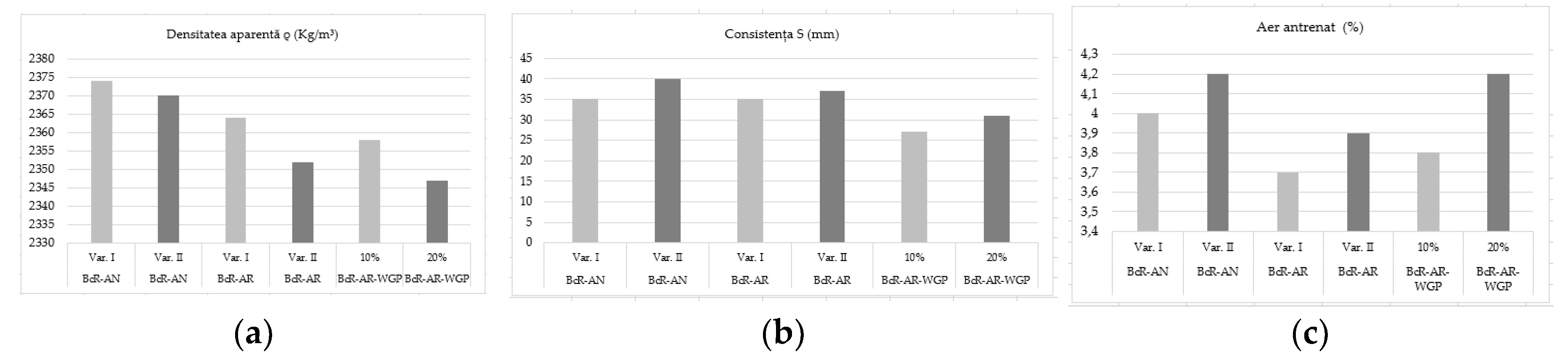
3.1. Characteristics of Fresh State Concrete for Road Pavement
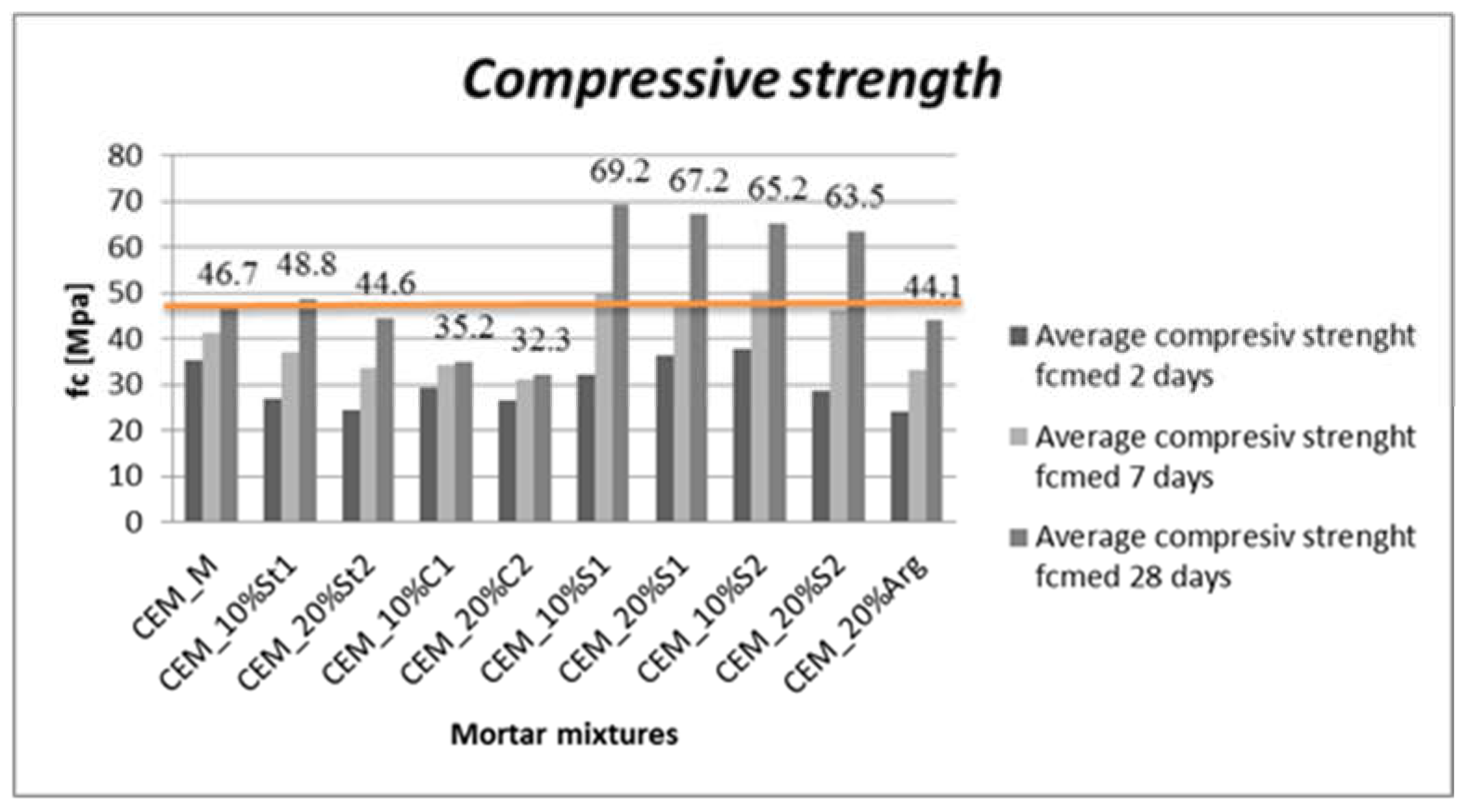
3.2. Hardened BcR composite properties
3.3. Microstructural determinations
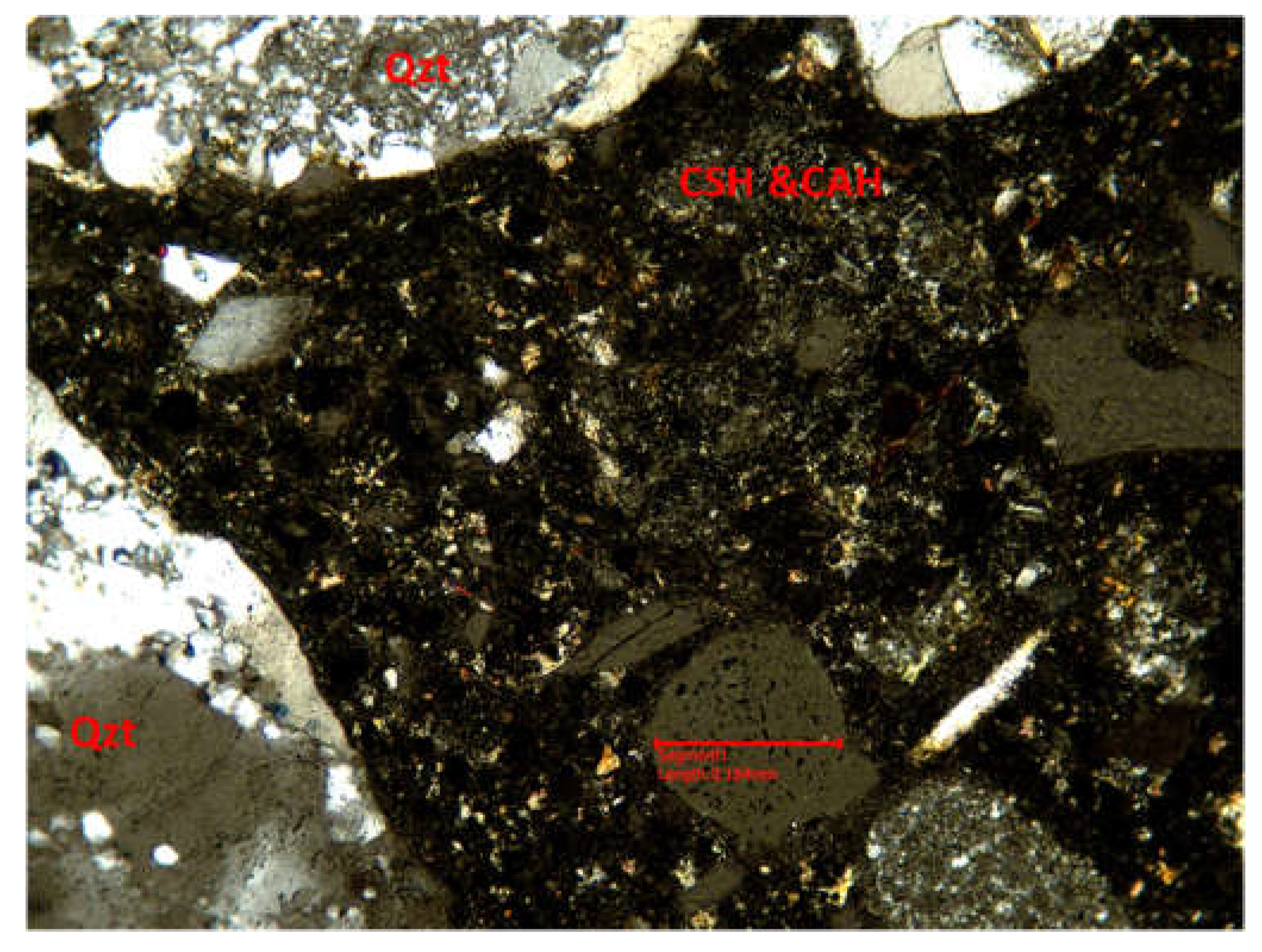
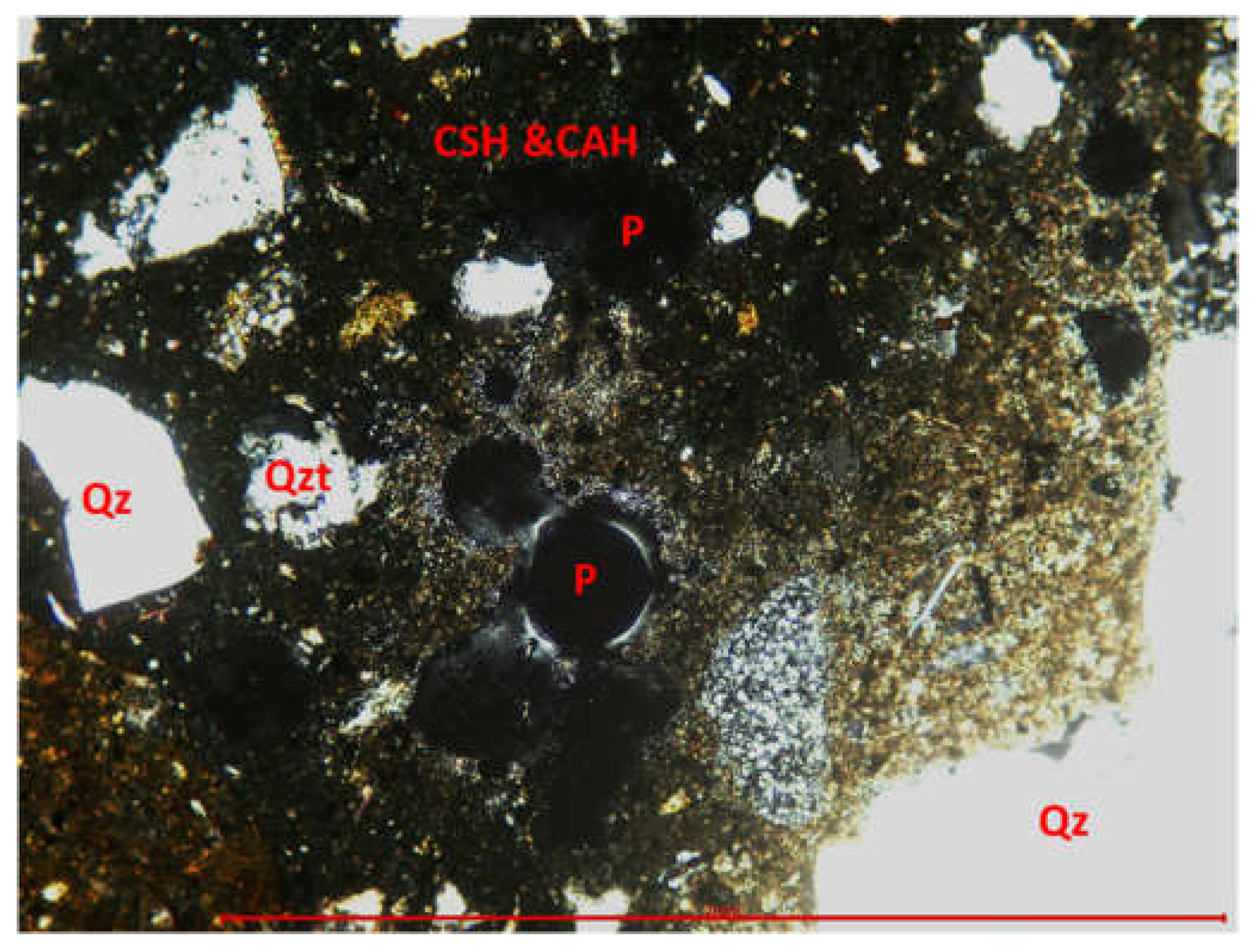
3.3.1. Optical microscopy using polarized light
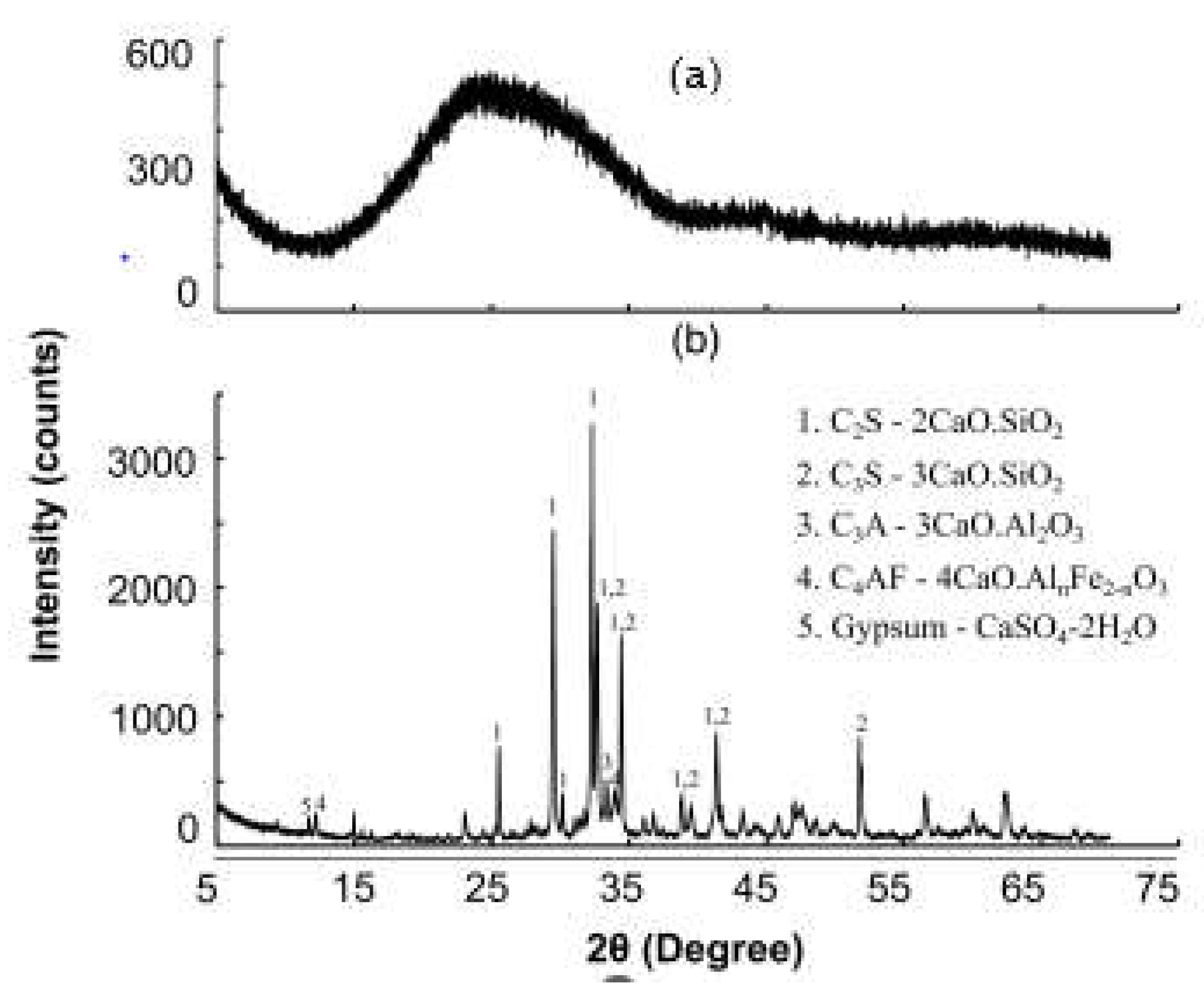
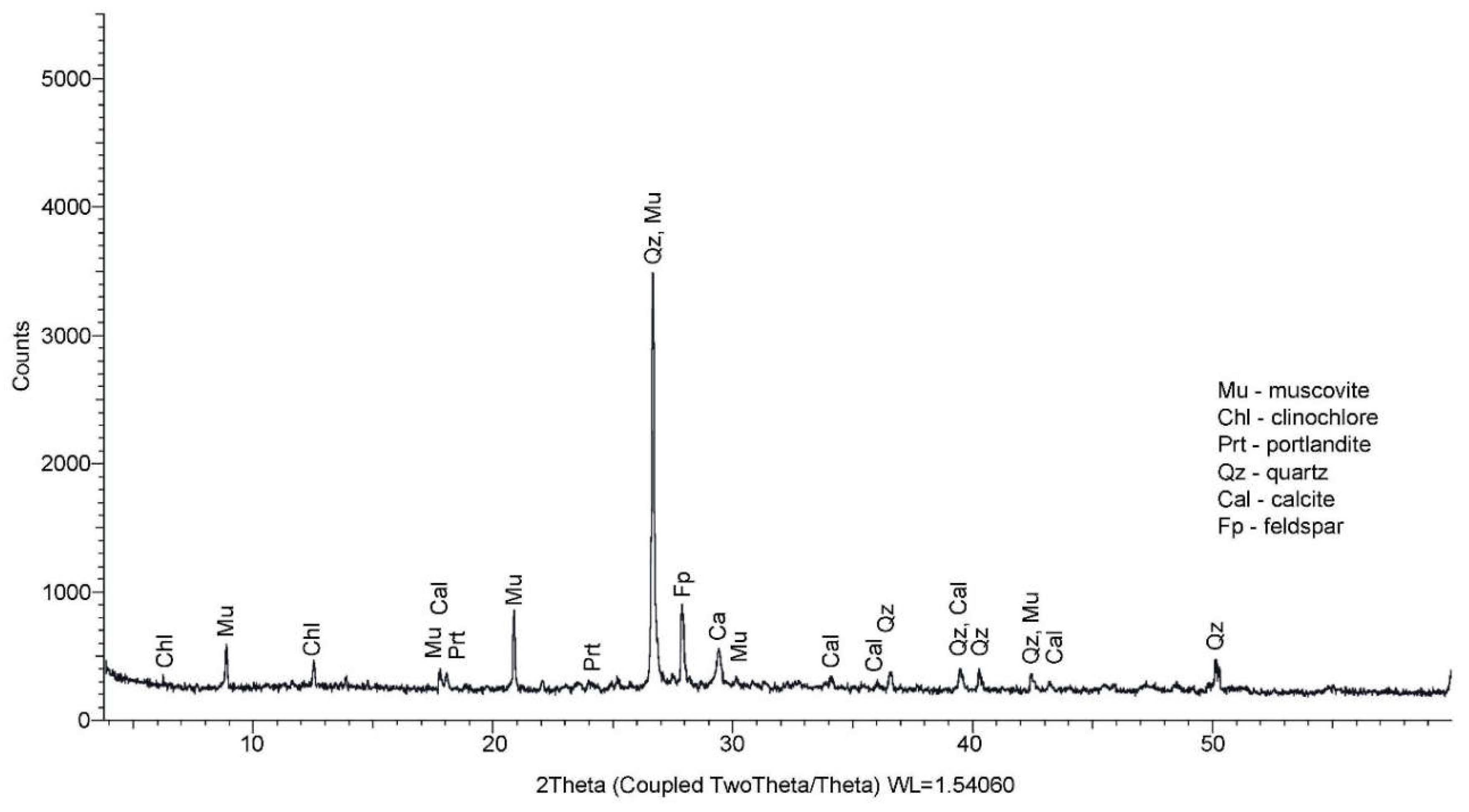
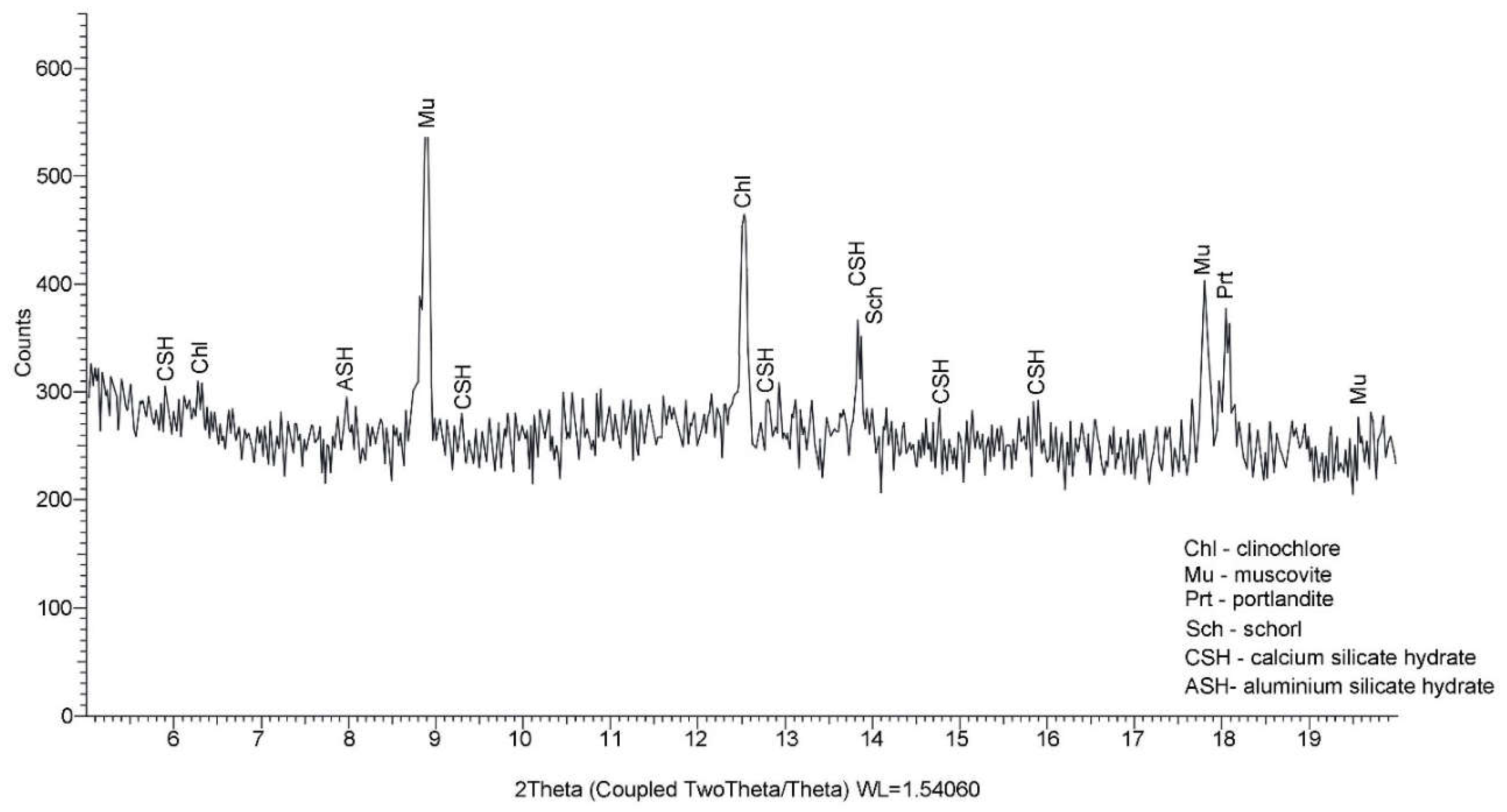
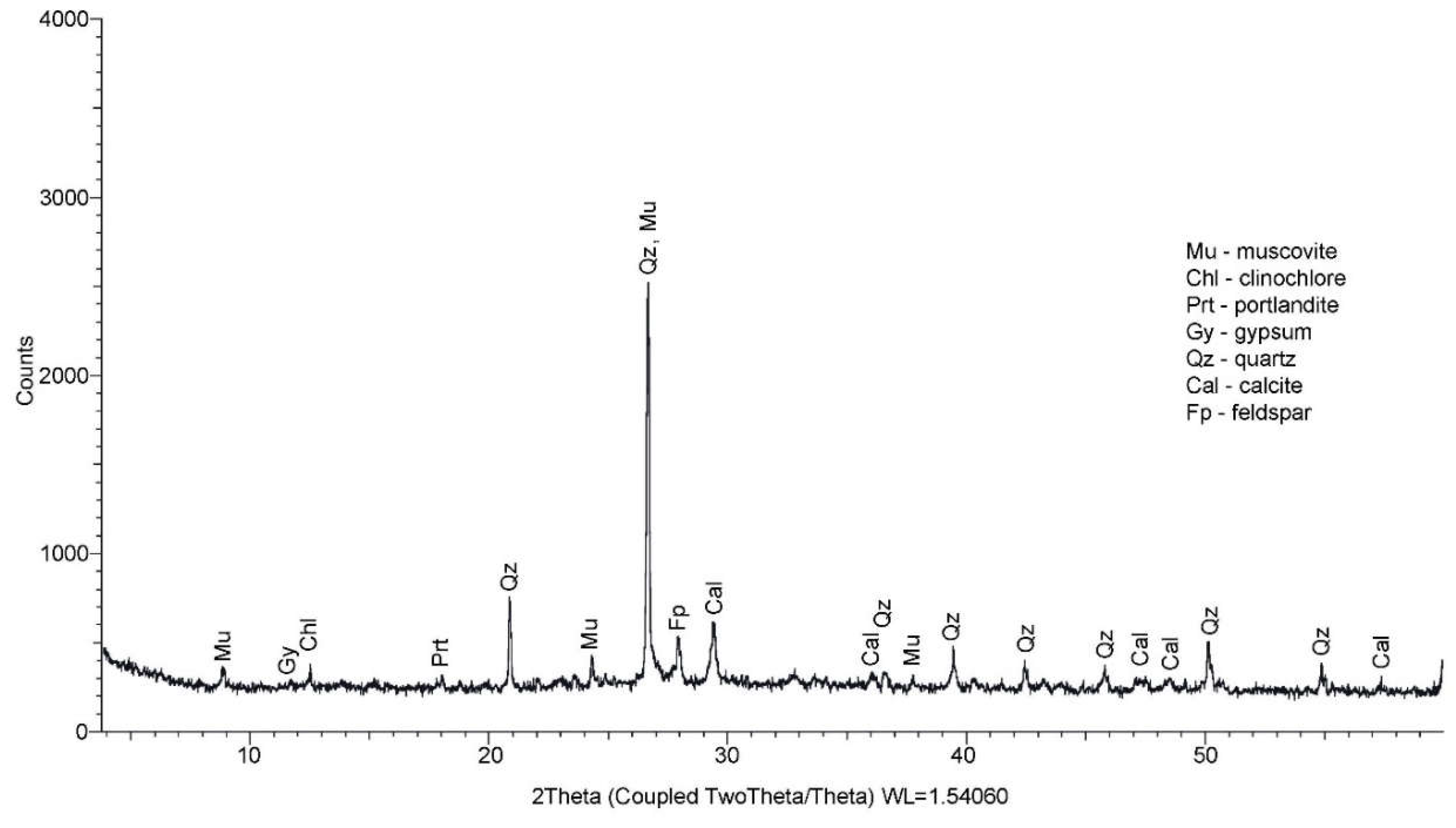
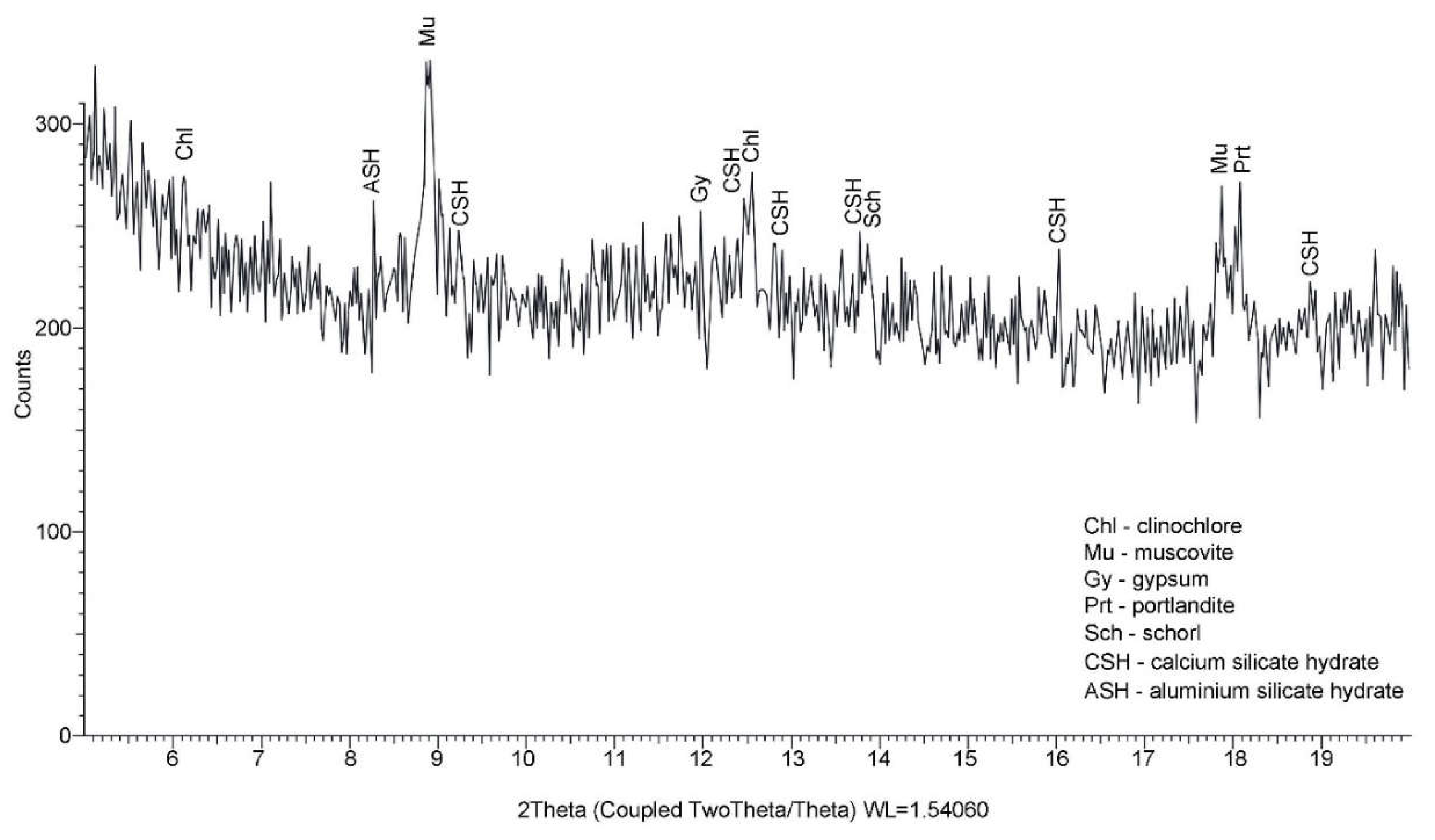
2.3.2. X-ray diffraction by the Powder method (PXRD) for the calitative analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Performance of the BcR composites fresh properties
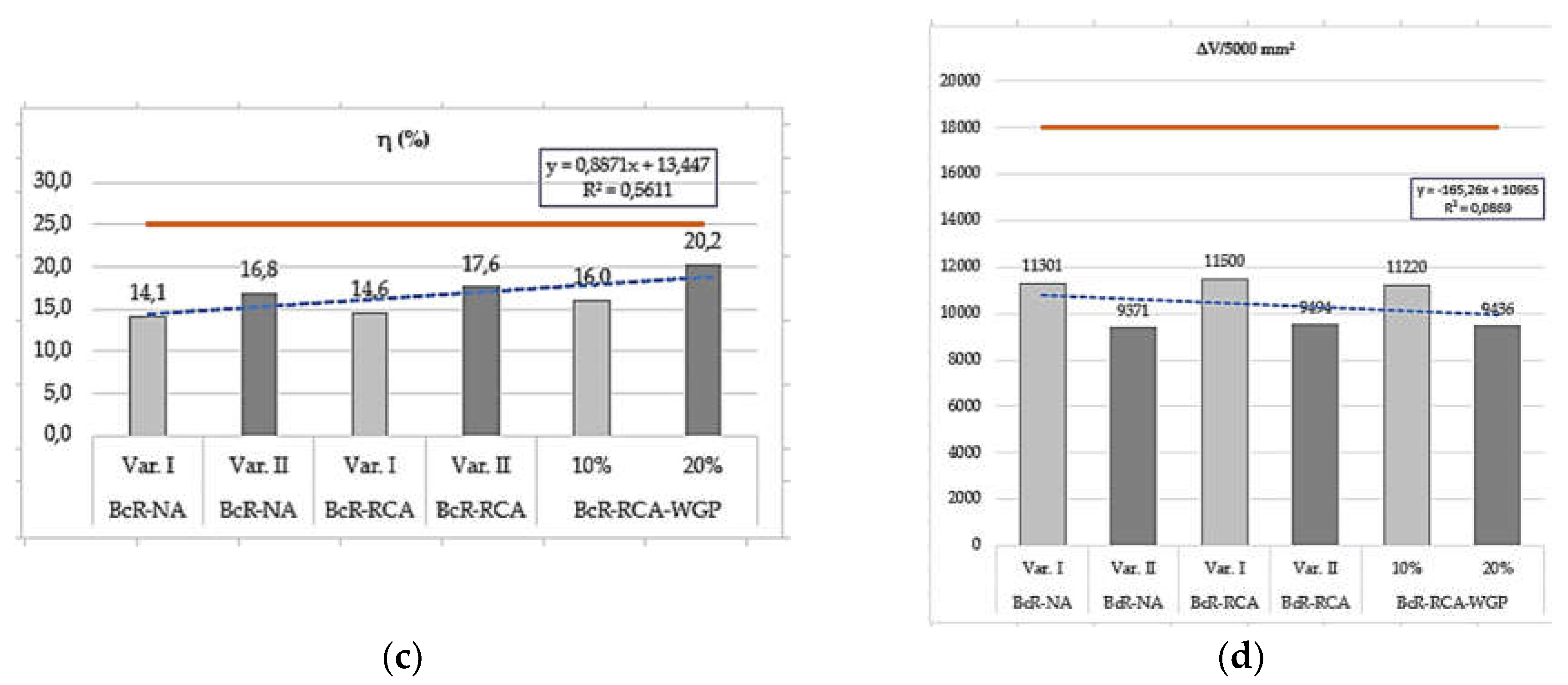
4.2. Performance of the BcR composites hard properties
4.2. Performance of the BcR by PXRD test
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- https://www.revistasinteza.ro/economia-de-la-liniar-la-circular. (Accessed on ). 24 May.
- https://legislatie.just.ro/Public/DetaliiDocumentAfis/253009. (Accessed on ). 24 May.
- Romanian Government, Strategia națională privind economia circulară. Proiect. https://sgg.gov.ro/1/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Strategia-economie-circulara_18.08.2022.pdf. (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- Ionescu, B.A.; Barbu, A.M.; Lăzărescu, A.V.; Rada, S.; Gabor, T.; Florean, C. The Influ-ence of Substitution of Fly Ash with Marble Dust or Blast Furnace Slag on the Properties of the Alkali-Activated Geopolymer Paste. Coatings 2023, 13(2), 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, V.M. ; Making Concrete “Greener” With Fly Ash. ACI Conc. Int. 1999, 21, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Corbu, O.C.; Magureanu, C.; Onet, T. ; Szilagy,H. Economia de energie la realizarea betoanelor performante (Energy saving in the production of high-performance concrete). Conference: SME 2010, 20-21, 10, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 19, 343-354. www.cncs-uefiscdi. 20 May.
- Fadi, A.; Osama, Z.; Ali, M.; Fahad, A.; Saleh, A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Ain, S. Effect of fly ash and waste glass powder as a fractional substitute on the performance of natural fibers reinforced concrete. Eng. J. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cement Technology Roadmap: Carbon Emissions Reductions up to 2050. https://www.iea. (accessed on 10 March 2023)2050.
- US Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries: Cement. 2012. Available online: https://d9-wret.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/assets/palladium/production/mineral-pubs/mcs/mcs2012.pdf. 28 February.
- Cembureau. Available online: https://www.cembureau.eu/library/reports/2050-carbon-neutrality-roadmap/ (accessed on 21 February 2023).
- Aitcin, P.C. Cements of yesterday and today; Concrete of tomorrow. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, pp. 1349–1359.
- Sandu, A.V. Obtaining and Characterization of New Materials, Materials 2021, 14(21), 6606. [CrossRef]
- EU Construction & Demolition Waste Management Protocol, https://ec.europa. 2050.
- Corbu, O.; Chira, N.; Szilagyi, H.; Constantinescu, H. Ecological concrete by use of waste glass. In Proceedings of the 13th 13th SGEM GeoConference on Nano, Bio and Green – Technologies For A Sustainable Future, www.sgem.org SGEM 2013, Albena, Bulgaria, 2013, pp. 411–418, June 16-22.
- Corbu, A. Puskás, H. Szilágyi, C. Baeră. C16/20 CONCRETE STRENGTH CLASS DESIGN WITH RECYCLED AGGREGATES. JAES, 4(17), 2/2014, pp. 13-19. [CrossRef]
- Puskás, A.; Corbu, O.; Szilágyi, H.; Moga, L.M. Construction waste disposal practices: The recycling and recovery of waste. WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment, 2014, 191, 1313-1321. [CrossRef]
- Corbu, O.; Puskás, A.; Moga, L.; Szilagyi, H. Opportunities for increasing the recycling rate of mineral waste in construction industry, International Multidisciplinary Scientific Geo-Conference Surveying Geology and Mining Ecology Management, Albena, Bulgaria, SGEM 2015, 2(6), 203-210.
- Frondistou-Yannas, S. Waste Concrete as aggregate for new concrete. ACI Journal, 1977, 74, pp.
- Abhijeet, B.; Shadab, M. ; V.Vinayaka R. Utilization of waste glass powder and waste glass sand in the production of Eco-Friendly concrete. Con. Build. Mat. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John Ayibatunimibofa TrustGod,; Akosubo Iwekumo Stevyn.; Ann Diri Manfred. The Use of Calcined Waste Glass Powder as aPozzolanic Material, EJERS, 2019, Vol. 4, No. 12. [CrossRef]
- The Use of Calcined Waste Glass Powder as a Pozzolanic Material. Available from: https://www.researchgate. 21 May 3614.
- Raza, A. 2022; 10. [CrossRef]
- Lomesh, M.; Sariputt, R.B. R: Utilization of Pozzolanic Material and Waste Glass Powder in Concrete, 2022,, In book, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Zuheir, W.; Khalid, R.; Naji, N.; Mohammed, S. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Maher Yaseen; Sheelan Hama; Akram S. Mahmoud. 1: Shear behavior of reinforced concrete beams incorporating waste glass powder as partial replacement of cement, European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 2022, 27(1), 2022; -16. [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, P.; Vasugi, V. The potential use of waste glass powder in slag based geopolymer concrete-An environmental friendly material. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Mukhlis Behsoodi; Shafiullah Miakhil; Mohammad Mukhlis Behsoodi. Waste Glass Powder “An Alternative of Cement in Concrete” -A Review. IJCSRR 2022, ISSN: 2581-8341, Volume 05 Issue 07, page No. 2541. [CrossRef]
- Bompa, D.V.; Xu, B.; Corbu, O. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Ali Hassan Shalan; Mohamed M El-Gohary. Long-Term Sulfate Resistance of Blended Cement Concrete with Waste Glass Powder. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Sanni, S.H.; Hiremath, G.S.; Kambali, S.A.; Chavan, A.A. The Effect of Partial Replacement of Cement by Waste Green Glass Powder with Waste Plastic as Coarse Aggregate, i-manager’s Journal on Structural Engineering, 2022, 11(2), 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad Israr Pashtoon; Shafiullah Miakhil; Mohammad Mukhlis Behsoodi. Waste Glass Powder “An Alternative of Cement in Concrete”: A Review, IJCSRR, 2022, 5(7), 2541-2549. [CrossRef]
- Federico, M.; Chidiac, S.E. ; Waste glass as a supplementary cementitious material in concrete – Critical review of treatment methods. Cem. Concr. Compos., 2009, 31(8), 606–610. [CrossRef]
- Hogland, J.; Hogland, W. Waste glass in the production of cement and concrete – A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2014, 2(3), 1767–1775. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zheng, K. A review on the use of waste glasses in the production of cement and concrete, Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 52(2), 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abendeh, R.M.; AbuSalem, Z.T.; Bani Baker, M.I.; Khedaywi, T.S. Concrete containing recycled waste glass: strength and resistance to freeze–thaw action. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers – Construction Materials 2021, 174(2), 75-87. [CrossRef]
- Hornea, L.; Gorea, M.; Har, N. Study of (Pb, Ba) - CRT glass waste be-haviour as a partial aggregate replacement in cement mortars. Studia UBB Chemia 2017, Tom II, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İlker Bekir Topçu.; Hasan Selim Şengel. Properties of concretes produced with waste concrete aggregate. Cem. Con. Res. 2004, 34(8), 1307-1312. [CrossRef]
- NE 014 The norm for the execution of cement concrete road pavements in a fixed and sliding formwork system. Matrix Romania, Bucharest 2002, ISBN 978-973-755-185-6, 2007.
- SR EN 206 Concrete - Specification, performance, production and conformity. 2014.
- Poteras, G. Reciclarea Materialelor Provenite Din Demolări și Dezafectări (Recycling Materials resulting from demolition and decommissioning). Revista Salubritatea 2006, 1(17)).
- Roy, S.; Ahmad, S.I.; Rahman, M.S.; Salauddin, M. Experimental investigation on the influence of induction furnace slag on the fundamental and durability properties of virgin and recycled brick aggregate concrete. R. in Eng., 2023, 17, 100832. [CrossRef]
- Tobo, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Kuwayama, M.; Ozawa, T.; Tanaka, T. Solidification conditions to reduce porosity of air-cooled blast furnace slag for coarse aggregate. Jurnal of the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, 2013, 99(8), 532-541. [CrossRef]
- Verian, K.P.; Panchmatia, P.; Olek, J.; Nantung, T. Pavement concrete with air-cooled blast furnace slag and dolomite as coarse aggregates: Effects of deicers and freeze-thaw cycles. TRR 2015, 2508(1), 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, Y.; Tobo, H.; Watanabe, K. Development of manufacturing process for blast furnace slag coarse aggregate with low water absorption, JFE Technical Report 2018, 23, 97-101.
- SR EN 933-1, Tests for geometrical properties of aggregates - Part 1: Determination of particle size distribution - Sieving method, ASRO Bucharest, 2012.
- SR EN 1097-6 Tests for mechanical and physical properties of aggregates. Part 6 Determination of particle density and water absorption, ASRO Bucharest, 2013.
- SR EN 1097-2 Tests for mechanical and physical properties of aggregates.. Part 2: Methods for the determination of resistance to fragmentation, ASRO Bucharest, 2010.
- SR EN 1097-1 Tests for mechanical and physical properties of aggregates. Part 1: Determination of the resistance to wear (micro-Deval), ASRO Bucharest, 2011.
- SR EN 933-3 Tests for geometrical properties of aggregates. Part 3: Determination of particle shape – Flakiness Index, ASRO Bucharest, 2012.
- SR EN 197-1 Standard Cement- Part 1: Composition, specification, and conformity criteria common cements; ASRO Bucharest, 2011.
- SR EN 196-1:2005 Methods of testing cement - Part 1: Determination of strength, ASRO Bucharest, 2005.
- SR EN 196-2:2014 Method of testing cement - Part 2: Chemical analysis of cement Métodos de ensayo de cementos, ASRO Bucharest, 2014.
- SR EN 196-3:2016 Methods of testing cement - Part 3: Determination of setting times and soundness, ASRO Bucharest, 2016.
- Corbu, O.; Ioani, A.M.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Meiţă, V.; Szilagyi, H.; Sandu, A.V. “The pozzolanic activity level of powder waste glass in comparisons with other powders.” KEM 2015, 660, 237–243. [CrossRef]
- Taha, B.; Nounu, G. “Properties of concrete contains mixed colour waste recycled glass as sand and cement replacement.” Con. Build. Mat. 2008, 22 (5), 713–720. [CrossRef]
- Vafaei, M. ; Allahverdi. A. High strength geopolymer binder based on waste-glass powder.” Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28(1), 215–222. [CrossRef]
- Manoj Kumar Meena, Jagriti Gupta, Bharat Nagar. “PERFORMANCE OF CONCRETE BY USING GLASS POWDER” An Experimental Study. IRJET 2018, 5(9). www.irjet.
- Corbu, O.; Bompa, D.V.; Szilagyi, H. Eco-efficient cementitious composites with large amounts of waste glass and plastic. Proc.Inst. Civ. Eng.-Eng. Sustain. 2021, 175(2), 64–74. [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A. Mansour, Mohd Hanif Bin Ismail, Qadir Bux alias Imran Latif, Abdullah Faisal Alshalif, Abdalrhman Milad, Walid Abdullah Al Bargi, A Systematic Review of the Concrete Durability Incorporating, Recycled Glass, Sustainability 2023, 15(4), 3568. [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pozzolanic_activity (accessed on 20 April 2023).
- ASTM C618, Standard Specification for Coal Fly Ash and Raw or Calcined Natural Pozzolan for Use in Concrete.
- Jercan, S. Concrete Roads. Corvin Publishing House, Deva, Romania: 2002.
- Raki, L.; Beaudoin, J.; Alizadeh, R.; Makar, J.; Sato, T. Cement and concrete nanoscience and nanotechnology. Materials 2010, 3(2), 918–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayan, A. ; Value-added Utilisation of Waste Glass in Concrete, IABSE SYMPOSIUM MEL-BOURNE 2002, Cem. Conc. Res. [CrossRef]
- Ismail Khairul, Nizar.; Mustafa Al Bakri, A.M. Ismail Khairul Nizar.; Mustafa Al Bakri, A.M.; Rafiza Abd Razak.; Hussin Kamarudin.; Alida Abdullah.; Yahya Zarina. Study on Physical and Chemical Properties of Fly Ash from Different Area in Malaysia. KEM 2014, 594-595, 985-989. [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wang, Q.; Xie, C.; Xue, Y.; Duan, Y.; Cui, X. The Effect of Fineness on the Hydration Activity Index of Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag. Materials 2019, 12(18), 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, L. Influence of fineness on the cementitious properties of steel slag. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 117, 629–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- [68] Matos, A.M.; Sousa-Coutinho, J. Waste glass powder in cement: macro and micro scale study. JACR 2016, 28(7), 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bompa, D.V.; Xu, B.; Corbu, O. Evaluation of One-Part Slag–Fly-Ash Alkali-Activated Mortars Incorporating Waste Glass Powder. Journal of ASCE 2022, 34(12). [CrossRef]
- https://www.ct.upt.ro/studenti/cursuri/lucaci/Imbr_rutiere_rigide. 2023.
- SR EN 1008 Mixing water for concrete.; ASRO Bucharest, 2003.
- SR EN 934-2+A1 Concrete admixtures; ASRO Bucharest, 2012.
- SR EN 12620+A1 Aggregates for concrete; ASRO Bucharest, 2008.
- SR 667 Natural aggregates and processed stone for roads; ASRO Bucharest, 2001.
- Yadav, S.R. 2009.
- Hansen, T.D.; Narud, H. Strength of recycled concrete made from crushed concrete coarse aggregate. ACI Conc. Int., Design and Construction 1983, 5(1), 79-83. https://www.concrete.org/publications/internationalconcreteabstractsportal.aspx? 9140. [Google Scholar]
- SR EN 12350-2 Testing fresh concrete - Part 2. Slump-test, ASRO Bucharest, 2009.
- SR EN 12350-6 Testing fresh concrete - Part 6. Density ASRO Bucharest, 2009.
- SR EN 12350-7 Testing fresh concrete - Part 7. Air content - Pressure methods, ASRO Bucharest, 2009.
- SR EN 12390-5 Test on hardened concrete. Part 5. Bending tensile strength of specimens.; ASRO Bucharest, 2009.
- SR EN 12390-3 Standard for test-hardened concrete - Part 3. Compressive strength of test specimens; ASRO Bucharest, 2009.
- SR EN 12390-6 Testing hardened concrete - Part 6. Tensile splitting strength of test specimens, ASRO Bucharest, 2009.
- SR EN 12390-7Testing hardened concrete - Part 7. Density of hardened concrete, ASRO Bucharest, 2009.
- SR 3518 Tests on concrete. 2009.
- SR EN 1338 Concrete paving blocks – Requirements and test methods, ASRO Bucharest, 2004.
- SR EN 1339 Concrete paving flags.– Requirements and test methods, ASRO Bucharest, 2004.
- SR EN 1340 Concrete kerb units. – Requirements and test methods, ASRO Bucharest, 2004.
- SR CR 12793 Determination of the depth of the carbonation layer of hardened concrete; ASRO Bucharest, 2002.
- SR EN 12390-1 Testing hardened concrete - Part 1: Shape, dimensions and other requirements for specimens and moulds, ASRO Bucharest, 2012.
- Ahmad, J.; Tufail, R.F.; Aslam, F.; Mosavi, A.; Alyousef, R.; Javed, M.F.; Zaid, O.; Khan Niazi, M.S. A step towards sustainable self-compacting concrete by using partial substitution of wheat straw ash and bentonite clay instead of cement. Sustain 2021, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, P.; Abolhasani, M.; Mirzaei, F.; Kouhi Anbaran, M.R.; Khaksari, Y.; Famili, H. Influence of two types of nanosilica hydrosols on short-term properties of sustainable white portland cement mortar. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30(2), 4017289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abendeh, R.M.; AbuSalem, Z.T.; Bani Baker, M.I.; Khedaywi, T.S. Concrete containing recycled waste glass: strength and resistance to freeze–thaw action. Proceedings of the JCOMA 2020, 174(2), 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, Z.Z.; Al-Hashmi, E.A. Recycling of waste glass as a partial replacement for fine aggregate in concrete. Was. Man. 2009, 29(2), 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NE 012 Normative for the production of concrete and the execution of works in concrete, reinforced concrete and prestressed concrete Part 1: Production of concrete; Ministry of Development, Public Works and Administration, 2004.
- fib-Bulletins N° 42. Constitutive modelling for high strength / high performance concrete.State-of-art report ( ISBN 978-2-88394-082-6, 08). https://www.afgc.asso.fr/app/uploads/2010/07/fib_Bull42_NMG. 20 January.
- Corbu, O.; Puskas, A.; Szilagyi, H. C16/20 concrete strength class design with recycled aggregates, JAES 2014, ISSN: 2247-3769 / e-ISSN: 2284-7197, 4 (17), 13-19.
- Mehta, P.K.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Concrete: microstructure, properties, and materials. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Santhanam, M.; Rakesh, S.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Sen, S.; Ramna, R. V. Utilization of Air-Cooled Blast Furnace Slag As a 100 % Replacement of River Sand in Mortar and Concrete. Indian Concr. J. 2022, 96, 6–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu;T.Ispas The properties and technology of concrete. In Bucharest technical publishing house, Romania, Bucharest, 1997.
- Ahmad, J.; Aslam, F.; Martinez-Garcia, R.; de-Prado-Gil, J.; Qaidi, S.M.A.; Brahmia, A. Effects of waste glass and waste marble on mechanical and durability performance of concrete. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimienta, P.; Albert, B.; Huetb, B.; Dierkens, M.; Francisco, P.; Rougeaud, P. Durability performance assessment of non-standard cementitious materials for buildings: A general method applied to the French context. Fact sheet 1—Risk of steel corrosion induced by carbonation. RILEM Tech. Lett. 2016, 1, 102–108. [CrossRef]
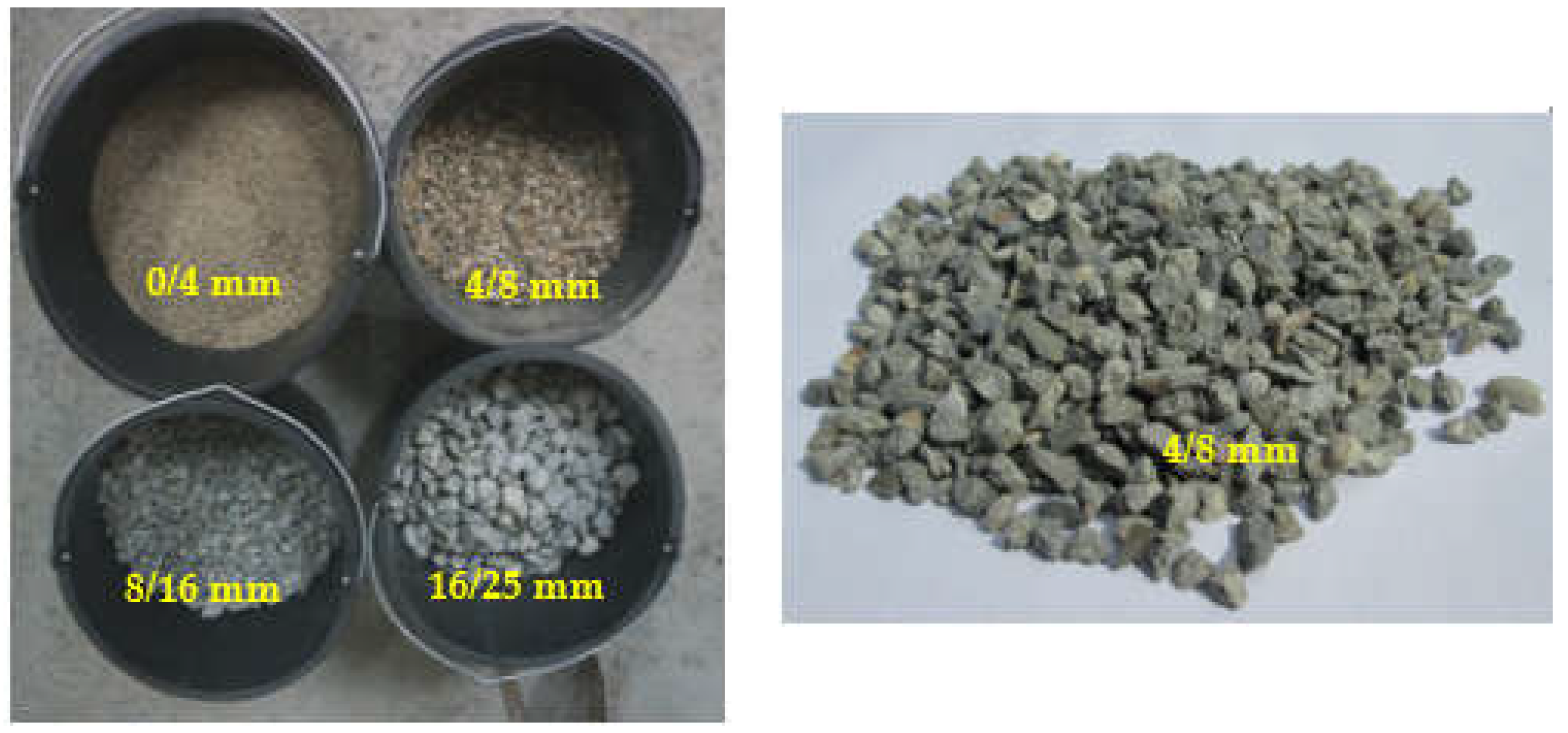
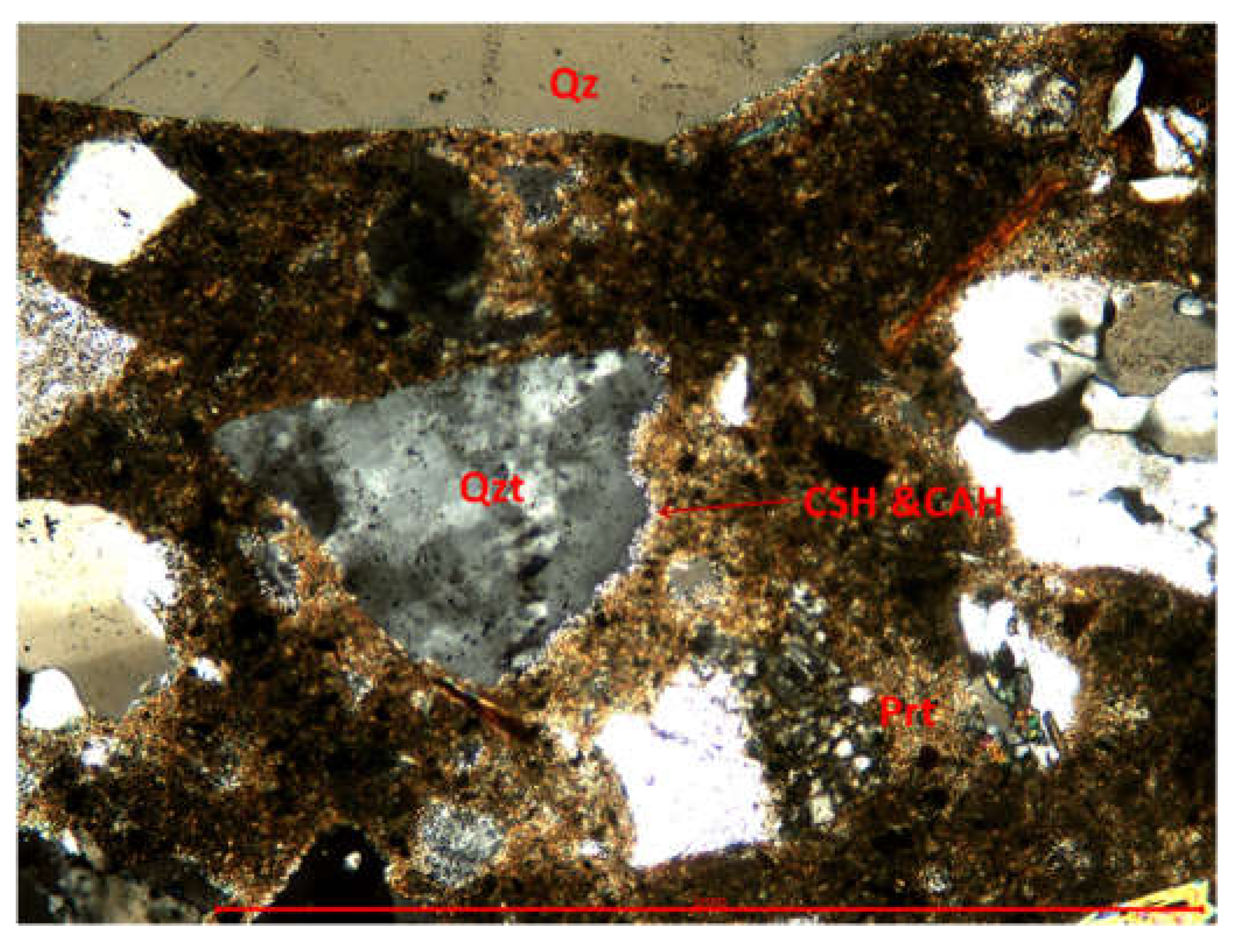
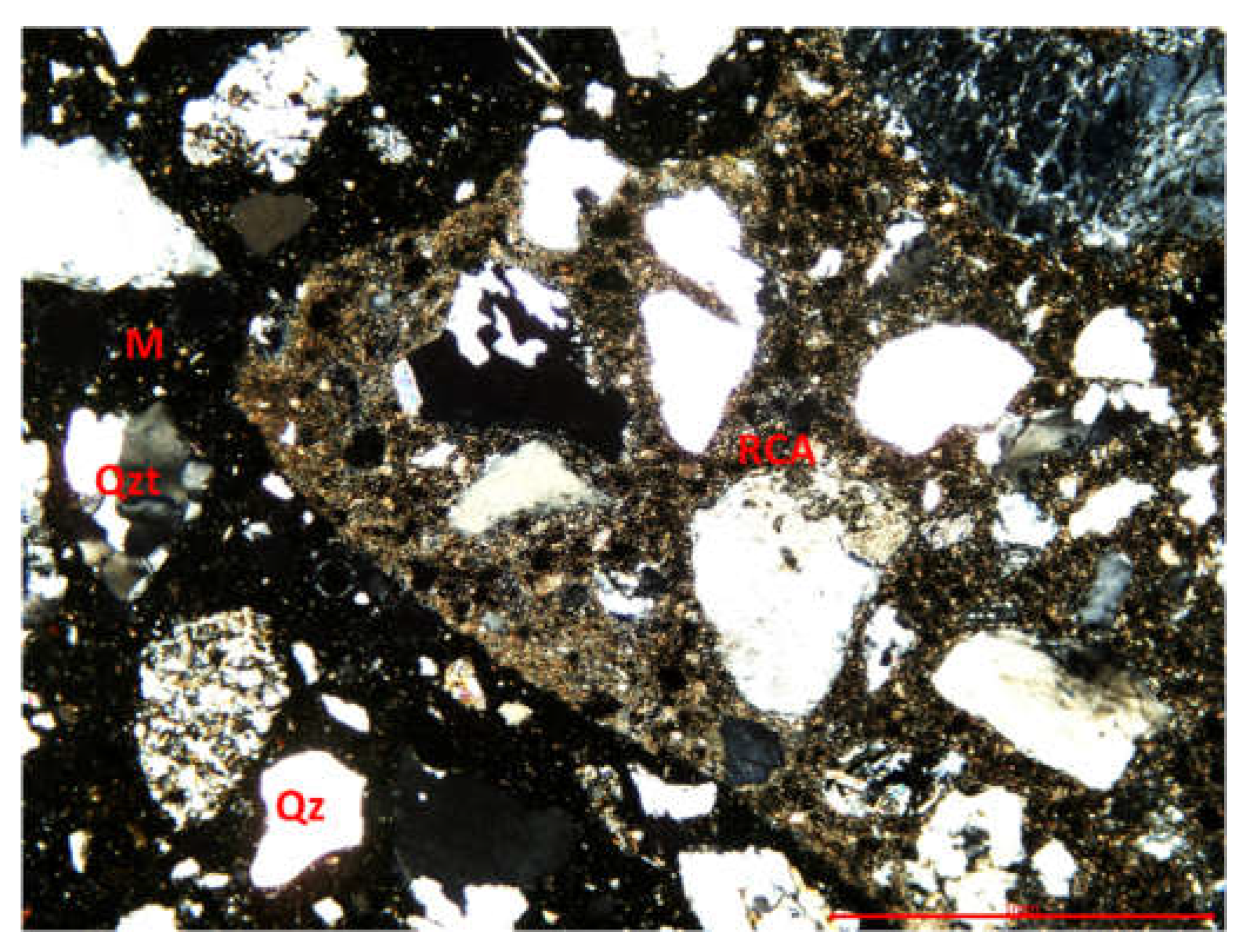
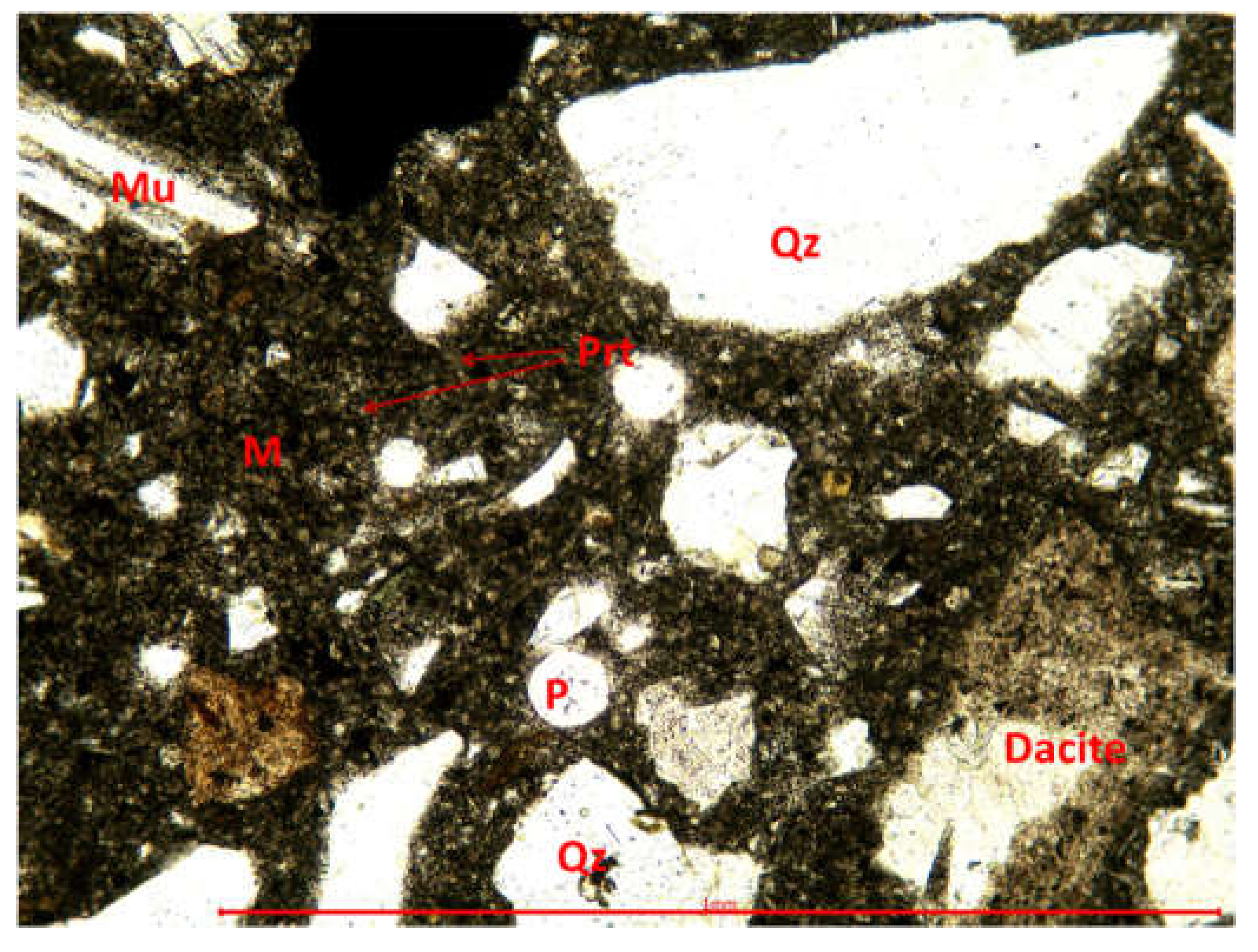









| Size of aggregate [mm] | Type of aggregate |
|---|---|
| 0/4 | Natural River Aggregate (NRA) for all mixes (gravel) |
| 4/8 | Crushed River Aggregates (CRA) (crushed gravel) |
| 4/8 | Recycled Concrete Aggregates (RCA) |
| 8/16 mm, 16/25 | Crushed aggregates / Chippings (CAC) for all mixes |
| Aggregate | Passes, in %, through the size sieve (mm): | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0,125 | 0,250 | 0,500 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 31,5 | |
| 0/4 mm | 4.23 | 15.18 | 38.30 | 64.70 | 86.30 | 99.43 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Aggregate | Passes, in %, through the size sieve (mm): | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0,125 | 0,250 | 0,500 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 31,5 | |
| 4/8 mm | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 1.33 | 27.50 | 96.90 | 100 | 100 |
| 8/16 mm | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 1.76 | 94.62 | 100 |
| Aggregate | Passes, in %, through the size sieve (mm): | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0,125 | 0,250 | 0,500 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 31,5 | |
| 4/8 mm | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 79.90 | 100 | 100 |
| Aggregate | Passes, in %, through the size sieve (mm): | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0,125 | 0,250 | 0,500 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 25 | |
| 8/16 mm | 1.00 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 7.27 | 95.51 | 100 |
| 16/25mm | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 5.02 | 100 |
| Symbol_Sort agregat | Characteristics of aggregates | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mm) | ρa (mg/m3) | ρrd (mg/m3) | ρssd (mg/m3) | WA24 (%) |
| NRA_0/4 | 2.700 | 2.570 | 2.630 | 3.00 |
| RCA_4/8 | 2,703 | 2,320 | 2,462 | 6,00 |
| CAC_8/16 | 2.650 | 2.560 | 2.610 | 1.40 |
| CAC_16/25 | 2.670 | 2.590 | 2.620 | 1.20 |
| Symbol of aggregate | Sorts of aggregates | LAmed (%) | Traffic class |
|---|---|---|---|
| RCA | 4/8, mm | 30,9 | Reduced |
| CRA | 4/8 mm | 31,0 | Reduced |
| CAC | 8/16 mm | 16,0 | Intensive |
| CAC | 16/25 mm | 15,0 | Intensive |
| Symbol of aggregate | Sorts of aggregates | MDEmed (%) | Traffic class |
|---|---|---|---|
| RCA | 4/8 mm | 20,8 | Medium |
| CRA | 4/8 mm | 10,1 | Intensive |
| CAC | 8/16, 16/25 mm | 14,0 | Intensive |
| Sorts/elementary aggregates di/Di | The nominal opening of the grill slots, mm | Ai | M1 | M2 | A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4/8 mm | 8/10 | 5 | 0 | 600 | 76 | 13 |
| 6.3/8 | 4 | 5 | ||||
| 5/6.3 | 3.15 | 29 | ||||
| 4/5 | 2.5 | 26 | ||||
| Characteristics CEM I 42, 5R | Value | According to | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clincher Portland (%) | data | data |
| Minor component (%) | 95 ÷ 100 | SR EN 197-1 | |
| Chemical Characteristics | Sulphate content (in the form of SO, %) | 0 ÷ 5 | SR EN 197-1 |
| Chloride content (%) | < 4 | SR EN 196-2 | |
| Loss of calcination (%) | < 0,1 | SR EN 196-2 | |
| Insoluble residue (%) | < 5 | SR EN 196-2 | |
| Physico-Mechanical Characteristics | Setting time (min.) | < 5 | SR EN 196-2 |
| Stability (mm) | > 60 | SR EN 196-3 | |
| Compressive strength at 2 days (MPa) | < 10 | SR EN 196-3 | |
| Compressive strength at 28 days (MPa) | > 20 | SR EN 196-1 | |
| Clincher Portland (%) | > 42,5 < 62.5 | SR EN 196-1 | |
| Oxides | SiO2 | K2O | Fe2SiO3 | CaO | Al2O3 | MgO | Na2O | Oder |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEM I 42.5R | 14,30 | 1,08 | 3,70 | 71,46 | 2,90 | 0,86 | 5,70 | - |
| WGP | 77,70 | 1,01 | 0,44 | 13,6 | 0,06 | 0,01 | 5,27 | 1,92 |
| WGP | Treceri, in %, prin sita de dimensiunea (mm): | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0,63 | 0,125 | 0,250 | 0,500 | |
| < 0,125 mm | 43,80 | 100,00 | 100 | 100 |
| Properties | Mechanical strength | Shrinkage | Abrasion resistance | Freeze-Thaw resistance | Modulus of elasticity | Hydration rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3S | Very high* | Low | Good | Very good | Very high | Moderate |
| Pavements realized | Nature of Aggregates | Sorts of Aggregates | Gradation of Total Aggregates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single layer | Natural Sand | 0/4 | |
| Two layers | Crushed Gravel | 4/8 | 0/25 |
| Chipping | 8/16 | ||
| Wearing course | Chipping | 16/25 |
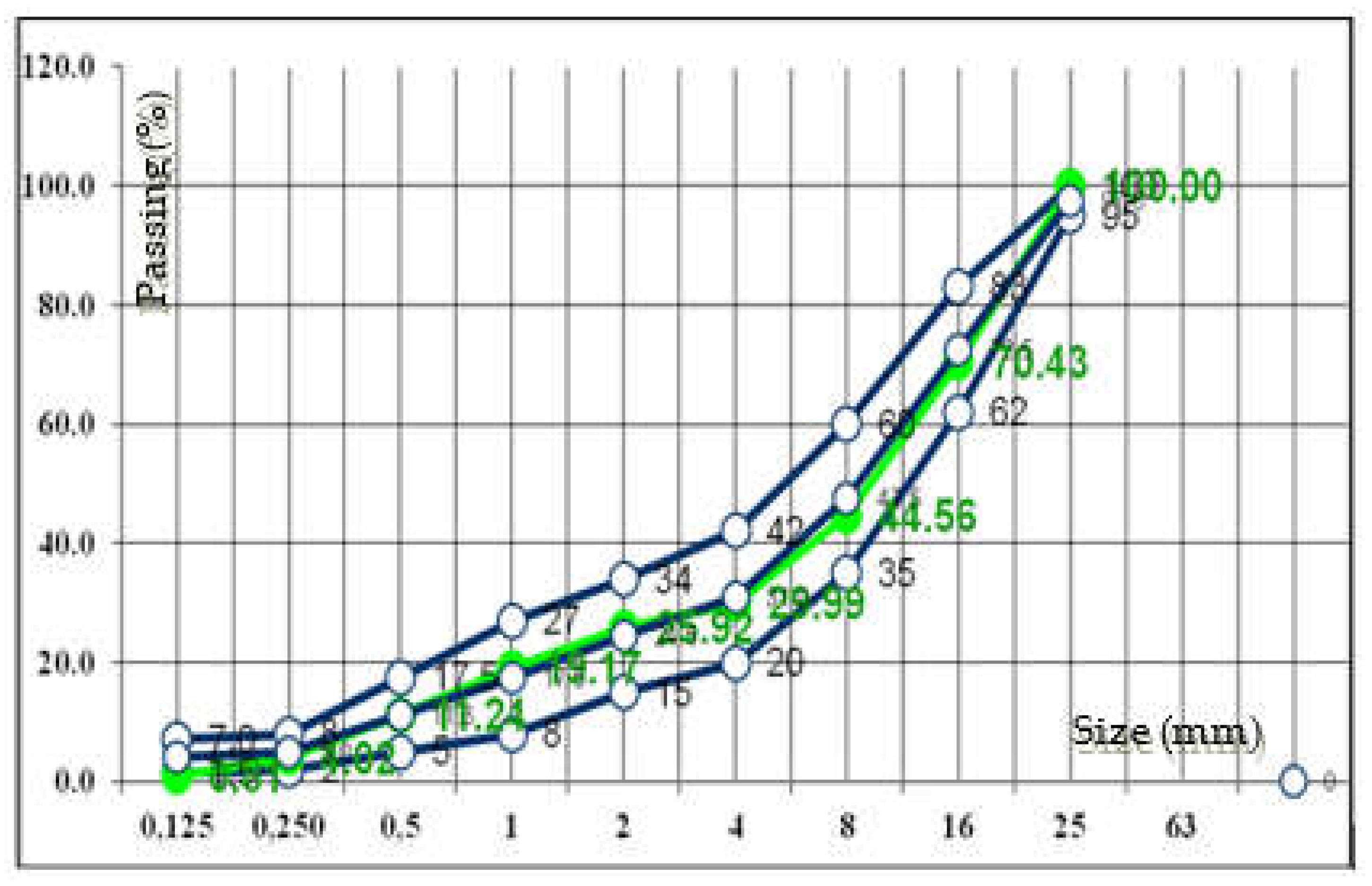
| Total gradation curves for the concrete mixtures | Passing % through sieve with size [mm] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0,125 | 0,250 | 0,5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 25 | |
| Concrete mixture with natural aggregates [38] | 1.29 | 4.64 | 11.59 | 19.51 | 26.06 | 32.86 | 47.58 | 70.43 | 100 |
| Concrete mixture with recycled aggregates | 0.81 | 4.02 | 11.24 | 19.17 | 25.92 | 29.99 | 44.56 | 70.43 | 100 |
| Lower limit | 1,5 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 15 | 20 | 35 | 62 | 100 |
| Upper limit | 7,0 | 8,0 | 17,5 | 27 | 34 | 42 | 60 | 83 | 100 |
| Design parameters BcR4 | Min. cement ratioCEM I 42,5 | (w/c) | Consistency Class S1 (mm) | Air void content (%) | Freeze-throw circles | fc28 days MPa | fct,fl 28 days MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NE 014 [38] andSR EN 206 [39] | 330 kg/m3 | max.0.45 | 10÷40 | 3.5+0.5 | 100 | min. 35 max. 50 | min.4 max.5 |
| Mix components for BcR-NA | BcR-NA | BcR-RCA | BcR-RCA-WGP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water/Cement ratio | 0,45 | 0,45 | 0,45 |
| Cement I 42,5R | 330 | 330 | 297 |
| DSP(WGP) < 0,125 mm – 10% | - | - | 33 |
| NRA – 0/4 mm | 569 | 569 | 569 |
| CRA – 4/8 mm | 303 | - | - |
| RCA – 4/8 mm | - | 303 | 303 |
| CAC – 8/16 mm | 455 | 455 | 455 |
| CAC – 16/25 mm | 569 | 569 | 569 |
| Admixture 1 (Master Glenium 115) – 1,80 % | 5,94 | 5,94 | 5,94 |
| Admixture 2 (MICROAir 107-2) - 0,25% | 0,285 | 0,285 | 0,285 |
| Aggregate proportions for the control mixtures | BcR-NA Var. I | BcR-NA Var. II |
|---|---|---|
| 0/4 mm | 30.0 % | 32.0 % |
| 4/8 mm | 16.0 % | 20.0 % |
| 8/16 mm | 24.0 % | 18.0 % |
| 16/25 mm | 30.0 %; | 30.0 % |
| Fresh property | UM | Performance level | Mix design | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BcR-NA/NA | BcR-RCA | BcR-RCA-WGP | ||||||
| Var. I | Var. II | Var. I | Var. II | 10% | 20% | |||
| Temperature (T) | °C | 5÷30 | 23 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 23 | 22 |
| Consistency (S) | mm | 10÷40 | 35 | 40 | 35 | 37 | 27 | 31 |
| Apparent Density (ρ) | Kg/m3 | 2400 | 2374 | 2370 | 2364 | 2352 | 2358 | 2347 |
| Entrained Airfor Aggreg. dmax-25 mm | % | 3,5÷4,5 (+0,5) | 4,0 | 4,2 | 3,7 | 3,9 | 3,8 | 4,2 |
| Hard property | UM | Performance level | Mix design | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BcR-NA/NA | BcR-RCA | BcR-RCA-WGP | ||||||
| Var. I | Var. II | Var. I | Var. II | 10% | 20% | |||
| Flexural strength (fct,fl) | MPa | 4.0÷5.0 | 6.7 | 5.4 | 5.6 | 5.5 | 5.4 | 4,3 |
| Compressive strength (fc) | MPa | 35÷45 | 84.2 | 69.2 | 83.1 | 69.4 | 80 | 62.0 |
| Splitting strength (fct,sp) | MPa | - | 4.5 | 3.7 | 4.4 | 3,7 | 4.5 | 3,5 |
| Density (ρa) | Kg/m3 | 2400 + 40 | 2430 | 2417 | 2425 | 2410 | 2420 | 2406,6 |
| Loss of strength (η) | % | < 25 | 14.11 | 16.8 | 14.60 | 17.6 | 16.0 | 20.2 |
| Volume loss due to abrasion (η) | ΔV/5000 mm2 | ΔV ≤ 18 000 mm3 | 11301 | 9371 | 11500 | 9494 | 11220 | 9436 |
| Depth of carbonation (dk) | mm | - | 0.5 | - | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 | |
| Hard property | UM | Performance level | Mix design | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BcR-NA | BcR-RCA | BcR-RCA-WGP | ||||||
| Var. I | Var. II | Var. I | Var. II | 10% | 20% | |||
| Flexural Strength (fct,fl) | MPa | 4.0÷5.0 | 6.7 | 5.4 | 5.6 | 5.5 | 5.4 | 4,3 |
| Compressive Strength (fc) | MPa | 35÷45 | 84.2 | 69.2 | 83.1 | 69.4 | 80.0 | 62.0 |
| Loss of Strength (η) | % | 25 | 14.11 | 16.8 | 14.60 | 17.6 | 16.0 | 20.2 |
| Achieved Strength Class | BcR | BcR4÷ BcR5 | BcR 5 | BcR 5 | BcR 5 | BcR 5 | BcR 5 | BcR 4 |
| Source | Mathematical relation (cylinders with H/ Φ- 300/150 or cube with l= 150 mm) |
|---|---|
| fib Bulletin 42 [95] | fcm = fck + Δf, Δf = 8 MPa |
| NE 012-1: 2022 [94] | fcm = fck + (6 ÷ 12) MPa |
| Mix | fct,fl | Cv1 | Cv2 | fc | Cv1 | Cv2 | η | Cv1 | Cv2 | ΔV | Cv1 | Cv2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Var. I | MPa | MPa | % | /5000 mm2 | ||||||||
| BcR-NA | 6.7 | 0.75 | 84.2 | 0.65 | 14.11 | 1.77 | 11301 | 1.59 | ||||
| BcR-RCA | 5.6 | 1.20 | 0.89 | 83.1 | 1.01 | 0.66 | 14.60 | 0.97 | 1.71 | 11500 | 0.98 | 1.57 |
| BcR-RCA-10%WGP | 5.4 | 1.24 | 0.93 | 80.0 | 1.05 | 0.69 | 16.00 | 0.88 | 1.56 | 11220 | 1.01 | 1.60 |
| Var. II | ||||||||||||
| BcR-NA | 5.4 | 0.93 | 69.2 | 0.79 | 16.80 | 1.49 | 9371 | 1.92 | ||||
| BcR-RCA | 5.5 | 0.98 | 0.91 | 69.4 | 0.997 | 0.79 | 17.60 | 0.95 | 1.42 | 9494 | 0.98 | 1.90 |
| BcR-RCA-20%WGP | 4.3 | 1.26 | 0.93 | 62.0 | 1.12 | 0.89 | 20.20 | 0.83 | 1.24 | 9436 | 0.99 | 1.91 |
| Var. I & II | ||||||||||||
| BcR-NA | 6.7 | 84.2 | 14.11 | 11301 | ||||||||
| 5.4 | 1.24 | 69.2 | 1.22 | 16.80 | 0.84 | 9371 | 1.21 | |||||
| BcR-RCA | 5.6 | 83.1 | 14.60 | 11500 | ||||||||
| 5.5 | 1.02 | 69.4 | 1.20 | 17.60 | 0.83 | 9494 | 1.21 | |||||
| BcR-RCA-WGP | 5.4 | 80.0 | 16.00 | 11220 | ||||||||
| 4.3 | 1.26 | 62.0 | 1.29 | 20.20 | 0.79 | 9436 | 1.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





