1. Introduction
Asian dust (AD) is composed of mineral aerosols derived from desert areas, such as the Taklimakan Desert and the Gobi Deserts in Mongolia and Northern China Desert [
1]. Although AD is a natural phenomenon, it can affect air quality, atmospheric visibility, and human health negatively [
2]. AD occurs most frequently and has the widest impact area during East Asian winter monsoon periods (from November to May of next year) and then be transported to northern China, Korea, and Japan, where it causes significant atmospheric pollution and health impacts [
3,
4,
56].
During an AD outbreak, not only natural aerosols but also anthropogenic pollutants can be transported downwind [
7,
8,
9,
10]. Among the anthropogenic pollutants, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) have drawn great attention due to their substantial carcinogenicity and mutagenicity [
11,
12]. PAHs principally originate from incomplete combustion of biomass or fossil fuels [
13]. The East Asia, especially northern China, always has severe PAHs emissions due to increasing utilization of fossil fuels and biomass fuels. Through investigation at the remote back-ground site in Japan (Kanazawa University Wajima Air Monitoring Station: KUWAMS), our previous researches indicated that PAHs from the East Asian continent can participate in long-range transport of air masses, which leads to enhanced pollutant concentrations and health risks at the affected site [
11,
12,
13,
14].
In addition, some reports suggest that AD not only acts as a carrier of pollutants but also is believed to expedite atmospheric chemical reactions due to the exist of transition metal ions and oxides [
15,
16]. However, our previous laboratory simulations showed that natural AD particles had a weak adsorption capacity for PAHs and did not promote the photodegradation of PAHs [
17]. Furthermore, a pilot comparative investigation of the background site in Japan indicate that the arrival of AD does not necessarily lead to an increase in long-range PAHs concentrations [
14]. Therefore, there has been no systematic study of the association between AD and atmospheric pollutants up to now, especially for carcinogenic PAHs with strong reactivity in the atmosphere during AD events. A systematic observation of combined pollution from ADs and air pollutants over long distances will play a critical role in understanding the effect of long-range transportation on the downstream environment.
In this study, the long-term observation of AD events and total suspended particulate (TSP) were carried out at KUWAMS, a background site in Japan, during the East Asian winter monsoon period from 2010 to 2021. The purposes were to evaluate the long-term variation of AD frequency and to compare the characteristics and source of particulate pollutants (TSP and PAHs) during AD events.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TSP sampling
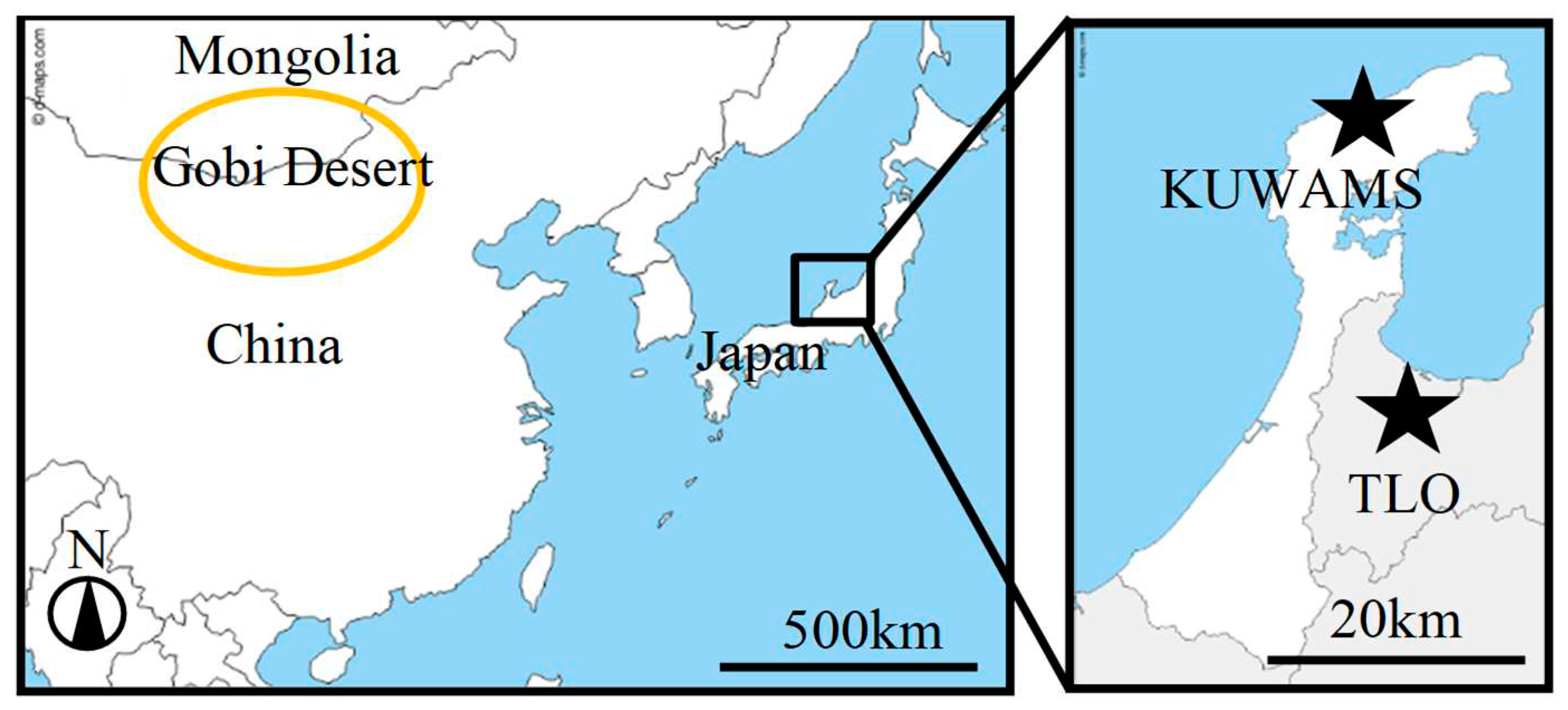
TSP sampling was conducted at KUWAMS (
Figure 1, Nishifutamatamachi, Wajima City, Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan, 37.4°N, 136.9°E; 60 m above sea level), which is located on the Noto Peninsula between western Japan and mainland China, 2.1 km from the coastline; it is a background site without any dominant anthropogenic emission source of air pollutants [
18,
19,
20,
21].
The TSP sampling work started at 9:00 am by high-volume air sampler (AH-600, Sibata Sci. Tech. Ltd., Saitama, Japan) with a quartz fiber filter (8 inch × 10 inch, 2500QAT- UP, Pallflex Products, Putnam, CT, USA) and a flow rate of 700 L/min. The filters were change weekly from January 01, 2010, to December 25, 2021. After sampling, the filters were dried in a desiccator, kept in the dark, weighed and kept in the refrigerator (-20°C) until use.
2.2. Asian dust period
The periods of the AD events were estimated by lidar images based on the Toyama Light Detection and Ranging Observatory database (TLO, 36.70°N, 137.10°E) (
Figure 1) [
22]. The straight-line distance between TLO and KUWAMS is 80.13 km (Southeast). LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a device that emits laser beams into the sky, measures and analyzes scattered light such as particles, and observes the vertical distribution of particles floating in the sky. The aerosol was identified by the depolarization ratio at 532 nm. Through lidar images of depolarization ratio, we can determine whether the scatterers are dust or spherical aerosols (mostly atmospheric pollutants), water clouds and ice clouds. As shown in
Figure S1, non-spherical particles such as dust storms show large values (above 0.1: Green color in lidar images), ice clouds have higher depolarization ratio, and water clouds have lower values, while the value of spherical aerosols, mostly atmospheric pollutants, are smaller (below 0.1) and exhibits in the blue color in images. In this study, we observed 54 AD events from 2010 to 2021, during the East Asian winter monsoon period.
2.3. Backward trajectory cluster analysis
The Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory model (HYSPLIT-4, Windows-based version, NOAA Air Resources Laboratory) was used to analyse the transport route of the air mass during the AD periods. The global data assimilation system (GDAS 1°) of days from 2010 to 2021 provided by the National Centres for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) was used. Seventy-two hours backward trajectories of arrival at KUWAMS (37.4°N, 136.9°E), at arrival heights of 1500 m during each AD were applied. According to HYSPLIT User's Guide, a total of 634 observed trajectories were clustered into 3 categories [
23].
2.4. PAHs analysis
Nine kinds of target PAHs (fluoranthene (FR), pyrene (Pyr), benz[a]anthracene (BaA), chrysene (Chr), benzo[b]fluoranthene (BbF), benzo[k]fluoranthene (BkF), benzo[a]pyrene (BaP), benzo[ghi]perylene (BgPe), and indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene (IDP)) were determined in each TSP sample [7, 8].
The methods of pretreatment, analysis and quality control were consistent with our previous study [
14]. Each filter was cut into small pieces. Then placed them in a flask and added with internal standards (pyrene-
d10 (Pyr-
d10), benzo[
a]pyrene-
d12 (BaP-
d12)). Targe PAHs were extracted via ultrasonic extraction with benzene/ethanol (3:1, v/v) which performed for twice. Then washed the extract with sodium hydroxide and sulfuric acid solutions, and twice with ultrapure water. After washing, 100 µL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was added to the solution. After concentrated by rotation evaporator, the extract was dissolved to 1.0 mL by acetonitrile. The organic solution was filter by 0.45 µm HLC-DISK membrane (Kanto Chemical Co., Tokyo, Japan). Twenty µL solution was injected into a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) system (LC-20A series, Shimadzu Inc., Kyoto, Japan) for quantitative determination.
2.5. Quality assurance and quality control
Particulate-bound PAHs were collected by quartz fiber filters. Before and after sampling, the filters were placed and weighted at stable conditions (temperature (21.5 ± 1.5 °C) and relative humidity (50 ± 5%)). Blank filters were used to measure the effects of background pollution, and no target compounds were found during the transport of blank samples. Analyze methods were confirmed by injecting PAHs standard solution into analysis system. The calibration curves of all PAHs had good linearity (r > 0.995). The relative standard deviations (
n = 3) of all PAHs were less than 5%. The internal standards recoveries of all samples ranged from 87% to 131%. The limit of determination is shown in
Table S1.
3. Results and discussions
3.1. Source of ADs during the sample period
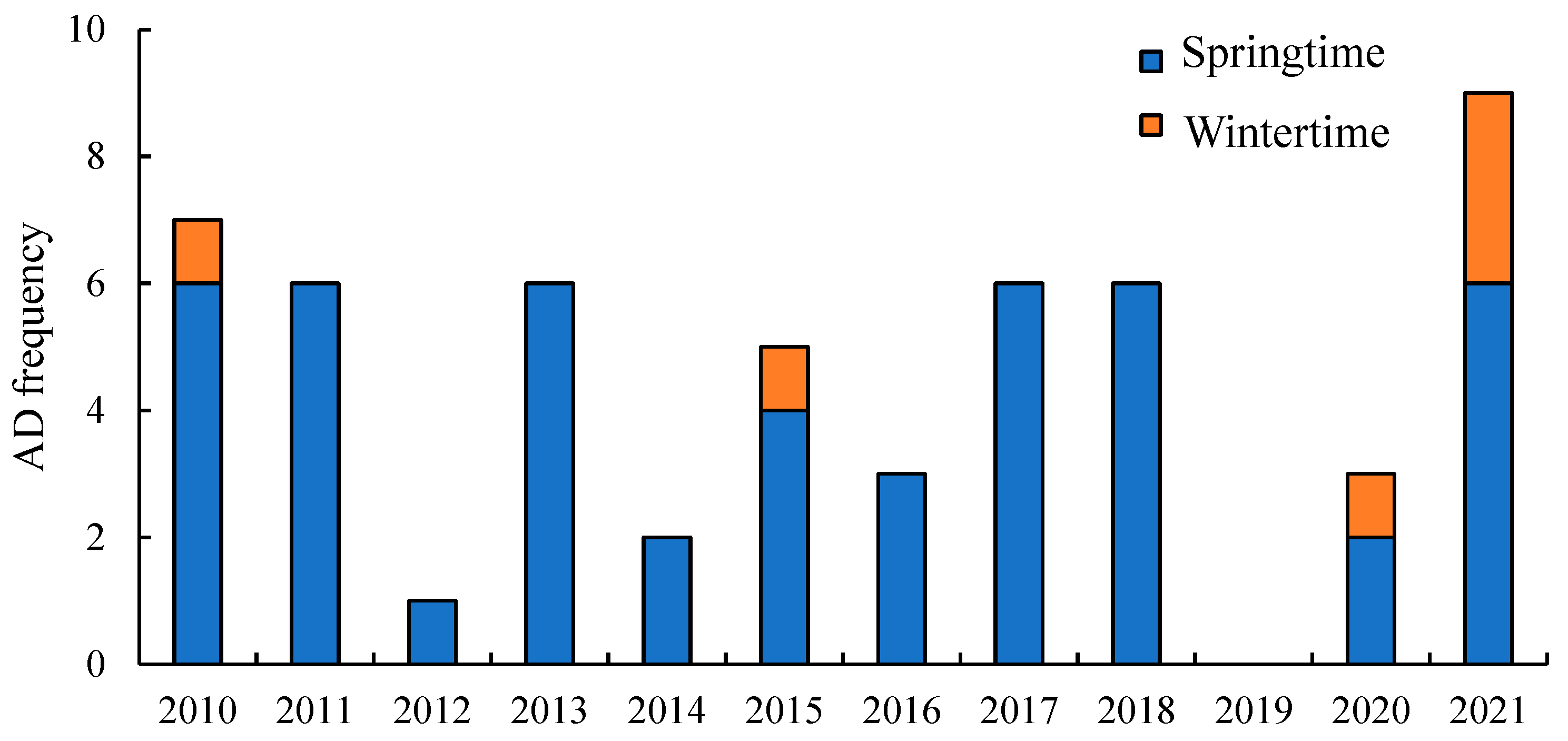
Figure 2 shows the frequency variation of AD events observed at KUWAMS in the East Asian winter monsoon period from 2010 to 2021. Each AD event was identified by lidar images from TLO station, and the AD event is regarded as one event if the dust phenomenon continuously lasted for consecutive days. The frequency of AD events from 2010 to 2021 was 4.9 times per year. The AD events were mostly happened in the springtime (from March to May), with a total of 48 times, while 6 AD events were observed in wintertime (from November to February), which was caused by the strong cyclone activity around the dust source regions in the springtime, which generates strong air convention and provides the dynamic conditions for the development of dust storms [
24].
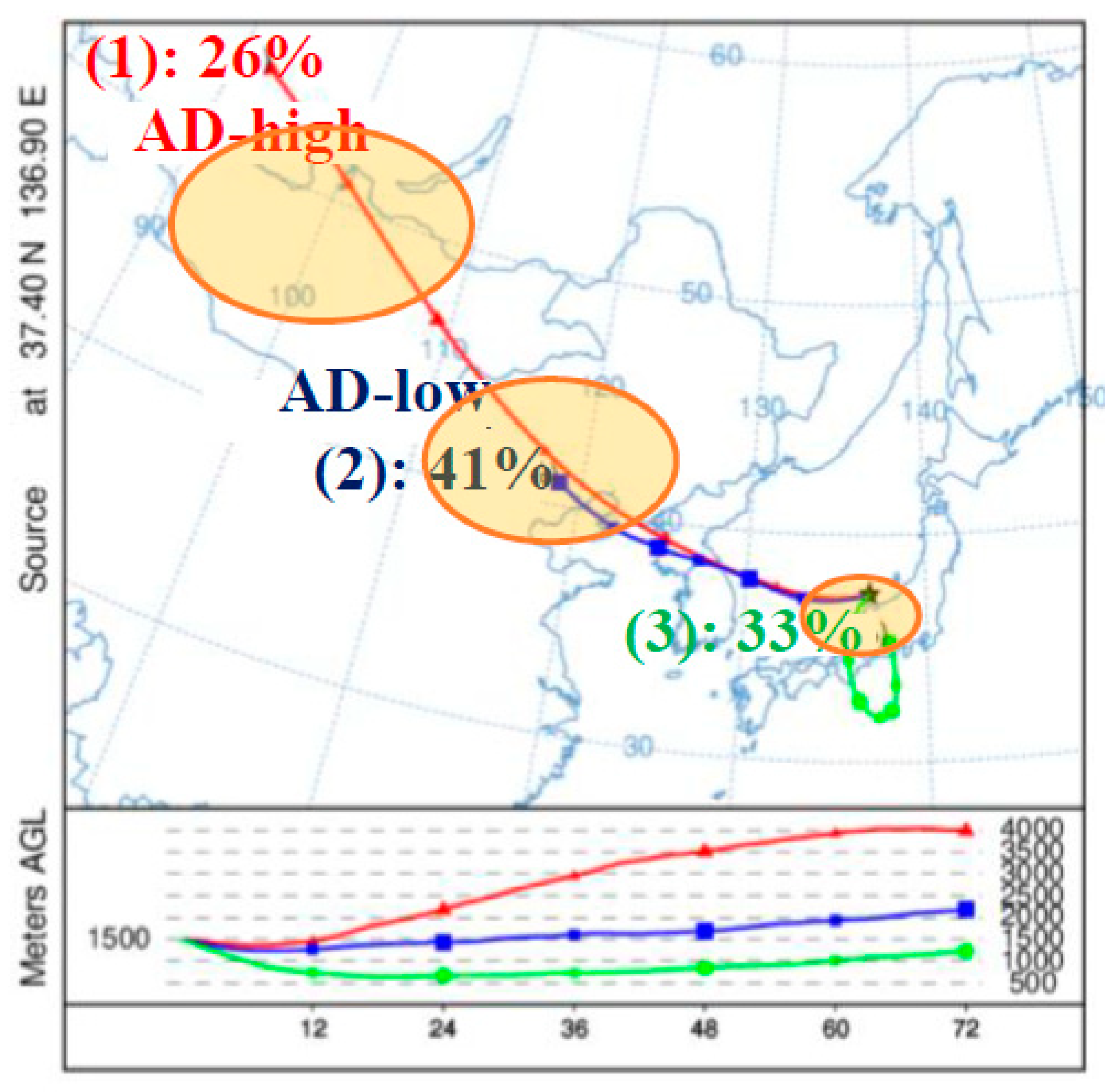
As mentioned above in 2.3, the backward trajectory cluster analysis was carried out to figure out the source of ADs, the transport pathway of each cluster will be explained dentally in this part. As shown in
Figure 3, the air masses that reach an altitude of 1500m above KUWAMS were divided into three categories. The category 1, which accounted for 26% of the total, was that the air mass over the Mongolia with the higher average transported height (around 4000 m) and faster transported speed (The speed calculated by linear distance of the trajectory was approximately 54.8 km/h), which was identified as AD-high for further discussion. The category 2 which accounted for 41% of the total was passed over northeast China at the lower average height (around 2500 m) with slower transported speed (The speed calculated by linear distance of the trajectory was around 21.5km/h) and was identified as AD-low. The category 3, accounting for 33%, showed the effect of local effects during the ADs, as the air mass came from Japan with the height lower than 1000 m, around the planet boundary layer showed in
Figure S2. Because the duration of each AD event ranged from 1 to 4 days, which was less than the sampling period (7 days) in this study (
Figure S1). Therefore, category 3 reflected that the transport pathway of air mass during non-AD period was included in sampling period. Via referring to lidar observation images at TLO and Sainshand during the sampling period (
Figure S1), prior to the ADs observed in TLO, strong ADs were already outbroken in Sainshand at an altitude of 5000 m from the ground generally, with the depolarization ratio (
δ532) ranged from 0.2 to 0.3. Through combining the results of backward trajectory cluster analysis and lidar observation, the sources of ADs in this study were considered as the Gobi Desert region in Mongolia (AD-high) and northeastern China (AD-low), respectively.
3.2. TSP concentration
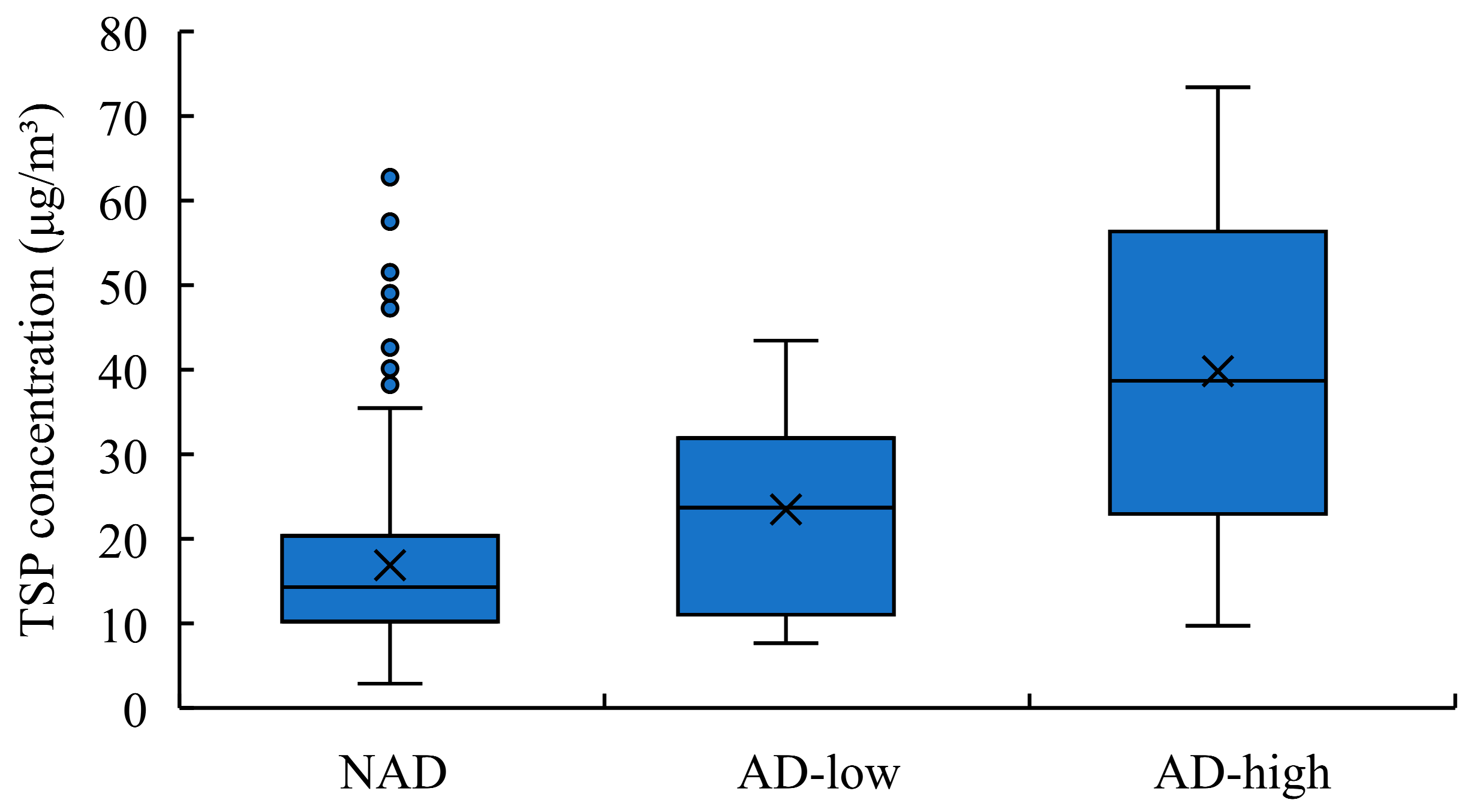
Figure 4 compared the TSP concentration at KUWAMS between different AD types (AD-high and AD-low) and the period of the ADs were not observed (non-AD: NAD). As shown in
Figure 4, TSP concentration was highest in AD-high (39.8 ± 19.5 μg/m³), followed by AD-low (23.5 ± 10.5 μg/m³) and NAD (16.9 ± 9.8 μg/m³). As the result of one-way ANOVA, TSP concentrations showed extremely significant difference between ADs (including AD-high and AD-low) and NADs (
p < 0.001); while there was also significant difference between AD-high and AD-low as the
p value was 0.003, which was consistent with previous studies [
8,
25]. This indicated that the higher transported altitude and wind speed, such as AD-high, had a more notable effect of TSP concentration enhancement, while, as for AD-low, the lower altitude and slower wind speed caused that AD particles tended to be deposited before the air mass reached Japan.
3.3. PAHs concentration, composition and source
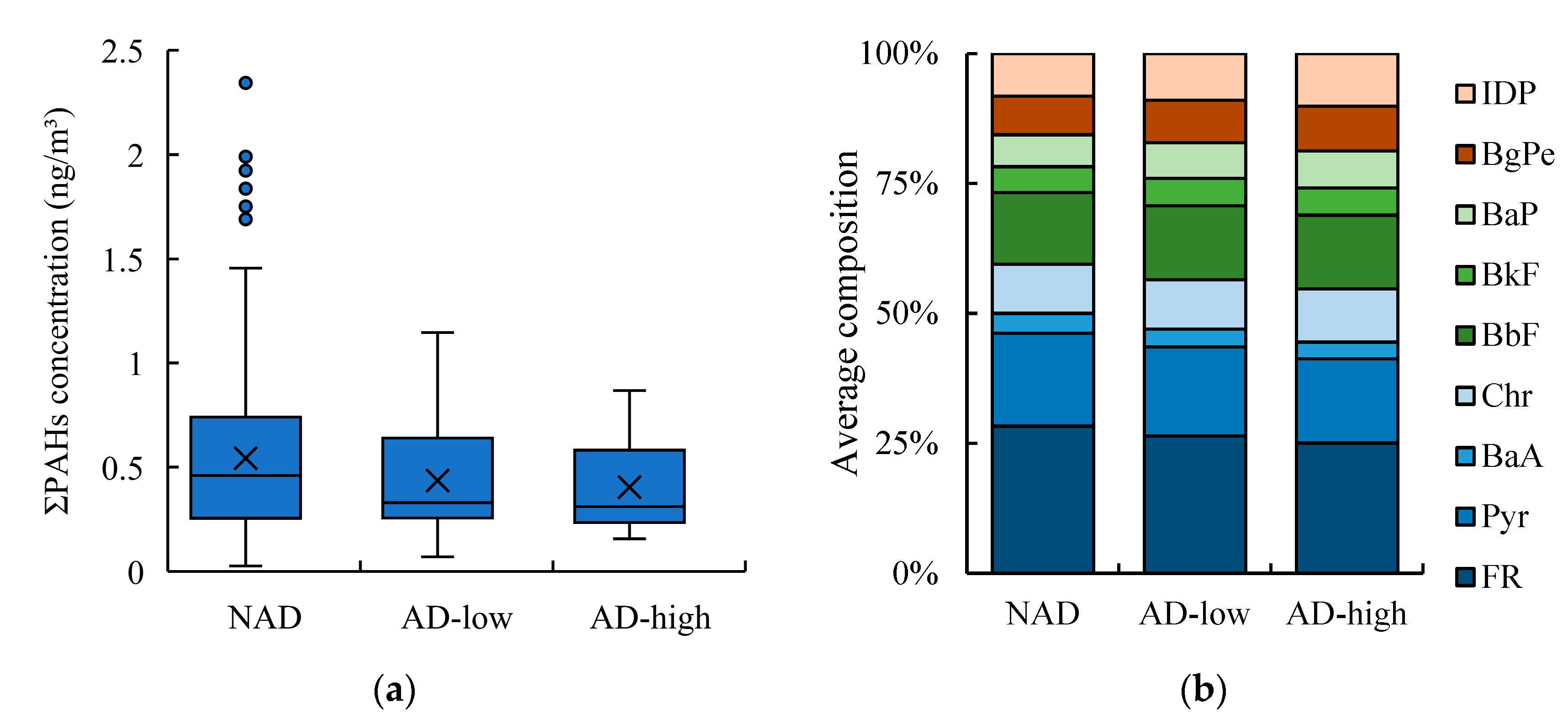
Figure 5(a) shows ΣPAHs (ΣPAHs = Flu + Pyr + BaA + Chr + BbF + BkF + BaP + BgPe+ IDP) concentrations variation in NAD, AD- low and AD- high of KUWAMS during the East Asian winter monsoon period from 2010 to 2021. The average PAHs concentration was the highest in NAD (543 ± 374 pg/m³), followed by AD-low (436 ± 266 pg/m³) and AD-high (411 ± 215 pg/m³). Be different from TSP concentration variation, PAHs concentration had no significant difference between NAD and ADs (including AD-high and AD-low) with the
p value was 0.500; and between AD-high and AD-low (
p = 0.687). The PAHs concentration also showed weak correlation with TSP (
r = 0.104).
Figure 5(b) show the composition of individual PAHs in total PAHs. Among each PAHs, FR, Pyr and BbF were predominant, with the average composition were 26.7 ± 4.29%, 17.6 ± 2.25% and 13.9 ± 2.02%, respectively. Among them, 4-ring PAHs (FR, Pyr, BaA, and Chr) had the predominant contribution in the whole period, with the average concentration was 0.313 ± 0.234 pg/m³, followed by 5-ring PAHs (total of BbF, BkF and BaP: 0.133 ± 0.093 pg/m³) and 6-ring PAHs (total of IDP and BgPe: 0.084 ± 0.052 pg/m³). As for different aerosol type, the contribution of 4-ring PAHs showed a reduce trend in NAD (57.7 ± 6.1%), AD-low (55.9 ± 2.7%) and AD-high (55.0 ± 4.5%). On the contrary, the contribution of 5-ring PAHs and 6-ring PAHs showed an increasing trend (5-ring PAHs: 25.4 ± 3.5%, 26.4 ± 1.6% and 26.6 ± 2.9% in NAD, AD-low and AD-high; 6-ring PAHs: 16.9 ± 3.8%, 17.7 ± 2.7% and 18.4 ± 3.2% in NAD, AD-low and AD-high). However, this variation didn’t show significant difference neither between NAD and ADs (including AD-low and AD-high; 4-ring PAHs:
p = 0.279; 5-ring PAHs:
p = 0.853; 6-ring PAHs:
p = 0.089), nor between AD-high and AD-low (4-ring PAHs:
p = 0.468; 5-ring PAHs:
p = 0.754; 6-ring PAHs:
p = 0.508).
These results illustrated that the occurrence and different type of ADs had nonsignificant on PAHs concentration and composition variation. This difference probably was contributed by the low accumulation of PAHs on AD particles. As previous laboratory studies have pointed out that the active groups on the AD particle surfaces tend to accumulate polar components, such as inorganic gases or water-soluble inorganic ions, while had weak adsorption to nonpolar PAHs and the adsorption of water vapor to AD particles further inhibit the accumulation of PAHs [
26,
27,
28,
29]. The kinetic model study also had proved that because of the extremely slow absorption rate of PAHs [
30].
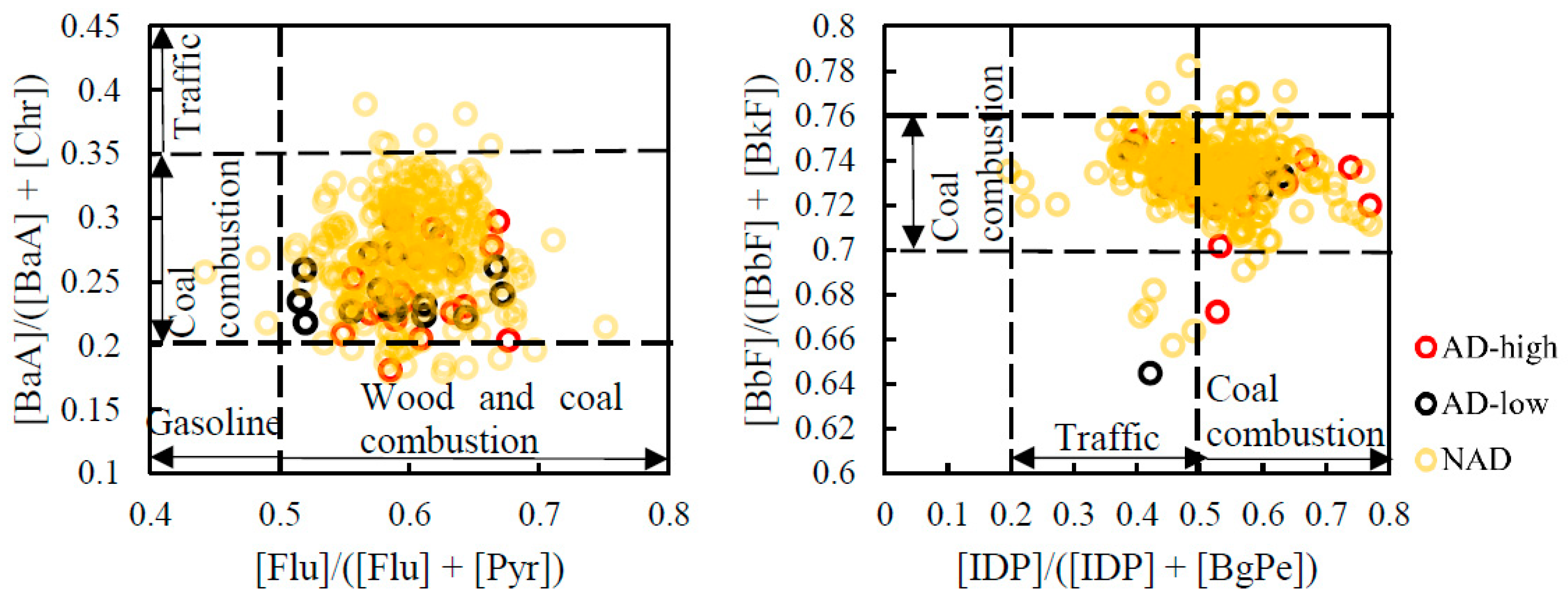
In this study, several PAHs isomer ratio ([Flu]/([Flu] + [Pyr]), [BaA]/([BaA] + [Chr]), [IDP]/([IDP] + [BgPe]) and [BbF]/([BbF] + [BkF])) were applied for identifying the major sources of PAHs qualifiedly. Related studies have reported that 4-ring PAHs were iconic species released from coal and biomass combustion; and most 5,6-ring PAHs were generated from vehicle emission. The result of diagnostic ratio in NAD, AD-low and AD-high were showed in
Figure 6. The distribution range of diagnostic ratio data of NAD, AD-low and AD-high was similar ( [FR]/ ([FR] + [Pyr]) (NAD: 0.45 - 0.69; AD-low: 0.52 - 0.67; AD-high: 0.56 - 0.67), [BaA]/ ([BaA] + [Chr]) (NAD: 0.18 - 0.39; AD-low: 0.22 - 0.30; AD-high: 0.22 - 0.30), [IDP]/ ([IDP] + [BgPe]) (NAD: 0.20 - 0.72; AD-low: 0.45 - 0.63; AD-high: 0.44 - 0.67), [BbF]/ ([BbF] + [BkF]) (NAD: 0.70 - 0.77; AD-low: 0.48 - 0.73; AD-high: 0.72 - 0.75) and there was no significant difference in either ratio (
p > 0.05). This result suggests that whether AD occurred or not and the types of AD will not affect the variation of PAHs emission source. Through comparing the ratio ranges among emissions, traffic emission, coal and biomass combustion were the main source of PAHs [
31,
32,
33,
34]. As shown in
Figure 6, coal combustion showed more notable contribution among PAHs emission sources, suggesting the overwhelm superiority of coal combustion on the PAHs concentrations in the East Asian winter monsoon period, which was consistent with previous study in KUWAMS, China and differed from the results in Korea where mainly contributed by vehicle emission [
9,
35,
36]. Combining with the result of backward trajectory analysis, we speculate that PAHs at KUWAMS were predominantly contribute by the emission in northern China, whether the AD happened or not.
3.4. Health risks of PAHs
PAHs have been well known for their serious carcinogenicity and mutagenicity [
37,
38,
39]. To evaluate the possible health risk of PAHs under the effects of AD, the toxic equivalent concentrations relative to BaP (TEQ) of each PAH and the inhalation lifetime cancer risk (ILCR) were calculated, as shown in the following equations [
40,
41]:
The TEQ of individual PAH was evaluated as BaP equivalent concentration (BaP
eq) since BaP is widely used as risk assessment for total PAHs and contribute to 40% - 80% cancer risk of PAHs (
Figure 7,
Table S2). As a result, the average TEQ of total PAHs in NAD, AD-low and AD-high were 0.05 ± 0.03 pg/m
3, 0.04 ± 0.03 pg/m
3, 0.04 ± 0.03 pg/m
3, respectively. The TEQ of total PAHs had nonsignificant variation in NAD, AD-low and AD-high (
p = 0.471) and all of them were less than the European Union standard (1 ng/m
3) (
Figure 7) [
42]. As for individual PAH, attributing to the similar PAH composition in NAD, AD-low and AD-high, the TEQ of each PAH was similar in each period. Except for BaP, the TEQ of IDP, BbF, BkF and BaA occupied for more than 30% in total PAHs, which suggest that the PAHs from traffic emission posted a higher carcinogenic risk to human health (
Figure S3). In addition, as the result of PAHs concentration reduction, the TEQ of total PAHs showed a similar decreasing trend in the ADs from 2010 to 2021, illustrating a reduction in PAHs health effects (
Figure S4).
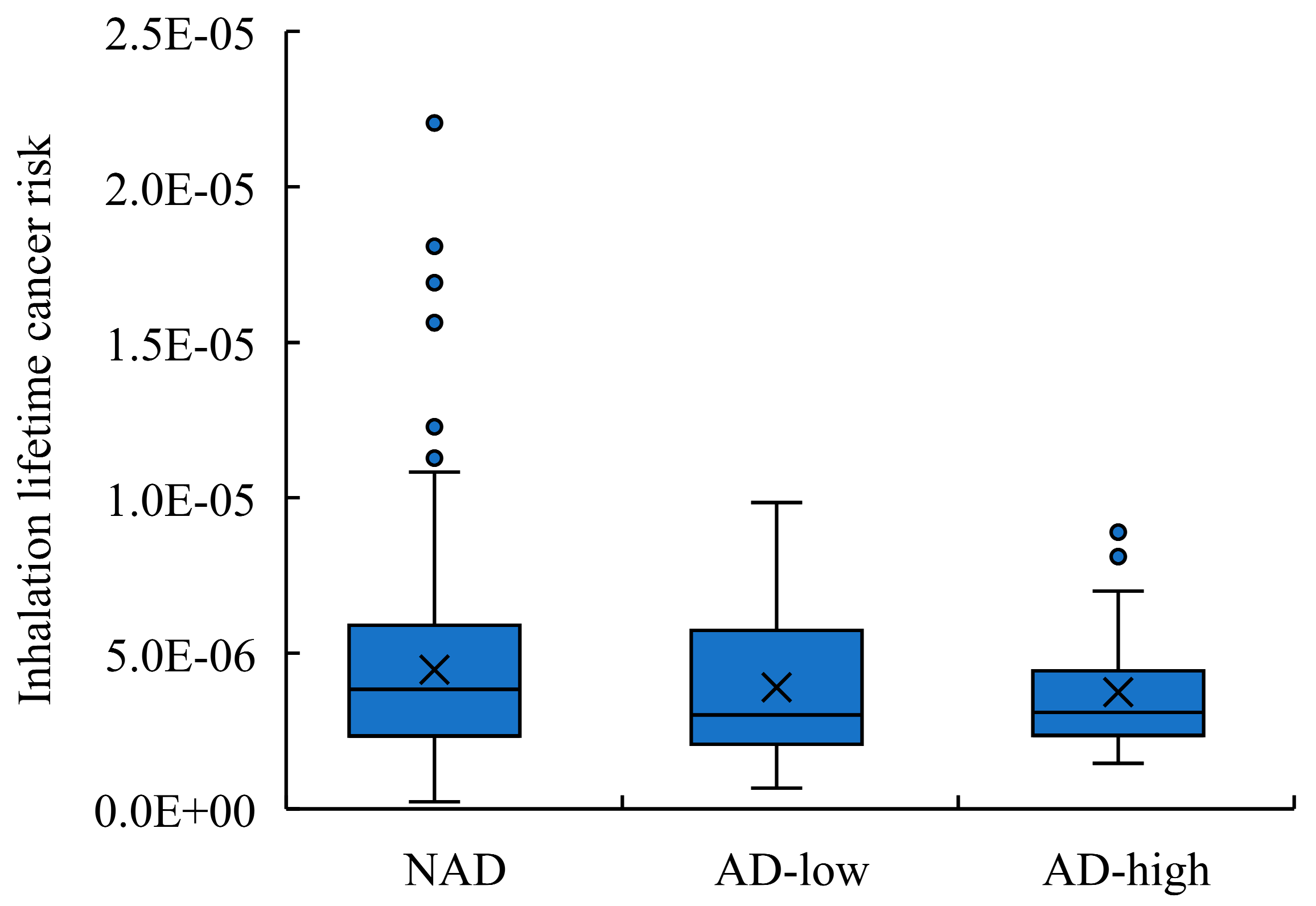
The ILCR value was calculated by multiplying the BaP
eq concentration by the unit cancer risk originating from the BaP (UR
BaP) [
40]. In this study, the value of UR
BaP was referred to the epidemiological data focused on coke oven workers (UR
BaP: 8.7 × 10
-5 ng/m
3) from World Health Organization [
36]. As a result, the ILCR in NAD, AD-low and AD-high were 3.01 × 10
-6, 2.28 × 10
-6, 2.23 × 10
-6 ng/m
3, respectively. The similar level of the ILCR in each periods suggests that AD had no significant effect on health risks caused by PAHs. Be similar with the variation of TEQ, the ILCR also showed a downward trend in ADs from 2010 to 2021 (
Figure S3). However, the ILCR were all exceed the acceptable level (10
-6) reported by the US EPA, indicating that the negative health effects of PAHs were noteworthy [
43].
4. Conclusions
In this study, TSP was collected at KUWAMS, a background site in Japan, during East Asian winter monsoon from January 01, 2010, to December 25, 2021. Nine kinds of PAHs were analyzed in each TSP sample. And AD frequency was monitored through the lidar images from Toyama lidar observation. As a result, from 2010 to 2021, the frequency of AD in Japan was at stable level. Under the effect of enhanced East Asian monsoon, the AD particles were able to be long-range transported from desert region under different transport pathways and resulted in a great increase in particulate matter concentration at KUWAMS in the AD periods. In contrast, the concentration and composition variations for PAHs differed from that for TSPs, indicating that AD does not necessarily lead to an effect on the change in PAHs characteristic. Based on the backwards trajectory analysis, the different concentration trends for PAHs and particulates were related to the heights of long-range air mass transport during the AD events: PAHs were affected by the air mass transported at lower altitude and generated from coal and traffic emission in northeastern China; particulate matters were under effect of air mass at higher altitude from the Gobi Desert. In addition, the ILCR values during the non-AD and AD periods remained similar and exceed the acceptable limit, indicating that the air quality in Japan still required attention.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure. S1. Lidar observation of Volume Depolarization Ratio (532 nm) during AD events from 2010 to 2021 at Sainshand (44.5 °N, 110.8 °E) and Toyama (36.70°N, 137.10°E). The green color in lidar observation images shows the dust aerosol, the blue color represents for spherical aerosol and the red color represents for ice cloud. Each AD event is marked in black block. The absence of the lidar observation images at Sainshand during 2013 (03, 04), 2014 (05), 2015 (02, 03, 04), 2021 (03, 04, 05) here is due to the lack of data in the official website. Red box represents for AD-high events, blue box represents for AD-low events and black box represents for AD events observed in Sainshand.; Figure S2. The height of planetary boundary layer during AD occurrence period from 2010 to 2021 over the Toyama area (longitude: 36 < x < 38, latitude: 136 < y < 137).; Figure S3. The proportion of each PAH BaPeq in different types of AD during long-term observation from 2010 to 2021.; Figure S4. ΣBaPeq and ILCR in AD events and AD frequency in the East Asian winter monsoon period from 2010 to 2021.; Table S1. LOD and LOQ of target PAHs.; Table S2. TEF of target PAHs.
Author Contributions
N.T. designed the sampling work, PAHs analyses for particulate matters; N.T., P.C.B., L.L.Z., H.Z., X.Z., and Y.W collected samples and conducted monitoring work; Y.W. analyzed the PAHs; P.C.B. performed statistical analysis; N.T. gave recommend to the paper.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Sasakawa Scientific Research Grant (2023-3026) from The Japan Science Society; the CHOZEN Project of Kanazawa University, Japan; and the cooperative research programs of Institute of Nature and Environmental Technology, Kanazawa University, Japan. We thank the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Air Resources Laboratory for providing the HYSPLIT 4 model (window-based). The authors acknowledge the Institute of Nature and Environmental Technology, Kanazawa University for the provision of the scientific data used in this publication (
https://ki-net.db.kanazawa-u.ac.jp/).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sullivan, R. C.; Guazzotti, S. A.; Sodeman, D. A.; Prather, K. A. Direct Observations of the Atmospheric Processing of Asian Mineral Dust. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics 2007, 7(5), 1213–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashima, S.; Yorifuji, T.; Bae, S.; Honda, Y.; Lim, Y.-H.; Hong, Y.-C. Asian Dust Effect on Cause-Specific Mortality in Five Cities across South Korea and Japan. Atmospheric Environment 2016, 128, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Huang, K.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Fu, J. S.; Zhang, W.; Tang, A.; Zhao, X. Asian Dust over Northern China and Its Impact on the Downstream Aerosol Chemistry in 2004. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres 2010, 115(11). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.-I.; Son, S.-W.; Kim, H. C.; Kim, S.-W.; Park, R. J.; Chen, D. Contrasting Synoptic Weather Patterns between Non-Dust High Particulate Matter Events and Asian Dust Events in Seoul, South Korea. Atmospheric Environment 2019, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Naoe, H.; Igarashi, Y.; Inomata, Y.; Sugimoto, N. Aerosol Concentrations Observed at Mt. Haruna, Japan, in Relation to Long-Range Transport of Asian Mineral Dust Aerosols. Atmospheric Environment 2010, 44(36), 4638–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, S.; Onishi, K.; Mu, H.; Kurozawa, Y. The Effect of Asian Dust Events on the Daily Symptoms in Yonago, Japan: A Pilot Study on Healthy Subjects. Archives of Environmental and Occupational Health 2011, 66(1), 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Hakamata, M.; Sato, K.; Okada, Y.; Yang, X.; Tatematsu, M.; Toriba, A.; Kameda, T.; Hayakawa, K. Atmospheric Behaviors of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons at a Japanese Remote Background Site, Noto Peninsula, from 2004 to 2014. Atmospheric Environment 2015, 120, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Zhang, H.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K.; Tang, N. Impact of the COVID-19 Outbreak on the Long-Range Transport of Particulate Pahs in East Asia. Aerosol and Air Quality Research 2020, 20(10), 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Xing, W.L.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K.; Wei, Y.; Tang, N. Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Common Air Pollutants at Wajima, a Remote Background Site in Japan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2020, 17(3). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, M.; Yoshikawa, A.; Muraki, H.; Arao, K.; Uno, I. Transport of Mineral and Anthropogenic Aerosols during a Kosa Event over East Asia. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 2002, 107(7–8), 3-1–3-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, L.L.; Chen, L.; Han, C.; Akutagawa, T.; Endo, O.; Yamauchi, M.; Neroda, A.; Toriba, A.; Tang, N. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Nitro-Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Five East Asian Cities: Seasonal Characteristics, Health Risks, and Yearly Variations. Environmental Pollution 2021, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Hayakawa, K.; Toriba, A.; Tang, N. Impact of COVID-19 Outbreak on the Long-Range Transport of Common Air Pollutants in KUWAMS. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 2021, 69(3), 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, K.; Tang, N.; Kameda, T.; Toriba, A. Atmospheric Behaviors of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in East Asia. Genes and Environment 2014, 36(3), 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Takami, A.; Sato, K.; Shimizu, A.; Yoshino, A.; Kaneyasu, N.; Matsuki, A.; Hayakawa, K.; Toriba, A.; Tang, N. Comparative Analysis of PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHS), Nitro-Pahs (NPAHS), and Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions (WSIIS) at Two Background Sites in Japan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2020, 17(21), 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; He, H. Synergistic Reaction between SO2 and NO2 on Mineral Oxides: A Potential Formation Pathway of Sulfate Aerosol. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14(5), 1668–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-Y.; Okada, Y.; Tang, N.; Matsunaga, S.; Tamura, K.; Lin, J.-M.; Kameda, T.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K. Long-Range Transport of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from China to Japan. Atmospheric Environment 2007, 41(13), 2710–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Yang, L.; Nakatsubo, R.; Wei, Y.; Bi, J.; Shima, M.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K.; Tang, N. Natural Aeolian Dust Particles Have No Substantial Effect on Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): A Laboratory Study Based on Naphthalene. Environmental Pollution 2020, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Hattori, T.; Taga, R.; Igarashi, K.; Yang, X.; Tamura, K.; Kakimoto, H.; Mishukov, V. F.; Toriba, A.; Kizu, R.; Hayakawa, K. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Nitropolycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Urban Air Particulates and Their Relationship to Emission Sources in the Pan-Japan Sea Countries. Atmospheric Environment 2005, 39(32), 5817–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Sato, K.; Tokuda, T.; Tatematsu, M.; Hama, H.; Suematsu, C.; Kameda, T.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K. Factors Affecting Atmospheric 1-, 2-Nitropyrenes and 2-Nitrofluoranthene in Winter at Noto Peninsula, a Remote Background Site, Japan. Chemosphere 2014, 107, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Hu, M.; Chen, B.; Han, C.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K.; Tang, N. Long-Term Variability of Inorganic Ions in TSP at a Remote Background Site in Japan (Wajima) from 2005 to 2015. Chemosphere 2021, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Nagao, S.; Chen, B.; Tang, N. Chemical Characteristics of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in Different Types of Asian Dust in Wajima, a Background Site in Japan. Atmosphere 2022, 13(8). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National institute for environment studies. Available online: https://www-lidar.nies.go.jp/Toyama/archives/.
- HYSPLIT Air Resources Laboratory: https://www.arl.noaa.gov/documents/reports/hysplit_user_guide.pdf.
- Lee, Y. G.; Ho, C.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J. Quiescence of Asian Dust Events in South Korea and Japan during 2012 Spring: Dust Outbreaks and Transports. Atmospheric Environment 2015, 114, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Ueda, H.; Matsuda, K.; Zhang, R.; Arao, K.; Kanai, Y.; Hasome, H. Model Study on Particle Size Segregation and Deposition during Asian Dust Events in March 2002. Journal of Geophysical Research D: Atmospheres 2004, 109(19), D19205 1-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Q.; Chen, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, J.; Tian, P.; An, T. The Mixing State of Mineral Dusts with Typical Anthropogenic Pollutants: A Mechanism Study. Atmospheric Environment 2019, 209, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, R. E.; Kubátová, A.; Kozliak, E. I. An Approach to the Estimation of Adsorption Enthalpies of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons on Particle Surfaces. Journal of Physical Chemistry A 2016, 120(30), 6029–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, N.; Romanias, M. N.; Riffault, V.; Thevenet, F. Investigating Water Adsorption onto Natural Mineral Dust Particles: Linking DRIFTS Experiments and BET Theory. Aeolian Research 2017, 27, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeineddine, M. N.; Romanias, M. N.; Riffault, V.; Thévenet, F. Heterogeneous Interaction of Various Natural Dust Samples with Isopropyl Alcohol as a Probe VOC. Journal of Physical Chemistry A 2018, 122(22), 4911–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamamura, S.; Sato, T.; Ota, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, N.; Hayakawa, K. Long-Range Transport of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) from the Eastern Asian Continent to Kanazawa, Japan with Asian Dust. Atmospheric Environment 2007, 41(12), 2580–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Torre-Roche, R. J.; Lee, W.-Y.; Campos-Díaz, S. I. Soil-Borne Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in El Paso, Texas: Analysis of a Potential Problem in the United States/Mexico Border Region. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2009, 163(2–3), 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, M. B.; Macdonald, R. W.; Vingarzan, R.; Mitchell, R. H.; Goyette, D.; Sylvestre, S. PAHs in the Fraser River Basin: A Critical Appraisal of PAH Ratios as Indicators of PAH Source and Composition. Organic Geochemistry 2002, 33(4), 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda-Castillo, V.; López-López, A.; Hernández-Mena, L.; Murillo-Tovar, M. A.; Díaz-Torres, J. J.; Hernández-Paniagua, I. Y.; del Real-Olvera, J.; León-Becerril, E. Atmospheric Distribution of PAHs and Quinones in the Gas and PM1 Phases in the Guadalajara Metropolitan Area, Mexico: Sources and Health Risk. Atmosphere 2018, 9(4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, P.C.; Zhang, L.L.; Hayakawa, K.; Nagao, S.; Tang, N. Variations in Traffic-Related Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in PM2.5 in Kanazawa, Japan, after the Implementation of a New Vehicle Emission Regulation. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China) 2022, 121, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Wang, Y.; Bai, P.C.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Hayakawa, K.; Toriba, A.; Tang, N. Characteristics and Health Risks of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Nitro-Pahs in Xinxiang, China in 2015 and 2017. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18(6), 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Tang, N.; Nagato, E.; Toriba, A.; Lin, J.-M.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Z.; Qing, W.; Yang, X.; Mishukov, V.; Neroda, A.; Chung, H. Y. Long-Term Trends in Urban Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Nitropolycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: China, Russia, and Korea from 1999 to 2014. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2020, 17(2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Xing, W.L.; Wang, Y.; Bai, P.C.; Zhang, L.L.; Hayakawa, K.; Toriba, A.; Wei, Y.; Tang, N. Assessing Approaches of Human Inhalation Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: A Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18(6), 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Wang, Y.; Bai, P.C.; Zhang, L.L.; Hayakawa, K.; Toriba, A.; Tang, N. Exposure to Atmospheric Particulate Matter-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Health Effects: A Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18(4), 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Morisaki, H.; Wei, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Hu, M.; Shima, M.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K.; Tang, N. PM2. 5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Nitro-Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons inside and Outside a Primary School Classroom in Beijing: Concentration, Composition, and Inhalation Cancer Risk. Science of the Total Environment 2020, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Development of a Relative Potency Factor (RPF) Approach for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH) Mixtures. External Review Draft; Environmental Protection Agency; Integrated Risk Information System: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Orakij, W.; Chetiyanukornkul, T.; Chuesaard, T.; Kaganoi, Y.; Uozaki, W.; Homma, C.; Boongla, Y.; Tang, N.; Hayakawa, K.; Toriba, A. Personal Inhalation Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Nitro-Derivatives in Rural Residents in Northern Thailand. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 2017, 189(10). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The World Health Report 2000: Health Systems: Improving Performance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000; ISBN 92-4-156198-X. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA (United States of Environmental Protection Agency). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund. In Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part B, Development of Risk-based Preliminary Remediation Goals); EPA/540/R-92/003; USA Office of Emerage and Remedial Response: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).