1. Introduction
With the intensification of global climate change and environmental pollution problems, a consensus has emerged in the international community regarding the need for a reduction in carbon emissions and the development of a low-carbon economy worldwide. Carbon peaking and carbon neutrality are two important measures in the global response to climate change; together, these also constitute an important development goal put forward by China [
1]. Industry, as an important pillar of economic development, is also one of the main sources of carbon emissions [
2]. The Second China Digital Carbon Neutrality Summit Forum pointed out that industrial green and low-carbon transformation is essential for integrating development and achieving emission reductions, and that energy transformation and digital twinning will act as a powerful stimulant to China's "dual carbon” goal of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality. As an important engine for China's green and low-carbon industrial transformation, the digital economy should be fully exploited for its potential to reduce carbon emissions. The stimulating power of the digital economy should also be used to achieve high-quality economic development and accelerate the achievement of digital and low-carbon transformation in the industrial field [
3,
4]. As a new economic form, the digital economy involves digital industrialization, industrial digitization and other evolutionary modes, and is characterized by constantly improving levels of economic and social digitization, networking, and intelligence; as such, the digital economy may now be understood as a central means by which China will achieve its national goals [
5,
6]. In 2022, the State Council issued the "14th Five-Year Plan for the Development of the Digital Economy" which anticipated that the added value generated by the core industries of the digital economy would account for 10% of GDP by 2025. Against this backdrop, the digital economy is also driving profound changes in the modes of production and governance, as well as the personal lifestyles of individuals; moreover, it has become a key force in reorganizing ecological resources and rebuilding economic structure.
Carbon emission reduction is now a hot topic of concern at home and abroad. Some scholars have focused on the influencing factors of carbon emissions, and offered different explanations of the factors which affect carbon emissions from the perspectives of economic growth [
7], industrial structure [
8], energy structure [
9], technological innovation [
10] and so on. Others have carried out studies on how to reduce carbon emission intensity, and found that the construction of an ecological civilization serves to promote demonstration zones [
11], adjustment of the spatial structure of strategic emerging industries [
8], implementation of the carbon emissions trading policy [
12] and development of digital finance [
13], in addition to other methods which have proven to be effective in curbing the intensity of carbon emissions. Carbon emission efficiency is the comparison relationship between various carbon-emission-related input variables and output variables, and plays an important role in the scientific testing of low-carbon efficiency [
14]. Research on carbon emission efficiency mainly involves considering its spatial and temporal evolution from the perspective of industries, enterprises and regions, as well as research on the factors affecting carbon emission efficiency [
12,
15]. A review of published research reveals that there have been few studies on industrial carbon emission efficiency, and these have mainly explored influencing factors using different modeling approaches [
16]. In addition, few studies have sought to analyze the changes and influencing mechanisms of industrial carbon emission efficiency from the perspective of regional development [
17], so that spatial heterogeneities at the regional level have been ignored. This has led to a lack of theoretical and data support for realizing digital and low-carbon transformation in the industrial sectors of developing countries, especially countries like China which have a sound industrial system but unbalanced regional economic development. For this reason, identifying spatio-temporal changes in industrial efficiency and their influencing factors in cities at different stages of development is the key to effective formulation of countermeasures to promote the low-carbon transformation of national industry and achieve high-quality economic development.
Since the adoption of the dual-carbon goal, the relationship between the digital economy and carbon emission efficiency has also become an academic research hotspot. The development of the digital economy breaks the constraints of geographic distance upon economic activities, strengthens regional connectivity, promotes synergistic development of technological innovation and common transformation of industrial structure in various regions, and influences cooperation and innovation in neighboring regions through the spatial spillover effect [
5,
17]. Some scholars have conducted research on the empowering effects of the digital economy on urban industrial carbon emission efficiency; such studies have shown that the development of digital economy can motivate the urban industrial sector to reduce pollution and carbon emissions, and improve industrial carbon emission efficiency [
18,
19,
20]. Because different cities are at different stages of socio-economic development, there is spatial heterogeneity in the impact of digital economy on industrial carbon emission efficiency [
21,
22]. Although published studies have paid attention to the nonlinear impact of digital economy on carbon efficiency, these have involved the mere addition of quadratic formulas to identify nonlinearity and verify the environmental Kuznets curve [
23,
24]; using such methods, it is easy to ignore the developmental differences of different cities, and to neglect the significance of practical guidance. In short, the question of how the development of digital economy affects industrial carbon emission efficiency has yet to be answered. Specifically, is there a nonlinear relationship between the two phenomena? Answering the above question is of potentially great significance for advancing the digital power of China, and for the Chinese achievement of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality. In this study, then, to make up for the shortcomings of previous research, we used balanced panel data of 270 Chinese cities from 2005 to 2020 as a research object: (1) to show the spatio-temporal evolution pattern of urban industrial carbon emission efficiency; (2) to analyze the aggregation characteristics of industrial carbon emission efficiency in Chinese cities using Global Moran's I statistics; and (3) to use the hierarchical regression model for panel data to explore the non-linear impact of the digital economy on the industrial carbon emission efficiency of cities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Global Moran's I
The global Moran's I statistic was used to analyze the overall spatial distribution of geographic elements, to determine whether all geographic elements were clustered or not, and to examine whether there was an obvious distribution pattern of geographic elements in space [
25]. The value of global Moran's I is normalized to [-1,1]. A Moran's I value greater than 0 indicates positive spatial correlation; the larger the value, the more pronounced the spatial correlation. A Moran's I value equal to 0 indicates that the elements are randomly distributed, and there is no correlation [
26]. The global Moran's I is calculated by the following formula:
where Moran's I is the global Moran's index;
and
denote the industrial carbon emission efficiency of elements
i and
j, respectively;
is the spatial weight matrix of elements
i and
j; and
denotes the average value of the industrial carbon emission efficiency of all elements.
2.2. The Panel Quantile Model
In this study, a panel quantile regression model was used to quantify the extent to which the main influencing factors affected the industrial carbon emission efficiency of cities at different stages of development. When the data distribution is non-normal, or the regression coefficients fluctuate greatly at different quartiles, quantile regression can capture the degree of influence of the explanatory variables at different quartile levels; in addition, regression results are less susceptible to the influence of outliers and more comprehensively encompass individual heterogeneity [
27]. The expression is as follows:
where
is the city industrial carbon emission efficiency;
represents the city industrial carbon emission efficiency at the
θth quantile;
is the vector of exogenous variables for city
i in year
t;
is denoted as the kth quantile level;
represents the vector of estimated coefficients;
i is the city studied; t is the year of the study; and
is the unobserved individual effect.
2.3. Variable Description
(1) Explained variable: industrial carbon emission efficiency. Industrial carbon emission efficiency was measured by applying the super-efficiency EBM model, which takes into account undesired outputs, by including industrial input and output factors in the analytical framework [
28,
29]. Among these, the input factors were industrial capital stock, industrial labor force, industrial land use, industrial energy input and industrial water input. For the output factors, the deflated industrial gross domestic product of each prefecture-level city was taken as the desired output, and the city’s carbon emission was taken as the non-desired output. Carbon emissions were obtained by summing the product of the cities' industrial natural gas consumption, industrial liquefied petroleum gas consumption and industrial electricity consumption, with their respective carbon emission factors.
(2) Explanatory variable: digital economy. In this study, we measured the level of urban digital economy using the evaluation system and measurement method of Zhao et al. [
30], and constructed a digital economy development index with four dimensions, namely, digital infrastructure, digital industry, digital innovation and digital application. Digital infrastructure was expressed by the number of cell phone subscribers and internet users per 100 people; digital industrial base was expressed by per capita telecommunication business revenue; digital innovation capacity was expressed by the ratio of computer and software employees to the number of employees and the number of patents related to the digital economy per 10,000 people; digital application was expressed by the Digital Inclusive Finance Index. In order to avoid bias caused by subjective factors, the entropy method was used to determine the index weights.
(3) Control variables: relevant variables were introduced to control the accuracy of results relating to the impact of the digital economy on industrial carbon emission efficiency. Per capita GDP denotes the per capita gross domestic product, which represents the level of regional economic development, with economically developed regions having a higher level of industrialization [
31]. Population size is an important variable which reflects increases in carbon emissions through energy consumption at the household level [
32]. Urbanization represents the stage of urban development, and the expansion of the urban scale promotes the expansion of the urban industrial system and also promotes the transformation and upgrading of enterprises. Increased size of industrial enterprises promotes economic development, but also brings about environmental pollution, which negatively affects urban economic high-quality development [
17]. Government intervention impacts regional economic development, industrial structure adjustment and the level of technological innovation [
33]. Science and technology input helps to improve the level and efficiency of industrial scientific and technological progress, and suppresses the intensity of industrial carbon emissions. Foreign direct investment promotes industrial development, and also provides a channel for highly polluting and energy-consuming enterprises to transfer to regions with less stringent environmental regulations [
34].
2.4. Data Sources
For this study, considering the principles of data authenticity and availability, we collected and organized panel data of 270 cities in China in 2005, 2010, 2015 and 2020, so as to explore the impact of digital economy on industrial carbon emission efficiency. The data were obtained from the China Statistical Yearbook, the China Energy Statistical Yearbook and provincial yearbooks. In order to eliminate unit differences among the data and unify the scale, all the data were standardized. The descriptive statistics of relevant variables are shown in
Table 1.
3. Results
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Industrial Carbon Emission Efficiency in Chinese Cities
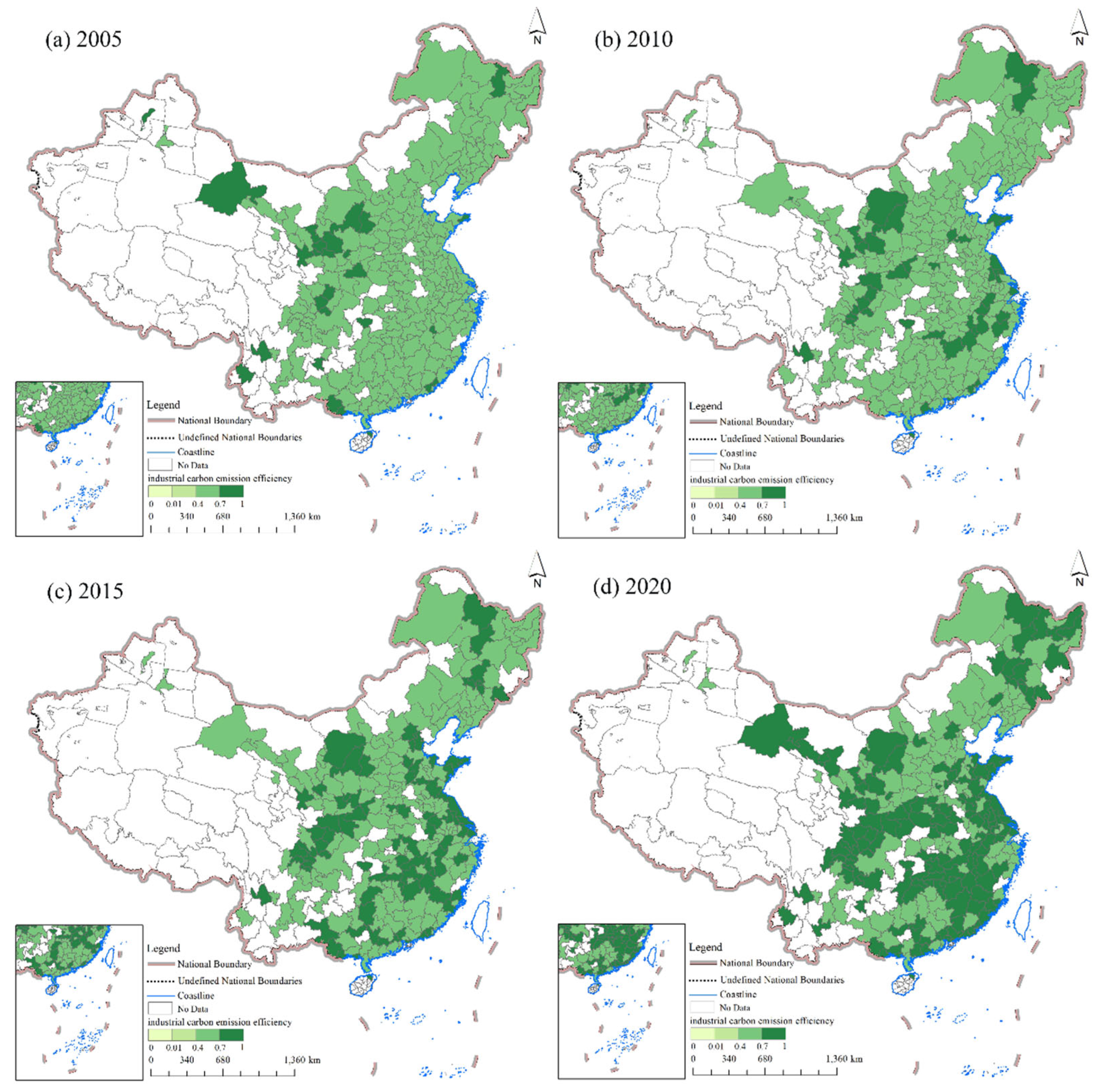
In order to visualize the spatio-temporal variability of industrial carbon emission efficiency of Chinese cities, the industrial carbon emission efficiency of Chinese cities was classified into three levels based on efficiency values, as follows: low efficiency (0–0.4); medium efficiency (0.41–0.7); and high efficiency (0.71–1). A zero value indicated no data (
Figure 1). The industrial carbon emission efficiency of Chinese cities showed an upward trend from 2005 to 2020, with urban industrial carbon emission efficiency increasing from 0.59 in 2005 to 0.73 in 2020. It may be that since China's accession to the WTO in 2001, the process of industrialization in China has rapidly advanced so that, in recent years, the industrial structure has been optimized and upgraded, and economic development has shifted to high-quality development, with a consequent rise in urban industrial carbon emission efficiency. The number of cities with high industrial carbon emission efficiency in the eastern region increased significantly between 2005 and 2020, mainly due to the transfer of heavy industry, industrial restructuring, a rising proportion of new industries, and the gradual clean-up of their energy consumption structure [
35]. The spatial distribution pattern of urban industrial carbon emission efficiency from 2005 to 2020 showed higher values in the south and lower values in the north. Urban industrial carbon emission efficiency was mostly at a medium level in 2005 and 2010, with high-efficiency cities concentrated in Shaanxi, Ningxia and Gansu. By 2020, the numbers of cities with medium and high carbon efficiencies were almost equal. There were 28 high-efficiency cities in 2010, 88 such cities in 2015, and 153 in 2020. The lower industrial carbon emission efficiency of cities in northern China may be explained as follows: northern Chinese provinces are rich in coal and petrochemical energy, and are characterized by high levels of traditional-energy extraction and consumption; their urban development has thus been highly dependent on carbon-intensive industries, resulting in lower industrial carbon emission efficiency. In contrast, the Shandong Peninsula city cluster, the Yangtze River Delta region, and the Pearl River Delta region are all characterized by strong scientific and technological innovation and industrial integration development capabilities, high levels of industrial integration, and extensive energy-saving and consumption-reduction efforts, resulting in high levels of industrial carbon emission efficiency; as a result, these regions are at the forefront of China's economic transformation and development today [
36]. We also found that cities with high industrial carbon emission efficiency are surrounded by circles of medium- and low-efficiency cities. This may be due to the pursuit of industrial upgrading and transformation in developed regions, as well as the relocation of high-pollution and high-energy-consumption industries and the transfer of industries to economically underdeveloped regions, leading to low industrial carbon emission efficiency. In northeast China, cities with high industrial carbon emission efficiency are concentrated in provincial capitals and their neighboring cities, such as Changchun, Baicheng, Heihe, Suihua and Mudanjiang. Industries in northeastern cities are mainly heavy industries which are characterized by high consumption of resources and energy and low energy-utilization efficiency. This explains why the industrial carbon emission efficiency of most cities in northeastern China is still at a relatively low level.
3.2. Aggregation Characteristics of Industrial Carbon Emission Efficiency in Chinese Cities
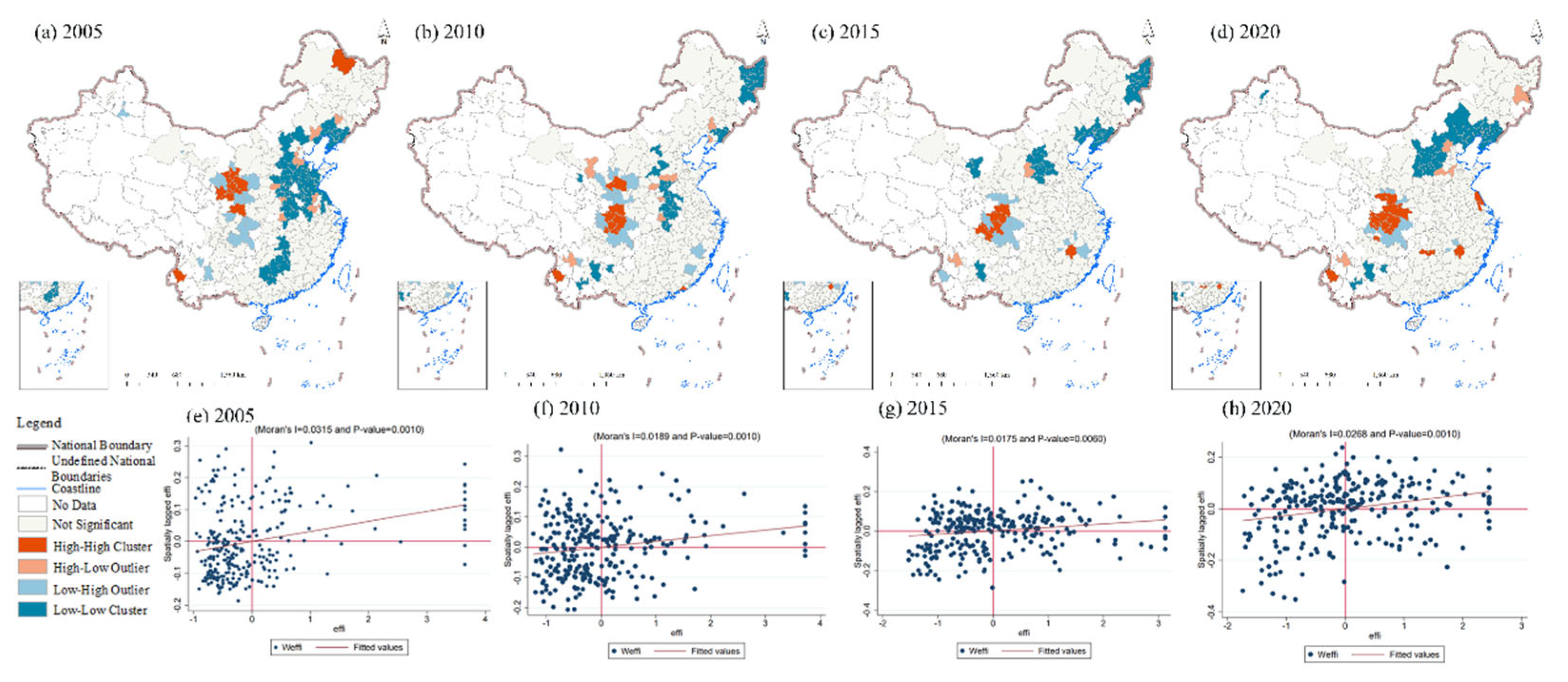
In this paper, the Global Moran's I statistic and LISA distribution was used to test the spatial correlation of urban industrial carbon emission efficiency and to characterize its spatial agglomeration (
Figure 2). We found that the spatial autocorrelation of industrial carbon emission efficiency in Chinese cities is significant, that this correlation is increasing and stabilizing, and that the pattern of spatial agglomeration is relatively fixed. The Global Moran's I of industrial carbon emission efficiency of 270 Chinese cities is greater than zero and passes the significance test at the 95% level. In addition, cities with similar industrial carbon emission efficiency are spatially clustered (
Figure 1). The center of gravity of high-high-agglomeration cities tends to move southward with time and the number of cities increases, while the center of gravity of low-low-agglomeration cities moves northward and the number of cities decreases. Since 2005, the center of gravity of high-high agglomeration cities has moved from Gansu to Shaanxi, and the new high-high concentration cities are Baoshan in Yunnan, Lianyungang and Huaian in Jiangsu, and Guangyuan, Mianyang and Dazhou in Sichuan. Tianshui has remained a high-high agglomeration city. However, high-high concentration has disappeared in the resource-oriented city of Heihe in northeast China. The heavy industry system, which is highly dependent on resource consumption, has long been the economic pillar of the northeastern region; consequently, it is difficult for enterprises in this region to transform and upgrade, and improvements in industrial carbon emission efficiency have been slow as a result. The industrial transfer from the eastern region to the central and western regions has been mainly dominated by high consumption and high emission industries, and the improvement of energy utilization and carbon reduction technology in the northwestern region has a lag relative to that of the districts and counties in the developed regions, which makes it difficult to break through the bottleneck of the city's industrial carbon emission efficiency for a certain period of time [
37]. Therefore, the center of gravity of cities with high concentration has shifted to economically developed cities and regions, due to improved environmental regulations and increased efforts towards corporate pollution control which prompt cities to accelerate their elimination of backward production capacity and high-pollution industries, thus reducing carbon emissions caused by resource and energy consumption, and improving carbon emission efficiency.
Cities with low-low agglomeration were distributed in Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration, Yangtze River Delta Region and Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region in the early stages of the study period, but were concentrated in Shanxi, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning and other provinces by the end of the study period. We may note that, on the one hand, Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration has cultivated and developed strategic emerging industries with a focus on industrial structure adjustment and optimization, thus promoting reductions in energy usage and in consumption. In addition, the Yangtze River Delta region has made full use of its industrial base and port conditions to achieve a rapid development of advanced manufacturing industries, high levels of industrial agglomeration and research and development (R&D) investment, a strong capacity for scientific and technological innovation, and extensive industrial integration and development, all of which have increased the industrial carbon emission efficiency of cities in this region [
36]. Similarly, in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, adjustments in industrial structure and environmental pollution controls have served to effectively control carbon emission levels, and urban industrial carbon emission efficiency has been improved [
38]. On the other hand, Shanxi and Inner Mongolia are provinces characterized by high levels of traditional energy extraction and consumption; in areas like these, coal-based energy utilization is relatively crude, carrying the transfer of high-energy-consuming enterprises from Beijing; as a result, urban development has been highly dependent on carbon-intensive industries, and the enhancement of urban industrial carbon emission efficiency has been slow in these areas.
China's central and southern regions have developed urban economies, relatively clean energy consumption structures, and fewer carbon-intensive manufacturing industries, so that the application of innovative green technologies by enterprises has been more common, and higher industrial carbon emission efficiency has been attained. The eastern region plays a leading role in achieving China's "carbon peak, carbon neutral" energy saving and emission reduction goals. The central and western regions must now seize the opportunity to actively promote industrial intelligence and low-carbon development, improve urban industrial carbon emission efficiency, and work to promote high-quality economic development and sustainable development in China. It should be noted that there are problems such as industrial homogeneity and inefficient resource utilization in various regions; however, these may serve to strengthen inter-regional exchanges and cooperation in terms of technology and talents, reduce the phenomenon of inter-regional transfer of polluting industries, and achieve a coordinated development of the digital economy, while at the same time rationally and efficiently configuring digital economy resources according to the actual economic growth situation of each region, as well as reducing the inter-regional development gaps, and better exploiting the carbon emission reduction effect of the digital economy [
39].
3.3. Basic Regression Analysis (BRA)
Table 2 presents basic estimation results showing how digital economy affects urban industrial carbon emission efficiency.
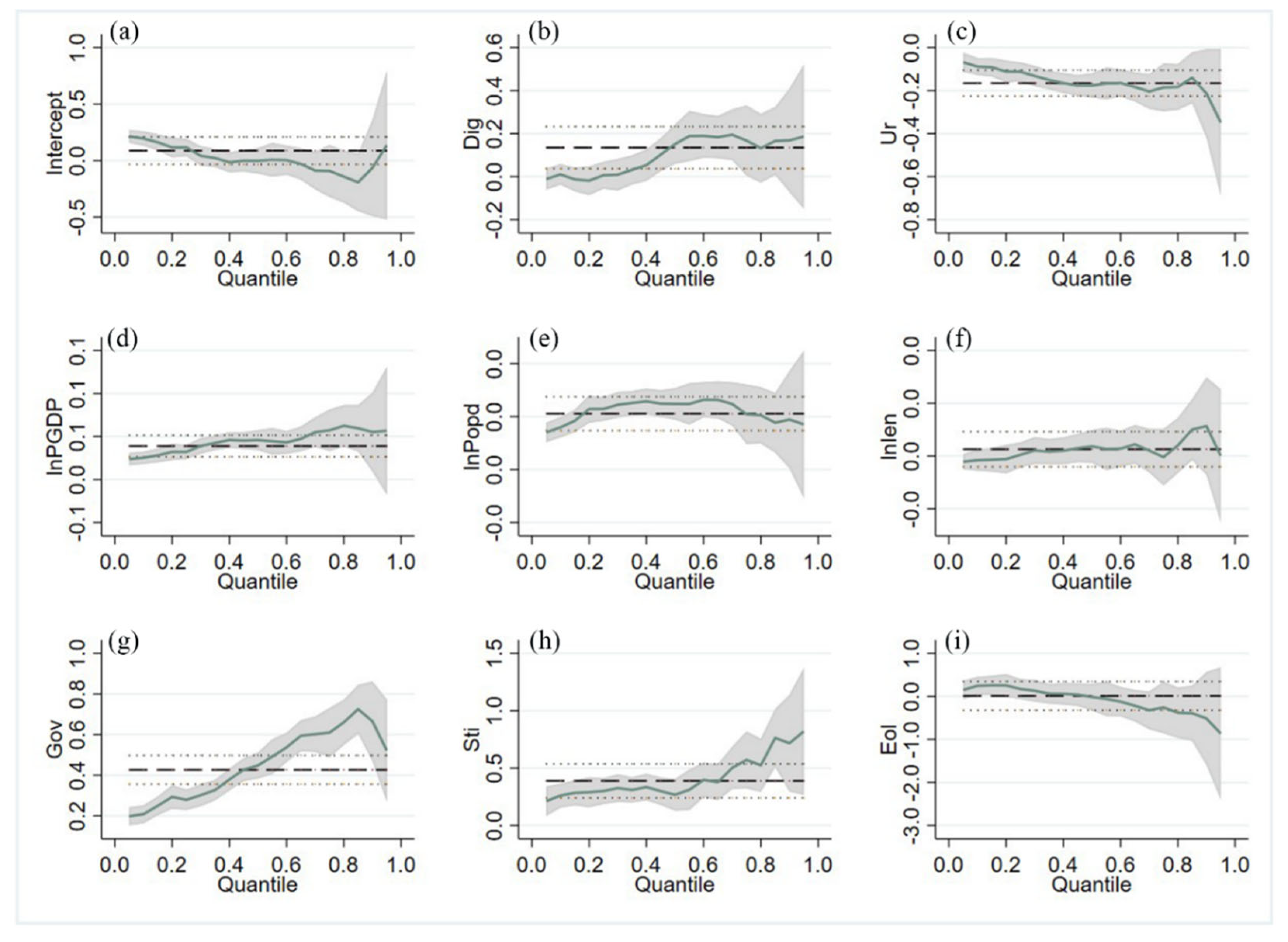
Figure 2 shows the distribution of regression elasticity coefficients of factors affecting industrial carbon emission efficiency in cities. It can be seen that the influence of socio-economic factors on industrial carbon emission efficiency involves stage differences. Among these, column (1) shows results without adding any control variables, while column (2) shows estimation results with the addition of the remaining city economic indicators. As can be seen in
Table 2, in comparison with column (1) without control variables, the explanatory power of the model rises in column (2) after city economic characteristics and government intervention variables are added, although the regression coefficients of digital economy decrease slightly. After controlling for other factors, we may state that digital economy has a positive effect on improving urban industrial carbon emission efficiency which is significant at the 5% confidence level.
The regression coefficients of digital economy become larger with the increase in quartiles, and the positive effect of digital economy gradually strengthens, with the greatest negative effect in the lowest quartile. This shows that there is a significant inverted-U-shaped relationship between digital economy and urban industrial carbon emission efficiency, so that digital economy increases carbon emissions and inhibits industrial carbon emission efficiency in the early stages of development, but inhibits carbon emissions and increases industrial carbon emission efficiency in the mature stage of development. This finding is similar to the results of previous studies [
32]. The environmental Kuznets curve shows that when the economic growth level is low, people have little demand for environmental quality. Facing the pressure of economic assessment, local governments pay more attention to the economy and neglect environmental protection, adopting the development mode of "pollute first, treat later".
When the level of economic growth increases and per capita GDP rises, people's demand for high-pollution, high-energy consumption products decreases while demand for more environmentally friendly products rises. In order to adapt to changes in consumer demand, then, enterprises adapt to the development trend of the digital economy and promote industrial technological innovation, including industrial digital transformation and upgrading, thereby reducing the intensity of their industrial carbon emissions and improving industrial carbon emission efficiency [
5].
The regression coefficient of population size is positive, so that the regression coefficient increases and then decreases with the increase in quartiles, with a positive effect on the enhancement of urban industrial carbon emission efficiency in the middle quartile, and more obvious inhibitory effects in the low and high quartiles. Urbanization has a significant negative effect on industrial carbon emission efficiency; the regression coefficient decreases with the increase in quartiles, and the inhibitory effect of urbanization is more critical in the high quartile. Urbanization drives the development of urban industrialization, resulting in the generation of jobs which attract people and resources, with a resulting increase in population density; this is conducive to the effective allocation of energy resources and to the achievement of higher profits. The level of urban industrialization then rises, urban industrial carbon emission declines, and industrial carbon emission efficiency is thereby improved [
40].
Per capita GDP, government intervention, and science and technology input all have a positive effect on urban industrial carbon emission efficiency at the 1% significance level at different quantiles. The regression coefficient of science and technology input increases with the increase in quartiles, and the positive effect is gradually strengthened. In the stage of high-quality development, new green energy technology replaces the traditional high-pollution and high-energy-consumption production mode, the industrial structure is upgraded, urban industrial carbon emission efficiency reaches a high level, and the industrial development mode is more environmentally friendly. Science and technology input can provide practical methods which can help industry to achieve low-carbon and zero-carbon development at a technical level, and efficiently empower industrial green and low-carbon transformation, resulting in lower carbon emissions and improve industrial carbon emission efficiency [
41]. The improvement of industrial carbon emission efficiency in turn promotes the scientific and technological innovation and upgrading in the industry.
The regression coefficient of foreign direct investment is 0.0125. This does not pass the significance test, and indicates that foreign direct investment may have a certain positive effect on urban industrial carbon emission efficiency, but this linear relationship was not confirmed by the statistical model. The regression coefficient of industrial enterprise size is 0.0026. This also fails the significance test. It can be seen that the regression coefficient keeps changing with the increase in quartiles. This indicates that there is an inverted-U-shaped relationship between industrial enterprise size and urban industrial carbon emission efficiency. In the early stages of development, the rapid development of high-value-added industries requires more energy and resource consumption, leading to an increase in industrial carbon emissions and inhibiting industrial carbon emission efficiency. As industrial enterprises continue to expand, to become transformed and upgraded, a more advanced industrial structure emerges which can aid the reduction of carbon emissions and improve industrial carbon emission efficiency [
42]. In short, industrial transformation and upgrading is the key to achieving carbon emission reduction and improving industrial carbon emission efficiency in both high- and low-scoring cities [
43].
Figure 3.
Regression elastic coefficient distribution of influencing factors of industrial carbon emission efficiency.
Figure 3.
Regression elastic coefficient distribution of influencing factors of industrial carbon emission efficiency.
4. Discussion
In this study, we sought to assess the spatio-temporal evolution characteristics of industrial carbon emission efficiency in 270 cities in China from 2005 to 2020, thereby covering the period of rapid development and transformation and upgrading of China's industrial capacity, and providing historical information for reference in the future development of industrial transformation. The panel data used in this study do not cover all the cities in China, however, and so do not summarize the industrial carbon emission efficiency of every region in the country.
There is a significant inverted-U-shaped relationship between the digital economy and urban industrial carbon emission efficiency, with the digital economy first increasing energy consumption and carbon emissions in the early stages of development, and then reducing carbon emissions and improving industrial carbon emission efficiency in later stages. Therefore, it is necessary to accelerate the application and promotion of the digital economy as an emerging economic model, in order to promote the low-carbon transformation of urban industry, rationally optimize the layout of the urban industrial system, and guide the green transformation of the industrial structure, especially in urban agglomerations such as the Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Delta, which are characterized by high levels of industrial development. It is also necessary to consider the spatial spillover effect of the digital economy, utilize the advantages of network dissemination and information sharing made available by the digital economy, enhance its spatial contribution to industrial carbon productivity, strengthen the exchange and cooperation mechanism between the southeast region and the inland northwest region, and jointly explore the coordinated development route of the digital economy. Government intervention, science and technology input, foreign direct investment, and the development of the digital economy are also important in improving urban industrial carbon emission efficiency. The government should formulate effective environmental regulation strategies, reduce the proportion of high-pollution and high-energy-consumption industries in inefficient district cities, strengthen the catalytic effect of science and technology innovation on enterprise upgrading, and at the same time optimize foreign investment input to enhance its spatial contribution to industrial carbon productivity. The government should formulate effective environmental regulation strategies to reduce the proportion of high-pollution and high-energy-consumption industries in inefficient districts and cities, strengthen the catalytic effect of scientific and technological innovation on enterprise upgrading, and at the same time optimize the structure of foreign direct investment.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we used balanced panel data of 270 Chinese cities from 2005 to 2020 as a research object: (1) to show the spatio-temporal evolution pattern of urban industrial carbon emission efficiency; (2) to analyze the aggregation characteristics of industrial carbon emission efficiency in Chinese cities using the Global Moran's I statistic; and (3) to use the hierarchical regression model for panel data to explore the non-linear impact of the digital economy on the industrial carbon emission efficiency of cities. The main conclusions are as follows:
(1) During 2005–2020, the industrial carbon emission efficiency of Chinese cities exhibited an upward trend, with a spatial distribution pattern of high in the south and low in the north. Urban industrial carbon emission efficiency was mostly at a medium level in 2005 and 2010. On the whole, China's urban industrial carbon emission efficiency increased significantly from 2005 to 2020, and urban industrialization shifted from high-speed development to high-quality development.
(2) The spatial autocorrelation of industrial carbon emission efficiency in Chinese cities is significant, the correlation is increasing and stabilizing, and the pattern of spatial agglomeration is relatively fixed. The center of gravity of high-high agglomeration cities has moved from Gansu to Shaanxi, and the number of such cities has increased. At the beginning of the study period, low-low agglomeration cities were distributed in Shandong Peninsula urban agglomeration, Yangtze River Delta region and Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, but were concentrated in Shanxi, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning and other provinces by the end of the study period. In addition, the total number of low-low agglomeration cities declined.
(3) There is a significant inverted-U-shaped relationship between the digital economy and urban industrial carbon emission efficiency. The digital economy increases carbon emissions and inhibits industrial carbon emission efficiency at the early stage of development, and inhibits carbon emissions at the mature stage of development. Urbanization has a significant negative effect on industrial carbon emission efficiency; per capita GDP, government intervention, and science and technology input also have significant negative effects. The positive effects of per capita GDP, government intervention, and science and technology input on urban industrial carbon emission efficiency are significant at the 1% level in different quartiles, and the inverse-U-shaped relationship between industrial enterprise size and urban industrial carbon emission efficiency is observed, indicating that industrial transformation and upgrading is the key to realize carbon emission reduction and improve industrial carbon emission efficiency in cities in the high and low quartiles.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.J. and S.L.; methodology, Z.L.; software, X.L.; validation, L.J., S.L. and C.C.; formal analysis, L.J.; investigation, Z.L. and X.L.; resources, C.C.; data curation, Z.L.; writing—original draft preparation, L.J. and S.L.; writing—review and editing, C.C. and X.L.; visualization, C.C.; supervision, Z.L.; project administration, Z.L.; funding acquisition, C.C. and X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by "Humanities and Social Sciences Project funded by the Ministry of Education" , grant number”20YJCZH087”, "National Natural Science Foundation" ,grant number” 42202280”, "Basic Scientific Research Funds of China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing)—Top Innovative Talents Cultivation Fund for Doctoral Postgraduates" ,grant number” BBJ2023020”, and" Special Fund for Basic Scientific Research Funds of Central Universities and University Student Innovation Training Project of China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing)" ,grant number”202202051”.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
All data included in this study are available upon request by contacting the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Recent Progress and Emerging Strategies for Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality in China. Greenhouse Gases 2023, ghg.2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Bu, F.; Razzaq, A.; Ge, W.; Peng, J.; Yang, X.; Xu, Y. When Will China’s Industrial Carbon Emissions Peak? Evidence from Machine Learning. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2023, 30, 57960–57974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Tang, C.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Hao, Y. The Emerging Driving Force of Energy Consumption in China: Does Digital Economy Development Matter? Energy Policy 2022, 165, 112997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, P.-F.; Zeng, M. Assessing the Impact of Digital Economy on Green Development Efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Energy Economics 2022, 112, 106127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.Y.; Chen, L.; Ren, J.J. Research on the Carbon Reduction of digital Economy Development—With a Discussion on Moderating Effect of Heterogeneous Environmental Regulation. Resources & Industries 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J. The Dynamic Impact of Digital Economy on Carbon Emission Reduction: Evidence City-Level Empirical Data in China. Journal of Cleaner Production 2022, 351, 131570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Ding, Y.; Niu, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, G. Economic Growth, Energy Conservation and Emissions Reduction: A Comparative Analysis Based on Panel Data for 8 Asian-Pacific Countries. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 2121–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuai, X.; Feng, J. High Resolution Carbon Emissions Simulation and Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis Based on Big Data in Nanjing City, China. Science of The Total Environment 2019, 686, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, J.B. CO2 Emissions, Energy Consumption, and Output in France. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 4772–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, B.; Yin, S. Is Technological Innovation Effective for Energy Saving and Carbon Emissions Reduction? Evidence From China. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 83524–83537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Hu, H.; Xie, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Shen, X. An Empirical Relationship between Urbanization and Carbon Emissions in an Ecological Civilization Demonstration Area of China Based on the STIRPAT Model. Environ Dev Sustain 2023, 25, 2465–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Su, Z.; Chiao, C. Carbon Emissions Trading Policy, Carbon Finance, and Carbon Emissions Reduction: Evidence from a Quasi-Natural Experiment in China. Econ Change Restruct 2022, 55, 1445–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Feng, S.; Chen, K.; Li, M. Impact of Digital Finance on Regional Carbon Emissions: An Empirical Study of Sustainable Development in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Yue, S.; Chen, H. Carbon Emission Efficiency of China’s Industry Sectors: From the Perspective of Embodied Carbon Emissions. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 283, 124655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Kao, C.H. Efficient Energy-Saving Targets for APEC Economies. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wei, Z.; Ge, Q.; Guo, Q. Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Carbon Emission Efficiency in Chinese Cities. Frontiers in Environmental Science 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Meng, X. Carbon Emission Scenario Prediction and Peak Path Selection in China. Energies 2023, 16, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.S.; Sun, S. The enabling effect of digital economy on urban industrial carbon productivity in China. Resources Science 2022, 44, 2399–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Mu, R.; Zhan, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J. Digital Economy, Energy Efficiency, and Carbon Emissions: Evidence from Provincial Panel Data in China. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 852, 158403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Jiang, T. Does the Development of the Digital Economy Improve Carbon Emission Efficiency? Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Zhou, J. Digital Economy and Carbon Emission Performance: Evidence at China’s City Level. Energy Policy 2022, 165, 112927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.Y.; Zhang, Y. The Impact of Digital Economy on Industrial Carbon Emission Efficiency: Evidence from Chinese Provincial Data. Mathematical Problems in Engineering 2022, 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.D.; Qi, M.J. Is There an Inverted "U" Shaped Relationship Between Carbon Emissions and Economic Growth in Tianjin: A Re-Examination Based on the Topic Decoupling Theory. Tianjin Economy 2017, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Li, R. Could the Digital Economy Increase Renewable Energy and Reduce Carbon Emissions? Empirical Research on EKC in 67 Countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, P.A.P. The Interpretation of Statistical Maps. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological) 1948, 10, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, X.; Huo, L. Digital Economy, Spatial Spillover and Industrial Green Innovation Efficiency: Empirical Evidence from China. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Fu, L. Spatial Imbalance, Dynamic Evolution and Convergence of the Digital Economy: Analysis Based on Panel Data of 278 Cities in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, D. The Impact Mechanism of China’s Carbon Emission Trading Policy on Industrial Energy Efficiency under Multiple Innovation Approaches. Frontiers in Energy Research 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Ma, D.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, N.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; An, B.; Xiao, Y. Spatiotemporal Differentiation of Carbon Emission Efficiency and Influencing Factors: From the Perspective of 136 Countries. Science of The Total Environment 2023, 879, 163032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, S.K. Digital economy, entrepreneurship, and high-quality economic development: Empirical evidence from urban China. Journal of Management World 2020, 36, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jiang, W.; Tang, Z.; Han, M. Pathways to Peak Carbon Emissions in China by 2030: An Analysis in Relation to the Economic Growth Rate. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.J.; Chen, J.; Fan, T.Z.; Lv, Y.Q. The Impact of Digital Economy Development on Carbon Emissions - A Panel Data Analysis Based on 278 Prefecture-Level Cities. South China Finance 2022, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-L.; Zhao, B.; Ding, L.-L.; Miao, Z. Government Intervention, Market Development, and Pollution Emission Efficiency: Evidence from China. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 757, 143738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.C.; Caetano, R. The Impact of Foreign Direct Investment on Emission Reduction Targets: Evidence from High- and Middle-Income Countries. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics 2020, 55, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z. Characteristics Analysis and Factor Decomposition Based on the Regional Difference Changes in China’s CO2 Emission. Journal of Natural Resources 2014, 29, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Lin, X.Q.; Wang, D.; Cui, W.J. Spatial-temporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of industrial carbon emission efficiency in eastern coastal areas of China. Journal of Xi'an University of Technology 2022, 38, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Xie, Z.H.; Wang, Z.H. The spatiotemporal pattern evolution and influencing factors of CO2 emissions at the county level of China. Acta Geographica Sinica 2021, 76, 3103–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Elder, M. Major developments in China’s national air pollution policies in the early 12th five-year plan period. Institute for global environmental strategies, Policy report no. 2013-02, Kanagawa, Japan.
- Liu, Y.F.; Shi, Q.; Liu, C. Empirical Study on Regional Industrial Carbon Emissions —Performance and Its Factors in Yangtze Delta of China. Journal of Hunan University of Commerce 2013, 20, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.S.; Zhou, L. The Mechanism and Effect of Urbanization and Real Estate Investment on Carbon Emissions in China. Scientia Geographica Sinica 2019, 39, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 4Sun, Z.R.; Fan, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, H.C. Structural Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Spatial Correlation Network of Green Science and Technology Innovation Efficiency in China. Economic Geography 2022, 42, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.H. A Study on the Relationship Among R&D Input,Upgrading Industrial Structure and Carbon Emission. Journal of Industrial Technological Economics 2019, 38, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.W.; Zhao, R.Q.; Huang, X.J.; Chen, Z.G. Research on Carbon Emission Estimation and Factor Decomposition of China from 1995 to 2005. Journal of Natural Resources 2010, 25, 1284–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).