Submitted:
22 September 2023
Posted:
25 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
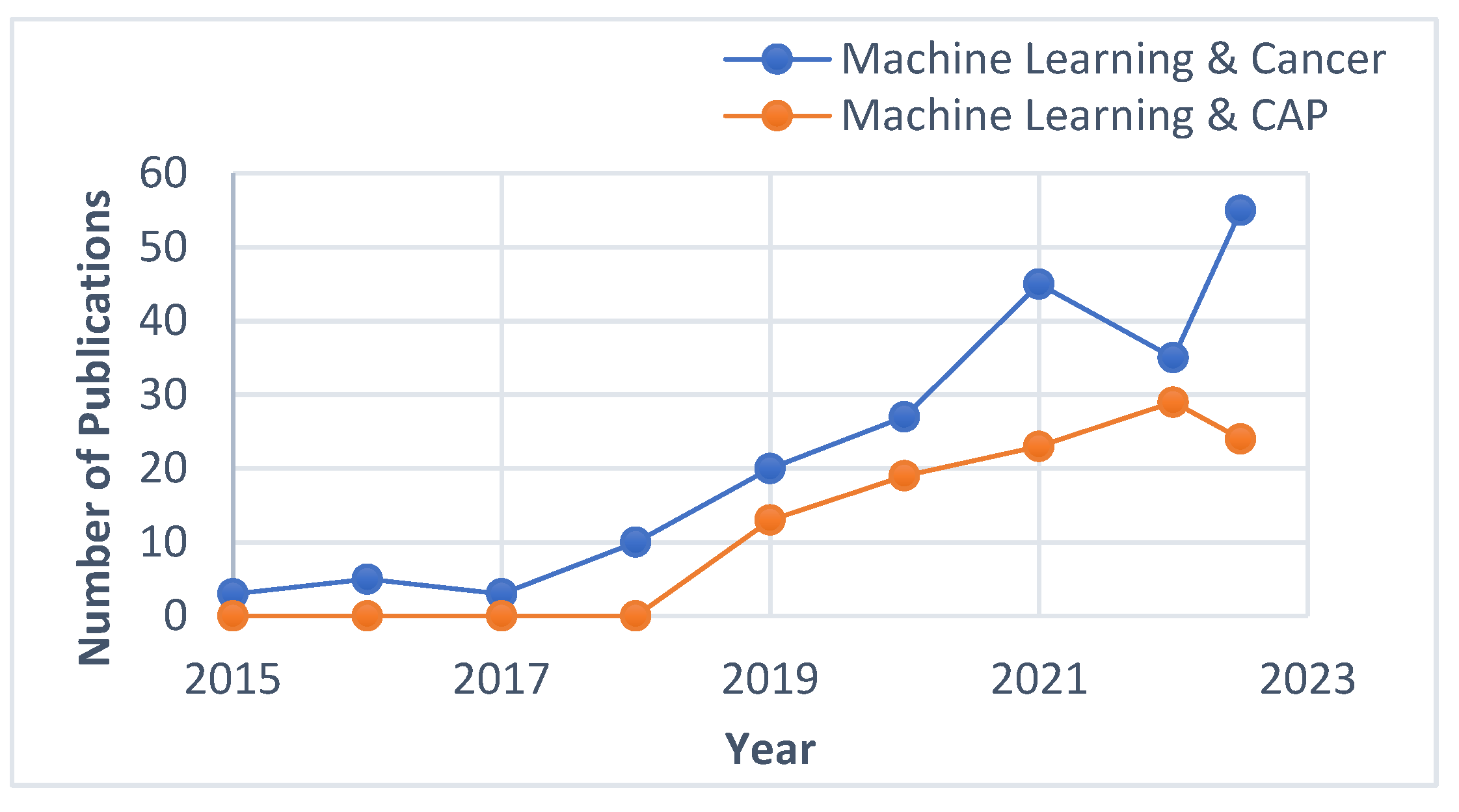
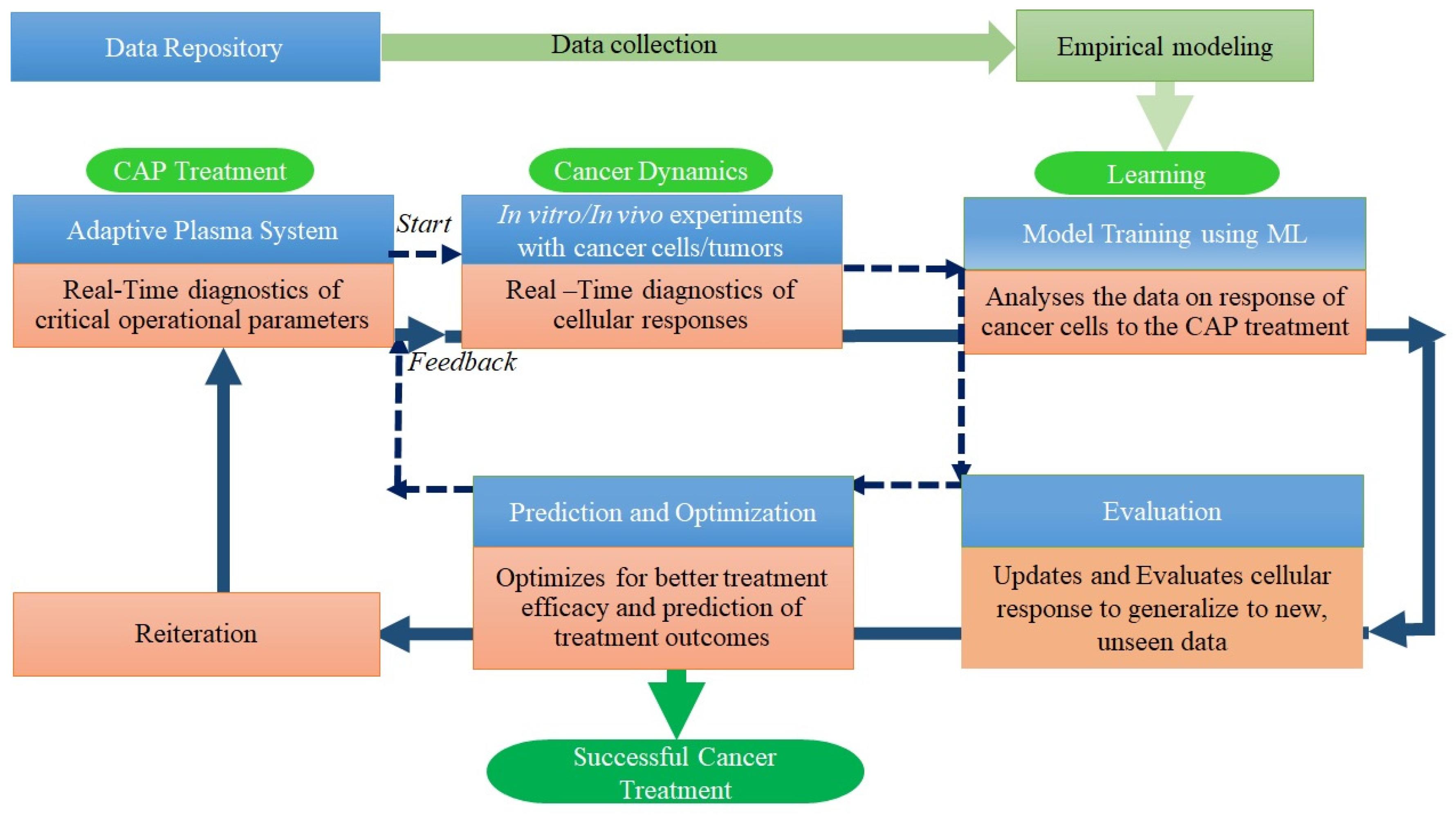
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical modeling
3. AI techniques for Adaptive Plasma system
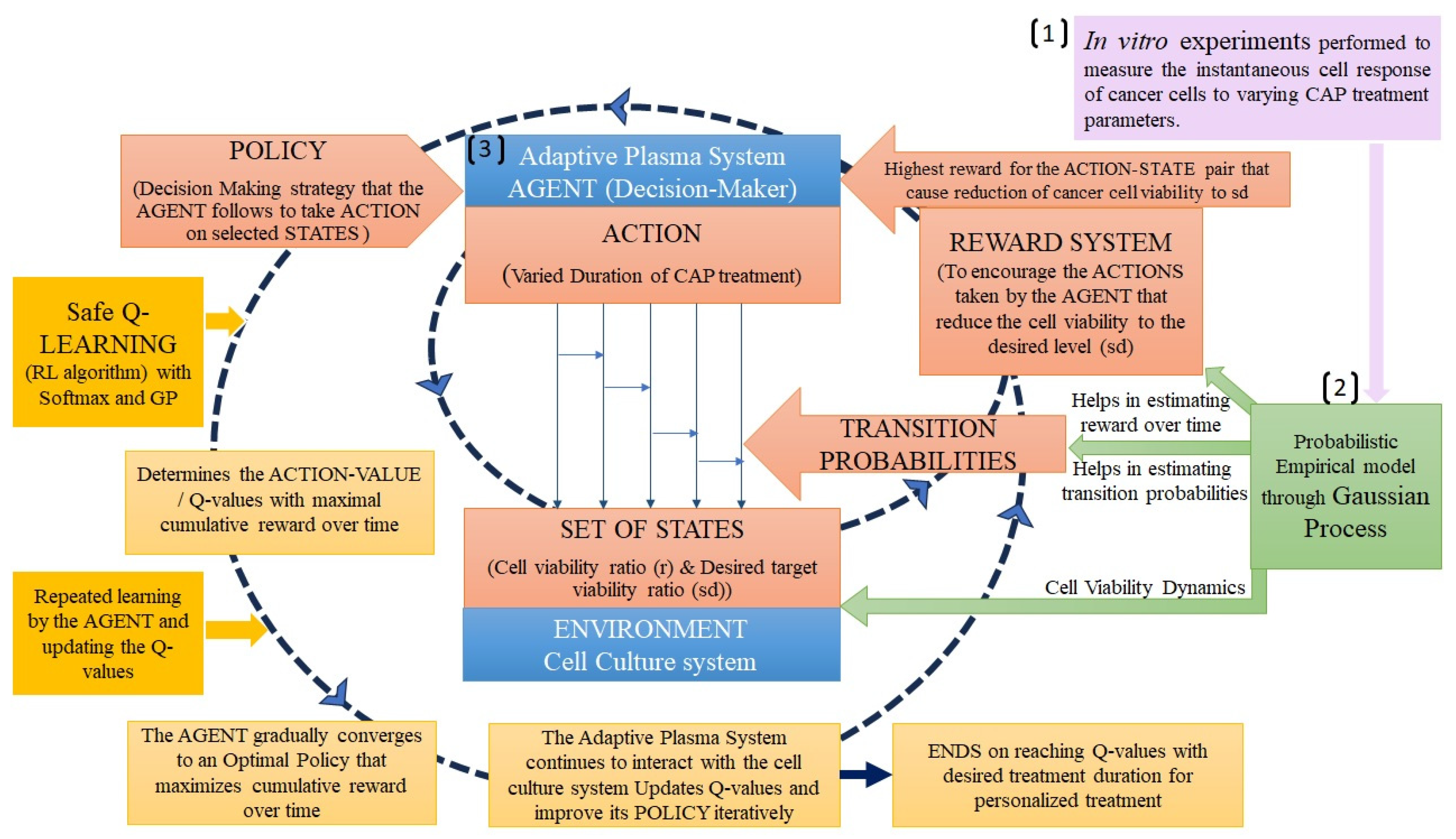
3.1. Reinforcement learning
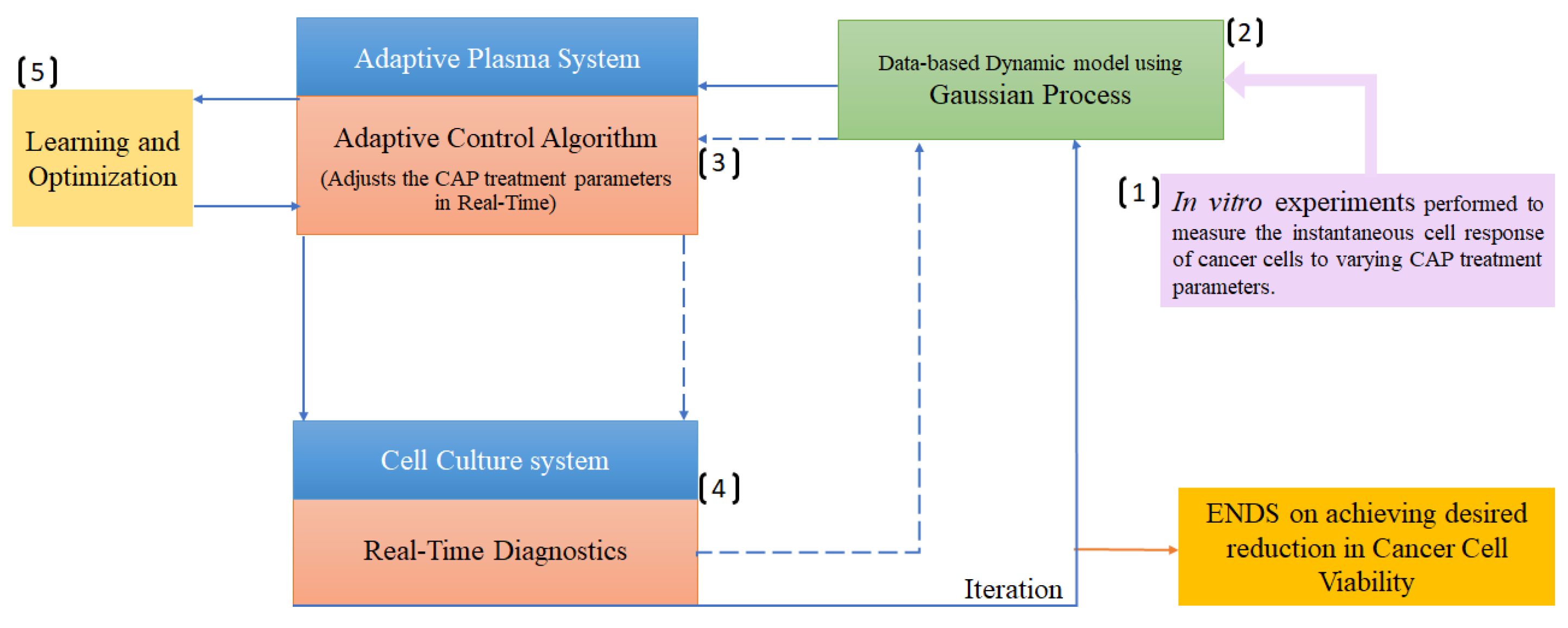
3.2. Gaussian process regression
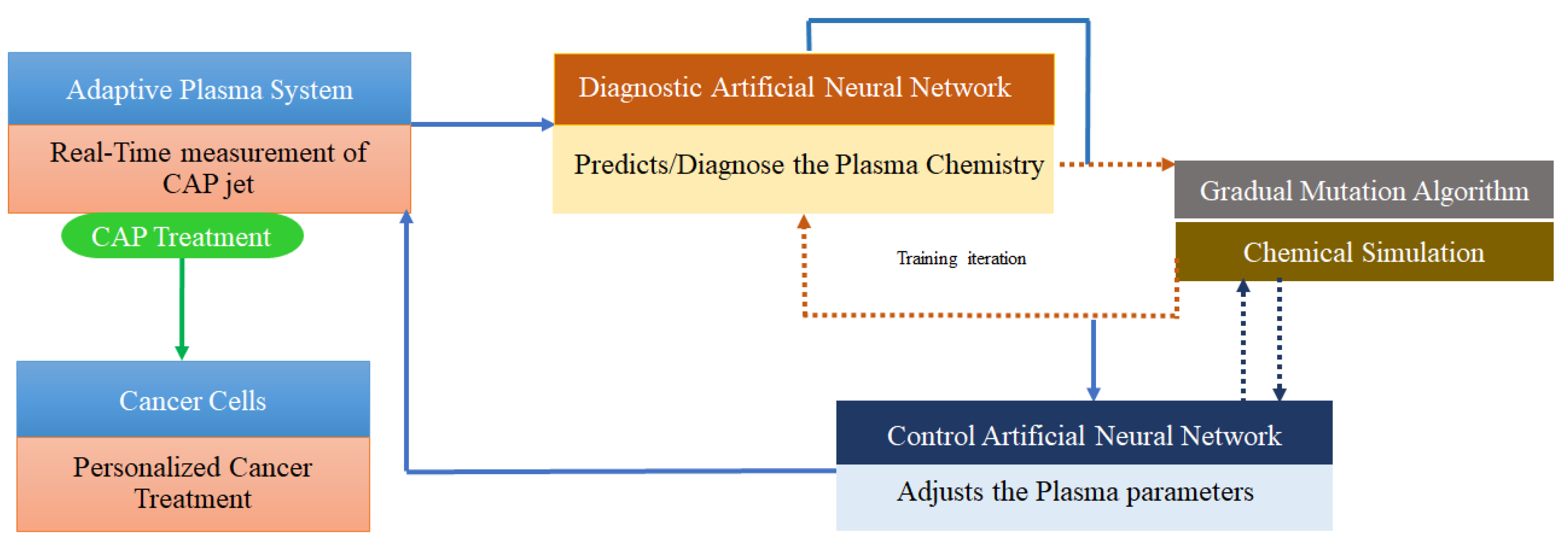
3.3. Deep learning
4. AI in Real-Time diagnostics
4.1. Real-time diagnosis of operational parameters of CAP sources
4.2. Real-time diagnosis of the cell responses to CAP treatment
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martines, E. Plasma Technology for Biomedical Applications; MDPI, 2020.
- Duarte, S.; Panariello, B. H. D. Comprehensive Biomedical Applications of Low Temperature Plasmas. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 693, 108560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bran\`y, D.; Dvorská, D.; Halašová, E.; Škovierová, H. Cold Atmospheric Plasma: A Powerful Tool for Modern Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domonkos, M.; Tichá, P.; Trejbal, J.; Demo, P. Applications of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Technology in Medicine, Agriculture and Food Industry. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, D.; Canal, C. Application of Plasma Technology in Bioscience and Biomedicine. Applied Sciences. MDPI 2021, p 7203.
- Laroussi, M.; Bekeschus, S.; Keidar, M.; Bogaerts, A.; Fridman, A.; Lu, X.; Ostrikov, K.; Hori, M.; Stapelmann, K.; Miller, V.; Reuter, S.; Laux, C.; Mesbah, A.; Walsh, J.; Jiang, C.; Thagard, S. M.; Tanaka, H.; Liu, D.; Yan, D.; Yusupov, M. Low-Temperature Plasma for Biology, Hygiene, and Medicine: Perspective and Roadmap. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2022, 6, 127–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, S.; Khan, R.; Rana, J. N.; Javed, R.; Iqbal, M.; Choi, E. H.; Han, I. Review on the Biomedical and Environmental Applications of Nonthermal Plasma. Catalysts 2023, 13, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, B.; Bezbaruah, R.; Rynjah, D.; Newar, A.; Sengupta, S.; Pegu, P.; Dey, N.; Bora, S. C.; Barman, D. Cold Atmospheric Plasma: A Noteworthy Approach in Medical Science. Sci. Pharm. 2023, 2, 46–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moszczyńska, J.; Roszek, K.; Wiśniewski, M. Non-Thermal Plasma Application in Medicine—Focus on Reactive Species Involvement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Wang, Q.; Adhikari, M.; Malyavko, A.; Lin, L.; Zolotukhin, D. B.; Yao, X.; Kirschner, M.; Sherman, J. H.; Keidar, M. A Physically Triggered Cell Death via Transbarrier Cold Atmospheric Plasma Cancer Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 34548–34563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornin, J.; Labay, C.; Tampieri, F.; Ginebra, M.-P.; Canal, C. Evaluation of the Effects of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Plasma-Treated Liquids in Cancer Cell Cultures. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 2826–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenaga, Y.; Takamatsu, T.; Aizawa, T.; Moriya, S.; Matsumura, Y.; Iwasawa, A.; Okino, A. Influence of Controlling Plasma Gas Species and Temperature on Reactive Species and Bactericidal Effect of the Plasma. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11(24), 11674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feibel, D.; Golda, J.; Held, J.; Awakowicz, P.; Schulz-von der Gathen, V.; Suschek, C. V.; Opländer, C.; Jansen, F. Gas Flow-Dependent Modification of Plasma Chemistry in ΜAPP Jet-Generated Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Its Impact on Human Skin Fibroblasts. Biomed. 2023, 11, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Keidar, M. A Map of Control for Cold Atmospheric Plasma Jets: From Physical Mechanisms to Optimizations. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trelles, J. P. Pattern Formation and Self-Organization in Plasmas Interacting with Surfaces. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 393002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar,M. Adaptive and Self-Adaptive Plasma Cancer Therapeutic Platform. US patent, 11517366, 2022.
- Yan, D.; Cui, H.; Zhu, W.; Talbot, A.; Zhang, L. G.; Sherman, J. H.; Keidar, M. The Strong Cell-Based Hydrogen Peroxide Generation Triggered by Cold Atmospheric Plasma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjika, E.; Pal-Ghosh, S.; Tang, A.; Kirschner, M.; Tadvalkar, G.; Canady, J.; Stepp, M. A.; Keidar, M. Adaptation of Operational Parameters of Cold Atmospheric Plasma for in vitro Treatment of Cancer Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9269–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweigert, I.; Zakrevsky, D.; Gugin, P.; Yelak, E.; Golubitskaya, E.; Troitskaya, O.; Koval, O. Interaction of Cold Atmospheric Argon and Helium Plasma Jets with Bio-Target with Grounded Substrate Beneath. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.; Dhruv, A.; Balaras, E.; Keidar, M.; Martinez, L.; Dhruv, A.; Balaras, E.; Keidar, M. On Self Organization: Model for Ionization Wave Propagation with Targets of Varying Electrical Properties. PSST 2022, 31, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar, M. Plasma for Cancer Treatment. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2015, 24, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar, M. Plasma Cancer Therapy, 1st ed.; Keidar, M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, E.; El-Dessoky, M. M.; Khan, M. A. Mathematical Model to Understand the Dynamics of Cancer, Prevention Diagnosis and Therapy. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, S. I.; Matadi, M. B.; Xulu, S. S. Optimal Control Analysis of a Mathematical Model for Breast Cancer. Math. Comput. Appl. 2018, 23, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Li, L.; Yang, T.; Cohen, P. S.; Sun, G. Biphasic Mathematical Model of Cell--Drug Interaction That Separates Target-Specific and off-Target Inhibition and Suggests Potent Targeted Drug Combinations for Multi-Driver Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers (Basel). 2020, 12, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormuth, D. A.; Jarrett, A. M.; Davis, T.; Yankeelov, T. E. Towards an Image-Informed Mathematical Model of in Vivo Response to Fractionated Radiation Therapy. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, R. J.; Weigelin, B.; Beltman, J. B. Mathematical Modelling Based on in Vivo Imaging Suggests CD137-Stimulated Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Exert Superior Tumour Control Due to an Enhanced Antimitotic Effect on Tumour Cells. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13, 2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, P. A.; Coria, L. N.; Plata, C. Personalized Immunotherapy Treatment Strategies for a Dynamical System of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya, D. A.; Dogra, P.; Wang, Z.; Haider, M.; Ehab, J.; Jeong, D. K.; Ghayouri, M.; Lauwers, G. Y.; Thomas, K.; Kim, R. ; others. A Mathematical Model to Estimate Chemotherapy Concentration at the Tumor-Site and Predict Therapy Response in Colorectal Cancer Patients with Liver Metastases. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13, 444. [Google Scholar]
- Yonekura, Y.; Toki, H.; Watabe, T.; Kaneda-Nakashima, K.; Shirakami, Y.; Ooe, K.; Toyoshima, A.; Nakajima, H.; Tomiyama, N.; Bando, M. Mathematical Model for Evaluation of Tumor Response in Targeted Radionuclide Therapy with 211At Using Implanted Mouse Tumor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari Laleh, N.; Loeffler, C. M. L.; Grajek, J.; Sta\vnková, K.; Pearson, A. T.; Muti, H. S.; Trautwein, C.; Enderling, H.; Poleszczuk, J.; Kather, J. N. Classical Mathematical Models for Prediction of Response to Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1009822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italia, M.; Wertheim, K. Y.; Taschner-Mandl, S.; Walker, D.; Dercole, F. Mathematical Model of Clonal Evolution Proposes a Personalised Multi-Modal Therapy for High-Risk Neuroblastoma. Cancers (Basel). 2023, 15, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrett, A. M.; Bloom, M. J.; Godfrey, W.; Syed, A. K.; Ekrut, D. A.; Ehrlich, L. I.; Yankeelov, T. E.; Sorace, A. G. Mathematical Modelling of Trastuzumab-Induced Immune Response in an in Vivo Murine Model of HER2+ Breast Cancer. Math. Med. Biol. a J. IMA 2019, 36, 381–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budithi, A.; Su, S.; Kirshtein, A.; Shahriyari, L. Data Driven Mathematical Model of FOLFIRI Treatment for Colon Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Mirzaei, N.; Su, S.; Sofia, D.; Hegarty, M.; Abdel-Rahman, M. H.; Asadpoure, A.; Cebulla, C. M.; Chang, Y. H.; Hao, W.; Jackson, P. R. ; others. A Mathematical Model of Breast Tumor Progression Based on Immune Infiltration. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1031. [Google Scholar]
- Bekker, R. A.; Kim, S.; Pilon-Thomas, S.; Enderling, H. Mathematical Modeling of Radiotherapy and Its Impact on Tumor Interactions with the Immune System. Neoplasia 2022, 28, 100796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitsouni, V.; Tsilidis, V. Mathematical Modeling of Tumor-Immune System Interactions: The Effect of Rituximab on Breast Cancer Immune Response. J. Theor. Biol. 2022, 539, 111001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Liang, G.; Tian, T.; Zhang, X. Mathematical Modeling and Analysis of Tumor Chemotherapy. Symmetry (Basel). 2022, 14, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, S.; Winter, M.; Rahman, Z.-A. S. A.; Al-Yasir, Y. I. A.; Zeb, A. Dynamical Behavior of a Cancer Growth Model with Chemotherapy and Boosting of the Immune System. Mathematics 2023, 11, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Alvarenga, J. C.; Minzoni-Alessio, A.; Olvera-Chávez, A.; Cruz-Pacheco, G.; Chimal-Eguia, J. C.; Hernández-Ru\’\iz, J.; Álvarez-Blanco, M. A.; Bautista-Hernández, M. Y.; Quispe-Siccha, R. M. A Mathematical Model to Optimize the Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Treatment Sequence for Triple-Negative Locally Advanced Breast Cancer. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Triana, O.; Pérez-Mart\’\inez, A.; Ram\’\irez-Orellana, M.; Pérez-Garc\’\ia, V. M. Dual-Target CAR-Ts with on-and off-Tumour Activity May Override Immune Suppression in Solid Cancers: A Mathematical Proof of Concept. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Bao, J.; Shao, Y. Mathematical Modeling of Therapy-Induced Cancer Drug Resistance: Connecting Cancer Mechanisms to Population Survival Rates. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikarla, V.; Awuah, D.; Brummer, A. B.; Caserta, E.; Krishnan, A.; Pichiorri, F.; Minnix, M.; Shively, J. E.; Wong, J. Y. C.; Wang, X. ; others. A Mathematical Modeling Approach for Targeted Radionuclide and Chimeric Antigen Receptor t Cell Combination Therapy. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13, 5171. [Google Scholar]
- Guzev, E.; Jadhav, S. S.; Hezkiy, E. E.; Sherman, M. Y.; Firer, M. A.; Bunimovich-Mendrazitsky, S. Validation of a Mathematical Model Describing the Dynamics of Chemotherapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia In Vivo. Cells 2022, 11, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nave, Op.; Sigron, M. A Mathematical Model for the Treatment of Melanoma with the BRAF/MEK Inhibitor and Anti-PD-1. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nave, O. A Mathematical Model for Treatment Using Chemo-Immunotherapy. Heliyon 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozkurt, F.; Yousef, A.; Bilgil, H.; Baleanu, D. A Mathematical Model with Piecewise Constant Arguments of Colorectal Cancer with Chemo-Immunotherapy. Chaos, Solitons \& Fractals 2023, 168, 113207. [Google Scholar]
- Salim, S. S.; Malinzi, J.; Mureithi, E.; Shaban, N. Mathematical Modelling of Chemovirotherapy Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Model. Simul. 2023, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Choe, B. Y.; Suh, T. S.; Sung, W. A Mathematical Model for Predicting Patient Responses to Combined Radiotherapy with CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cells 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavkova, K. P.; Patel, S. H.; Cacini, Z.; Kazerouni, A. S.; Gardner, A. L.; Yankeelov, T. E.; Hormuth, D. A. Mathematical Modelling of the Dynamics of Image-Informed Tumor Habitats in a Murine Model of Glioma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Thirumalai, D. A Mathematical Model for Phenotypic Heterogeneity in Breast Cancer with Implications for Therapeutic Strategies. J. R. Soc. Interface 2022, 19, 20210803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veith, T.; Schultz, A.; Alahmari, S.; Beck, R.; Johnson, J.; Andor, N. Mathematical Modeling of Clonal Interference by Density-Dependent Selection in Heterogeneous Cancer Cell Lines. Cells 2023, 12, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khailov, E.; Grigorieva, E. Optimal Melanoma Treatment Protocols for a Bilinear Control Model. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Su, S.; Shahriyari, L. Investigating Optimal Chemotherapy Options for Osteosarcoma Patients through a Mathematical Model. Cells 2021, 10, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.; Bennett, J.; Patten, T. Practical Understanding of Cancer Model Identifiability in Clinical Applications. Life 2023, 13, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, L. C.; Costa, R. S.; Valério, D. An Overview of Mathematical Modelling in Cancer Research: Fractional Calculus as Modelling Tool. Fractal and Fractional. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute August 1, 2023, p 595. [CrossRef]
- Uçar, E.; Özdemir, N. New Fractional Cancer Mathematical Model via IL-10 Cytokine and Anti-PD-L1 Inhibitor. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farman, M.; Batool, M.; Nisar, K. S.; Ghaffari, A. S.; Ahmad, A. Controllability and Analysis of Sustainable Approach for Cancer Treatment with Chemotherapy by Using the Fractional Operator. Results Phys. 2023, 106630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elharrar, X.; Barbolosi, D.; Ciccolini, J.; Meille, C.; Faivre, C.; Lacarelle, B.; André, N.; Barlesi, F. A Phase Ia/Ib Clinical Trial of Metronomic Chemotherapy Based on a Mathematical Model of Oral Vinorelbine in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Rationale and Study Protocol. BMC Cancer 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smalley, I.; Kim, E.; Li, J.; Spence, P.; Wyatt, C. J.; Eroglu, Z.; Sondak, V. K.; Messina, J. L.; Babacan, N. A.; Maria-Engler, S. S.; De Armas, L.; Williams, S. L.; Gatenby, R. A.; Chen, Y. A.; Anderson, A. R. A.; Smalley, K. S. M. Leveraging Transcriptional Dynamics to Improve BRAF Inhibitor Responses in Melanoma. EBioMedicine 2019, 48, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, N.; Jullion, A.; Ferretti, S.; Fabre, C.; Meille, C. Translational Modeling of Anticancer Efficacy to Predict Clinical Outcomes in a First-in-Human Phase 1 Study of MDM2 Inhibitor HDM201. AAPS J. 2021, 23(2), 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüningk, S. C.; Peacock, J.; Whelan, C. J.; Brady-Nicholls, R.; Yu, H. H. M.; Sahebjam, S.; Enderling, H. Intermittent Radiotherapy as Alternative Treatment for Recurrent High Grade Glioma: A Modeling Study Based on Longitudinal Tumor Measurements. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, D.; Barnett, E.; Scher, H. I.; Xavier, J. B. Optimizing the Future: How Mathematical Models Inform Treatment Schedules for Cancer. Trends Cancer 2022, 8, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leder, K.; Pitter, K.; Laplant, Q.; Hambardzumyan, D.; Ross, B. D.; Chan, T. A.; Holland, E. C.; Michor, F. Mathematical Modeling of Pdgf-Driven Glioblastoma Reveals Optimized Radiation Dosing Schedules. Cell, 2014, 156, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J. A.; Tanguturi, S. K.; Cagney, D.; Shin, K. Y.; Youssef, G.; Aizer, A.; Rahman, R.; Hammoudeh, L.; Reardon, D.; Lee, E.; Dietrich, J.; Tamura, K.; Aoyagi, M.; Wickersham, L.; Wen, P. Y.; Catalano, P.; Haas-Kogan, D.; Alexander, B. M.; Michor, F. Phase I Study of a Novel Glioblastoma Radiation Therapy Schedule Exploiting Cell-State Plasticity. Neuro. Oncol. 2023, 25, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar, M.; Yan, D.; Beilis, I. I.; Trink, B.; Sherman, J. H. Plasmas for Treating Cancer: Opportunities for Adaptive and Self-Adaptive Approaches. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Lin, L.; Gjika, E.; Lee, T.; Keidar, M. Mathematical Modeling and Control for Cancer Treatment with Cold Atmospheric Plasma Jet. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2019, 51, 185202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Bekeschus, S.; Yan, D.; Hori, M. ; Keidar,M; Laroussi,M. Plasma-Treated Solutions (PTS) in Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tampieri, F.; Gorbanev, Y.; Sardella, E. Plasma-Treated Liquids in Medicine: Let’s Get Chemical. Plasma Process. Polym. 2023, e2300077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stache, A. B.; Mih\uail\ua, I.; Gerber, I. C.; Dragoș, L. M.; Mihai, C. T.; Ivanov, I. C.; Topal\ua, I.; Gorgan, D.-L. Optimization of Indirect CAP Exposure as an Effective Osteosarcoma Cells Treatment with Cytotoxic Effects. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé-Martí, X.; Vilella, T.; Labay, C.; Tampieri, F.; Ginebra, M. P.; Canal, C. Thermosensitive Hydrogels to Deliver Reactive Species Generated by Cold Atmospheric Plasma: A Case Study with Methylcellulose. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 3845–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyavko, A.; Yan, D.; Wang, Q.; Klein, A.L.; Patel, K.C.; Sherman, J.H.; Keidar, M. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Cancer Treatment, Direct versus Indirect Approaches. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 1494–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poramapijitwat, P.; Thana, P.; Sukum, P.; Liangdeng, Y.; Kuensaen, C.; Boonyawan, D. Selective Cytotoxicity of Lung Cancer Cells—A549 and H1299—Induced by Ringer’s Lactate Solution Activated by a Non-Thermal Air Plasma Jet Device, Nightingale®. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2023, 43, 805–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miebach, L.; Mohamed, H.; Wende, K.; Miller, V.; Bekeschus, S. Pancreatic Cancer Cells Undergo Immunogenic Cell Death upon Exposure to Gas Plasma-Oxidized Ringers Lactate. Cancers 2023, 15, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlik, T.; Gudkova, V.; Razvolyaeva, D.; Pavlova, M.; Kostukova, N.; Miloykovich, L.; Kolik, L.; Konchekov, E.; Shimanovskii, N. The Role of Autophagy and Apoptosis in the Combined Action of Plasma-Treated Saline, Doxorubicin, and Medroxyprogesterone Acetate on K562 Myeloid Leukaemia Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, N.; Liu, J.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, J.; Kang, C.; Gao, L.; Shi, X.; Zhang, G. Comparison of Direct and Indirect Low-Temperature Plasma Triggering Immunogenic Cell Death in B16F10 Melanoma. Plasma Process. Polym. 2023, 20, e2200206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtson, C.; Bogaerts, A. On the Anti-Cancer Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and the Possible Role of Catalase-Dependent Apoptotic Pathways. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtson, C.; Bogaerts, A. The Quest to Quantify Selective and Synergistic Effects of Plasma for Cancer Treatment: Insights from Mathematical Modeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martemucci, G.; Costagliola, C.; Mariano, M.; D’andrea, L.; Napolitano, P.; D’Alessandro, A. G. Free Radical Properties, Source and Targets, Antioxidant Consumption and Health. Oxygen 2022, 2, 48–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaan, A. A.; Bakhrebah, M. A.; AlSaihati, H.; Alhumaid, S.; Alsubki, R. A.; Turkistani, S. A.; Al-Abdulhadi, S.; Aldawood, Y.; Alsaleh, A. A.; Alhashem, Y. N. ; others. Artificial Intelligence for Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2022, 14, 5595. [Google Scholar]
- Koteluk, O.; Wartecki, A.; Mazurek, S.; Kołodziejczak, I.; Mackiewicz, A. How Do Machines Learn? Artificial Intelligence as a New Era in Medicine. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Ercan, U. K.; Özdemir, G. D.; Özdemir, M. A.; Güren, O. Plasma Medicine: The Era of Artificial Intelligence. Plasma Process. Polym. 2023, e2300066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galuzio, P. P.; Cherif, A. Recent Advances and Future Perspectives in the Use of Machine Learning and Mathematical Models in Nephrology. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2022, 29, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Shi, H.; Wang, H. Machine Learning and AI in Cancer Prognosis, Prediction, and Treatment Selection: A Critical Approach. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2023, 16, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonzanini, A. D.; Shao, K.; Graves, D. B.; Hamaguchi, S.; Mesbah, A. Foundations of Machine Learning for Low-Temperature Plasmas: Methods and Case Studies. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2023, 32, 024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jung, S.; Park, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, J. Effective Liver Cancer Diagnosis Method Based on Machine Learning Algorithm. In 2014 7th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Informatics; 2014; pp 714–718.
- Glučina, M.; Lorencin, A.; An\djelić, N.; Lorencin, I. Cervical Cancer Diagnostics Using Machine Learning Algorithms and Class Balancing Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawade, S.; Bhansali, A.; Patil, K.; Shaikh, D. Application of the Convolutional Neural Networks and Supervised Deep-Learning Methods for Osteosarcoma Bone Cancer Detection. Healthc. Anal. 2023, 3, 100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, C.; Rotemberg, V.; Codella, N. C. F.; Tschandl, P.; Rinner, C.; Akay, B. N.; Apalla, Z.; Argenziano, G.; Halpern, A.; Lallas, A.; et al. A Reinforcement Learning Model for AI-Based Decision Support in Skin Cancer. Nat. Med. 2023, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengash, H. A.; Alamgeer, M.; Maashi, M.; Othman, M.; Hamza, M. A.; Ibrahim, S. S.; Zamani, A. S.; Yaseen, I. Leveraging Marine Predators Algorithm with Deep Learning for Lung and Colon Cancer Diagnosis. Cancers (Basel). 2023, 15, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrash, M. R.; Mirbagheri, E.; Mashoufi, M.; Kazemi-Arpanahi, H. Optimizing Prognostic Factors of Five-Year Survival in Gastric Cancer Patients Using Feature Selection Techniques with Machine Learning Algorithms: A Comparative Study. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2023, 23, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pais, R. J.; Lopes, F.; Parreira, I.; Silva, M.; Silva, M.; Moutinho, M. G. Predicting Cancer Prognostics from Tumour Transcriptomics Using an Auto Machine Learning Approach. In Medical Sciences Forum; 2023; Vol. 22, p 6.
- Bostanci, E.; Kocak, E.; Unal, M.; Guzel, M. S.; Acici, K.; Asuroglu, T. Machine Learning Analysis of RNA-Seq Data for Diagnostic and Prognostic Prediction of Colon Cancer. Sensors 2023, 23, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Ye, B.; Wu, L.; Ni, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Wang, D. Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Survival Prognosis in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Luo, J.; Wan, H.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, H.; Feng, J.; Wen, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. ; others. Evaluation of Machine Learning Algorithms for the Prognosis of Breast Cancer from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Database. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0280340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botlagunta, M.; Botlagunta, M. D.; Myneni, M. B.; Lakshmi, D.; Nayyar, A.; Gullapalli, J. S.; Shah, M. A. Classification and Diagnostic Prediction of Breast Cancer Metastasis on Clinical Data Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H. Application of Machine Learning Algorithm in Predicting Distant Metastasis of T1 Gastric Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengash, H. A.; Alamgeer, M.; Maashi, M.; Othman, M.; Hamza, M. A.; Ibrahim, S. S.; Zamani, A. S.; Yaseen, I. Leveraging Marine Predators Algorithm with Deep Learning for Lung and Colon Cancer Diagnosis. Cancers (Basel). 2023, 15, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prelaj, A.; Boeri, M.; Robuschi, A.; Ferrara, R.; Proto, C.; Lo Russo, G.; Galli, G.; De Toma, A.; Brambilla, M.; Occhipinti, M. ; others. Machine Learning Using Real-World and Translational Data to Improve Treatment Selection for NSCLC Patients Treated with Immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel). 2022, 14, 435. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, D.; Han, S. K.; Ha, D.; Shin, K.; Kim, S. Network-Based Machine Learning in Colorectal and Bladder Organoid Models Predicts Anti-Cancer Drug Efficacy in Patients. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shu, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Tang, L.; Mo, W.; Shao, G.; Shao, F. Machine Learning-Based Radiomics Nomogram Using Magnetic Resonance Images for Prediction of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Efficacy in Breast Cancer Patients. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Dang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Gui, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, T.; Zeng, Y.; Tan, L.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, M. ; others. Predicting the Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer Using Deep Learning of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Videos. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2183. [Google Scholar]
- Arezzo, F.; La Forgia, D.; Venerito, V.; Moschetta, M.; Tagliafico, A. S.; Lombardi, C.; Loizzi, V.; Cicinelli, E.; Cormio, G. A Machine Learning Tool to Predict the Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannet, P.; Coudray, N.; Donnelly, D. M.; Jour, G.; Illa-Bochaca, I.; Xia, Y.; Johnson, D. B.; Wheless, L.; Patrinely, J. R.; Nomikou, S. ; others. Using Machine Learning Algorithms to Predict Immunotherapy Response in Patients with Advanced Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, R.; Basit, S. A.; Shamsi, J. A.; Fan, X.; Nawaz, M.; Yan, H.; Alam, T. Machine Learning Based Personalized Drug Response Prediction for Lung Cancer Patients. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Ha, D.; Lee, J.; Kim, I.; Park, M.; Im, S.-H.; Shin, K.; Kim, S. Network-Based Machine Learning Approach to Predict Immunotherapy Response in Cancer Patients. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Bo, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Su, Q.; Wang, J. ; others. Machine Learning to Predict the Response to Lenvatinib Combined with Transarterial Chemoembolization for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2023, 15, 625. [Google Scholar]
- Fujima, N.; Shimizu, Y.; Yoshida, D.; Kano, S.; Mizumachi, T.; Homma, A.; Yasuda, K.; Onimaru, R.; Sakai, O.; Kudo, K. ; others. Machine-Learning-Based Prediction of Treatment Outcomes Using MR Imaging-Derived Quantitative Tumor Information in Patients with Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinomas: A Preliminary Study. Cancers (Basel). 2019, 11, 800. [Google Scholar]
- Arezzo, F.; La Forgia, D.; Venerito, V.; Moschetta, M.; Tagliafico, A. S.; Lombardi, C.; Loizzi, V.; Cicinelli, E.; Cormio, G. A Machine Learning Tool to Predict the Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhelwa, A. Y.; Kichenadasse, G.; McKinnon, R. A.; Rowland, A.; Hopkins, A. M.; Sorich, M. J. Machine Learning for Prediction of Survival Outcomes with Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors in Urothelial Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Brendel, M.; Wu, N.; Ge, W.; Zhang, H.; Rietschel, P.; Quek, R. G. W.; Pouliot, J.-F.; Wang, F.; Harnett, J. Machine Learning Models for Identifying Predictors of Clinical Outcomes with First-Line Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Li, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Wu, F.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X. Prognostic Models Using Machine Learning Algorithms and Treatment Outcomes of Occult Breast Cancer Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savić, M.; Kurbalija, V.; Ilić, M.; Ivanović, M.; Jakovetić, D.; Valachis, A.; Autexier, S.; Rust, J.; Kosmidis, T. The Application of Machine Learning Techniques in Prediction of Quality-of-Life Features for Cancer Patients. Comput. Sci. Inf. Syst. 2023, 20, 381–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Li, X.; Gan, Y.; Han, S.; Rong, P.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Zhou, L. Artificial Intelligence Assists Precision Medicine in Cancer Treatment. Front. Oncol. 2023, 12, 998222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charalambous, A.; Dodlek, N. Big Data, Machine Learning, and Artificial Intelligence to Advance Cancer Care: Opportunities and Challenges. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2023, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Lee, T.; Keidar, M. Reinforcement Learning with Safe Exploration for Adaptive Plasma Cancer Treatment. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2022, 6, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonzanini, A. D.; Shao, K.; Stancampiano, A.; Graves, D. B.; Mesbah, A. Perspectives on Machine Learning-Assisted Plasma Medicine: Toward Automated Plasma Treatment. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2022, 6, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K. J.; Makrygiorgos, G.; Mesbah, A. Towards Personalized Plasma Medicine via Data-Efficient Adaptation of Fast Deep Learning-Based MPC Policies. Am. Control Conf. 2023, 2769–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yan, D.; Lee, T.; Keidar, M. Self-Adaptive Plasma Chemistry and Intelligent Plasma Medicine. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2022, 4, 2100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littman, M. L.; Szepesvári, C. A Generalized Reinforcement-Learning Model: Convergence and Applications. In ICML, 1996, 310–318.
- Chen, C. L.; Dong, D. Y.; Li, H. X.; Tarn, T. J. Hybrid MDP Based Integrated Hierarchical Q-Learning. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2011, 54, 2279–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Hou, Z.; Yao, X.; Liu, Y.; Sirigiri, J. R.; Lee, T.; Keidar, M. Introducing Adaptive Cold Atmospheric Plasma: The Perspective of Adaptive Cold Plasma Cancer Treatments Based on Real-Time Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Phys. Plasmas 2020, 27, 063501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Keidar, M. Artificial Intelligence without Digital Computers: Programming Matter at a Molecular Scale. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2022, 4, 2200157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidon, D.; Pei, X.; Bonzanini, A. D.; Graves, D. B.; Mesbah, A. Machine Learning for Real-Time Diagnostics of Cold Atmospheric Plasma Sources. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2019, 3(5), 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesbah, A.; Graves, D. B. Machine Learning for Modeling, Diagnostics, and Control of Non-Equilibrium Plasmas. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 30LT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaplotnik, R.; Primc, G.; Vesel, A. Optical Emission Spectroscopy as a Diagnostic Tool for Characterization of Atmospheric Plasma Jets. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witman, M.; Gidon, D.; Graves, D. B.; Smit, B.; Mesbah, A. Sim-to-Real Transfer Reinforcement Learning for Control of Thermal Effects of an Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2019, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. T.; Gao, S. H.; Ai, F. Efficient Numerical Simulation of Atmospheric Pulsed Discharges by Introducing Deep Learning. Front. Phys. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Der Gaag, T.; Onishi, H.; Akatsuka, H. Arbitrary EEDF Determination of Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma by Applying Machine Learning to OES Measurement. Phys. Plasmas 2021, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Der Gaag, T.; Nezu, A.; Akatsuka, H. Practical Considerations of the Visible Bremsstrahlung Inversion (VBI) Method for Arbitrary EEDF Determination in Cold Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2022, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Gaag, T.; Nezu, A.; Akatsuka, H. Partial EEDF Analysis and Electron Diagnostics of Atmospheric-Pressure Argon and Argon-Helium DBD Plasma. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2023, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Niu, P. H.; Chen, C. W.; Cheng, Y. C. Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks to Classify the Discharge Current of a Cold Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma Jet. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2023, 51, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, M.; Yan, D.; Limanowski, R.; Lin, L.; Keidar, M. Recognizing Cold Atmospheric Plasma Plume Using Computer Vision. Plasma 2022, 5, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Gershman, S.; Raitses, Y.; Keidar, M. Multi-Scale Plasma Chemistry Using Physics-Informed Neural Network. J. Phys D Appl. Phys.in review.
- Kim, D. H.; Hong, S. J. Use of Plasma Information in Machine-Learning-Based Fault Detection and Classification for Advanced Equipment Control. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2021, 34, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, A.; Lipa, D.; Ptasinska, S. DNA Strand Breaks and Denaturation as Probes of Chemical Reactivity versus Thermal Effects of Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jets. ACS Omega 2022. [CrossRef]
- Sabrin, S.; Karmokar, D. K.; Karmakar, N. C.; Hong, S. H.; Habibullah, H.; Szili, E. J. Opportunities of Electronic and Optical Sensors in Autonomous Medical Plasma Technologies. ACS Sensors 2023, 8, 974–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trieschmann, J.; Vialetto, L.; Gergs, T. Machine Learning for Advancing Low-Temperature Plasma Modeling and Simulation. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Mitra, A.; Pathak, S.; Prasad, S.; Zhang, A. S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X. F.; Banerjee, A. Recent Advancements, Limitations, and Future Perspectives of the Use of Personalized Medicine in Treatment of Colon Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggelopoulos, C. A.; Christodoulou, A.-M.; Tachliabouri, M.; Meropoulis, S.; Christopoulou, M.-E.; Karalis, T. T.; Chatzopoulos, A.; Skandalis, S. S. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Attenuates Breast Cancer Cell Growth through Regulation of Cell Microenvironment Effectors. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 826865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, J.; Wu, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, J. S.; Shim, G.; Oh, Y.-K. External Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Responsive on-Site Hydrogel for Remodeling Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Biomaterials 2023, 299, 122162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Zhu, K. Cold Atmospheric Plasma: Novel Opportunities for Tumor Microenvironment Targeting. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 7189–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrakova, E.; Biryukov, M.; Troitskaya, O.; Gugin, P.; Milakhina, E.; Semenov, D.; Poletaeva, J.; Ryabchikova, E.; Novak, D.; Kryachkova, N. ; others. Chloroquine Enhances Death in Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells Exposed to Cold Atmospheric Plasma Jet. Cells 2023, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kniazeva, V.; Tzerkovsky, D.; Baysal, Ö.; Kornev, A.; Roslyakov, E.; Kostevitch, S. Adjuvant Composite Cold Atmospheric Plasma Therapy Increases Antitumoral Effect of Doxorubicin Hydrochloride. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1171042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, A.; Qarqash, S.; Römer, S.; Schoon, J.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Niethard, M.; Reichert, J. C.; Wassilew, G. I.; Tzvetkov, M. V; Haralambiev, L. Enhancing the Impact of Chemotherapy on Ewing Sarcoma Cells through Combination with Cold Physical Plasma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, V.; Adhikari, M.; Lin, L.; Sherman, J. H.; Keidar, M. Theranostic Potential of Adaptive Cold Atmospheric Plasma with Temozolomide to Checkmate Glioblastoma: An In Vitro Study. Cancers (Basel). 2022, 14, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.; Cao, X.; Shen, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G. Injectable Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Activated Immunotherapeutic Hydrogel for Enhanced Cancer Treatment. Biomaterials 2023, 122189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, Z.; Wen, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Zeng, Y.; Dotti, G.; Wirz, R. E.; Gu, Z. Transdermal Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Mediated Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2020, 117, 3687–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, S.; Shanei, A.; Sazgarnia, A.; Attaran, N.; Aledavood, S. A. The Synergistic Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma Mediated Gold Nanoparticles Conjugated with Indocyanine Green as an Innovative Approach to Cooperation with Radiotherapy. Cell J. 2023, 25, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Kenari, A. J.; Siadati, S. N.; Abedian, Z.; Sohbatzadeh, F.; Amiri, M.; Gorji, K. E.; Babapour, H.; Zabihi, E.; Ghoreishi, S. M.; Mehraeen, R. ; others. Therapeutic Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Its Combination with Radiation as a Novel Approach on Inhibiting Cervical Cancer Cell Growth (HeLa Cells). Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 111, 104892. [Google Scholar]
- Pansare, K.; Vaid, A.; Singh, S. R.; Rane, R.; Visani, A.; Ranjan, M.; Krishna, C. M.; Sarin, R.; Joseph, A. Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma Jet and Gamma Radiation Treatments on Gingivobuccal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Breast Adenocarcinoma Cells. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqual-Melo, G.; Sagwal, S. K.; Freund, E.; Gandhirajan, R. K.; Frey, B.; von Woedtke, T.; Gaipl, U.; Bekeschus, S. Combination of Gas Plasma and Radiotherapy Has Immunostimulatory Potential and Additive Toxicity in Murine Melanoma Cells in Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, K.; Manaloto, E.; Casey, A.; Cribaro, G. P.; Byrne, H. J.; Tian, F.; Barcia, C.; Conway, G. E.; Cullen, P. J. ; others. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Induces ATP-Dependent Endocytosis of Nanoparticles and Synergistic U373MG Cancer Cell Death. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5298. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Yu, H.; Ding, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Keidar, M.; Zhang, W. Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Iron Oxide-Based Magnetic Nanoparticles for Synergetic Lung Cancer Therapy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 130, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, Z.; Biparva, P.; Rafiei, A.; Kardan, M.; Hadavi, S. Combination Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma with Green Synthesized Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles in the Treatment of Melanoma Cancer Model. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0279120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Fan, R.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D. Violet Phosphorene Nanosheets and Cold Atmospheric Plasma for Synergetic Cancer Therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 145884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canady, J.; Murthy, S. R. K.; Zhuang, T.; Gitelis, S.; Nissan, A.; Ly, L.; Jones, O. Z.; Cheng, X.; Adileh, M.; Blank, A. T.; Colman, M. W.; Millikan, K.; O’Donoghue, C.; Stenson, K. M.; Ohara, K.; Schtrechman, G.; Keidar, M.; Basadonna, G. The First Cold Atmospheric Plasma Phase I Clinical Trial for the Treatment of Advanced Solid Tumors: A Novel Treatment Arm for Cancer. Cancers, 2023, 15, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Selected Parameters of the CAP sources for Real-Time diagnostics | Input Data obtained from | ML and computational techniques employed | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotational and Vibrational temperatures | OES | Linear regression (Supervised ML) | [124] |
| Substrate characteristics | OES | k-Means Clustering (Unsupervised ML) | [124] |
| Separation distance between the electrodes | Electro-Acoustic Emission | Gaussian Process Regression (Supervised probabilistic ML) | [124] |
| Electron energy distribution function (EEDF) | OES | Genetic Algorithm (metaheuristic algorithm) | [129] |
| EEDF | OES, Momentum-transfer cross section | Visible Bremmsstrahlung Inversion (Supervised ML) | [130,131] |
| Time-series current signals from APPJ (discharge type and working gas) | Sensors/Probes | Convolutional neural networks (DL) | [132] |
| Plasma Plume length | Video frames of the plasma plume captured using a camera (iPhone 11) | Computer Vision algorithms | [133] |
| Temperature setpoint | Simulated data from thermal dynamics model of plasma-substrate interactions | Reinforcement learning | [127] |
| Self-Adaptive Plasma Chemistry Gas input densities and Energy levels |
OES | Artificial Neural Networks (DL), Gradual Mutation Algorithm | [119] |
| Pulse Discharge characteristics (current density and gap voltage) | Simulated fluid model data of time and pulse rise rate | Deep neural networks (DL) | [128] |
| Plasma chemistry (tokamak) | FTIR | Physics Informed Neural Networks | [134] |
| Input data | Real-time diagnostics | Advanced control and Prediction methodss | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAP treatment duration and Discharge voltage applied | Cell viability Luminescence Assay | Model Predictive Control (MPC) |
[67] |
| Cancer Cell viability ratio | Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS), operational parameters | GP regression, MPLC | [122] |
| Cancer Cell viability ratio | EIS, Cell viability assays, operational parameters | GP, Safety Q – Reinforcement learning | [116] |
| Voltage applied, irradiation time, frequency of the plasma and flow rate of the feed gas on the extent of DNA damage | Agarose gel electrophoresis, UV fluorescence Imaging | Artificial Neural Networks (supervised DL) Physics Guided Neural Network (supervised DL |
[136] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





