Submitted:
17 August 2023
Posted:
21 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Focused Questions
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Research
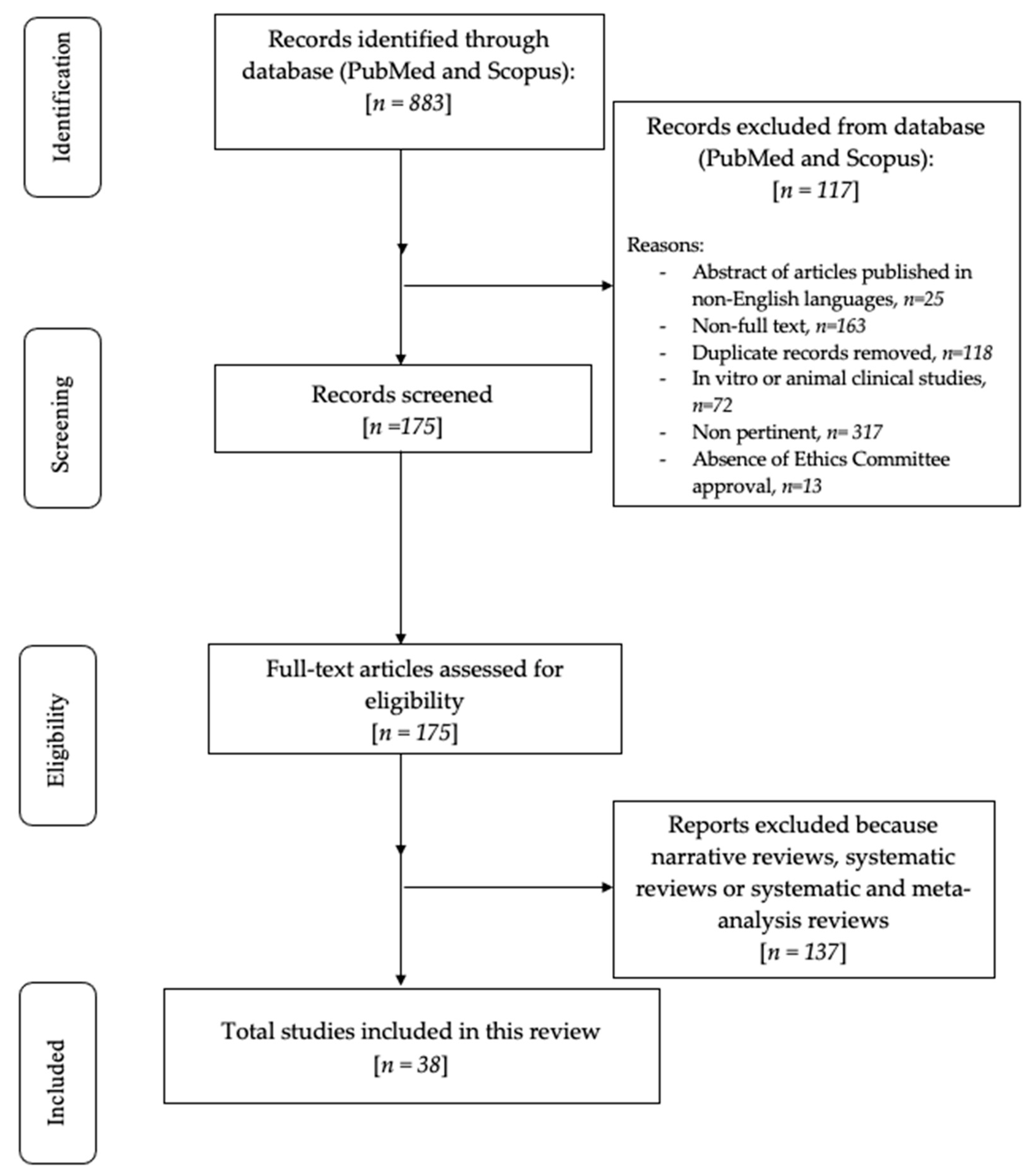
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Features of pain
4.2. Features of orthodontic pain
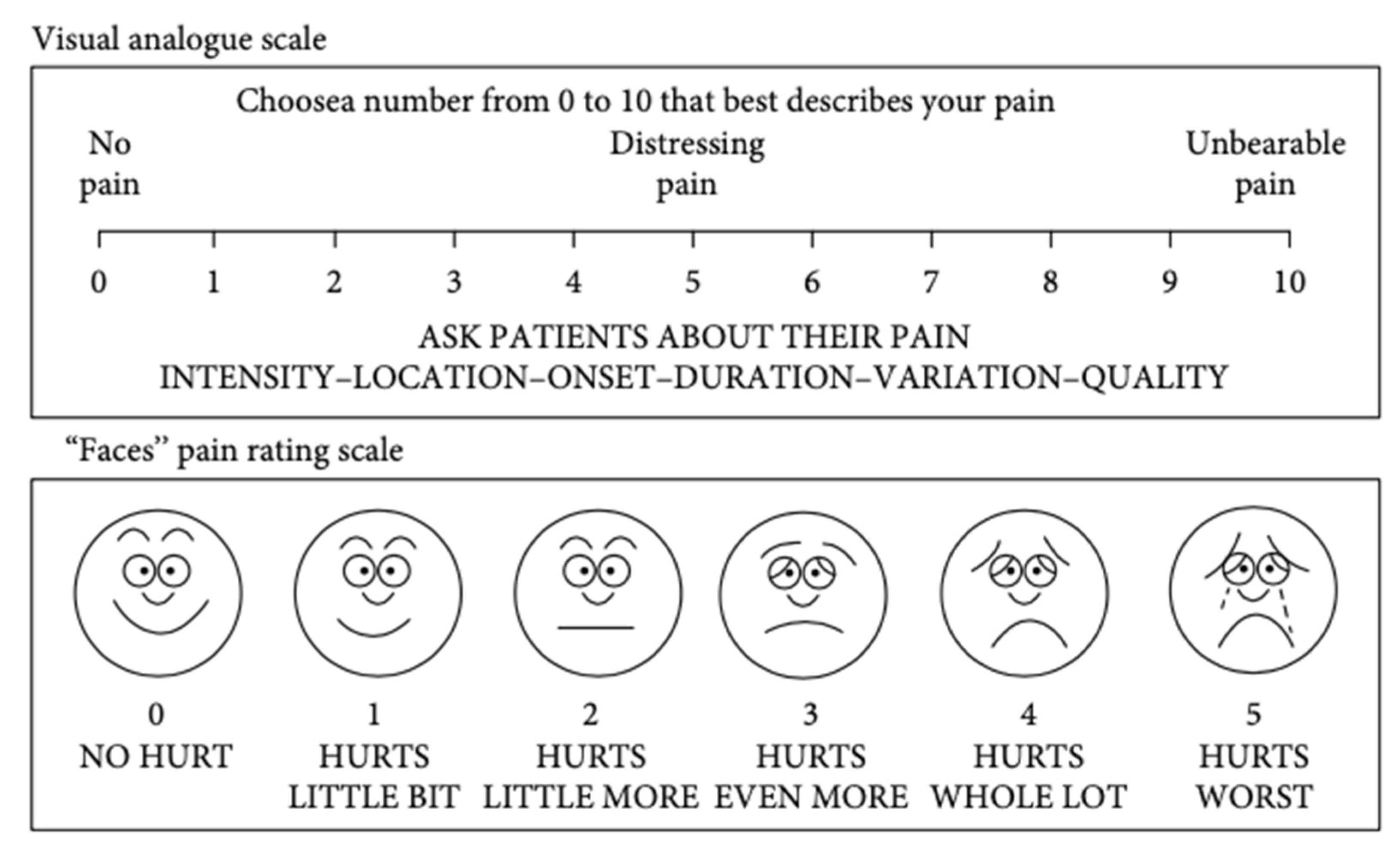
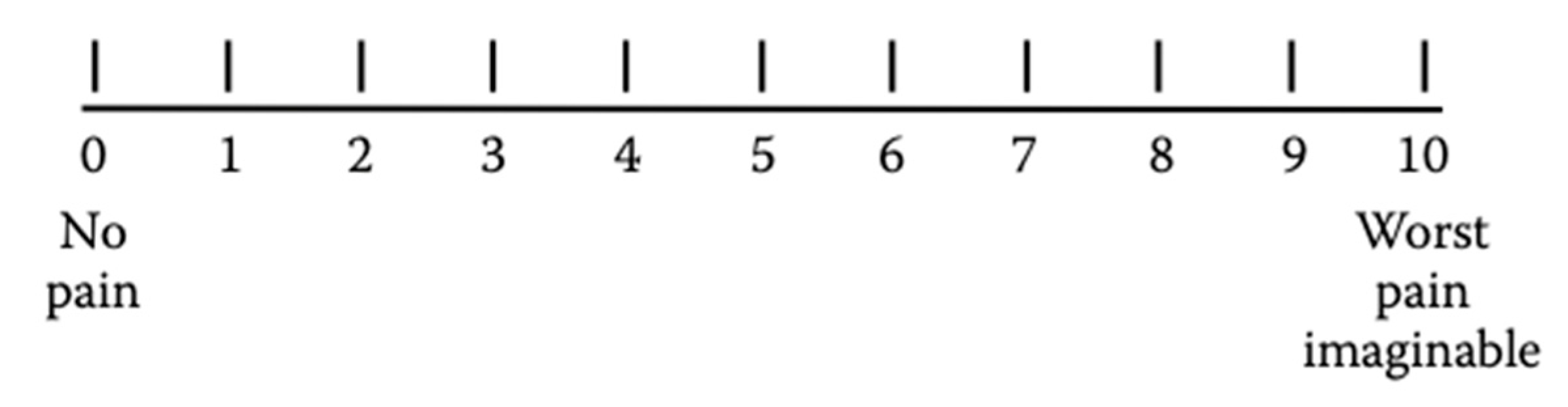
4.3. Pain intensity assessment
4.4. Pain assessment in children

5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergius, M.; Kiliaridis, S.; Berggren, U. Pain in orthodontics. A review and discussion of the literature. J Orofac Orthop. 2000, 61, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, P.; Kess, B.; Wilson, S. Perception of discomfort by patients undergoing orthodontic treatment. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1989, 96, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazancı, F.; Aydoğan, C.; Alkan, Ö. Patients' and parents' concerns and decisions about orthodontic treatment. Korean J Orthod. 2016, 46, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, S. Discontinuation of orthodontic treatment relative to patient age. J Dent. 1974, 2, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, V. Orthodontic pain: from causes to management--a review. Eur J Orthod. 2007, 29, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V. Non-completion of Active Orthodontic Treatment. British Journal of Orthodontics. 1992, 19, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxman, A.D.; Guyatt, G.H. Validation of an index of the quality of review articles. J Clin Epidemiol. 1991, 44, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, A.M.; Khalid, W. Questionnaire designing and validation. J Pak Med Assoc. 2012, 62, 514–516. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia de Yebenes Prous, M.A.; Rodriguez Salvanes, F.; Carmona Ortells, L. [Validation of questionnaires]. Reumatol Clin 2009, 5, 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, S.N.; Carr, D.B.; Cohen, M.; Finnerup, N.B.; Flor, H.; Gibson, S.; Keefe, F.J.; Mogil, J.S.; Ringkamp, M.; Sluka, K.A.; Song, X.J.; Stevens, B.; Sullivan, M.D.; Tutelman, P.R.; Ushida, T.; Vader, K. The revised International Association for the Study of Pain definition of pain: concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain. 2020, 161, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer Lindsay, N.; Chen, C.; Gilam, G.; Mackey, S.; Scherrer, G. Brain circuits for pain and its treatment. Sci Transl Med. 2021, 13, eabj7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstone, C. The Biomechanics of Tooth Movement. In Vistas in Orthodontics; Kraus, B.S., Riedel, R.A., Eds.; Lea & Febiger: Philadelphia, 1962; pp. 197–213. [Google Scholar]
- Erdinç, A.M.; Dinçer, B. Perception of pain during orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances. Eur J Orthod 2004, 26, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firestone, A.R.; Scheurer, P.A.; Bürgin, W.B. Patients' anticipation of pain and pain-related side effects, and their perception of pain as a result of orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances. Eur J Orthod 1999, 21, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; McGrath, C.; Hägg, U. Changes in oral health-related quality of life during fixed orthodontic appliance therapy. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2008, 133, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Chan, C. The pain and discomfort experienced during orthodontic treatment: A randomized controlled clinical trial of two initial aligning arch wires. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 1992, 102, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Mai, L.X.; Li, Y.R. Oral health-related quality of life of fixed orthodontic appliance therapy in adult patients. Chin J Stomal Res 2012, 4, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Scheurer, P.A; Firestone, A.R.; Bürgin, W.B. Perception of pain as a result of orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances. Eur J Orthod 1996, 18, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.F.; Moerenhout, R.G. The pain experience and psychological adjustment to orthodontic treatment of preadolescents, adolescents, and adults. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1991, 100, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, P.C.; Espinosa, D.G.; Mecenas, P.; Flores-Mir, C.; Normando, D. Pain level between clear aligners and fixed appliances: a systematic review. Prog Orthod. 2020, 21, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.G.; Knapman, Y.M. Attitudes to orthodontic treatment. Br J Orthod. 1985, 12, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.L. An investigation into the initial discomfort caused by placement of an archwire. Eur J Orthod 1984, 6, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, D.; Garten, L.; Kopf, A.; Pathel, N.B. Pain management in children. In Guide to Pain Management in Low-Resource Settings; Int Assoc Study Pain, 2010; pp. 255–267. [Google Scholar]
- Breivik, H. Assessment of pain. BJA: British Journal of Anaesthesia 2008, 101, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.D.; Van Nostran, W. Assessing pain intensity with the visual analog scale: a plea for uniformity. J Clin Pharmacol. 2014, 54, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawker, G.A.; Mian, S.; Kendzerska, T.; French, M. Measures of adult pain: Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS Pain), Numeric Rating Scale for Pain (NRS Pain), McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ), Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Chronic Pain Grade Scale (CPGS), Short Form-36 Bodily Pain Scale (SF-36 BPS), and Measure of Intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain (ICOAP). Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011, 63 (Suppl 11), S240–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huskisson, E.C. Visual analogue scales. In Pain measurement and assessment; Melzack, R., Ed.; New York Raven Press, 1983; pp. 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Younger, J.; McCue, R.; Mackey, S. Pain outcomes: a brief review of instruments and techniques. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2009, 13, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Townsend, M.; Berman, L.B.; Keller, J.L. A comparison of Likert and visual analogue scales for measuring change in function. J Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddio, A.; O'Brien, L.; Ipp, M.; Stephens, D.; Goldbach, M.; Koren, G. Reliability and validity of observer ratings of pain using the visual analog scale (VAS) in infants undergoing immunization injections. Pain. 2009, 147, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, D.B.; Strout, T.D. The minimum clinically significant difference in patient-assigned numeric scores for pain. Am J Emerg Med. 2005, 23, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasoud, N.N. Pain perception among patients treated with passive self-ligating fixed appliances and Invisalign® aligners during the first week of orthodontic treatment. Korean J Orthod. 2018, 48, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.B.; McGorray, S.P.; Womack, R.; Quintero, J.C.; Perelmuter, M.; Gibson, J.; Dolan, T.A.; Wheeler, T.T. A comparison of treatment impacts between Invisalign aligner and fixed appliance therapy during the first week of treatment. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2007, 131, 302–e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diddige, R.; Negi, G.; Kiran, K.V.S.; Chitra, P. Comparison of pain levels in patients treated with 3 different orthodontic appliances - a randomized trial. Med Pharm Rep. 2020, 93, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, M.P.; Karoly, P.; Braver, S. The measurement of clinical pain intensity: a comparison of six methods. Pain. 1986, 27, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieliński, J.; Morawska-Kochman, M.; Zatoński, T. Pain assessment and management in children in the postoperative period: A review of the most commonly used postoperative pain assessment tools, new diagnostic methods and the latest guidelines for postoperative pain therapy in children. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2020, 29, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawawi, K.H. Acceptance of orthodontic miniscrews as temporary anchorage devices. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2014, 8, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.; Sharma, S.; Jensen, M.P. The utility and validity of pain intensity rating scales for use in developing countries. Pain Rep 2018, 3, e672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Closs, S.J.; Barr, B.; Briggs, M. et al. A comparison of five pain assessment scales for nursing home residents with varying degrees of cognitive impairment. J Pain Symptom Manage 2004, 27, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghadir, A.H.; Anwer, S.; Iqbal, A.; Iqbal, Z.A. Test-retest reliability, validity, and minimum detectable change of visual analog, numerical rating, and verbal rating scales for measurement of osteoarthritic knee pain. J Pain Res. 2018, 11, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Spencer, R.J.; Littlewood, S.J.; O'Dywer, L.; Barber, S.K.; Russell, J.S. A multicenter randomized controlled trial to compare a self-ligating bracket with a conventional bracket in a UK population: Part 2: Pain perception. Angle Orthod. 2016, 86, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manworren, R.C.; Stinson, J. Pediatric Pain Measurement, Assessment, and Evaluation. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2016, 23, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, A.; Stinson, J.N.; McGrath, P.J. Measurement of self-reported pain intensity in children and adolescents. J Psychosom Res. 2010, 68, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinson, J.N.; Kavanagh, T.; Yamada, J.; Gill, N.; Stevens, B. Systematic review of the psychometric properties, interpretability and feasibility of self-report pain intensity measures for use in clinical trials in children and adolescents. Pain. 2006, 125, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, V.; Bergman, S.; Henoch, I. et al. Pain and pain management in children and adolescents receiving hospital care: a cross-sectional study from Sweden. BMC Pediatr. 2002, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garra, G.; Singer, A.J.; Taira, B.R.; Chohan, J.; Cardoz, H.; Chisena, E.; Thode, H.C. Jr. Validation of the Wong-Baker FACES Pain Rating Scale in pediatric emergency department patients. Acad Emerg Med. 2010, 17, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.L.; Baker, C.M. Pain in children: comparison of assessment scales. Pediatr Nurs. 1988, 14, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, A.; Hoggart, B. Pain: a review of three commonly used pain rating scales. J Clin Nurs. 2005, 14, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, B.; Daoust, R.; Doyon-Trottier, E.; Dauphin-Pierre, S.; Gravel, J. Validation and properties of the verbal numeric scale in children with acute pain. Pain. 2010, 149, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Rodríguez, E.; Miró, J.; Castarlenas, E. A comparison of four self-report scales of pain intensity in 6- to 8-year-old children. Pain. 2012, 153, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castarlenas, E.; Miró, J.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, E. Is the verbal numerical rating scale a valid tool for assessing pain intensity in children below 8 years of age? J Pain. 2013, 14, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, M.C.; Bocato, J.R.; Berger, S.B.; Oltramari, P.V.P.; de Castro Ferreira Conti, A.C.; de Almeida, M.R.; Freire Fernandes, T.M. Perceived pain during rapid maxillary expansion in children with different expanders. Angle Orthod. 2021, 91, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasagan, S.; Subramanian, A.K.; Selvaraj, A.; Marya, A. Pain Perception Associated with Mini-Implants and Interventions for Pain Management: A Cross-Sectional Questionnaire-Based Survey. Biomed Res Int. 2021, 2021, 4842865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, G.H.; Bushnell, C.M.; Lavigne, G.J. Comparison of verbal and visual analogue scales for measuring the intensity and unpleasantness of experimental pain. Pain. 1989, 37, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beecher, H.K. Measurement of subjective responses: quantitative effects of drugs; Oxford University Press, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, J.; Melzack, R. The McGill Pain Questionnaire: Development, psychometric properties, and usefulness of the long form, short form, and short form-2. In Handbook of pain assessment; Turk, D.C., Melzack, R., Eds.; The Guilford Press, 2011; pp. 45–66. [Google Scholar]
- Melzack, R.; Katz, J. The McGill Pain Questionnaire: appraisal and cur- rent status. In Handbook of pain assessment; Turk, D.C., Melzack, R., Eds.; Guilford Press: New York, 1990; pp. 152–168. [Google Scholar]
- Shroff, R.; Dabholakar, T. . Mc Gill Pain Questionnaire: A Cross-Cultural Adaptation Study in Chronic Neck Pain. Int J Physio 2023, 10, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkie, D.J.; Savedra, M.C.; Holzemer, W.L.; Tesler, M.D.; Paul, S.M. Use of the McGill Pain Questionnaire to measure pain: a meta-analysis. Nurs Res. 1990, 39, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzack, R.; Katz, J.; Jeans, M.E. The role of compensation in chronic pain: analysis using a new method of scoring the McGill Pain Questionnaire. Pain. 1985, 23, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzack, R. The short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire. Pain. 1987, 30, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, E.; Fercec, J.; Šćepan, I.; Glišić, B.; Nedeljković, N.; Juloski, J.; RudolF, R. The correlation between pain perception among patients with six different orthodontic archwires and the degree of dental crowding. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2015, 143, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Banerjee, R.; Shenoy, U.; Agarkar, S.; Bhattacharya, S. Effect of orthodontic pain on quality of life of patients undergoing orthodontic treatment. Indian J Dent Res. 2018, 29, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




